Introduction
Growing evidence associates sepsis with a network of dysfunctional processes, including a poorly coordinated immune system response[
1]. Sepsis is a serious organ dysfunction that results in millions of fatal cases per year[
2]. This disease can be caused by a variety of infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens [
3]. Its main symptoms include fever, low blood pressure, an abnormal resting heartbeat tachycardia, and an uncharacteristically high white blood cell count[
4]. The immune system during sepsis contributes to systemic inflammation, tissue damage, and organ failure affecting the kidney, respiratory system, the heart, or the brain[
5]. Advances in understanding the pathophysiology of sepsis have led to the development of targeted therapies, such as immunomodulatory agents, that aim to restore immune system balance and improve patient outcomes[
6]. However, various trials utilizing immune-modulatory agents to tackle sepsis have not produced promising results, highlighting the need for continued research to better understand how to challenge this complex disease [
7].
Tregs are essential in the pathophysiology of septic complications by suppressing the adaptive immune response. Currently, the sepsis course of diseases is defined by an initial cytokine storm caused by the innate immune system response to invading microbes. This phase is usually followed by a cycle of hyper-hypoimmune reactions. This cycle results in cell exhaustion and cell death. Intriguingly, postmortem studies have discovered a significant reduction in the numbers of CD4 and CD8 T cells, pinpointing the role of dysfunctional Treg as a critical obstacle toward homeostasis during sepsis. A higher frequency of Tregs has been found in septic shock patients' blood. Additionally, a negative link between the frequency of Tregs and sepsis severity is evident in sequential organ failure, among other parameters [
8,
9]. These findings were further supported by an animal investigation that found that, in contrast to sham mice, the percentages of CD4+CD25+ Tregs were considerably higher 24 hours after abdominal sepsis induction using cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)[
10,
11].
How Tregs become dysfunctional in sepsis is currently unknown. In normal conditions, Tregs are considered the guardians of the immune system; they prevent excessive immune responses by suppressing other immune cells. The suppression mechanisms can take two forms. First, known as the indirect form, Tregs inhibit dendritic cells through various pathways, including CTLA4, CD28, CD80, CD86, LFA1, A20, CD40-CDO4L, neuropilin 1, and LAG3 [
12]. CTLA-4 and Foxp3 were reported to be highly expressed in the blood of septic patients [
13]. Direct inhibition of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells includes the production of suppressive cytokines such as TGFβ, IL10, and IL35, consumption of cytokines such as IL2, and induction of apoptosis through the TRAIL, CD3, CD46, CD25, and BIM pathways. Interestingly, elevated IL-10 and TGF-β levels have been reported in the blood of septic patients [
14,
15]. Additionally, Tregs can regulate ATP and ADP by interacting with CD73, CD39, APRT, A2A receptors, and p2ry11 receptors. Furthermore, Tregs can also regulate NFAT pathways through the IL4, ICER, PPARγ, GIT, and CBCLB pathways. It can also regulate calcium signaling in the responding cells by controlling the NFKB, PPP3CA, PPP3CB, PPP3CC, and IKAA pathways. Treg is known to be regulated by FoxP3 [
16,
17]. However, FoxP3 levels in many cases in transcriptomic studies of blood do not necessarily mirror real cases as the number of CD4+ and CD25+ FoxP3 is limited. The exact method by which the Treg function is destabilized remains unknown. scRNA-seq has the advantage of allowing inspection of Treg cells on molecular levels with higher accuracy.
In this report, we investigated the genetic networks controlled by FoxP3 that ultimately lead to excessive suppression of immune cells by Tregs. To do that, we analyzed a host of microarray, bulk RNA seq, and scRNA-seq studies, as well as extensive evolutionary studies. Our results pinpointed the role of a dysfunctional metabolic network in Tregs, manifested by increased itaconate production through the upregulation of the gene ACOD1 through putative interaction with other genes associated with metabolism and expressed particularly in the mitochondria, such as CD36.
2. Methods
Our workflow consisted of the following workflow. First, we analyzed the genomic pathway upregulated in septic blood samples. Then we focused on deciphering the association between Treg and the resulting upregulated pathway through scRNA-seq analysis by conducting two different analyses. (i) We analyzed the difference in expression of genes of interest resulting from the previous section utilizing the FoxP3 and FoXP3Δ datasets; (ii) This was followed by a co-localization analysis of genes of interest with FoxP3. Then we validated our hypothesis for the involvement of the resulting genes of interest in Treg function.
Datasets
We analyzed four different public datasets. First, we conducted a bulk RNA-seq analysis using the public microarray GSE65088 [
18]. The dataset included ex vivo blood samples that were divided into control and treated groups. The treated groups contained samples that were subjected to one of four types of infection, namely two bacterial microbes (
Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli) and two fungal pathogens (
Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus), while the control blood samples were treated by HBSS. All samples were treated for 4–8 hours, followed by standard processing using RNA isolation, followed by bulk RNA-seq sequencing using Illumina [
18]. After that, To investigate the role of Acod1 in Tregs, we compared the transcriptome of FoxP3WT Tregs and Foxp3KO Tregs using the public dataset (GEO: GSE176236) [
19]. In this dataset, FoxP3WT Tregs were isolated from the lamina propria of Foxp3-DTR-GFP+ mice. Whereas in the case of knock-out mice, Foxp3DTR-GFP/loxp-Thy1.1-STOP-loxp-GFP markers were used to isolate Foxp3KO. 10X sequencing was followed according to the manufacturer's instructions. The third dataset included five healthy controls and five patients with proven sepsis from the Emergency Department, Surgical Critical Care Division, Tongji Trauma Center, Tongji Hospital, and Tongji Medical College. We examined scRNA-seq from the complete blood transcriptome of these patients (GSE224095). In the fourth dataset, eight-week-old WT or Irg1-/-C57bl/6 mice were infected with a combination of the 17 host-adapted P. aeruginosa clinical isolates (106 total CFU per animal in 50 uL) or WT PAO1. The mice were sacrificed sixteen hours after infection, their lungs were removed, and single-cell suspensions of the lungs were prepared, followed by 10x scRNA-seq.
RNA-seq analysis
RNA-seq analysis was done in R using limma [
20]. Briefly, we used the limma RNA-seq differential gene expression approach to compute the non-parametric approximations of mean-variance relationships. This made it possible for us to calculate the weights and empirical Bayes shrinkage of variance parameters for a linear model analysis of log-transformed counts. Differential expression analysis was performed to determine the differences in gene expression between infected and non-infected samples by fitting a linear model to quantify the variability in the data using lmFit. First, the statistically significant DEGs were used for gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) based on gene ontology biological process databases, GO (Biological Process, Cellular Component, and Molecular Function), KEGG (Pathways), Reactome (Pathways), and WikiPathways. The GeneTrail3 software was used for this. For this investigation, upregulated genes from each group were uploaded to the server. A gene enrichment analysis was conducted using overrepresentation. Over-representation analysis (ORA) evaluates if a group of variables is more common in a set of results than we would anticipate by chance. The ORA was run with its default settings to control the false discovery rate. Second, using Cytoscape, we used BiNGO to find pathways that are overrepresented in infected septic samples. BiNGO is built as a plugin for Cytoscape, which is an open-source bioinformatics software platform [
21].
scRNA-seq analysis
Cell clustering was achieved, as previously noted, using the Seurat R tool[
22]. Specifically, cell clustering was performed using the nonlinear dimensional reduction methodology in conjunction with the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) method. We analyzed each of the cell clusters using paired differential expression analysis, using parameters recommended for data with batch effect, to find flag genes of the cell clusters with average fold change (FC) expression compared with other included clusters >2. Our study utilized Library Seurat and dplyr in R to analyze quality control metrics, filter cells, normalize data, cluster cells, and identify cluster biomarkers. Low-quality cells were removed using a threshold of 200 to 7,000 genes per cell, and cells with over 10% of the mitochondrial genome were excluded. The "sctransform" package was used for normalization, and the "RunUMAP" function was used for clustering cells. The "FindAllMarkers" function identified specific markers for each cell cluster, and the "DoHeatmap" function displayed the top genes in each cluster. The "VlnPlot" function provided expression probability distributions across cell clusters.
Results
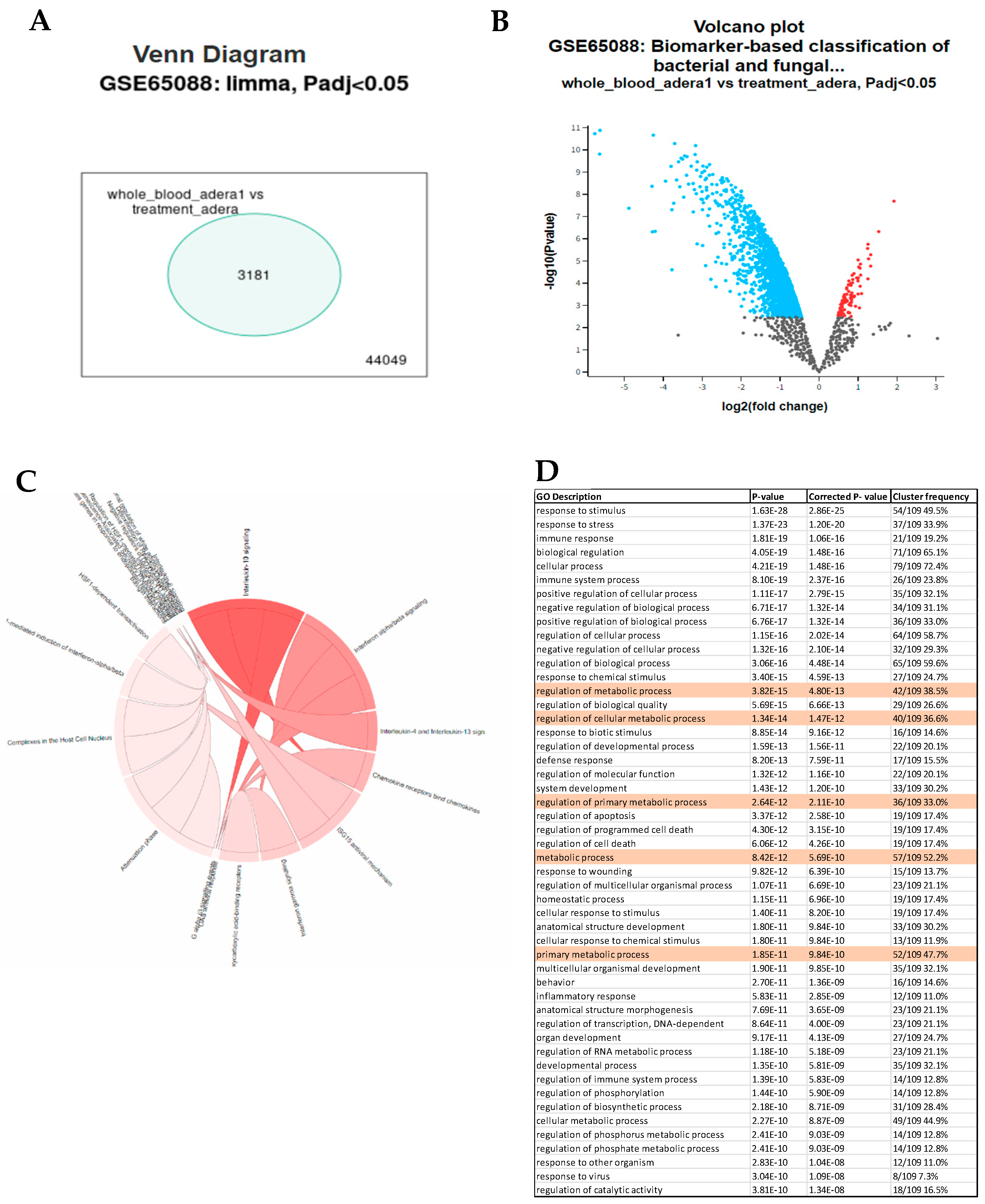
We conducted several analyses of public data to pinpoint how Tregs contribute to sepsis. First, we analyzed blood samples infected with various types of bacteria and fungi. We found that the genes differ significantly by the type of infection. However, in general, we found various differentiated genes that were common to all treated samples investigated. For example, in the case of C. albicans, LAG3, CD40, and A2A seem to be upregulated, indicating Treg could be suppressing dendritic cells in sepsis through indirect pathways (
Figure 1A,B). Several proinflammatory markers were upregulated, such as IL6, TNF, and IL1 (
Figure 1B). The Treg effect was also found in the overrepresentation of various Treg pathways, such as IL10 and IL4, in the OVA (
Figure 1C). Interestingly, our results also showed that several genes related to metabolism were also upregulated, such as Acod1 (Aconitate decarboxylase 1) (
Figure 1B,D).
Next, we analyzed the public GEO (GSE176236) to investigate the effect of FoxP3 on Treg. We discovered that Acod1 is tightly controlled by FoxP3 in Tregs, and it could be playing a role in regulation of Rorc inhibition of FoxP3 in an auto-inhibition loop. To investigate the role of Acod1 in Tregs, we compared the transcriptome of FoxP3WT Tregs and Foxp3KO Tregs using the public dataset (GEO: GSE176236). In this dataset, FoxP3WT Tregs were isolated from the lamina propria of Foxp3-DTR-GFP+ mice. Whereas in the case of knock-out mice, Foxp3DTR-GFP/loxp-Thy1.1-STOP-loxp-GFP markers were used to isolate Foxp3KO. We performed RNA-seq analysis using edgeR and Glimma in R. We found that the samples separate according to their PCA analysis, showing that FoxP3 is playing a primary role in determining the differentiation pattern of colon-induced Tregs (
Figure 2A). Acod1 as well as two of its upstream regulators (e.g., Phlpp1 and Trat1 that control Acod1 expression through regulation of PKC) are upregulated in the WT Tregs. We found that Cebpb, which is directly upregulating Acod1, is also upregulated in WT Tregs (
Figure 2B). Similarly, Swap70, which is known to upregulate Nfkβ, which in turn positively regulates ACOD1, is upregulated in the WT Tregs (
Figure 2B,C). Conversely, IL17A and IL6 were downregulated; however, the Th17 pathway was enriched, confirming selected genes role in Treg function (
Figure 2D).
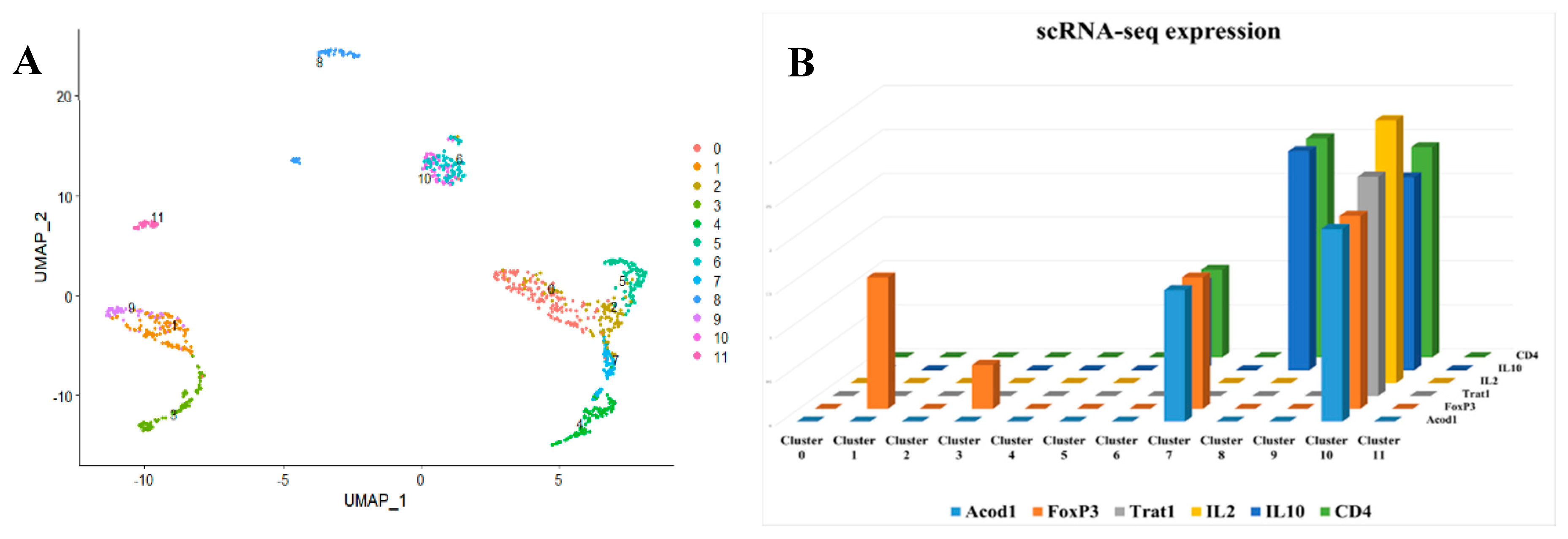
After that, we analyzed single cells from peripheral immune cells extracted from the colon. We discovered that ACOD1 is particularly expressed in Tregs (
Figure 3A,B).
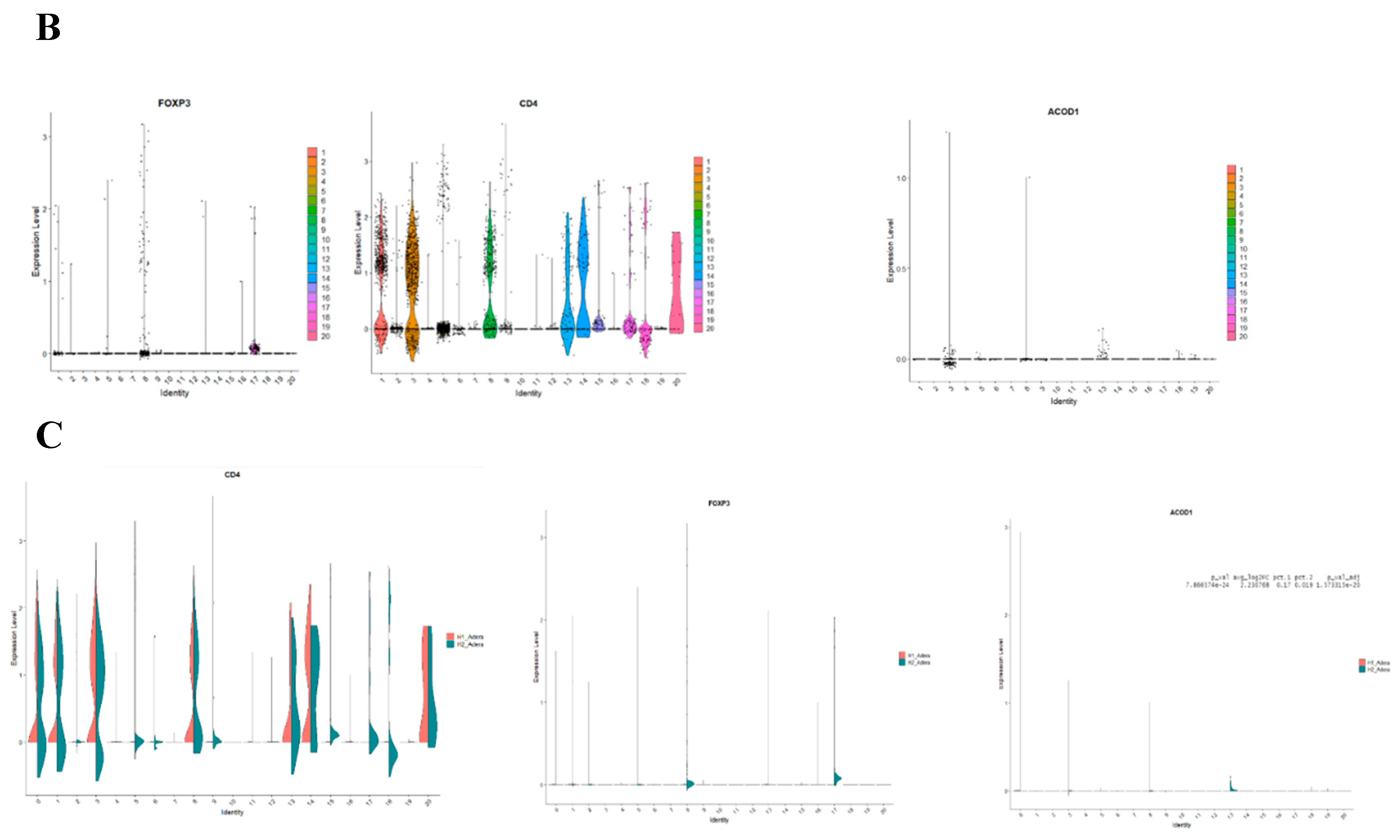
Following that, we conducted a thorough analysis of the difference in transcriptomic between control and sepsis patients on a single cell level. Our results revealed that the cells can be clustered into 20 different types. Notably, most of the clusters showed mixtures of the two conditions, which indicate that they are the same type of cells that have changed their expression levels based on sepsis. However several clusters were only upregulated in one of the conditions, such as clusters 12 and 17 which seem to be exclusively expressed in sepsis (
Figure 4A). To focus on FoxP3+ Tregs, we compared clusters based on the differential expression between them. We found that FoxP3 and CD4+ are both differentially expressed in clusters 1,2,5,8,13,16 and 17 Shifting our focus to ACOD1, we found that it is exclusively expressed in clusters 3,8 and 13 (
Figure 4B). Hence we conducted a deferential expression analysis based on clusters. Our analysis revealed that FoxP3 and ACOD1 are solely deferentially expressed in cluster 8 between sepsis and control patients. Although CD4 is highly expressed in cluster 8 in relationship to other clusters we did not detect a difference in the expression of CD4 in cluster 8, indicating that CD4+ is ubiquitously expressed in this particular cluster. Additionally, this information indicates that there is no difference in the CD4+ FOXP3+ACOD1 frequency cluster, however, the difference is the expression of ACOD1 and FOXP3 between the two conditions (
Figure 4C).
We looked deeper into the data, by comparing other genes that are also expressed between sepsis and non-sepsis patients in the cluster phenotyped as CD4+FOXP3+ACOD1+ T cells. The gene list of differentially expressed genes included LYZ, S100A8, GPX1, FOS, MND1, CD36, NRG1, and CST3 among others (
Figure 5A). To assess the location of ACOD1 within the cell, we mined Human Atlas for its expression, our investigations indicate that ACOD1 is likely to be expressed in the mitochondria (
Figure 5B).
Finally, we investigated the effect of ACOD1 using scRNA-seq. In this interesting dataset, mice with
Acod1 WT or
Acod1-/- were infected to induce sepsis. Our results were able to identify 23 different cell clusters (
Figure 6A). Interestingly, we found that FoxP3 expression is affected by knocking on ACOD1 in sepsis (
Figure 6B,C). This downregulation was also seen in CD4 expression and downstream metabolic interactors of ACOD1, such as CD36 (
Figure 6B,C).
Discussion
Our results revealed that various metabolic pathways are enriched in sepsis. Sepsis is a vicious disease that affects millions of lives around the world[
23]. Its symptoms progress from a minor infection to sequential organ failure, which can end in mortality. The etiology of sepsis consists of three main phases, namely, a cytokine storm followed by a malicious cycle of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses. The reason behind Treg's continuous activation in sepsis is currently unknown [
9]. We investigated this question by conducting a bulk RNA-seq analysis using blood samples infected with sepsis-inducing microbes. Our results indicated that the IL4 and IL10 pathways are enriched in sepsis (
Figure 1). One of the main functions of IL10 is that it can resist switching metabolic pathways induced by inflammatory stimuli, where it reduces oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis [
24,
25]. Also, by suppressing mTOR activity, IL-10 encourages the process of mitophagy, which removes damaged mitochondria with high reactive oxygen species and low membrane potential.
Our investigation pinpointed the metabolic regulator ACOD1 as a primary actor in Tregs during sepsis. ACOD1, through the production of itaconate, contributes to signal transduction and metabolic reprogramming, as Itacnaote is a central source of acetyl-coA. To perform its function, various signal transduction networks such as TLRs and IFNAR, adapter proteins (e.g., MYD88), ubiquitin ligases (e.g., A20), and transcription factors (e.g., NF-κB, IRFs, and STATs) control ACOD1 expression, regulating itaconate production, oxidative stress, and antigen processing [
26]. However, whether ACOD1 plays a role in Treg toward sepsis is not yet known. Our results showed that ACOD1 and FoxP3 seem to be specifically expressed in Treg-like cells (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). FoxP3 and ACOD1 seem to mutually regulate each other's expression (
Figure 2 and
Figure 6). During sepsis, our study showed that ACOD1 and FoxP3 are upregulated in Treg-like cells (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
Our report results show that ACOD1 is associated with another metabolite regulator; CD36. CD36 is a class B scavenger receptor found on the surfaces of various immune cells, including macrophages, monocytes, and non-immune cells. It binds to various extracellular ligands, including thrombospondin domain proteins, long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), and molecules with molecular patterns [
27]. Recent studies have linked LCFA binding and transport to a potential binding pocket in the CD36 extracellular domain, although the atomic structure of CD36 remains unsolved [
28]. CD36 is upregulated by cytokines such as CSF, IL4, and IL10 [
29,
30]. In Tregs, CD36 acts as a pattern recognition receptor that facilitates fatty acid (LCFA) transport. LCFA binding to CD36 triggers intracellular signaling events, adjusting lipid metabolism, including dissociation of SFK Fyn and enrichment of liver kinase B1, activating the AMPK pathway, and upregulating fatty acid oxidation (FAO) [
31,
32,
33]. In turn, FAO drives acetyl-CoA production from Itaconate [
34]. Interestingly, our results show that knocking out ACOD1 reduced the level of CD36 (
Figure 6). We hypothesize that during sepsis, the transport of LCFAs to the cell is mediated by CD36. Oxidization of LCFAs leads to the conversion of itaconate produced by ACOD1 to acetyl-CoA. Itaconate further activates FoxP3 and mediates the production of IL10 and IL4. These anti-inflammatory cytokines maintain the activation of CD36, leading to a vicious cycle of anti-inflammatory responses in sepsis. Taken together, our results indicate that targeting ACOD1 can potentially ease the sepsis prognosis.