Submitted:
14 February 2024
Posted:
19 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
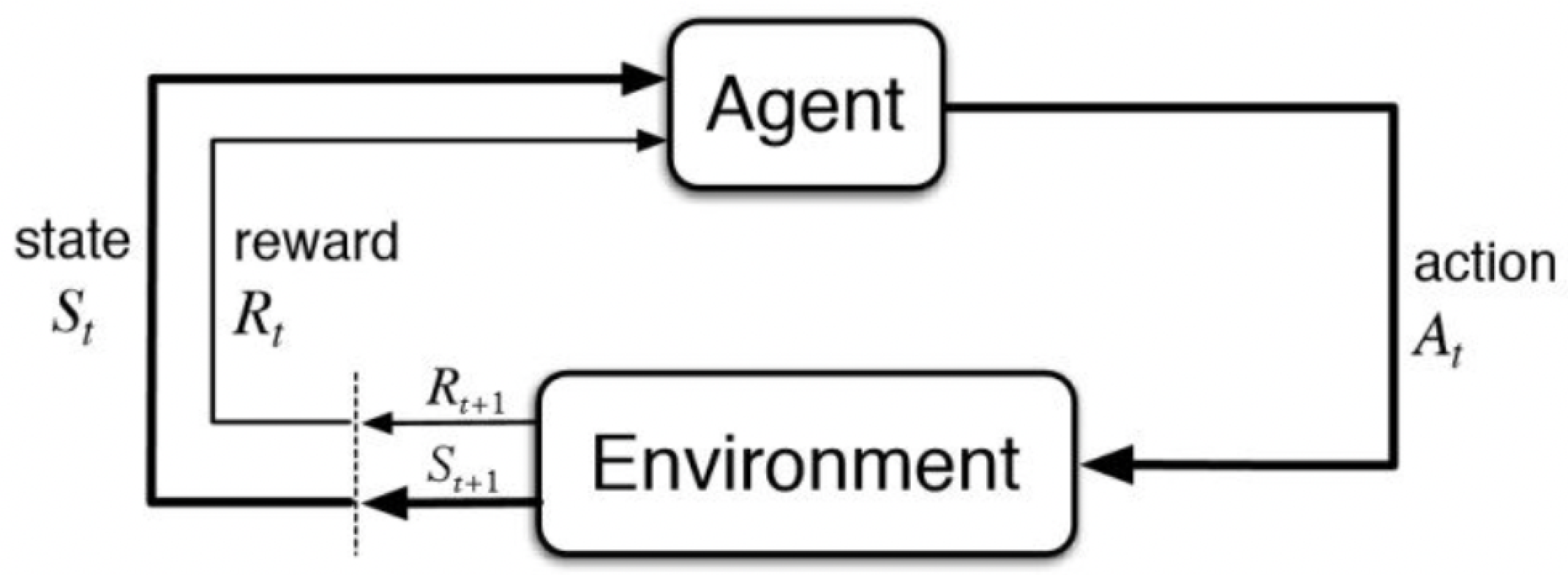
- Reinforcement Learning: A machine learning approach where an agent refines decision-making skills by interacting with the environment, guided by rewards or penalties for actions, progressively improving decisions [18].
- Emergent Behavior: For Reinforcement Learning agents, emergent behaviors relate to unpredictable actions arising from the combination of simpler actions; in collaborative robotics, it’s the robot’s ability to exhibit unplanned responses from interactions [9].
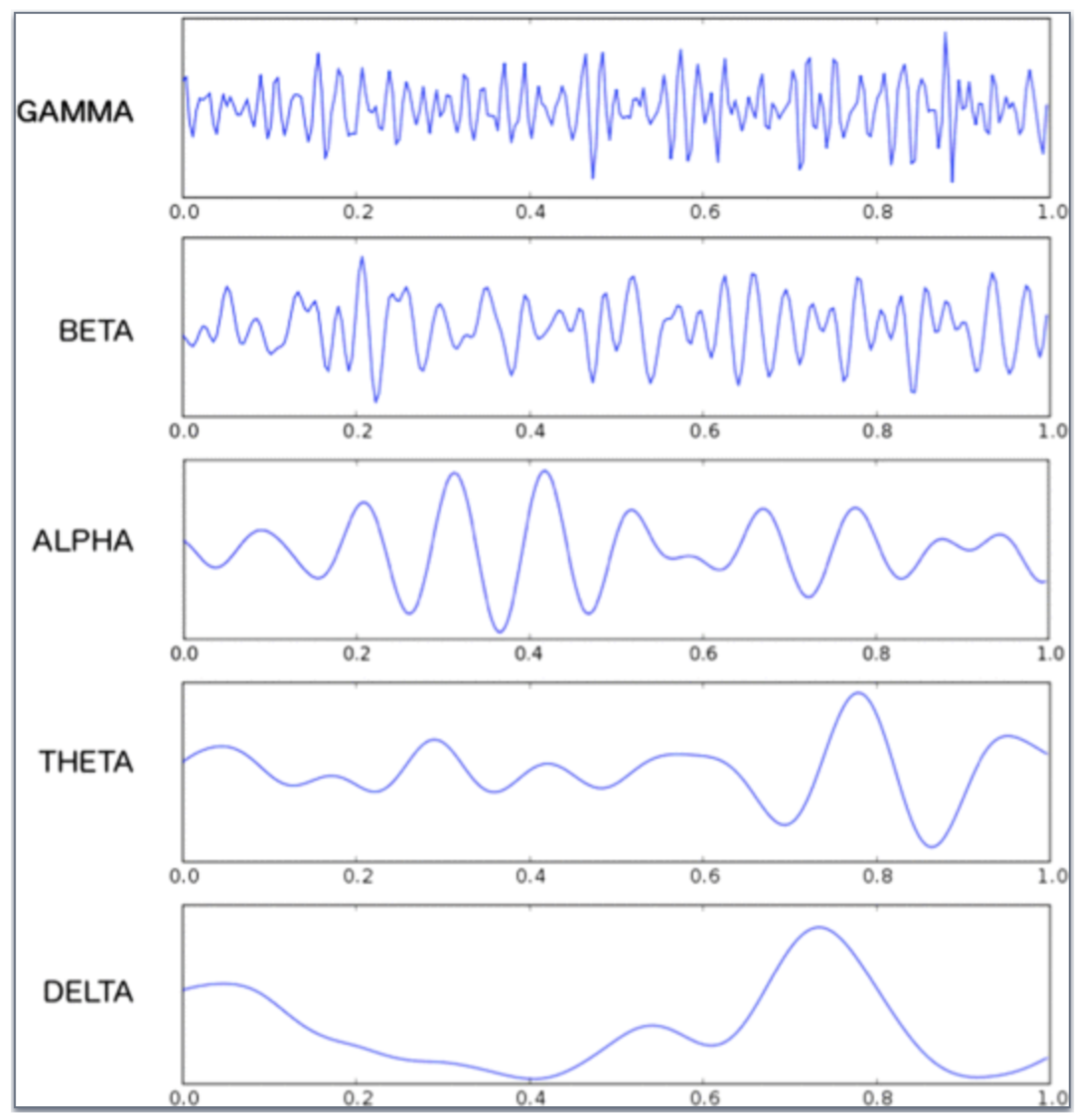
- EEG Sensors: Devices measuring brain electrical activity, valuable for monitoring neural signals and cognitive processes, particularly in assessing the mental state of human operators in collaborative robotics [19].
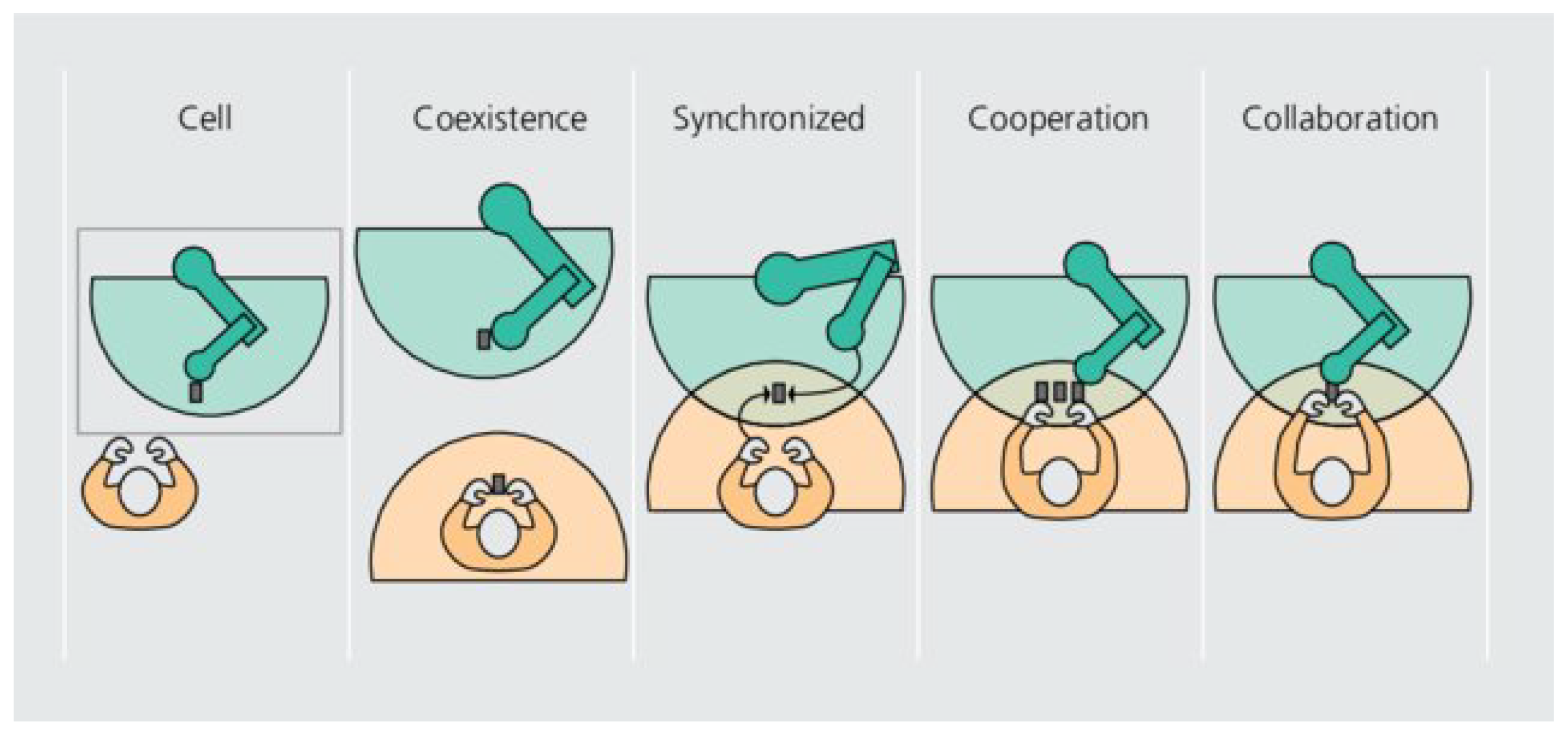
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Dynamic interactions between humans and robots in collaborative settings, encompassing communication, cooperation, and the study of their collaboration in shared workspaces [20]. In construction, innovative categorizations have been developed leading to better approaches in Human-Robot Interaction problems[21].
- Virtual Reality (VR): An immersive technology that transports users to computer-generated environments, offering a multisensory experience that can simulate real-world scenarios, impacting fields such as education, robotics, gaming, and therapy [22].
2. Materials and Methods
3. State of the Art
3.1. EEG based Brain-Computer Interface Approaches in Collaborative Robot Control
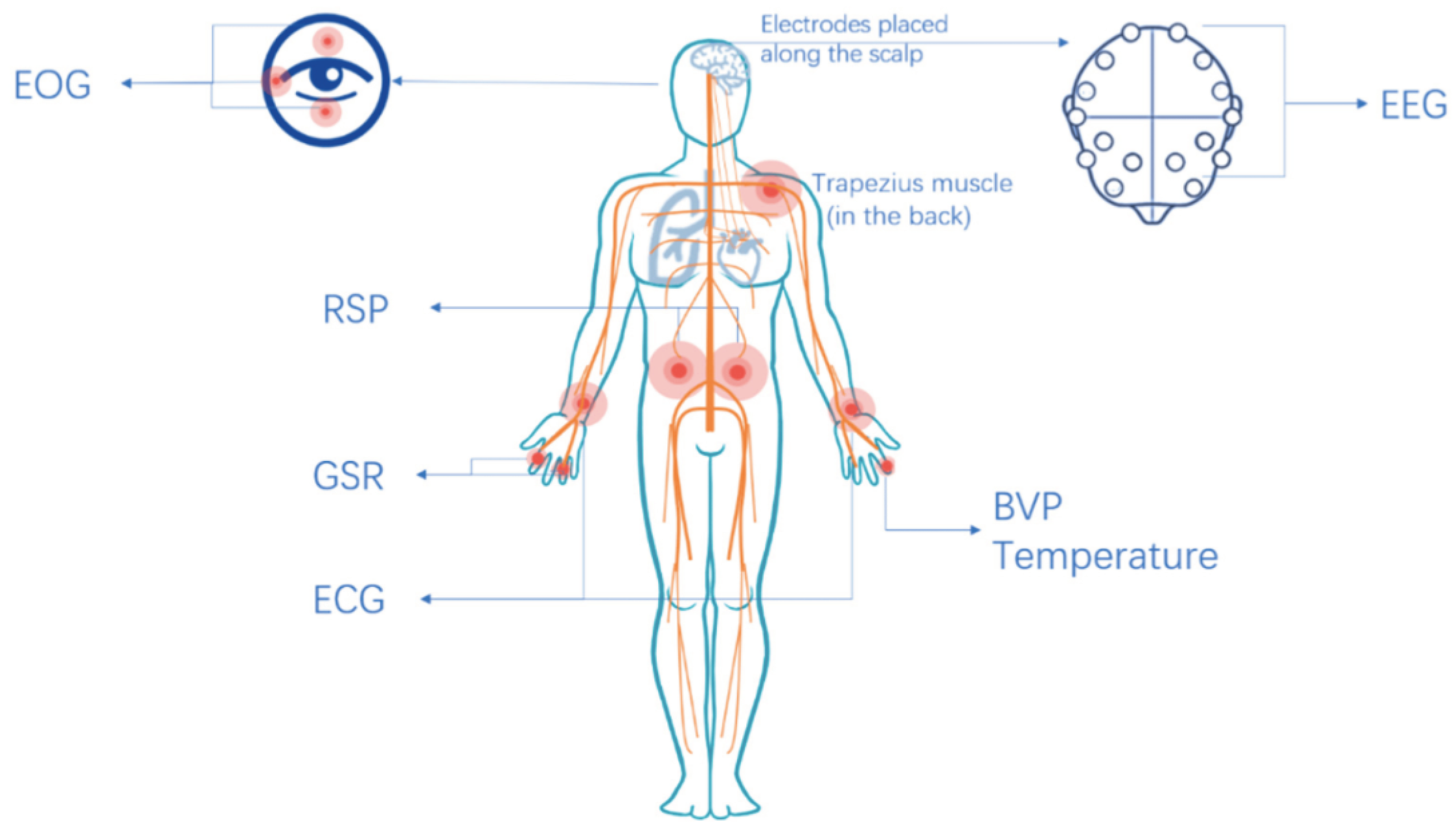
3.2. Additional Human State Measuring Techniques for Collaborative Robotics
3.3. Immersive Technologies as a Safe Training Ground for Reinforcement Learning in Human-Interactive Robotics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| HRI | Human-Robot Interaction |
| ICA | Independent Component Analysis |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| BCI | Brain Computer Interfaces |
| ERP | Error Related Potentials |
| ErrP | Error Potential-related events |
| HAR | Human Robot Recognition |
| BDI | Beck Depression Inventory |
| PSS | Perceived Stress Questionnaire |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| MR | Mixed Reality |
| HDT | Human Digital Twins |
References
- Weiss, A.; Wortmeier, A.K.; Kubicek, B. Cobots in industry 4.0: A roadmap for future practice studies on human–robot collaboration. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2021, 51, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, F.; Asad, M.M.; Ibrahim, B. Collaborative Robots and Industrial Revolution 4.0 (IR 4.0). 2020 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Smart Technologies (ICETST). IEEE, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Parsons, H. Human factors in industrial robot safety. Journal of Occupational Accidents 1986, 8, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, W.; Bender, M.; Braun, M.; Rally, P.; Scholtz, O. Lightweight robots in manual assembly – best to start simply! Examining companies’ initial experiences with lightweight robots; 2016.
- Pearce, M.; Mutlu, B.; Shah, J.; Radwin, R. Optimizing makespan and ergonomics in integrating collaborative robots into manufacturing processes. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, V.D.; Pasquale, V.D.; Giubileo, V.; Miranda, S. Human-Robot Collaboration: an analysis of worker’s performance. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragic, D.; Gustafson, J.; Karaoguz, H.; Jensfelt, P.; Krug, R. Interactive, Collaborative Robots: Challenges and Opportunities. Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence; International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization: California, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, T.B. Human-robot interaction: Status and challenges. Hum. Factors 2016, 58, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, J.; Bagnell, J.A.; Peters, J. Reinforcement learning in robotics: A survey. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2013, 32, 1238–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, J.; Bagnell, J.A.; Peters, J. Reinforcement learning in robotics: A survey. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2013, 32, 1238–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormushev, P.; Calinon, S.; Caldwell, D. Reinforcement Learning in Robotics: Applications and Real-World Challenges. Robotics 2013, 2, 122–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, L.; Greeff, M.; Hall, A.W.; Yuan, Z.; Zhou, S.; Panerati, J.; Schoellig, A.P. Safe Learning in Robotics: From Learning-Based Control to Safe Reinforcement Learning. Annual Review of Control, Robotics, and Autonomous Systems 2022, 5, 411–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction; MIT press, 2018.
- Maurtua, I.; Ibarguren, A.; Kildal, J.; Susperregi, L.; Sierra, B. Human–robot collaboration in industrial applications: Safety, interaction and trust. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2017, 14, 172988141771601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Jia, Y. Learning and comfort in human–robot interaction: A review. Appl. Sci. (Basel) 2019, 9, 5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawangjai, P.; Hompoonsup, S.; Leelaarporn, P.; Kongwudhikunakorn, S.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. Consumer Grade EEG Measuring Sensors as Research Tools: A Review. IEEE Sensors Journal 2020, 20, 3996–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdea, G. Invited review: the synergy between virtual reality and robotics. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation 1999, 15, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelbling, L.P.; Littman, M.L.; Moore, A.W. Reinforcement learning: A survey. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1996, 4, 237–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Gomez, A.F.; DelPreto, J.; Gil, S.; Guenther, F.H.; Rus, D. Correcting robot mistakes in real time using EEG signals. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2017.
- Goodrich, M.A.; Schultz, A.C. Human-Robot Interaction: A Survey. Foundations and Trends® in Human-Computer Interaction 2007, 1, 203–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.B.; Singh, R.; Oytun, M.; Adami, P.; Woods, P.J.; Becerik-Gerber, B.; Soibelman, L.; Copur-Gencturk, Y.; Lucas, G.M. A multidimensional taxonomy for human-robot interaction in construction. Automation in Construction 2023, 150, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M.; Sanchez-Vives, M.V. Enhancing our lives with immersive virtual reality. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
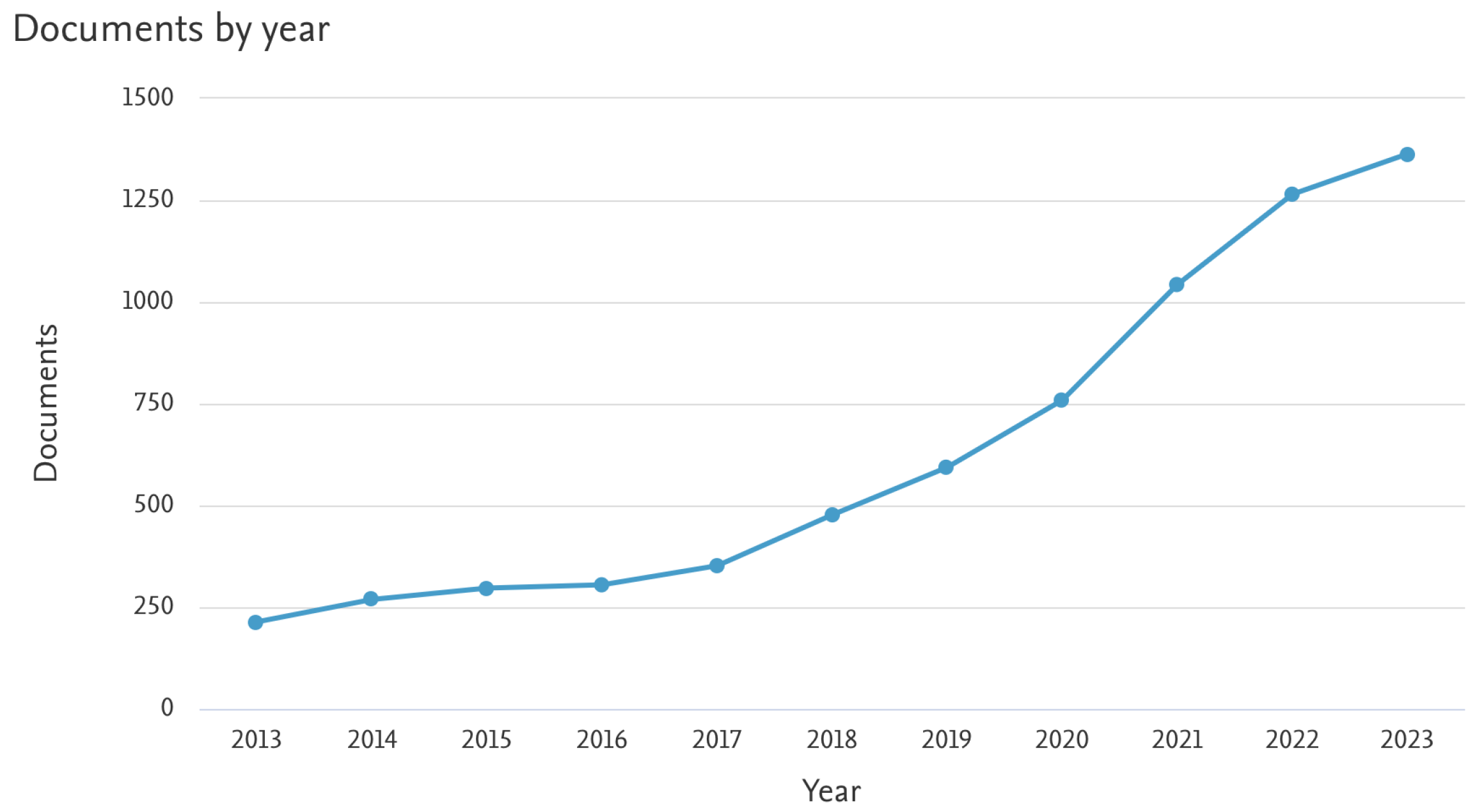
- Google Scholar Search Engine. https://scholar.google.com. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
- Scopus Database. https://www.scopus.com. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
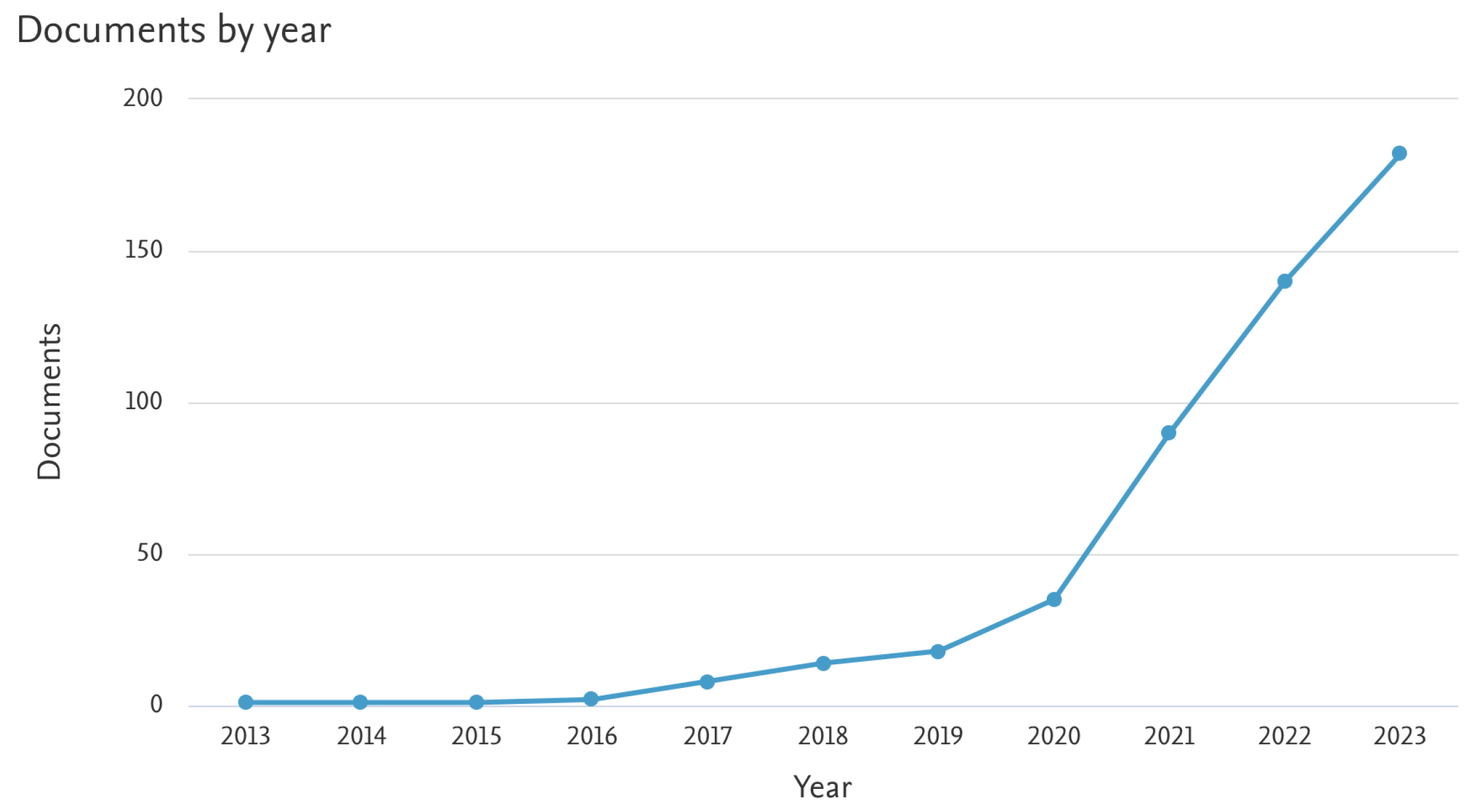
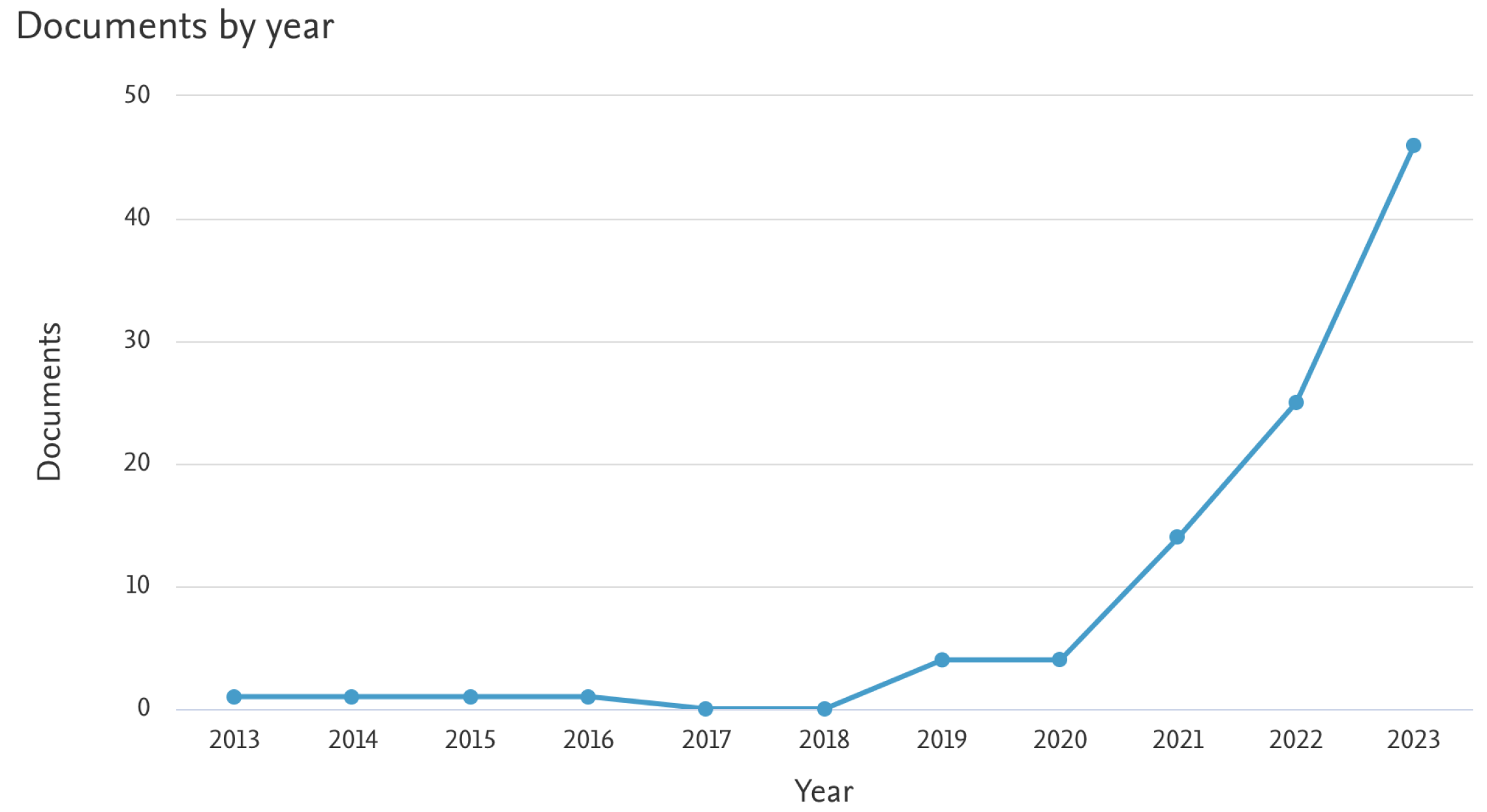
- Scopus. Search results for ’reinforcement learning AND collaborative robotics’ with publications between 2012 and 2024. https://www.scopus.com, 2024. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
- Scopus. Search results for ’reinforcement learning AND EEG’ with publications between 2012 and 2024. https://www.scopus.com, 2024. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
- Scopus. Search results for ’reinforcement learning AND virtual reality AND collaborative robotics’ with publications between 2012 and 2024. https://www.scopus.com, 2024. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
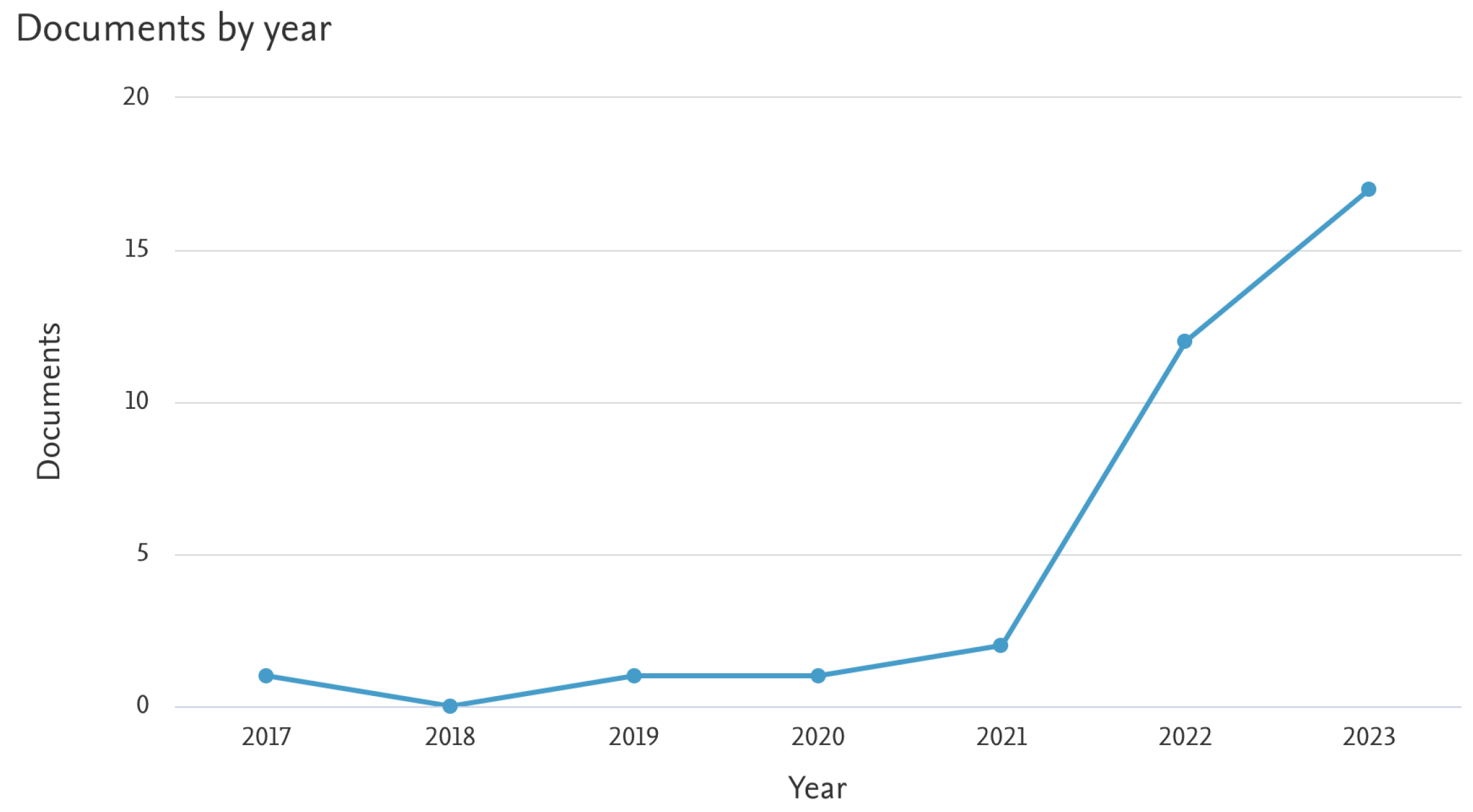
- Scopus. Search results for ’reinforcement learning AND EEG AND collaborative robotics’ with publications between 2012 and 2024. https://www.scopus.com, 2024. Accessed on January 1, 2024.
- Toichoa Eyam, A.; Mohammed, W.M.; Martinez Lastra, J.L. Emotion-driven analysis and control of human-robot interactions in collaborative applications. Sensors (Basel) 2021, 21, 4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcão, S.M.; Fonseca, M.J. Emotions Recognition Using EEG Signals: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing 2019, 10, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayesteh, S.; Ojha, A.; Jebelli, H. Workers’ trust in collaborative construction robots: EEG-based trust recognition in an immersive environment. In Automation and Robotics in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction Industry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R.; Niculescu-Mizil, A. An empirical comparison of supervised learning algorithms. Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning - ICML ’06. ACM Press, 2006, ICML ’06. [CrossRef]
- Pontil, M.; Verri, A. Properties of Support Vector Machines. Neural Computation 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, I.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; He, X.; Lapborisuth, P.; Xu, J.; Watkins-Valls, D.; Sajda, P.; Allen, P. Accelerated Robot Learning via Human Brain Signals, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lv, Q.; Li, J.; Bao, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, S. A reinforcement learning method for human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, M.; Lorenzini, M.; Constable, M.D.; De Momi, E.; Becchio, C.; Ajoudani, A. Maximising Coefficiency of Human-Robot Handovers through Reinforcement Learning 2023. [CrossRef]
- Iturrate, I.; Montesano, L.; Minguez, J. Robot reinforcement learning using EEG-based reward signals. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE, 2010.
- Millán, J.D.R. Combining brain-computer interfaces and assistive technologies: state-of-the-art and challenges. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W.J.; Goss, B.; Coles, M.G.H.; Meyer, D.E.; Donchin, E. A Neural System for Error Detection and Compensation. Psychological Science 1993, 4, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.J.C.H.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Machine Learning 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, R.; Ghosh, L.; Konar, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Nagar, A.K. EEG-induced autonomous game-teaching to a robot arm by human trainers using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Games 2022, 14, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, N.; Botvinick, M.M.; Cohen, J.D. The neural basis of error detection: Conflict monitoring and the error-related negativity. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 111, 931–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrez, P.W.; del R Millan, J. Error-related EEG potentials generated during simulated brain-computer interaction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotte, F.; Congedo, M.; Lécuyer, A.; Lamarche, F.; Arnaldi, B. A Review of Classification Algorithms for EEG-based Brain–computer Interfaces. Journal of Neural Engineering 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Cusano, N. EEG-based empathic safe cobot. Machines 2022, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.J.; Fan, Y.C.; Lv, J.T.; Zhou, C.L. Deep reinforcement learning from error-related potentials via an EEG-based brain-computer interface. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, 2018.
- Shu, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, X. A Review of Emotion Recognition Using Physiological Signals. Sensors 2018, 18, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onose, G.; Grozea, C.; Anghelescu, A.; Daia, C.; Sinescu, C.J.; Ciurea, A.V.; Spircu, T.; Mirea, A.; Andone, I.; Spânu, A.; Popescu, C.; Mihăescu, A.S.; Fazli, S.; Danóczy, M.; Popescu, F. On the feasibility of using motor imagery EEG-based brain-computer interface in chronic tetraplegics for assistive robotic arm control: a clinical test and long-term post-trial follow-up. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnasch, L.; Schweidler, P.; Schmidt, H. The potential of robot eyes as predictive cues in HRI-an eye-tracking study. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 10, 1178433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal, M.A.; Ortiz Barcina, S.; García Herrero, S.; López Perea, E.M. Working with collaborative robots and its influence on levels of working stress. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, L.; Rodríguez, Í.; Rodríguez, N.; Usamentiaga, R.; García, D.F. Robot guidance using machine vision techniques in industrial environments: A comparative review. Sensors (Basel) 2016, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddiar, D.R.; Nini, B.; Sabokrou, M.; Hadid, A. Vision-based human activity recognition: a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 30509–30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Ren, B. Robot obstacle avoidance system using deep reinforcement learning. Ind. Rob. 2022, 49, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohindru, V.; Singla, S. A review of anomaly detection techniques using computer vision. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Lecture notes in electrical engineering, Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 669–677. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.S.; Goldman, M.E.; Gomes, J.; Matza, D.; Horowitz, S.F. The effect of stress and fatigue on cardiac rhythm in medical interns. J. Electrocardiol. 1992, 25, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xintarakou, A.; Sousonis, V.; Asvestas, D.; Vardas, P.E.; Tzeis, S. Remote cardiac rhythm monitoring in the era of smart wearables: Present assets and future perspectives. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 853614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellhammer, D.H.; Wüst, S.; Kudielka, B.M. Salivary cortisol as a biomarker in stress research. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CARERE, C.; VANOERS, K. Shy and bold great tits (Parus major): body temperature and breath rate in response to handling stress. Physiology amp; Behavior 2004, 82, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.R.; Britt, T.W.; Cutlip, W.D.; Templeton, J.L. Social blushing. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Koku, G. Beck depression inventory. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 2016, 66, 174–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G. Beck Depression Inventory–II, 2011. Title of the publication associated with this dataset: PsycTESTS Dataset.
- Jumani, A.K.; Siddique, W.A.; Laghari, A.A.; Abro, A.; Khan, A.A. Virtual reality and augmented reality for education. In Multimedia Computing Systems and Virtual Reality; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2022; pp. 189–210. [Google Scholar]
- LaValle, S.M. Virtual reality; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Parong, J.; Mayer, R.E. Learning science in immersive virtual reality. J. Educ. Psychol. 2018, 110, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneis, D.J.A.; Parker, A.S.; Johanson, M.B.; Butcher, A.; Davoodi, E.; Acker, L.; Botvinick, M.M.; Modayil, J.; White, A.; Pilarski, P.M. Assessing Human Interaction in Virtual Reality With Continually Learning Prediction Agents Based on Reinforcement Learning Algorithms: A Pilot Study 2021. [CrossRef]
- Caudell, T.P.; Mizell, D.W. Augmented reality: an application of heads-up display technology to manual manufacturing processes. Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. IEEE, 1992.
- Craig, A.B. Understanding Augmented Reality: Concepts and Applications; Morgan Kaufmann, 2013.
- Berryman, D.R. Augmented reality: a review. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2012, 31, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.; Stapleton, C.; Hughes, D.; Smith, E. Mixed reality in education, entertainment, and training. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 2005, 25, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fu, Y.; Lu, W.; Pan, Y. Augmented reality-enabled human-robot collaboration to balance construction waste sorting efficiency and occupational safety and health. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 348, 119341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurek, K.A.; Cittadini, R.; Prades, R.M.; Matheson, E.; Di Castro, M. Enhanced Human–Robot Interface With Operator Physiological Parameters Monitoring and 3D Mixed Reality. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 39555–39576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaciu, F.; Crisan, N.; Vaida, C.; Andras, I.; Pusca, A.; Gherman, B.; Radu, C.; Tucan, P.; Al Hajjar, N.; Pisla, D. Integration of Virtual Reality in the Control System of an Innovative Medical Robot for Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery. Sensors 2023, 23, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Mucksavage, P.; Kerbl, D.C.; Huynh, V.B.; Etafy, M.; McDougall, E.M. Validation Study of a Virtual Reality Robotic Simulator—Role as an Assessment Tool? Journal of Urology 2012, 187, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiao, W.; Yu, R.; Johnson, M.T.; Zhang, Y. Virtual Reality Robot-Assisted Welding Based on Human Intention Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2020, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, A.; Slater, M. Encouraging bystander helping behaviour in a violent incident: a virtual reality study using reinforcement learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, S.B.i.; Silva, P.A.; Branco, D.; Pinto, A.; Carvalho, C.; Menezes, P.; Almeida, J.; Pilacinski, A. Virtual reality for safe testing and development in collaborative robotics: Challenges and perspectives. Electronics (Basel) 2022, 11, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirzadeh, A.; Chen, X.; Yin, W.; Yi, Z.; Björkman, M.; Kragic, D. Human-centered collaborative robots with deep reinforcement learning 2020. arXiv:cs.RO/2007.01009.
- Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Yang, G.; Zheng, P.; Song, C.; Yuan, Y.; Wuest, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. Human Digital Twin in the context of Industry 5.0. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2024, 85, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Queralta, J.P.; Westerlund, T. Sim-to-Real Transfer in Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robotics: a Survey. 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). IEEE, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Marmpena, M.; Garcia, F.; Lim, A.; Hemion, N.; Wennekers, T. Data-driven emotional body language generation for social robotics 2022.
- Paolillo, A.; Colella, F.; Nosengo, N.; Schiano, F.; Stewart, W.; Zambrano, D.; Chappuis, I.; Lalive, R.; Floreano, D. How to compete with robots by assessing job automation risks and resilient alternatives. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabg5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, S.; Brunori, C. What to do when the robots come? Non-formal education in jobs affected by automation. Int. J. Manpow. 2021, 42, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, B.J.; Koh, J.T.K.V. A cognitive model for human willingness in human-robot interaction development. SIGGRAPH Asia 2014 Designing Tools For Crafting Interactive Artifacts; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- van Maris, A.; Zook, N.; Caleb-Solly, P.; Studley, M.; Winfield, A.; Dogramadzi, S. Designing ethical social robots-A longitudinal field study with older adults. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, H.; Sorell, T. Ethical values and social care robots for older people: an international qualitative study. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2017, 19, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Document Reference | Reinforcement Learning | Immersive technologies | Human-Factor Sensors | Collaborative Robotics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toichoa Eyam, A. et al. (2021) [29] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Borboni, A. et al. (2022) [45] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Shayesteh,S. et al. (2022) [31] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Zhang, R. et al. (2022) [35] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Lagomarsino, M. et al (2023) [36] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Brenneis, D.J.A. et al. (2021) [65] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Rovira, A. et al. (2022) [75] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Iturrate, I. et al. (2010) [37] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Kar , R. et al. (2022) [41] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Luo, T.J. et al. (2018) [46] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Badia, S.B.i. et al. (2022) [76] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Ghadirzadeh, A. et al. (2020) [77] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Kragic, D. et al. (2016) [7] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Salazar-Gomez, A.F. et al. (2017) [19] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Onose, G. et al. (2012)[48] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Simone, V.D. et al. (2022) [6] | ✓ | |||
| Pearce, M. et al. (2018) [5] | ✓ | |||
| Sheridan, T.B. et al. (2016) [8] | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Zhu, X. et al. (2022) [53] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Wang, B. et al. (2022) [78] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





