Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site description and experimental design
2.2. Sampling collection and determination
2.3. Data analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth characteristics of the 25 rape varieties
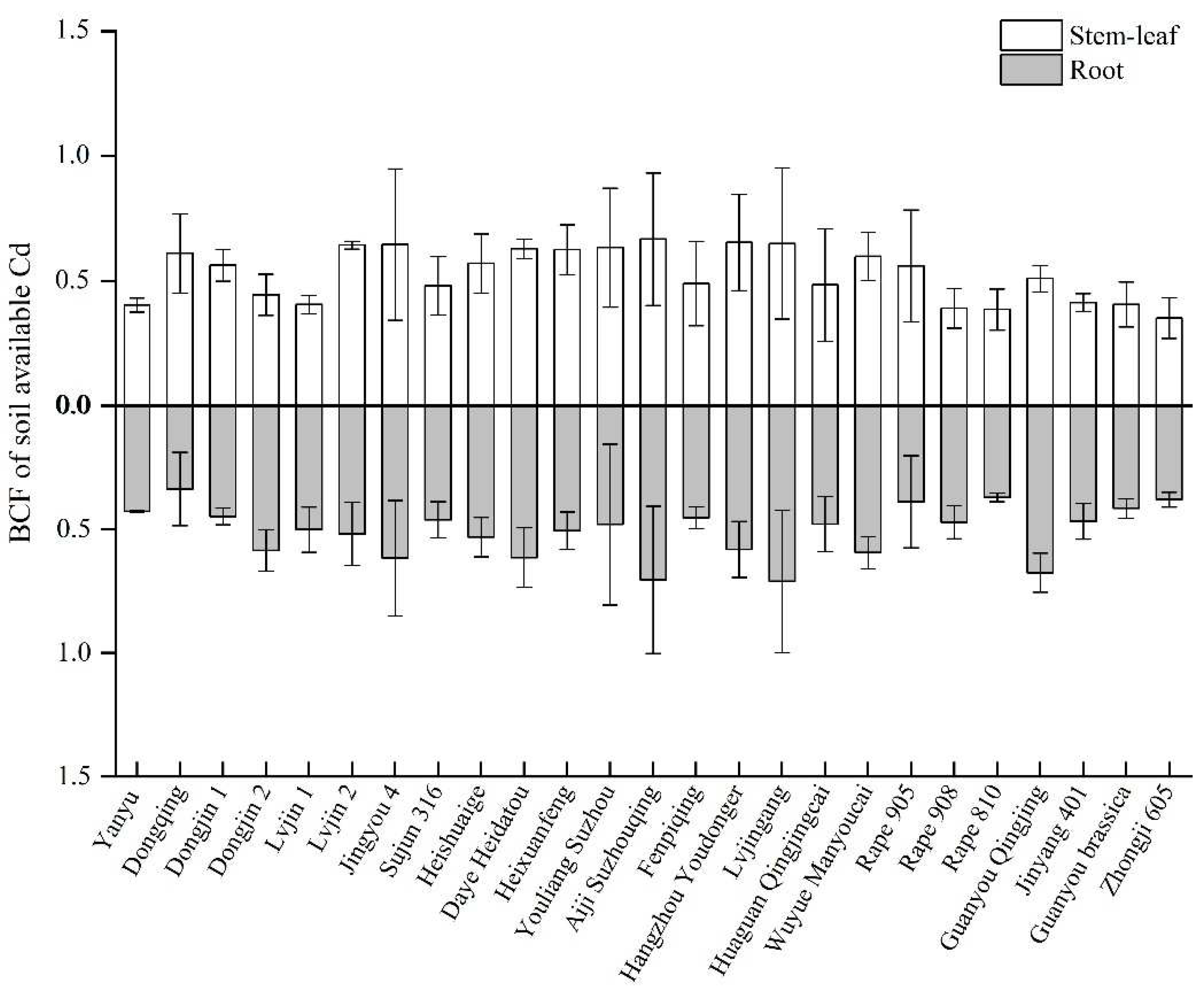
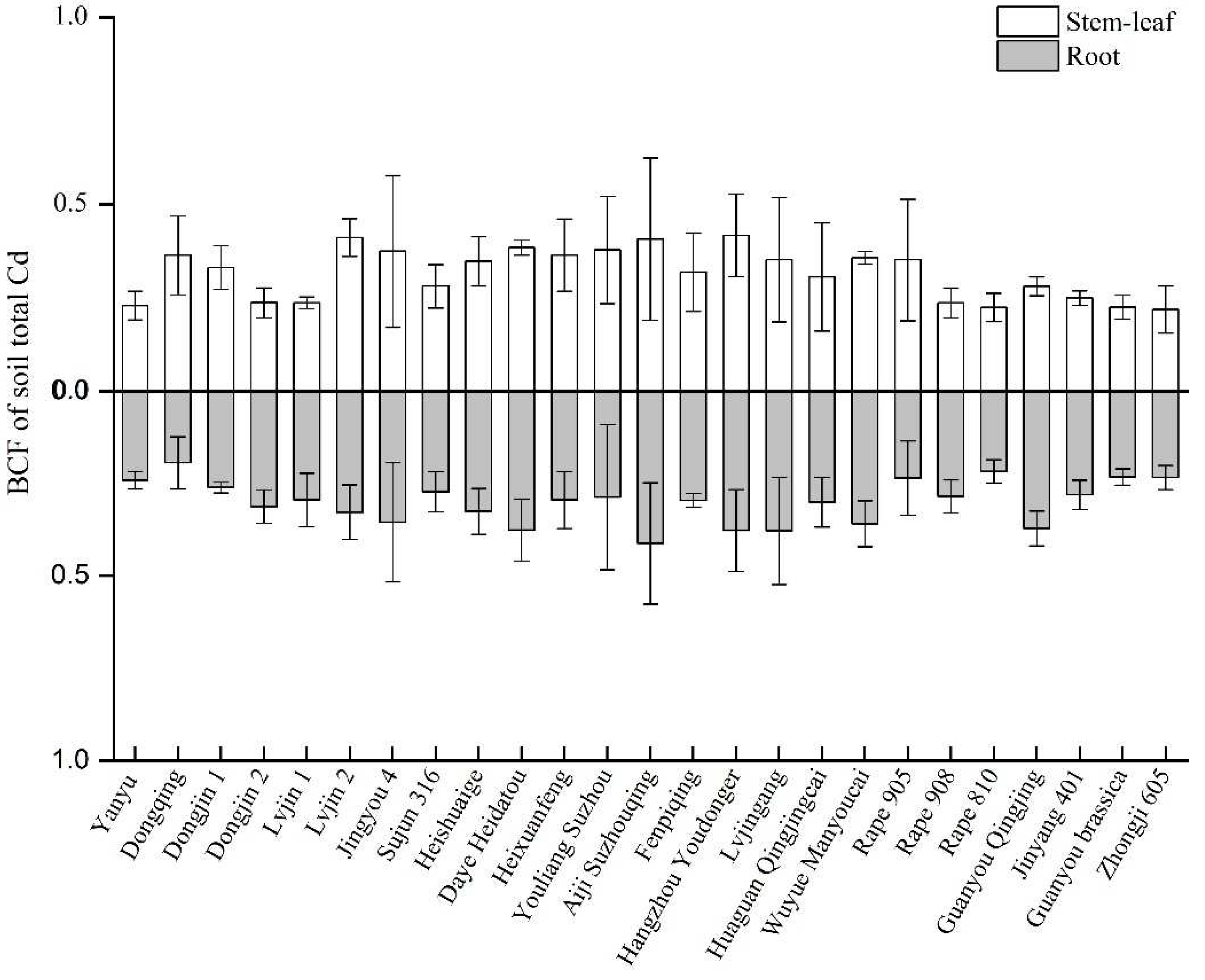
3.2. Cd contents in plant and soil with different rape varieties
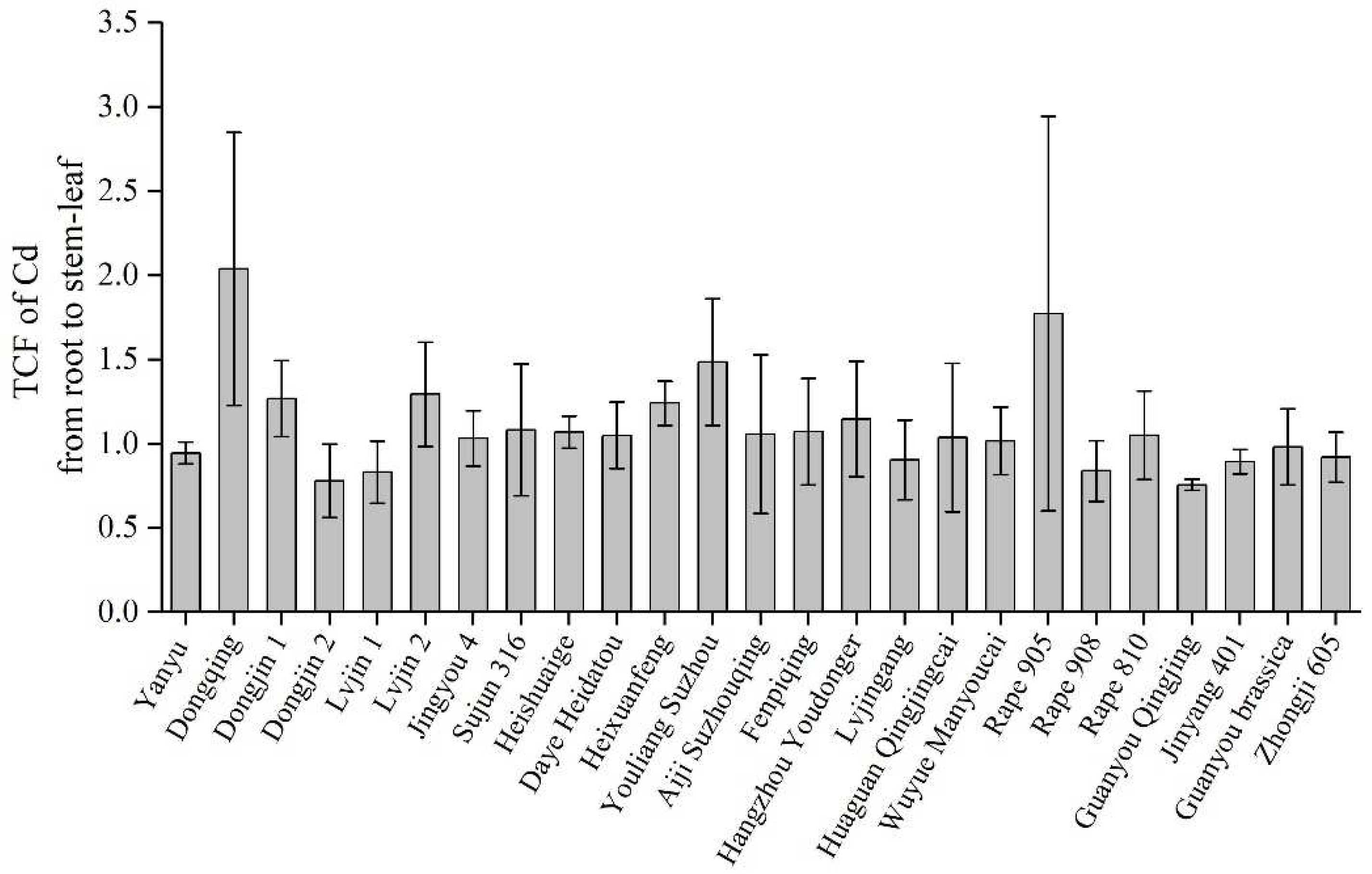
3.3. Cd accumulation and transport characteristics in 25 rape varieties
3.4. Cd uptaked by the 25 rape varieties
| Rape Variety | Uptake of Cd (μg·plant-1) | Stem-leaf(%) | Root(%) | Rape Variety | Uptake of Cd (μg·plant-1) | Stem-leaf(%) | Root(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yanyu | 5.22±1.70 | 95.45±0.35 | 4.55±0.35 | Fenpiqing | 4.56±2.48 | 94.48±2.92 | 5.52±2.92 |
| Dongqing | 6.02±2.76 | 97.62±0.81 | 2.38±0.81 | Hangzhou Youdonger | 10.23±4.83 | 96.20±1.16 | 3.80±1.16 |
| Dongjin 1 | 6.55±3.50 | 97.01±1.74 | 2.99±1.74 | Lvjingang | 7.37±3.33 | 95.24±1.47 | 4.76±1.47 |
| Dongjin 2 | 7.23±3.39 | 95.57±1.66 | 4.43±1.66 | Huaguan Qingjingcai | 6.22±3.32 | 95.11±2.41 | 4.89±2.41 |
| Lvjin 1 | 5.18±0.86 | 94.62±1.51 | 5.38±1.51 | Wuyue Manyoucai | 6.40±0.90 | 96.29±0.25 | 3.71±0.25 |
| Lvjin 2 | 11.14±1.18 | 97.0±0.69 | 3.0±0.69 | Rape 905 | 9.01±6.55 | 96.86±2.54 | 3.14±2.54 |
| Jingyou 4 | 6.82±4.74 | 95.17±0.82 | 4.83±0.82 | Rape 908 | 3.98±1.58 | 95.58±0.42 | 4.42±0.42 |
| Sujun 316 | 7.73±5.52 | 95.56±2.53 | 4.44±2.53 | Rape 810 | 4.69±1.33 | 95.66±0.75 | 4.34±0.75 |
| Heishuaige | 6.79±4.71 | 94.44±0.34 | 5.56±0.34 | Guanyou Qingjing | 7.76±0.23 | 92.10±1.49 | 7.90±1.49 |
| Daye Heidatou | 8.56±4.82 | 95.0±1.14 | 5.0±1.14 | Jinyang 401 | 3.86±0.47 | 94.53±0.14 | 5.47±0.14 |
| Heixuanfeng | 7.26±5.68 | 96.85±1.0 | 3.15±1.0 | Guanyou brassica | 4.83±2.36 | 93.92±2.30 | 6.08±2.30 |
| Youliang Suzhou | 5.76±5.64 | 96.77±0.49 | 3.23±0.49 | Zhongji 605 | 4.11±2.94 | 94.71±1.64 | 5.29±1.64 |
| Aiji Suzhouqing | 6.62±5.47 | 92.81±6.97 | 7.19±6.97 |
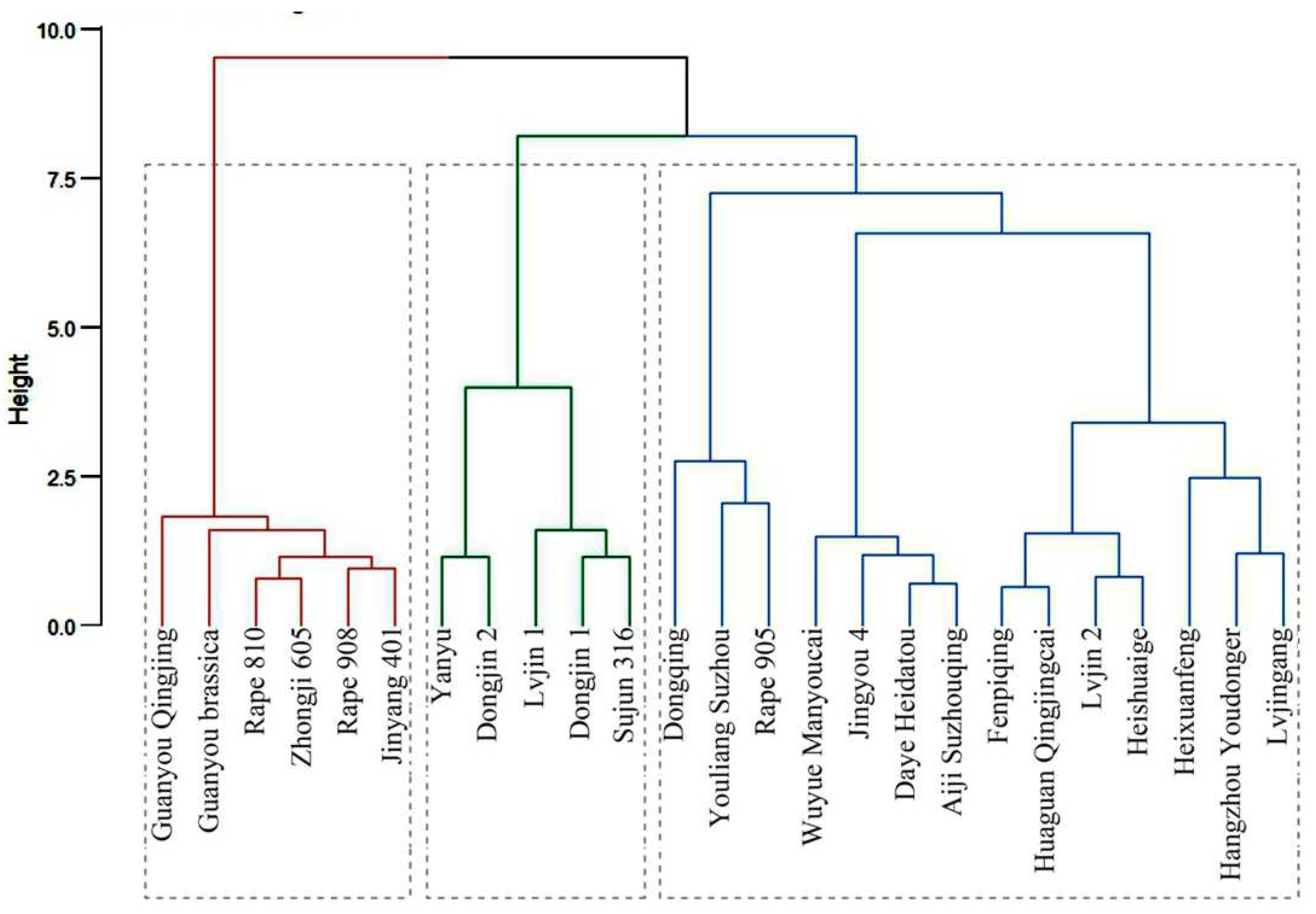
3.5. Cluster analysis on Cd accumulation in 25 rape varieties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K. Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils – To mobilize or to immobilize? Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2014, 266(4), 141–166. [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.S.; Kawakami, T.; Nagasawa, S.; Serikawa, Y.; Motoyama, A.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; Weragoda, S.K.; Yatigammana, S.K.; Amarasooriya, A.A.G.D. Arsenic, cadmium, lead, and chromium in well water, rice, and human urine in Sri Lanka in relation to chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology. Journal of Water and Health. 2018, 16, 212–222. [CrossRef]
- China Environmental Protection Industry. National soil pollution survey bulletin[EB/OL]. (2014-4-17).[2019-8-2]http://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm. 2014.
- Yuan, T.; Gu, J.; Zhou, H.; Huang, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Liao, B. Translocation and accumulation of cadmium and lead in the tissues of 39 rape cultivars grown in a polluted farmland. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2020, 27(13), 15888-15900. [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Hamid, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Yang, X. The Cd phytoextraction potential of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii-oilseed rape intercropping system under different soil types and comprehensive benefits evaluation under field conditions. Environ Pollut. 2021, 285, 117504. [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, F.; Huang, D.J. Effects of three organic materials on the availability of cadmium in soil and cadmium accumulation and translocation in rice plants. . Journal of Agro-Environment Science. 2020, 39, 2143–2150 (In Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Clarke, J.M.; Duguid, S.; Chaney, R.L. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. The Science of the Total Environment. 2008, 390, 301-310. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sheng, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y. Remediation of Cd-contaminated acidic paddy fields with four-year consecutive liming. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2020, 188, 109903. [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Tsai, C.C.; Tsui, C.C.; Cheng, S.F.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, H.T. Digestion methods for total heavy metals in sediments and soils. Water Air & Soil Pollution. 2002, 141, 189-205. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.P.; Zhou, F.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, H.S. Effects of Cassava-Peanut Intercropping on the Absorption of Cadmium and Available Nutrient in Rhizospheree Soi. Research of Environmental Sciences. 2018, 31(2), 303-309 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Mendiburu, F.2013. Agricolae: Statistical procedures for agricultural research. R package Version 1.1-4.
- Oksanen, J. ; Blanchet, F.G. ; Kindt, R. ; Legendre, P. 2013. Vegan: community ecology package. R Package Version 2.0-7.
- GB 15618-2018. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land [S].
- Wang, N.; Nan, Z.R.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, W.F.; Zhou, T.; Li, C.C.; Li, P.; Jin, C.; Luo, H.Z.; Xue, S.Y. Distribution, enrichment and migration characteristics of heavy metals in rape under Cd/Pb stress. Journal of Lanzhou University 2012, 12(48), 18-22 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.M.; Ai, S.Y.; Tang, M.D.; Li, M.J.; Yao, J.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Ceng, Z.B. Effect of amendment on Cd uptake by Brassia chinensis in Cd-contaminated soils. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture. 2010, 18(3), 654-658 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Tu, J.F.; Li, J.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, D.Y. Effects of Cd on rape growth and antioxidant enzyme system. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 2006, 17(1), 102-106 (in Chinese).
- Jiang, H.D.; Zhou, Q.; Li, N.; Sun, X.F. Effect of Cd on the growth and physiological characteristics of rape seedlings. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences. 2006, 28(1), 39-43 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Q.; Cheng, W.D. Differences in Cadmium Tolerance between Germination and Seedling Growth of Rapeseed and Mustard. Zhejiang Agricultural Science. 2005, 6(5), 436-438 (in Chinese).
- Han, C.; Shen, H.Y.; Ye, J.; Li, F.X. Effect of Simulation of Cadmium Pollution Growth, Cadmium Accumulation and Its Subcellular Distribution in Two Varieties in Two Varieties of Brassica pekinensis Rupr. Northern Horticulture. 2014, 10, 9-12 (in Chinese).
- Xue, R.L.; Huang, Y.M.; Mai, S.Q. Effect of Cadmium on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics and Bio-Accumulation of Pakchoi in Different Fertilizing. Journal of Agro-Enviroment Science. 2010, 29, 020-025 (in Chinese).
- Wang, J.Q.; Ru, S.H.; Su, D.C. Effects of Indian mustard and oilseed rape co cropping on absorbing insoluble cadmium of contaminated soil. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae. 2004, 24(5), 890-894 (in Chinese).
- Su, D.C.; Huang, H.Z. The phytoremediation potential of oilseed rape (B. juncea) as a hyperaccumulator for cadmium contaminated soil. China Environmental Science. 2002, 22(1), 48-51 (in Chinese).
- McKenna, I.M.; Chaney, R.L.; Williams, F.M. The effects of cadmium and zinc interactions on the accumulation and tissue distribution of zinc and cadmium in lettuce and spinach. Environmental Pollution. 1993, 79, 113-120. [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.J.; Ni, W.Z. Effects of Integrated Fertilization with Commercial Organic Mature and Chemical Fertilizers on Heavy Metal Balance in Soi-l Rape Cropping System. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation. 2006, 20(3), 32-35 (in Chinese).
- Wang, J.Q.; Liu, B.; Su, D.C. Selection of oilseed rapes as a hyperaccumulator for cadmium. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei. 2003, 26(1), 13-16 (in Chinese).
- Jiang, H.M.; Li, S.Q.; Han, X.F.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.X. Progresses on the Effect of Cadmium for Plant and Their Tolerant Mechanism. Guandong Weiliang Yansu Kexue 2012, 19(5), 1-6 (in Chinese).
- Gao, Q.L. Differences in Cd absorption and accumulation among different varieties of rapeseed. 2007, China Agricultural University (in Chinese): Beijing.
- Sun, S.S.; Wang, W.J.; Ma, Z.H.; Lv, Z.X.; Li, R.Q.; Jia, L.L.; Liang, A.P. Enrichment of heavy metals Pb and Cd in leafy vegetables and the effects on their growth. Hubei Agricultural Sciences. 2019, 58(24), 72-75 (in Chinese).
- Gao, Q.L.; Xu, J.F. Investigations of the Difference of Cadmium Accumulated in various Kinds of rapes. Journal of Xi'an Technological University. 2015, 35(6), 479-482 (in Chinese).
- Ma, J.J.; Zhu, J.T.; Chen, F.; Wu, H.P.; Zou, D.W. Alleviation effects on unitary and mixed rare-earth elements on the accumulation of heavymetals in rapes. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei. 2004, 27(1), 25-29 (in Chinese).
- Zhou, Y.L.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.B.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.W.; Han, W. Characteristics of Soil Selenium-cadmium Migration and Accumulation and Its Bioeffectiveness in Typical Geological High Background Area. Environmental Science. 2023, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1895.X.20231205.1255.009 (in Chinese).
- Chang, H.W.; Gui, J.; Li, H.L. Research progress of factors affecting Cd bioaccumulation in soil-rice system. Environmental Science & Technology. 2022, 45(S1), 282-295.
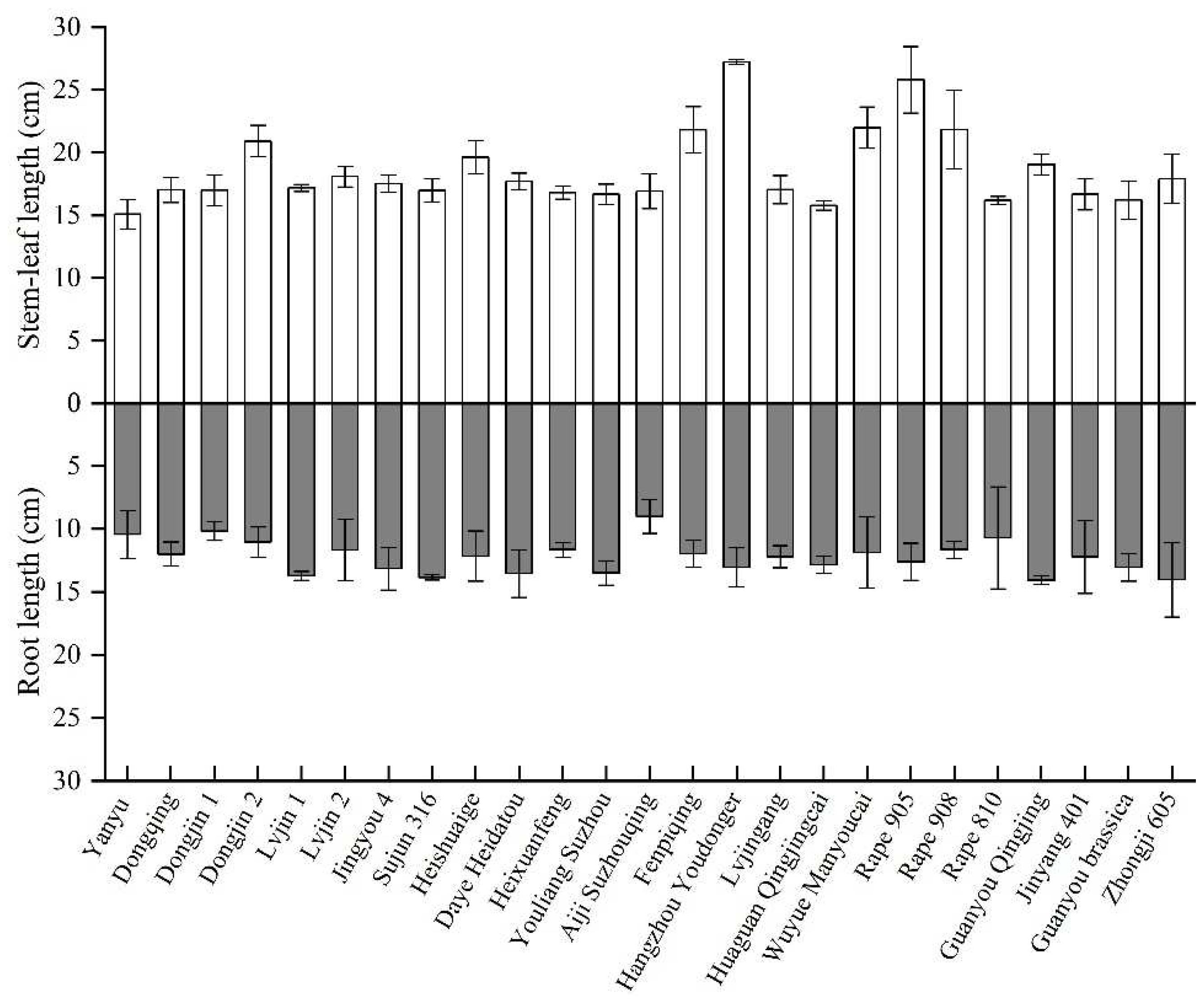
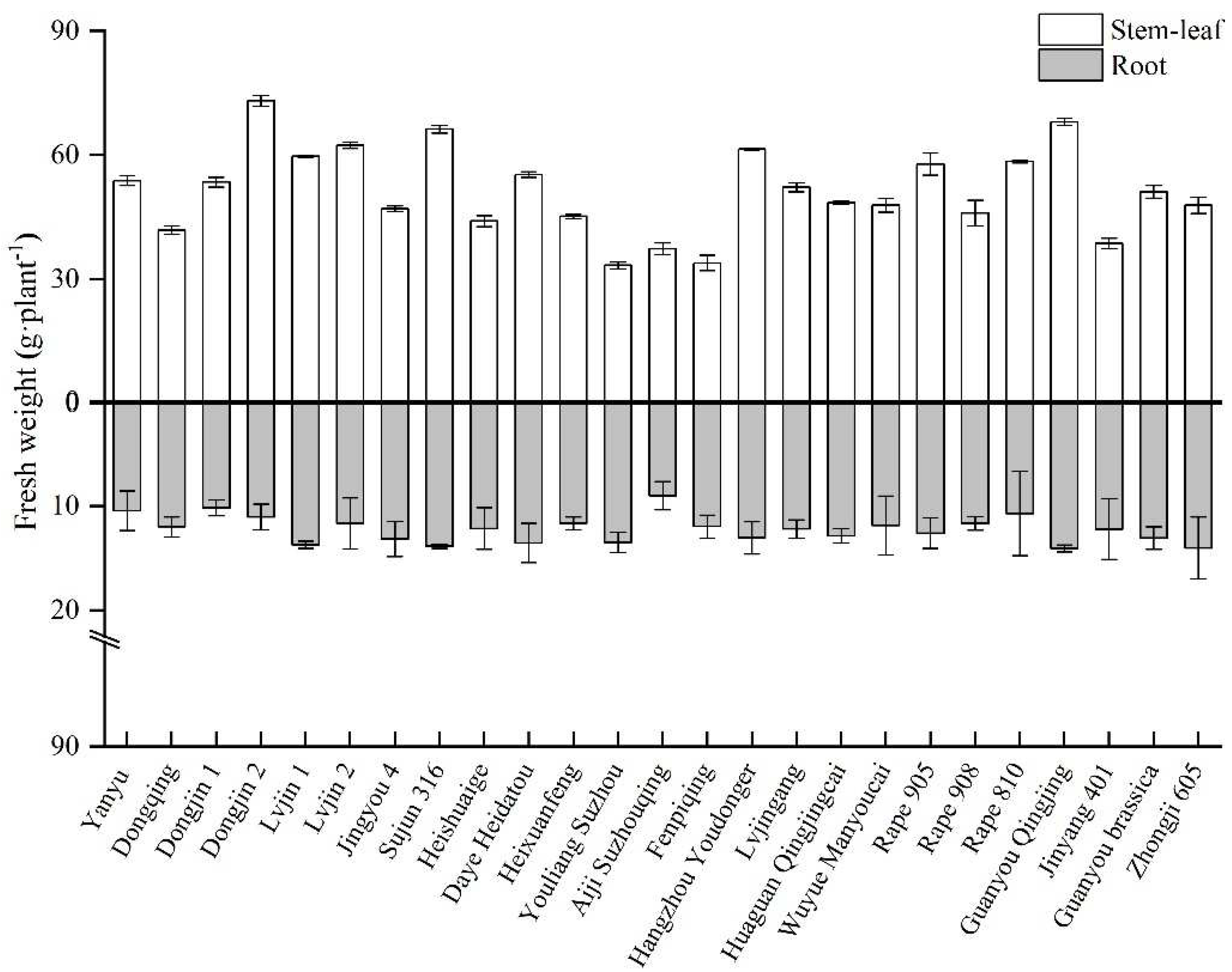
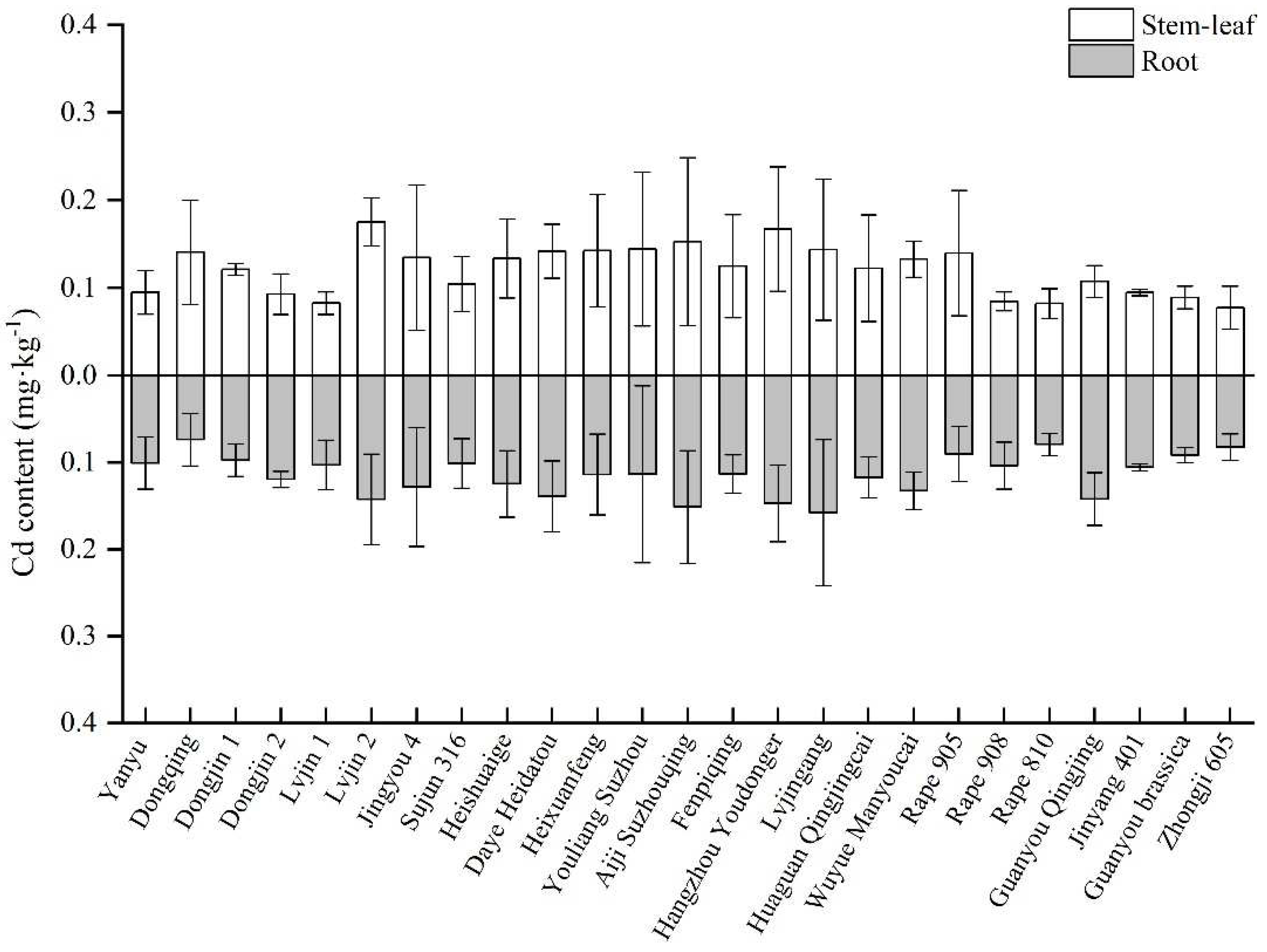
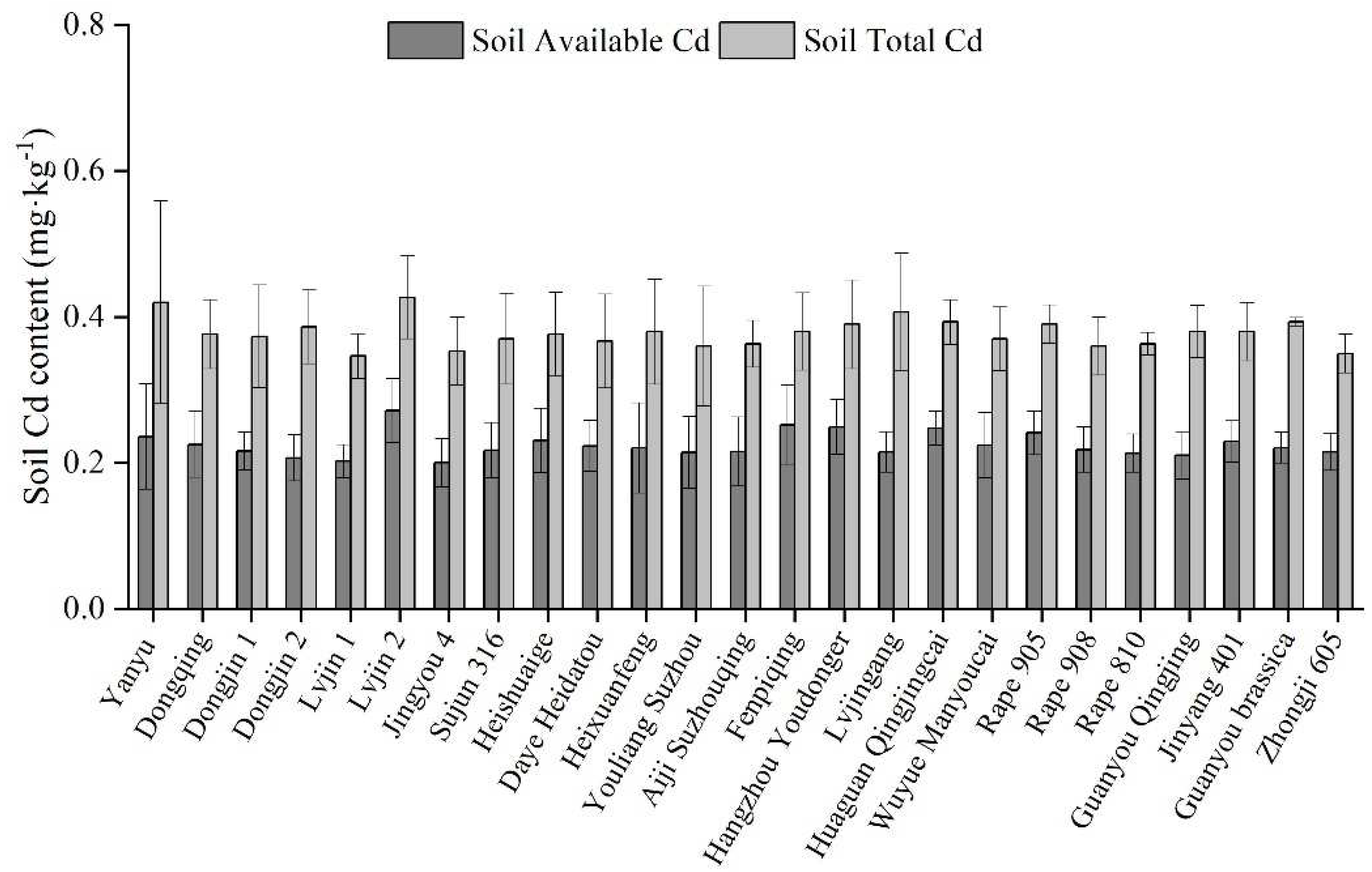
| No. | Name | No. | Name | No. | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yanyu | 10 | Daye Heidatou | 19 | Rape 905 |
| 2 | Dongqing | 11 | Heixuanfeng | 20 | Rape 908 |
| 3 | Dongjin 1 | 12 | Youliang Suzhou | 21 | Rape 810 |
| 4 | Dongjin 2 | 13 | Aiji Suzhouqing | 22 | Guanyou Qingjing |
| 5 | Lvjin 1 | 14 | Fenpiqing | 23 | Jinyang 401 |
| 6 | Lvjin 2 | 15 | Hangzhou Youdonger | 24 | Guanyou brassica |
| 7 | Jingyou 4 | 16 | Lvjingang | 25 | Zhongji 605 |
| 8 | Sujun 316 | 17 | Huaguan Qingjingcai | ||
| 9 | Heishuaige | 18 | Wuyue Manyoucai |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





