Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
07 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
- Drug
- 2.
- Cell lines
- 3.
- Cell viability assay
- 4.
- Identification and analysis of dexmedetomidine targets
- 5.
- QPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction)
| PRKDC: F: 5'- CAGAAGGCTGCCACAGGAA -3' R: 5'- GCTGATCGTCTGAAGACCTC -3' |
| IDO1: F: 5'- TGCCTTCAGCTCCGTCACTT -3' R: 5'- GATCCCAGGTGAGGGGACAA -3' |
| MIF: F: 5'- CACATGCTGCCTGGCATTCT -3' R: 5'- GTCACTGTCTGCTGCTGCCA -3' |
| KCNH2: F: 5'- AGTGGCATCCATTGCTTCTC -3' R: 5'- AGTGCTGCCCAATGTCTGTC -3' |
| CHRM3: F: 5'- CAGCTAAAACCGGTGCTCCA -3' R: 5'- GCGTCTTGCATTGCTCACCA -3' |
| KCNN: F: 5'- CTCGGTACTTGGCCTTCATG -3' R: 5'- GCTTGGTGGTGGTCTTGCAT -3' |
| GAPDH F: 5'- TGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGT -3' R: 5'- TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCAATG -3' |
- 6.
- Western blotting
- 7.
- Immunostaining
- 8.
- Antibodies
- 9.
- Plasmids and transfection of cells
- 10.
- Protein-ligand docking
- 11.
- Statistical analysis
Results
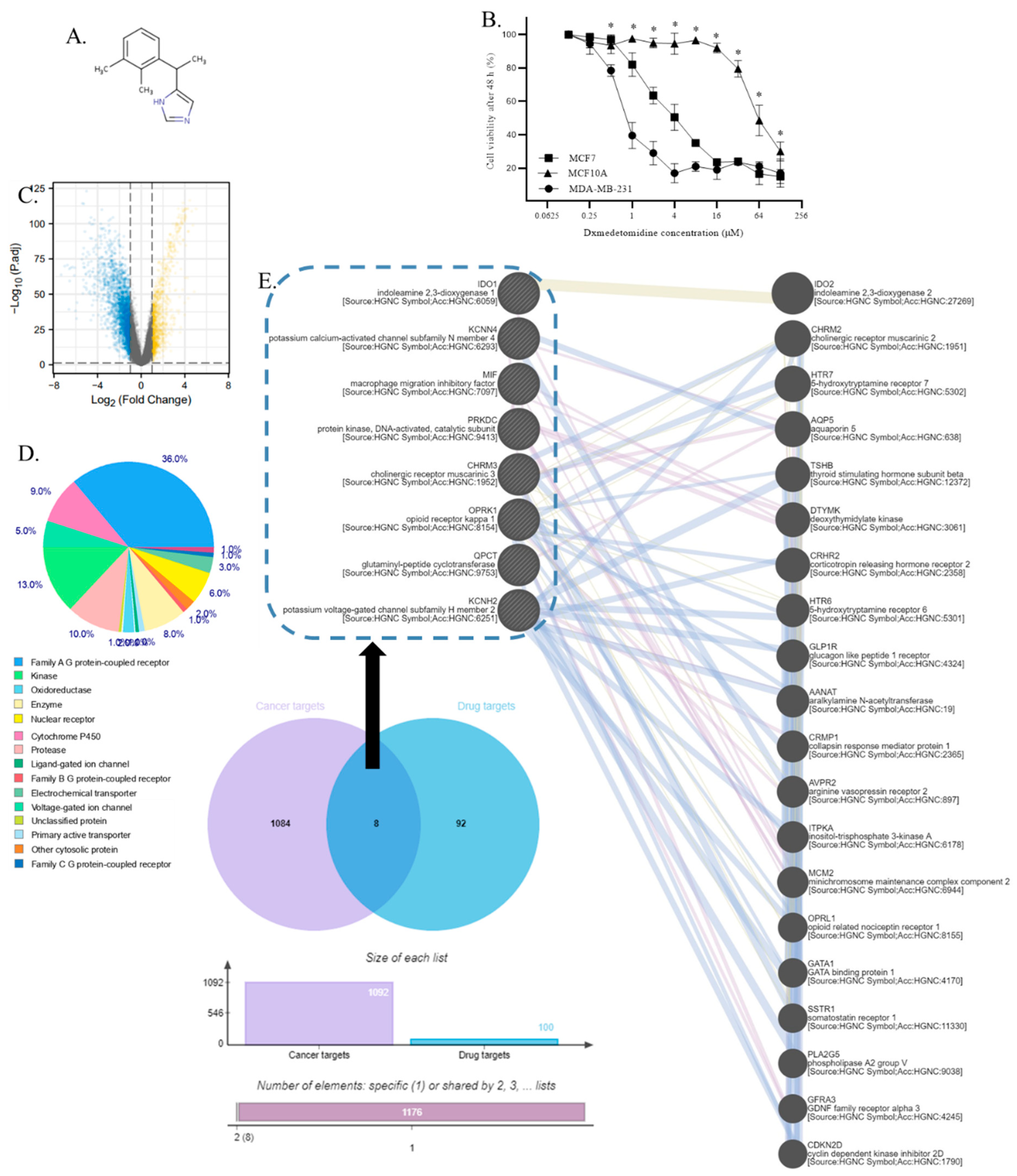
- Dexmedetomidine selectively inhibits TNBC cells
- 2.
- PRKDC, IDO1, OPRK1, QPCT, MIF, KCNH2, CHRM3, and KCNN4 were identified as dexmedetomidine targets in TNBC
- 3.
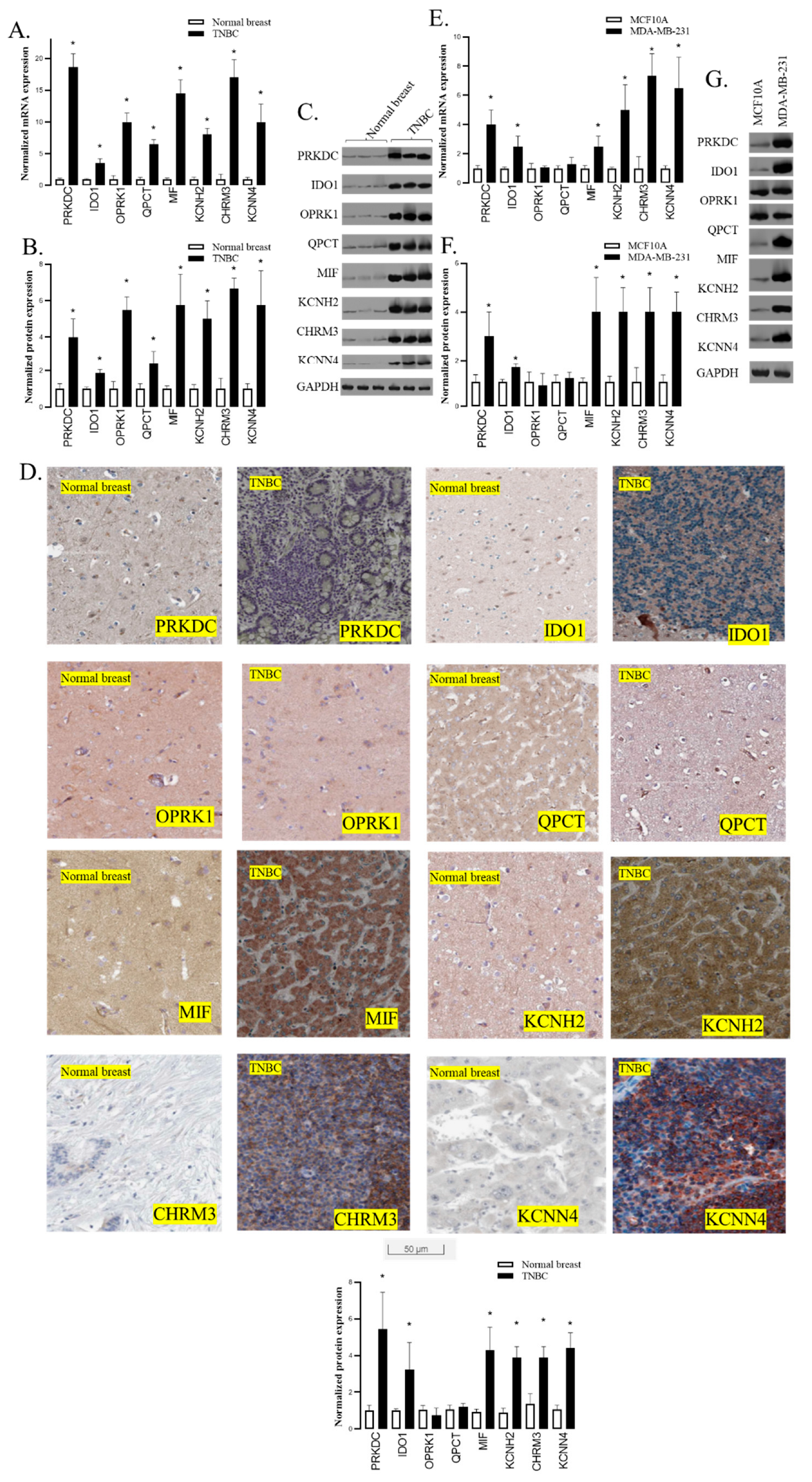
- PRKDC, IDO1, MIF, KCNH2, CHRM3, and KCNN4 were overexpressed in TNBC tissues
- 4.
- PRKDC, IDO1, MIF, KCNH2, CHRM3, and KCNN4 were overexpressed in TNBC cells
- 5.
- Gene annotation from the GeneCard of PRKDC, IDO1, MIF, KCNH2, CHRM3, and KCNN4
- 6.
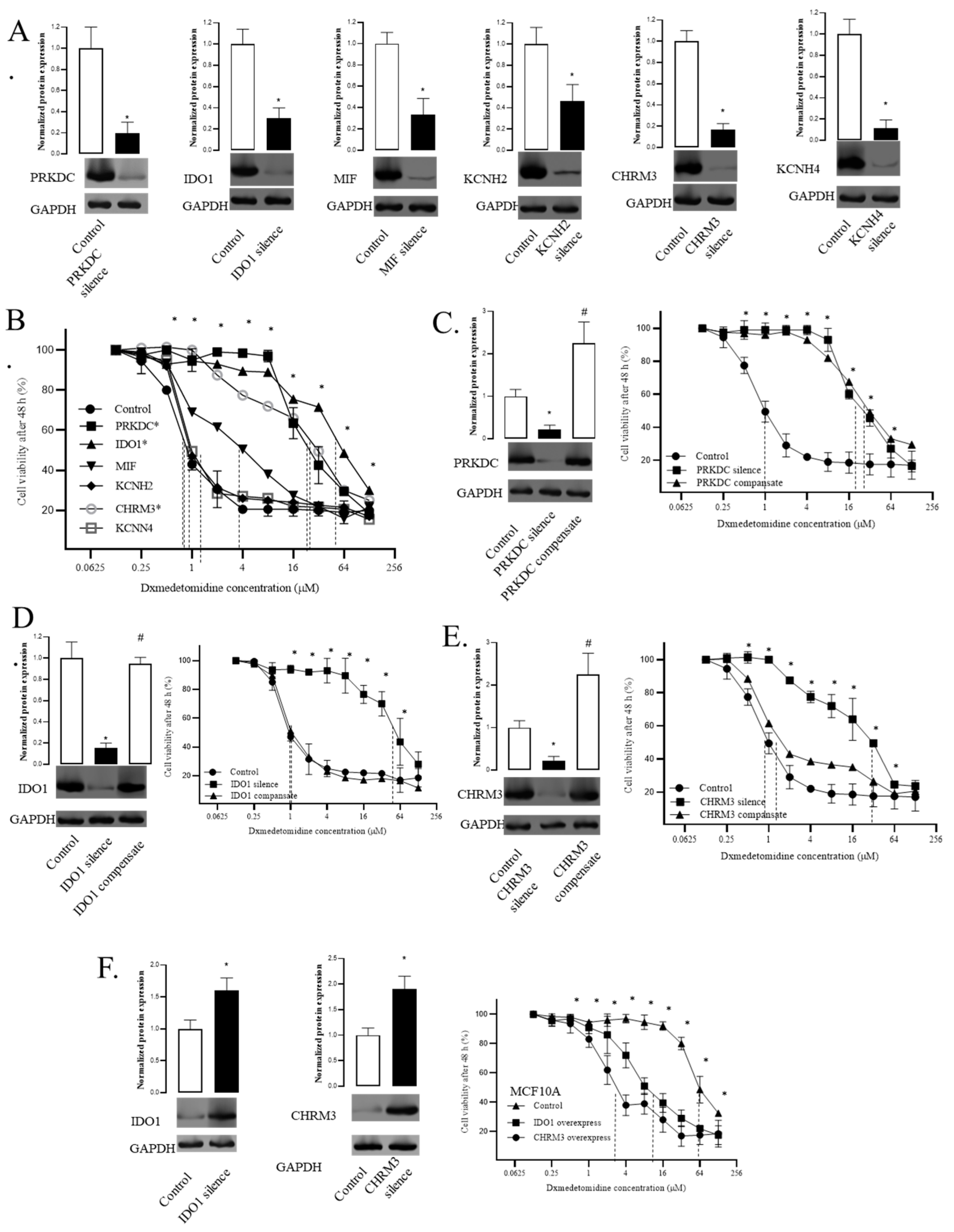
- Silencing PRKDC, IDO1, and CHRM3 decreased the sensitivity of TNBC cells to dexmedetomidine
- 7.
- Compensation of IDO1 and CHRM3 recovered the sensitivity of TNBC cells to dexmedetomidine
- 8.
- Overexpression of IDO1 and CHRM3 increased the sensitivity of breast cells to dexmedetomidine
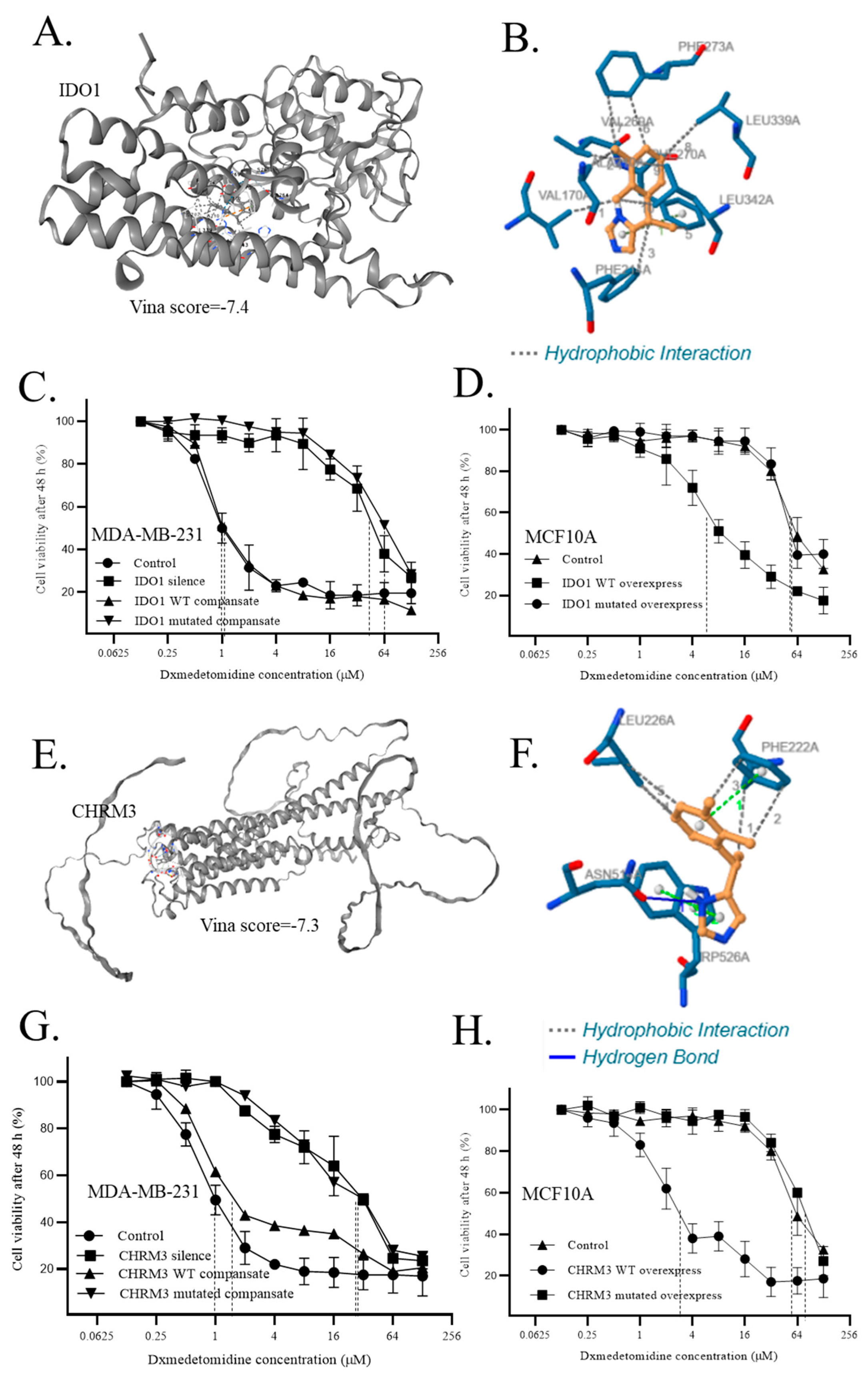
- 9.
- Direct interaction of dexmedetomidine to IDO1 and CHRM3 regulated the sensitivity of cells to dexmedetomidine
Discussions
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Availability of data and materials
Acknowledgements
Competing interests
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Abbreviations
- BrCa (breast cancer)
- TNBC (Triple-negative breast cancer)
- DEG (Differential expression gene)
- DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium)
- CCK8 (Cell Counting Kit-8)
- TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas)
- FBS (Fetal Bovine Serum)
- ECL (Enhanced Chemiluminescence)
- GAPDH (Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Dehydrogenase)
- PRKDC (protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide)
- IDO1 (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1)
- OPRK1 (opioid receptor kappa 1)
- QPCT (glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase)
- MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor)
- KCNH2 (potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (Eag-related), member 2)
- CHRM3 (cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 3)
- KCNN4 (potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4)
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022; 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, M.A.; Oza, G.; Sharma, A.; Arriaga, L.G.; Hernández Hernández, J.M.; Rotello, V.M.; Ramirez, J.T. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review of Conventional and Advanced Therapeutic Strategies. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2020; 17. [Google Scholar]
- Smrekar, K.; Belyakov, A.; Jin, K. Crosstalk between triple negative breast cancer and microenvironment. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xu, F.; Cui, S.; Guan, X. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Novel Biomarker Optimizing Treatment for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Clinical breast cancer 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimonte, S.; Palma, G.; Cascella, M.; Cuomo, A. Phytocannabinoids in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment: Current Knowledge and Future Insights. Anticancer Res 2023, 43, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zeng, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Tu, J.; Nephew, K.P.; Long, X. Glutamine metabolism in breast cancer and possible therapeutic targets. Biochemical pharmacology 2023, 210, 115464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Z.J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.J.; Yao, L. An EMT-Related Gene Signature to Predict the Prognosis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Adv Ther 2023, 40, 4339–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershoni, A.; Hassin, O.; Nataraj, N.B.; Baruch, S.; Avioz-Seligman, A.; Pirona, A.C.; Fellus-Alyagor, L.; Salame, T.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Mallel, G.; et al. TAZ facilitates breast tumor growth by promoting an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment. Molecular oncology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, L.M.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, Y.F.; Chen, J.L.; Chao, T.C.; Lai, J.I.; Lien, P.J.; Lin, Y.S.; Feng, C.J.; Chen, Y.J.; et al. Correlation of an immune-related 8-gene panel with pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with primary breast cancers. Transl Oncol 2023, 38, 101782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewunmi, O.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Rosen, J.M. Targeted inhibition of lncRNA Malat1 alters the tumor immune microenvironment in preclinical syngeneic mouse models of triple negative breast cancer. Cancer immunology research 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Current Treatment Landscape for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Journal of clinical medicine 2023, 12 (4).
- Stămat, L.B.; Dinescu, S.; Costache, M. Regulation of Inflammasome by microRNAs in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: New Opportunities for Therapy. International journal of molecular sciences, 2023; 24. [Google Scholar]
- Manoochehri, M.; Borhani, N.; Gerhäuser, C.; Assenov, Y.; Schönung, M.; Hielscher, T.; Christensen, B.C.; Lee, M.K.; Gröne, H.J.; Lipka, D.B.; et al. DNA methylation biomarkers for noninvasive detection of triple-negative breast cancer using liquid biopsy. Int J Cancer 2023, 152, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nature reviews. Clinical oncology 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Sahin, A.A.; Huo, L.; Ward, K.C.; O'Regan, R.; Torres, M.A.; Meisel, J.L. Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2017, 161, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Ding, A.; Lin, Y.; Wu, S.X.; Lin, J. Potential Therapeutic Application of Local Anesthetics in Cancer Treatment. Recent patents on anti-cancer drug discovery, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Effect of Propofol on breast Cancer cell, the immune system, and patient outcome. BMC anesthesiology 2018, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Effects of local anesthetics on breast cancer cell viability and migration. BMC cancer 2018, 18, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Comparing volatile and intravenous anesthetics in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2018. vol. 78: American Association for Cancer Research; 2018: 2162.
- Liu, H. A Prospective for the Potential Effect of Local Anesthetics on Stem-Like Cells in Colon Cancer. Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research, 2020; 25, 18927–18930. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. A clinical mini-review: Clinical use of Local anesthetics in cancer surgeries. The Gazette of Medical Sciences 2020, 1, 030–034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Lidocaine Suppresses Viability and Migration of Human Breast Cancer Cells: TRPM7 as A Target for Some Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2021, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Dexmedetomidine: present and future directions. Korean journal of anesthesiology 2019, 72, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, G.M. Dexmedetomidine: A Review of Its Use for Sedation in the Intensive Care Setting. Drugs 2015, 75, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clinical pharmacokinetics 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, A.; Gao, C. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Perioperative Dexmedetomidine Administered as an Adjunct to General Anesthesia: A Meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, J.S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Yang, F.S.; Cheng, Y.J. Effects of Dexmedetomidine Infusion on Inflammatory Responses and Injury of Lung Tidal Volume Changes during One-Lung Ventilation in Thoracoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mediators of inflammation 2018, 2018, 2575910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, H.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Xiang, L.; Wang, P.; et al. Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARgamma, C/EBPalpha, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2017, 13, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, P.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Ou, L.; Wu, Z.; et al. Changes in related circular RNAs following ERbeta knockdown and the relationship to rBMSC osteogenesis. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2017, 493, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Weng, J. A Comprehensive Bioinformatic Analysis of Cyclin-dependent Kinase 2 (CDK2) in Glioma. Gene 2022, 146325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Han, Y. Potential Roles of Cornichon Family AMPA Receptor Auxiliary Protein 4 (CNIH4) in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Research Square 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H. Clinical powers of Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase Complex Interacting Multifunctional Protein 1 (AIMP1) for head-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer biomarkers : section A of Disease markers, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Weng, J. A Pan-Cancer Bioinformatic Analysis of RAD51 Regarding the Values for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Prediction. Frontiers in oncology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T. Pan-cancer genetic analysis of cuproptosis and copper metabolism-related gene set. Frontiers in oncology 2022, 12, 952290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y. Potential roles of Cornichon Family AMPA Receptor Auxiliary Protein 4 (CNIH4) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer biomarkers : section A of Disease markers, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. A pan-cancer-bioinformatic-based literature review of TRPM7 in cancers. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2022; 108302. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Pan-cancer profiles of the cuproptosis gene set. American journal of cancer research 2022, 12, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T. Pan-cancer genetic analysis of disulfidptosis-related gene set. bioRxiv, 2023; 2023.2002.25.529997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Expression and potential immune involvement of cuproptosis in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Genetics, 2023; 274-275, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hengrui, L. An example of toxic medicine used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for cancer treatment. J Tradit Chin Med 2023, 43, 209–210. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T. A bioinformatic study of IGFBPs in glioma regarding their diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic prediction value. Am J Transl Res 2023, 15, 2140–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T. Pan-cancer genetic analysis of disulfidptosis-related gene set. Cancer Genet 2023, 278-279, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019; 20. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, S.; Bordoloi, M. Molecular Docking: Challenges, Advances and its Use in Drug Discovery Perspective. Current drug targets 2019, 20, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome biology 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Research 2019, 47 (W1), W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, D.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Shaping the interaction landscape of bioactive molecules. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, L. EVenn: Easy to create repeatable and editable Venn diagrams and Venn networks online. Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao 2021, 48, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38 (Web Server issue), W214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Current protocols in bioinformatics 2016, 54, 1.30.31–31.30.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: expanding the scope of the protein-ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49 (W1), W530–w534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Piñero, C.; Bruzzone, A.; Sarappa, M.; Castillo, L.; Lüthy, I. Involvement of α2-and β2-adrenoceptors on breast cancer cell proliferation and tumour growth regulation. British journal of pharmacology 2012, 166, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigelson, H.S.; Teras, L.R.; Diver, W.R.; Tang, W.; Patel, A.V.; Stevens, V.L.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Bouzyk, M. Genetic variation in candidate obesity genes ADRB2, ADRB3, GHRL, HSD11B1, IRS1, IRS2, and SHC1 and risk for breast cancer in the Cancer Prevention Study II. Breast cancer research : BCR 2008, 10, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; Gao, H.; Xiang, L.U.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X.; et al. Antiosteoporotic effect of icariin in ovariectomized rats is mediated via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2016, 12, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haixia, W.; Shu, M.; Li, Y.; Panpan, W.; Kehuan, S.; Yingquan, X.; Hengrui, L.; Xiaoguang, L.; Zhidi, W.; Ling, O. Effectiveness associated with different therapies for senile osteopo-rosis: a network Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2020, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- BOUHENNI, H. Study of combined effect of some medicinal plants and probiotics against Helicobacter pylori responsible for gastroduodenal diseases. Journal of Functional Foods, 2023; 107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xie, R.; Dai, Q.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, B. Exploring the mechanism underlying hyperuricemia using comprehensive research on multi-omics. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LIU, H. Toxic medicine used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for cancer treatment: are ion channels involved? Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2022, 42, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Association between sleep duration and depression: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders 2023, 335, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T. MAPK signaling pathway-based glioma subtypes, machine-learning risk model, and key hub proteins identification. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Feng, Z.; Ou, L.; Zou, Y.; Sang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Gan, G.; Zhang, G.; Yao, M. Syzygium aromaticum enhances innate immunity by triggering macrophage M1 polarization and alleviates Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Journal of Functional Foods 2023, 107, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Mukherjee, M.B.; Jin, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, K.; Liu, Q.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. The Potential Effect of General Anesthetics in Cancer Surgery: Meta-Analysis of Postoperative Metastasis and Inflammatory Cytokines. Cancers 2023, 15, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, R. Effect of Herba Epimedium Extract on Bone Mineral Density and Microstructure in Ovariectomised Rat. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences 2016, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Ou, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Effects of water extract from epimedium on neuropeptide signaling in an ovariectomized osteoporosis rat model. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2018, 221, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, H.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Xiang, L.; Wang, P.; Fang, J. Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPAR gamma, C/EBP gamma, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD, and jagged1 proteins and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats. In: International journal of molecular medicine: 2016: SPANDIDOS PUBL LTD POB 18179, ATHENS, 116 10, GREECE; 2016: S77-S77.
- Gfeller, D.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Shaping the interaction landscape of bioactive molecules. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, D.; Yeh, S.R. Human tryptophan dioxygenase: a comparison to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Am Chem Soc 2007, 129, 15690–15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théate, I.; van Baren, N.; Pilotte, L.; Moulin, P.; Larrieu, P.; Renauld, J.C.; Hervé, C.; Gutierrez-Roelens, I.; Marbaix, E.; Sempoux, C.; et al. Extensive profiling of the expression of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 protein in normal and tumoral human tissues. Cancer immunology research 2015, 3, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L. IDO in the Tumor Microenvironment: Inflammation, Counter-Regulation, and Tolerance. Trends in immunology 2016, 37, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.Y.; Muller, A.J.; Sharma, M.D.; DuHadaway, J.; Banerjee, T.; Johnson, M.; Mellor, A.L.; Prendergast, G.C.; Munn, D.H. Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells by stereoisomers of 1-methyl-tryptophan correlates with antitumor responses. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblish, H.K.; Hansbury, M.J.; Bowman, K.J.; Yang, G.; Neilan, C.L.; Haley, P.J.; Burn, T.C.; Waeltz, P.; Sparks, R.B.; Yue, E.W.; et al. Hydroxyamidine inhibitors of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase potently suppress systemic tryptophan catabolism and the growth of IDO-expressing tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 2010, 9, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.E.; Sun, L. Targeting the IDO1/TDO2-KYN-AhR Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy - Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2018, 39, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Fuchs, D.; Widner, B.; Glover, C.; Henderson, D.; Allen-Mersh, T. Serum tryptophan decrease correlates with immune activation and impaired quality of life in colorectal cancer. British journal of cancer 2002, 86, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanam, S.; Alvarado, D.; Khouri, A.; Dieckgraefe, B.; Bishnupuri, K.; Ciorba, M. PD-236 defining the signaling pathways and functional role for kynurenine metabolites in the normal and neoplastic colon epithelium. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 2017, 23, S77–S78. [Google Scholar]
- Ala, M. The footprint of kynurenine pathway in every cancer: a new target for chemotherapy. Eur J Pharmacol 2021, 896, 173921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ou, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, X. Icaritin induces MC3T3-E1 subclone14 cell differentiation through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling activation. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2017, 94, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran, N.; Lafita-Navarro, M.C.; Hao, Y.-H.; Kilgore, J.A.; Perez-Castro, L.; Braverman, J.; Borenstein-Auerbach, N.; Kim, M.; Lesner, N.P.; Mishra, P. MYC promotes tryptophan uptake and metabolism by the kynurenine pathway in colon cancer. Genes & development 2019, 33, 1236–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Hu, W.; Ji, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zang, L.; Yan, R. A positive feedback between IDO1 metabolite and COL12A1 via MAPK pathway to promote gastric cancer metastasis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mithaiwala, M.N.; Santana-Coelho, D.; Porter, G.A.; O'Connor, J.C. Neuroinflammation and the Kynurenine Pathway in CNS Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2021, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. Nav channels in cancers: Nonclassical roles. Global Journal of Cancer Therapy 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 7 (TRPM7) in Cell Viability: A Potential Target to Suppress Breast Cancer Cell Cycle. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. A prospective for the role of two-pore channels in breast cancer cells. Global Journal of Cancer Therapy 2020, 6, 001–––003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yao, M.; Xu, J.; Quan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, R.; Gao, W.-Q. Autocrine activation of CHRM3 promotes prostate cancer growth and castration resistance via CaM/CaMKK–mediated phosphorylation of Akt. Clinical cancer research 2015, 21, 4676–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wen, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. CHRM3 is a novel prognostic factor of poor prognosis in patients with endometrial carcinoma. American journal of translational research 2015, 7, 902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Gene symbol | Entrez gene summary |
| PRKDC | It functions with the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer protein in DNA double-strand break repair and recombination. The protein encoded is a member of the PI3/PI4-kinase family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010] |
| IDO1 | It is a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. This enzyme is thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation, and antioxidant activity. Through its expression in dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages this enzyme modulates T-cell behavior by its peri-cellular catabolization of the essential amino acid tryptophan. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| MIF | This gene encodes a lymphokine involved in cell-mediated immunity, immunoregulation, and inflammation. It plays a role in the regulation of macrophage function in host defense through the suppression of anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. This lymphokine and the JAB1 protein form a complex in the cytosol near the peripheral plasma membrane, which may indicate an additional role in integrin signaling pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| KCNH2 | This gene encodes a voltage-activated potassium channel belonging to the eag family. It shares sequence similarity with the Drosophila ether-a-go-go (eag) gene. Mutations in this gene can cause long QT syndrome type 2 (LQT2). Transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| CHRM3 | The muscarinic cholinergic receptors belong to a larger family of G protein-coupled receptors. The functional diversity of these receptors is defined by the binding of acetylcholine and includes cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degeneration, and potassium channel mediation. Muscarinic receptors influence many effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The muscarinic cholinergic receptor 3 controls smooth muscle contraction and its stimulation causes secretion of glandular tissue. Alternative promoter use and alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that have different tissue specificities. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016] |
| KCNN4 | The protein encoded by this gene is part of a potentially heterotetrameric voltage-independent potassium channel that is activated by intracellular calcium. Activation is followed by membrane hyperpolarization, which promotes calcium influx. The encoded protein may be part of the predominant calcium-activated potassium channel in T-lymphocytes. This gene is similar to other KCNN family potassium channel genes, but it differs enough to possibly be considered as part of a new subfamily. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Interactions | Residue | Amino acid | Distance | Amino acid changes to |
| Hydrophobic Interactions1 | 170A | VAL | 2.92 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions2 | 210A | ALA | 3.69 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions3 | 214A | PHE | 3.76 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions4 | 269A | VAL | 3.41 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions5 | 270A | PHE | 3.79 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions6 | 273A | PHE | 3.55 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions7 | 273A | PHE | 3.95 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions8 | 339A | LEU | 3.61 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions9 | 342A | LEU | 3.31 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions10 | 342A | LEU | 3.43 | SER |
| Interactions | Residue | Amino acid | Distance | Amino acid changes to |
| Hydrophobic Interactions1 | 222A | PHE | 3.56 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions2 | 222A | PHE | 3.76 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions3 | 222A | PHE | 3.67 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions4 | 226A | LEU | 3.58 | SER |
| Hydrophobic Interactions5 | 226A | LEU | 3.92 | SER |
| Hydrogen Bonds | 514A | ASN | 2.44 | ALA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




