Submitted:
12 February 2024
Posted:
14 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
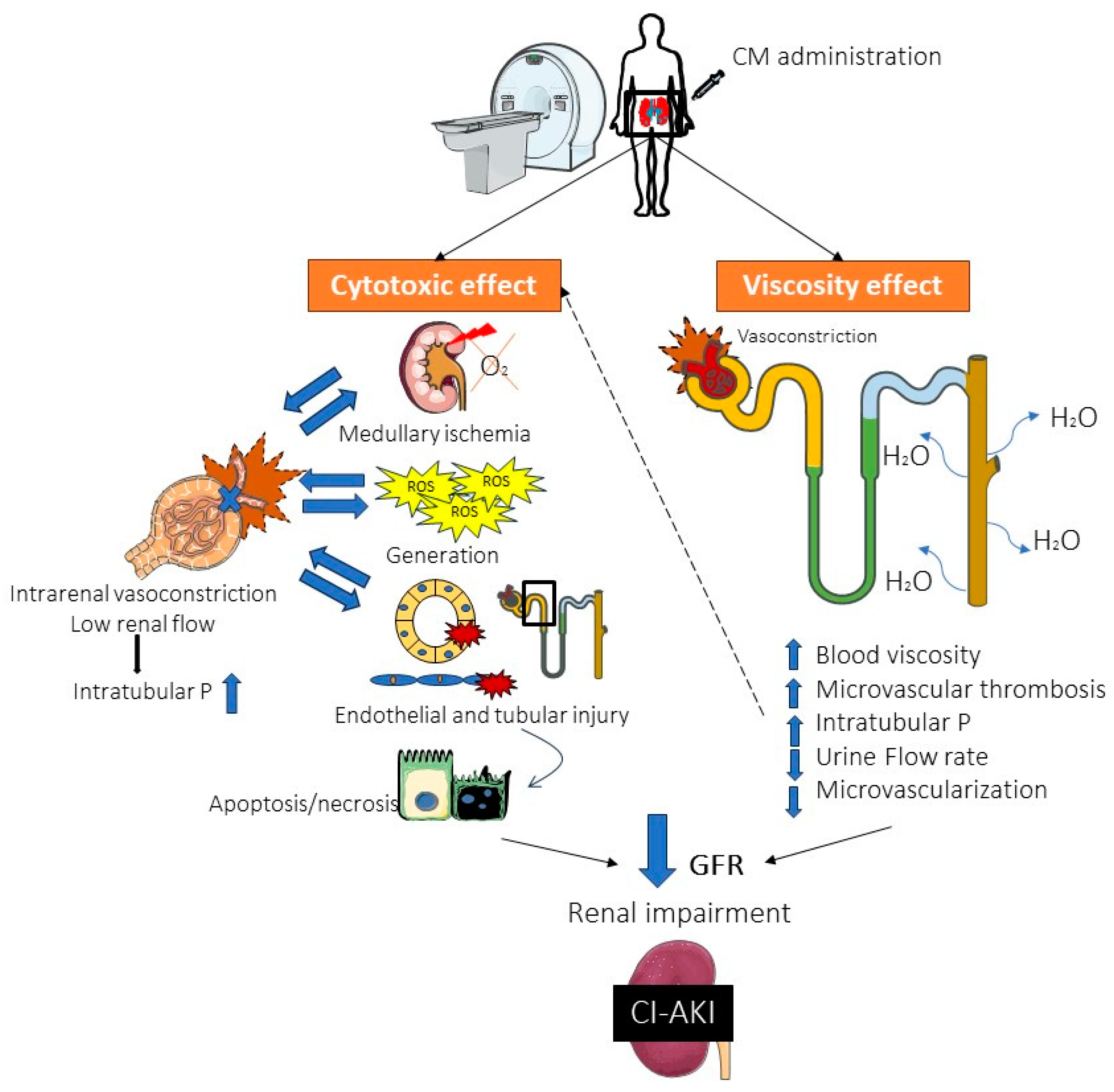
2. Pathophysiology of CI-AKI
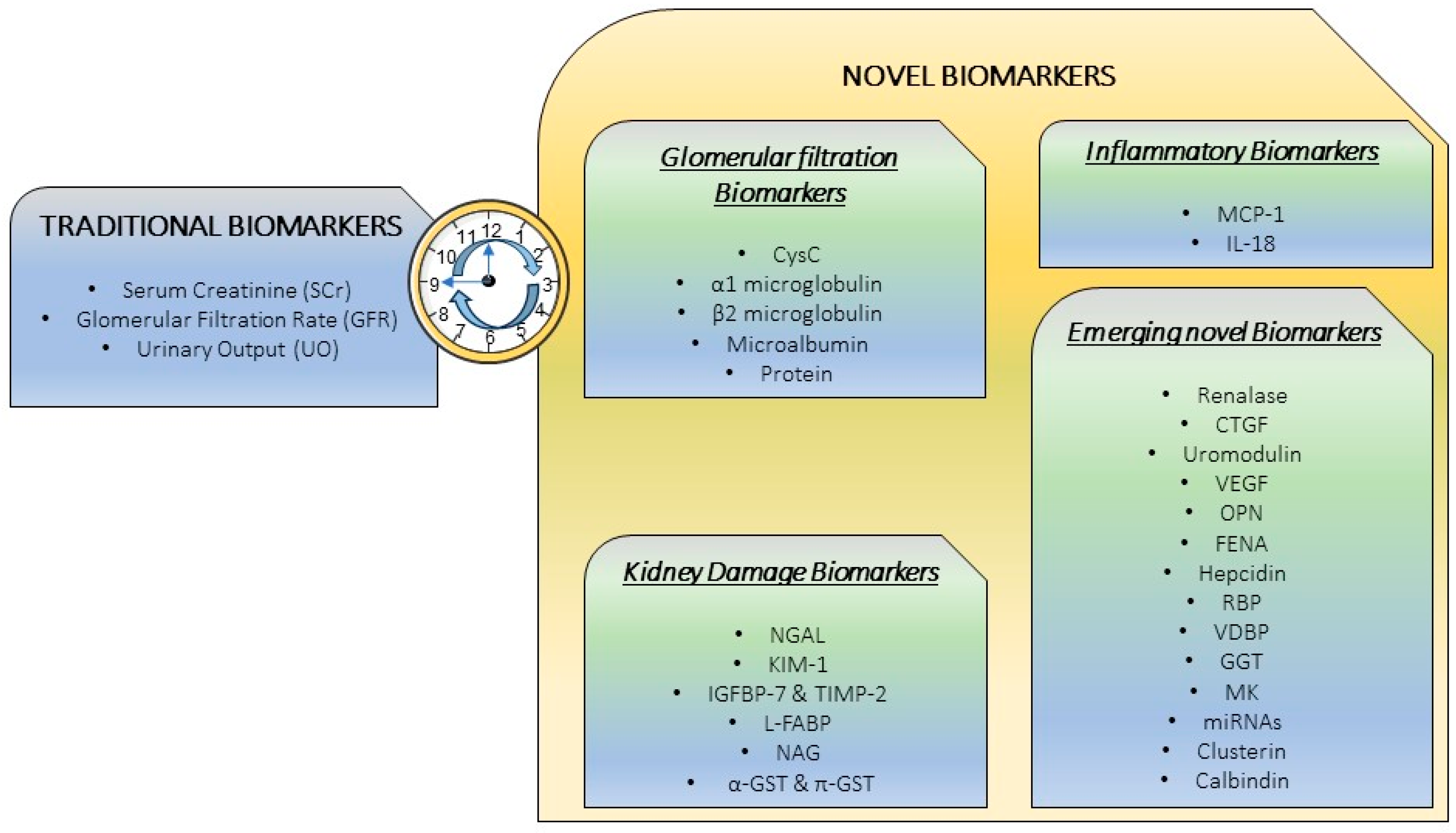
3. Traditional “Gold Standard” Markers
3.1. Serum creatinine (SCr)
3.2. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
3.3. Urinary Output (UO)
4. Novel Biomarkers: The necessity for a precise CI-AKI diagnosis
4.1. Glomerular filtration biomarkers
4.1.1. Cystatin C (CysC)
4.1.2. α1-Microglobulin (α1-m)
4.1.3. β2-Microglobulin (β2-m)
4.1.4. Microalbuminuria
4.1.5. Proteinuria
4.2. Inflammatory biomarkers
4.2.1. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1)
4.2.2. Interleukin 18 (IL-18)
4.3. Kidney damage biomarkers
4.3.1. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
4.3.2. Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1)
4.3.3. Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2)
4.3.4. Liver Fatty Acid-Binding Protein (L-FABP)
4.3.5. N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAG)
4.3.6. α, π glutathione S-transferase (α-GST, π-GST)
4.4. Emerging novel biomarkers
4.4.1. Renalase
4.4.2. Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF)
4.4.3. Uromodulin
4.4.4. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
4.4.5. Osteopontin (OPN)
4.4.6. Fractional Excretion of Sodium (FENa)
4.4.7. Hepcidin
4.4.8. Retinal Binding Protein (RBP)
4.4.9. Vitamin D Binding Protein (VDBP)
4.4.10. Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
4.4.11. Midkine (MK)
4.4.12. MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
4.4.13. Clusterin
4.4.14. Calbindin
5. Combination of Biomarkers: a Future Approach
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreucci, M.; Solomon, R.; Tasanarong, A. Side effects of radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors, and prevention. BioMed Res Int 2014, 2014, 741018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, R.; Nikolsky, E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int Suppl 2006, 100, S11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisbord, S.D.; Palevsky, P.M. Contrast-associated Acute Kidney Injury. Crit Care Clin 2015, 31, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.J.; Tsai, S.F. Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Undergoing Intravenous Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography-The Incidence of Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, H.S. Guidelines for contrast media from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003, 181, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008, 51, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreucci, M.; Faga, T.; Pisani, A.; Sabbatini, M.; Russo, D.; Michael, A. Prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy through a knowledge of its pathogenesis and risk factors. ScientificWorldJournal 2014, 2014, 823169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreucci, M.; Faga, T.; Pisani, A.; Sabbatini, M.; Michael, A. Acute kidney injury by radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis and prevention. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 362725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreucci, M.; Faga, T.; Serra, R.; De Sarro, G.; Michael, A. Update on the renal toxicity of iodinated contrast drugs used in clinical medicine. Drug Healthc Patient Saf 2017, 9, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, R.; Dangas, G.D.; Weisbord, S.D. Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. N Engl J Med 2019, 380, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.A.; Choi, J.P.; Feghali, G.A.; Schussler, J.M.; Stoler, R.M.; Vallabahn, R.C.; Mehta, A. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016, 68, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney International Supplements 2012, 2(1). Available online: https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/KDIGO-2012-AKI-Guideline-English.pdf (accessed on 31 01 2024).
- Nusca, A; Miglionico, M.; Proscia, C.; Ragni, L.; Carassiti, M.; Pepe, F.L.; Di Sciascio, G. Early prediction of contrast-induced acute kidney injury by a “bedside” assessment of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin during elective percutaneous coronary interventions. PloS one 2018, 13, e0197833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguori, C.; Quintavalle, C.; Donnarumma, E.; Condorelli, G. Novel biomarkers for contrast-induced acute kidney injury. BioMed Res Int 2014, 2014, 568738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreucci, M.; Faga, T.; Riccio, E.; Sabbatini, M.; Pisani, A.; Michael, A. The potential use of biomarkers in predicting contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 2016, 9, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussap, M.; Noto, A.; Fanos, V.; Van Den Anker, J.N. Emerging biomarkers and metabolomics for assessing toxic nephropathy and acute kidney injury (AKI) in neonatology. BioMed Res Int 2014, 2014, 602526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; Voors, A.A.; Navis, G.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Current and novel renal biomarkers in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 2012, 17, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Gault, M.H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, R.; Goldstein, S. Real-time measurement of glomerular filtration rate. Curr Opin Crit Care 2017, 23, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QPI-1002 Phase 3 for Prevention of Major Adverse Kidney Events (MAKE) in Subjects at High Risk for AKI Following Cardiac Surgery. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03510897 (accessed on 31 01 2024).
- Randomized double blind placebo-controlled phase II study on the effects of EA-230 on the innate immune response following on-pump cardiac surgery. 2016. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=eudract_number:2015-005600-28 (accessed on 31 01 2024).
- Kellum, J.A.; Sileanu, F.E.; Murugan, R.; Lucko, N.; Shaw, A.D.; Clermont, G. Classifying AKI by Urine Output versus Serum Creatinine Level. JAm Soc Nephrol 2015, 26, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsky, D.; Nikolsky, E. Contrast-induced nephropathy in interventional cardiology. Int J of Nephrol Renovasc Dis 2011, 4, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slocum, J.L.; Heung, M.; Pennathur, S. Marking renal injury: can we move beyond serum creatinine? Transl Res 2012, 159, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royakkers, A.A.; van Suijlen, J.D.; Hofstra, L.S.; Kuiper, M.A.; Bouman, C.S.C.; Spronk, P.E.; Schultz, M.J. Serum cystatin C-A useful endogenous marker of renal function in intensive care unit patients at risk for or with acute renal failure? Curr Med Chem 2007, 14, 2314–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briguori, C.; Visconti, G.; Rivera, N.V.; Focaccio, A.; Golia, B.; Giannone, R.; Castaldo, D.; De Micco, F.; Ricciardelli, B.; Colombo, A. Cystatin C and contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Circulation 2010, 121, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budano C, Andreis A, De Filippo O, Bissolino, A.; Lanfranco, G.; Usmiani, T.; Gai, M.; Levis, M.; Bergamasco, L.; Marra, S.; Rinaldi, M.; De Ferrari, G.M. A single cystatin C determination before coronary angiography can predict short and long-term adverse events. Int J Cardiol 2020, 300, 73–79. [CrossRef]
- Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Malyszko, J.; Sitniewska, E.; Malyszko, J.S.; Dobrzycki, S. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) correlations with cystatin C, serum creatinine and eGFR in patients with normal serum creatinine undergoing coronary angiography. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007, 22, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickli, H.; Benou, K.; Ammann, P.; Fehr, T.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Petridis, H.; Riesen, W.; Wüthrich, R.P. Time course of serial cystatin C levels in comparison with serum creatinine after application of radiocontrast media. Clinical Nephrol 2004, 61, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, R.J.; Mehran, R.; Natarajan, M.K.; Doucet, S.; Katholi, R.E.; Staniloae, C.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Labinaz, M.; Gelormini, J.L.; Barrett, B.J. Contrast-induced nephropathy and long-term adverse events: cause and effect? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2009, 4, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, H.; Hildebrand, L.; Schirdewahn, C.; Eitel, I.; Adams, V.; Fuernau, G.; Erbs, S.; Linke, A.; Diederich, K-W.; Nowak, M.; Desch, S.; Gutberlet, M.; Schulere, G. Impact of high-dose N-acetylcysteine versus placebo on contrast-induced nephropathy and myocardial reperfusion injury in unselected patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. The LIPSIA-N-ACC (Prospective, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Leipzig Immediate PercutaneouS Coronary Intervention Acute Myocardial Infarction N-ACC) Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010, 55, 2201–2209. [CrossRef]
- Droppa, M.; Desch, S.; Blasé, P.; Eitel, I.; Fuernau, G.; Schuler, G.; Adams, V.; Thiele, H. Impact of N-acetylcysteine on contrast-induced nephropathy defined by cystatin C in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary angioplasty. Clin Res Cardiol 2011, 100, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, J.; Duarte, R.; Dix-Peek, T.; Dickens, C.; Manga, P.; Naicker, S. Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prediction of Outcomes in Contrast-Induced Nephropathy. Int J Nephrol 2020, 2020, 8568139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, I.; Papaioannou, V.; Papanas, N.; Dragoumanis, C.; Petala, A.; Theodorou, V.; Gioka, T.; Vargemezis, V.; Maltezos, E.; Pneumatikos, I. Alpha1-microglobulin as an early biomarker of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: a prospective cohort study. Hippokratia 2014, 18, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Heise, D.; Rentsch, K.; Braeuer, A.; Friedrich, M.; Quintel, M. Comparison of urinary neutrophil glucosaminidase-associated lipocalin, cystatin C, and α1-microglobulin for early detection of acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011, 39, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiyanti, S.S.; Loho, T. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) biomarker. Acta Med Indones 2012, 44, 246–255. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, K.T.; Kakajiwala, A.; Dietzen, D.J.; Goss, C.W.; Gu, H.; Dharnidharka, V.R. Using the newer Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes criteria, beta-2-microglobulin levels associate with severity of acute kidney injury. Clin kidney J 2018, 11, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Pate, G.E.; Shalansky, S.; Al-Shamari,A.; Webb, J.G.; Buller, C.E.; Humphries, K.H. N-acetylcysteine reduces urinary albumin excretion following contrast administration: evidence of biological effect. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007, 22, 2520–2524. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, S.; Yuba, M.; Mori, H.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, K.; Ishii, H.; Murohara, T. Increased pre-procedural urinary microalbumin is associated with a risk for renal functional deterioration after coronary computed tomography angiography. Int J Cardiol 2017, 230, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, S.K.; Matheny, M.E.; Abdel-Kader, K.; Greevy Jr, R.A.; Bian, A.; Fly, J.; Chen, G.; Speroff, T.; Hung, A.M.; Ikizler, T.A.; Siew, E.D. Acute kidney injury is a risk factor for subsequent proteinuria. Kidney Int 2018, 93, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskinpasa, S.; Altun, B.; Akoglu, H.; Yildirim, T.; Agbaht, K.; Yilmaz, R.; Peynircioglu, B.; Cil, B.; Aytemir, K.; Turgan, C. An uninvestigated risk factor for contrast-induced nephropathy in chronic kidney disease: proteinuria. Ren Fail 2013, 35, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, C.R.; Devarajan, P. New biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 2008, 36 (4 Suppl), S159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, R.; Mo, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X. Proteinuria as an independent risk factor for contrast-induced acute kidney injury and mortality in patients with stroke undergoing cerebral angiography. J Neurointerv Surg 2017, 9, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, R.; Johnson, A.; Siew, E.D.; Ikizler, T.A.; Ware, L.B.; Wurfel, M.M; Himmelfarb, J.; Zager, R.A. MCP-1 gene activation marks acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011, 22, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, G.; Mancini, V.; Galleggiante, V.; Rutigliano, M.; Vavallo, A.; Battaglia, M.; Ditonno, P. Emerging urinary markers of renal injury in obstructive nephropathy. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 303298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinke, H.; Masuda, S.; Togashi, Y.; Ikemi, Y.; Ozawa, A.; Sato, T.; Kim, Y.H.; Mishima, M.; Ichimura, T.; Bonventre, J.V.; Matsubara, K. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 are noninvasive biomarkers of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in lung cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2015, 76, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Zhaohui, N.; Ben, H.; Leyi, G.; Jianping, L.; Huili, D.; Jiaqi, Q. Urinary IL-18 and NGAL as early predictive biomarkers in contrast-induced nephropathy after coronary angiography. Nephron Clin Pract 2008, 108, c176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, W.; Qian, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, J. Urinary interleukin-18 as an early indicator to predict contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Exp Ther Med 2014, 8, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.B.; Liu, G.L.; Yu, Z.Q.; Pan, P. Urinary KIM-1, IL-18 and Cys-c as early predictive biomarkers in gadolinium-based contrast-induced nephropathy in the elderly patients. Clin Nephrol 2013, 80, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulent Gul, C.; Gullulu, M.; Oral, B.; Aydinlar, A.; Oz, O.; Budak, F.; Yilmaz, Y.; Yurtkuran, M. Urinary IL-18: a marker of contrast-induced nephropathy following percutaneous coronary intervention? Clin Biochem 2008, 41, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.; Kinnin, M.; McEneaney, D.; Menown, I.; Kurth, M.; Lamont, J.; Morgan, N.; Harbinson, M. Prediction of contrast induced acute kidney injury using novel biomarkers following contrast coronary angiography. QJM 2018, 111, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Prada, A.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zahedi, K.; Yang, J.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc mNephrol 2003, 14, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Mori, K.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol 2004, 24, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alge, J.L.; Arthur, J.M. Biomarkers of AKI: a review of mechanistic relevance and potential therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 10, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragas, N.; Qiu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Samstein, B.; Deng, S-X.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Viltard, M.; Yu, W.; Forster, C.S.; Gong, G.; Liu, Y.; Kulkarni, R.; Mori,K.; Kalandadze, A.; Ratner, A.J.; Devarajan, P.; Landry, D.W.; D’Agati, V.; Lin, C-S.; Barasch, J. The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat Med 2011, 17, 216–222. [CrossRef]
- Filiopoulos, V.; Biblaki, D.; Lazarou, D.; Chrisis, D.; Fatourou, M.; Lafoyianni, S.; Vlassopoulos, D. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as an early predictive marker of contrast-induced nephropathy in hospitalized patients undergoing computed tomography. Clin Kidney J 2013, 6, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiopoulos, V.; Biblaki, D.; Vlassopoulos, D. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a promising biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy after computed tomography. Ren Fail 2014, 36, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilcher, G.; Ribitsch, W.; Otto, R.; Portugaller, R.H.; Quehenberger, F.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; Zweiker, R.; Stiegler, P.; Brodmann, M.; Weinhandl, K.; Horina, J.H. Early detection and intervention using neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) may improve renal outcome of acute contrast media induced nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial in patients undergoing intra-arterial angiography (ANTI-CIN Study). BMC Nephrol 2011, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasanarong, A.; Hutayanon, P.; Piyayotai, D. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin predicts the severity of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing elective coronary procedures. BMC Nephrol 2013, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintavalle, C.; Anselmi, C.V.; De Micco, F.; Roscigno, G.; Visconti, G.; Golia, B.; Focaccio, A.; Ricciardelli, B.; Perna, E.; Papa, L.; Donnarumma, E.; Condorelli, G.; Briguori, C. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Cir Cardiovas Interv 2015, 8, e002673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafkas, N.; Liakos, C.; Zoubouloglou, F.; Dagadaki, O.; Dragasis, S.; Makris, K. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as an Early Marker of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy After Elective Invasive Cardiac Procedures. Clin Cardiol 2016, 39, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, L.F.; Severiche-Bueno, D.F.; Bustamante, C.A.; Murillo, S.; Soni, N.J.; Poveda, M.; Gomez, E.; Buitrago, R.; Rodriguez, A. Serum levels of neutrophil Gelatinase associated Lipocalin (NGAL) predicts hemodialysis after coronary angiography in high risk patients with acute coronary syndrome. BMC Nephrol 2020, 21, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, W.; Schilcher, G.; Quehenberger, F.; Pilz, S.; Portugaller, R.H.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; Zweiker, R.; Brodmann, M.; Stiegler, P.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Pickering, J.W.; Horina, J.H. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) fails as an early predictor of contrast induced nephropathy in chronic kidney disease (ANTI-CI-AKI study). Sci Rep 2017, 7, 41300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, T.; Bonventre, J.V.; Bailly, V.; Wei, H.; Hession, C.A.; Cate, R.L.; Sanicolaet, M. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prozialeck, W.C.; Vaidya, V.S.; Liu, J.; Waalkes, M.P.; Edwards, J.R.; Lamar, P.C.; Bernard, A.M.; Dumont, X.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1 is an early biomarker of cadmium nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int 2007, 72, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, T.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, S.A.; Stevens, J.L.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2004, 286, F552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.K.; Waikar, S.S.; Johnson, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Dent, C.L.; Devarajan, P.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 2008, 73, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, C.R.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Garg, A.X.; Kadiyala, D.; Shlipak, M.G.; Koyner, J.L.; Edelstein, C.L.; Devarajan, P.; Patel, U.D.; Zappitelli, M.; Krawczeski, C.D.; Passik, C.S.; Coca; S. G.; TRIBE-AKI Consortium. Performance of kidney injury molecule-1 and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI after cardiac surgery. Clinical J Am Soc Nephrol 2013, 8, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbisetti, V.; Waikar, S.S.; Antoine, D.J.; Smiles, A.; Wang, C.; Ravisankar, A.; Ito, K.; Sharma, S.; Ramadesikan, S.; Lee, M.; Briskin, R.; De Jager, P.L.; Ngo, T.T.; Radlinski, M.; Dear, J.W.; Park, K.B.; Betensky, R.; Krolewski, A.S.; Bonventre, J.V. Blood kidney injury molecule-1 is a biomarker of acute and chronic kidney injury and predicts progression to ESRD in type I diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 25, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.H.; Ronco, C.; Okusa, M.D. The role of inflammation in the cardio-renal syndrome: a focus on cytokines and inflammatory mediators. Semin Nephrol 2012, 32, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoulakis, C.; Fragkiadoulaki, I.; Karkala, P.; Georgiadis, G.; Zisis, I.-E.; Stivaktakis, P.; Kalogeraki, A.; Tsiaoussis, I.; Burykina, T.; Lazopoulos, G.; Tsarouhas, K.; Kouretas, D.; Tsatsakis, A. Contrast-induced nephropathy in an animal model: Evaluation of novel biomarkers in blood and tissue samples. Toxicol Rep 2019, 6, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, R.L.; Stewart, S.R.; Thompson, K.L.; Zhang, J. Kidney injury biomarkers in hypertensive, diabetic, and nephropathy rat models treated with contrast media. Toxicol Pathol 2013, 41, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdeniz, D.; Celik, H.T.; Kazanci, F.; Yilmaz, H.; Yalcin, S.; Bilgic, M.A.; Ruzgaresen, N.; Akcay, A.; Eryonucu, B. Is Kidney Injury Molecule 1 a Valuable Tool for the Early Diagnosis of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy? J Investig Med 2015, 63, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa, I.; Montoliu, C.; Urios, A.; Andrés-Costa, M.J.; Giménez-Garzó, C.; Juan, I.; Puchades, M.J.; Blasco, M.L.; Carratalá, A.; Sanjuán, R.; Miguel, A. Urinary KIM-1, NGAL and L-FABP for the diagnosis of AKI in patients with acute coronary syndrome or heart failure undergoing coronary angiography. Heart Vessels 2015, 30, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, D.Y.; Kellum, J.A. Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Intervention in Acute Kidney Injury. Contrib Nephrol 2016, 187, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Ricci, Z. The concept of risk and the value of novel markers of acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2013, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ardiles, T.; Artigas, A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bell, M.; Bihorac, A.; Birkhahn, R.; Cely, C.M.; Chawla, L.S.; Davison, D.L.; Feldkamp, T.; Forni, L.G.; Gong, M.N.; Gunnerson, K.J.; Haase, M.; Hackett, J.; Honore, P.M.; Hoste, E.A.J.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Joannidis, M.; Kim, P.; Koyner, J.L.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Lissauer, M.E.; Marx, G.; McCullough, P.A.; Mullaney, S.; Ostermann, M.; Rimmelé, T.; Shapiro, N.I.; Shaw, A.D.; Shi, J.; Sprague, A.M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Vinsonneau, C.; Wagner, L.; Walker, M.G.; Wilkerson, R.G.; Zacharowski, K.; Kellum, J.A. Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2013, 17, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyner, JL, Shaw, AD, Chawla, LS, Hoste, E.A.J.; Bihorac, A.; Kashani, K.; Haase, M.; Shi, J.; Kellum, J.A.; Sapphire Investigators. Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2)⋅IGF-Binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7) Levels Are Associated with Adverse Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 26, 1747–1754. [CrossRef]
- Gocze, I.; Koch, M.; Renner, P.; Zeman, F.; Graf, B.M.; Dahlke, M.H.; Nerlich, M.; Schlitt, H.J.; Kellum, J.A.; Bein, T. Urinary biomarkers TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 early predict acute kidney injury after major surgery. PloS One 2015, 10, e0120863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrier, J.F.; Thomas, C.; Grober, J.; Duez, H.; Percevault, F.; Souidi, M.; Linard, C.; Staels, B.; Besnard, P. Statin induction of liver fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) gene expression is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha-dependent. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 45512–45518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Noiri, E.; Ono, Y.; Doi, K.; Negishi, K.; Kamijo, A.; Kimura, K.; Fujita, T.; Kinukawa, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Goto, M.; Shinozaki, N.; Ohshima, S.; Sugaya, T. Renal L-type fatty acid-binding protein in acute ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007, 18, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo-Ikemori, A.; Sugaya, T.; Matsui, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Kimura, K. Roles of human liver type fatty acid binding protein in kidney disease clarified using hL-FABP chromosomal transgenic mice. Nephrology (Carlton) 2011, 16, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portilla, D.; Dent, C.; Sugaya, T.; Nagothu, K.K.; Kundi, I.; Moore, P.; Noiri, E.; Devarajan, P. Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 2008, 73, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Tangri, N.; Komenda, P.; Kausha, A.; Sood, M.; Brar, R.; Gill, K.; Walker, S.; MacDonald, K.; Hiebert, B.M.; Arora, R.C.; Rigatto, C. Urinary, Plasma, and Serum Biomarkers’ Utility for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Cardiac Surgery in Adults: A Meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2015, 66, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Sugaya, T.; Node, K.; Ueda, Y.; Koide, H. Urinary excretion of liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 2006, 47, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liangos, O.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Vaidya, V.S.; Han, W.K.; Wald, R.; Tighiouart, H.; W MacKinnon, R.W.; Li, L.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Pereira, B.J.G.; Bonventre, J.V.; Jaber, B.L. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(D)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007, 18, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzi, C.; Petrini, C.; Rizza, V.; Arrigo, G.; Napodano, P.; Paparella, M.; D’Amico, G. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase excretion is a marker of tubular cell dysfunction and a predictor of outcome in primary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002, 17, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, B.; Chinchole, S.; Lobo, V.; Gang, S.; Rajapurkar, M. Enzymuria pattern in early post renal transplant period: Diagnostic usefulness in graft dysfunction. Indian J Clin Biochem 2004, 19, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, Y.; Tamura, M.; Sakuyama, T.; Aiba, K.; Eto, S.; Yuda, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Nishikawa, K. Early measurement of urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase helps predict severe hyponatremia associated with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. J Infect Chemother 2015, 21, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, VS.; Waikar, S.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Collings, F.B.; Sunderland, K.; Gioules, C.; Bradwin, G.; Matsouaka, R.; Betensky, R.A.; Curhan, G.C.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary biomarkers for sensitive and specific detection of acute kidney injury in humans. Clin Transl Sci 2008, 1, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Ji, J.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, S.H.; Lin, Y.M.; Bo, J.; Qian, J.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Ding, X.Q. Assessment of urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase as an early marker of contrast-induced nephropathy. J Int Med Res 2011, 39, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzer, M.; Alpay, H.; Baykan, Ö.; Erdem, A.; Demir, I.H. Serum NGAL, cystatin C and urinary NAG measurements for early diagnosis of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Ren Fail 2016, 38, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Kubo, S.; Morishita, Y.; Nishikawa, K.; Ikeda, K.; Itoi, T.; Hosoi, H. Kidney injury biomarkers after cardiac angiography in children with congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 2019, 14, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, V.F.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Tighiouart, H.; Liangos, O.; dos Santos, O.F.; Jaber, B.L. Urinary α-GST and π-GST for prediction of dialysis requirement or in-hospital death in established acute kidney injury. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.A.; Koyner, J.L.; Murray, P.T. Urinary glutathione S-transferases in the pathogenesis and diagnostic evaluation of acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: a critical review. Curr Opin Crit Care 2010, 16, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susantitaphong, P.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Tighiouart, H.; Kouznetsov, D.; Liangos, O.; Jaber, B.L. Urinary α- and π-glutathione s-transferases for early detection of acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass. Biomarkers 2013, 18, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K,H. ; Wang, C.H.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, T.M.; Wu, P.C.; Lai, C.H.; Tseng, L.J.; Tsai, P.R.; Connolly, R.; Wu, V.C. Urinary π-glutathione S-transferase Predicts Advanced Acute Kidney Injury Following Cardiovascular Surgery. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 26335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; L,i G. ; Wang, P.; Velazquez, H.; Yao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Peixoto, A.; Crowley, S.; Desir, G.V. Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. J Clin Invest 2005, 115, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Wang, P.; Tang, L.; Baroni, S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Desir, G.V. Renalase protects against ischemic AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 2013, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Velazquez, H.; Moeckel, G.; Chang, J.; Ham, A.; Lee, H.T.; Safirstein, R.; Desir, G.V. Renalase prevents AKI independent of amine oxidase activity. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 25, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Xing, T.; Wang, F.; Wang, N. Renalase protects against contrast-induced nephropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats. PloS One 2015, 10, e0116583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybraniec, M.T.; Bożentowicz-Wikarek, M.; Chudek, J.; Mizia-Stec, K. Urinary renalase concentration in patients with preserved kidney function undergoing coronary angiography. Nephrology (Carlton) 2018, 23, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybraniec, M.T.; Mizia-Stec, K. Renalase and Biomarkers of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Cardiorenal Med 2015, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Rayego, S.; Rodrigues-Díez, R.; Rodriguez, J.S.; Rodrigues-Díez, R.; Rodríguez-Vita, J.; Carvajal, G.; Aroeira, L.S.; Selgas, R.; Mezzano, S.A.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. CTGF promotes inflammatory cell infiltration of the renal interstitium by activating NF-kappaB. J Am Soc Nephrol 2009, 20, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilari, S.; Yang, B.; Sharma, A.; McCall, D.L.; Misra, S. Increased transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and pSMAD3 signaling in a Murine Model for Contrast Induced Kidney Injury. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Achkar, T.M.; Wu, X.R. Uromodulin in kidney injury: an instigator, bystander, or protector? Am J Kidney Dis 2012, 59, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawnay, A.B.; Thornley, C.; Nockler, I.; Webb, J.A.; Cattell, W.R. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein excretion and aggregation during intravenous urography. Relevance to acute renal failure. Invest Radiol 1985, 20, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.; Freedman, D.B.; Howell, M.J.; Hine, A.L. Contrast-medium-induced acute renal failure and Tamm-Horsfall proteinuria. Br J Radiol 1984, 57, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Gaber, A.O.; Jones, J.D. Oxygen free radical involvement in urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein excretion after intrarenal injection of contrast medium. Radiology 1990, 175, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garimella, P.; Jaber, B.L.; Tighiouart, H.; Liangos, O.; Bennett, M.R.; Devarajan, P.; El-Achkar, T.M.; Sarnak, M.J. Association of Preoperative Urinary Uromodulin with AKI after Cardiac Surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017, 12, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, M.R.; Pyles, O.; Ma, Q.; Devarajan, P. Preoperative levels of urinary uromodulin predict acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Pediatr Nephrol 2018, 33, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijvers, B.F.; Flyvbjerg, A.; De Vriese, A.S. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in renal pathophysiology. Kidney Int 2004, 65, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ari, E.; Kedrah, A.E.; Alahdab, Y.; Bulut, G.; Eren, Z.; Baytekin, O.; Odabasi, D. Antioxidant and renoprotective effects of paricalcitol on experimental contrast-induced nephropathy model. Br J Radiol 2012, 85, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, B. The role of osteopontin in kidney diseases. Inflamm Res 2019, 68, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; McCarthy, C.P.; Shrestha, S.; Gaggin, H.K.; Mukai, R.; Magaret, C.A.; Rhyne, R.F.; Januzzi Jr, J.L. A clinical, proteomics, and artificial intelligence-driven model to predict acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Clin Cardiol 2019, 42, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitland, S.; Nakstad, E.R.; Berg, J.P.; Trøseid, A.M.S.; Brusletto, B.S.; Brunborg, C.; Lundqvist, C.; Sunde, K. Urine β-2-Microglobulin, Osteopontin, and Trefoil Factor 3 May Early Predict Acute Kidney Injury and Outcome after Cardiac Arrest. Crit Care Res Pract 2019, 2019, 4384796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinel, C.H. The FENa test. Use in the differential diagnosis of acute renal failure. Jama 1976, 236, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Minutolo, R.; Cianciaruso, B.; Memoli, B.; Conte, G.; De Nicola, L. Early effects of contrast media on renal hemodynamics and tubular function in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 1995, 6, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, R.; Kumazaki, T.; Tajima, H.; Hayashi, H.; Kuwako, T.; Hakozaki, K.; Kiriyama, T. Urinary excretion of vasoactive factors following contrast media exposure in humans. Nephron Clin Pract 2005, 101, c150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.B.; Yang, S.K.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Pan, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.Q. Mitochondria-targeted peptides prevent on contrast-induced acute kidney injury in the rats with hypercholesterolemia. Ren Fail 2013, 35, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzavacca, P.; Ishikawa, K.; Bailey, M.; May, C.N.; Bellomo, R. Systemic and renal hemodynamic effects of intra-arterial radiocontrast. Intensive Care Med Exp 2014, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermann, M.; Philips, B.J.; Forni, L.G. Clinical review: Biomarkers of acute kidney injury: where are we now? Crit Care 2012, 16, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowle, J.R.; Ostland, V.; Calzavacca, P.; Licari, E.; Ligabo, E.V.; Echeverri, J.E.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Haase-Fielitz, A.; Haase, M.; Westerman, M.; Bellomo, R. Greater increase in urinary hepcidin predicts protection from acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012, 27, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowle, J.R.; Westerman, M.; Bellomo, R. Urinary hepcidin: an inverse biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass? Curr Opin Crit Care 2010, 16, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaf, D.E.; Rajapurkar, M.; Lele, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Boerger, E.A.S.; Mc Causland, F.R.; Eisenga, M.F.; Singh, K.; Babitt, J.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Christov, M.; Waikar, S.S. Iron, Hepcidin, and Death in Human AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 2019, 30, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyszko, J.; Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Malyszko, J.S.; Koc-Zorawska, E.; Matuszkiewicz-Rowinska, J.; Dobrzycki, S. Hepcidin - Potential biomarker of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Adv Med Sci 2019, 64, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatse, J.O. Human retinol-binding protein: its relationship to renal function in renal diseases. West Afr J Med 1991, 10, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sadat, U.; Walsh, S.R.; Norden, A.G.; Gillard, J.H.; Boyle, J.R. Does oral N-acetylcysteine reduce contrast-induced renal injury in patients with peripheral arterial disease undergoing peripheral angiography? A randomized-controlled study. Angiology 2011, 62, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaykovska, L, Heunisch, F, von Einem, G, Alter, M. L.; Hocher, C.F.; Tsuprykov, O.; Dschietzig, T.; Kretschmer, A.; Hocher, B. Urinary Vitamin D Binding Protein and KIM-1 Are Potent New Biomarkers of Major Adverse Renal Events in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. PloS One 2016, 11, e0145723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadio, C.; Tramonti, G.; Lucchesi, A.; Giordani, R.; Lucchetti, A.; Bianchi, C. Gamma-glutamyltransferase is a reliable marker for tubular effects of contrast media. Renal Fail 1998, 20, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksuz, F.; Yarlioglues, M.; Cay, S.; Celik, I.E.; Mendi, M.A.; Kurtul, A.; Cankurt, T.; Kuyumcu, S.; Canpolat, U.; Turak, O. Predictive Value of Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase Levels for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Who Underwent Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Am J Cardiol 2015, 116, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyszko, J.; Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Koc-Zorawska, E.; Malyszko, J.S.; Kobus, G.; Dobrzycki, S. Midkine: a novel and early biomarker of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 879509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.F.; Bekele, S.; O’Dwyer, M.J.; Prowle, J.R. MicroRNAs in Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2018, 140, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Jing, Y.; Hao, J.; Frankfort, N.C.; Zhou, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, R. MicroRNA-21 in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Cao, X.; Zou, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen,bZ.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Z. MicroRNA-21 and risk of severe acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after adult cardiac surgery. PloS One 2013, 8, e63390. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Zhang, T.; Ding, D.; Zhang, W.F.; Wang, X.L.; Sun, Z.; Hu, L.H.; Qin, S.Y.; Shen, L.H.; He, B. Circulating MicroRNA-188, -30a, and -30e as Early Biomarkers for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J Am Heart Assoc 2016, 5, e004138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Moon, A. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity and its biomarkers. Biomol Ther 2012, 20, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, F.; Perentes, E.; Cordier, A.; Roth, D.R.; Verdes, P.; Grenet, O.; Pantano, S.; Moulin, P.; Wahl, D.; Mahl, A.; End, P.; Staedtler, F.; Legay, F.; Carl, K.; Laurie, D.; Chibout, S.D.; Vonderscher, J.; Maurer, G. Urinary clusterin, cystatin C, beta2-microglobulin and total protein as markers to detect drug-induced kidney injury. Nat Biotechnol 2010, 28, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinken, P.; Starckx, S.; Barale-Thomas, E.; Looszova, A.; Sonee, M.; Goeminne, N.; Versmissen, L.; Buyens, K.; Lampo, A. Tissue Kim-1 and urinary clusterin as early indicators of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Toxicol Pathol 2012, 40, 1049–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguan, C.Y.C.; Guan, Q.; Gleave, M.E.; Du, C. Promotion of cell proliferation by clusterin in the renal tissue repair phase after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 2014, 306, F724–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Guan, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Gleave, M.E.; Nguan, C.Y.C.; Du, C. Relationship of clusterin with renal inflammation and fibrosis after the recovery phase of ischemia-reperfusion injury. BMC Nephrol 2016, 17, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, Y.; Akalya, K.; Murali, T.; Vathsala, A.; Tan, C.S.; Low, S.; Lim, H.N.; Teo, B.W.; Lau, T.; Ong, L.; Chua, H.R. Serial Quantification of Urinary Protein Biomarkers to Predict Drug-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Curr Drug Metab 2019, 20, 656–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.; Fuchs, T.C.; Henzler, T.; Matheis, K.A.; Herget, T.; Dekant, W.; Hewitt, P.; Mally, A. Evaluation of a urinary kidney biomarker panel in rat models of acute and subchronic nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2010, 277, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palviainen, M.; Raekallio, M.; Rajamäki, M.M.; Linden, J.; Vainio, O. Kidney-derived proteins in urine as biomarkers of induced acute kidney injury in sheep. Vet J 2012, 193, 287–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, B.; Wen, X.; Mercke, N.; Gomez, M.; O’Bryant, C.; Bowles, D.W.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Joy, M.S.; Aleksunes, L.M. Profiling of Kidney Injury Biomarkers in Patients Receiving Cisplatin: Time-dependent Changes in the Absence of Clinical Nephrotoxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2017, 101, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Wen, X.; Mercke, N.; Gomez, M.; O’Bryant, C.; Bowles, D.W.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Joy, M.S.; Aleksunes, L.M. Time-dependent changes in kidney injury biomarkers in patients receiving multiple cycles of cisplatin chemotherapy. Toxicol Rep 2020, 7, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.R.; Babitz, S.K.; Vlasakova, K.; Wong, A.; Noyes, S.L.; Boshoven, W.; Grady, P.; Zimmerman, C.; Engerman, S.; Gebben, M.; Tanen, M.; Glaab, W.E.; Sistare, F.D. Evaluation of Urinary Renal Biomarkers for Early Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury Following Partial Nephrectomy: A Feasibility Study. Eur Urol Focus 2020, 6, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.F.; Li, J.M.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; He, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Bai, X.; Xie, F.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Performance of urinary NGAL and L-FABP in predicting acute kidney injury and subsequent renal recovery: a cohort study based on major surgeries. Clin Chem Lab Med 2014, 52, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.M.; Hill, E.G.; Alge, J.L.; Lewis, E.C.; Neely, B.A.; Janech, M.G.; Tumlin, J.A.; Chawla, L.S.; Shaw; A. D.; SAKInet Investigators. Evaluation of 32 urine biomarkers to predict the progression of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 2014, 85, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybraniec, M.T.; Chudek, J.; Bożentowicz-Wikarek, M.; Mizia-Stec, K. Prediction of contrast-induced acute kidney injury by early post-procedural analysis of urinary biomarkers and intra-renal Doppler flow indices in patients undergoing coronary angiography. J Interv Cardiol. 2017, 30, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




