1. Introduction
In the early period of experimental trials on the possible beneficial effects of probiotics and their action pathways, it was a fairly common practice to use a “heat-killed probiotic” group as a kind of a second control group [1-3]. This group was used to address the question of whether living or dead bacteria or any of their organelles or bacteria components are really beneficial. With time, it became apparent that, practically, there was no difference in how the probiotics work and so, slowly, the practice of using a heat-killed probiotic group ceased.
However, the enormous progress achieved recently in the use of cell cultures for testing specifically the immunomodulatory effects of probiotics on a distinct cell type [i.e. keratinocytes or endothelial cells], has revived the old practice of using dead bacteria, now in the form of bacteria lysates – independently of the method used for their lysis – in order to make the experimentation easier and less interrelated to external factors and/or the peculiarities of the organism as a whole [
4,
5].
The same subject, viewed from another angle, that of the clinician, has brought the confirmation of the beneficial effect of non-viable bacteria or their fragments or by products and, in the next few years, will resolve the presumed risk of bacteremia induction in the severely ill, immune-compromised patients treated with probiotics [
6].
However, this new era of knowledge has also led to a variety of terms used to refer to them, such as heat-killed, inactivated or non-viable, dead probiotics, paraprobiotics or postbiotics, cell fragments, and bacterial lysates, all describing the same entity, but unfortunately resulting in a confusion in terminology [
7]. Thus, in October 2021, a group of experienced scientists, from both basic science and clinical fields, under the auspices of the International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics [ISAPP] convened to clearly determine the conditions under which the various "modified forms" derived from live probiotics could be referenced under the same name: "postbiotics". Today, postbiotics are defined as the “preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their cellular components that confers a health benefit on the host”, including in this the killed microbial cells, with or without metabolites and excluding purified products [i.e., proteins, peptides, exopoly-saccharides and SCFAs] [
8].
The establishment of this consensus led to a surge in publications in review form from November 2021, numerically disproportionate to the "production" of primary research, experimental or clinical. Of course, it should be noted that, in recent years, the expansion of the ease for someone to publish in a high impact factor, open access journal, after peer review, has facilitated the publication of thousands of articles in the form of reviews or narrated reviews, without their necessarily being systematic reviews, as required by “classical” journals, many of which accepted such articles only upon author invitation. In practice, the new condition means that, theoretically, anyone could publish a review paper.
The present study, therefore, aims to provide insights and analyze the subject connection and experience of the authors in relation to postbiotics, published in reviews after October 2021. In other words, this is a groundbreaking study to identify the scientific orientation and perspectives of the first and last authors, by analyzing - by means of bibliometry - their publications touching on the broader subject of the microbiome and probiotics, in order to answer the question of whether the published reviews are written by authors with a deep knowledge of the subject or the review is simply the result of a thorough literature analysis performed by somebody – probably a young scientist – with no or only slight involvement with the topic.
3. Results
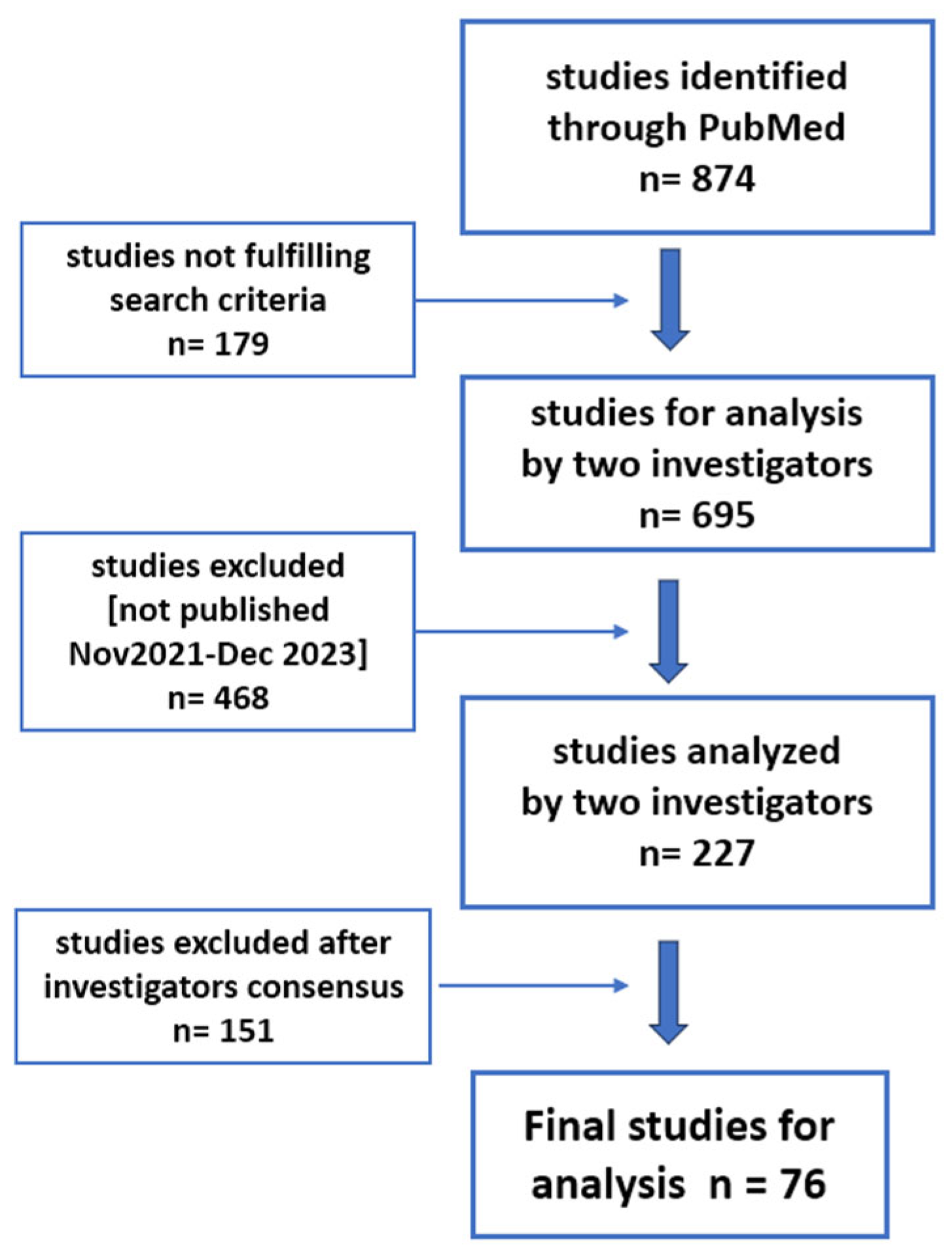
Our search strategy in the PubMed database initially identified a total of 874 records. After setting as screening filters the terms “review” or “systematic review”, 179 publications were excluded; following the next filter, relating to the publication time frame [November 2021 to December 2023], another 468 were excluded, leaving 227 for analysis. These studies were initially screened by two authors, independently, and in the case of discrepancy, by a third. Finally, 76 articles remained to be analyzed after the exclusion of a further 151. These articles were published over a 26-month period - a mean of 2.92 articles per month. The search outcome is displayed as a flowchart in
Figure 1.
3.1. Initial Data Retrieved from the Selected Articles
3.1.1. Demographics
The search covered a 26-month period, beginning in November 2021, the date of the publication of the consensus formally defining the term “postbiotics” [
8]. The cumulative demographics are presented in (
Table 1).
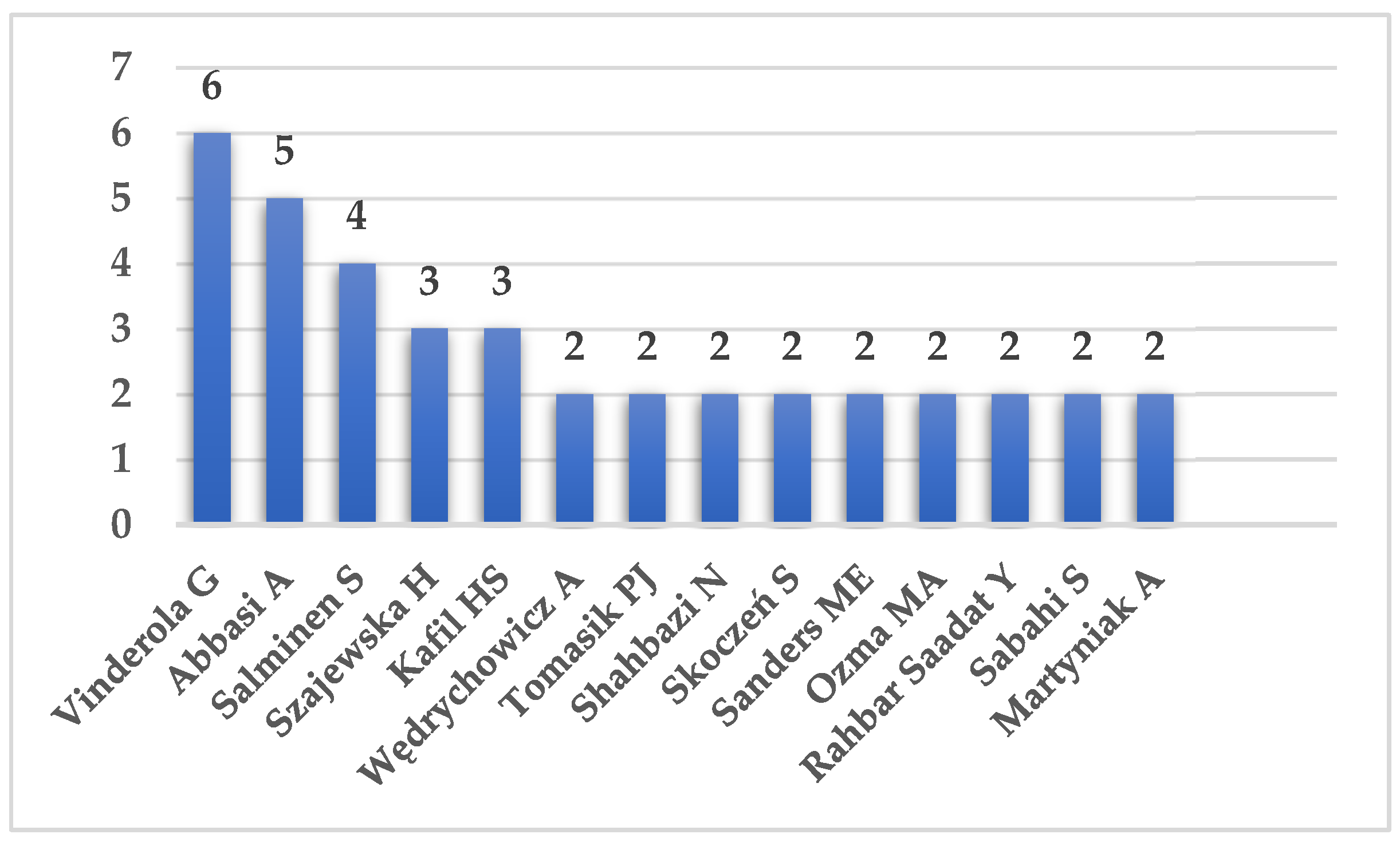
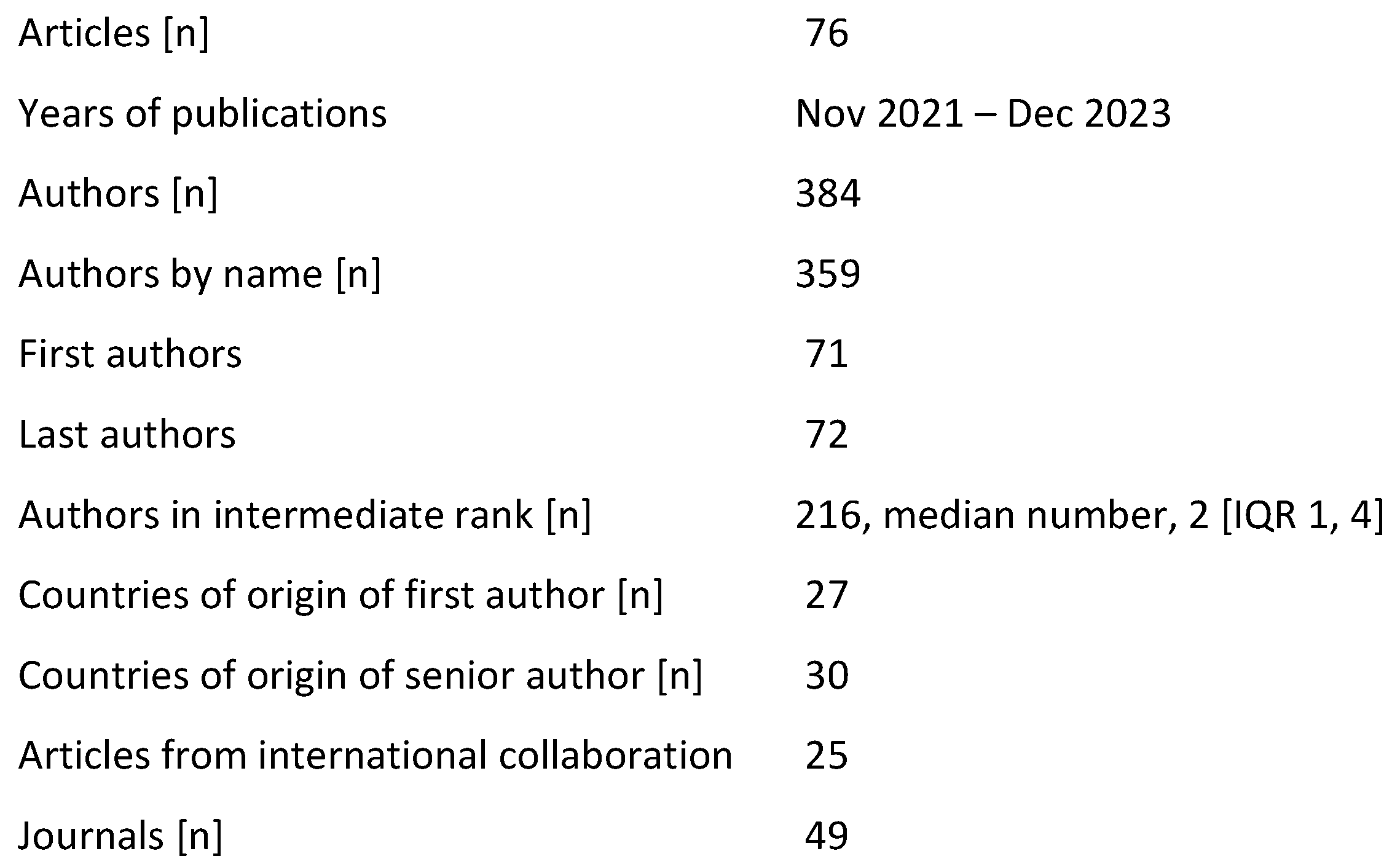
The 76 papers have a total of 384 named authors. Of these - independently of the authorship rank - Vinderola G, from Argentina, authored 6 papers – which means his name was found 6 times within the 384 authors –, Abbasi A, from Iran, authored 5 papers, Salminen S, from Finland, 4, Szajewska H from Poland, and Kafil H from Iran, 3 papers each. Additionally, another 9 scientists authored 2 papers each. This means that there were 359 scientists, writing in collaboration with others, one or more of the 76 articles (
Figure 2).
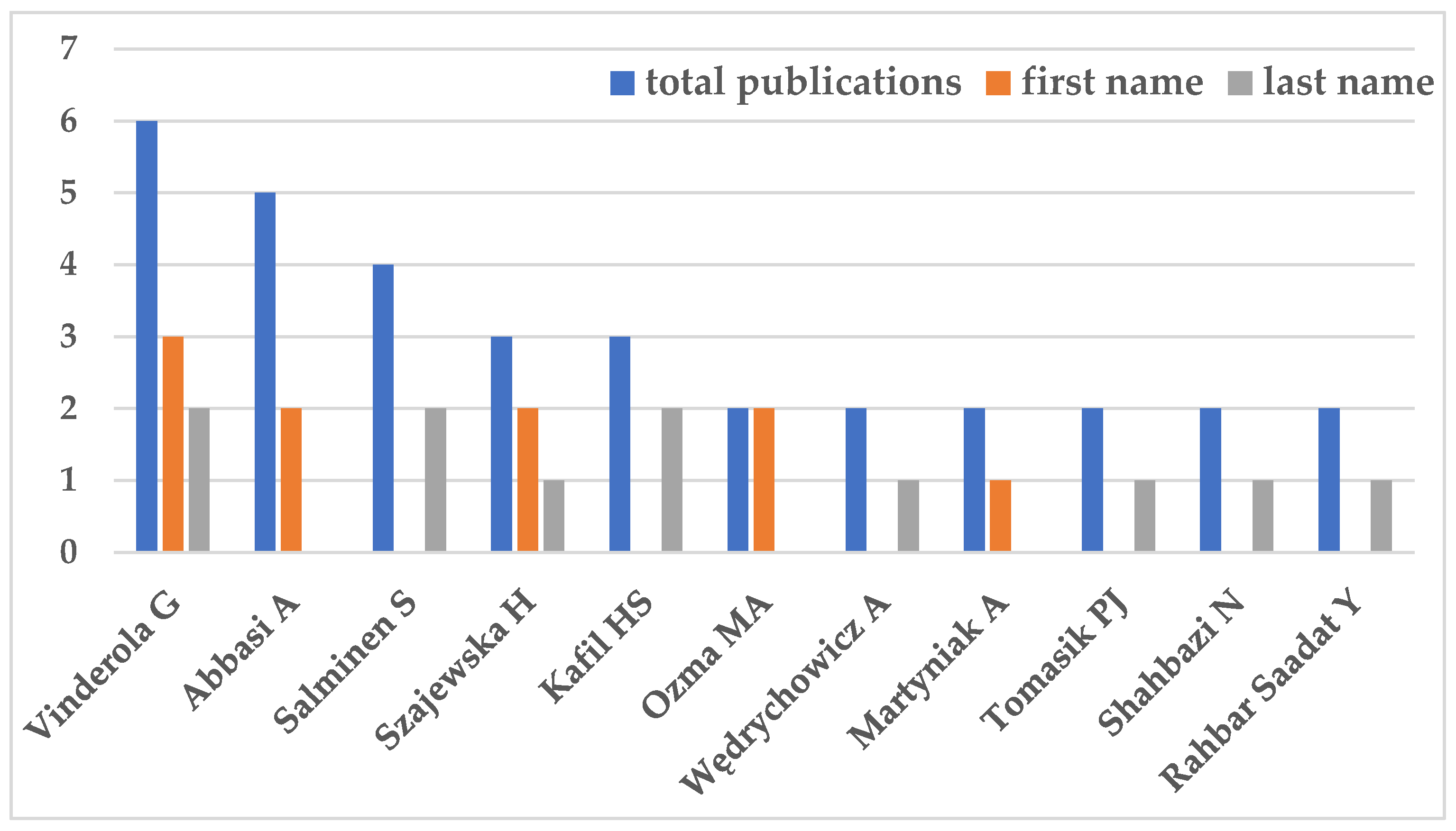
From the 14 authors with more than one publication, most were either first or last authors: Vinderola G, having authored 6 papers, was first author in 3 and last author in 2; Abbasi A having authored 5 papers was first in 2; Salminen S with 4 publications and Kafil HS with 3 had authored 2 papers each as seniors; and Szajewska H having authored 3 papers was first author in 2 and senior in 1. From the 9 authors of 2 papers, Ozma MA and Martyniak A were first author in two and one, respectively; Wędrychowicz A, Tomasik PJ, Shahbazi N and Rahbar Saadat Y, had one publication each as last/senior author; and 3 had no papers as first or last author (
Figure 3).
Given that from the 76 papers one had a single author, we have 76 first and 75 last authors. Or, after taking into consideration the multiple authorship of some scientists, we finally had 71 first and 72 last authors.
After exclusion of the first and last authors, there remained 233 authors serving as authors in the middle ranks, meaning there is a median of 2 [IQR; 1, 4] middle authors in each paper, ranging from 0 to 12. These authors are outside the parameters of this study and will not be further referred to.
3.1.2. Countries of Affiliation of First Authors
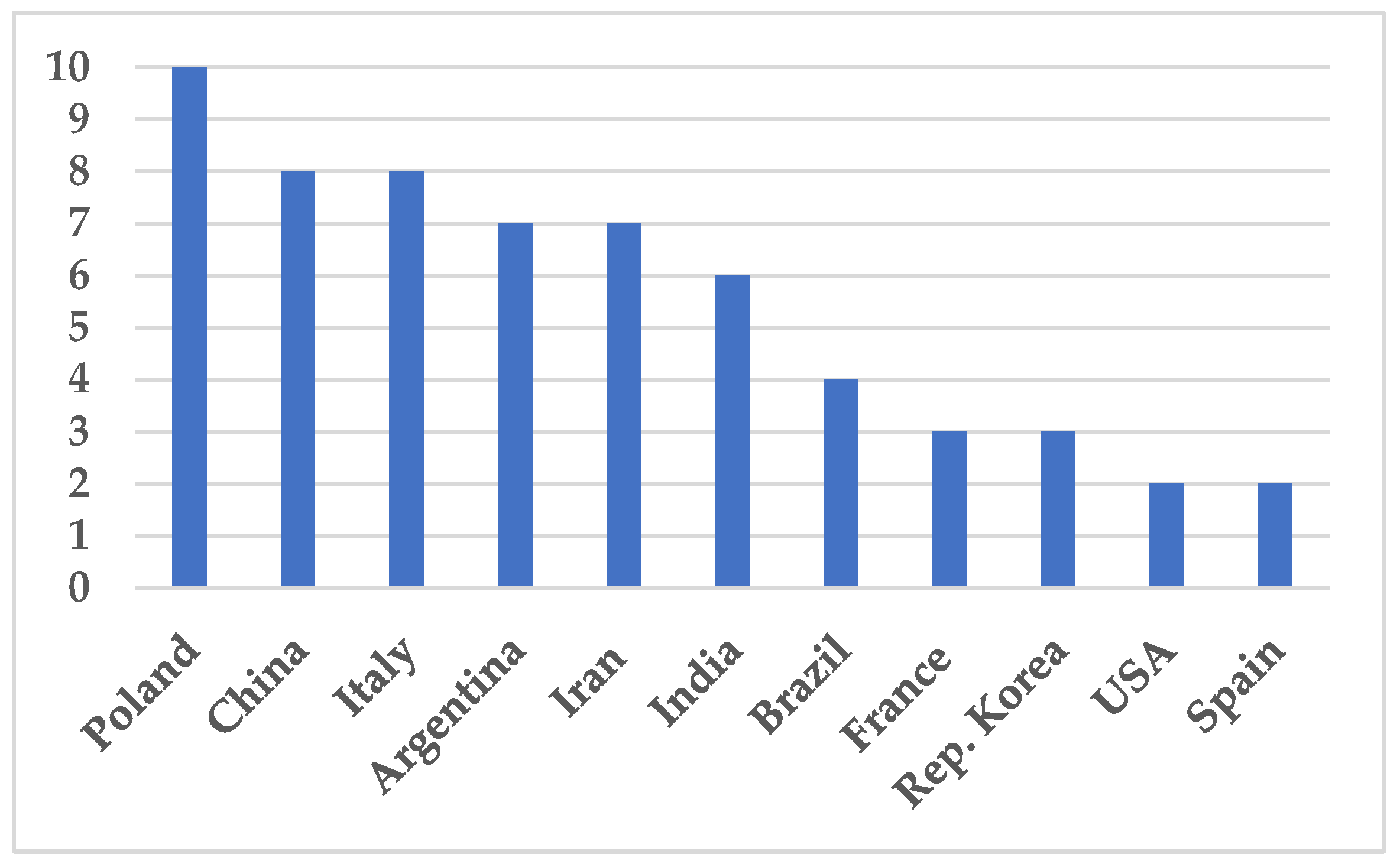
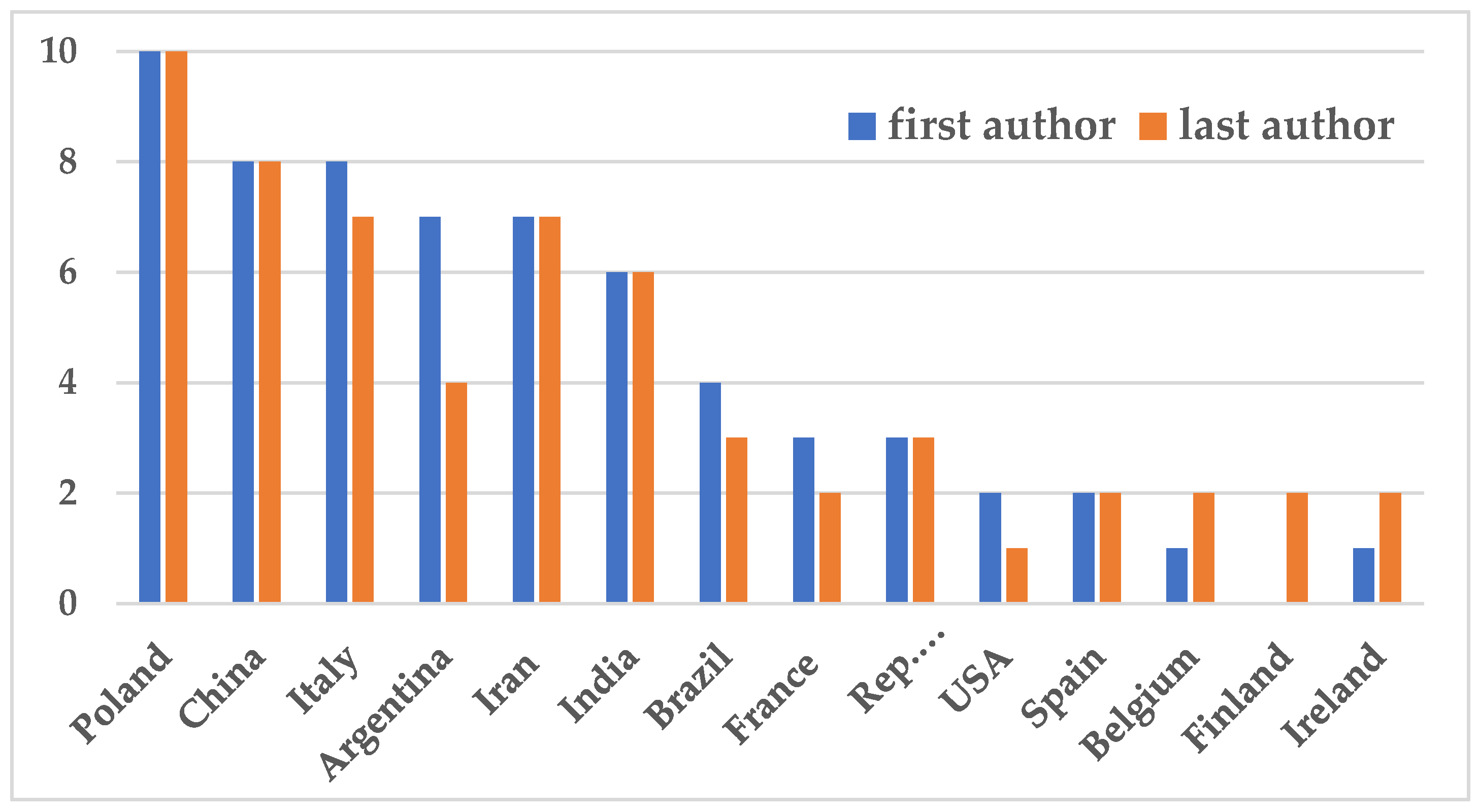
According to the country of residence and work of the first authors, eleven countries had the greatest productivity - 60 articles - contributing 2 or more papers each; thus, 60 publications came from 11 countries and the remaining 16 from another 16 countries. Poland was top with 10 publications, followed by China and Italy with 8 and Argentina and Iran with 7 (
Figure 4).
Four authors presented having double countries affiliation, but only the first referred was counted: Spivak I. comes from Israel and Germany; Scarpellini E. from Italy and Belgium; Vera-Santander VE. from Mexico and UK; and Bozzetti V. from USA and Italy.
3.1.3. Countries of Affiliation of Last Authors
Last authors came from 30 countries, thirteen of which had the greatest productivity - 58 articles, - contributing 2 or more papers each, and the remaining 17 publications came from another 17 countries. As a consequence of the collaboration among countries, there is a slight difference in the rank of countries from which the last authors came in relation to that of the first authors. The country with the highest productivity was Poland again, with 10 publications, followed by China, Iran and Italy with 7 each, then Argentina and India with 4 each [rate 5.33%], and Brazil and The Republic of Korea with 3 each [rate 4%]. The number of studies per country is presented in (
Figure 5).
A significant difference related to Argentina, which, while having 7 articles of first authorship, had 4 only in the list of last authors, the difference being attributable to its collaboration with other countries. Similar is observed with Brazil, France and USA - one publication less than the number with first authors. The opposite is true for Belgium and Ireland which have two articles in the last but only one in the first author list. Finally, Finland, Bangladesh, Colombia, Canada and Thailand had no publications from first authors, but did have last authors - Finland two and the other four one each [data not shown in Figures].
3.1.4. Country Collaboration Networks
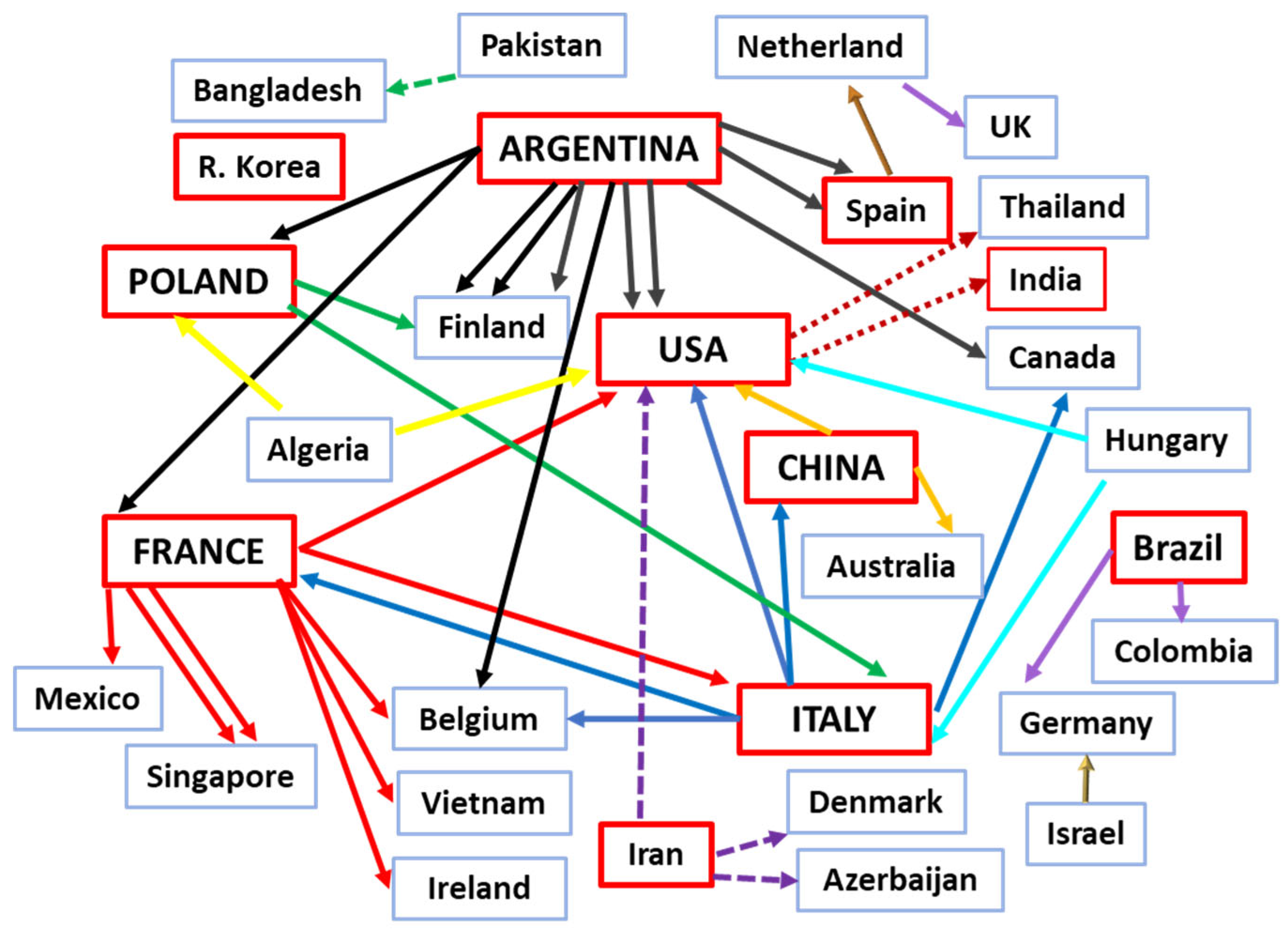
In fifty-one out of the 76 articles [rate 67.1%] all the authors came from the same country, while the remaining 25 articles were the result of collaboration between authors from 2 to 7 countries: in 15 cases from two countries; in 6 from three; and 4 publications coming from the collaboration of 4, 4, 5 and 7 countries. The 7-country collaboration came from France [with Mexico, Singapore, Italy, Belgium, Vietnam and Ireland] and that of 5 from Argentina [with France, Spain, Finland, and Belgium].
It is of interest to note that of Argentina’s total of 7 publications, 5 involved collaborations with other countries, meaning co-authorship with a total of 11 countries. France had collaboration with 8 countries. Poland’s total of 10 articles, however, involved collaboration with another country in only 2 [with Italy and Finland]. China and Italy, with a total of 8 articles each, each collaborated with other countries in only two instances [USA or Australia and USA or France, respectively]; Iran with 7 articles collaborated in only one case - with USA, Denmark and Azerbaijan; India with 6 articles and The Republic of Korea with 3 – had no collaboration; and Brazil with a total of 4 articles collaborated in 2 - with Colombia and Germany, respectively (
Figure 6).
3.2. Institutions of First Authors
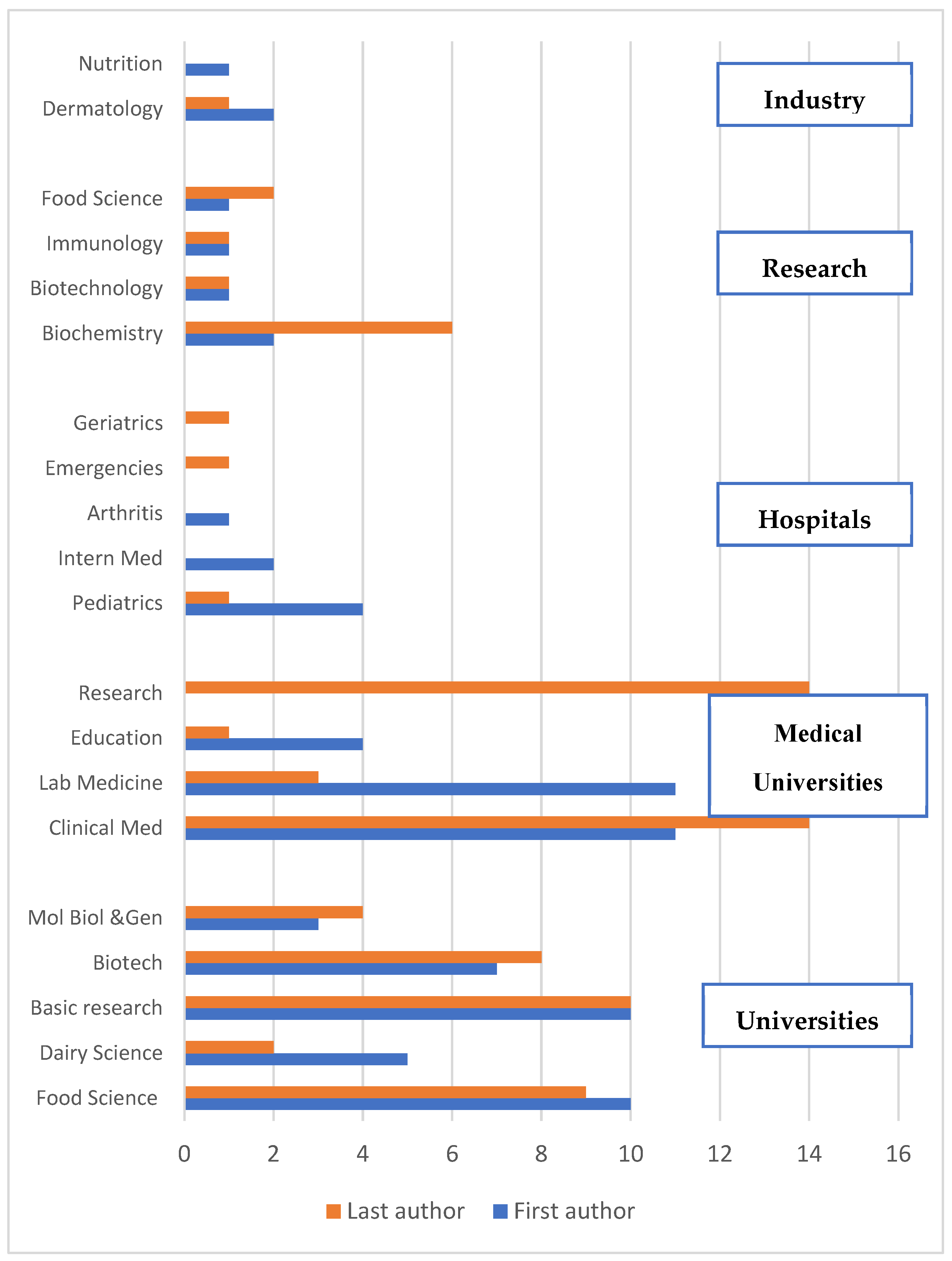
The first authors of the 76 publications are affiliated to universities [n=35], to medical universities [n=26], to hospitals [not related to medical schools, n=7], to independent research centers [n=5] and to industry [n=3] (
Figure 7).
The 35 articles coming from non-medical universities are from departments dealing with food science [n=15, included 5 in dairy science], basic research [n=10], biotechnology [n=7] and molecular biology & genetics [n=3]. The 26 papers from medical universities are equally distributed between clinical and laboratory medicine [n=11 each category] as well as another 4 from student research. The 7 articles from non-university hospitals come: 4 from the departments of pediatrics and 1 each from departments of internal medicine, nephrology & hypertension, and arthritis. Finally, 3 articles from industry are related to research in dermatology [n=2] and nutrition [n=1] (
Figure 8).
3.3. Institutions of Last Authors
The last authors of the 75 publications [one article out of the 76 has a single author [counted as first] are affiliated to universities [n=33], to medical universities [n=32], to hospitals [not related to medical schools, n=3], to independent research centers [n=6] and to industry [n=1]. 3 authors - Viderola G, Salminen S and Kafil HS - authored two articles each as seniors, but counted as different authors [
Figure 7]. Their specialties are presented in
Figure 8.
The 33 articles coming from non-medical universities are from departments dealing with food science [n=11, - including 1 in Dairy Science], basic research [n=10], biotechnology [n=8], and molecular biology & genetics [n=4]. The 26 papers from medical universities are from clinical [n=14] and laboratory medicine - research [n=17], as well as another 1 from student research. The 3 articles from non-university hospitals come from departments of pediatrics, emergency medicine, and geriatrics. Finally, one article, coming from industry, is related to research in dermatology.
3.4. Journals of Publication
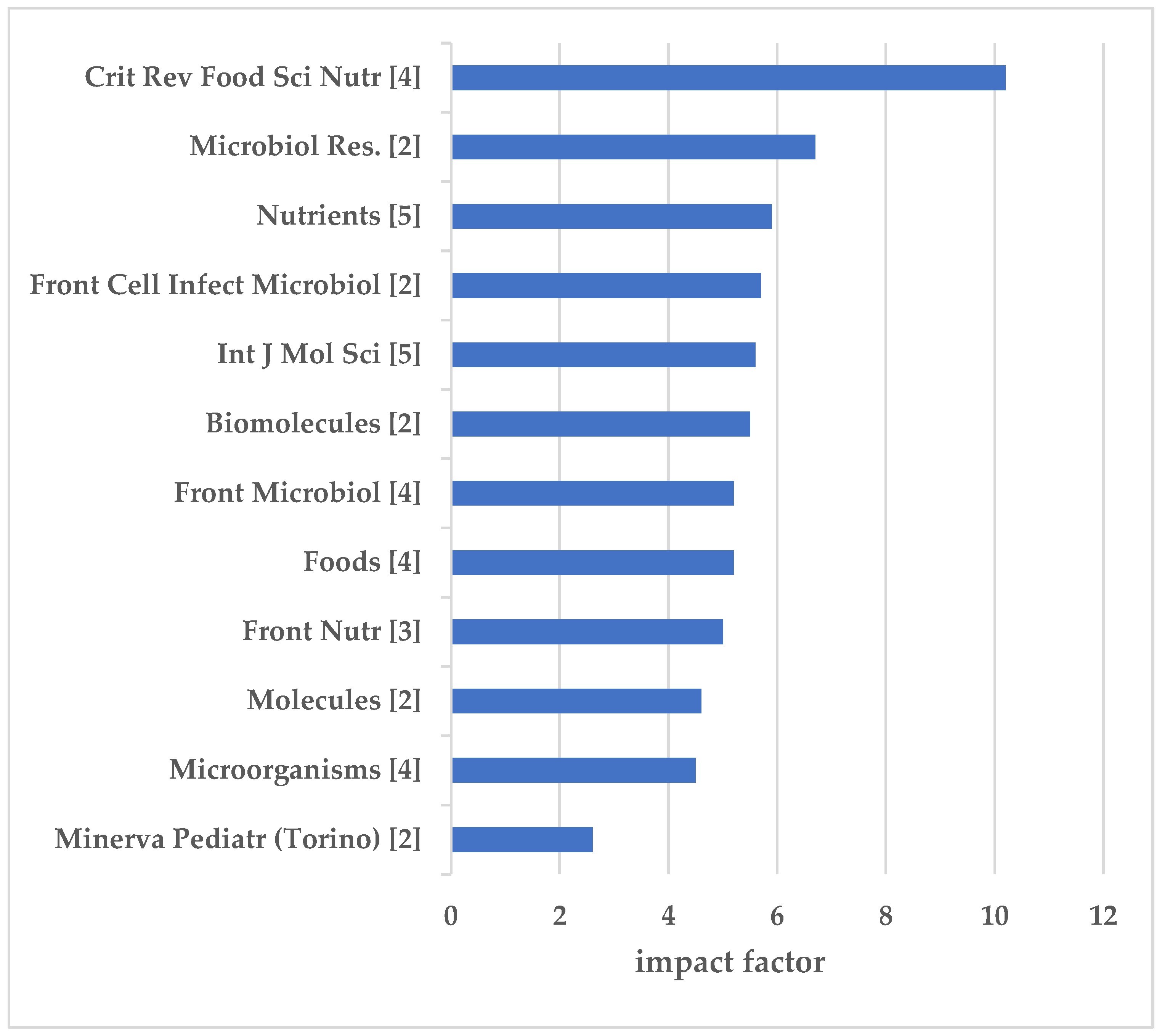
The 76 articles were published in 49 journals; twelve hosting almost half of the publications, [n = 39, rate 51.3 %], the remaining 37 publications [48.67%] being distributed between another 37 journals. Nutrients and Int J Mol Sci were ranked first in frequency, with 5 publications each; followed by Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, Foods, Front Microbiol, and Microorganisms, with 4 publications each (
Figure 9).
3.5. Journal Impact Factor
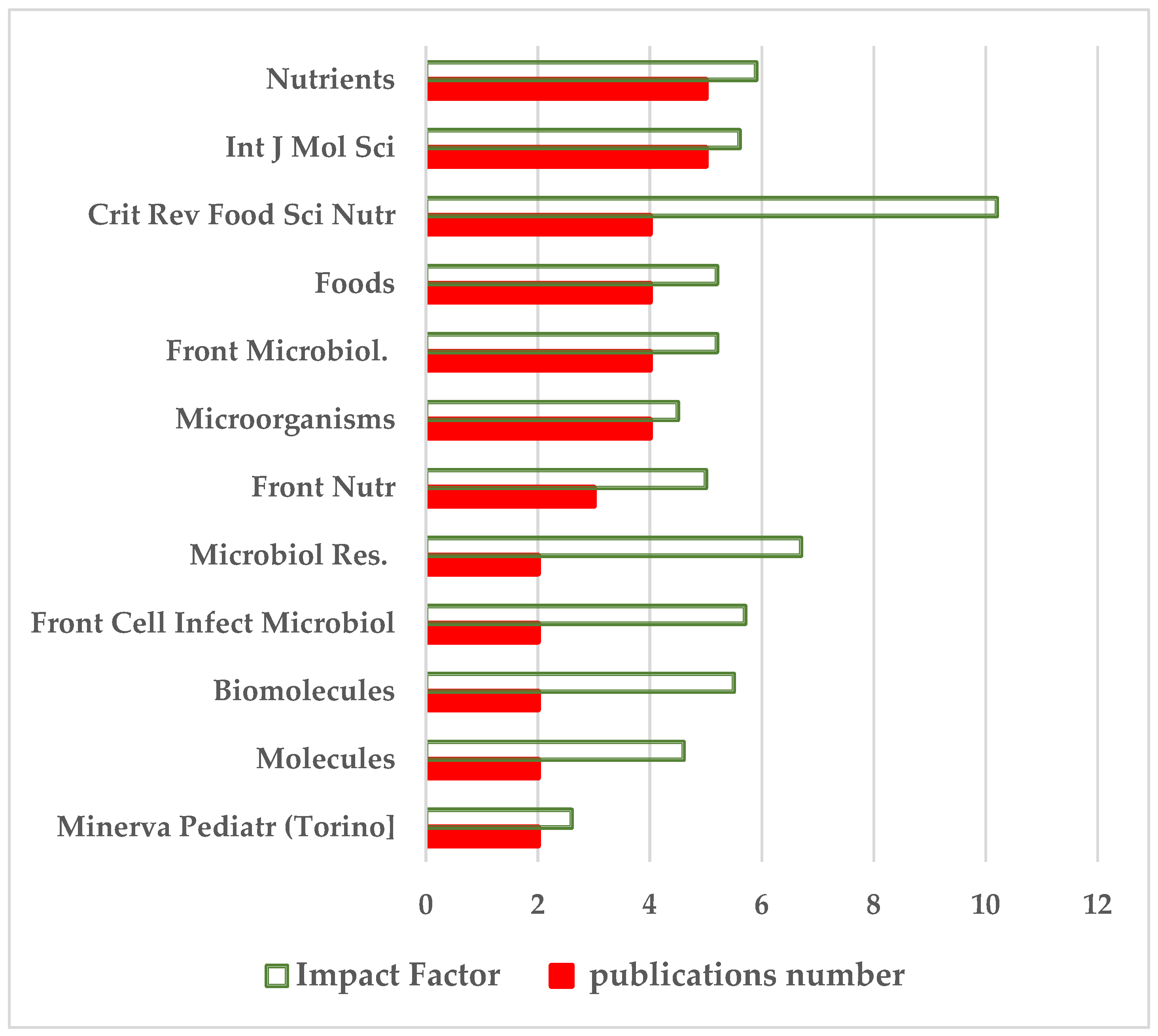
Among the 12 journals hosting the 39 articles, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr [Taylor & Francis], with 4 publications, has the highest IF = 10.2, followed by Microbiol Res [Elsevier] with 2 publications and IF 6.7. Then follow Nutrients with IF 5.9 and Int J Mol Sci with 5.6 - 5 publications each (
Figure 10). Six out of the 12 journals belong to the MDPI publisher, 3 to Frontiers, one to Elsevier, one to Taylor & Fransis and one to Minerva Medica publishers; this means that 22 out of 39 articles are published by MDPI journals, 9 by Frontiers, four by Taylor & Fransis, two by Elsevier, and two by Minerva Medica.
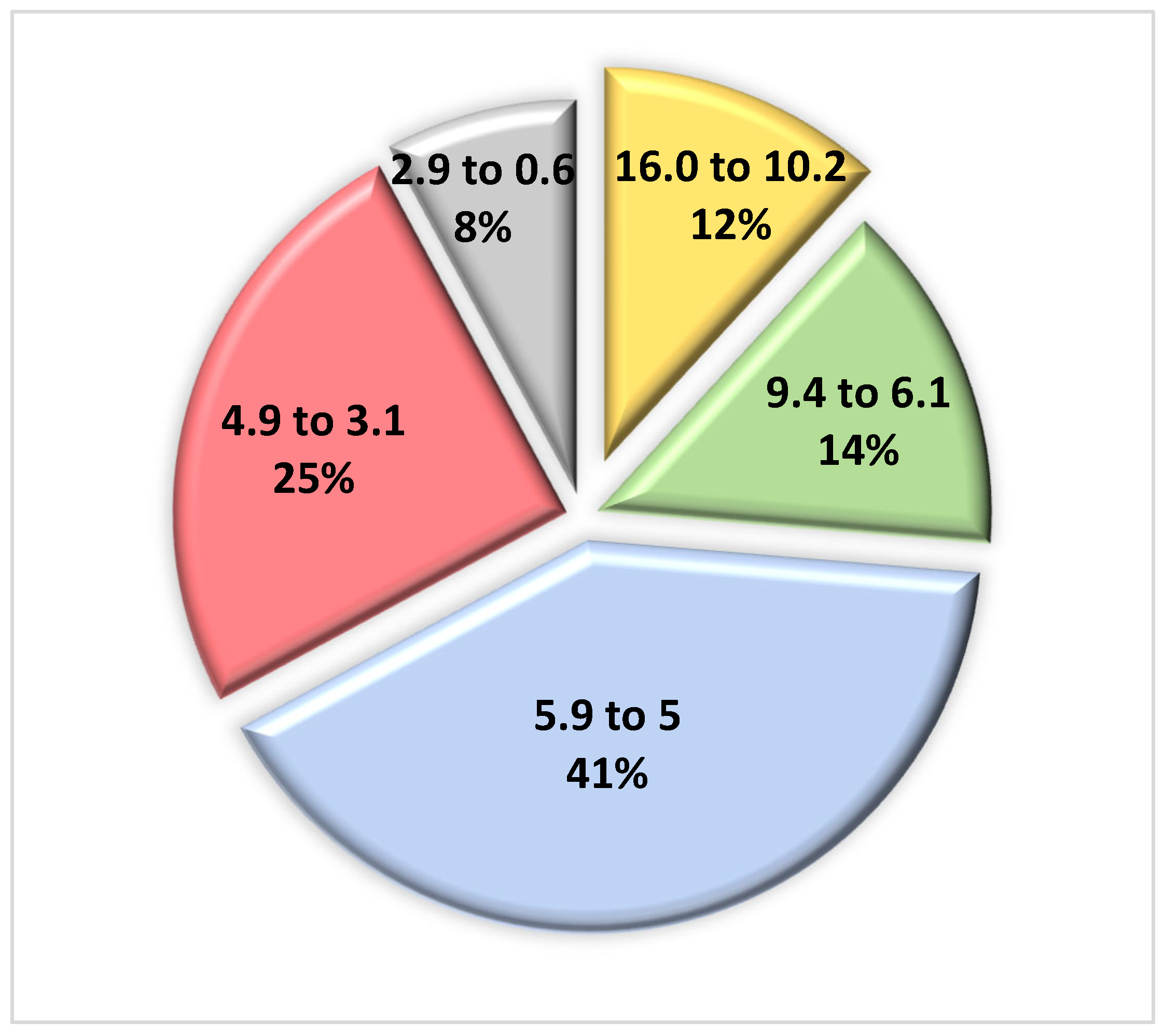
However, the remaining 37 articles are also published in significant journals, some of them with a higher impact factor than those given above. The top five journals with an Impact Factor of between 16.0 and 11.2 are presented in
Table 2. Another 15 journals have an Impact Factor between 9.4 and 5.2 and the remaining 17 an Impact Factor between 4.9 and 0.6.
When we classified all 76 articles according to their Impact Factor, we found nine with an Impact Factor of between 16.0 and 10.2, 11 articles between 9.4 and 6.1, 31 articles between 5.9 and 5, 15 articles of between 4.9 and 3.1 and the remaining 6 of between 2.9 and 0.6. Almost half [n=31] are published in journals with an IF 5.9 to 5.0 (
Figure 11).
3.6. Number of Citations Received and Most Cited Authors
The limited time frame of analysis [November 2021 to December 2023], means a short time for the articles to be cited. The top-10 publications with the highest number of citations are presented in (
Table 3).
At the top, with 53 citations, is the publication of Martyniak A, from Poland, in Biomolecules [IF 5.5], which has the advantage of being one of the 4 articles published in November-December 2021, giving it the longest exposure. However, the 8th in rank is an article by Scarpellini E et al, from Italy in collaboration with Belgium, published in Int J Environ Res Public Health [IF, 4.6], and received just 28 citations, although published at the same time - December 2021. Looking into these top-10 authors/articles we note that from the authors with more than one publication as first or last, Vinderola G. and Abbasi A. keep the 3rd [46 citations] and 6th rank [34 citations], and Martyniak A. the 1st [53 citations]; and, as expected, there is no article published in 2023.
3.7. First Author Productivity in Related Topics
We then ranked the first authors according to their productivity in articles relating to the “microbiome” and/or “probiotics”. Nine authors [14 articles] were found to have 10 or more publications each, which implies that the authors are significantly involved in the general topic of the microbiome/probiotics (
Table 4). Szajewska H. from Poland ranked first, with 92 related publications, followed by Vinderola G. from Argentina with 41 related publications; these two are the top authors on postbiotics, having published 3 and 6 papers respectively. Another 24 authors [29 articles] have contributed 2 to 8 publications each, related to the “microbiome” and/or “probiotics”.
It is of great importance to underline that there are 15 first authors who authored only one publication relating to the “microbiome” and/or “probiotics”, their names being in either rank; and another 18 having zero publications. In other words, almost half [rate 43.4%] of the 76 publications have as first author a “young” investigator in the topic. From the 15 articles whose first author had one publication, in 2 articles the last author was also “young” in the topic, with only one publication; and another 2 had 2 publications each. Two articles had as last authors Vinderola G. from Argentina [41 related publications] and Van de Wiele T. from Belgium [33 related publications]. Finally, the productivity of the last authors who, like the remaining 18 first authors, had/have zero related publications is somewhat disappointing (
Table 5).
3.8. Last Author Productivity
We then similarly ranked the last authors according to their maximum productivity in articles relating to the “microbiome” and/or “probiotics”. There were 72 last authors, since 3 [Viderola G, Salminen S and Kafil HS] authored two articles each as last, and one article had a single author, considered as first.
Ten authors [12 articles] were found to have 20 or more publications, and another 11 authors [12 articles] between 18 and 10 publications. Three of these were seniors in 2 publications each: Salminen S. from Finland [142 related papers], Vinderola G. from Argentina [with 41 related papers] – already noted as first author in another 3 papers -, and Kafil HS from Iran [16 related papers]. Thirty-eight authors [38 articles] have between 8 and 2 related publications. However, there are 7 last authors with only one related publication and 6 with zero (
Table 6).
Combining the findings, we realized that in only one case was the final author with zero previous publications listed on an article with an experienced first author [14 related publications - Gueniche A, coming from the industry]. The remaining 5 last authors, unfortunately were teamed with 5 of the 18 first authors, with also zero related publication. That means 5 of the 76 articles were written by scientists with no previous knowledge or experience in this narrow topic of the microbiome or probiotics.
Regarding the 7 articles, the last authors of which have 1 related publication: 3 had a first author with zero, and another 2 with one related publication, while the remaining two had first authors with 3 and 4 related articles, respectively. In other words, there are 5 more articles written by authors, first and last, with little relationship to the topic (
Table 5).
On the other hand, there are four articles written by at authors with the maximum number of publications relating to probiotics and/or the microbiome - Salminen S [142 related publications], Szajewska H [92 publications], and Vinderola G [41 publications].
4. Discussion
Bibliometric analysis is an effective numerical analysis measure of the scientific contribution to a specific research field in a specific period of time, as well as of the relationships between these publications, i.e., to ascertain which authors, scientific centers, countries, and journals have the greatest influence in the advances in the given field of science [
9]. Bibliometry represents a branch of the library and information sciences that, by using statistical methods, analyzes research articles, both to get a general idea of the current state of research on a narrow scientific topic of interest and to measure the scientific level of the researchers/authors of the relative publications [
10,
11].
To our knowledge, this is the first bibliometric analysis which not only presents the dynamics of the production of a specific category article in this field but also attempts to analyze the scientific productivity of the authors in the broader field. We analyzed publications on postbiotics with the peculiarity of being only review articles and authored within a very strict time frame, ultimately aiming to determine how relevant to this professional field were the authors of those reviews. To better understand how our analysis differs from standard bibliometry, we must emphasize the difference in the main purpose of the analysis by first addressing a basic question: what is a review article and who is qualified to be an author?
A review article is an attempt by one or more scientists to perform a comprehensive summary of the current understanding on a specific research topic, based on previously published research, and, more importantly, to focus on discrepancies in the literature, gaps in knowledge, and recommendations for future research, concluding with comments inspired by their own knowledge and experience. In other words, a review is considered a critical analysis of current thought in the field, the basis for this, and the strength of the evidence, followed by suggestions for new directions of research. Thus, a review must be written by a person who has gained some authority on the particular topic after working for a number of years in the given field and with relevant research publications of his own [12-14].
Journals regularly invite expert authors or accept proposal for review papers. However, journals are increasingly vying for review articles which usually get more citations that original research – to gain popularity and increase the impact factor. At the same time young scientists consider that a written review hints at their knowledge and expertise in the field, while also increasing their record of citations - almost a prerequisite for attaining a post at most universities, or for receiving funding [
15].
In the present bibliometric analysis of 76 review papers dealing with postbiotics, we found five articles [rate 6.58%] written by scientists [first and last authors] with no previous deep knowledge or professional experience of topics relevant to the microbiome and/or probiotics. Additionally, there were 5 more articles [rate 6.58%] whose last authors had only one related publication, while the first author had zero publications in 3 cases and one related publication in 2 cases.
Our decision to take into account only first and last authors was based on the assumption that the first name is the main author responsible for the paper, and the last is either the senior author or possibly the supervisor of the work [
15]. On this basis we found 18 first authors with no previous publications relating to the microbiome and/or probiotics, and another 15 with only one. In other words, almost half [rate 43.4%] of the 76 publications have as the first author a very new – on this scientific topic – investigator. Of these, only two articles had senior authors and mentors of the young first authors and a double-digit number of related publications: Vinderola G from Argentina with 41 and Van de Wiele T from Belgium with 33.
These findings by no means suggest that all authors are new to this specific research topic: there are 9 first authors with 10 or more related articles, the first in rank being Szajewska H [92 publications], followed by Vinderola G. with 41 and Indrio F. with 38 (
Table 4). Regarding last, there are 10 authors having 20 or more related articles, the first in the rank being Salminen S from Finland with 142 publications, who is also the first name on the publication of the consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics] [
8], followed again by Szajewska H. and Lebeer S. with 76 (
Table 6).
It is, however, important to note that: [i] the great majority of the authors [most of them serving as both first and last] who have a double-digit number of publications on the microbiome and/or probiotics also have long experience in this topic and are positively involved as members of the board of directors in the consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics organized by the International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics [ISAPP]; [ii] there is a gap in the scientific productivity of first and last authors between the top ten and those with no previous publications.
Thus, we come to our first question: “why do we need 76 reviews in 26 months?” - an average of almost 3 review publications per month. The most obvious explanation is that while probiotics and their “products” have always been used and described in the literature, now, suddenly, due to the consensus of ISAPP [
8], many authors found the golden opportunity to write a review on this emerging hot topic, with the aim of gaining prestige and recognition [
16]. On the other hand, it is a common secret that many publishers welcome review articles. It is a very efficient policy to increase the percentage of review articles per published issue, especially those in areas of high research interest, even regardless of their true scientific value, in order to increase the impact factor of the journal [
16]. And it is well known that review articles gain more citations than original research, as is also true for international multiple collaborations over single-country articles [
17], as well as for studies with well-known names as authors or with a large number of authors [
16] all leading ultimately to a higher IF, since citations is the nominator of the equation for IF.
Another observation relates to the specialization of the centers of origin of the publications. Although at first glance there appears to be an almost equal number of medical universities and all the other scientific universities/institutions involved, the degree of clinical research in medicine is very low. We acknowledge the difficulties and restrictions to performing research studies involving humans, which are even greater in relation to sick patients. That is not to say that research involving animals or cell cultures is easier or simpler, but, despite basic research being acknowledged as both invaluable and irreplaceable we really urgently need applied medical research, both to improve health and, primarily, to treat disease. Postbiotics are today recognized, due to their benefit of not being live microbes, to be the opening of new horizons of hope for thousands of immunocompromised patients hesitating to receive probiotics or whose physicians are reluctant to prescribe them [
6,
18].
The most known and used bibliometric measure is the journal impact factor [IF]. In recent years it is acknowledged to be the basic measure of the quality of scientific research output, although it has its limitations. Authors generally aim to publish in journals with the highest impact factor, as a quantifiable measure of their scientific success [
16] – ‘if my paper weren’t so informative and well written it would not have been accepted by such a high IF journal’ - although this measure clearly reflects the journal’s scientific impact and not that of the individual article. On the other hand, grant agencies take into serious account the journals in which the applicant has published to rate their track record [
15], while the open access policy highly increases the visibility of the articles. The most known journals are the most read and consequently most referenced, generating a higher request for evaluation of papers and competition for recognition. In the present bibliometry we found 9 articles published in journals with an IF between 16 and 10, 42 articles published in journals with an IF between 10 and 5, and 25 articles in journals with an IF between 5 and 0.6; however, it is of interest that 39 out of 76 articles [rate 51.3% -
Figure 10] were published in 12 journals with an IF between 10.2 [Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr – 4 articles] and 4.5 [Microorganisms – 4 articles]. Based on this finding, one could suggest that these 12 journals are the most popular among authors or the most relative to the topic [
11].
However, it is not entirely correct to assess the scientific impact of a paper and compare it with another in terms of the IF of the journal of publication, since journal IF depends on many things, including the publication area of the journal and the nature of the research [basic research or clinical practice] [
16].
It is nonetheless true that, from a practical point of view, medical doctors in clinical practice lack the same opportunities and time to write a scientific work in comparison to full-time researchers [
19].
On the other hand, it is well known that the number of times an article is cited is a good way of measuring its impact in a specific field over a period of time, and this in turn allows the evaluation of both the authors and the journal itself [
20]. However, it is important to understand that gathering citations is a time-dependent process, a new study, in whatever category, requiring at least 2 to 5 years for accumulation of enough citations to be used as a reliable bibliometric indicator [
21]. In the present analysis, the time frame - November 2021 to December 2023 - is seriously prohibitive, and thus the top-10 cited articles were published only in the last two months of 2021 and in 2022, – there is no article published in 2023 with a decent number of citations.
It is believed that an article by an author well-known in his/her scientific field will have many citations. The same is considered true for publications resulting from an international collaboration [
17]. In the present list of the top 10 most cited articles only the publication by Venterola et al, in 3rd place with 46 citations, fulfills both characteristics: It is authored by 3 well-known scientists - Vinderola G, Sanders ME, and Salminen S and comes from the collaboration of 3 countries: Argentina, USA and Finland.
In the present bibliometric analysis, there was a rather small number of articles written in collaboration with scientists from other countries: only 25 articles [rate 33%] were the result of collaboration among authors from 2 to 7 countries; the top being France, followed by Argentina. Of course, one could question the need for international collaboration in writing a review article, as collaboration usually occurs in clinical studies in order to speed up the collection of similar cases; or in multi-factorial laboratory studies, in which new and sophisticated analyses need to be performed in a specialized center which could be anywhere in the world.
The present bibliometry does have some potential limitations: [i] only the PubMed database was used; however, it is the most common and established source for bibliometry; [ii] we distributed collaboration equally among countries, although the degree of involvement of each author was not known. Sometimes, a scientist contributes as author while a visitor to a Lab, but his country is written as his affiliation; [iii] unfortunately, it was not possible to assess the quality and impact of the publications by the citations list, as almost all the articles published in 2023 have very-very few or even zero citations; the same also applies for the h-index.