Submitted:
10 February 2024
Posted:
12 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Physiology of NMDA receptors
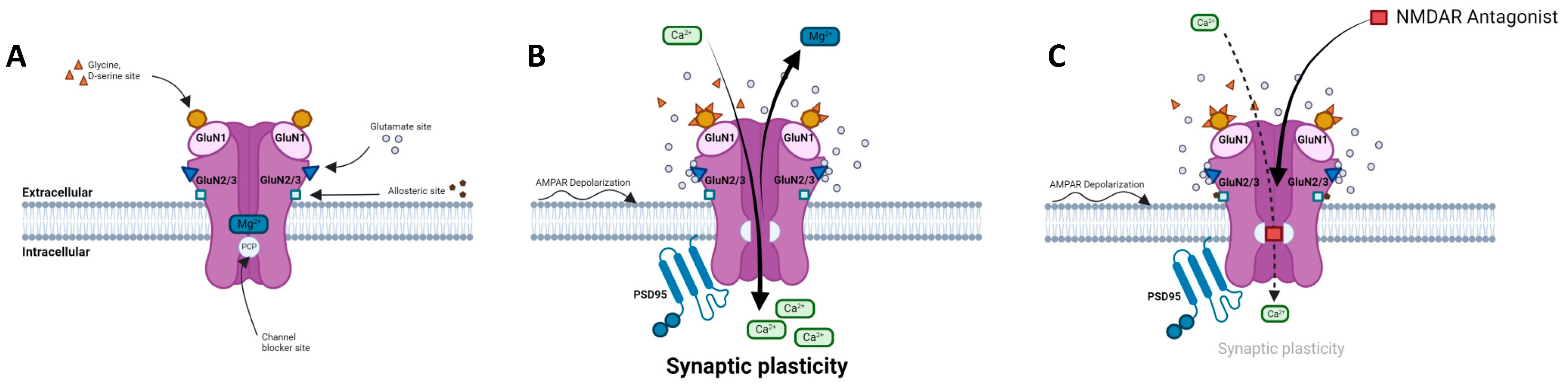
2.1. Structure, composition, localization
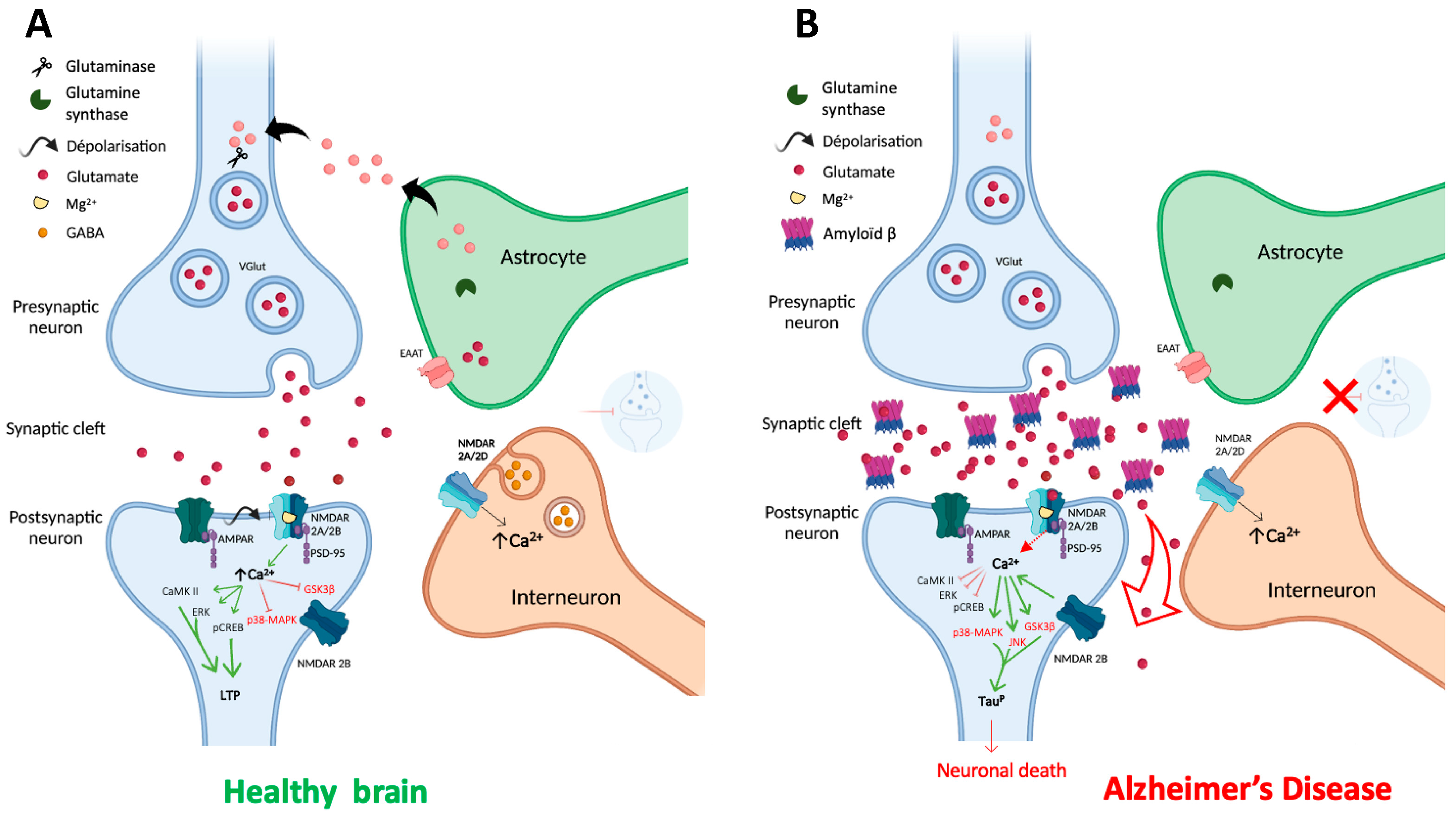
2.2. NMDARs in the glutamatergic synapse
2.3. Regulation of NMDAR activity
2.4. NMDARs modulators
3. The impact of NMDARs in neurodegenerative diseases
3.1. Alzheimer's disease
3.2. Huntington's disease
3.3. Parkinson's disease
4. Fluoroethylnormemantine (FENM): a new generation NMDAR uncompetitive antagonist
4.2. FENM as an anxiolytic agent in PTSD
4.3. FENM as a neuroprotective agent in AD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABD | agonist binding domain |
| AD | Alzheimer's disease |
| AMPAR | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
| Aβ | amyloid-β |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CaMKII | calcium moduling kinase II |
| cAMP | 3’,5’-adenosine monophosphate |
| cGMP | 3’,5’-guanosine monophosphate |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding protein |
| CTD | carboxyl C-terminal domain |
| DYRK1A | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1 |
| EAAT | excitatory amino acid transporter |
| ERK1/2 | extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 |
| FENM | fluoroethylnormemantine |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| HD | Huntington's disease |
| HEK-293 | human embryonic kidney 293 cells |
| L-Dopa | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| LTD | long-term depression |
| LTP | long-term potentiation |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| PCP | phencycline |
| PD | Parkinson's disease |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| PSD-95 | postsynaptic density protein 95 |
| PTSD | post-traumatic-stress-disorder |
| RCPG | G protein-coupled receptor |
| SANT | sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter |
| tPA | tissue-type plasminogen activator |
References
- Greenamyre, J.T.; Maragos, W.F.; Albin, R.L.; Penney, J.B.; Young, A.B. Glutamate transmission and toxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 1988, 12, 421–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volianskis, A.; France, G.; Jensen, M.S.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Jane, D.E.; Collingridge, G.L. Long-term potentiation and the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Res 2015, 1621, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, G. , Baudry, M. The biochemistry of memory: a new and specific hypothesis. Science 1984, 8, 1057–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, R.-Y. Basic roles of key molecules connected with NMDAR signaling pathway on regulating learning and memory and synaptic plasticity. Mil Med Res 2016, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E. NMDA receptor C-terminal signaling in development, plasticity, and disease. F1000Res 2019, 8, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, A.N.V.D.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Hofer, M.; Ghosh, P.; Heinemann, S. Ionotropic glutamate-receptor gene expression in hypothalamus: Localization of AMPA, kainate, and NMDA receptor RNA with in situ hybrid-ization. J Comp Neurol 1994, 343, 428–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, K.R.; Westbrook, G.L. The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J Neurosci 1999, 19, 4180–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.R.; Dubé, G.R.; Egles, C.; Liu, G. Distribution, density, and clustering of functional glutamate receptors before and after synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 2000, 84, 1573–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usherwood, P.N.; Machili, P.; Leaf, G. L-Glutamate at insect excitatory nerve-muscle synapses. Nature 1968, 219, 1169–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, L.; Bregestovski, P.; Ascher, P.; Herbet, A.; Prochiantz, A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature 1984, 307, 462–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.W.; Ascher, P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 1987, 325, 529–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Manabe, T.; Takahashi, T. Presynaptic long-term depression at the hippocampal mossy fiber-CA3 synapse. Science 1996, 273, 648–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malenka, R.C.; Kauer, J.A.; Perkel, D.J.; Nicoll, R.A. The impact of postsynaptic calcium on synaptic trans-mission--its role in long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci 1989, 12, 444–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, P.; Delumeau, J.C.; Tence, M.; Cordier, J.; Glowinski, J.; Premont, J. Somatostatin potentiates the alpha 1-adrenergic activation of phospholipase C in striatal astrocytes through a mechanism involving arachidonic acid and glutamate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991, 88, 9016–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.W.; Cotman, C.W. Plasticity in hippocampal excitatory amino acid receptors in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Res 1986, 3, 672–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Goldberg, M.P.; Choi, D.W. Ketamine protects cultured neocortical neurons from hypoxic injury. Brain Res 1986, 380, 186–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, P.; Baudry, M. Calcium dependent aspects of synaptic plasticity, excitatory amino acid neurotransmission, brain aging and schizophrenia: a unifying hypothesis. Neurobiol Aging 1987, 8, 362–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, R. Transmitter systems involved in neural plasticity underlying increased anxiety and defense-implications for understanding anxiety following traumatic stress. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1997, 21, 755–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevalk, G.D.; Nicklas, W.J. Evidence that the loss of the voltage-dependent Mg2+ block at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor underlies receptor activation during inhibition of neuronal metabolism. J Neurochem 1992, 59, 1211–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Chen, H.S.; Zhang, D.; Lipton, S.A. Memantine preferentially blocks extrasynaptic over synaptic NMDA receptor currents in hippocampal autapses. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 11246–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroebel, D.; Casado, M.; Paoletti, P. Triheteromeric NMDA receptors: from structure to synaptic physiology. Curr Opin Physiol 2018, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol Rev 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell LD, Johnson KM. Characterization of the inhibition of excitatory amino acid-induced neurotransmitter release in the rat striatum by phencyclidine-like drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1986, 238, 938–46. [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev, N.; Schoepfer, R.; Monyer, H.; Ruppersberg, J.P.; Günther, W.; Seeburg, P.H.; Sakmann, B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science 1992, 257, 1415–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Williams, Z.; Goodman, C.B.; Oriaku, E.T.; Harris, C.; Thomas, M.; Soliman, K.F.A. Effects of NMDA receptor inhibition by phencyclidine on the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 558–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Ascher, P.; Neyton, J. High-affinity zinc inhibition of NMDA NR1-NR2A receptors. J Neurosci 1997, 17, 5711–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou. Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Cummings, J.; Roldan, L.A.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex. Nature 1994, 368, 144–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazot, P.L.; Stephenson, F.A. Molecular dissection of native mammalian forebrain NMDA receptors containing the NR1 C2 exon: direct demonstration of NMDA receptors comprising NR1, NR2A, and NR2B subunits within the same complex. J Neurochem 1997, 69, 2138–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Yasuda, R.P.; Dunah, A.W.; Wolfe, B.B. The majority of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complexes in adult rat cerebral cortex contain at least three different subunits (NR1/NR2A/NR2B). Mol Pharmacol 1997, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hallaq, R.A.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Wenthold, R.J. NMDA di-heteromeric receptor populations and associated proteins in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2007, 27, 8334–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monyer, H.; Sprengel, R.; Schoepfer, R.; Herb, A.; Higuchi, M.; Lomeli, H.; Burnashev, N.; Sakmann, B.; Seeburg, P.H. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science 1992, 256, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, D.J.A.; Livesey, M.R.; Hardingham, G.E. Influence of GluN2 subunit identity on NMDA receptor function. Neuropharmacology 2013, 74, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Otaño, I.; Luján, R.; Tavalin, S.J.; Plomann, M.; Modregger, J.; Liu, X.-B.; Jones, E.G.; Heinemann, S.F.; Lo, D.C.; Ehlers, M.D. Endocytosis and synaptic removal of NR3A-containing NMDA receptors by PAC-SIN1/syndapin1. Nat Neurosci 2006, 9, 611–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Wu, A.; Berglund, K.; Gu, X.; Jiang, M.Q.; Talati, J.; Zhao, J.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. Pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease by deficiency of NMDA receptor subunit GluN3A. Alzheimers Dement 2022, 18, 222–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, T.; Abi Gerges, S.; David, M.; Diana, M.A.; Paoletti, P. Unmasking GluN1/GluN3A excitatory glycine NMDA receptors. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harney, S.C.; Jane, D.E.; Anwyl, R. Extrasynaptic NR2D-containing NMDARs are recruited to the synapse during LTP of NMDAR-EPSCs. J Neurosci 2008, 28, 11685–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halassa, M.M.; Fellin, T.; Haydon, P.G.; 2007. The tripartite synapse: roles for gliotransmission in health and disease. Trends Mol Med 2007, 13, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, A.; Yamaya, Y.; Saiki, S.; Kanemoto, M.; Hirose, G.; Beesley, J.; Pleasure, D. Non-N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors mediate oxygen--glucose deprivation-induced oligodendroglial injury. Brain Res 2000, 854, 207–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, A.S.; Tzvetavona, I.D.; Trevisiol, A.; Baltan, S.; Dibaj, P.; Kusch, K.; Möbius, W.; Goetze, B.; Jahn, H.M.; Huang, W.; Steffens, H.; Schomburg, E.D.; Pérez-Samartín, A.; Pérez-Cerdá, F.; Bakhtiari, D.; Matute, C.; Löwel, S.; Griesinger, C.; Hirrlinger, J.; Kirchhoff, F.; Nave, K.-A. Oligodendroglial NMDA receptors regulate glucose import and axonal energy metabolism. Neuron 2016, 91, 119–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palygin, O.; Lalo, U.; Pankratov, Y. Distinct pharmacological and functional properties of NMDA receptors in mouse cortical astrocytes. Br J Pharmacol 2011, 163, 1755–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamsky, A.; Kol, A.; Kreisel, T.; Doron, A.; Ozeri-Engelhard, N.; Melcer, T.; Refaeli, R.; Horn, H.; Regev, L.; Groysman, M.; London, M.; Goshen, I. Astrocytic activation generates de novo neuronal potentiation and memory enhancement. Cell 2018, 174, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, G.; Araque, A. Astrocytes potentiate transmitter release at single hippocampal synapses. Science 2007, 317, 1083–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneberger, C.; Papouin, T.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Rusakov, D.A. Long-term potentiation depends on release of D-serine from astrocytes. Nature 2010, 463, 232–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalo, U.; Koh, W.; Lee, C.J.; Pankratov, Y. The tripartite glutamatergic synapse. Neuropharmacology 2021, 199, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunatha, P.; Vosoughi, A.; Kauppinen, T.M.; Jackson, M.F. Microglial NMDA receptors drive pro-inflammatory responses via PARP-1/TRMP2 signaling. Glia 2020, 68, 1421–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.D.; Lester, R.A.; Tong, G.; Jahr, C.E.; Westbrook, G.L. The time course of glutamate in the synaptic cleft. Science 1992, 258, 1498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarker, S.; Bojja, S.L.; Gurram, P.C.; Mudgal, J.; Arora, D.; Nampoothiri, M. Astrocytic glutamatergic transmission and its implications in neurodegenerative disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, F.; Moon, C.; Schlüter, O.M.; Wang, H. Bi-directional regulation of CaMKIIα phosphorylation at Thr286 by NMDA receptors in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurochem 2012, 122, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, A.S.; Jenkins, M.A.; Banke, T.G.; Schousboe, A.; Makino, Y.; Johnson, R.C.; Huganir, R.; Traynelis, S.F. Mechanism of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II regulation of AMPA receptor gating. Nat Neurosci 2011, 14, 727–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gong, R.; Qin, L.; Bao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Gao, S.; Yang, H.; Ni, J.; Yuan, T.-F.; Lu, W. Trafficking of NMDA receptors is essential for hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation. Cell Rep 2022, 40, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niethammer, M.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M. Interaction between the C terminus of NMDA receptor subunits and multiple members of the PSD-95 family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases. J Neurosci 1996, 16, 2157–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseini, A.E.; Schnell, E.; Chetkovich, D.M.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 2000, 290, 1364–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, I.A.; Hall, D.D.; Hell, J.W. Selectivity and promiscuity of the first and second PDZ domains of PSD-95 and syn-apse-associated protein 102. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 21697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiumelli, H.; Jabaudon, D.; Magistretti, P.J.; Martin, J.L. BDNF stimulates expression, activity and release of tissue-type plasminogen activator in mouse cortical neurons. Eur J Neurosci 1999, 1999 11, 1639–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.T.; Teng, H.K.; Zaitsev, E.; Woo, N.T.; Sakata, K.; Zhen, S.; Teng, K.K.; Yung, W.H.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lu, B. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science 2004, 306, 487–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulkey, R.M.; Herron, C.E.; Malenka, R.C. An essential role for protein phosphatases in hippocampal long-term depression. Science 1993, 261, 1051–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jo, J.; Jia, J.-M.; Lo, S.-C.; Whitcomb, D.J.; Jiao, S.; Cho, K.; Sheng, M. Caspase-3 activation via mitochondria is required for long-term depression and AMPA receptor internalization. Cell 2010, 141, 859–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, C.; Malenka, R.C. NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012, 4, a005710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloodgood, B.L.; Giessel, A.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Biphasic synaptic Ca influx arising from compartmentalized elec-trical signals in dendritic spines. PLoS Biol 2009, 7, e1000190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanté, F.; Cavalier, M.; Cohen-Solal, C.; Guiramand, J.; Vignes, M. Developmental switch from LTD to LTP in low frequency-induced plasticity. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 981–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, K.W.; Standley, S.; McCallum, J.; Dune Ly, C.; Ehlers, M.D.; Wenthold, R.J. Molecular determinants of NMDA receptor internalization. Nat Neurosci 2001, 4, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosshans, D.R.; Clayton, D.A.; Coultrap, S.J.; Browning, M.D. LTP leads to rapid surface expression of NMDA but not AMPA receptors in adult rat CA1. Nat Neurosci 2002, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Clemente, A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Roche, K.W. Diversity in NMDA receptor composition: many regulators, many consequences. Neuroscientist 2013, 19, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, K.; Philpot, B.D. Regulation of NMDA receptor subunit expression and its implications for LTD, LTP, and metaplasticity. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1081–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wong, T.P.; Pozza, M.F.; Lingenhoehl, K.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Auberson, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T. Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 2004, 304, 1021–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellone, C.; Nicoll, R.A. rapid bidirectional switching of synaptic NMDA receptors. Neuron 2007, 55, 779–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, J.P.; Ladépêche, L.; Seth, H.; Bard, L.; Varela, J.; Mikasova, L.; Bouchet, D.; Rogemond, V.; Honnorat, J.; Hanse, E.; Groc, L. Surface dynamics of GluN2B-NMDA receptors controls plasticity of maturing glutamate synapses. EMBO J 2014, 33, 842–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Clemente, A.; Matta, J.A.; Isaac, J.T.R.; Roche, K.W. Casein kinase 2 regulates the NR2 subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors. Neuron 2010, 67, 984–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Clemente, A.; Gray, J.A.; Ogilvie, K.A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Roche, K.W. Activated CaMKII couples GluN2B and casein kinase 2 to control synaptic NMDA receptors. Cell Rep 2013, 3, 607–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgdorff, A.J.; Choquet, D. Regulation of AMPA receptor lateral movements. Nature 2002, 417, 649–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opazo, P.; Labrecque, S.; Tigaret, C.M.; Frouin, A.; Wiseman, P.W.; De Koninck, P.; Choquet, D. CaMKII triggers the diffusional trapping of surface AMPARs through phosphorylation of stargazin. Neuron 2010, 67, 239–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumioka, A.; Yan, D.; Tomita, S. TARP phosphorylation regulates synaptic AMPA receptors through lipid bilayers. Neuron 2010, 66, 755–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, A.C.; Zhang, C.L.; Georges, F.; Royer, L.; Breillat, C.; Hosy, E.; Petersen, J.D.; Humeau, Y.; Choquet, D.; 2017. Hippocampal LTP and contextual learning require surface diffusion of AMPA receptors. Nature 2017, 549, 384–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardoni, F.; Schrama, L.H.; Kamal, A.; Gispen, W.H.; Cattabeni, F.; Di Luca, M. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity involves competition between Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and postsynaptic density 95 for binding to the NR2A subunit of the NMDA receptor. J Neurosci 2001, 21, 1501–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardoni, F.; Mauceri, D.; Fiorentini, C.; Bellone, C.; Missale, C.; Cattabeni, F.; Di Luca, M. CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation regulates SAP97/NR2A interaction. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 44745–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauceri, D.; Gardoni, F.; Marcello, E.; Di Luca, M. Dual role of CaMKII-dependent SAP97 phosphorylation in mediating trafficking and insertion of NMDA receptor subunit NR2A. J Neurochem 2007, 100, 1032–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, W.G.; Ehlers, M.D.; Kameyama, K.; Doherty, C.; Ptak, J.B.; Riley, C.T.; Huganir, R.L. Characterization of protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit using phosphorylation site-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 5157–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.B.; Blanpied, T.A.; Swanson, G.T.; Zhang, C.; Ehlers, M.D.; 2001. An NMDA receptor ER retention signal regulated by phosphorylation and alternative splicing. J Neurosci 2001, 21, 3063–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.B.; Blanpied, T.A.; Ehlers, M.D. Coordinated PKA and PKC phosphorylation suppresses RXR-mediated ER retention and regulates the surface delivery of NMDA receptors. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 755–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Tanimura, A.; Kiyama, Y.; Tezuka, T.; Watabe, A.M.; Katayama, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Inoue, Takeshi, Izumi-Nakaseko, H. ; Kakuta, S.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Umemori, H.; Inoue, Takafumi, Murphy, N.P.; Hashimoto, K.; Kano, M.; Manabe, T.; Yamamoto, T. Involvement of NMDAR2A tyrosine phosphory-lation in depression-related behaviour. EMBO J 2009, 28, 3717–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, C.; Arató, K.; Fernández-Fernández, J.M.; Valderrama, A.; Sindreu, C.; Fillat, C.; Ferrer, I.; de la Luna, S.; Altafaj, X. ; 2014. DYRK1A-mediated phosphorylation of GluN2A at Ser1048 regulates the surface expression and channel activity of GluN1/GluN2A receptors. Front Cell Neurosci 8, 331. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chang, C.-P.; Lin, C.-J.; Lai, H.-L.; Kao, Y.-H.; Cheng, S.-J.; Chen, H.-M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Faivre, E.; Buée, L.; Blum, D.; Fang, J.-M.; Chern, Y. Adenosine augmentation evoked by an ENT1 inhibitor improves memory impairment and neuronal plasticity in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 8936–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Komai, S.; Tezuka, T.; Hisatsune, C.; Umemori, H.; Semba, K.; Mishina, M.; Manabe, T.; Yamamoto, T. Characterization of Fyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation sites on GluR epsilon 2 (NR2B) subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 693–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.M.; Nong, Y.; Almeida, C.G.; Paul, S.; Moran, T.; Choi, E.Y.; Nairn, A.C.; Salter, M.W.; Lombroso, P.J.; Gouras, G.K.; Greengard, P. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-β. Nat Neurosci 2005, 8, 1051–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, L. Simvastatin enhances NMDA receptor GluN2B expression and phosphorylation of GluN2B and GluN2A through increased histone acetylation and Src signaling in hippo-campal CA1 neurons. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 411–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Meng, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-P.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, T.-T.; Gong, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T. Enriched environment enhances histone acetylation of NMDA receptor in the hippocampus and improves cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Neural Regen Res 2020, 15, 2327–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G.; Anderson, E.; Lynch, G.S.; Baudry, M. Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature 1986, 319, 774–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Butcher, S.P.; Morris, R.G. The NMDA receptor antagonist D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate (D-AP5) impairs spatial learning and LTP in vivo at intracerebral concentrations comparable to those that block LTP in vitro. J Neurosci 1992, 12, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.; Watkins, J.C.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Jane, D.E.; Volianskis, A. The 1980s: d-AP5, LTP and a decade of NMDA receptor discoveries. Neurochem Res 2019, 44, 516–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzi, A.; Herdon, H.; Schwarz, A.; Bertani, S.; Crestan, V.; Turrini, G.; Bifone, A. Pharmacological stimulation of NMDA receptors via co-agonist site suppresses fMRI response to phencyclidine in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008, 201, 273–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Vicknasingam, B.; Cheung, Y.-W.; Zhou, W.; Nurhidayat, A.W.; Jarlais, D.C.D.; Schottenfeld, R. To use or not to use: an update on licit and illicit ketamine use. Subst Abuse Rehabil 2011, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothula, S.; Kato, T.; Liu, R.-J.; Wu, M.; Gerhard, D.; Shinohara, R.; Sliby, A.-N.; Chowdhury, G.M.I.; Behar, K.L.; Sanacora, G.; Banerjee, P.; Duman, R.S. Cell-type specific modulation of NMDA receptors triggers antidepressant actions. Mol Psychiatr 2021, 26, 5097–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Brown, K.A.; Georgiou, P.; Yuan, P.; Zarate, C.A.; Thompson, S.M.; Gould, T.D. NMDA Receptor Activation-Dependent Antidepressant-Relevant Behavioral and Synaptic Actions of Ketamine. J Neurosci 2023, 43, 1038–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T.; Su, T.P.; Parish, D.W.; Nabeshima, T.; Privat, A. PRE-084, a sigma selective PCP derivative, attenuates MK-801-induced impairment of learning in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1994, 49, 859–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, J.P.; Delumeau, J.C.; Glowinski, J.; Prémont, J.; Doble, A. Antagonism by riluzole of entry of calcium evoked by NMDA and veratridine in rat cultured granule cells: evidence for a dual mechanism of action. Br J Pharmacol 1994, 113, 261–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, B.D.; Kratzer, U.; Schmidt, W.J. Riluzole, a glutamate release inhibitor, and motor behavior. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1998, 358, 181–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanauskas, N.; Nistri, A. Riluzole blocks persistent Na+ and Ca2+ currents and modulates release of glutamate via presynaptic NMDA receptors on neonatal rat hypoglossal motoneurons in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 2008, 27, 2501–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, R.M.; Cappiello, A.; Anand, A.; Oren, D.A.; Heninger, G.R.; Charney, D.S.; Krystal, J.H. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 2000, 47, 351–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, R.; Rappaport, M.; Nichtenhauser, R.; Zukin, S.R.; 1987. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801: a potent and specific ligand of the brain phencyclidine/sigma-receptor. Brain Res 1987, 435, 235–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, I.J.; Hughes, N.; Carroll, C.B.; Brotchie, J.M. Reversal of parkinsonian symptoms by intrastriatal and systemic manipulations of excitatory amino acid and dopamine transmission in the bilateral 6-OHDA lesioned marmoset. Behav Pharmacol 1995, 6, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.J.; Huang, H.; Pritchett, D.B.; Lynch, D.R. Interactions between ifenprodil and the NR2B subunit of the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem 1996, 271, 9603–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarre, S.; Lanza, M.; Makovec, F.; Artusi, R.; Caselli, G.; Michotte, Y. In vivo neurochemical effects of the NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonist CR 3394 in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2008, 584, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. The NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as a symptomatological and neuro-protective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: preclinical evidence. Int J Geriat Psychiatr 2003, 18, S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakawa-Hirachi, T.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Ohgidani, M.; Haraguchi, Y.; Monji, A. Effect of memantine, an an-ti-Alzheimer’s drug, on rodent microglial cells in vitro. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanpied, T.A.; Clarke, R.J.; Johnson, J.W. ;. Amantadine inhibits NMDA receptors by accelerating channel closure during channel block. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 3312–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, F.; Schwarz, M. Dextromethorphan reduces functional deficits and neuronal damage after global ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1996, 74, 153–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, E.; Topic, B.; De Souza Silva, M.A.; Fink, H.; Buddenberg, T.; Huston, J.P. ; 2003. NMDA-receptor antagonism via dextromethorphan and ifenprodil modulates graded anxiety test performance of C57BL/6 mice. Behav Pharmacol 14, 245–9. [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, P.; Waltimo, A.; Waltimo, T.; Könönen, M.; Pertovaara, A.; 1997. Differential effects of noxious conditioning stimulation of the cheek by capsaicin on human sensory and inhibitory masseter reflex responses evoked by tooth pulp stimulation. J Dent Res 1997, 76, 1561–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbroum, A.A.; Gorodetzky, A.; Nirkin, A.; Kollender, Y.; Bickels, J.; Marouani, N.; Rudick, V.; Meller, I. Dextromethorphan for the reduction of immediate and late postoperative pain and morphine consumption in orthopedic oncology patients: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Cancer 2002, 95, 1164–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbroum, A.A.; Bender, B.; Nirkin, A.; Chazan, S.; Meller, I.; Kollender, Y. Dextromethorphan-associated epidural patient-controlled analgesia provides better pain- and analgesics-sparing effects than dextrome-thorphan-associated intravenous patient-controlled analgesia after bone-malignancy resection: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study. Anesth Analg 2004, 98, 714–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K. Ifenprodil discriminates subtypes of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: selectivity and mechanisms at recombinant heteromeric receptors. Mol Pharmacol 1993, 44, 851–9. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S.; Kishi, T.; Nomura, I.; Sakuma, K.; Okuya, M.; Ikuta, T.; Iwata, N. The efficacy and safety of memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Opin Drug Safety 2018, 17, 1053–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Pizon, A.F.; Brooks, D.E. Dextromethorphan-induced serotonin syndrome. Clin Toxicol 2008, 46, 771–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, M.C.; Hantraye, P.; Dolan, R.; Palfi, S.; Maziére, M.; Brouillet, E.; 1997. Quantifiable bradykinesia, gait abnormalities and Huntington’s disease-like striatal lesions in rats chronically treated with 3-nitropropionic acid. Neuroscience 1997, 79, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albin, R.L.; Greenamyre, J.T. Alternative excitotoxic hypotheses. Neurology 1992, 42, 733–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, M.; Fukumoto, H.; Newell, K.L.; Growdon, J.H.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Frosch, M.P.; Albert, M.S.; Hyman, B.T.; Irizarry, M.C. Early Aβ accumulation and progressive synaptic loss, gliosis, and tangle formation in AD brain. Neurology 2004, 62, 925–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheff, S.W.; Price, D.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; Mufson, E.J. Hippocampal synaptic loss in early Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 2006, 27, 1372–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, C.; Smania, N.; Pedrinolla, A.; Munari, D.; Gandolfi, M.; Picelli, A.; Varalta, V.; Benetti, M.V.; Brugnera, A.; Federico, A.; Muti, E.; Tamburin, S.; Schena, F.; Venturelli, M. Comparison between physical and cognitive treatment in patients with MIC and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 3138–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E.; Ince, P.G.; Lace, G.; Forster, G.; Shaw, P.J.; Matthews, F.; Savva, G.; Brayne, C.; Wharton, S.B.; 2010. Astrocyte phenotype in relation to Alzheimer-type pathology in the ageing brain. Neurobiol Aging 2010, 31, 578–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Nguyen, L.N.; Kessels, H.W.; Hagiwara, H.; Sisodia, S.; Malinow, R. Amyloid beta from axons and dendrites reduces local spine number and plasticity. Nat Neurosci 2010, 13, 190–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jin, M.; Koeglsperger, T.; Shepardson, N.E.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble Aβ oligomers inhibit long-term potentiation through a mechanism involving excessive activation of extrasynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 6627–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Companys-Alemany, J.; Turcu, A.L.; Vázquez, S.; Pallàs, M.; Griñán-Ferré, C. Glial cell reactivity and oxidative stress prevention in Alzheimer’s disease mice model by an optimized NMDA receptor antagonist. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 17908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, Z.; Belli, L.; Toniolo, S.; Sancesario, G.; Bianconi, C.; Martorana, A. ; 2013. Amyloid β, Glutamate, Exci-totoxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Are We on the Right Track? CNS Neurosci Ther 19, 549–55. [CrossRef]
- Ittner, L.M.; Ke, Y.D.; Delerue, F.; Bi, M.; Gladbach, A.; van Eersel, J.; Wölfing, H.; Chieng, B.C.; Christie, M.J.; Napier, I.A.; Eckert, A.; Staufenbiel, M.; Hardeman, E.; Götz, J. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-β toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Cell 2010, 142, 387–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitolo, O.V.; Sant’Angelo, A.; Costanzo, V.; Battaglia, F.; Arancio, O.; Shelanski, M. Amyloid beta -peptide inhibition of the PKA/CREB pathway and long-term potentiation: reversibility by drugs that enhance cAMP signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002, 99, 13217–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordji, K.; Becerril-Ortega, J.; Nicole, O.; Buisson, A. Activation of extrasynaptic, but not synaptic, NMDA receptors modifies amyloid precursor protein expression pattern and increases amyloid-ß production. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 15927–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.C.; Wong, C.K.; Yung, K.K. Modulation of the gene expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR2B subunit in the rat neostriatum by a single dose of specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotide. Neurochem Int 2001, 39, 319–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Sze, C.-I. N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A and NR2B messenger RNA levels are altered in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 2002, 200, 11–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynd, M.R.; Scott, H.L.; Dodd, P.R. Differential expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR2 isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 2004, 90, 913–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishizen-Eberz, A.J.; Rissman, R.A.; Carter, T.L.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Wolfe, B.B.; Armstrong, D.M. Biochemical and molecular studies of NMDA receptor subunits NR1/2A/2B in hippocampal subregions throughout pro-gression of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neurobiol Dis 2004, 15, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, S.W.Y.; Vinters, H.V.; Cummings, J.L.; Wong, P.T.-H.; Chen, C.P.L.-H.; Lai, M.K.P. Alterations in NMDA receptor subunit densities and ligand binding to glycine recognition sites are associated with chronic anxiety in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2008, 29, 1524–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.A.; Ashford, W.; Ernesto, C.; Saxton, J.; Schneider, L.S.; Clark, C.M.; Ferris, S.H.; Mackell, J.A.; Schafer, K.; Thal, L.J. The severe impairment battery: concurrent validity and the assessment of longitudinal change in Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord, 2.
- Tariot, P.N.; Farlow, M.R.; Grossberg, G.T.; Graham, S.M.; McDonald, S.; Gergel, I.; for the Memantine Study Group. Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease already receiving donepezil. A randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 2004, 291, 317–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimica, N.; Presecki, P. Side effects of approved antidementives. Psychiatr Danub 2009, 21, 108–13. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, A.; Mahjoub, Y.; Shaver, L.; Pringsheim, T. Prevalence and Incidence of Huntington’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov Disord 2022, 37, 2327–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, A.; Albin, R.L.; Anderson, K.D.; D’Amato, C.J.; Penney, J.B.; Young, A.B. Differential loss of striatal projection neurons in Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988, 85, 5733–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroud, T.; Gray, J.; Ivashina, J.; Conneally, P.M. Differences in duration of Huntington’s disease based on age at onset. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 1999, 66, 52–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Beck, C.A.; Darwin, K.; Nichols, P.; Brocht, A.F.D.; Biglan, K.M.; Shoulson, I.; Huntington Study Group COHORT Investigators. Natural history of Huntington disease. JAMA Neurol 2013, 70, 1520–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyao, M.; Ambrose, C.; Myers, R.; Novelletto, A.; Persichetti, F.; Frontali, M.; Folstein, S.; Ross, C.; Franz, M.; Abbott, M. ; 1993. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington’s disease. Nat Genet 4, 387–392. [CrossRef]
- McKinstry, S.U.; Karadeniz, Y.B.; Worthington, A.K.; Hayrapetyan, V.Y.; Ozlu, M.I.; Serafin-Molina, K.; Risher, W.C.; Ustunkaya, T.; Dragatsis, I.; Zeitlin, S.; Yin, H.H.; Eroglu, C. Huntingtin is required for normal excit-atory synapse development in cortical and striatal circuits. J Neurosci 2014, 34, 9455–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Licitra, F.; Underwood, B.R.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Huntington’s disease: mechanisms of pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2017, 7, a024240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Savanenin, A.; Reddy, P.H.; Liu, Y.F. Polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin promotes sensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors via post-synaptic density 95. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 24713–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.B.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Hollingsworth, Z.; Albin, R.; D’Amato, C.; Shoulson, I.; Penney, J.B. NMDA receptor losses in putamen from patients with Huntington’s disease. Science 1988, 241, 981–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albin, R.L.; Young, A.B.; Penney, J.B.; Handelin, B.; Balfour, R.; Anderson, K.D.; Markel, D.S.; Tourtellotte, W.W.; Reiner, A. Abnormalities of striatal projection neurons and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in pre-symptomatic Huntington’s disease. N Engl J Med 1990, 322, 1293–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, C.; Ariano, M.A.; Calvert, C.R.; Flores-Hernández, J.; Chandler, S.H.; Leavitt, B.R.; Hayden, M.R.; Levine, M.S.; 2001. NMDA receptor function in mouse models of Huntington disease. J Neurosci Res 2001, 66, 525–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.J.; Levine, M.S. Changes in expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits occur early in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Dev Neurosci 2006, 28, 230–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarabek, B.R.; Yasuda, R.P.; Wolfe, B.B. Regulation of proteins affecting NMDA receptor-induced excitotoxicity in a Huntington’s mouse model. Brain 2004, 127, 505–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faideau, M.; Kim, J.; Cormier, K.; Gilmore, R.; Welch, M.; Auregan, G.; Dufour, N.; Guillermier, M.; Brouillet, E.; Hantraye, P.; Déglon, N.; Ferrante, R.J.; Bonvento, G. In vivo expression of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin by mouse striatal astrocytes impairs glutamate transport: a correlation with Huntington’s disease subjects. Hum Mol Genet 2010, 19, 3053–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, M.Y.; Detloff, P.J.; Wang, P.L.; Tsien, J.Z.; Albin, R.L. In vivo evidence for NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in a murine genetic model of Huntington disease. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 3200–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, B.; Liu, X.; Wan, Q. Differential roles of GluN2A- and GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in neuronal survival and death. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 2012, 4, 211–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Fukunaga, Y.; Bading, H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci 2002, 5, 405–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010, 11, 682–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Poirier, M.A.; Liang, Y.; Pei, Z.; Weiskittel, C.E.; Smith, W.W.; DeFranco, D.B.; Ross, C.A. Depletion of CBP is directly linked with cellular toxicity caused by mutant huntingtin. Neurobiol Dis 2006, 23, 543–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saft, C.; Burgunder, J.-M.; Dose, M.; Jung, H.H.; Katzenschlager, R.; Priller, J.; Nguyen, H.P.; Reetz, K.; Reilmann, R.; Seppi, K.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B. Symptomatic treatment options for Huntington’s disease (guidelines of the German Neurological Society). Neurol Res Pract 2023, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2018, 46 Suppl 1, S30–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablo-Fernández, E.; Lees, A.J.; Holton, J.L.; Warner, T.T. Prognosis and neuropathologic correlation of clinical subtypes of Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 2019, 76, 470–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatsua, T.; Sawadab, M. L-Dopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease: past, present, and future. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2009, 15 Suppl 1, S3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastide, M.F.; Meissner, W.G.; Picconi, B.; Fasano, S.; Fernagut, P.-O.; Feyder, M.; Francardo, V.; Alcacer, C.; Ding, Y.; Brambilla, R.; Fisone, G.; Jon Stoessl, A.; Bourdenx, M.; Engeln, M.; Navailles, S.; De Deurwaerdère, P.; Ko, W.K.D.; Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Groc, L.; Rodriguez, M.-C.; Gurevich, E.V.; Quik, M.; Morari, M.; Mellone, M.; Gardoni, F.; Tronci, E.; Guehl, D.; Tison, F.; Crossman, A.R.; Kang, U.J.; Steece-Collier, K.; Fox, S.; Carta, M.; Angela Cenci, M.; Bézard, E. Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 2015, 132, 96–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, M.; Paganini, F.; Stocchi, S.; Mela, F.; Beani, L.; Bianchi, C.; Morari, M. Plasticity of glutamatergic control of striatal acetylcholine release in experimental parkinsonism: opposite changes at group-II metabotropic and NMDA receptors. J Neurochem 2003, 84, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.C.; Gunasekar, P.G.; Borowitz, J.L.; Isom, G.E. Dopamine-induced apoptosis is mediated by oxidative stress and Is enhanced by cyanide in differentiated PC12 cells. J Neurochem 2000, 74, 2296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, V.A.; Morin, N.; Grégoire, L.; Morissette, M.; Di Paolo, T. Changes in glutamate receptors in dyskinetic parkinsonian monkeys after unilateral subthalamotomy. J Neurosurg 2015, 123, 1383–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen Metman, L.; Blanchet, P.J.; van den Munckhof, P.; Del Dotto, P.; Natté, R.; Chase, T.N. A trial of dextromethorphan in parkinsonian patients with motor response complications. Mov Disord 1998, 13, 414–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascol, O.; Fabbri, M.; Poewe, W. Amantadine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and other movement disorders. Lancet Neurol 2021, 20, 1048–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitti, R.J.; Rajput, A.H.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Offord, K.P.; Schroeder, D.R.; Ho, M.M.; Prasad, M.; Rajput, A.; Basran, P. Amantadine treatment is an independent predictor of improved survival in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1996, 46, 1551–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merello, M.; Nouzeilles, M.I.; Cammarota, A.; Leiguarda, R. Effect of memantine (NMDA antagonist) on Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind crossover randomized study. Clin Neuropharmacol 1999, 22, 273–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Poroikov, V.V. Pharmacological profile of natural and synthetic compounds with rigid adamantane-based scaffolds as potential agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 529, 1225–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samnick, S.; Ametamey, S.; Leenders, K.L.; Vontobel, P.; Quack, G.; Parsons, C.G.; Neu, H.; Schubiger, P.A. Electrophysiological study, biodistribution in mice, and preliminary PET evaluation in a rhesus monkey of 1-amino-3-[18F]fluoromethyl-5-methyl-adamantane (18F-MEM): a potential radioligand for mapping the NMDA-receptor complex. Nucl Med Biol 1998, 25, 323–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ametamey, S.M.; Samnick, S.; Leenders, K.L.; Vontobel, P.; Quack, G.; Parsons, C.G.; Schubiger, P.A. Fluorine-18 radiolabelling, biodistribution studies and preliminary PET evaluation of a new memantine derivative for imaging the NMDA receptor. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 1999, 19, 129–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ametamey, S.M.; Bruehlmeier, M.; Kneifel, S.; Kokic, M.; Honer, M.; Arigoni, M.; Buck, A.; Burger, C.; Samnick, S.; Quack, G.; Schubiger, P.A. PET studies of 18F-memantine in healthy volunteers. Nucl Med Biol 2002, 29, 227–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, A.D.; Casanova, M.F.; Kleinman, J.E.; De Souza, E.B. PCP and sigma receptors in brain are not altered after repeated exposure to PCP in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 1991, 4, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Salabert, A.-S.; Fonta, C.; Fontan, C.; Adel, D.; Alonso, M.; Pestourie, C.; Belhadj-Tahar, H.; Tafani, M.; Payoux, P. Radiolabeling of [18F]-fluoroethylnormemantine and initial in vivo evaluation of this innovative PET tracer for imaging the PCP sites of NMDA receptors. Nucl Med Biol 2015, 42, 643–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salabert, A.-S.; Mora-Ramirez, E.; Beaurain, M.; Alonso, M.; Fontan, C.; Tahar, H.B.; Boizeau, M.L.; Tafani, M.; Bardiès, M.; Payoux, P. Evaluation of [18F]FNM biodistribution and dosimetry based on whole-body PET im-aging of rats. Nucl Med Biol 2018, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaurain, M.; Talmont, F.; Pierre, D.; Péran, P.; Boucher, S.; Hitzel, A.; Rols, M.-P.; Cuvillier, O.; Payoux, P.; Salabert, A.-S. Pharmacological characterization of [18F]-FNM and evaluation of NMDA receptors activation in a rat brain injury model. Mol Imaging Biol 2023, 25, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarate, C.A.; Singh, J.B.; Carlson, P.J.; Brutsche, N.E.; Ameli, R.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006, 63, 856–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- aan het Rot, M.; Collins, K.A.; Murrough, J.W.; Perez, A.M.; Reich, D.L.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010, 67, 139–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, J.; Dolzani, S.D.; Tilden, S.; Christianson, J.P.; Kubala, K.H.; Bartholomay, K.; Sperr, K.; Ciancio, N.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. ; 2016. Previous ketamine produces an enduring blockade of neurochemical and behavioral effects of uncontrollable stress. J Neurosci 36, 153–61. [CrossRef]
- Brachman, R.A.; McGowan, J.C.; Perusini, J.N.; Lim, S.C.; Pham, T.H.; Faye, C.; Gardier, A.M.; Mendez-David, I.; David, D.J.; Hen, R.; Denny, C.A. Ketamine as a prophylactic against stress-induced depressive-like behavior. Biol Psychiatr 2016, 79, 776–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, J.C.; LaGamma, C.T.; Lim, S.C.; Tsitsiklis, M.; Neria, Y.; Brachman, R.A.; Denny, C.A. Prophylactic ketamine attenuates learned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1577–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, K.T.; Killeen, T.K.; Brewerton, T.; Lucerini, S. Comorbidity of psychiatric disorders and posttraumatic stress disorder. J Clin Psychiatr 2000, 61 Suppl 7, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, J.R.; Rothbaum, B.O.; van der Kolk, B.A.; Sikes, C.R.; Farfel, G.M. Multicenter, double-blind comparison of sertraline and placebo in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatr 2001, 58, 485–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.K.; Le Pen, G.; Eckmier, A.; Rubinstenn, G.; Jay, T.M.; Denny, C.A. Fluoroethylnormemantine, a novel derivative of memantine, facilitates extinction learning without sensorimotor deficits. Int J Neuropychopharmacol 2021, 24, 519–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.K.; Luna, V.M.; Shannon, M.E.; Hunsberger, H.C.; Mastrodonato, A.; Stackmann, M.; McGowan, J.C.; Ru-binstenn, G.; Denny, C.A. Fluoroethylnormemantine, a novel NMDA receptor antagonist, for the prevention and treatment of stress-induced maladaptive behavior. Biol Psychiatr 2021, 90, 458–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T.; Phan, V.-L.; Privat, A. The anti-amnesic effects of sigma1 (σ1) receptor agonists confirmed by in vivo antisense strategy in the mouse. Brain Res 2001, 898, 113–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couly, S.; Denus, M.; Bouchet, M.; Rubinstenn, G.; Maurice, T. Anti-amnesic and neuroprotective effects of fluoroethylnormemantine in a pharmacological mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2020, 24, 142–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Slunt, H.H.; Ratovitski, T.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Borchelt, D.R. Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: a comparison of strategies. Biomol Eng 2001, 17, 157–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Fadale, D.J.; Anderson, J.; Xu, G.M.; Gonzales, V.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Lee, M.K.; Younkin, L.H.; Wagner, S.L.; Younkin, S.G.; Borchelt, D.R. Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of the 42 residue β-amyloid peptide in vivo: evidence for augmentation of a 42-specific γ secretase. Hum Mol Genet 2004, 13, 159–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds | Modulator | Selectivity | Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-AP5 | Hight selective competitive antagonist | GluN2A | Inhibits excitatory response. Impacts behavioural learning, blocks plasticity (LTP). | [90,91,92] |
| Riluzole | Competitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Indirect block of NMDAR. Protect from motor deficit | [98,99,100] |
| Phencyclidine | Selective uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2B/D(PCP site) | Induces psychotic and dissociative schizophrenia-like symptoms. Impairs NMDAR neurotransmission in vivo. | [93] |
| Ketamine | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2B/D(PCP site) | Applied in post-synapse : inhibits excitatory pyramidal neuron in extra-synaptic GluN2B. Applied in pre-synapse: inhibits GluN2D in interneuron (induces disinhibition of glutamate release in post-synapse). Up-regulates hippocampal AMPARs (GluA1/GluA2). antidepressant. | [95,101] |
| Dizocilpine | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2B/D(PCP site) | Anticonvulsant, antidepressant. Induces memory impairments. | [97,102] |
| Ifenprodil | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Blocks GluN2B (140-fold preference for NR2B over NR2A subunits). Induces an inhibition of GluN2R receptor currents. anti-Parkinsonian effect. | [103,104,105] |
| Memantine | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Blocks GluN2B extra-synaptic and induces glutamatergic excitotoxicity. Used for moderate-to-severe AD. | [106,107] |
| Amantadine | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Blocks GluN1/GluN2B by accelerating channel closure during channel block. Used as antiparkinsonian drug | [108] |
| Dextrometorphan | Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2A | Blocks GluN2A subunit. Prevent neuronal damage and modulates pain sensation | [109,110,111,112,113] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





