Submitted:
02 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
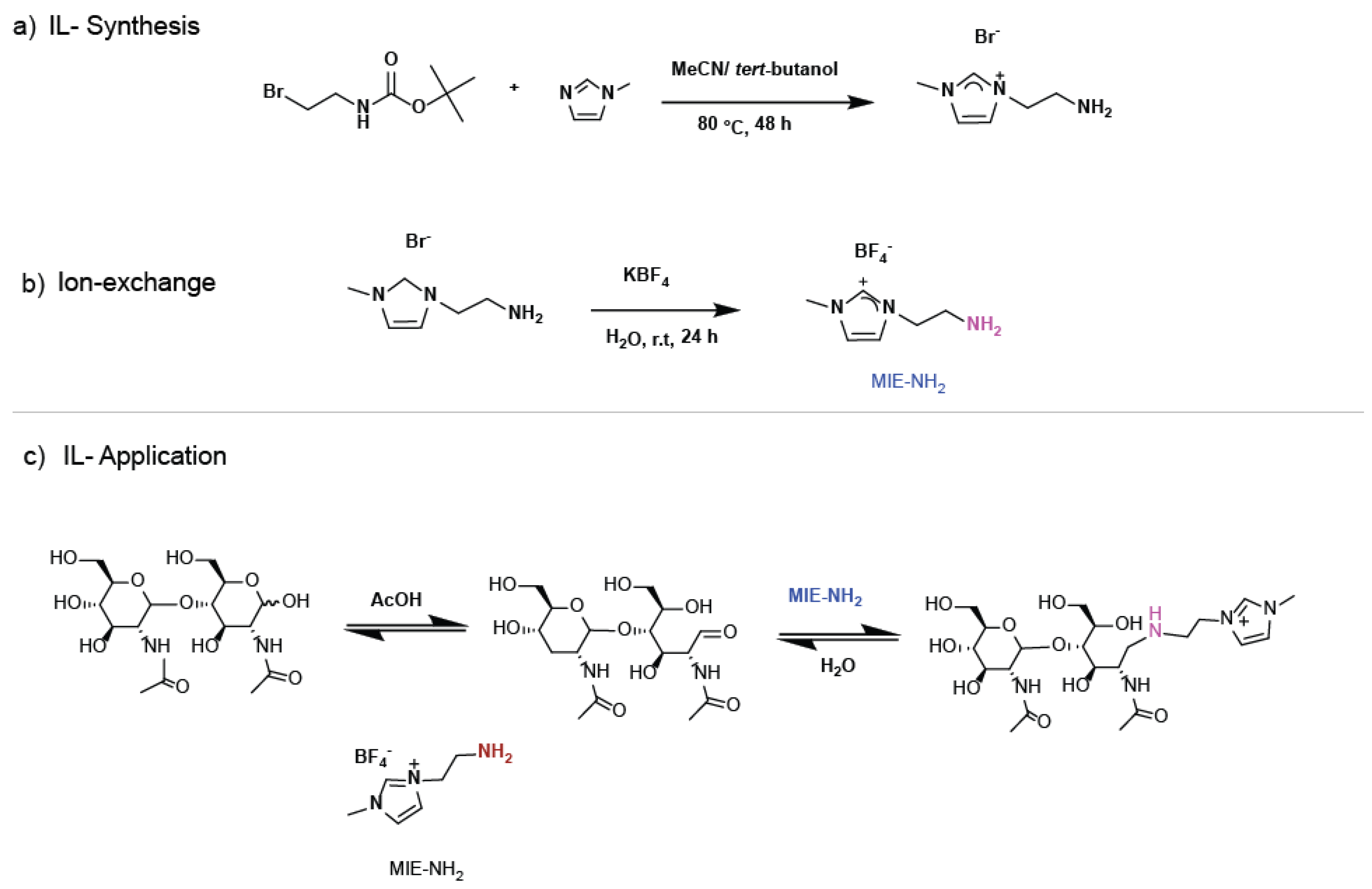
2.2. Synthesis of Ionic Liquid-[1-(2-aminoethyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazole-3-ium] MIE-NH2][BF4-])
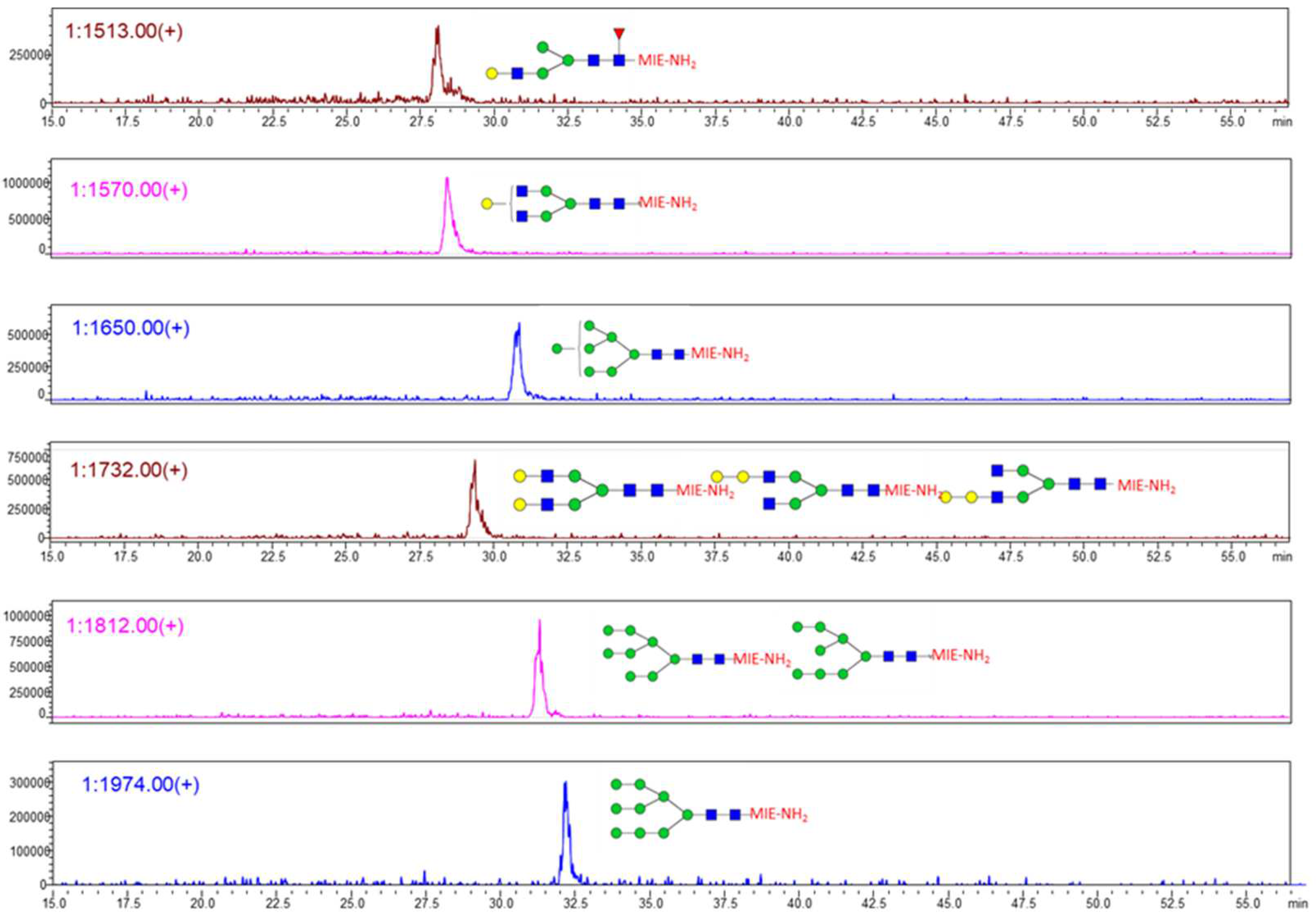
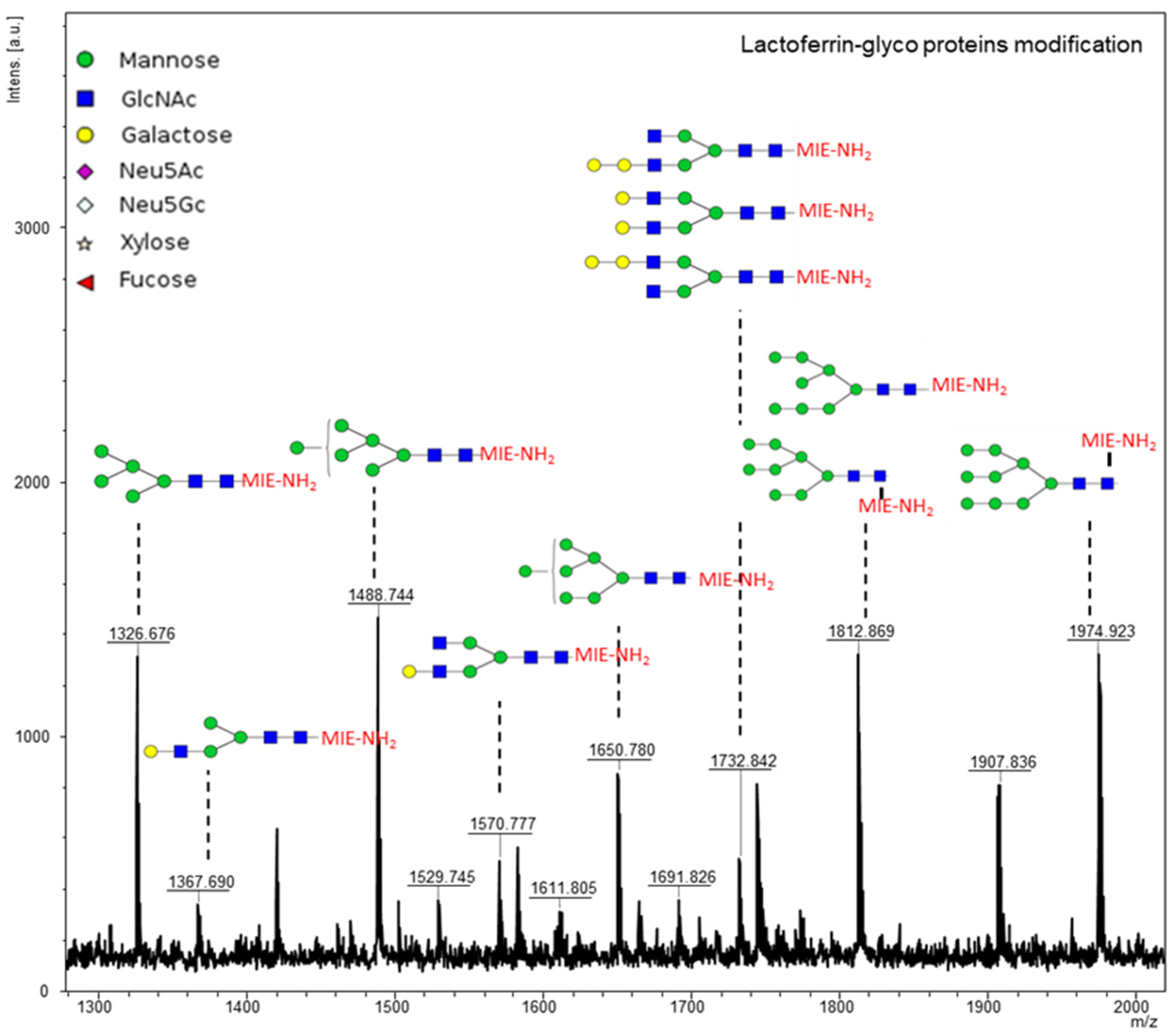
2.3. Derivatization N-Glycans of Lactoferrin with ILs-NH2
2.4. Molecular Docking
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Pharmacological and Antiviral Activities of IL-Lactoferrin Molecule
4.2. Mechanistic Study of the Inhibition of Coronavirus Activity by Small Molecules of Lactoferrin (IL-Lf)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campione, E.; Lanna, C.; Cosio, T.; Rosa, L.; Conte, M.P.; Iacovelli, F.; Romeo, A.; Falconi, M.; Del Vecchio, C.; Franchin, E.; et al. Lactoferrin Against SARS-CoV-2: In Vitro and In Silico Evidences. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 666600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Abdelmoneem, M.A.; Hassanin, I.A.; Abd Elwakil, M.M.; Elnaggar, M.A.; Mokhtar, S.; Fang, J.Y.; Elkhodairy, K.A. Lactoferrin, a Multi-Functional Glycoprotein: Active Therapeutic, Drug Nanocarrier & Targeting Ligand. Biomaterials 2020, 263, 120355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorland, L.H. Lactoferrin: A Multifunctional Glycoprotein. Apmis 1999, 107, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan, M.C.; Jones, R.A.; Tran, A.T. Recent Developments of Ionic Liquids in Oligosaccharide Synthesis: The Sweet Side of Ionic Liquids. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 375, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerneni, C.K.; Pathak, V.; Pathak, A.K. Imidazolium Cation Supported Solution-Phase Assembly of Homolinear α(1→6)-Linked Octamannoside: An Efficient Alternate Approach for Oligosaccharide Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6307–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Cai, P.; Sun, C.; Pan, Y. Application of Ionic Liquids in Separation and Analysis of Carbohydrates: State of the Art and Future Trends. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da S. Vieira, D.; Polveiro, R.C.; Butler, T.J.; Hackett, T.A.; Braga, C.P.; Puniya, B.L.; Teixeira, W.F.P.; de M. Padilha, P.; Adamec, J.; Feitosa, F.L.F. An in Silico, Structural, and Biological Analysis of Lactoferrin of Different Mammals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirardello, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Voglmeir, J.; Galan, M.C. Recent Applications of Ionic Liquid-Based Tags in Glycoscience. Carbohydr. Res. 2022, 520, 108643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, R.P. Rapid and Sensitive Methods for the Analysis and Identification of O-Glycans from Glycoproteins; 2017; ISBN 9789462955660.
- Senan, A.M.; Akkoc, S.; Reem, A. Modification and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Iron Free with Methylimidazolium N-Ethylamine Ionic Liquid as Potential Drugs Anti SARS-CoV-2. 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Jo, J.Y.; Tuomivaara, S.T.; Lim, J.M. Isotope Labeling Strategies of Glycans for Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Glycomics. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, S.J.; Hitchen, P.G.; Haslam, S.M.; Dell, A. Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of N-Linked and O-Linked Glycans. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Pharmacotherapeutics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 12–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavandi, S.; Zare, I.; VaezJalali, M.; Dadashi, M.; Azarian, M.; Akbari, A.; Ramezani Farani, M.; Zalpoor, H.; Hajikhani, B. Structural and Non-Structural Proteins in SARS-CoV-2: Potential Aspects to COVID-19 Treatment or Prevention of Progression of Related Diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, N.D.; Mohan, J.; Kushwaha, B.; Ghazi, T.; Nwabuife, J.C.; Koorbanally, N.; Chuturgoon, A.A. A Comprehensive Review on the Global Efforts on Vaccines and Repurposed Drugs for Combating COVID-19. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Senan, A.M.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. 1-(2-Aminoethyl)-3-Methyl-1H-Imidazol-3-Ium Tetrafluoroborate: Synthesis and Application in Carbohydrate Analysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senan, A.M.; Akkoc, S.; Reem, A. Modification and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Iron Free with Methylimidazolium N-Ethylamine Ionic Liquid as Potential Drugs Anti SARS-CoV-2. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zou, M.; Liu, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, X.; Pang, G.; Huang, L.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Based Quantitative and Qualitative Analyses Reveal N-Glycan Changes of Bovine Lactoferrin at Different Stages of Lactation. Lwt 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.; Arce, A.; Francisco, M.; Rodríguez, O.; Soto, A. Liquid-Liquid Equilibria for Systems Composed by 1-Methyl-3- Octylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic Liquid, Thiophene, and n-Hexane or Cyclohexane. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhrer, M.; Balog, C.I.A.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Deelder, A.M.; Hokke, C.H. New Features of Site-Specific Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) Glycosylation Uncovered by Nano-LC-MS with Repeated Ion-Isolation/Fragmentation Cycles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Gen. Subj. 2005, 1723, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevsky, A.; Aniana, A.; Coates, L.; Bonnesen, P. V.; Nashed, N.T.; Louis, J.M. Contribution of the Catalytic Dyad of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease to Binding Covalent and Noncovalent Inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokic, G.; Hillen, H.S.; Tegunov, D.; Dienemann, C.; Seitz, F.; Schmitzova, J.; Farnung, L.; Siewert, A.; Höbartner, C.; Cramer, P. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase Stalling by Remdesivir. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B.J.; Beldar, S.; Seitova, A.; Hutchinson, A.; Mannar, D.; Li, Y.; Kwon, D.; Tan, R.; Wilson, R.P.; Leopold, K.; et al. Structure and Activity of Human TMPRSS2 Protease Implicated in SARS-CoV-2 Activation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Ratia, K.; Cooper, L.; Kong, D.; Lee, H.; Kwon, Y.; Li, Y.; Alqarni, S.; Huang, F.; Dubrovskyi, O.; et al. Design of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro Inhibitors for COVID-19 Antiviral Therapy Leveraging Binding Cooperativity. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.T.; Er, M.; Akkoç, S. Molecular Modeling and In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity Studies of Some Imidazole and Isoxazole Derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1282, 135066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, A. Software News and Update AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 32, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Gray, J.S.S.; Montgomery, R. The Glycans of Horseradish Peroxidase. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 287, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Shin, J.S. Free Energy Analysis of ω-Transaminase Reactions to Dissect How the Enzyme Controls the Substrate Selectivity. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszelewski, D.; Lavandera, I.; Clay, D.; Guebitz, G.M.; Rozzell, D.; Kroutil, W. Formal Asymmetric Biocatalytic Reductive Amination. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9337–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk-Weeber, R.L.; Dijkhuizen, L.; van Leeuwen, S.S. Large-Scale Quantitative Isolation of Pure Protein N-Linked Glycans. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 479, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geib, Y.; Dietrich, U.; Chauhan, G.; Madou, M.J.; Kalra, S.; Chopra, V.; Ghosh, D.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Kim, C.H.; Xiong, X.; et al. Potential Therapeutic Agents and Associated Bioassay Data for COVID-19 and Related Human Coronavirus Infections. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luan, J.; Zhang, L. Molecular Docking of Potential SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease Inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayipo, Y.O.; Ahmad, I.; Najib, Y.S.; Sheu, S.K.; Patel, H.; Mordi, M.N. Molecular Modelling and Structure-Activity Relationship of a Natural Derivative of o-Hydroxybenzoate as a Potent Inhibitor of Dual NSP3 and NSP12 of SARS-CoV-2: In Silico Study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, L.A.; Lange, S.M.; Cesare, V.D.; Matthews, S.P.; Nirujogi, R.S.; Cole, I.; Hope, A.; Cunningham, F.; Toth, R.; Mukherjee, R.; et al. Biochemical Characterization of Protease Activity of Nsp3 from SARS-CoV-2 and Its Inhibition by Nanobodies. PLoS One 2021, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Mahasenan, K. V.; Bhardwaj, A.; Wiest, O.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. Production of Proteins of the SARS-CoV-2 Proteome for Drug Discovery. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 19983–19994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hauner, D.; Laureanti, J.A.; Agustin, K.; Raugei, S.; Kumar, N. Mechanistic Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease to Accelerate Design of Covalent Inhibitors. Sci. Reports 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, K.G.; Sharanya, C.S.; Abhithaj, J.; Francis, D.; Sadasivan, C. Drug Repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 Using E-Pharmacophore Based Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics with Main Protease as the Target. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, D.; Patamia, V.; Scala, A.; Sciortino, M.T.; Piperno, A.; Rescifina, A. Putative Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease from A Library of Marine Natural Products: A Virtual Screening and Molecular Modeling Study. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V.; Hayashi, Y.; Jung, S.H. An Overview of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL Protease Inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and Small Molecule Chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6595–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Warshel, A. Exploring the Mechanism of Covalent Inhibition: Simulating the Binding Free Energy of α-Ketoamide Inhibitors of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 4601–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.P.; Gebauer, N.W.A.; Bontha, M.; Khazaieli, M.; James, R.M.; Brown, J.B.; Kumar, N. 3D-Scaffold: A Deep Learning Framework to Generate 3D Coordinates of Drug-like Molecules with Desired Scaffolds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 12166–12176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
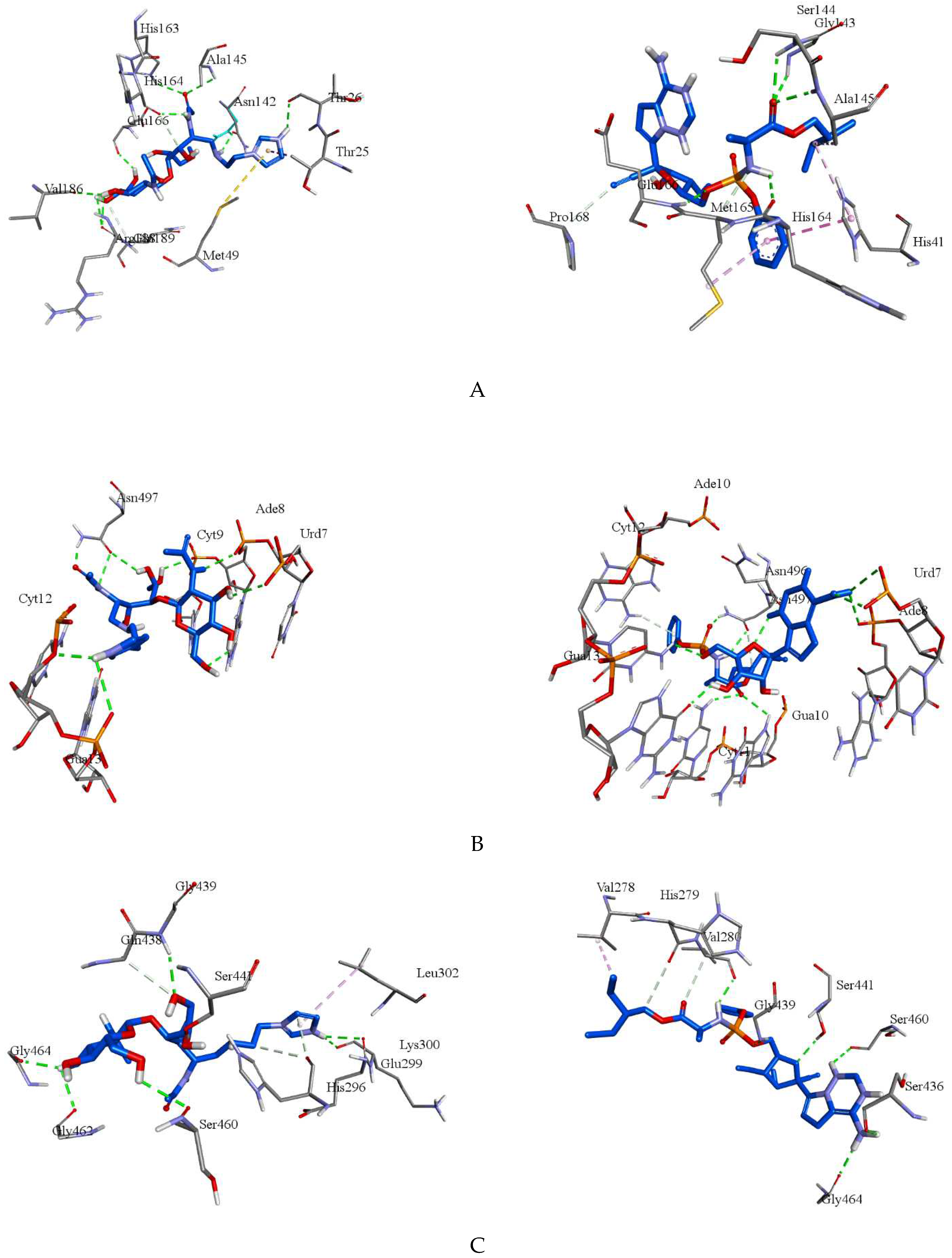
| Compounds | Target | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
Hydrogen bonding points |
Other interaction points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule | 8GFN | -7.5 | Thr26, Asn142, Ala145, His163, His164, Glu166, Val186, Arg188(2) | Thr25a, Met49b, Gln189c |
| Remdesivir | 8GFN | -8.0 | Gly143, Ser144, Ala145, His164, Glu166 | His41d, His41e, Ala145e, Met165c, Met165e, Pro168c |
| Molecule | 7B3B | -7.7 | Urd7, Ade8(2), Cyt9(2), Cyt12, Gua13, Asn497(3) | - |
| Remdesivir | 7B3B | -8.9 | Urd7(2), Ade8, Gua10, Cyt11, Cyt12, Gua13, Asn496, Asn497(2) | Ade10c |
| Molecule | 7MEQ | -5.5 | Glu299, Lys300, Gly439, Ser441, Ser460, Gly462, Gly464 | His296(2)c, Gln438c |
| Remdesivir | 7MEQ | -7.0 | Val280, Ser436, Gly439, Ser441, Ser460, Gly464 | Val278e, His279c, Val280c |
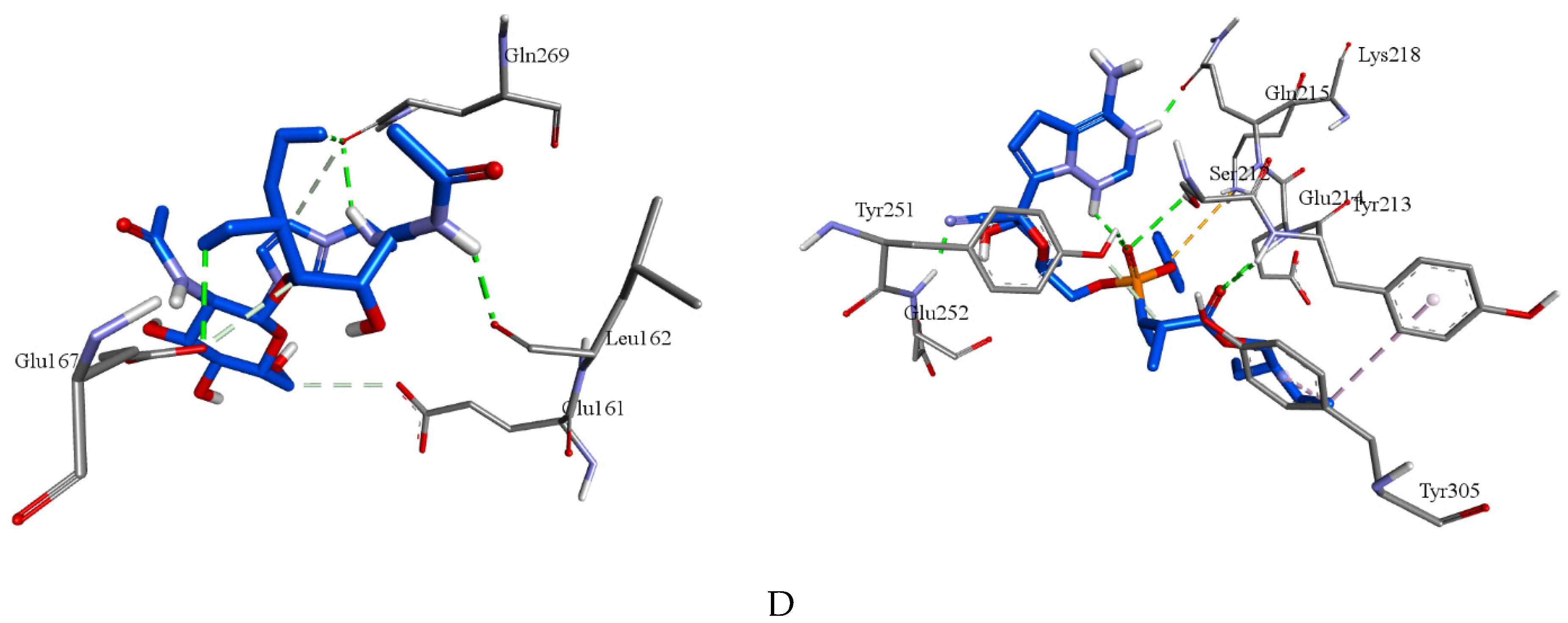
| Molecule | 7LLF | -5.4 | Leu162, Glu167, Gln269(2) | Glu161c, Glu167c, Gln269c |
| Remdesivir | 7LLF | -6.5 | Ser212, Tyr213, Glu214, Gln215, Tyr251, Glu252 | Tyr213e, Lys218f, Tyr251c, Tyr305e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





