1. Introduction
With the ending of the COVID-19 pandemic declared by the World Health Organization, the number of new cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections has declined. Unfortunately, the virus continues to persist with over 65 million registered cases of survivors with post-COVID-19 sequelae, also known as LongCOVID-19 (LongC) [
1]. LongC can manifest in individuals of all different ages and backgrounds and is associated with the severity of acute phase disease [
2]. The estimated incidence rate is 50-70% for hospitalized patients, 10-30% for non-hospitalized cases, and 10-12% in vaccinated persons [
1]. The highest percentage diagnosis of LongC is in individuals age 36-50 years old who are non-hospitalized with a mild acute illness as they represent the majority of COVID-19 cases [
3]. Thirty-one percent of LongC cases have no identified preexisting chronic comorbidities, and females are more likely than males to be diagnosed with LongC [
3].
LongC is thought to be a multi-organ syndrome with a broad array of clinical manifestations suggestive of underlying pulmonary, cardiovascular, endocrine, hematologic, renal, gastrointestinal, immunological and/or neurological disease [
4]. LongC neurological sequelae (nLongC) can involve both the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the central nervous system (CNS). PNS symptoms include muscle weakness, myalgias, hyposmia, hypogeusia, hearing loss/tinnitus, and sensorimotor deficits [
5]. CNS symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, headache, sleep disorders, cognitive impairment, emotional/mood disorders, dizziness and dysautonomia [
5]. Putative mechanisms for nLongC include neuroinflammation, autoantibody generation, microclot formation, blood vessel damage, and neuronal injury [
1]. Currently, there are no established effective diagnostic tools or treatments for nLongC.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoparticles secreted by most cells carrying molecular cargo that not only reflect the current physiological state of the secreting cell but also upon uptake, EVs can elicit responses in recipient cells that promote health or disease [
6]. EVs can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) into the periphery where they can serve as biomarkers of brain disease or as propagators of pathologic conditions. Alternatively, harmful EVs secreted by cells in the periphery can cross the BBB into the brain to facilitate neurological damage. EVs have been implicated in SARS-CoV-2 infection, LongC and nLongC [
7,
8]. Our lab investigations utilized neuronal-enriched EVs (nEVs) immunopurified from plasma with anti-L1CAM monoclonal antibodies as vehicles and biomarkers of neurological diseases [
9]. We previously reported on the plasma and nEV contents from people with nLongC at a time point 2-3 months post-infection. Compared to the plasma and nEVs obtained from pre-pandemic controls, we saw protein changes indicative of a peripheral cytokine reaction with differentially expressed neurodegenerative proteins [
10].
In this study, we examined the plasma and nEVs of a nLongC cohort at a time point of around 1-year post-infection and compared a larger set of protein profiles to those individuals who have fully recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection (Cov) as well as pre-COVID-19 controls. We found both Cov and nLongC groups still had elevated IL-1β while nLongC now showed elevated IL-8 in the plasma. In addition, plasma cortisol and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) were elevated in both Cov and nLongC groups. A high proportion of the nEV proteins associated with neurodegeneration (Aβ42, FGF-21, KLK-6, pTau181, TDP-43, HMGB1) were significantly upregulated in nLongC while a two were significantly upregulated only in Cov (Aβ40, tTau). These results suggest a shift in the cytokine profile with a distinct set of injurious proteins present in some individuals that may contribute to altered nEV cargo and ongoing COVID-19 neurological sequelae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Blood Collection
Volunteers with a documented history of SARS-CoV-2 as evidenced by a positive viral RNA PCR or antigen test result from nasal or throat swab were recruited from the Veterans Affairs Health Care System, San Francisco and from advertising in social media from the San Francisco Bay Area. All volunteers were greater than 5 months post SARS-CoV-2 infection. All participants signed a written informed consent approved by the University of California, San Francisco Institutional Review Board. The nLongC subjects all had neurological complaints which included at least one of the following: difficulty with memory or concentration, or increased anxiety or depression. Exclusion criteria included past and present seizures, head trauma, loss of consciousness greater than 15 minutes, alcohol and/or substance abuse/dependence within 3 months of participation, HIV, and pregnancy. Cov participants were also greater than 5 months post infection with no complaints of residual infection. Fasting whole blood was collected in EDTA tubes between February 2022 and May 2023. Plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected and frozen in aliquots at -80 °C.
For the healthy controls (HC), frozen plasma collected from pre-pandemic individuals were purchased from Blood Centers of the Pacific (Vitalant, San Francisco, California, USA) and stored at -80 °C until use.
2.2. APOE Genotyping
Frozen PBMCs were thawed in a 37 °C water bath and cells collected by centrifugation at 500 xg for 10 minutes. Two million PBMCs were lysed with RLT Lysis Buffer (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA, catalog # 1053393) and DNA isolated using the AllPrep DNA/RNA Mini kit (Qiagen, catalog # 80204). The PBMC DNA was added to TaqMan™ Fast Advanced Master Mix reagents (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA, catalog # 4444554), amplified and subjected to TaqMan™ SNP Genotyping Assays for rs429358 and rs7412 (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, PN 4351379) using the ABI ViiA 7 (Applied Biosystems Co., Waltham, MA, USA) instrument for endpoint PCR. Data were analyzed using the TaqMan™ SDS software (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Inc.). A positive control for ε3/ε4 (Coriell Institute for Medical Research, Camden, NJ, USA, catalog # NG11755) was included in the assay.
The APOE gene is polymorphic at the two nucleotides rs429358 and rs7412, resulting in 6 possible genotypes: e2/e2, e2/e3, e2/e4, e3/e3, e3/e4 and e4/e4 [
11].
2.3. Plasma Multiplex Cytokine Analysis
Seven plasma cytokines (IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNFα and IFNγ) were measured using the V-PLEX Viral Panel 2 Human Kit multiplex assay from Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) (Rockville, MD, USA, catalog # K15346D-1) per manufacturer’s instructions. Detection ranges for the different analytes were as follows: IL-1β, 0.149–610 pg/mL; IL-4, 0.0515-211 pg/mL; IL-6, 0.168-690 pg/mL; IL-8, 0.149-612 pg/mL; IL-10, 0.0869-356 pg/mL; TNFα, 0.0896-367 pg/mL and IFNγ, 0.366-1500 pg/mL. All assays were performed in duplicate and the results read using the QuickPlex SQ 120 instrument (MSD). Analyses were done using DISCOVERY WORKBENCH® 4.0 software (MSD).
2.4. Plasma Cortisol, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and BDNF ANALYSES
Plasma cortisol and CRP (high sensitivity, CRPH) were run at the San Francisco VA Health Care Clinical Laboratory. Cortisol was run on a Becton Dickson (BD) DXI600 machine and the CRPH was analyzed on a BD AUJ800 machine.
Since platelets can release stored brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) upon activation, we used platelet poor plasma (PPP) in the BDNF assays. PPP was prepared by centrifuging the EDTA plasma at 10,000 xg for 10 minutes at 4 °C and collecting the clarified plasma. Both pro- and mature BDNF in the PPP were measured using the Total BDNF Quantikine ELISA kit available from bio-techne R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA, catalog # BDNT00) per manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5. nEV Isolation
Neuronal-enriched extracellular vesicles (nEVs) were purified from frozen plasma as previously described [
10] with modifications. Briefly, 2.5 units of thrombin (Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, Massachusetts, catalog # T4648) was added for 1 hour to 500 μL of plasma to remove fibrils and coagulation proteins, followed by centrifugation at 6000 xg for 20 minutes. Total EVs (tEV) were then polymer precipitated by adding 252 μL of ExoQuick
TM Exosome Precipitation Solution (Systems Biosciences, Palo Alto, California, USA; catalog # EXOQ20A-1) to the clarified plasma in the presence of 3X protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Rockford, Illinois, catalog # 78446). The precipitated tEV pellets were resuspended in 700 μL water containing 1X protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Four μg of biotinylated L1CAM monoclonal antibody (Clone 5G3, Thermo-Fisher Scientific, catalog # 13-1719-82) in 3% BSA was then added for 2 hours at room temperature followed by addition of 80 μL of streptavidin-conjugated agarose beads (Pierce
TM Streptavidin Plus UltraLink
TM Resin from Thermo-Fisher Scientific, catalog #53117) in 3% BSA for 1 hour at RT. The L1CAM+ EV agarose bead complexes were washed and 200 μL of 0.1M Glycine-HCl (pH3) added for 10 seconds on ice followed by centrifugation at 4500 xg for 5 minutes at 4 °C. Supernatants containing the released nEVs were collected, neutralized with 30 μL Tris-HCl (pH8), aliquoted and stored at -80 °C until analysis.
2.6. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
NTA was performed on intact nEV samples to determine size and particle counts. Data were generated using a ZetaView® x30 QUATT instrument (Particle Metrix GmbH, Inning am Ammersee, Germany) with a 488 nm laser-equipped chamber. Instrument calibration was performed using a known concentration of 100 nm polystyrene beads. Eleven positions were counted and analyzed using the ZetaView version 8.05.16 SP3 software. Each position was measured for 2 cycles using a sensitivity of 75 and a shutter value of 100. Triplicate readings were performed for each sample and the average reported.
2.7. Tetraspanins Multiplex Assay
Intact nEVs were quantified for tetraspanin protein levels using MSD assays for CD9, CD63, CD81 (MSD, Rockville, MD, USA, custom kit catalog #K15228N-1 using antibody set catalog #s F215M-3-8, F2215L-3/-8 and F215N-3-8). All MSD assays were performed according to manufacturer’s instructions and each sample was tested in duplicate. All analyses were done using a QuickPlex SQ 120 instrument (MSD) and DISCOVERY WORKBENCH 4.0® software.
2.8. EV Lysate Preparation
Immediately after isolation (see section 2.5 above), a portion of the nEVs were lysed for protein analyses using 2X volume of lysis buffer containing a final concentration of 0.25% BSA, 2X protease and phosphatase inhibitors, and M-PERTM Mammalian Protein Extraction Reagent (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, catalog # 78501). Lysates were freeze-thawed twice, aliquoted and stored at -80 °C until analysis.
2.9. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) on nEV Lysates
ELISAs were performed on the nEV lysates to determine protein levels for Alix (ALG-2-interacting protein X, also known as programmed cell death 6-interacting protein), high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and NeuN (neuronal nuclei protein, also known as RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3 [RBFOX3]) using the following commercially-available kits: Alix (Lifeome, Oceanside, California, USA, catalog # CSB-EL017673HU, range: 0.031-2 ng/mL), HMGB1 (Novus Biologicals, LLC, Centennial, CO, USA, catalog #NBP2-62766, range: 0.031 – 2 ng/mL) and NeuN (Abbexa LLC, Houston, Texas, USA, catalog # abx541982, range: 0.312 – 20 ng/mL). All ELISAs were performed according to manufacturer’s instructions and each sample was analyzed in duplicate. Protein concentrations were determined by absorbance using a SpectraMax M5 plated reader (Molecular Devices, LLC, San Jose, CA, USA) with Softmax Pro 7 software (Molecular Devices).
2.10. Luminex Multiplex Assay for Neurodegeneration Proteins
Luminex bead assays were performed on the nEV lysates using a Neurodegeneration 9-plex Human ProcartaPlexTM panel from ThermoFisher (catalog #EPX090-15836-901) with a Luminex LX200 instrument using Luminex xMAP Technology. The procedure was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Results were analyzed using MilliplexTM Analyst version 5.1 software. The 9 nEV proteins analyzed by the Luminex assay were Aβ 1-40 (detection range: 451–1,847,000 pg/mL), Aβ 1-42 (range: 0.42–1700 pg/mL), fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21, range: 8.64–35,400 pg/mL), kallikrein-related peptidase 6 (KLK6, range: 5.57–22,800 pg/mL), neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, range: 54–221,900 pg/mL), neurogranin (NRGN, range: 10–41,600 pg/mL), TAR DNA binding protein 43 (TDP-43, range: 96–393,200 pg/mL), total Tau (range: 20–80,000 pg/mL), and p-T181-tau (range: 1.95–2000 pg/mL).
2.11. Statistical Analysis and Bioinformatics
All statistical analyses were done using GraphPad Prism 10 software (GraphPad Software Inc., Boston, MA, USA). Since the data values were not distributed normally, the Mann Whitney U test was used when comparing the group medians between two groups (Figure 5A) and the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by post-hoc Dunn’s test was used when comparing the group medians between three groups (Figures 2A, 3A, 4ABC and 5A). For correlation analyses, Spearman 2-tailed correlation was used.
Several computational tools and software were used to classify and detect biomarkers associated with nLongC. Data analyses were carried out using MATLAB (Version R2023a, The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA) and R (Version 4.2.2; R Core Team). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was performed using the online platform provided by the Gene Ontology Consortium (
http://geneontology.org/) to explore the biological implications of the identified genes. For functional annotation, Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) (
https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp) and g:Profiler (ELIXIR, Tartu, Estonia;
https://biit.cs.ut.ee/gprofiler/gost) were used.
4. Discussion
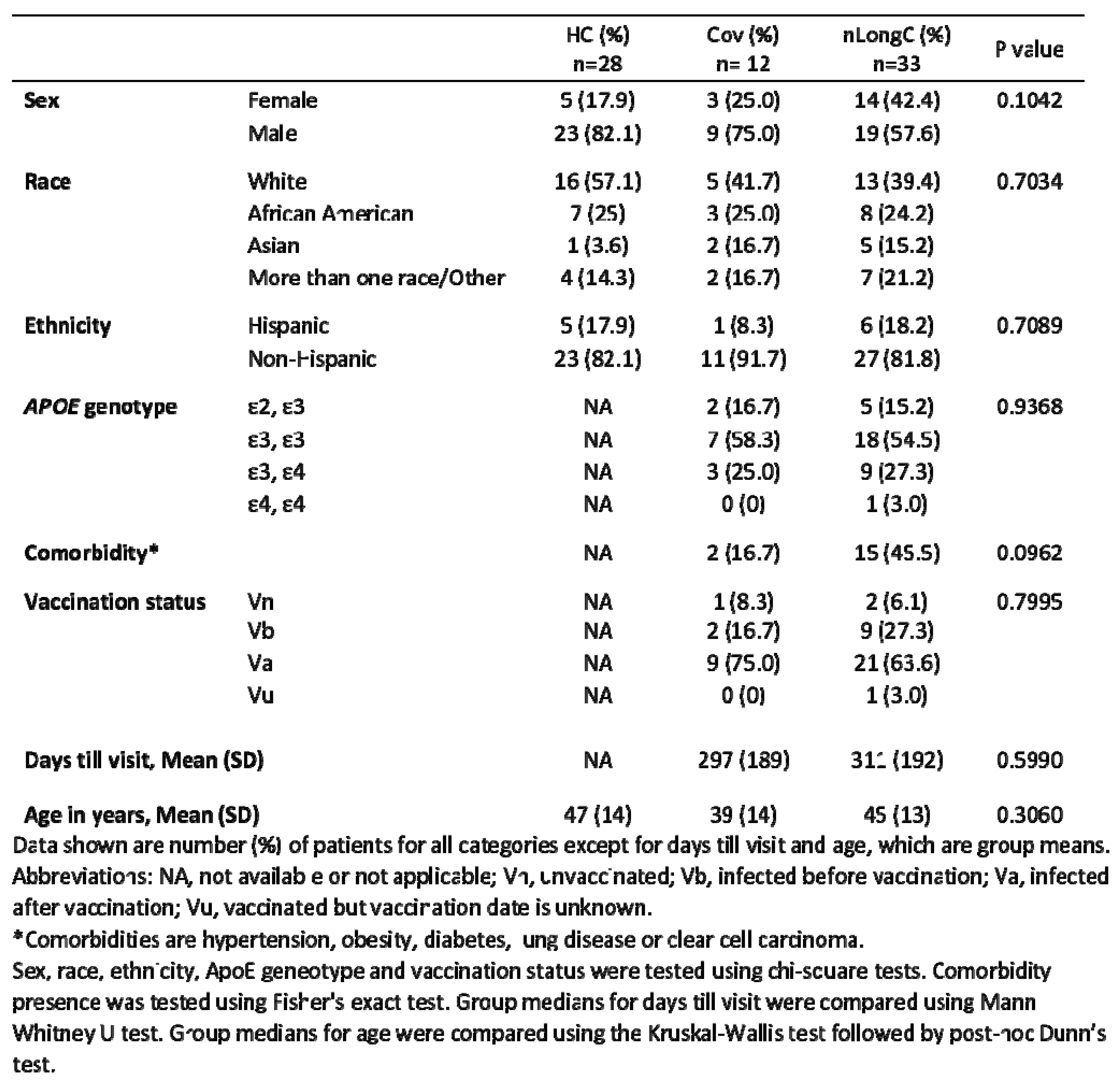
This was a pilot study with a small sample size of 28 pre-pandemic COVID-19 controls, 12 recovered individuals, and 33 subjects with self-reported persisting neurological symptoms with a focus on blood protein biomarkers of nLongC. Others have reported female sex and comorbidity presence as being risk factors for LongC [
21,
22]. In our cohort, these risk factors did not reach statistical significance (
Table 1).
We previously analyzed the plasma and nEVs of nLongC subjects who were 36 – 103 days post-infected (average 77 days) with, likely, the 614 SARS-CoV-2 variant given the time of infection (early 2020) [
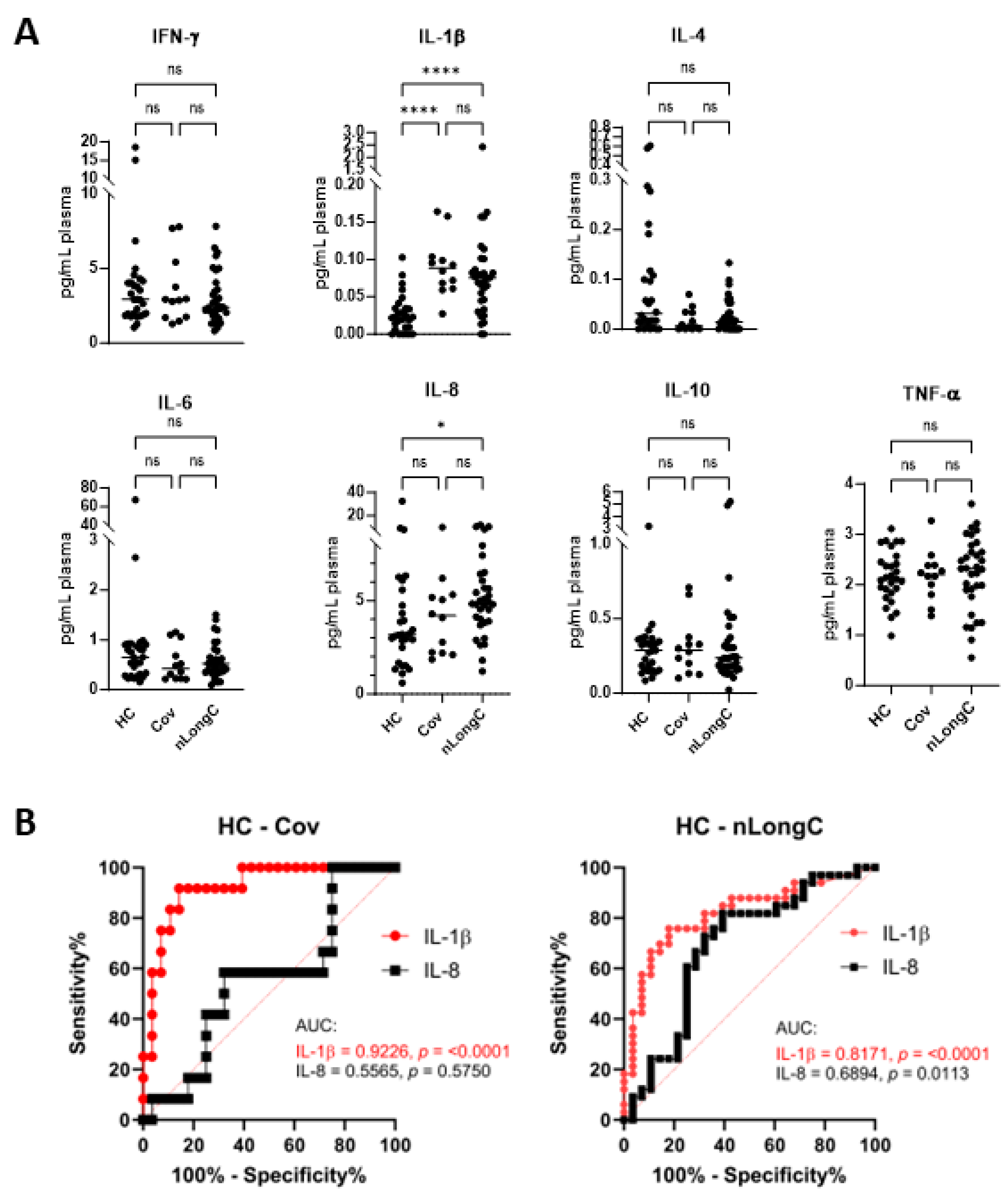
10]. These early nLongC subjects showed elevations in IL-1β, IL-4 and IL-6. The elevated IL-1β finding here in all COVID-19-infected individuals, regardless of lingering sequelae (
Figure 2A), is consistent with other published reports [
17,
23,
24]. In contrast, our current cohort who were infected later and who experienced nLongC for a longer time (mean of 311 days), showed a different plasma cytokine profile with elevations in IL-1β and IL-8. The shift from IL-4 and IL-6 to IL-8 may be a result of the two different cohorts being infected with different viral variants, vaccination response or timing to recovery. The increased plasma IL-1β and IL-8 found in this study has also been reported in a larger LongC cohort with a mean post-infection time of 140 days [
25]. In the elderly, elevated IL-8, and not IL-1β, has been associated with poor memory, speed domains and motor functions [
26]. In addition, higher plasma IL-8 levels were found in patients with AD that correlated with cognition severity [
27]. Because others have found similar pathological elements between SARS-CoV-2 infection and AD [
28,
29], it is tempting to speculate that increased IL-8 may play an important role in the neurological sequelae of COVID-19.
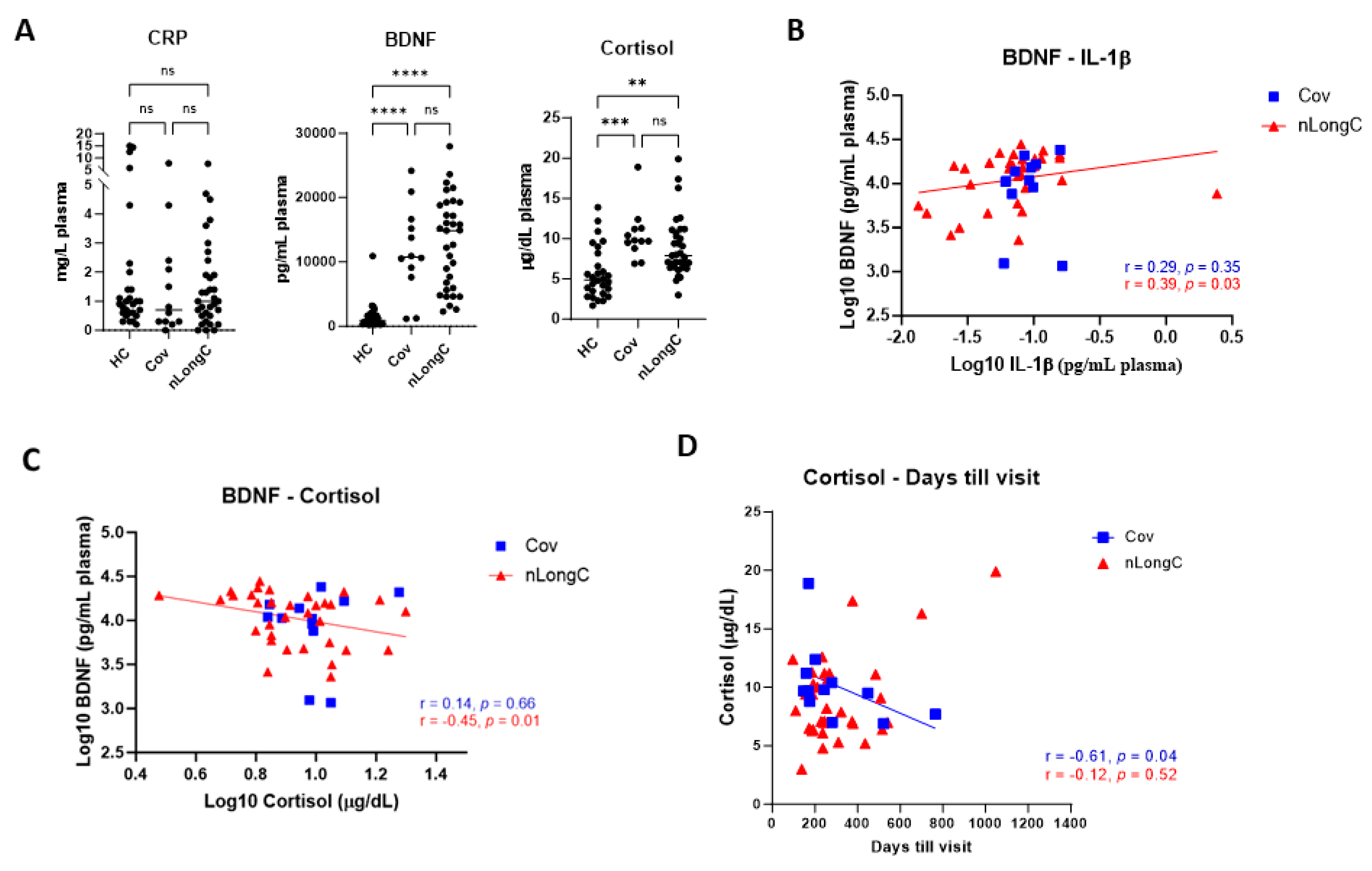
Cytokines, as well as C reactive protein (CRP), can be measures of acute inflammation and have been found to be elevated in early COVID-19 infection. [
30]. Published results on CRP levels between LongC and those people recovered from COVID-19 vary. There are many reasons for this including sampling criteria, limitation in biomarker discovery and hospitalization. One review based on literature studies, suggested that overexpression of IL-6, CRP and TNFα for 1 or more months post-infection may constitute a core set of biomarkers for LongC even though when compared to recovered patients, only 6/10, 3/20 and 3/20 studies found increased IL-6, CRP and TNFα, respectively [
31]. Our present study found no increase in peripheral IL-6, TNFα or CRP (Figures 2A, 3A). This may be a reflection that LongC is not a continuation of an acute inflammatory condition.
Under normal conditions, cortisol binds to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), eliciting anti-inflammatory effects. However prolonged or excessive cortisol may result in a compensatory down-regulation or resistance to GR-mediated signaling, leading to pro-inflammatory effects [
32]. In the present study, cortisol was significantly elevated in both Cov and nLongC groups compared to HCs (
Figure 3A), although the levels were still within the normal range of 10-20 μg/dL [
33]. Over time after infection, we saw a decrease in cortisol in recovered COVID individuals but not in people with nLongC (
Figure 3D). Continued elevated cortisol levels in nLongC individuals may have negative cognitive effects. Changes in levels of cortisol have been reported in people at risk for mental illness, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic [
33]. Other studies have shown an association of increased plasma cortisol to elevated Aβ burden as seen by PiB-PET imaging which can discriminate between healthy control persons, those with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and those with AD [
34,
35]. The fact that there was also an increase in Aβ42 in nEVs from people with nLongC that was not seen in nEVs from people who recovered from Cov (
Figure 5A) further supports the hypothesis that persistently elevated cortisol may facilitate the neurological sequelae seen in some COVID individuals by possibly increasing Aβ42 deposition. A recent publication by Klein et al. using a larger cohort of 275 individuals with or without LongC showed decreased cortisol in the LongC group compared to healthy, uninfected vaccinated controls and previously infected, vaccinated controls without persistent symptoms [
25]. The difference in results between our study and the Klein study may be due to the different post-infection times of the LongC cohorts. In the Klein study, the average post-infection time was much longer at around 450 days, while in our study it was shorter at 311 days. Since injury to the adrenal glands has been reported in LongC individuals as a result of immune damage leading to hypocortisolemia [
36], it is possible that the elevated cortisol levels we saw in our nLongC cohort will diminish over time as continued inflammation delivers more harm to the adrenal tissue.
Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) is a neurotrophin that modulates synaptic plasticity and promotes neurogenesis [
37,
38]. It crosses the BBB and can be measured in the brain [
39]. Since BDNF is a trophic factor, it’s thought that a decrease in BDNF could contribute to neuro-degeneration and, indeed, it is significantly decreased in people with AD [
40]. However, further studies looking at people with MCI showed an increase in peripheral BDNF as a compensatory mechanism with early AD showing higher levels and late AD showing lower levels of BDNF when compared to controls [
41,
42]. In this study we found in nLongC individuals, there was a moderate positive correlation of IL-1β to BDNF (
Figure 3B) and a moderate negative correlation to cortisol (
Figure 3C). Since high cortisol reduces BDNF expression under stressful conditions [
19], our data suggest that people with nLongC may be under chronic stress due to the systemic inflammation and may respond initially with a compensatory elevated level of BDNF that signals MCI. However over time, BDNF may decline to a level that signals more severe neurological dysfunction and cognitive impairment. Since MCI is thought to be a continuum to AD, measuring BDNF further out in time in LongCOVID-19 may illuminate this pattern.
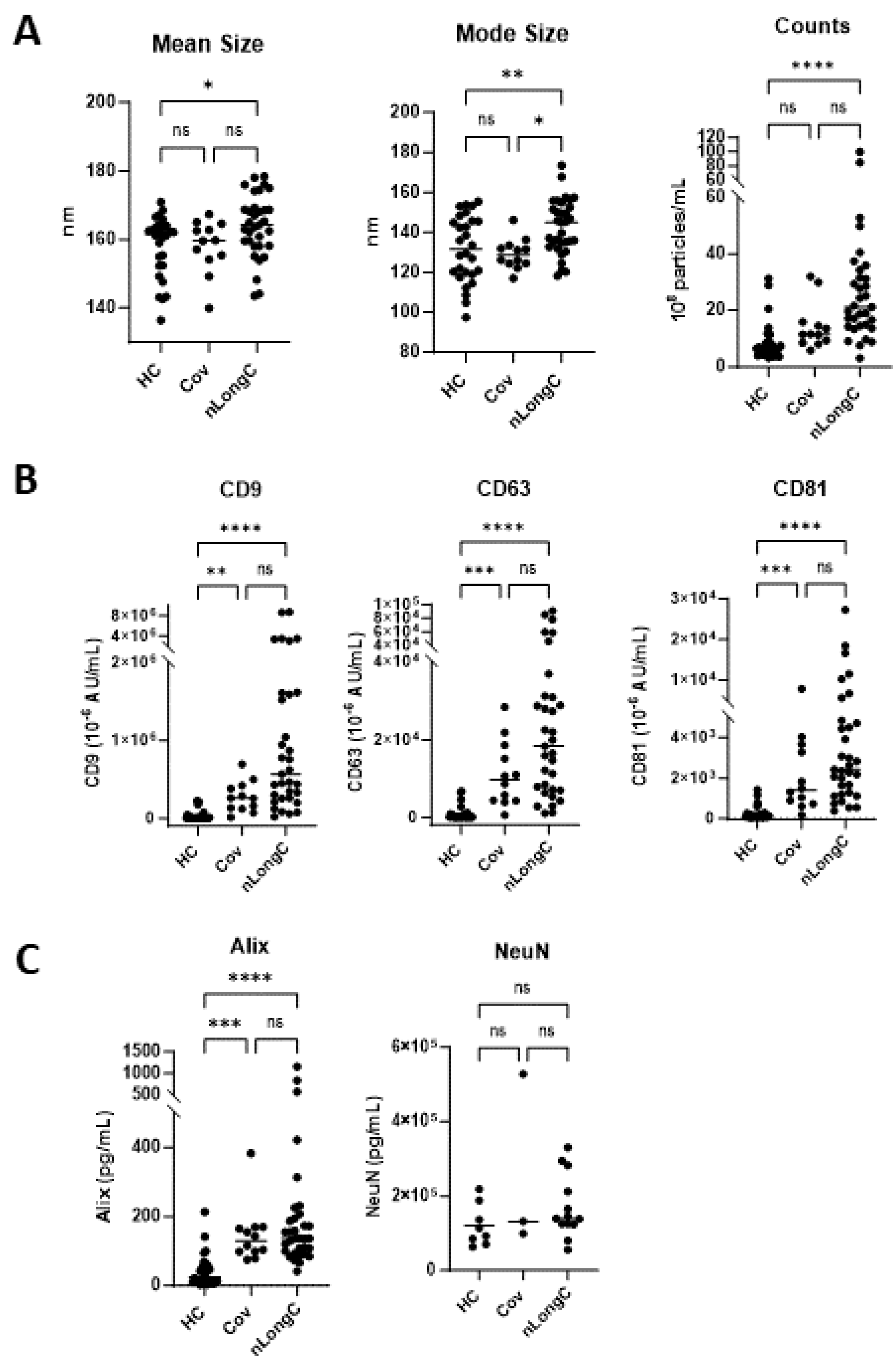
Neuronal enriched extracellular vesicles may be a good indicator of neuronal health in real time. It is less invasive than cerebrospinal fluid and less complex than total EVs from the periphery. Our lab is the first to study nEVs as biomarkers of LongC. In our previous report on nLongC, we analyzed nEVs and found that the neurodegenerative proteins in a multiplex assay were all significantly increased in people with LongC, with or without neurological symptoms [
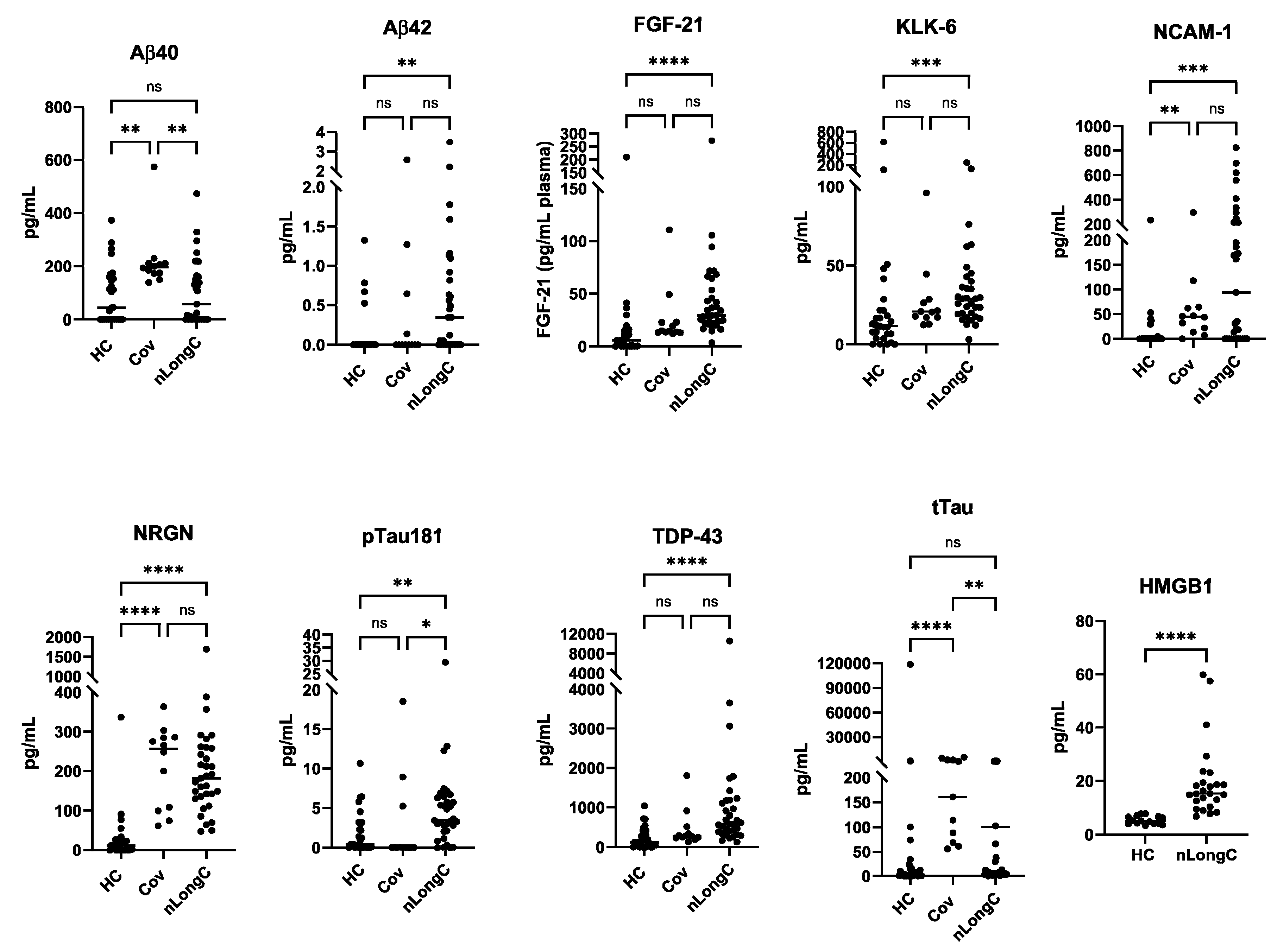
10]. We did not test people without LongC. In the present study, it is clear that there are differences between recovered persons and those with nLongC. There are no differences in Aβ42, FGF-21, KLK-6, pTau181 and TDP-43 cargo in nEVs from the HC and Cov groups. However, people who had COVID-19 infection and recovered, do have altered nEV cargo with increases in Aβ40, NCAM-1, NRGN, and tTau, suggesting that neurons are still affected. People recovered from COVID-19 infection also have increased IL-1β, cortisol and BDNF. These biomarkers are not normal and need to be followed longitudinally to see if they revert to normal. Most troubling are the sustained high levels of the other toxic proteins, Aβ42, FGF-21, KLK-6, pTau181 and TDP-43, observed in nEVs from nLongC individuals. When we reported this in nEVs of people with nLongC in 2021, we speculated that this secretion might be a positive mechanism for neurons to expel toxic proteins. This may still be a possibility but at some point over time, this accumulation may have negative consequences on cogntion.
HMGB1 is a nuclear protein that promotes inflammation [
43] and we reported an increase of this protein previously with nEVs from nLongC individuals [
10] and in HIV-infected individuals with cognitive impairment [
44]. When released in the brain, it can activate microglia and when released in the periphery from EVs can promote inflammation [
45].
There are several limitations to this study. Because the participant numbers are small, these results will need to be confirmed with a larger cohort. The rigorous assessment of cognitive dysfunction is missing as the participants’ mental status was self-reported. However, in spite of a lack of vigorous neurocognitive testing, there were still significant biological differences in the groups. We speculate that self-reporting of a change in cognition may precede any clinical neurological testing results. Going forward a more standardized assessment of cognitive health should be used. People with pre-existing cognitive impairment or clinical psychiatric illness were not included. With these drawbacks, the data suggest emerging significant differences in several measurable parameters between healthy pre-pandemic controls and people recovering from COVID-19 and those with neurological complaints, suggesting a biological rationale for these conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.T. and L.P.; methodology, N.T., T.K., E.M, L.P., J.M.F., K.D.; software, N.T., J.S., T.K.; formal analysis, N.T., L.P.; investigation, N.T., L.P.; resources, L.P., J.M.F.; data curation, N.T., K.D.; writing—original draft, N.T., L.P.; writing—review and editing, N.T., L.P., T.K., J.S., E.M., J.M.F., K.D.; project administration, L.P.; funding acquisition, L.P., J.M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
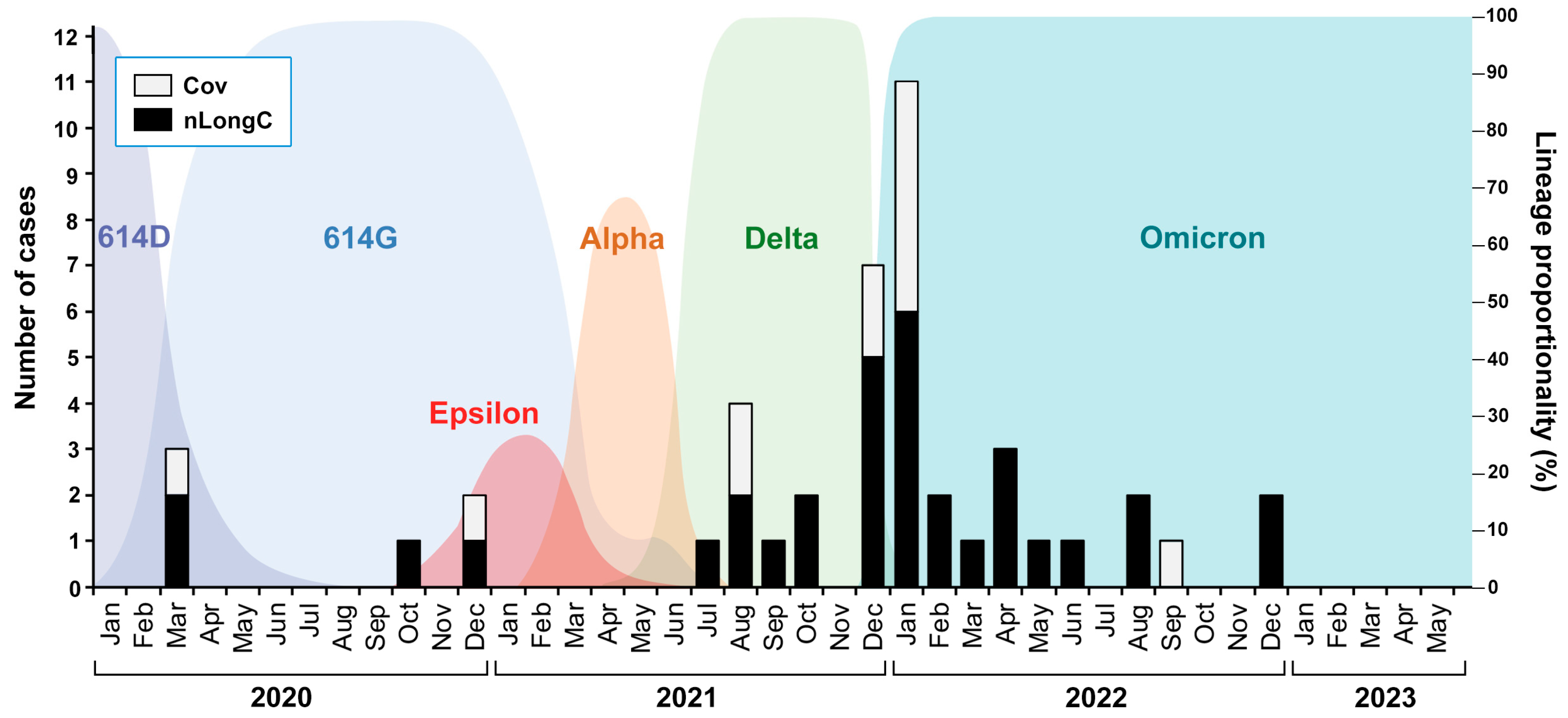
Figure 1.
nLongC and Cov participants were infected over a period of 3 years with likely different SARS-CoV-2 variants. The COVID-19 cases described in this study are shown as black and white bars superimposed onto a background of SARS-CoV-2 variants described by Wang et al. 2022 [
12] and Lam et al. 2020 [
13].
Figure 1.
nLongC and Cov participants were infected over a period of 3 years with likely different SARS-CoV-2 variants. The COVID-19 cases described in this study are shown as black and white bars superimposed onto a background of SARS-CoV-2 variants described by Wang et al. 2022 [
12] and Lam et al. 2020 [
13].
Figure 2.
Plasma cytokines. (A) Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) analysis for 7 cytokines showed a significant increase in IL-1β for both Cov and nLongC groups. IL-8 was increased only in the nLongC group. Horizontal bars indicate group medians which were compared using Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn tests. P value symbols are as follows: ns = p > 0.05, *p ≤ 0.05) and ****p ≤ 0.0001. HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33). (B) Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves for significantly differentially expressed plasma cytokines, Il-1β and IL-8. Area under curve (AUC) is shown in graphs. Significantly differentially expressed cytokines are displayed for each pair of groups: IL-1β (solid red line) and IL-8 (solid black line).
Figure 2.
Plasma cytokines. (A) Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) analysis for 7 cytokines showed a significant increase in IL-1β for both Cov and nLongC groups. IL-8 was increased only in the nLongC group. Horizontal bars indicate group medians which were compared using Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn tests. P value symbols are as follows: ns = p > 0.05, *p ≤ 0.05) and ****p ≤ 0.0001. HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33). (B) Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves for significantly differentially expressed plasma cytokines, Il-1β and IL-8. Area under curve (AUC) is shown in graphs. Significantly differentially expressed cytokines are displayed for each pair of groups: IL-1β (solid red line) and IL-8 (solid black line).
Figure 3.
Plasma levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF), C-reactive protein (CRP) and cortisol. (A) People with Cov and nLongC had elevated levels of BDNF and cortisol without increased CRP (Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests). ns = p > 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. BDNF had a moderate positive correlation with IL-1β in the nLongC group (B) (Spearman r = 0.39, p = 0.03) and a moderate negative correlation with cortisol (C) (Spearman r = -0.45, p = 0.0087). (D) Cortisol decreased over time in Cov subjects but not in nLongC individuals. For all panels, HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33).
Figure 3.
Plasma levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF), C-reactive protein (CRP) and cortisol. (A) People with Cov and nLongC had elevated levels of BDNF and cortisol without increased CRP (Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests). ns = p > 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. BDNF had a moderate positive correlation with IL-1β in the nLongC group (B) (Spearman r = 0.39, p = 0.03) and a moderate negative correlation with cortisol (C) (Spearman r = -0.45, p = 0.0087). (D) Cortisol decreased over time in Cov subjects but not in nLongC individuals. For all panels, HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33).
Figure 4.
Characterization of nEVs. (A) Nanotracking analysis (NTA) showed larger and more abundant nEVs for nLongC. (B) nEV tetraspaninins CD9, CD63 and CD81 were all increased in both Cov and nLongC groups. (C) Exosomal protein Alix is increased in both Cov and nLongC groups while NeuN is present in all nEVs at similar levels between the three groups. For NeuN, there were fewer values in each group due to insufficient sample availability: HC (N=8), Cov (N=3), nLongC (N=13). Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests were performed for all comparisons. ns = p > 0.05, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Group sample sizes for all (except NeuN) were HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33).
Figure 4.
Characterization of nEVs. (A) Nanotracking analysis (NTA) showed larger and more abundant nEVs for nLongC. (B) nEV tetraspaninins CD9, CD63 and CD81 were all increased in both Cov and nLongC groups. (C) Exosomal protein Alix is increased in both Cov and nLongC groups while NeuN is present in all nEVs at similar levels between the three groups. For NeuN, there were fewer values in each group due to insufficient sample availability: HC (N=8), Cov (N=3), nLongC (N=13). Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests were performed for all comparisons. ns = p > 0.05, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Group sample sizes for all (except NeuN) were HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33).
Figure 5.
Neuronal protein cargo in nEVs. nEV lysates were analyzed using a 9-plex Luminex neurodegeneration panel and ELISA for HMGB1. Concentrations were normalized to plasma volume. All of the proteins except Aβ40 and tTau were increased in nEVs from the nLongC group. For the Cov group, only 4 proteins were elevated (Aβ40, NCAM-1, NRGN, tTau). Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests were performed for all comparisons. ns = p > 0.05), *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Group sample sizes were HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33), except for HMGB1 which were HC (N=15) and nLongC (N=25).
Figure 5.
Neuronal protein cargo in nEVs. nEV lysates were analyzed using a 9-plex Luminex neurodegeneration panel and ELISA for HMGB1. Concentrations were normalized to plasma volume. All of the proteins except Aβ40 and tTau were increased in nEVs from the nLongC group. For the Cov group, only 4 proteins were elevated (Aβ40, NCAM-1, NRGN, tTau). Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by post-hoc Dunn’s tests were performed for all comparisons. ns = p > 0.05), *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Group sample sizes were HC (N=28), Cov (N=12) and nLongC (N=33), except for HMGB1 which were HC (N=15) and nLongC (N=25).
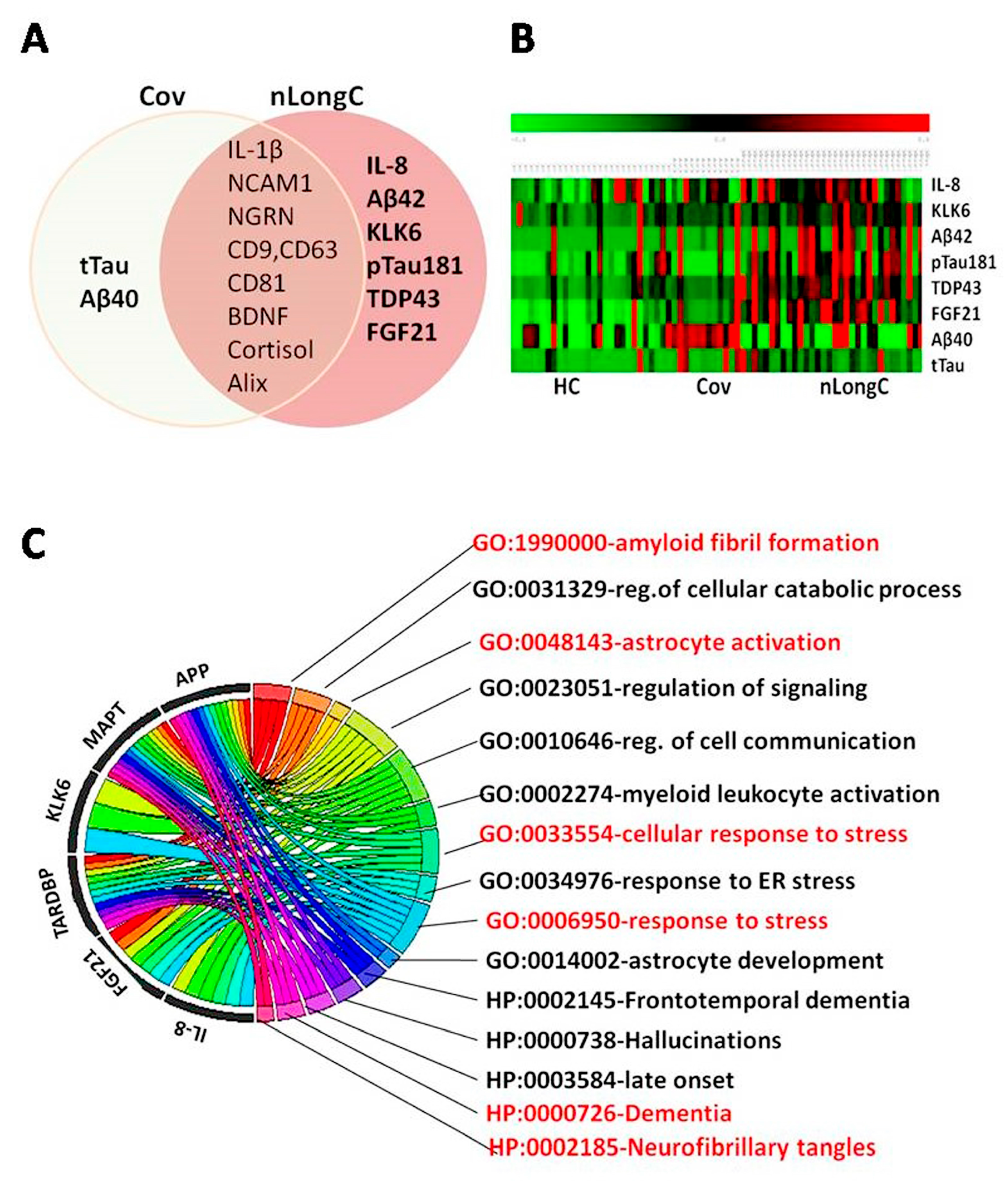
Figure 6.
Biomarker and informatics classification analyses for nLongC. (A) Venn diagram delineating the biomarkers used in the study. (B) Heatmap of eight critical biomarkers protein levels, with samples from healthy controls (HC) on the left, Cov in the middle, and nLongC on the right. Red represents higher expression and green represents lower expression. (C) Chord diagram depicting the connections between the genes and their associated GO and HP terms, providing insights into the biological processes and functions related to nLongC pathogenesis.
Figure 6.
Biomarker and informatics classification analyses for nLongC. (A) Venn diagram delineating the biomarkers used in the study. (B) Heatmap of eight critical biomarkers protein levels, with samples from healthy controls (HC) on the left, Cov in the middle, and nLongC on the right. Red represents higher expression and green represents lower expression. (C) Chord diagram depicting the connections between the genes and their associated GO and HP terms, providing insights into the biological processes and functions related to nLongC pathogenesis.
Table 1.
Demographics of healthy control, Cov and nlongC groups.
Table 1.
Demographics of healthy control, Cov and nlongC groups.