Submitted:
02 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Characteristics
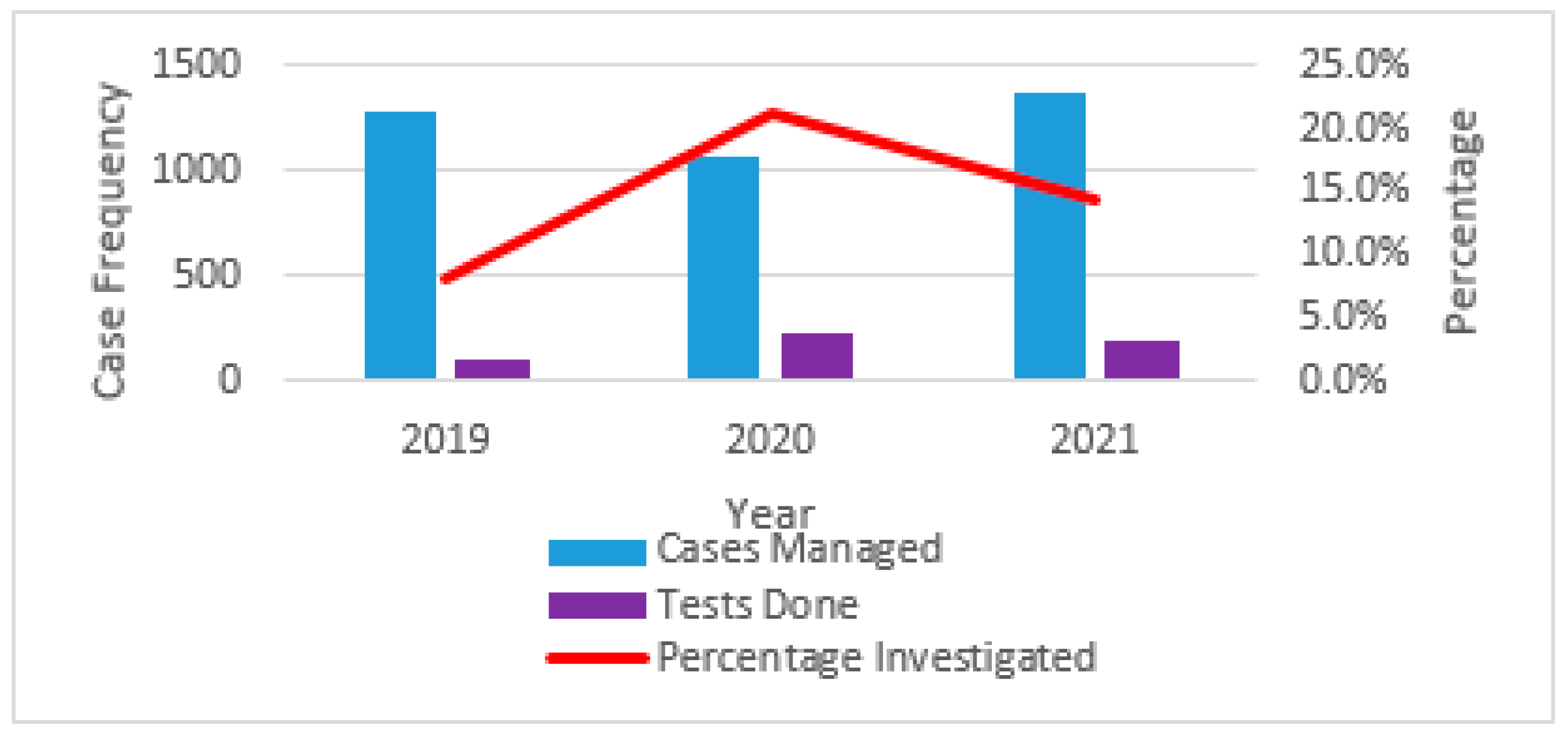
2.2. Prevalence of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
2.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Selected Bacteria Responsible for Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections
2.3.1. Major Bacteria Responsible for the Observed SSTI
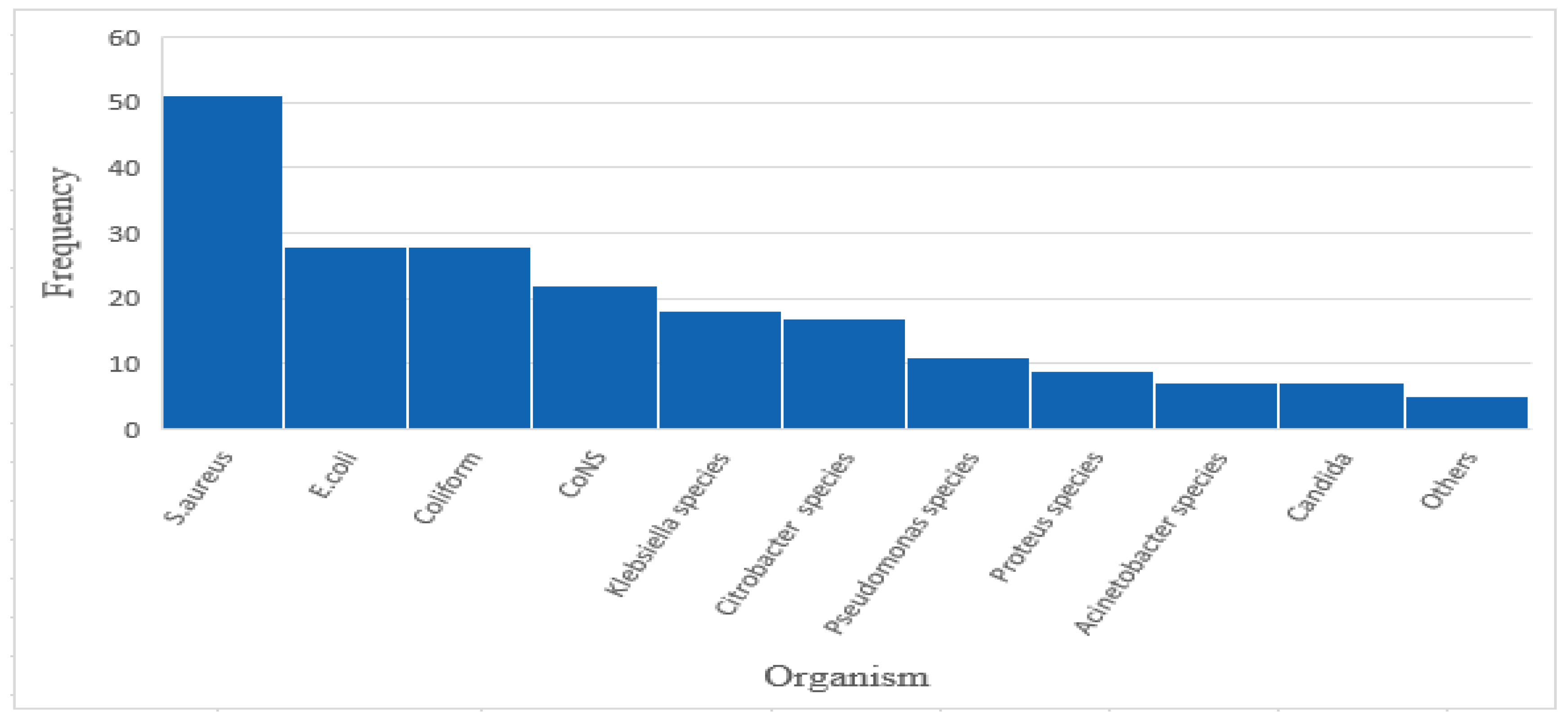
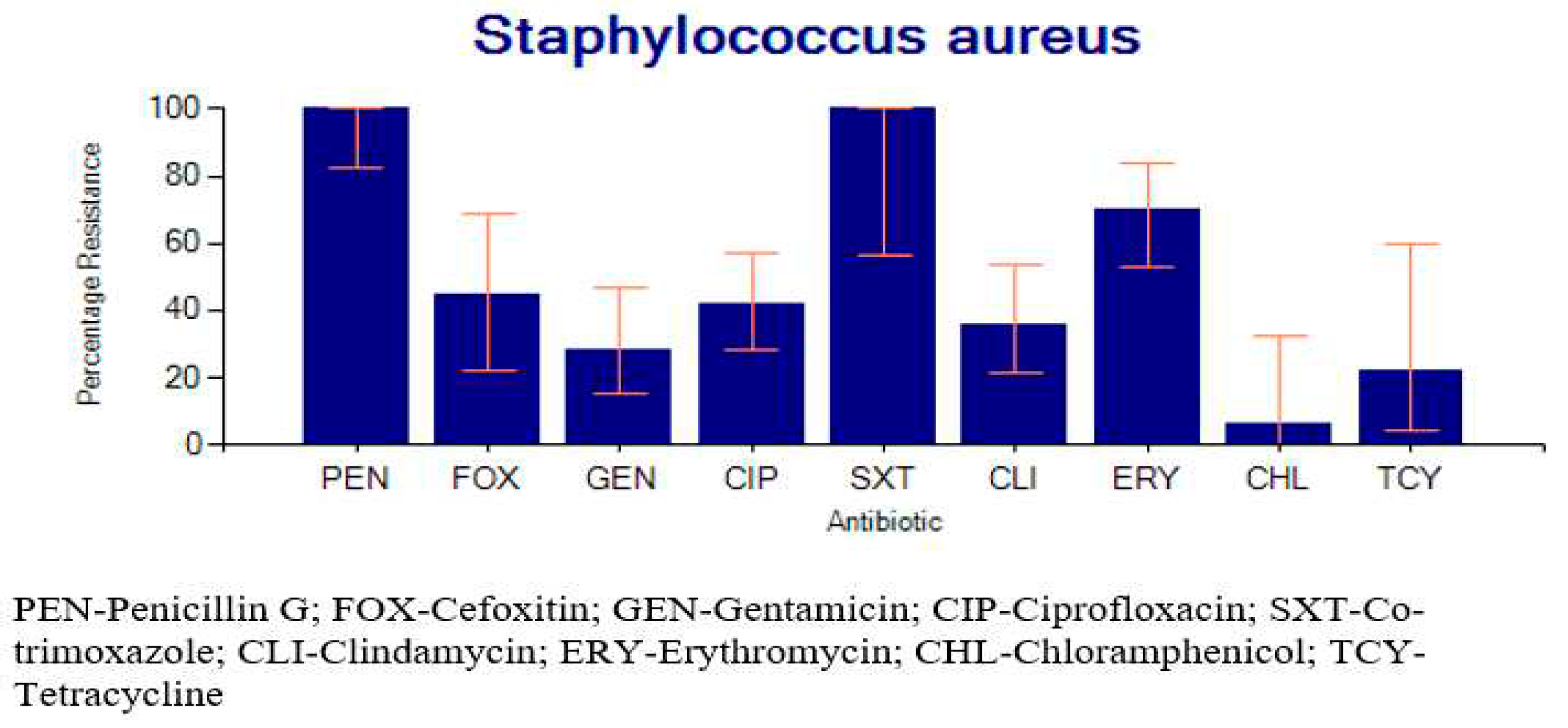
2.3.2. Percentage Resistance of the Bacteria to Common Antibiotics
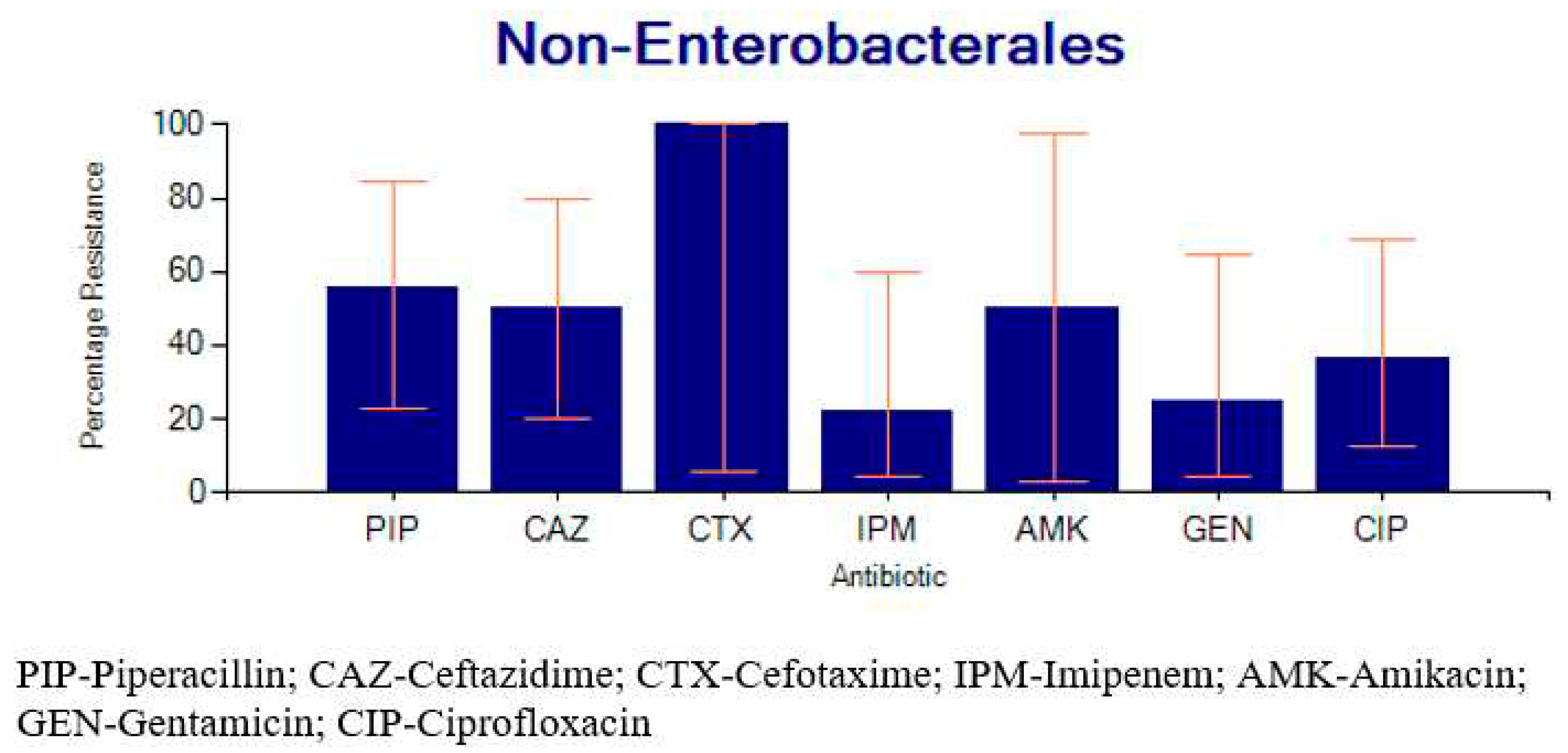
2.4. Factors Associated with SSTI
2.5. Factors Associated with MDR Pathogens Responsible for SSTI.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Setting
4.3. Laboratory Procedures
4.4. Study Population and Sampling
4.5. Data Collection
4.5.1. Extraction of Laboratory Generated Data
4.5.2. Review of Patients’ Files
4.5.3. Data Extraction from the District Health Information System
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Kiggundu R, Wittenauer R, Waswa J, Nakambale HN, Kitutu FE, Murungi M, et al. Point prevalence survey of antibiotic use across 13 hospitals in Uganda. Antibiotics. 2022;11(2):199. [CrossRef]
- Lai PS, Bebell LM, Meney C, Valeri L, White MC. Epidemiology of antibiotic-resistant wound infections from six countries in Africa. BMJ global health. 2018;2(Suppl 4):e000475. [CrossRef]
- O'neill J. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. Rev Antimicrob Resist. 2014.
- Mestrovic T, Aguilar GR, Swetschinski LR, Ikuta KS, Gray AP, Weaver ND, et al. The burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO European region in 2019: A cross-country systematic analysis. The Lancet Public Health. 2022;7(11):e897-e913. [CrossRef]
- Bonniface M, Nambatya W, Rajab K. An evaluation of antibiotic prescribing practices in a rural refugee settlement district in Uganda. Antibiotics. 2021;10(2):172. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary NA, Munawar MD, Khan MT, Rehan K, Sadiq A, Bhatti HW, et al. Epidemiology, bacteriological profile, and antibiotic sensitivity pattern of burn wounds in the burn unit of a tertiary care hospital. Cureus. 2019;11(6). [CrossRef]
- Okello N, Oloro J, Kyakwera C, Kumbakumba E, Obua C. Antibiotic prescription practices among prescribers for children under five at public health centers III and IV in Mbarara district. PLoS One. 2020;15(12):e0243868. [CrossRef]
- Peetermans M, de Prost N, Eckmann C, Norrby-Teglund A, Skrede S, De Waele J. Necrotizing skin and soft-tissue infections in the intensive care unit. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2020;26(1):8-17. [CrossRef]
- Sartelli M, Guirao X, Hardcastle TC, Kluger Y, Boermeester M, Raşa K, et al. 2018 WSES/SIS-E consensus conference: recommendations for the management of skin and soft-tissue infections. World Journal of Emergency Surgery. 2018;13(1):1-24. [CrossRef]
- Uganda, Go. Uganda National National Action Plan for Antimicrobial Resistance 2018-2023 [cited 2023 29/11/2023]. Available from: https://www.cphl.go.ug/sites/default/files/2020-02/Uganda%20National%20Action%20Plan%20for%20Antimicrobial%20Resistance%202018-%202023-compressed_0.pdf.
- Alamrew K, Tadesse TA, Abiye AA, Shibeshi W. Surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis and incidence of surgical site infections at Ethiopian Tertiary-Care Teaching Hospital. Infectious Diseases: Research and Treatment. 2019;12:1178633719892267. [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, T. The burden of aerobic bacterial nosocomial infections, associated risk factors and antibiotic susceptibility patterns in a surgical site in Ethiopia: A systematic review. J Surg Surgical Res. 2020;6(2):126-32.
- Kefale B, Tegegne GT, Degu A, Molla M, Kefale Y. Surgical site infections and prophylaxis antibiotic use in the surgical ward of public hospital in Western Ethiopia: a hospital-based retrospective cross-sectional study. Infection and Drug Resistance. 2020:3627-35. [CrossRef]
- Morgan E, Hohmann S, Ridgway JP, Daum RS, David MZ. Decreasing incidence of skin and soft-tissue infections in 86 US emergency departments, 2009–2014. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2019;68(3):453-9. [CrossRef]
- Mancuso G, Midiri A, Gerace E, Biondo C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens. 2021;10(10). [CrossRef]
- Salamzade R, Manson AL, Walker BJ, Brennan-Krohn T, Worby CJ, Ma P, et al. Inter-species geographic signatures for tracing horizontal gene transfer and long-term persistence of carbapenem resistance. Genome Medicine. 2022;14(1):37. [CrossRef]
- Chaoui L, Mhand R, Mellouki F, Rhallabi N. Contamination of the surfaces of a health care environment by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. International journal of microbiology. 2019;2019. [CrossRef]
- Dégbey C, Kpozehouen A, Coulibaly D, Chigblo P, Avakoudjo J, Ouendo E-M, et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated With Surgical Site Infections in the University Clinics of Traumatology and Urology of the National University Hospital Centre Hubert Koutoukou Maga in Cotonou. Frontiers in Public Health. 2021;9:629351. [CrossRef]
- Wong KA, Holloway S. An observational study of the surgical site infection rate in a General Surgery Department at a General Hospital in Malaysia. Wounds Asia. 2019;2(2):10-9.
- Alkaaki A, Al-Radi OO, Khoja A, Alnawawi A, Alnawawi A, Maghrabi A, et al. Surgical site infection following abdominal surgery: a prospective cohort study. Canadian journal of surgery. 2019;62(2):111. [CrossRef]
- Lakoh S, Yi L, Sevalie S, Guo X, Adekanmbi O, Smalle IO, et al. Incidence and risk factors of surgical site infections and related antibiotic resistance in Freetown, Sierra Leone: a prospective cohort study. Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control. 2022;11(1):1-12. [CrossRef]
- Wang B, Xiao X, Zhang J, Han W, Hersi SA, Tang X. Epidemiology and microbiology of fracture-related infection: a multicenter study in Northeast China. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2021;16(1):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Liang Z, Rong K, Gu W, Yu X, Fang R, Deng Y, et al. Surgical site infection following elective orthopaedic surgeries in geriatric patients: incidence and associated risk factors. International Wound Journal. 2019;16(3):773-80. [CrossRef]
- Zejnullahu VA, Isjanovska R, Sejfija Z, Zejnullahu VA. Surgical site infections after cesarean sections at the University Clinical Center of Kosovo: rates, microbiological profile and risk factors. BMC infectious diseases. 2019;19(1):1-9.
- Sway A, Nthumba P, Solomkin J, Tarchini G, Gibbs R, Ren Y, et al. Burden of surgical site infection following cesarean section in sub-Saharan Africa: a narrative review. International journal of women's health. 2019:309-18. [CrossRef]
- Sisay M, Worku T, Edessa D. Microbial epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance patterns of wound infection in Ethiopia: a meta-analysis of laboratory-based cross-sectional studies. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2019;20(1):1-19. [CrossRef]
- Wangoye K, Mwesigye J, Tungotyo M, Twinomujuni Samba S. Chronic wound isolates and their minimum inhibitory concentrations against third generation cephalosporins at a tertiary hospital in Uganda. Scientific Reports. 2022;12(1):1195. [CrossRef]
- Hope D, Ampaire L, Oyet C, Muwanguzi E, Twizerimana H, Apecu RO. Antimicrobial resistance in pathogenic aerobic bacteria causing surgical site infections in Mbarara regional referral hospital, Southwestern Uganda. Scientific reports. 2019;9(1):17299. [CrossRef]
- Wekesa YN, Namusoke F, Sekikubo M, Mango DW, Bwanga F. Ceftriaxone-and ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella species, Escherichia coli, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus dominate caesarean surgical site infections at Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda. SAGE Open Medicine. 2020;8:2050312120970719. [CrossRef]
- Mukagendaneza MJ, Munyaneza E, Muhawenayo E, Nyirasebura D, Abahuje E, Nyirigira J, et al. Incidence, root causes, and outcomes of surgical site infections in a tertiary care hospital in Rwanda: a prospective observational cohort study. Patient Safety in Surgery. 2019;13:1-8. [CrossRef]
- Kaye KS, Petty LA, Shorr AF, Zilberberg MD. Current epidemiology, etiology, and burden of acute skin infections in the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2019;68(Supplement_3):S193-S9. [CrossRef]
- Pal S, Sayana A, Joshi A, Juyal D. Staphylococcus aureus: A predominant cause of surgical site infections in a rural healthcare setup of Uttarakhand. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 2019;8(11):3600. [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska I, Ziółkowski G, Wójkowska-Mach J, Bielecki T. Can surgical site infections be controlled through microbiological surveillance? A three-year laboratory-based surveillance at an orthopaedic unit, retrospective observatory study. International orthopaedics. 2019;43:2009-16. [CrossRef]
- Alfouzan W, Al Fadhli M, Abdo N, Alali W, Dhar R. Surgical site infection following cesarean section in a general hospital in Kuwait: trends and risk factors. Epidemiology & Infection. 2019;147:e287. [CrossRef]
- GLASS. GLASS manual for antimicrobial resistance surveillance in common bacteria causing human infection. 2023 [cited 2023 29/11/2023]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/372741/9789240076600-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.28th ed. CLSI guideline M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2018.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.30th ed. CLSI guideline M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2020.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.31st ed. CLSI guideline M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2021.
- Kizito, O. Comparative study of proportions of post-operative sepsis _ maternity versus general surgical ward. Cogent Medicine. 2021;8(1):1889100. [CrossRef]
- Chellan G, Shivaprakash S, Karimassery Ramaiyar S, Varma AK, Varma N, Thekkeparambil Sukumaran M, et al. Spectrum and prevalence of fungi infecting deep tissues of lower-limb wounds in patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2010;48(6):2097-102. [CrossRef]
- Kalan L, Grice EA. Fungi in the Wound Microbiome. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2018;7(7):247-55. [CrossRef]
- Yousif SM, Abakar AD, Nour BY, Ibrahim SO, Elhasan OMA, Yousif MA, et al. Frequency and antimicrobials susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus associated with wound infections in surgery department, wad madani teaching hospital, sudan. Pharmacology & Pharmacy. 2021;12(12):334-43. [CrossRef]
- Alsehemi AF, Alharbi EA, Alammash BB, Alrais AI, Elbadawy HM, Alahmadi YM. Assessment of risk factors associated with multidrug-resistant organism infections among patients admitted in a tertiary hospital - a retrospective study. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2023;31(6):1084-93. [CrossRef]
- Ray GT, Suaya JA, Baxter R. Incidence, microbiology, and patient characteristics of skin and soft-tissue infections in a U.S. population: a retrospective population-based study. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2013;13(1):252. [CrossRef]
- Almuhayawi MS, Alruhaili MH, Gattan HS, Alharbi MT, Nagshabandi M, Al Jaouni S, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Induced Wound Infections Which Antimicrobial Resistance, Methicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant: Assessment of Emergence and Cross Sectional Study. Infect Drug Resist. 2023;16:5335-46. [CrossRef]
- Denis Edema, JN. Six dead, 11 injured as cement truck rams into taxi along Jinja-Kampala highway: Monitor; 2022 [Available from: https://www.monitor.co.ug/uganda/news/national/six-dead-11-injured-as-cement-truck-rams-into-taxi-along-jinja-kampala-highway-4045636.
- Onyango, J. One critically injured in accident involving 3 vehicles: NTV; 2023 [Available from: https://www.ntv.co.ug/ug/news/national/one-critically-injured-in-accident-involving-3-vehicles-4136380.
- Richard N. Fatal Jinja Road Accident: Next media; 2021 [Available from: https://nbs.ug/2021/12/fatal-jinja-road-accident/.
- Jinja-RRH. About Jinja Regional Referral Hospital 2022 [cited 2023 09/09/2023]. Available from: https://jinjahospital.go.ug/about-us/.
- SANAS. Accredited organizations/Medical Laboratories/Jinja Regional Referral Hospital Laboratory 2021 [cited 2023 09/09/2023]. Available from: https://www.sanas.co.za/Pages/index.aspx.
- Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(3):268-81. [CrossRef]
| Variable | n | (%) | |
| Year of Case | 2019 | 44 | 16.4 |
| 2020 | 120 | 44.8 | |
| 2021 | 104 | 38.8 | |
| Sex | Male | 148 | 55.2 |
| Female | 120 | 44.8 | |
| Age Category | ≤12 | 48 | 17.9 |
| 13-18 | 31 | 11.6 | |
| 19-35 | 84 | 31.3 | |
| 36-59 | 76 | 28.4 | |
| ≥60 | 29 | 10.8 | |
| Ward/Department | Accidents and emergency | 16 | 6.0 |
| Gynecology | 13 | 4.9 | |
| Maternity | 15 | 5.6 | |
| Medical | 15 | 5.6 | |
| Surgical | 88 | 33 | |
| Outpatient Department | 38 | 14.2 | |
| Orthopedics | 34 | 12.7 | |
| Private wing | 8 | 3.0 | |
| Pediatrics | 10 | 3.7 | |
| Others | 31 | 11.6 | |
| Unknown | 51 | 19 | |
| On antibiotics before testing | Yes | 176 | 65.7 |
| No | 92 | 34.3 | |
| Undergoing surgery | Yes | 11 | 4.1 |
| No | 98 | 36.6 | |
| Unknown | 159 | 59.3 | |
| Ward/Department | Total no. of Patients |
Infection Frequency |
Percentage |
| Pediatrics | 10 | 8 | 80 |
| Medical | 15 | 8 | 53 |
| Accidents and emergency | 16 | 7 | 43.7 |
| Surgical | 88 | 66 | 75 |
| Outpatient | 38 | 25 | 65.7 |
| Maternity | 15 | 8 | 53 |
| Orthopedics | 34 | 20 | 58.8 |
| Private | 8 | 6 | 75 |
| Antenatal | 13 | 7 | 53.8 |
| Others | 31 | 23 | 74.2 |
| Antibiotic name | Antibiotic class | Breakpoints | NumberTested | %R | %I | %S | %R, 95%C.I. | %S, 95%C.I. |
| *Cefoxitin | Cephems | S >= 22 | 18 | 44.4 | 0.0 | 55.6 | 22.4-68.7 | 31.3-77.6 |
| Chloramphenicol | Phenicols | 13 - 17 | 16 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 81.3 | 0.3-32.3 | 53.7-95.0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | Quinolones | 16 - 20 | 48 | 41.7 | 16.7 | 41.7 | 27.9-56.7 | 27.9-56.7 |
| Clindamycin | Lincosamides | 15 - 20 | 36 | 36.1 | 16.7 | 47.2 | 21.3-53.8 | 30.8-64.3 |
| Erythromycin | Macrolides | 14 - 22 | 37 | 70.3 | 21.6 | 8.1 | 52.8-83.6 | 2.1-23.0 |
| Gentamicin | Aminoglycosides | 13 - 14 | 35 | 28.6 | 8.6 | 62.9 | 15.2-46.5 | 44.9-78.0 |
| Penicillin G | Penicillins | S >= 29 | 23 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 82.2-100 | 0.0-17.8 |
| Tetracycline | Tetracyclines | 15 - 18 | 9 | 22.2 | 44.4 | 33.3 | 3.9-59.8 | 9.0-69.1 |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | Folate pathway inhibitors | 11 - 15 | 7 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.1-100 | 0.0-43.9 |
| Antibiotic name | Antibiotic class | Breakpoints | NumberTested | %R | %I | %S | %R, 95%C.I. | %S,95%C.I. |
| Amikacin | Aminoglycosides | 15 - 16 | 19 | 15.8 | 26.3 | 57.9 | 4.2-40.5 | 34.0-78.9 |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid | Beta-lactam+Inhibitors | 14 - 17 | 7 | 71.4 | 0.0 | 28.6 | 30.3-94.9 | 5.1-69.7 |
| Ampicillin | Penicillins | 14 - 16 | 35 | 97.1 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 83.4-99.9 | 0.0-12.3 |
| Cefotaxime | Cephalosporin III | 23 - 25 | 18 | 77.8 | 16.7 | 5.6 | 51.9-92.6 | 0.3-29.4 |
| Ceftazidime | Cephalosporin III | 18 - 20 | 38 | 73.7 | 10.5 | 15.8 | 56.6-86.0 | 6.6-31.9 |
| Cefuroxime | Cephalosporin II | 15 - 17 | 10 | 80.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 44.2-96.5 | 3.5-55.8 |
| Chloramphenicol | Phenicols | 13 - 17 | 78 | 46.2 | 10.3 | 43.6 | 34.9-57.8 | 32.6-55.3 |
| Ciprofloxacin | Fluoroquinolone | 22 - 25 | 83 | 51.8 | 9.6 | 38.6 | 40.6-62.8 | 28.3-49.9 |
| Gentamicin | Aminoglycosides | 13 - 14 | 71 | 33.8 | 12.7 | 53.5 | 23.3-46.1 | 41.4-65.3 |
| Imipenem | Carbapenems | 20 - 22 | 45 | 15.6 | 8.9 | 75.6 | 7.0-30.1 | 60.1-86.6 |
| Meropenem | Carbapenems | 20 - 22 | 5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0-53.7 | 46.3-100 |
| Tetracycline | Tetracyclines | 12 - 14 | 18 | 72.2 | 0.0 | 27.8 | 46.4-89.3 | 10.7-53.6 |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | Folate pathway inhibitors | 11 - 15 | 21 | 90.5 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 68.2-98.3 | 0.2-25.9 |
| Variable | Infection | Bivariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ward, n (%) | No (n=90) | Yes (n=178) | cPR(95%CI),p-value | aPR(95%CI), p-value |
| A&E | 9(10.0) | 7(3.9) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Gynecology | 6(6.7) | 7(3.9) | 1.23(0.58-2.61) 0.58 | 1.32 (0.61-2.88) 0.48 |
| Maternity | 7(7.8) | 8(4.5) | 1.22(0.59-2.53)0.59 | 1.30 (0.61-2.77) 0.48 |
| Medical | 7(7.8) | 8(4.5) | 1.22(0.59-2.53) 0.59 | 1.28 (0.61-2.70) 0.51 |
| OPD | 13(14.4) | 25(14.0) | 1.50(0.82-2.75) 0.18 | 1.60 (0.86-2.98) 0.13 |
| Orthopedics | 14(15.6) | 20(11.2) | 1.34(0.72-2.51) 0.35 | 1.43 (0.76-2.69) 0.26 |
| Other | 8(8.9) | 23(12.9) | 1.69 (0.94-3.07) 0.08 | 1.81 (0.98-3.35) 0.05 |
| Private | 2(2.2) | 6(3.4) | 1.71(0.86-3.40) 0.12 | 1.86 (0.91-3.77) 0.08 |
| Pediatrics | 2(2.2) | 8(4.5) | 1.83(0.97-3.46) 0.06 | 1.78 (0.92-3.46) 0.08 |
| Surgical | 22(24.4) | 66(37.1) | 1.71(0.97-3.03) 0.06 | 1.78 (1.00-3.18) 0.04 |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Female | 43(47.8) | 77(43.3) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Male | 47(52.2) | 101(56.7) | 1.06(0.89-1.26) 0.48 | 1.04 (0.86-1.24) 0.702 |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||||
| 12&below yrs. | 14(15.6) | 34(19.1) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 13-18yrs | 10(11.2) | 21(11.8) | 0.95(0.70-1.29) 0.77 | 0.97 (0.70-1.33) 0.841 |
| 19-59yrs | 31(34.4) | 53(29.8) | 0.89(0.69-1.13) 0.35 | 0.90 (0.68-1.19) 0.479 |
| 60+yrs | 35(38.9) | 70(39.3) | 0.94(0.75-1.18) 0.60 | 0.92 (0.71-1.19) 0.534 |
| Undergoing surgery, n (%) | ||||
| No | 85(94.4) | 172(96.6) | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 5(5.6) | 6(3.6) | 0.81(0.47-1.40) 0.46 | |
| Surgical type, n (%) | ||||
| Elective | 2(2.2) | 3(1.7) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Others | 88 (97.7) | 175 (98.3) | 1.10 (0.54-2.28) 0.77 | 0.52 (0.20-1.30) 0.162 |
| Hospital admission >48hrs, n (%) | ||||
| No | 49(54.4) | 100 (56.2) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 41(45.6) | 78(43.8) | 0.97(0.82-1.16) 0.78 | 1.004 (0.79-1.27) 0.974 |
| Year of case | ||||
| 2019 | 13 (14.4) | 31 (17.4) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2020 | 45 (50) | 75 (42.1) | 0.89 (0.70-1.12) 0.32 | 0.96 (0.73-1.27) 0.790 |
| 2021 | 32 (35.6) | 72 (40.5) | 0.98 (0.78-1.23) 0.88 | 1.05 (0.80-1.37) 0.732 |
| Antibiotic use before testing | ||||
| No | 31 (34.4) | 61 (34.3) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 59 (65.6) | 117 (65.7) | 1.002 (0.84-1.20) 0.97 | 1.04 (0.82-1.32) 0.721 |
| Type of theatre | ||||
| Others | 86 (95.6) | 172 (96.6) | 1.00 | |
| Main theatre | 4 (4.4) | 6 (3.4) | 1.11 (0.66-1.86) 0.68 | |
| Variable | MDR | Bivariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ward, n (%) | No (n=189) | Yes (n=79) | cPR(95%CI), p-value | aPR(95%CI), p-value |
| A&E | 12(6.4) | 4(5.1) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| gynecology | 8(4.2) | 5(6.3) | 1.54(0.51-4.60) 0.44 | 1.21 (0.39-3.74) 0.742 |
| maternity | 11(5.8) | 4(5.1) | 1.07(0.32-3.53)0.91 | 0.88 (0.25-3.09) 0.842 |
| medical | 12(6.4) | 3(3.8) | 0.80(0.21-3.00) 0.74 | 0.71 (0.19-2.67) 0.616 |
| OPD | 28(14.8) | 10(12.7) | 1.05(0.39-2.87)0.92 | 1.05 (0.39-2.80) 0.917 |
| Orthopedics | 25(13.2) | 9(11.4) | 1.06(0.38-2.93) 0.91 | 0.84 (0.29-2.41) 0.739 |
| Other | 22(11.6) | 9(11.4) | 1.16(0.42-3.20) 0.77 | 1.50 (0.54-4.15) 0.432 |
| Private | 5(2.7) | 3(3.8) | 1.50(0.44-5.16) 0.52 | 1.49 (0.45-4.95) 0.512 |
| Pediatrics | 8(4.2) | 2(2.5) | 0.80(0.18-3.60) 0.77 | 1.49 (0.29-7.39) 0.627 |
| Surgical | 58(30.7) | 30(38.0) | 1.36 (0.56-3.35) 0.49 | 1.18 (0.47-2.94) 0.719 |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Female | 88(46.6) | 32(40.5) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Male | 101(53.4) | 47(59.5) | 1.19(0.81-1.74) 0.36 | 1.25 (0.84-1.88) 0.276 |
| Age, n (%) | ||||
| 12&below yrs. | 40(21.2) | 8(10.1) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 13-18yrs | 22(11.6) | 9(11.4) | 1.74(0.75-4.03) 0.19 | 2.14 (0.79-5.73) 0.13 |
| 19-59yrs | 54(28.6) | 30(38.0) | 2.14 (1.06-4.29) 0.03 | 2.30 (1.02-5.23) 0.04 |
| 60+yrs | 73(38.6) | 32(40.5) | 1.82(0.91-3.67) 0.09 | 1.96 (0.87-4.12) 0.10 |
| Undergoing surgery, n (%) | ||||
| No | 181(95.8) | 76(96.2) | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 8(4.2) | 3(3.8) | 0.92(0.34-2.46) 0.87 | |
| Surgical type, n (%) | ||||
| Elective | 2(1.1) | 3(3.8) | 3.69 (0.60-22.52) 0.15 | |
| Others | 187 (98.9) | 76(96.2) | 1.00 | |
| Hospital admission >48hrs, n (%) | ||||
| No | 112(59.3) | 37(46.8) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 77(40.8) | 42(53.2) | 1.42(0.98-2.05) 0.063 | 1.17 (0.71-1.94) 0.541 |
| Year of case | ||||
| 2019 | 36 (19) | 8 (10.1) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2020 | 85 (45) | 35 (44.3) | 1.60 (0.81-3.19) 0.17 | 1.34 (0.61-3.03) 0.45 |
| 2021 | 68 (36) | 36 (45.6) | 1.90 (0.96-3.76) 0.06 | 1.63 (0.75-3.55) 0.21 |
| Antibiotic use before testing | ||||
| No | 72 (38.1) | 20 (25.3) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 117 (61.9) | 59 (74.7) | 1.54 (0.99-2.39) 0.05 | 1.28 (0.73-2.24) 0.38 |
| Type of theatre | ||||
| Others | 182 (96.3) | 76 (96.2) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Main theatre | 7 (3.7) | 3 (3.8) | 1.02 (0.39-2.68) 0.97 | 0.91 (0.34-2.46) 0.855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




