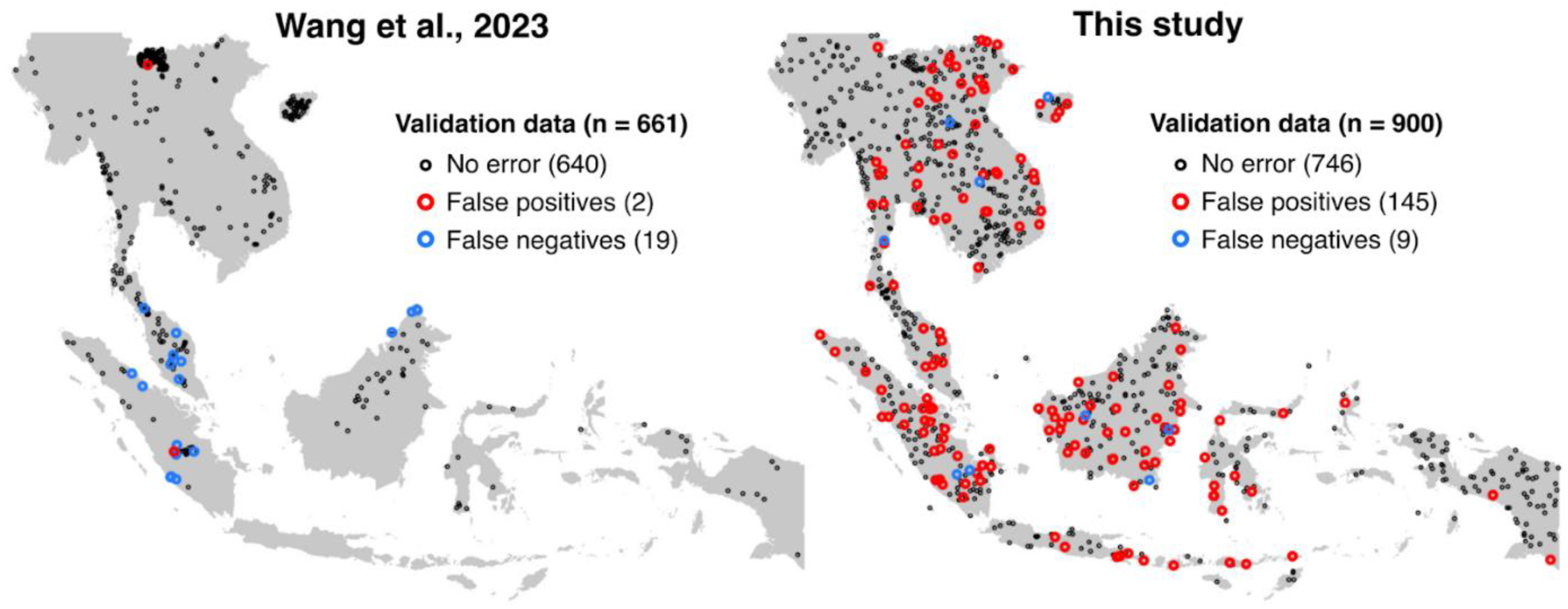
Objective validation, confidence intervals and area estimates require objective sampling methods [2], but Wang et al.’s approach does not fulfil this requirement. The validation points are clustered, which results in bias: the total mapped rubber area in China is 1.10 Mha (7.8% of the total mapped area) but accounts for 59.9% (182/304 points) of the validation points. In contrast, the mapped rubber in Indonesia totals 4.75 Mha (33.5% of the mapped total) but receives only 4 points (1.3%). Furthermore, their validation is incomplete, as it excludes areas that were viewed as ‘nonforest’ in a reference map in their reference data and thus neglects any error due to undetected rubber plantations in these areas.
We generated accuracy metrics and area estimates using stratified random sampling. We sampled 300 points in Wang et al.’s class ‘Rubber’, 300 points in ‘Forest’, and 300 points in ‘Nonforest’. For each point, we assessed the actual cover using visual (nonautomated) checking of high-resolution images and Sentinel-2 time series images. Unlike Wang et al., we included ‘nonforest’, as these areas must also be reflected in accuracy and area estimates. We also distinguished rubber monoculture from ‘Jungle rubber’ (mixed species multistrata agroforest), which by area includes most of the rubber planted in the region, particularly in Indonesia and Thailand [3].
Our resulting accuracy metrics are much lower than the published values, with user and producer accuracies of 48.7% and 68.1%, respectively, for ‘Rubber’ (monoculture). When Jungle rubber is included, the user and producer accuracies are 51.7% and 55.6%, respectively. These values contrast with the published 99.3% and 57.2% values. The difference in commission error (complementing user accuracy) reveals that the rubber map includes considerable areas of nonrubber (
Figure 1).
We checked the commission error in Wang et al.’s map of rubber [1] using validated data for planted oil palm [4] and pulpwood [5,6]. In total, 0.63 Mha of area mapped as rubber by Wang et al. overlaps with that identified as oil palm, representing 4.4% of the mapped rubber across the six countries. This proportion is highest in Malaysia (22.0%) and Indonesia (7.5%). The commission error for the oil palm dataset (user accuracy >80%) indicates errors in the mapping of rubber. In addition, 10.2% of the rubber plants mapped in Indonesia are pulpwood plantations (mostly Acacia sp. or Eucalyptus sp.), according to a reference database obtained by visual interpretation of these very distinct fast-growing monoculture tree plantations.
Wang et al.’s mapped rubber area of 14.15 Mha [1] includes extensive errors, and their overall estimate of 24.59 ± 4.62 Mha derives from a flawed validation. The mapped area of rubber is imperfect and includes errors of omission and commission. The area estimate is a statistical measure derived from validation points that aims to provide the actual area along with (objective) confidence intervals
3. Reflecting our concerns, we attempted to review these estimates for the eight countries based on our own validation points (
Table 1). Furthermore, we produced area estimates of planted rubber within known old growth forest in 2000. To achieve this goal, we increased the number of validation points in old growth forests to a total of 300 points per class, as the initial sampling had insufficient points in these areas. This approach provides estimates of rubber-associated deforestation since 2001, as it infers that the rubber area in 2021 was a old growth forest in 2000.
Our estimates of 13.15 ± 3.95 Mha for rubber (including monoculture and mixed) and 10.11 ± 2.99 Mha (only including monoculture) are substantially lower than the estimated 24.59 ± 4.6 reported by Wang et al. for the eight countries [1]. While their ‘conservative’ rubber mapped area (14.15 Mha) lies within the bounds of our estimates, the magnitude of their commission and omission errors and biases that result from the selective (nonobjective) validation remain concerning.
Our deforestation estimates are 0.57 ± 0.30 Mha (only monoculture) and 0.60 ± 0.30 Mha (monoculture and mixed). Wang et al. overestimated deforestation due to rubber both because they confused rubber with other tree crops known to cause considerable deforestation, such as oil palm and pulpwood, and because of mistaken tree loss from the loss of old growth forest. Wang et al.’s approach consisted of mapping disturbances observed during 1993-2000 and 2001-2016 within the 2021 mapped rubber area. They mention the importance of excluding prior tree plantations [1] but failed to repeat and assess this concern in their conclusions. While seeking each “first deforestation date”, they include any tree cover loss (not just forest). These methods use a criterion to exclude pixels with sparse vegetation from the time series, but this approach distinguishes forests from other dense vegetation with tree cover. Thus, replanting and other changes in tree cover can be incorrectly labelled deforestation (and subsequently misrepresented as loss of old growth forest).
We explored whether Wang et al.’s assessment of deforestation [1] included cover change outside recognised old growth forest by comparing their putative rubber deforestation (2001-2016) against old growth forest in 2000. Wang et al. acknowledged that the term ‘deforestation’ includes any type of tree cover loss since 1993 and not only the loss of natural forest, such as the conversion or rotation of agroforests, plantation forests, agricultural tree crops and rubber itself [1], but also emphasises the resulting figures as if they were assumed to be good approximations of forests. This represents a major source of uncertainty. We found that 71.2% of the claimed ‘deforestation’ occurred outside recognised old growth forests in 2000 [5]. With its long history of rubber production, Thailand has experienced these problems, with tree loss outside recognised old growth forests accounting for 94.6% of the deforestation estimates of Wang et al. [1]
To conclude, Wang et al.’s assessments [1] appear misleading. Their rubber maps present high omission and commission errors, and their area estimates are unreliable. Our analysis indicated that the old growth forest converted to rubber plantations in Southeast Asia after 2001 was significantly lower than the mapped 2.98 Mha and estimated 2.49 ± 0.35 Mha (our 95% upper-bound deforestation estimate is 0.90 Mha). As sophisticated satellite methods become increasingly useful for promoting conservation and overseeing land use, adhering to good practices remains essential for ensuring their credibility. We urge Wang et al. to reassess their findings to better inform policy interventions.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the ideas presented and writing and approved the final text. AD performed the validation and related analyses.
References
- Wang, Y. High-resolution maps show that rubber causes substantial deforestation. Nature 2023, 623, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, P. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote sensing of Environment 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penot, E., Chambon, B. & Wibawa, G. in Proceedings of International Rubber Conference. 1-26.
- Descals, A. High-resolution global map of smallholder and industrial closed-canopy oil palm plantations. Earth System Science Data 2021, 13, 1211–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaveau, D.L. Slowing deforestation in Indonesia follows declining oil palm expansion and lower oil prices. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0266178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaveau, D.L. Rise and fall of forest loss and industrial plantations in Borneo (2000–2017). Conservation Letters 2019, 12, e12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).