Submitted:
08 February 2024
Posted:
09 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
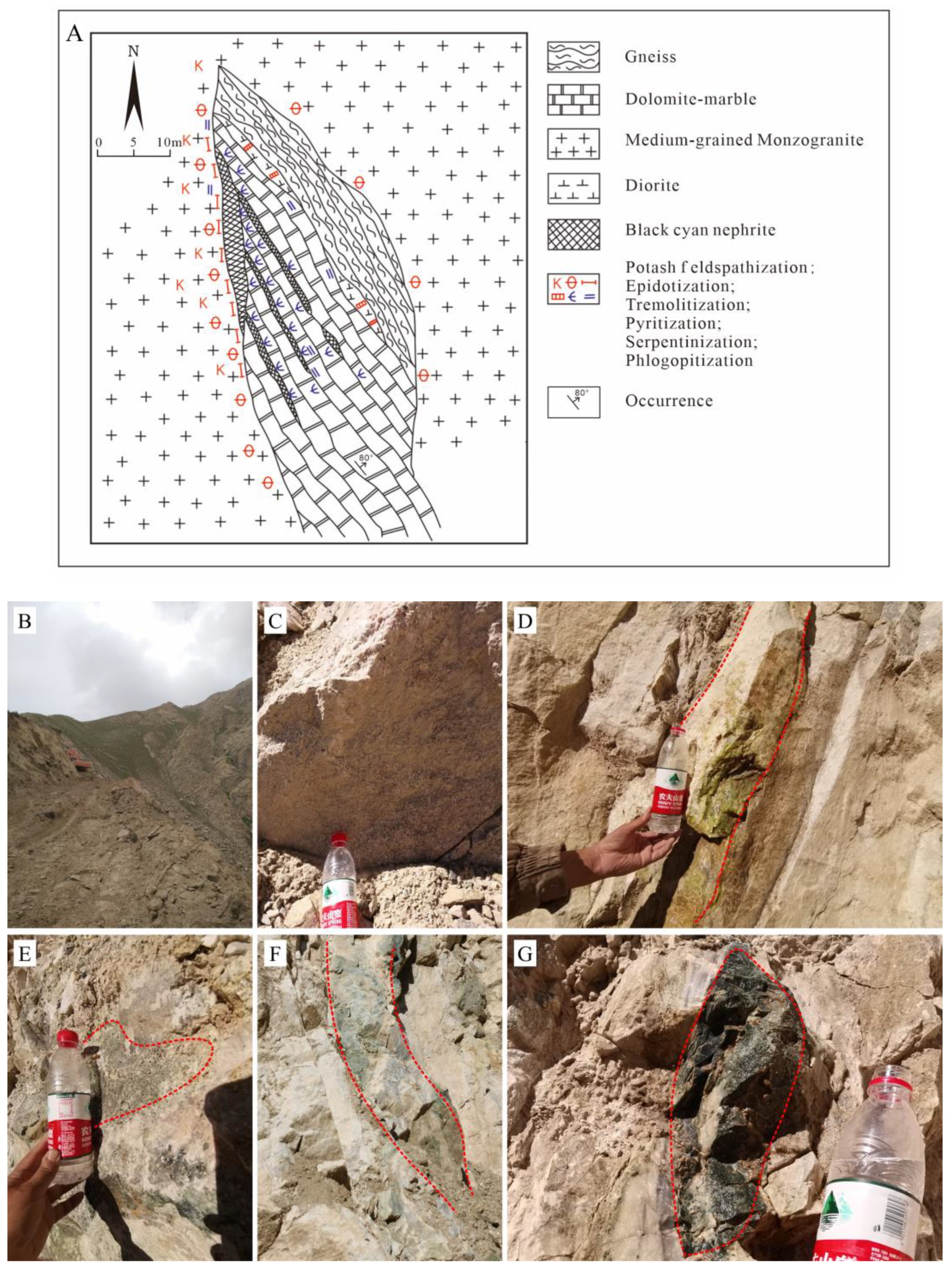
2.1. Mergou nephrite Deposit
2.2. Materials
3. Methods
4. Results
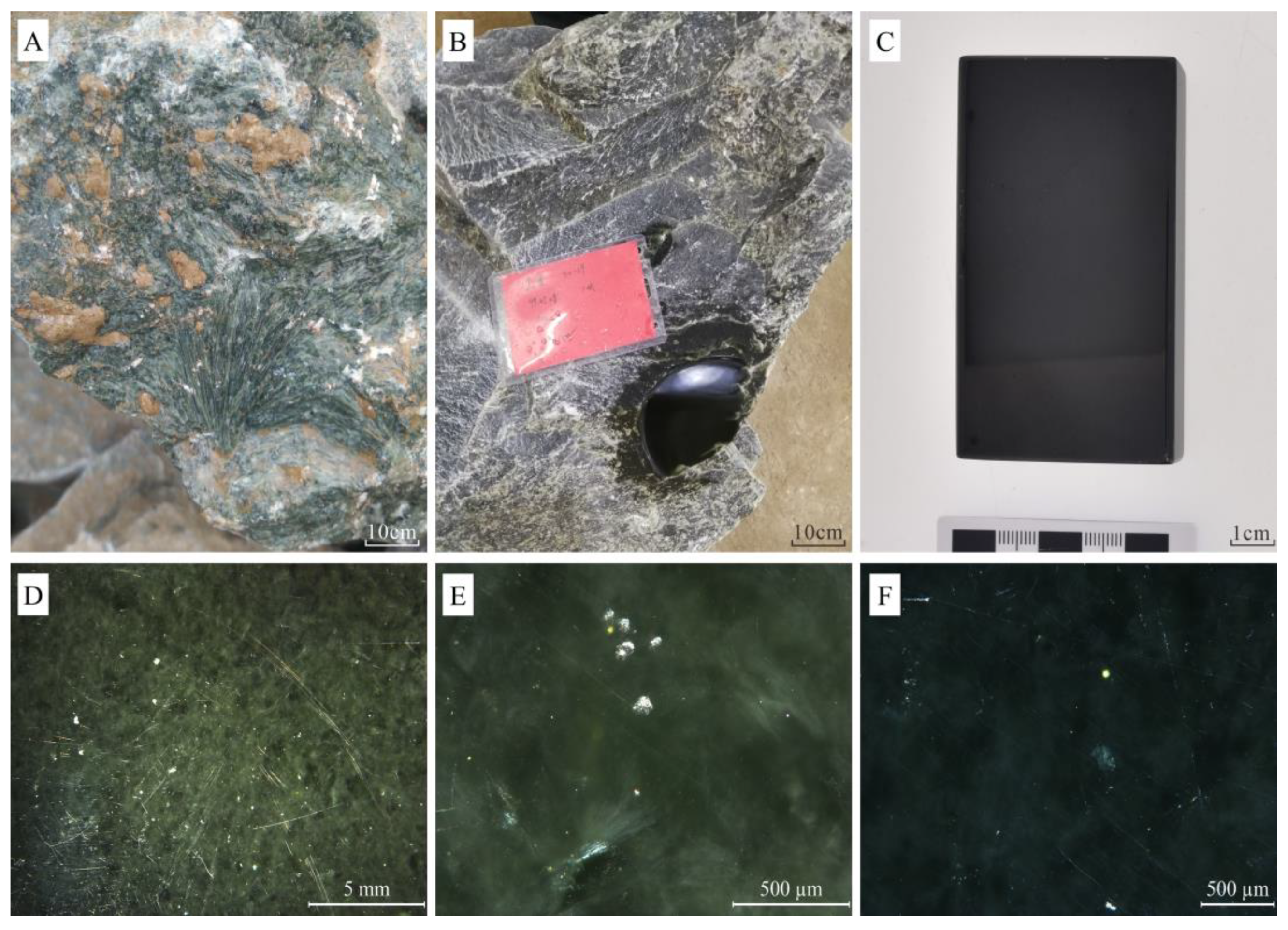
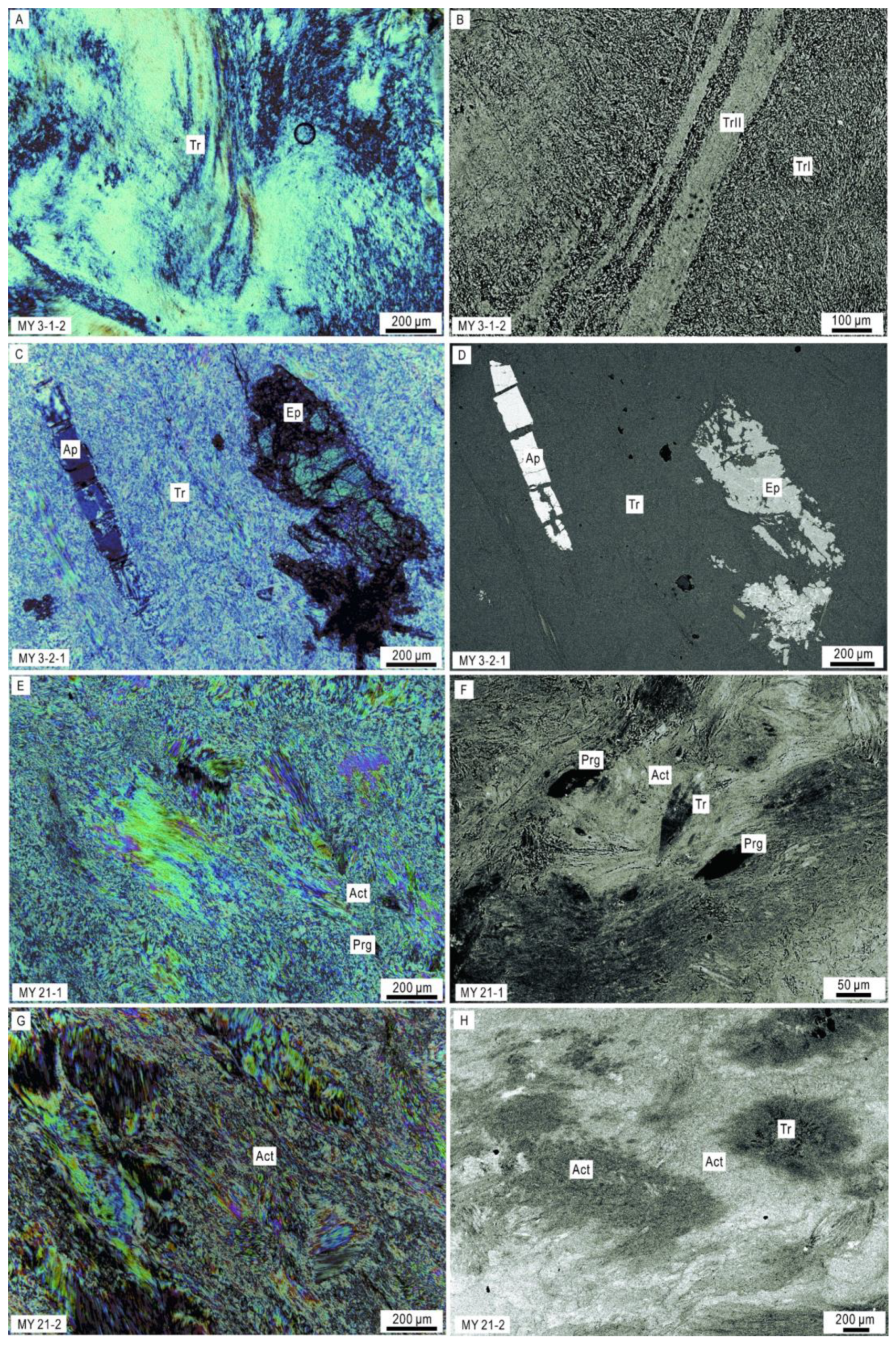
4.1. Petrological Characteristics
4.1.1. Mineral components characteristics
4.1.2. Chemical Composition
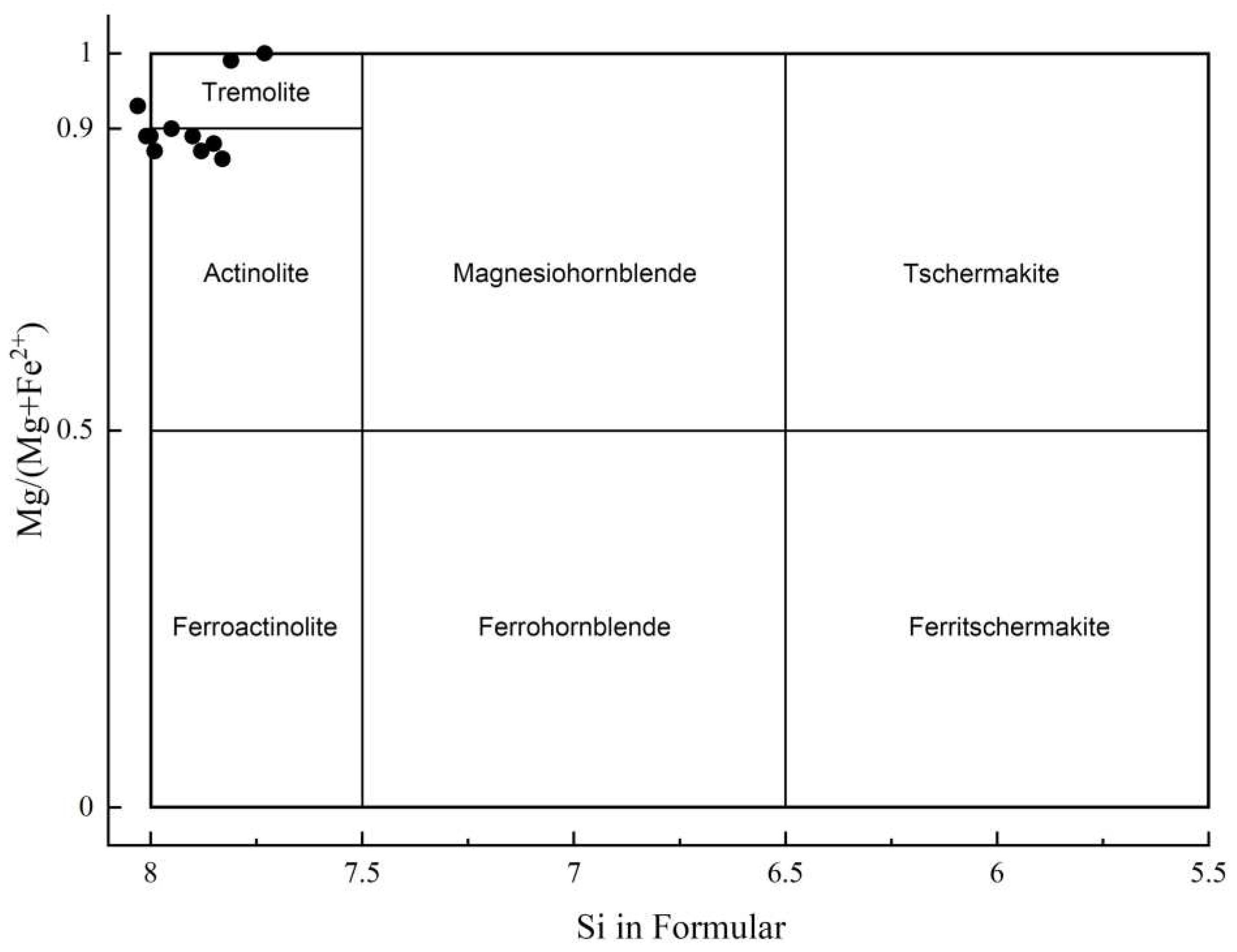
- Tremolite - Actinolite: Tremolite in Margou black-black cyan nephrite exhibits 7.73-8.03 a.p.f.u. Si at the T site, 4.43-4.92 a.p.f.u. Mg at the C site, and 1.89-1.96 a.p.f.u. Ca at the B site. This is slightly lower than the Xinjiang Hetian area sample of nephrite, which features 8.00-8.08 a.p.f.u. Si at the T site, 4.61-4.73 a.p.f.u. Mg at the C site, and 1.88-2.0 a.p.f.u. Ca at the B site [5]. The characteristics of actinolite component of Margou black-black cyan nephrite, actinolite exhibits 7.83-8.01 a.p.f.u. Si at the T site, 4.25-4.62 a.p.f.u. Mg at the C site, and 1.77-1.96 a.p.f.u. Ca at the B site, with Ca exceeding 1.50 a.p.f.u. at the B site. The FeO content ranges from 0.08% to 6.29 wt.%, higher than white nephrite (FeO=0.07~1.09 wt.%) and green nephrite (FeO=0.17~4.93 wt.%), but similar to Xinjiang black nephrite (FeO=4.11~14.39 wt.%) and lower than Guangxi black nephrite (FeO=11.67~25.75 wt.%) [19].
- Epidote: In Margou black-cyan nephrite from Qiemo County, epidote exhibits a relatively high FeO content (11.43%~12.04%), with SiO2 and CaO contents of 40.72%~41.67% and 23.57%~23.69%, respectively. The atomic composition of each unit of epidote has the following geochemical characteristics (a.p.f.u): Si=3.15~3.21, Al=2.05~2.09, and Ca=1.95~1.96 (Table 1).
- Pargasite: Pargasite in the black nephrite has almost the same composition, with SiO2 content ranging from 46.69% to 46.73%, MgO from 20.21% to 21.18%, and CaO from 13.80% to 13.99%. The atomic composition of each unit of pargasite has the following geochemical characteristics (a.p.f.u) : Si=6.50~6.53, Al=1.97~2.12 and Ca=2.07~2.09 (Table 1).
| Sample No. | 21-1-1A1 | 21-1-1A2 | 21-1-2A3 | 3-2-1-1C | 3-2-1-2A | 3-2-1-2B | 3-1-2-3A | 21-2-1A1 | 3-1-2-3B |
| SiO2 | 46.69 | 46.73 | 54.49 | 54.43 | 41.67 | 40.72 | 0.09 | 27.98 | 0.16 |
| TiO2 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 12.93 | 11.97 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 22.58 | 22.92 | 0.00 | 15.32 | 0.02 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| FeO | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 4.96 | 11.43 | 12.04 | 0.08 | 14.39 | 55.52 |
| MnO | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 2.99 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.24 |
| MgO | 20.21 | 21.18 | 17.95 | 11.24 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 21.74 | 0.01 |
| CaO | 13.99 | 13.8 | 26.02 | 24.02 | 23.69 | 23.57 | 54.93 | 0.30 | 0.03 |
| Na2O | 2.22 | 2.10 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| K2O | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| P2O5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 41.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| F | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.36 | 0.21 | 0.00 |
| Total | 98.13 | 98.20 | 99.12 | 100.38 | 99.87 | 99.71 | 99.85 | 80.52 | 56.03 |
| Si | 6.50 | 6.53 | 1.99 | 2.09 | 3.21 | 3.15 | 0.01 | 3.07 | - |
| Ti | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| Al | 2.12 | 1.97 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.05 | 2.09 | 0.00 | 1.98 | - |
| Cr | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| Fe2+ | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 1.32 | - |
| Mn | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | - |
| Mg | 4.20 | 4.41 | 0.98 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 3.55 | - |
| Ca | 2.09 | 2.07 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 5.01 | 0.04 | - |
| Na | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| K | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| P | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.97 | 0.00 | - |
| Total | 15.69 | 15.72 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 7.99 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 9.90 | - |
| Mineral | Pargasite | Pargasite | Diopside | Diopside | Epidote | Epidote | Apatite | Chlorite | Ferric hydroxide |
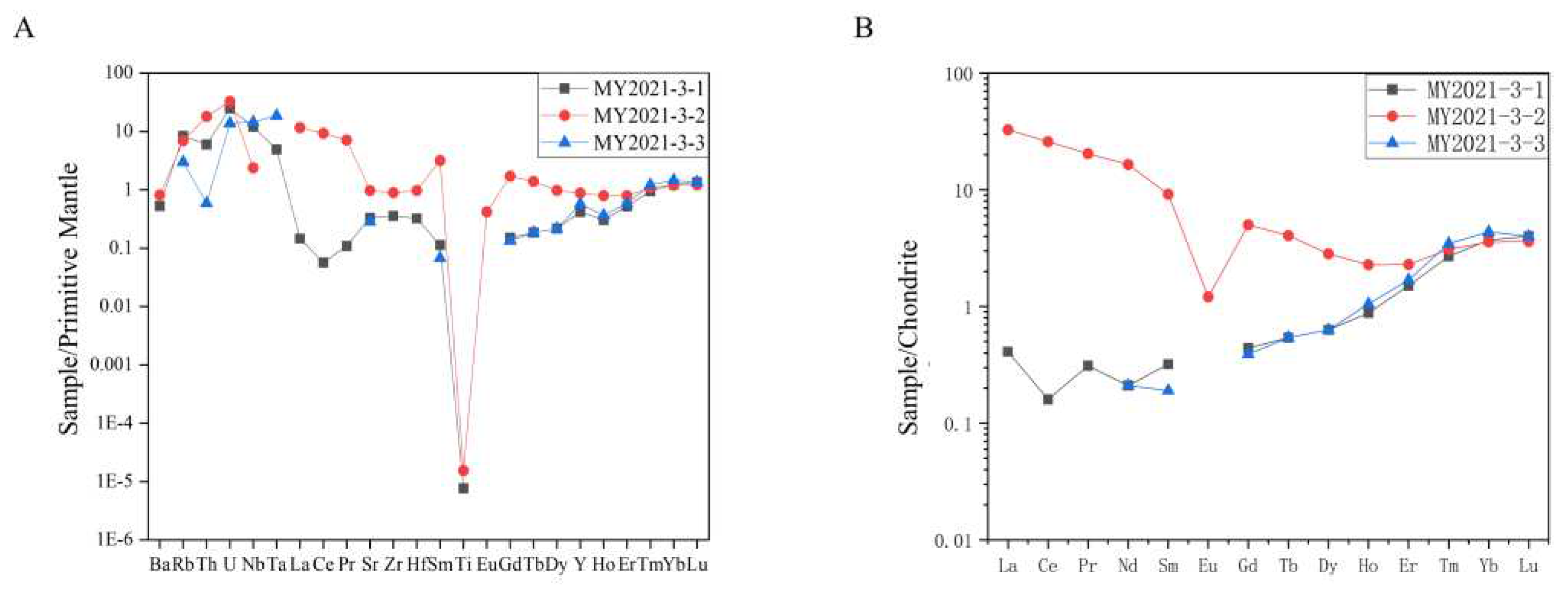
4.2. Bulk-rock major and trace elements
4.3. Rare Earth Elements Characteristics
5. Discussion
5.1. Genetic Types of Qiemo Margou black cyan and Black nephrite
5.2. Coloration Factors of Qiemo Margou black cyan and black nephrite
6. Conclusions
References
- Harlow, G.E.; Sorensen, S.S. Jade (Nephrite and Jadeitite) and Serpentinite: Metasomatic Connections. Int. Geol. Rev. 2005, 47, 113–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L. Systematic Gemology; Geological Publishing House, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Jia, Y.H.; Liu, Y. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Types of Gobi in Ruqiang-Qiemo Xinjian. Rock and Mineral Analysis. 2019, 38, 316–325, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T.; Wang, S.Q. Discovery and Discussion on Cat’s Eye of Qiemo Sugar nephrite in Xinjiang. In Proceedings of China International Jewelry Academic Exchange Conference(2019), Beijing, China; 2019; Volume 11, pp. 244–249, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Formation and Coloration Factors of marble-type Hetian Jade in Hetian Region of Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2018, 37, 1011–1026, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.J.; et al. The genesis and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Pishan brown nephrite bearing Mg-skarn deposit in Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2017, 36, 259–273, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T.; Wang, S.Q. Study on the "silk effect" of transparent gray-purple nephrite. In Proceedings of China International Jewelry Academic Exchange Conference(2021), Beijing, China; 2021; Volume 1, pp. 216–223, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Gil, G.; Yan, L.; et al. Timing of formation and cause of coloration of brown nephrite from the Tiantai Deposit, South Altyn Tagh, northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 131, 0169–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.-X.; Schmadicke, E.; Li, Q.-L.; et al. Age determination of nephrite by in-situ SIMS U-Pb dating syngenetic titanite: A case study of the nephrite deposit from Luanchuan, Henan, China. In Annual Compilation of Academic Papers of the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015 (15th) - Science and Technology Support System; 2016; pp. 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, G.H.; Xu, L.G.; et al. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Nephrite Jade from Yinggelike Deposit, Altyn Tagh (Xinjiang, NW China). Minerals. 2020, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Petrology and geochronology of the Yushigou nephrite jade from the North Qilian Orogen, NW China: Implications for subduction-related processes. Lithos. 2021, 380–381, 105894, ISSN 0024-4937. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.Q. The Petrogeochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Age of Nephrite Placer Deposit in Xiuyan Liaoning. Rock Miner. Anal. 2019, 38, 438–448, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Maituohuti, A.; et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, mineral compositions and geochemistry of placer nephrite in the Yurungkash and Karakash River deposits, West Kunlun, Xinjiang, northwest China: Implication for a Magnesium Skarn. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 699–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Shi, G.H.; et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of placer nephrite from Hetian, Xinjiang, Northwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 21, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Wu, R.H. Study on color and colorimetry of Hetian jade. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 1999, 418–422, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.; Zhao, Q.H.; Pei, L.; et al. study of Mineralogy and spectral characteristics of Dahua black Nephrite from Dahua in Guangxi. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2017, 37, 2237–2241, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.D.; Shi, G.H.; Liu, Y. Vibrational Spectra of Black Species of Hetian Nephrite (Tremolite Jade) and Its Color Genesis. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 681–685, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Black Nephrite’s Characteristics and Preliminary Study of Graphite’s Influence on its Quality. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumchi, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.; Liao, Z.T.; Qi, L.J.; et al. Black Nephrite Jade from Guangxi, Southern China. Gems Geol. 2019, 55, 198–215. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.L. Study on Mineralogical Characteristics and Genesis of Gemstones “Sprinkle Gold Black Cyan Nephrite" in Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Geosciences, Shijiazhuang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, C.W.; Shen, M.Y.; Yin, K. Gemmological Characteristic and Genetic Mineralogy on Pyrite-Chlorite-Bearing Actinolite Jade. J. Gemstones Gemol. (Engl. Chin.) 2020, 22, 1–12, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.L.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.X. Study on the Spectral Identification Characteristics of "Heiqing" and "Heibi". Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 1,292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Du, J.M.; Li, J.J.; Jiang, B.H. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of green nephrite from Dahua, Guangxi, Southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Study on Genesis of Luodian Nephrite Deposit, Guizhou Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.H. Handbook of Transparent Mineral Thin Section Identification; Geological Publishing House, 2006. (in Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Study on petro-mineral Features and genetic Mechanism of Luodian jade in Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Mineral inclusions and SHRIMP U–Pb dating of zircons from the Alamas nephrite and granodiorite: Implications for the genesis of a magnesian skarn deposit. Lithos. 2015, 212–215, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.F.; Gan, F.X.; Ma, B.; et al. Structural and nondestructive componential analysis on several Nephrite from different provenances. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 5, 1197–1202, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Li, J.M.; Lei, J.L.; et al. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of nephrite from Panshi, Jilin, Northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 0169–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y. Study on Petro-mineral Features and Genetic Mechanism of Ruoqiang Nephrite, Xinjiang Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Peng, F.; Wang, W.W.; et al. Spectroscopic Characteristics and Origin Tracing of Nephrite from Dahua, Guangxi and Luodian, Guizhou. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 1294–1299, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ilaria, A; Rosangela, B. Nephrite jade from val malenco, italy: review and update. Gems Gemol. 2013, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T. Characteristics and Genesis of Hetian Jade Gobi Materials in Southern Xinjiang. J. Gems Gemol. 2018, 20, 27–38, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]

| Sample No. | 21-1-A1 | 21-1-A2 | 21-1-A3 | 21-1-A4 | 21-2-A1 | 21-2-A2 | 21-2-A3 | 21-2-A4 | 21-3-A1 | 21-3-A2 | 21-3-A3 |
| SiO2 | 57.67 | 56.68 | 56.54 | 57.74 | 57.9 | 56.71 | 56.11 | 56.41 | 57.28 | 56.51 | 56.86 |
| TiO2 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 1.99 | 2.18 | 0.59 | 0.20 | 0.83 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 0.36 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| FeO | 0.43 | 0.17 | 5.56 | 3.03 | 4.29 | 4.91 | 5.29 | 6.29 | 5.26 | 4.71 | 4.66 |
| MnO | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| MgO | 23.44 | 24.30 | 21.21 | 21.53 | 21.63 | 22.06 | 20.01 | 21.05 | 22.58 | 21.03 | 21.14 |
| CaO | 14.13 | 13.85 | 13.38 | 13.77 | 13.1 | 12.73 | 13.05 | 13.55 | 12.82 | 12.13 | 12.4 |
| Na2O | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| K2O | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.09 |
| BaO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| NiO | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| F | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.19 |
| Cl | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Total | 98.72 | 98.25 | 98.31 | 96.77 | 98.17 | 97.30 | 95.25 | 98.96 | 99.62 | 97.75 | 96.24 |
| T-Si | 7.81 | 7.73 | 7.88 | 8.03 | 7.95 | 7.90 | 7.99 | 7.83 | 7.85 | 8.00 | 8.01 |
| T-Al | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sum-T | 8.00 | 8.00 | 7.98 | 8.03 | 8.00 | 7.97 | 8.00 | 7.94 | 7.95 | 8.00 | 8.01 |
| C-Al | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| C-Cr | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C-Mg | 4.73 | 4.92 | 4.41 | 4.46 | 4.43 | 4.58 | 4.25 | 4.36 | 4.62 | 4.44 | 4.44 |
| C-Fe2+ | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.38 | 0.47 | 0.50 |
| C-Ti4+ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C-Mn2+ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C-Ca | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sum-C | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.01 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| B-Mg | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| B-Fe2+ | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| B-Mn | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| B-Ca | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.92 | 1.89 | 1.93 | 1.83 | 1.96 | 1.88 | 1.77 | 1.84 | 1.87 |
| B-Na | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| B-K | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Sum-B | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.91 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.99 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.99 | 1.97 |
| A-Ca | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| A-Na | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| A-K | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sum-A | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sum-Cat | 15.02 | 15.11 | 15.10 | 14.94 | 15.00 | 15.09 | 14.99 | 15.13 | 15.11 | 14.99 | 14.98 |
| Mg/(Mg+Fe2+) | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| Mineral | Tremolite | Tremolite | Actinolite | Tremolite | Tremolite | Actinolite | Actinolite | Actinolite | Actinolite | Actionlite | Actinolite |
| Nephrite Name | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite | Black-Cyan Nephrite |
| Sample | Content(wt%) | ||
| MY 2021-3-1 |
MY 2021-3-2 |
MY 2021-3-3 |
|
| SiO2 | 56.65 | 56.38 | 56.91 |
| Al2O3 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.53 |
| CaO | 13.10 | 13.20 | 13.45 |
| TFe2O3 | 5.40 | 6.11 | 4.68 |
| FeO | 4.54 | 5.09 | 3.97 |
| K2O | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| MgO | 21.90 | 21.30 | 22.20 |
| MnO | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.30 |
| Na2O | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| TiO2 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| BaO | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Fe3+ | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.32 |
| LOI |
2.52 | 2.44 | 2.75 |
| Total | 105.17 | 105.90 | 104.90 |
| Sample | Content(μg/g) | |||
| MY 2021-3-1 |
MY 2021-3-2 |
MY 2021-3-3 |
Average | |
| Li | 4.80 | 4.10 | 4.40 | 4.43 |
| Be | 18.2 | 15.05 | 12.90 | 15.38 |
| Cr | 14.00 | 21.00 | 6.00 | 13.67 |
| Mn | 2010.00 | 2400.00 | 2100.00 | 2170.00 |
| Co | 34.60 | 36.90 | 30.60 | 34.03 |
| Ni | 3.50 | 4.50 | 2.50 | 3.50 |
| Cu | 4.40 | 4.30 | 2.70 | 3.80 |
| Zn | 105.00 | 127.00 | 135.00 | 122.33 |
| Ga | 1.10 | 1.50 | 1.30 | 1.30 |
| Rb | 5.30 | 4.40 | 1.90 | 3.87 |
| Sr | 7.00 | 20.50 | 6.00 | 11.17 |
| Mo | 2.01 | 1.58 | 0.55 | 1.38 |
| Cd | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| In | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.069 | 0.03 |
| Cs | 1.75 | 1.93 | 1.06 | 1.58 |
| Ba | 3.70 | 5.70 | <0.50 | 3.13 |
| Ti | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| Pb | 5.30 | 10.30 | 7.60 | 7.73 |
| Bi | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Th | 0.51 | 1.54 | 0.05 | 0.70 |
| U | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.50 |
| Nb | 8.60 | 1.70 | 10.30 | 6.87 |
| Ta | 0.20 | <0.05 | 0.76 | 0.32 |
| Zr | 4.00 | 10.00 | <2.00 | 4.67 |
| Hf | 0.10 | 0.30 | <0.10 | 0.13 |
| Sn | 0.40 | 0.50 | 2.30 | 1.07 |
| Sb | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.24 |
| TI | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| W | 0.80 | 0.20 | 1.20 | 0.73 |
| As | <0.20 | <0.20 | 0.40 | 0.13 |
| V | 11.00 | 14.00 | 11.00 | 12.00 |
| La | 0.10 | 8.00 | <0.10 | 2.70 |
| Ce | 0.10 | 16.50 | <0.10 | 5.53 |
| Pr | 0.03 | 1.96 | <0.02 | 0.66 |
| Nd | 0.10 | 7.80 | 0.10 | 2.67 |
| Sm | 0.05 | 1.41 | 0.03 | 0.50 |
| Eu | <0.02 | 0.07 | <0.02 | 0.02 |
| Gd | 0.09 | 1.02 | 0.08 | 0.40 |
| Tb | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Dy | 0.16 | 0.72 | 0.16 | 0.35 |
| Ho | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| Er | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.30 |
| Tm | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| Yb | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.64 |
| Lu | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Sc | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 0.47 |
| Y | 1.90 | 4.00 | 2.6 | 2.83 |
| δEu | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.06 |
| [La/Yb]N | 0.12 | 9.73 | 0.00 | 3.28 |
| LREE | 0.38 | 35.74 | 0.13 | 12.08 |
| HREE | 1.35 | 3.16 | 1.51 | 2.01 |
| ∑REE | 1.73 | 38.9 | 1.64 | 14.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




