Submitted:
09 February 2024
Posted:
09 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Deep Learning Techniques
2.1. Popular CNN Model and Their Architectures
- 1.
- Mobile-Net
- 2.
- Alex.Net
- 3.
- DenseNet
- 4.
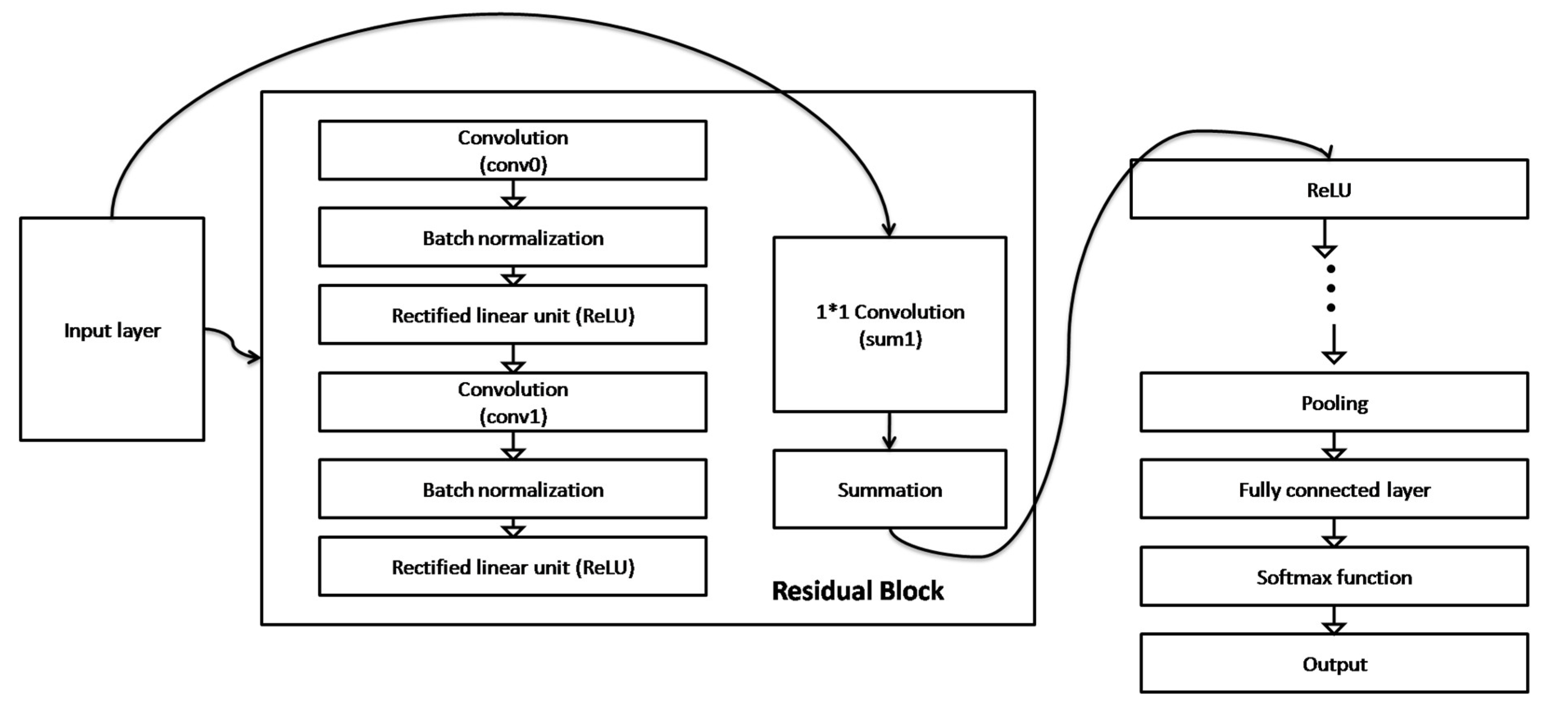
- Residual Network (ResNet)
2.2. Literature on Image Classification Problem Using Pre-Trained Models
- 1.
- Relevant Literatures on image classification with Alex.Net
- 2.
- Relevant Literatures on object detection with Mobile-Net
- 3.
- Relevant Literatures on object detection with DenseNet
- 4.
- Relevant Literatures on object detection with ResNet
2.3. Identified Knowledge Gaps in the Reviewed Deep Learning Techniques
2.4. Bridging the Gaps with Real-Time Object Detection Models
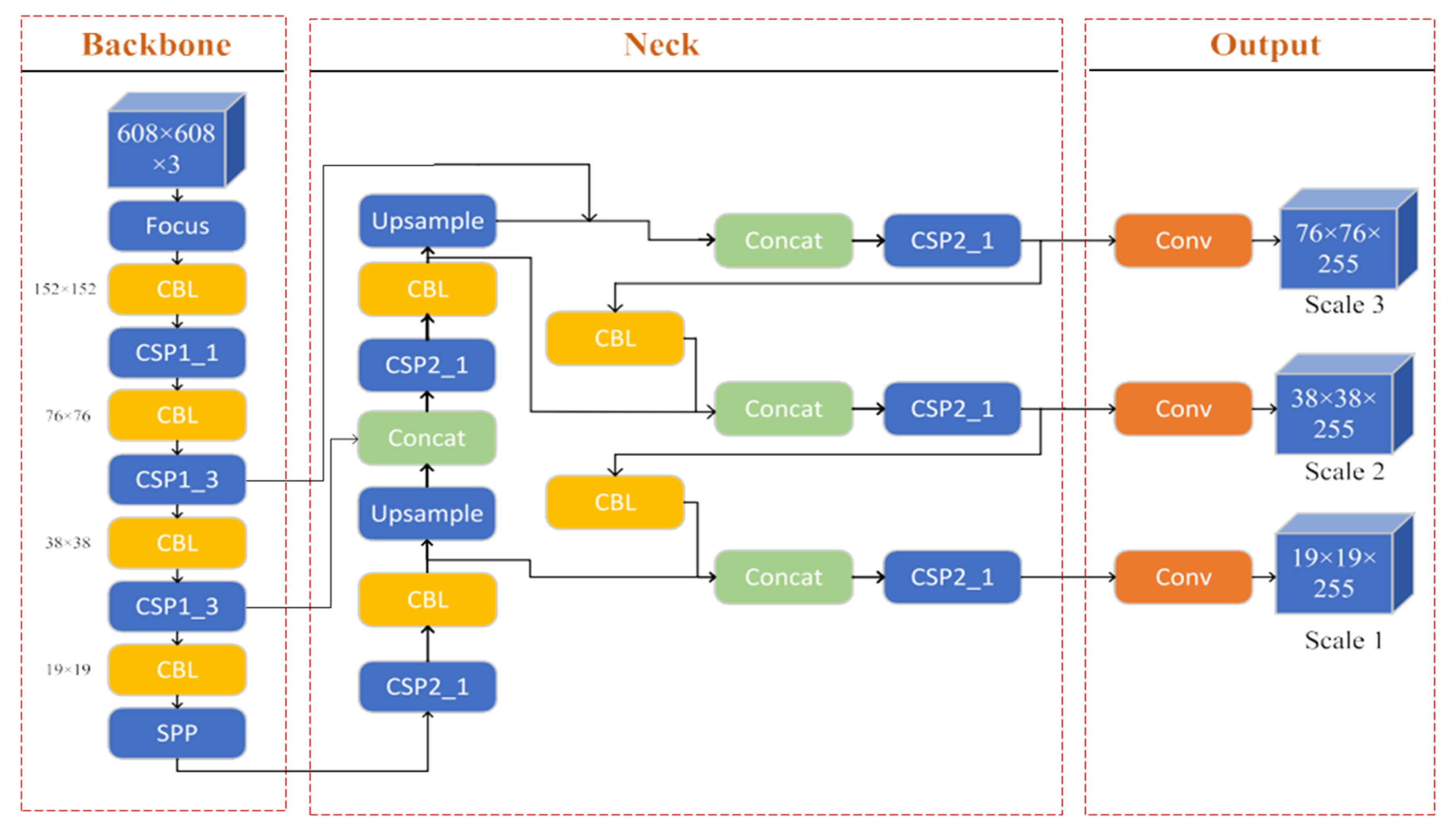
2.5. Literature Review on the Application of YOLO for Real-Time Object Detection
2.6. Current Challenges of YOLOV for Object Detection
2.7. Review of Techniques to Address Occlusion and Objects in a Changing Environment
2.8. Open Research Gaps Not Addressed in Object of Interest Detection Literature Reviewed
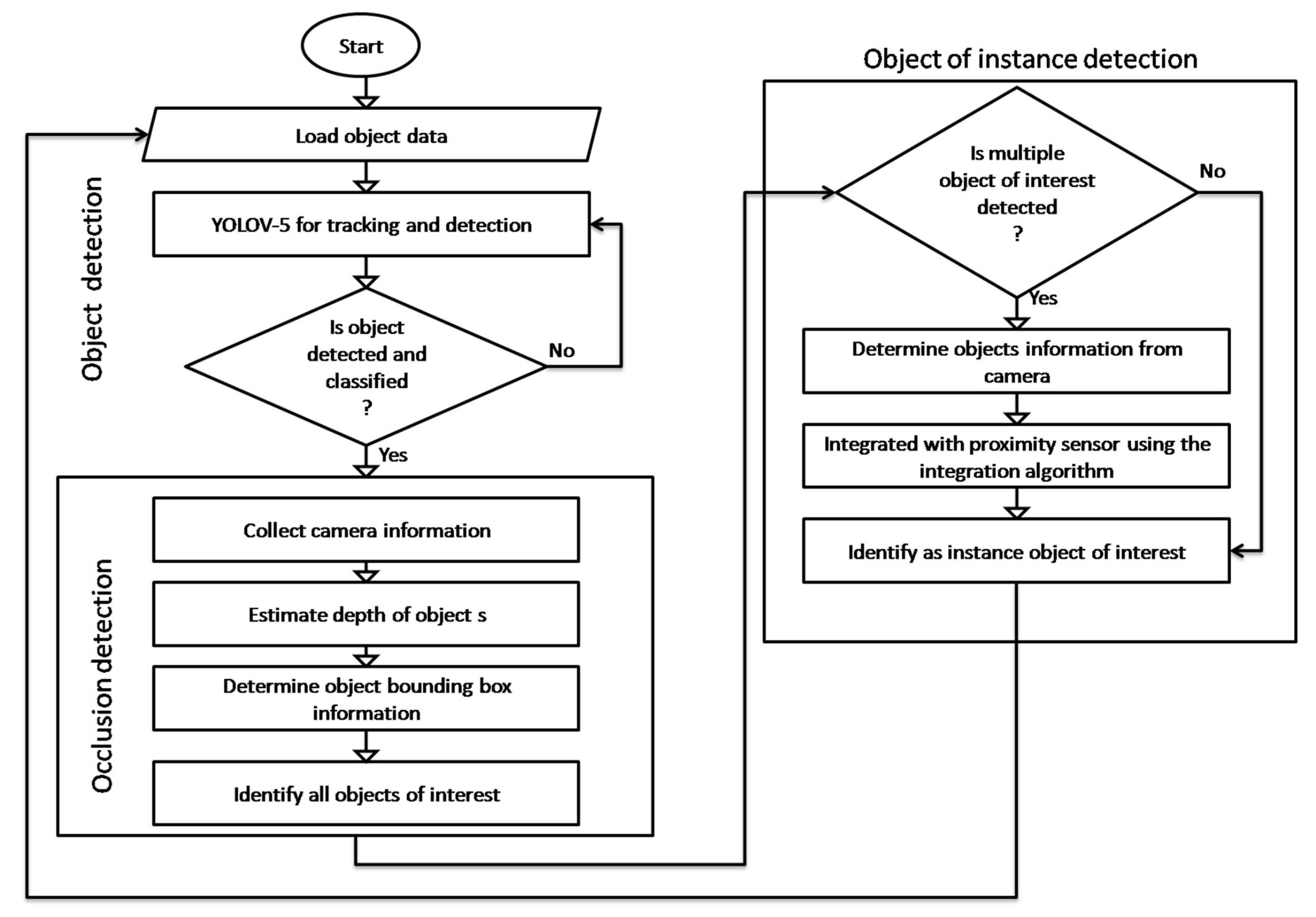
3. Recommended Occlusion Based Object of Instance Detection (OBOID) Technique
3.1. Modeling Assumptions
3.2. Integration Algorithm (Algorithm 1[M1] )
- Start
- Load object of interest detection model
- Apply camera calibration to convert pixel information to coordinate
- Collect object distance from environment using ultrasonic sensor
- Align coordinated of classified images with ultrasonic measurement using time stamp and spatial information
- Synchronize the time measurements and spatial information
- Apply kalman filtering to combine classification output with distance measurements
- Apply matching rules using time and distance threshold settings
- Identify as the instance object of interest
- End
3.3. Limitation of the OBOID
4. Conclusion
References
- Alzahrani, N.; Al-Baity, H.H. Object Recognition System for the Visually Impaired: A Deep Learning Approach using Arabic Annotation. Electronics 2023, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Bai, Q.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Miao, Y. Review of Image Classification Algorithms Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. arXiv, 2013 1311; arXiv:1311.2524. [Google Scholar]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. DeepPose: Human Pose Estimation via Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 25 September 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-Scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 25 September 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yeung, D.Y. Learning a Deep Compact Image Representation for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems—Volume 1, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; 809–817; NIPS’13. Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, ; pp, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a Deep Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Computer Vision— ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Alagarsamy, S. , Rajkumar D., Syamala L., Niharika L., (2023), “An Real Time Object Detection Method for Visually Impaired Using Machine Learning,” International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, pp. -6. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S. A Brief Survey of Color Image Preprocessing and Segmentation Techniques. J. Pattern Recognit. Res. 2011, 1, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Rodríguez, M.A. Review: Feature Extraction and Image Processing. Comput. J. 2004, 47, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . D, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, C.; Wang, X. Learning the Classifier Combination for Image Classification. J. Comput. 2011, 6, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaobing, H. , Zhong, Y. , Cao, L., and Zhang, L. (). Pre-Trained AlexNet Architecture with Pyramid Pooling and Supervision for High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Huang, H.; Lee, J.; Chen, C. Multi-scale ResNet for real-time underwater object detection. Signal, Image and Video Processing. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, F.; Ullah, I.; Shah, A.; Khan, R.; Choi, A.; Anwar, M. Design and implementation of real-time object detection system based on single-shoot detector and OpenCV. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1039645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, G. (2021) “Vanishing gradient problem in Deep neural networks; causes and possible solutions” source [http://www.towardsdatascinece. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X. Convolutional Neural Networks with Gated Recurrent Connections. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 3421–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1137; 12. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Sagana, C. et al., (2021)”Object Recognition System for Visually Impaired People,” 2021 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (DISCOVER), Nitte, India, pp. [CrossRef]
- Z. Cai, Y. Ou, Y. Ling, J. Dong, J. Lu and H. Lee, “Feature Detection and Matching With Linear Adjustment and Adaptive Thresholding,” in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 189735-18 9746, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S. , Khatravath P., Surineni N. and Mulinti R., “Object Detection and Action Recognition using Computer Vision,” 2023 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Smart Systems (ICSCSS), Coimbatore, India, 2023, pp. [CrossRef]
- Au, J. , Reid D. and Bill A., “Challenges and Opportunities of Computer Vision Applications in Aircraft Landing Gear,” 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 2022, pp. -10. [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, H. DetTrack: An Algorithm for Multiple Object Tracking by Improving Occlusion Object Detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , Yang P., Zhang N., & Hou J., (2023) Edge-Assisted Lightweight Region-of-Interest Extraction and Transmission for Vehicle Perception. arXiv:, arXiv:2308.16417v1 [cs.
- yu, S.-E.; Chung, K.-Y. Detection Model of Occluded Object Based on YOLO Using Hard-Example Mining and Augmentation Policy Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , Yang P., Zhang N., & Hou J., (2023) Edge-Assisted Lightweight Region-of-Interest Extraction and Transmission for Vehicle Perception. arXiv:, arXiv:2308.16417v1 [cs.
- Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, H. DetTrack: An Algorithm for Multiple Object Tracking by Improving Occlusion Object Detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. , Zhang P., Sun Y., Deng X., Yang Y.,&Chen L., (2022) High-Speed Extraction of Regions of Interest in Optical Camera Communication Enabled by Grid Virtual Division. Sensors 2022, 22, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yoon, I.; Paik, J. Object Occlusion Detection Using Automatic Camera Calibration for a Wide-Area Video Surveillance System. Sensors 2016, 16, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, C.; Grimson, W.E.L. Adaptive background mixture models for real–time tracking. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.-E.; Chung, K.-Y. Detection Model of Occluded Object Based on YOLO Using Hard-Example Mining and Augmentation Policy Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hataya, R.; Zdenek, J.; Yoshizoe, K.; Nakayama, H. Meta Approach to Data Augmentation Optimization. arXiv, 2006; arXiv:2006.07965. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, K.; Jalil, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, B.; Murad, M.; Khan, W.U.; He, Y. Context-Aware and Occlusion Handling Mechanism for Online Visual Object Tracking. Electronics 2021, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. , Zhang P., Sun Y., Deng X., Yang Y.,&Chen L., (2022) High-Speed Extraction of Regions of Interest in Optical Camera Communication Enabled by Grid Virtual Division. Sensors 2022, 22, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodney, L. , Dong Z., & Mubarak S., (2017) ClusterNet: Detecting Small Objects in Large Scenes by Exploiting Spatio-Temporal Information. arXiv:, arXiv:1704.02694v2 [cs.
- Li, W. , Zhou J., Li X., Cao Y., & Jin G., (2023) Few-shot object detection on aerial imagery via deep metric learning and knowledge inheritance. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 122 (2023) 103397. [CrossRef]
- Santra, S. , Mukherjee, P., Sardar, P., Mandal, S., Deyasi, A. (2020). Object Detection in Clustered Scene Using Point Feature Matching for Non-repeating Texture Pattern. In: Basu, T., Goswami, S., Sanyal, N. (eds) Advances in Control, Signal Processing and Energy Systems. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 591. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Patrick, L. (2023)”Deep learning based object detection in clustered scene; https://towardsdatascience. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, B.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; et al. T-cnn: Tubelets with convolutional neural networks for object detection from videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 28, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Hashmi, K.A.; Pagani, A.; Liwicki, M.; Stricker, D.; Afzal, M.Z. Survey and Performance Analysis of Deep Learning Based Object Detection in Challenging Environments. Sensors 2021, 21, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Sharma, K.V.; Mehta, D.J.; Maharaj, K.T. A: State of the Art in Deep Learning Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects.
- Forecasting and Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10543. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y. , Kiya H. (2019)” Convolutional neural network considering local and global features for image enhancement”; IEEE 19; International conference on image processing, Taiwan, 2019; pp. 2110-2114.
- P. E. Kekong, I.A. Ajah., U.C. Ebere (). Real Time Drowsy Driver Monitoring and Detection System Using Deep Learning Based Behavioural Approach. International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering 2019, 9, 11–21.
- Eneh, P. C, Ene I.I., Egoigwe V.S. Ebere U.C. (2019). Deep Artificial Neural Network Based Obstacle Detection and Avoidance for a Holonomic Mobile Robot. International Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology Vol.5, No.1; ISSN (1573-1405); p –ISSN 0920-5691 Impact factor: 3.
- Palwankar, T. , & Kothari K., (2022) Real Time Object Detection using SSD and MobileNet. International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET) ISSN:.
- Maurício, J.; Domingues, I.; Bernardino, J. Comparing Vision Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification: A Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.M. Theoretical Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network: Concepts, Architectures, Applications, Future Directions. Computation 2023, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, W.; Ehtisham, R.; Bahrami, A.; Camp, C.; Mir, J.; Ahmad, A. Assessment of Convolutional Neural Network Pre-Trained Models for Detection and Orientation of Cracks. Materials 2023, 16, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stančić, A.; Vyroubal, V.; Slijepčević, V. Classification Efficiency of Pre-Trained Deep CNN Models on Camera Trap Images. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depth wise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficient net: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Honmote, H. , Katta P., Gadekar S., & Kulkarni M., (2022) Real Time Object Detection and Recognition using MobileNet-SSD with OpenCV. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) http://www.ijert.org ISSN:, 0100; 01, IJERTV11IS010070 www.ijert.org Vol. 11 Issue 01, January-2022. [Google Scholar]
- MathuraBai, B. , Maddali V., Devineni C., Bhukya I., & Bandari S., (2022) Object Detection using SSD-MobileNet. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet. 2: p-ISSN, 2395. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, A. , Shixin L., Shelembi J., & Hai Z., (2020) Real-Time Object Detection Using Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models MobileNet- SSD. © 2020 Association for Computing Machinery. ACM ISBN 978-1-4503-7673-0/20/01…$15. [CrossRef]
- Kayadibi, I. , Güraksın G., Ergün U., &Süzme N., (2022) An Eye State Recognition System Using Transfer Learning: AlexNet-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems (. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. , Liu J., Zhang S., Deng Q., Wang Z., Li Y., & Fan J., (2021) Detection of Oil Spill Using SAR Imagery Based on AlexNet Model. Hindawi Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume, 2021; Article ID 78 4812979, 14 pages. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Wang, S. M. Wang, S. Zheng, X. Li and X. Qin, “A new image denoising method based on Gaussian filter,” 2014 International Conference on Information Science, Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Sapporo, Japan, 2014, pp. [CrossRef]
- Li J., Chen W., Sun Y., Li Y., Peng Z., (2019) Object Detection Based on DenseNet and RPN. Proceedings of the 38th Chinese Control Conference July 27-30, 2019, Guangzhou, China.
- Yin, L. , Hong P., Zheng G., Chen H.,&Deng W., (2022) A Novel Image Recognition Method Based on DenseNet and DPRN. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Li H., Jia P., Zhang G., Wang T., & Hao X., (2019) Multi-Scale DenseNets-Based Aircraft Detection from Remote Sensing Images. Sensors 2019, 19, 5270; [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wu, Y. Improved YOLO-V3 with DenseNet for Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Target Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindarto, D. , (2023) Battle Models: Inception ResNet vs. Extreme Inception for Marine Fish Object Detection. Sinkron :Jurnal dan Penelitian Teknik Informatika Volume 8, Number 4, 23 DOI, 20 October; 8. [CrossRef]
- Omar, F. , Abdulrazzaq S., & Jasim M., (2020) Design and implementation of image-based object recognition. Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences ISSN, 20 February; 8.
- Rani, S. , Ghai D., Kumar S., Kantipudi P., Alharbi A., & Ullah M., (2022) Efficient 3D AlexNet Architecture for Object Recognition Using Syntactic Patterns from Medical Images. Hindawi Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Volume, 7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilan, A. , Emad M., & Alizadeh B., (2019) FPGA-based Implementation of a Real-Time Object Recognition System using Convolutional Neural Network. DOI 10.1109/TCSII.2019. E: IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 2922. [Google Scholar]
- Hiddir, S. Cetin T., Musa Y.,Detection of invisible cracks in ceramic materials using by pre-trained deep convolutional neural network” Neural Computing and Applications 34(2477)Neural Computing and Applications 34(2477). 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifeng, Z. ″Expression Recognition Using Improved AlexNet Network in Robot Intelligent Interactive System″ Internet of Robotic Things-Enabled Edge Intelligence Cognition for Humanoid Robots “Volume 2022 | Article ID 4969883. [CrossRef]
- Nawfal, J. , and Mungur A. (2022)”Performance evaluation between tiny YOLOV-3 and MobileNet SSDv1 for object detection,” IEEE, 4th Internaitonal conference on emerging trends in Electrical electronic and communication engineering, Mauritus, pp.
- Rakkshab, V. , Priyansh S., Kevin P. (2021)”Comparison of yolov3., yolov5 and MobileNet SSD V2 for real time mask detection, IRJET, ISSN 2395-0056, pp. 1156-1160.
- Chen, B. , Shen Y., & Sun K., (2020) Research on Object Detection Algorithm Based on Multilayer Information Fusion. Hindawi Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangodkar, D. , & Vimal V., (2021) Video Object Detection Using Densenet-Ssd. 1: Webology, Volume 18, Number 5, 2021 ISSN, 2021; 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubec, M.; Lieskovská, E.; Bučko, B.; Zábovská, K. Comparison of CNN-Based Models for Pothole Detection in Real-World Adverse Conditions: Overview and Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-End Object Detection With Learnable Proposals. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14454–14463. [Google Scholar]
- Suherman, E. , Rahman B., Hindarto D., & Santoso H., (2023) Implementation of ResNet-50 on End-to-End Object Detection (DETR) on Objects. Sinkron :Jurnal dan Penelitian Teknik Informatika Volume 8, Number 2, 23 DOI, 20 April; 8. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H. , & Rhee J., (2022) Application of YOLO and ResNet in Heat Staking Process Inspection. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H. , Kabir S. International Journal of Research Publications (IJRP.ORG)IJRP 2021, 69(1), 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwaseyi, E. , Martins E., Abraham E. (2023)”A comparative analysis of YOLOV-5 and YOLOV-7 object detection algorithms”;Journal of Computing and Social informatics (Vol 2; No. 1; pp. 1-12.
- Chourasia, A. , Bhojane R., Heda L. (2023)”Safety Helmet detection: A comparative analysis using YOLOV-4,5 and 7,”IEEE Xplore; International conference for advancement in Technology (ICONAT), Goa, India, pp. 1-8.
- Liu, X. , Li, G., Chen, W., Liu, B., Chen, M., Lu, S., 2022. Detection of dense citrus fruits by combining coordinated attention and cross-scale connection with weighted feature fusion. Appl. Sci. 12 (13), 6600. URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/13/6600. Number: 13 Publisher: Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. , Zhu Z., Ge H., Zhang Z., & Zang X., (2021) Effective Face Detector Based on YOLOv5 and Superresolution Reconstruction. Hindawi Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F. , Xing B., Luo J., Li D., Qian Y., Zhang C., Bai H., & Zhang H., (2023) An Efficient Object Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv5 for High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. , Chen Z., & Yu H., (2023) Enhanced YOLOv5: An Efficient Road Object Detection Method. Sensors 2023, 23, 8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, Z. , Iqbal, W.M., Hamid, K., Muhammad, B. A.H., NAzir, A.M., Qurra-Tul-Ann, and Hussain, N. (2023). “VOICE ASSISTED REAL-TIME OBJECT DETECTION USING YOLO V4-TINY ALGORITHM FOR VISUAL CHALLENGED”. Tianjin DaxueXuebao (Ziran KexueyuGongcheng Jishu Ban)/Journal of Tianjin University Science and Technology. ISSN (Online):, 2: E-Publication: Online Open Access Vol:56 Issue:02, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, S. , Priyadarshini, B.B.S., Patel, K.D., Patra, N., and Sahu, P.(2023). “A REAL-TIME HYBRID-YOLOV4 APPROACH FOR MULTICLASSIFICATIONAND DETECTION OF OBJECTS”. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology15th June 2023. Vol.101. No 11. 2023 Little Lion Scientific. ISSN:, 1: E-ISSN, 20 June 1817. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, H. , Jaleel, H., and Hameedi, S. (2021). “You Only Look Once (YOLOv3): Object Detection and Recognition for Indoor Environment”. Volume 7, Issue 6, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Zhelin, L. , Zhao L., Xu H., Pan M. (2020) “Lightweight ship detection method based on yolov3 and denseNet”Mathematical problems in Enineering; Hindawi, Vol. 20; ID 4813183;pp1-10.
- Tirupataiah, U. , Rao, N.K., Gokuruboyna, R.S., and Rao, S.S. (2019). “Real Time Object Detection in Images using YOLO”. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science,Engineering and Technology (IJIRSET). (A High Impact Factor, Monthly, Peer Reviewed Journal). Visit: www.ijirset.com. Vol. 8, Issue 8, 19. ISSN(Online): 2319-8753. 2: ISSN (Print), 20 August 2347. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M. , Rahman, A., and Ahmed, H. (2022). “Identifying Objects in Real-Time at the Lowest Framerate”. 20 August 2454. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S. , Singh V. (2012)”state o the art in visual object tracking” Informatica 31; publication at: https://www.researchgate. 2693. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S. , Singh V. (2011)” Robust object tracking under appearance change conditions based on Daubechies complex wavelet transform” Int. J. Multimedia Intelligence and Security, Vol. 2, Nos. at: https://www.researchgate. 2648. [Google Scholar]
- Hussan, T.I.M. , Saidulu, D., Anitha, P.T., Manikandan, A., and Naresh, P. (2022). “Object Detection and Recognition in Real Time Using Deep Learning for Visually Impaired People”. International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Research (IJEER). 2: Research Article | Volume 10, Issue 2 | Pages 80-86 | e-ISSN, 2347; 10. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Calero, M.; Astudillo, C.A.; Guevara, D.; Maza, J.; Lita, B.S.; Defaz, B.; Ante, J.S.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Armingol Moreno, J.M. Traffic Sign Detection and Recognition Using YOLO Object Detection Algorithm: A Systematic Review. Mathematics 2024, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P. , Mitra, S., Biswas, S., Roy, S., Chaudhuri, S.R., Ghosal, A., Dhar, P., and Majumder, A. (2021). “YOLO Algorithm Based Real-Time Object Detection”. 21| IJIRT | Volume 8 Issue 1 | ISSN: 2349-6002. 20 June.
- Mohana and Aradhya, R.H.V. (2019). “Object Detection and Tracking using Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Video Surveillance Applications”. (IJACSA) International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications,Vol. 10, No. 12, 2019 pp 517-530.
- Chadalawada, K.S. (2020). “Real Time Object Detection and Recognition using deep learning methods”. Master of Science in Computer Science.
- Jiang, P. , Ergu, D., Liu, F., Cai, Y., and Ma, B. (2022). “A Review of Yolo Algorithm Developments”. ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science, /: “A Review of Yolo Algorithm Developments”. ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 199 (2022) 1066–1073. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0)Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the The 8th International Conference on Information Technology andQuantitative Management (ITQM 2020 2021). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Fan & Hu, Miao. (2018). Memristor-based Deep Convolution Neural Network: A Case Study. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328091629_Memristorbased_ Deep_Convolution_Neural_Network_A_Case_Study/citations. 3280.
- Hu, X. , Zhang P., Sun Y., Deng X., Yang Y.,&Chen L., (2022) High-Speed Extraction of Regions of Interest in Optical Camera Communication Enabled by Grid Virtual Division. Sensors 2022, 22, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yoon, I.; Paik, J. Object Occlusion Detection Using Automatic Camera Calibration for a Wide-Area Video Surveillance System. Sensors 2016, 16, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, C.; Grimson, W.E.L. Adaptive background mixture models for real–time tracking. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.-E.; Chung, K.-Y. Detection Model of Occluded Object Based on YOLO Using Hard-Example Mining and Augmentation Policy Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, Z. A Robust Fabric Defect Detection Method Based on Improved RefineDet. Sensors 2020, 20, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hataya, R.; Zdenek, J.; Yoshizoe, K.; Nakayama, H. Meta Approach to Data Augmentation Optimization. arXiv, 2006; arXiv:2006.07965. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, K.; Jalil, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, B.; Murad, M.; Khan, W.U.; He, Y. Context-Aware and Occlusion Handling Mechanism for Online Visual Object Tracking. Electronics 2021, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
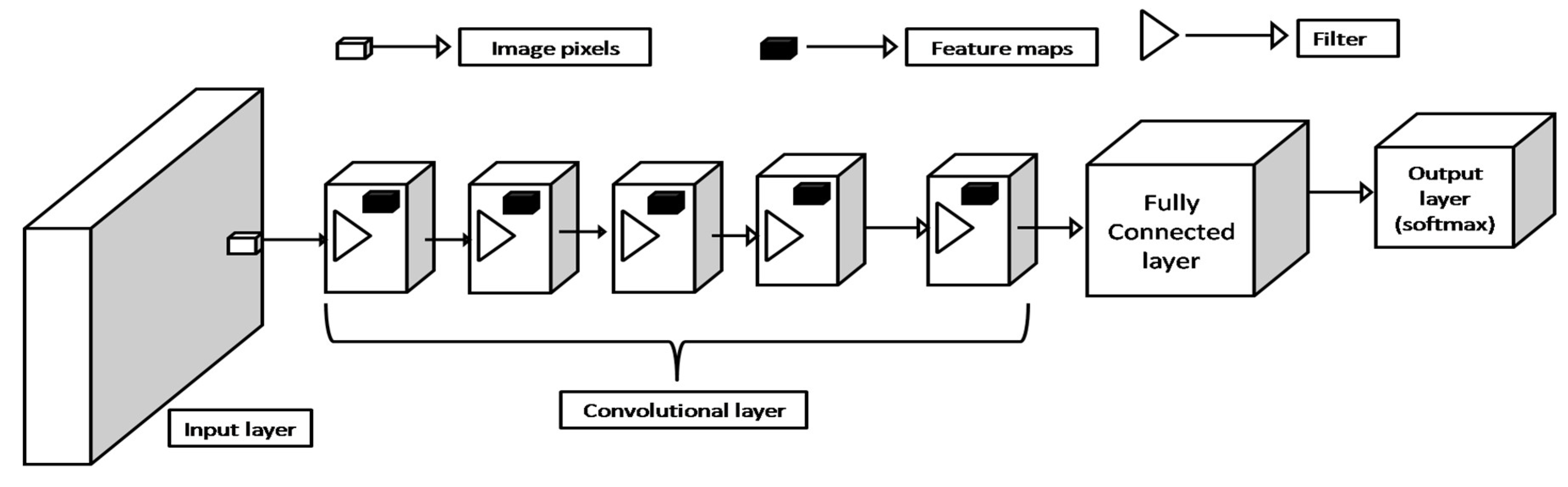
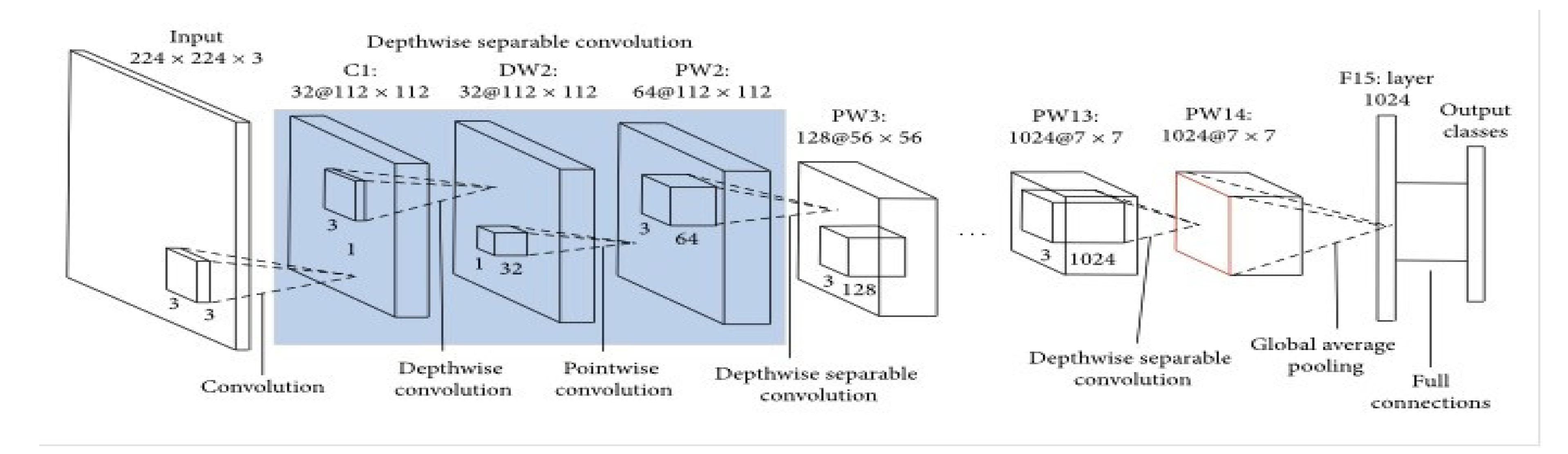
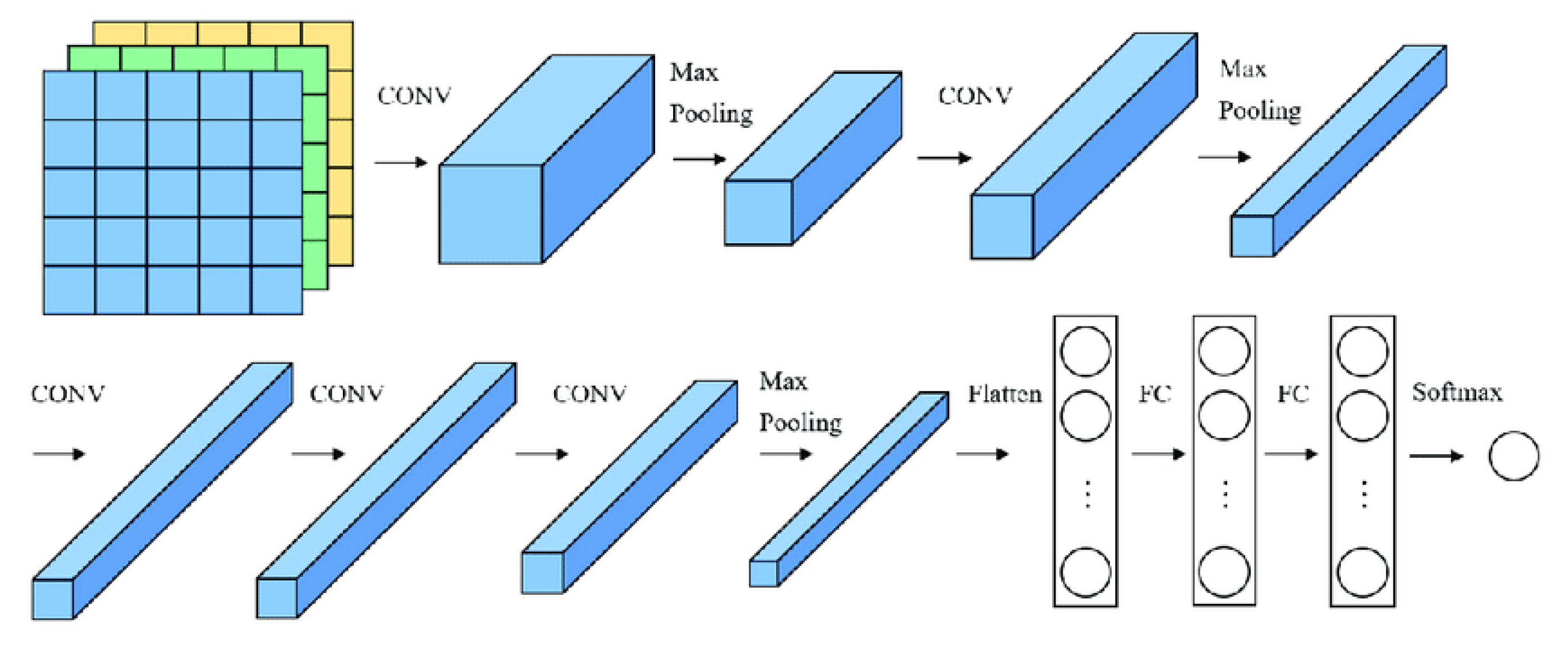
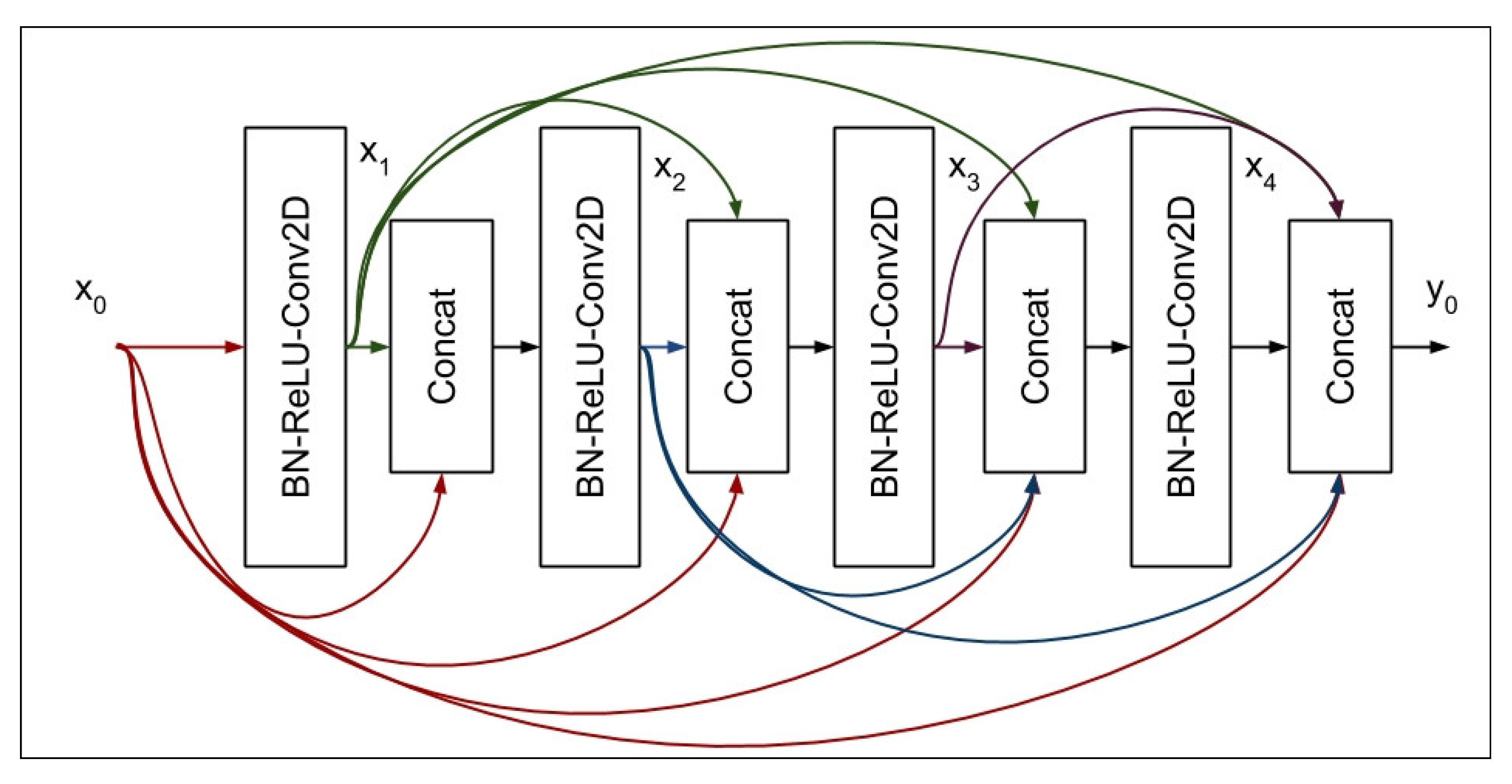
| Authors | Primary objectives | Methods | Findings | Research gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [78] | Object detection | Alex.net was fined with a CNN trained on Cifar-10 for object detection | The results recorded 98% classification accuracy | Occlusion was not addressed |
| [79] | Fine tune Alex.et as a 3D model for the classification of brain tumor. | Trained CNN with four brain tumor datasets which are Figshare, Brain MRI Kaggle, Medical MRI datasets and BraTS 2019 datasets | The average performance for accuracy is 99%, mAP reported 99%, sensitivity 87% and detection time of 1300ms. | Sensitivity can still be improved |
| [70] | Classification of eye behaviour | Applied Alex.net using the Zhejiang University (ZJU) and Closed Eyes in the Wild (CEW) dataset. | The average results recorded for both datasets, considering parameters such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, are 95% respectively which is good | Not reliable for real-time classification due to delay |
| [75] | Optimization of Alex.Net against overfitting | Guassian filter and Adam optimization was used to improve Alex.Net training and applied for the detection of oil spillage | The results when tested reported 99.76% for recall and 98.91% or accuracy. | Suffer delay during real-time application |
| [80] | Real-time classification | Applied Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) hardware to validate Alex.net model | Demonstrated image classification ability | Suffer delay |
| Authors | Primary objectives | Methods | Findings | Research gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15,67] | Object detection | The Mobile-Net-SSD was trained on MS Common Objects in Context (COCO) | The results reported 0.92 for accuracy, recall of 0.81 and mAP of 0.85, | Overall results need improvement |
| [68] | Object detection and obstacle avoidance | SSD-Mobile-Net-2 | The results when tested on five different objects reported an average accuracy of 97.8%. | It is not interactive |
| [69] | Multi-scale feature map detection and bounding box prediction in Mobile-Net for real-time object detection | SDD, Mobile-Net | The results reported an average accuracy of 89.53%. | Occlusion was not addressed |
| [84] | Comparative study on Mobile-Net and YOLOV for object detection | Mobile-Net, YOLOV-5, Nvidia Telse, 1160 and Jatson Nano | Mobile-Net has less object detection speed than YOLOV-5 | It is not interactive |
| Authors | Primary objectives | Methods | Findings | Research gap |
| [85] | Object detection | F-RCNN based DenseNet and SSD based DenseNet | mAP of 5.63 with F-RCNN-based DenseNet and 3.86 with SSD-based DenseNet | Overall results can be improved |
| [86] | Object detection | SDD-based DenseNet | mAP of 0.9854 | Delay speed |
| [73] | Object classification. | RPN-based DenseNet; PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets | PASCAL VOC reported 80.30% mAP and MS COCO dataset reported mAP of 55.0%, | Overall results can be improved |
| [74] | Object classification. | Deep Pyramidal Residual Networks (DPRN) and DenseNet; CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 | Accuracy of 83.98% for CIFAR10 and 51.19% for CIFAR100 | Results need improvement |
| [75] | Object detection | Multi-Scale DenseNets (MS-DenseNet | Recall of 94%, an F1-score of 92.7%, a training time of 0.168s and a detection time of 0.094s | Overall results can be improved |
| Authors | Primary objectives | Methods | Findings | Research gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [77] | detection of underwater objects with small sizes | Multi-scale-ResNet (M-ResNet). | mAP of 96.5%. | Cannot detect object of instance |
| [89] | End to end object detection | Detection Transformer (DETR) algorithm was applied to improve ResNet | average precision of 0.82 and mean average recall of 0.63, | Overall result need improvement |
| [90] | Object detection | YOLOV and ResNet | mAP of 95.1% and F1-score of 98% | Occlusion was not addressed |
| [91] | Indoor object detection | ResNet, Kaggle indoor scenes dataset | Accuracy of 74%. | Results need improvement |
| Author | Primary objective | Methods | Findings | Research gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [95] | Real-time object detection | Super-Resolution Reconstruction (SRR) was applied to optimize the performance of YOLOV-5. | Precision score of 88.2% | Need to improve accuracy |
| [96] | Object detection while address overlap in bounding box | Repetitive Convolution (RepConv), Transformer Encoder (T-E), and Bil Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network (BiFPN) modules were integrated in the architecture of YOLOV-5 | Accuracy of 90.06%, mAP of 90.06%) | Need to improve accuracy |
| [97] | Object detection with YOLOV-5 | Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network (BiFPN) for multi-scale diverse feature map fussion and Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) were integrated YOLOV-5 | Precision of 72.0%, recall of 42.1% and mAP of 49.4% | Overall result despite the success need improvement |
| [98] | Interactive object detection system | YOLO algorithm was trained with COCO dataset | mAP of 0.74 and 0.55. | Result need improvement |
| [99] | Comparative deep learning application on object detection | Compared Fast Recurrent Convolutional Network (F-RCNN), YOLO-v4, YOLO-v4-hybrid, YOLO-v3, and SSD on COCO dataset considering frame captured per seconds (fps), speed and mAP. | Hybrid YOLOV-4 reported 110.56fps, 0.986mAP and 16.01ms as the best model | High delay and may not be reliable for real-time classification |
| [100] | Indoor object detection | Applied YOLOV-3 for indoor object detection | Accuracy and mAP, reported (99% and 100%) | Did not address issues of bounding box overlapping |
| [101] | Address over-fitting, parameter overload, problem with YOLOV | DenseNet was applied for feature connection and spatial separation convolution for parameter reduction and optimization of YOLOV-3. | DenseNet based YOLOV-3 recorded mAP of 0.96. | Occlusion was not addressed |
| [102,103] | Address bounding box overlapping problem in YOLOV | F-RCNN was applied to optimize the bounding box prediction in YOLOV-3 | mAP reported 67.36% for the improved YOLOV; [66] reported, 0.45fps, 0.83 for YOLOV-3, as against 0.891, and 0.893 yielded by Faster RCNN. | Overall the results need to be improved |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





