1. Introduction
Adenosine, comprised of adenine and D-ribose, serves vital roles in all living organisms on several levels, from cellular metabolism through physiological regulation to the etiology of several diseases [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Beyond its structural role in nucleotides forming DNA or RNA molecules, it functions in energy transfer and signal transduction. Its diverse signaling and regulatory roles make adenosine a neurotransmitter and potent vasodilator [
5,
9,
10]. Intravenous administration of a restricted amount of adenosine affects the atrioventricular node to stop the arrhythmia, helps to dilate the blood vessels, and influences the blood flow [
5,
9,
11]. Adenosine overdose can lead to adverse effects, including chest pain, faintness, shortness of breath, and sensory tingling. Serious complications encompass worsening dysrhythmias and low blood pressure [
12]. Elevated adenosine levels in the blood can function as an immunotoxin, disrupting or destroying immune cells, and as a metabotoxin, causing health issues at sustained high concentrations [
13]. Chronic adenosine elevation, a consequence of adenosine deaminase deficiency (OMIM 102700), leads to severe combined immunodeficiency phenotype. Therefore, it can be concluded that the level of adenosine in the blood is a crucial parameter underlying the extent of its effects.
The intricate interplay between adenosine levels in the bloodstream and its role in regulating cardiovascular, neuronal, and immunological functions has become a subject of increasing interest and research. It is hypothesized that understanding the correlation between blood adenosine levels and its physiological responses holds significant promise for unraveling mechanisms that govern heart rate, vasodilation, and other crucial aspects of cardiovascular homeostasis. In this context, advancements in analytical techniques, such as liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) [
14], provide valuable tools for quantifying adenosine levels in blood [
15]. This method capitalizes on the synergistic combination of liquid chromatography, which separates individual components in a complex mixture, and mass spectrometry, which identifies and measures these components based on their mass-to-charge ratio. Even though several protocols for LC-based adenosine level estimation in plasma, serum, or blood have already been proposed, they operated without the appropriate internal standard reflecting the putative chemical of enzymatically stimulated changes of adenosine levels during sample processing and analysis. Those methods provided data about the level of adenosine in plasma samples of healthy donors, which varied significantly. Indeed, adenosine remained undetected or varied in ranges from 43 ±3 nM to 5.6 ±1.7 μM [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. The authors of the recently published method based on the LC-MS/MS method, when quantification of adenosine in the blood is done by using an external standard, concluded that adenosine levels in the blood are dependent on the time of investigation and may range from 0.33 ± 1.03 to 0.70 ±1.89 µM, depending on the examination time points [
15].
With the aim to establish a method that can provide a higher level of standardization, we have exploited the following: i) the possibility of enriching the blood sample with 13C-labeled adenosine before its processing and ii) the fact that adenosine is a sufficiently polar molecule for its direct injection and subsequent separation and concentration on polar columns before MS detection. In the context of adenosine analysis, we developed an LC-MS assay that is very sensitive, highly specific, and appropriately reproducible. This current method possesses the features of a reliable tool to explore the dynamic variations in adenosine concentrations within the blood. In addition, the versatility and simplicity of the designed LC-MS protocol allow for rapid and simultaneous quantification of adenosine alongside other analytes, such as inosine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine. The method may help to provide data that can contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the roles of blood adenosine in various physiological and pathological states.
2. Results and Discussion
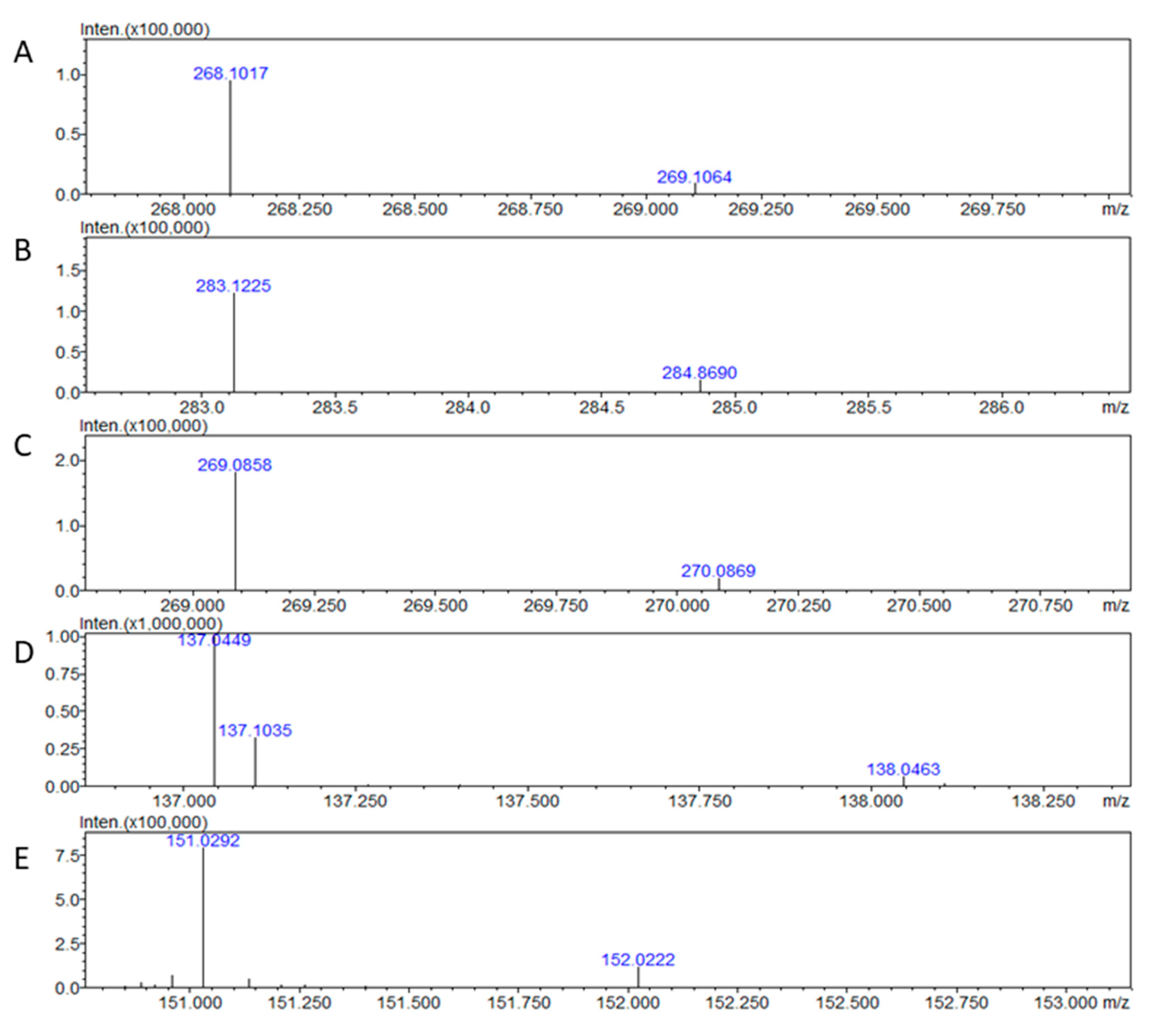
To test the capability of IT TOF-MS setup to detect adenosine, we directly injected solutions of both adenosine isotopes for primary detections and estimation of m/z values. The applied MS detection provided the signal for both isotopes of adenosine (
Figure 1A and B). The presence of adenosine peaks in obtained spectra at positive mode allowed us to estimate the values for m/z, AUP, and precision (
Table 1). In addition, the MS signals for inosine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine, which are catabolites of adenosine, were recorded too (
Figure 1C-E). The current hardware setup has not detected the uric acid.
With a focus on adenosine, we tested the possibility of its chromatographic separation on polar or ionic stationary phases. We tested three commercially available columns, SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC, SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC, and YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC.
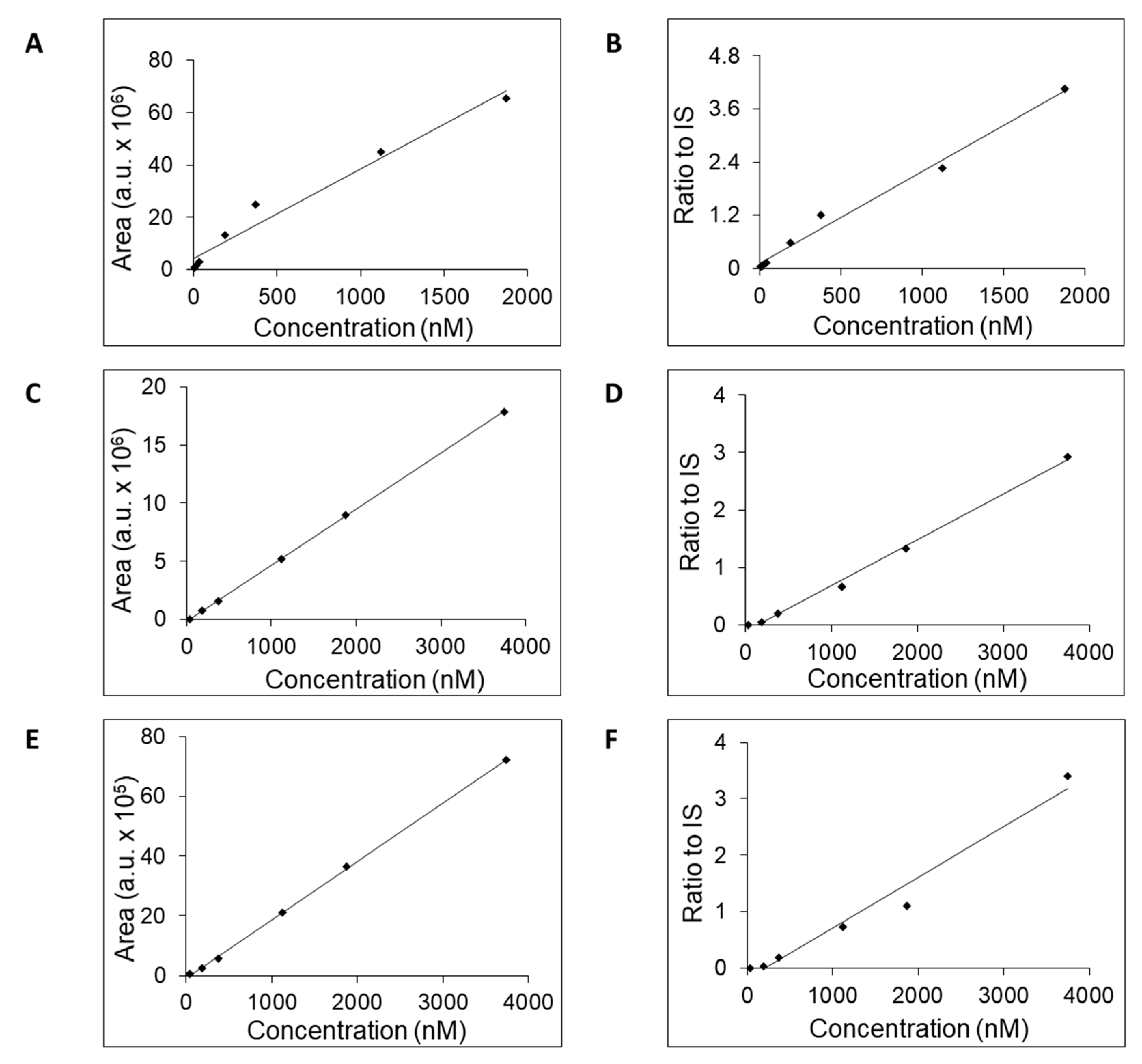
All three columns readily retained adenosine and were used to generate calibration curves (
Figure 2) and to estimate the LOQ, concentration range, linearity, and accuracy (
Table 2). For further work, we selected the column SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC due to favorable estimated values for LOQ and concentration range compared to the remaining two columns. The obtained values of SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC performance are comparable with HILIC-MS/MS protocol proposed by the research group of Gika [
15] when BEH Amide column was used.
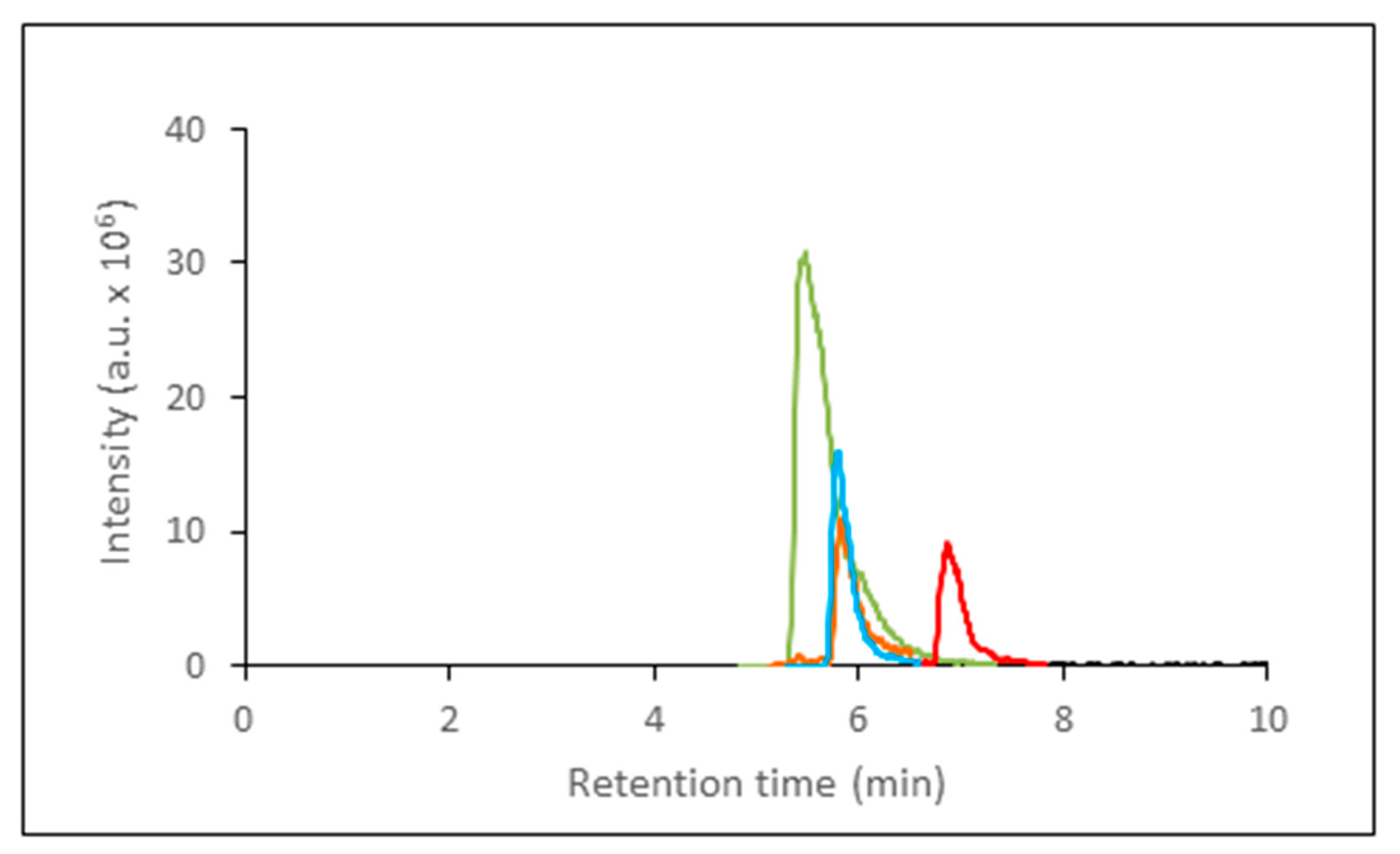
Since the column also retained inosine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine (
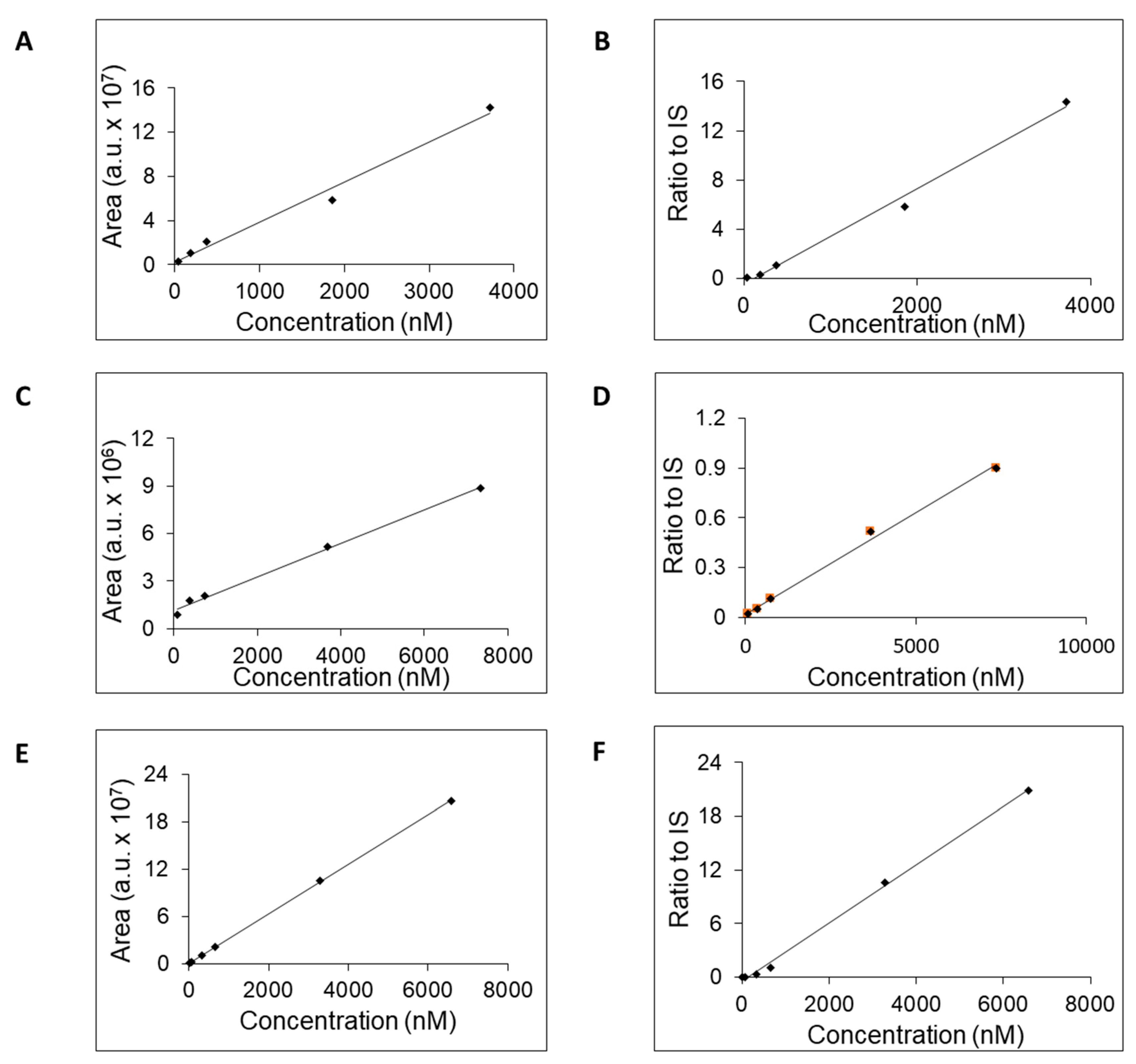
Figure 3) the calibration curves for these three compounds were generated (
Figure 4). The calibration curves were generated either without or with added isotopically enriched adenosine-13C10,15N5 that served the role of the IS. The exploitation of IS addition into the samples in the process of calibration curve generation increased their linearity (
Table 3) and accuracy [
21,
22].
To estimate the level of the total adenosine in blood, the freshly collected blood samples were transferred into the tubes containing adenosine-13C10,15N5 (see Methods part). The analysis of the processed blood samples revealed that the levels of adenosine and inosine in all tested samples are above LOQ in contrast to hypoxanthine (
Table 4). The obtained MS signal for xanthine was sufficiently high in two of five samples to allow its quantification (
Table 4). The estimated values for the molar concentration of total adenosine in blood varied from 0.1 to 4.3 µM, and of inosine were from 1.15 to 8.18 µM. Those values are comparable with already published data about the adenosine and inosine content in human fluids [
23,
24,
25]. Even the concentration of hypoxanthine in blood could reach a micromolar level [
26], the applied method did not allow it to be detected.
3. Materials and Methods
Blood samples of five randomly selected patients with repeat syncopal episodes were selected for evaluation of the method. The blood was collected and examined for blood adenosine levels during the clinical differential diagnostic process. Venous blood was taken from antecubital vein. Blood samples were processed as reported in sample processing section. All patients agreed with study participation, and signed a written informed consent for study participation prior to blood sampling.
Standards
Adenosine, inosine, xanthine, hypoxanthine, and 13C10,15N5-adenosine were purchased in highest available purity from Sigma Aldrich, Germany. The stock standard solutions in water were prepared for each compound with a mass concentration of 1 g/l. The stock solution of 13C10,15N5-adenosine was mixed with acetonitrile (Honeywell, Germany) to prepare acetonitrile enriched with 13C10,15N5-adenosine in the level of 0.1 mg/l. In this case 13C10,15N5-adenosine served the role of internal standard (IS). All other stock standard solutions were diluted to a solution containing 90 % (V/V) acetonitrile enriched with IS. For all experiments ultra-pure water generated by Milli-Q instrument was used, the resistivity of water was at least 18.2 MΩ·cm at 25 °C; with total organic carbon ≤ 5 ppb.
Collection tubes preparation
From solution containing 10 µg/ml of IS in acetonitrile, 100 μl was added into plastic collection tubes (BioRad, USA). The tubes were weight before and after addition of solution with internal standard. Mass difference of empty tubes and tubes with IS solution, served for calculation of exact volume of adenosine solution in acetonitrile with the aim to estimate the amount of adenosine that remains in tube after subsequent evaporation in Concentrator plus (Eppendorf, Germany). For this calculation the used value of density for acetonitrile was 786 kg/m3.
Sample processing
After collection, 0.5 ml of blood was transferred to prepared tubes containing 0.1 µg of IS and mixed with 1.5 ml of acetonitrile. Samples were stored then at -20 °C. Before analysis samples were vortexed and centrifuged at 10 000x g for 10 minutes. Subsequently 100 µl of supernatant were diluted with 400 µl of acetonitrile, frozen for 30 minutes at -20 °C for protein precipitation and following centrifugation at 10 000x g for 10 minutes. Supernatants were collected and transferred to glass vials for LC-MS analysis.
Liquid chromatography—mass spectrometry analysis
Prepared samples were analysed on LC-ESI-IT-TOF setup (Shimadzu, Japan) consisting of Liquid Chromatograph Nexera X2 and IT-TOFTM mass spectrometer. Part for liquid chromatography includes degasser (DGU-20A3R), two high pressure pumps (LC-30AD), autosampler (SIL-30AC), thermostat (CTO-20AC) and communication module (CBM-20A). For chromatographic separation of adenosine were tested three commercialy available columns, i.e., SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC (3 µm, 100 A, 150 x 2.1 mm) (Sigma Aldrich, Germany), SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC (5 µm, 150 x 2.1 mm )(Sigma Aldrich, Germany) and YMC-Triart-Diol-HILIC (1.9 µm, 150 x 2.1 mm) (YMC, Germany).
Two µl of sample were injected to LC-MS via autosampler at 4 °C. For chromatography separation on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC and SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC columns, the columns were equilibrated with initial composition of mobile phases for gradient elution. Applied gradient was as follows. Mobile phase A consists of 20 mM ammonium formate (Sigma Aldrich, Germany) solution in water and B of 100 % acetonitrile (Honeywell, USA). Initial conditions were 10 % A at a total flow rate of 0.2 ml/min. Subsequently, gradient changed to 80 % A in 24 min. After that, A returned to 10 % in 6 min and for additional 2 min was used to requilibrate the column before next injection. Chromatographic separation was run at 40 °C.
For chromatographic separation on YMC-Triart-Diol-HILIC column the same solutions A and B were used. The sample was injected on column that was preequilibrated with 10% A. Subsequently, the gradient changed to 60 % A in 13 min and then returned back to 10 % of A in during 7 min. The column was equilibrated with 10 % A for next 3 min.
Data were acquired in both modes, positive and negative. Ion spray voltage was set to 4.5 kV for positive and -3.5 kV for negative mode, and ion accumulation time was 40 ms. The temperature of the heat block and capillary desolvation line were 200 °C. Nitrogen nebulizing gas flow was 1.5 l/min and drying gas pressure was set to 200 kPa. The hardware was operated by LCMS Solutions v. 3.81 (Shimadzu) software.
The chromatographic separation was omitted to test the capability of the used setup to detect the componds of interest. In this case, direct injection mass spectrometry analysis (DIMS) was performed by injecting of two µl of standard solution with dissolved compound to mass concentration of 1 µg in one ml of solution A.
Data analysis
Acquired spectra were directly converted to mzxml format with LCMS Solutions v. 3.81 (Shimadzu) software and imported to Skyline v. 23.1. (MacCross Lab Software), an open source software for LC-MS data processing (
https://skyline.ms). Peaks of individual metabolites were extracted in order to obtain information such as mass to charge ratio (m/z), retention time and area under the peak (AUP). Metabolites identification was based on confirmation of retention time and m/z with standards. Mass to charge ratios were also confirmed with online libraries such as Pubchem (
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and mzCloud (
https://www.mzcloud.org/).
IS was used to obtain ratios for all analytes by dividing AUP of analyte with AUP of IS. Accuracy percentage was estimated by division of measured concentration and theoretical concentration for each concentration point in calibration curve. Precision is expressed as relative standard deviation of AUP or ratios by repeating measurement of the same sample. Limit of quantification is lowest concentration point in calibration curve. Linearity of the method was estimated by construction of calibration curve and calculation of coefficient of determination (R2).
4. Conclusions
We proposed and tested the method for estimation of adenosine and several of its catabolites in blood by LC-MS analysis. This method is based on the enrichment of a tested sample with adenosine-13C10,15N5, which serves the role of inert standard, and retention of adenosine on the polar stationary phase before MS detection. Such a procedure offers high sensitivity for detecting adenosine and its catabolites in blood even at low concentrations, which is crucial for studying its regulatory roles in different physiological processes. The integration of LC-MS into adenosine research not only refines the ability to quantify this nucleoside and its catabolites in blood accurately but also opens avenues for exploring its associations with cardiovascular dynamics, paving the way for a deeper understanding of its physiological significance and potential implications for cardiovascular health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M., R.P., M.S. and R.M.; methodology, J.Š., P.M., Z.L., R. M., validation, P.M., Z.L., M.J.P., T.B., M.S. and R.M.; formal analysis, J.Š. and R.M.; investigation, J.Š., P.M., Z.L., M.J.P., T.B., M.S. and R.M.; resources, P.M., Z.L., M.J.P., T.B., R.P. and M.S.; data curation, J.Š., P.M. and R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Š., M.S. and R.M..; writing—review and editing, J.Š., P.M., Z.L., M.J.P., T.B., R.P., M.S. and R.M.; visualization, J.Š.; supervision, M.S. and R.M.; project administration, R.M.; funding acquisition, P.M. and R.M.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee VUSCH, approval code: 21012019 on January 21th, 2019.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available under the request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Andrea Petrovská for her invaluable help in mathematical modeling of the probability of natural occurrence of individual isotopes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Boison, D.; Yegutkin, G.G. Adenosine Metabolism: Emerging Concepts for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwiddie, T.V.; Masino, S.A. The Role and Regulation of Adenosine in the Central Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, BB Adenosine, an Endogenous Distress Signal, Modulates Tissue Damage and Repair. Cell Death Differ 2007, 14, 1315–1323. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Camici, M.; Allegrini, S.; Pesi, R.; Tozzi, M.G. Metabolic Aspects of Adenosine Functions in the Brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 672182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guieu, R.; Deharo, J.-C.; Maille, B.; Crotti, L.; Torresani, E.; Brignole, M.; Parati, G. Adenosine and the Cardiovascular System: The Good and the Bad. JCM 2020, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskó, G.; Antonioli, L.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine Metabolism, Immunity and Joint Health. Biochemical Pharmacology 2018, 151, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, A. A Metabolic Immune Checkpoint: Adenosine in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegutkin, G.G.; Boison, D. ATP and Adenosine Metabolism in Cancer: Exploitation for Therapeutic Gain. Pharmacol Rev 2022, 74, 799–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headrick, J.P.; Ashton, K.J.; Rose’Meyer, R.B.; Peart, J.N. Cardiovascular Adenosine Receptors: Expression, Actions and Interactions. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2013, 140, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudry, M.; Vairo, D.; Marlinge, M.; Gaubert, M.; Guiol, C.; Mottola, G.; Gariboldi, V.; Deharo, P.; Sadrin, S.; Maixent, J.M.; et al. Adenosine and Its Receptors: An Expected Tool for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Coronary Artery and Ischemic Heart Diseases. IJMS 2020, 21, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieu, R.; Deharo, J.-C.; Ruf, J.; Mottola, G.; Kipson, N.; Bruzzese, L.; Gerolami, V.; Franceschi, F.; Ungar, A.; Tomaino, M.; et al. Adenosine and Clinical Forms of Neurally-Mediated Syncope. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2015, 66, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altstidl, J.M.; Gaede, L.; Troebs, M.; Marwan, M.; Achenbach, S. Side Effects and Major Adverse Cardiac Events Caused by Fractional Flow Reserve Measurement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 12,215 Patients. European Heart Journal 2022, 43, ehac5442022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pathological Overproduction: The Bad Side of Adenosine. British J Pharmacology 2017, 174, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handbook of Advanced Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Techniques; Holčapek, M. , Byrdwell, W.C., Eds.; Elsevier, Academic Press, AOCS Press: London, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-811732-3. [Google Scholar]
- Virgiliou, C.; Fragakis, N.; Sotiriadou, M.; Vassilikos, V.; Gerou, S.; Theodoridis, G.; Gika, H. HILIC-MS/MS Analysis of Adenosine in Patient Blood. Separations 2021, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Jáuregui, O.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Andrés-Lacueva, C. Characterization of the Human Exposome by a Comprehensive and Quantitative Large-Scale Multianalyte Metabolomics Platform. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13767–13775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capogrossi, M.C. ; Holdiness, MR; Israili, Z. H. Determination of Adenosine in Normal Human Plasma and Serum by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 1982, 227, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontyd, J.; Schrader, J. Measurement of Adenosine, Inosine, and Hypoxanthine in Human Plasma. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 1984, 307, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thane Eells, J.; Spector, R. Purine and Pyrimidine Base and Nucleoside Concentrations in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma. Neurochem Res 1983, 8, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, I.; Hoelzl, A.; Schliephake, F.; Hummel, T.; Chouker, A.; Lysenko, L.; Peter, K.; Thiel, M. EFFECTS OF ADENOSINE ON FUNCTIONS OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES FROM PATIENTS WITH SEPTIC SHOCK. Shock 2007, 27, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Boudreau, N.; Lévesque, A. Internal Standards for Quantitative LC-MS Bioanalysis. In LC-MS in Drug Bioanalysis; Xu, Q.A., Madden, TL, Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2012; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-1-4614-3828-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, A.; Furtado, M.; Garofolo, F. Importance of Using Highly Pure Internal Standards for Successful Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometric Bioanalytical Assays. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2009, 23, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traut, T.W. Physiological Concentrations of Purines and Pyrimidines. Mol Cell Biochem 1994, 140, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Metabolome Database: Showing Metabocard for Adenosine (HMDB0000050) Available online:. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000050 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Human Metabolome Database: Showing Metabocard for Inosine (HMDB0000195) Available online:. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000195 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Human Metabolome Database: Showing Metabocard for Hypoxanthine (HMDB0000157) Available online:. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000157 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
Figure 1.
Mass spectra were obtained for adenosine-12C10,14N5 (A), adenosine-13C10,15N5 (B), inosine (C), hypoxanthine (D), and xanthine (E). The spectra were obtained after direct injection of 2 ng of each compound in an IT-TOF mass spectrometer.
Figure 1.
Mass spectra were obtained for adenosine-12C10,14N5 (A), adenosine-13C10,15N5 (B), inosine (C), hypoxanthine (D), and xanthine (E). The spectra were obtained after direct injection of 2 ng of each compound in an IT-TOF mass spectrometer.
Figure 2.
Calibration curves of adenosine obtained by LC-MS analysis either on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC (A, B), or SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC (B, C), or YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC (E, F) column. The adenosine concentration was plotted against its AUC values (A, C, E) or the calculated ratios of AUC values for adenosine to IS (B, D, F).
Figure 2.
Calibration curves of adenosine obtained by LC-MS analysis either on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC (A, B), or SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC (B, C), or YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC (E, F) column. The adenosine concentration was plotted against its AUC values (A, C, E) or the calculated ratios of AUC values for adenosine to IS (B, D, F).
Figure 3.
Representative chromatogram of adenosine (green), xanthine (blue), hypoxanthine (orange), and inosine (red) after their separation on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC column. The compounds were detected after elution based on their m/z values by IT-TOF-MS.
Figure 3.
Representative chromatogram of adenosine (green), xanthine (blue), hypoxanthine (orange), and inosine (red) after their separation on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC column. The compounds were detected after elution based on their m/z values by IT-TOF-MS.
Figure 4.
Calibration curves of inosine (A, B), hypoxanthine (C, D), and xanthine (E, F) as measured AUC values (A, C, E) or calculated ratio to IS (B, D, F).
Figure 4.
Calibration curves of inosine (A, B), hypoxanthine (C, D), and xanthine (E, F) as measured AUC values (A, C, E) or calculated ratio to IS (B, D, F).
Table 1.
Estimated values of m/z, average values of area under the peak (AUP) for both isotopes of adenosine, and precision of measurement. Two ng of each adenosine isotope were directly injected into the IT-TOF mass spectrometer. Each isotope was injected six times (n = 6).
Table 1.
Estimated values of m/z, average values of area under the peak (AUP) for both isotopes of adenosine, and precision of measurement. Two ng of each adenosine isotope were directly injected into the IT-TOF mass spectrometer. Each isotope was injected six times (n = 6).
| Compound |
m/z |
AUP |
Precision |
| 106 a.u. |
% |
|
12C10,14N5-Adenosine |
268.1016 ±0.0004 |
31.3 ±5.4 |
17.4 |
|
13C10,15N5-Adenosine |
283.1212 ±0.0008 |
30.5 ±5.5 |
18.0 |
| Ratio |
- |
1.10 ±0.01 |
0.6 |
Table 2.
Acquired parameters for adenosine separation on three tested columns. The concentration ranges and parameters of linearity for calibration curves either for solutions of adenosine either without or enriched with internal standard (IS).
Table 2.
Acquired parameters for adenosine separation on three tested columns. The concentration ranges and parameters of linearity for calibration curves either for solutions of adenosine either without or enriched with internal standard (IS).
| Column |
Retention time |
Concentration
range |
Linearity (R2) |
LOQ |
Accuracy |
| min |
nM |
w/o IS |
w IS1
|
nM |
% |
| SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC |
5.5 |
3.75–1872 |
0.9702 |
0.9882 |
3.75 |
103.9 |
| SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC |
4.9 |
37.45–3745 |
0.9998 |
0.9955 |
37.45 |
125.3 |
| YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC |
5.5 |
37.45–3745 |
0.9996 |
0.9716 |
37.45 |
117.4 |
Table 3.
The values of retention times, m/z, and linearities for inosine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and adenosine estimated by LC-MS analysis, while separation was done on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC column.
Table 3.
The values of retention times, m/z, and linearities for inosine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and adenosine estimated by LC-MS analysis, while separation was done on SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC column.
| Compound |
Retention time |
Concentration range |
Linearity (R2) |
LOQ |
| |
min |
nM |
w/o IS |
w IS |
nM |
| Inosine |
6.9 |
37.2–3718 |
0.9858 |
0.9922 |
37.2 |
| Hypoxanthine |
5.8 |
73.5–7353 |
0.9951 |
0.9946 |
73.5 |
| Xanthine |
5.8 |
6.5–6579 |
0.9998 |
0.9977 |
6.5 |
| Adenosine |
5.5 |
3.75–1872 |
0.9702 |
0.9882 |
3.75 |
Table 4.
The estimated concentrations of total adenosine, inosine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine in blood samples from syncopic patients. Each sample was analyzed twice.
Table 4.
The estimated concentrations of total adenosine, inosine, hypoxanthine, and xanthine in blood samples from syncopic patients. Each sample was analyzed twice.
| Samples |
[Adenosine]
(µM) |
[Inosine]
(µM) |
[Xanthine]
(µM) |
| sample 1 |
0.92 |
1.66 |
< LOQ |
| sample 2 |
4.33 |
8.18 |
70.42 |
| sample 3 |
0.13 |
1.15 |
1.38 |
| sample 4 |
0.36 |
1.29 |
< LOQ |
| sample 5 |
2.78 |
3.66 |
< LOQ |
| Average ±SD |
1.7 ±1.8 |
3.2 ±3.0 |
ND. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).