1. Introduction
Obesity is one of the world’s largest problem responsible for 5% of total global mortality. Obesity is a chronic disease, characterized by presence of excessive body fat with a larger size and number of adipocytes in the body [
1]. It is officially classified as a global health disease by World Health Organization (WHO) and other international organizations like American medical association [
1,
2]. The Indian National Family Health Survey -5 provides an obesity report for the years 2019-2021 in the age group of 15-49 years. It showed an increase from 21 to 24% in women and an increase from 19% to 23% in men [
3]. In developing countries like India, obesity and increase in body mass index (BMI) are linked with numerous factors like growing urbanization, mechanized transport, increased availability of fast foods, reduced physical activity and increased television viewing time [
4]. It is believed that genetic factors, epigenetic predisposition and various external influences are of great importance in obesity development. Studies on gene expression mechanisms during the development of obesity provide potential facts for prevention, early diagnosis and management of obesity [
5].
miRNAs are endogenously initiated, short non-coding single stranded, 21-23 nucleotides long RNAs that negatively regulate or repress target gene expression at the post transcriptional level by pairing with the 3′- untranslated region (UTR) of their target miRNAs. These miRNAs are expressed in all cell types. They play an important role in both normal physiological processes and in the development of diseases such as obesity and cancer [
2,
5].
In addition to tissues these miRNAs were also found in body fluids such as serum, plasma, saliva, sweat, cerebrospinal fluid, tears, breast milk, peritoneal fluid, bronchial lavage, seminal fluid, follicular fluid and urine. These circulating MicroRNAs unlike regular miRNAs are highly stable when subjected to extreme conditions like boiling, high pH, prolonged storage time and multiple freeze thaw cycles while most cellular RNAs are rapidly destroyed [
6,
7]. Circulating miRNAs are protected from degradation by endogenous RNAase activity because they are contained in small membranous vesicles e.g., exosomes, exosome like vesicles, microparticles and apoptotic bodies, packed with HDLs, and linked to RNA binding proteins. As they are highly stable and easily detectable, they are very good target for extraction and quantification [
8].
Aerobic exercises are chosen as management tool for obesity. Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that will increase oxygen consumption. It is treated as the most effective exercise to lower body weight and body mass index. The American college of Sports and Medicine defines aerobic exercise as “any activity that uses large group of muscles, can be maintained continuously, and is rhythmic in nature”. Walking, cycling, jogging, running and swimming are all examples of aerobic exercise [
4]. Some Ci-miRNAs are specifically associated with obesity for instance circulating miRNA 423-5p [
8,
9,
10] and Ci- miRNA – 128-1 [
11]. Understanding how exercise affects gene regulation at the level of miRNAs will be crucial in maximizing the therapeutic benefits of aerobic exercise for human health [
12].
Despite researcher’s efforts to uncover the link between obesity and miRNAs, the importance of circulating MiRNAs for obesity remains unknown. With regard to obesity, different studies have revealed different miRNA expression profiles. Many studies have concentrated on animal systems, so there is a paucity of data on human individuals. When compared to the western population Asian populations have characteristically lower body mass index and a higher percentage of fat at a given BMI. These factors should be considered for full understanding of obesity related miRNAs [
13].
The aim of the study was to analyse the circulating miRNA 423-5p & miRNA 128 levels before intervention with obese and lean adults of age group 18-23 years and to evaluate the effect of exercise training on Ci-miRNA 423-5p & Ci- miRNA-128 and the blood parameters in obese adults.
2.1. Methodology
Ethical approval from the institutional ethical committee of TSRMMCH & RC was obtained to conduct the study (14/TSRMMCH&RC/ME-1/2020-IEC N0:20). The aim and procedure of the study was explained to the subjects, written consent from each subject was obtained. After detailed history taking, anthropometric measurements, a thorough general and systemic examinations were done. All the parameters were measured before and after aerobic exercise program for 6 months.
2.2. BMI Was Calculated by Using “Quetelet”s Index
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)2. The maximum limit of normal BMI as per WHO guidelines is 24.9 kg/m2. Therefore, subjects in this study were grouped into two, one with BMI < 25 and the other with BMI ≥ 25. After an overnight fast, the waist circumference was measured using a tape. To reduce abdominal tension during the measurement, the participant was instructed to relax before the measurement and take a few deep breaths. Subject instructed to stand with feet together, arms at sides, and weight evenly distributed across feet without shoes. In a standing position, the waist circumference was measured at the midpoint between the iliac crest and the lowest point of the rib cage at the end of a tidal expiration. Hip circumference is measured at a level parallel to the floor at the largest circumference of the buttocks [
14,
15,
16].
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
The blood pressure was measured using a mercury sphygmomanometer. The participant was directed to relax while remaining seated for a duration of five minutes. Two readings were taken every minute. If there was a difference of more than 5 mm Hg between the first two readings, a third reading was taken and the average of all three values was used [
17,
18].
2.4. Pulse Rate
The participant was directed to assume a comfortable posture. The pulse rate was measured for a duration of one minute while the subject’s forearm was maintained in a partially rotated posture with the wrist slightly bent [
19].
2.5. Sample Collection and RNA & DNA Extraction
In accordance to the specified protocol, samples were collected and preserved. In summary, venous blood samples collected from the individuals in the morning were subsequently centrifuged. The resulting serum samples and whole blood were then transported in ice storage boxes to the laboratory and then samples were immediately subjected to extraction. RNA extraction was performed using PureFast® miRNA mini spin purification kit (HELINI Biomolecules, India) and DNA was extracted from the whole blood using Qiagen QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Germany). The purity and concentrations of DNA were determined spectrophotometrically. Samples with a ratio of OD260/OD280 values greater than 1.8 were used for gene expression studies.
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
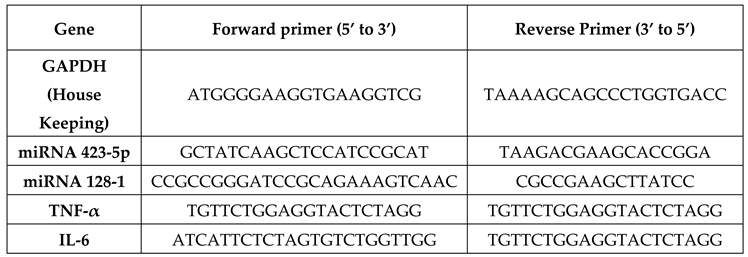
Real time quantitative PCR was performed to analyse gene expression. miRNA and cytokines were amplified in the presence of gene specific primers, housekeeping gene GAPDH; used with the primer concentration of 20pmol for GAPDH and gene specific primers. PCR amplification was performed using Bio-Rad CFX384 Touch Real-Time PCR (Bio-Rad, USA) under the following cycle conditions: 45 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15s, annealing/extension at 60°C for 1 min, and an initial cycle of 50°C for 2 min. GAPDH was used to normalize the relative quantification of the corresponding gene expression levels, which was computed using the 2
−ΔΔCt method. The target genes 423-5p & 128-1 microRNAs and the cytokines (IL-6 & TNF-α) was quantified using qPCR.
2.7. Aerobic Exercise Program
Subjects were asked to perform a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise program 150 minutes per week for 6 months [
20]. Subjects was asked to do brisk walking (4km/h MET score- 3-6) and to complete 10,000 steps/day calculated by step tracker. Instructions were provided so that the participants increase their walking distance by 1000 steps each week, until to perform at least 10,000 steps per day) [
21,
22]. Heart Rate (HR) was also monitored before and after aerobic training. Maximal HR% of 64-76% as suggested by The American College of Sports Medicine guidelines was considered as moderate intensity exercise. Each training session was consisting of a 15-minute warm-up, 30 minutes’ exercise giving a total exercise time of 45 minutes. Each session ended with 10 minutes of stretching exercises for five days. Two days strengthening exercises for individual muscle groups [
22].
4. Results
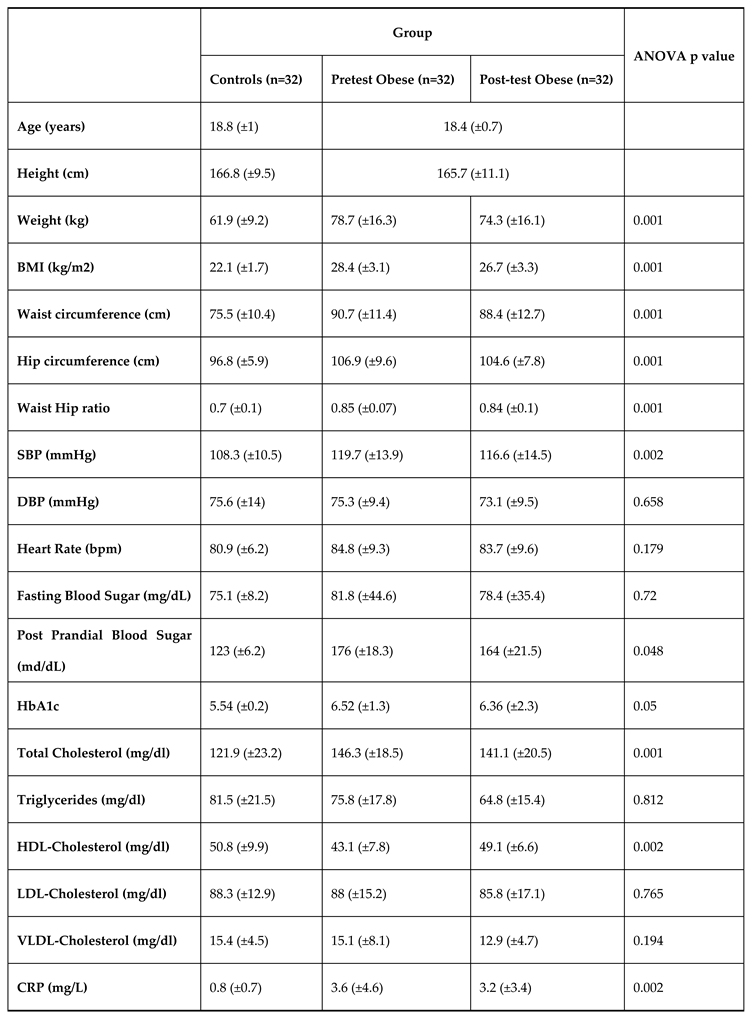
The demographic characteristics of study population are shown in
Table 1. Among the subjects, 32 (50%) obese subjects had Intervention and 32 (50%) non obese subjects were controls without intervention. There was equal distribution of males (n=16) and females (n=16) in both the groups. Groups were similar in terms of age, sex, heart rate, Diastolic blood pressure, fasting blood glucose, lipid levels including triglycerides, VLDL-cholesterol. However, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist hip ratio, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, HDL- cholesterol, LDL- cholesterol & C-reactive protein is significantly higher in obese subjects.
Table 1 expresses that the levels of FBS, PPBS & HbA1c were significantly altered (p<0.05) in the test subjected during the pretest and post-test of aerobic exercise. The levels between the healthy control and test group also had a significant difference.
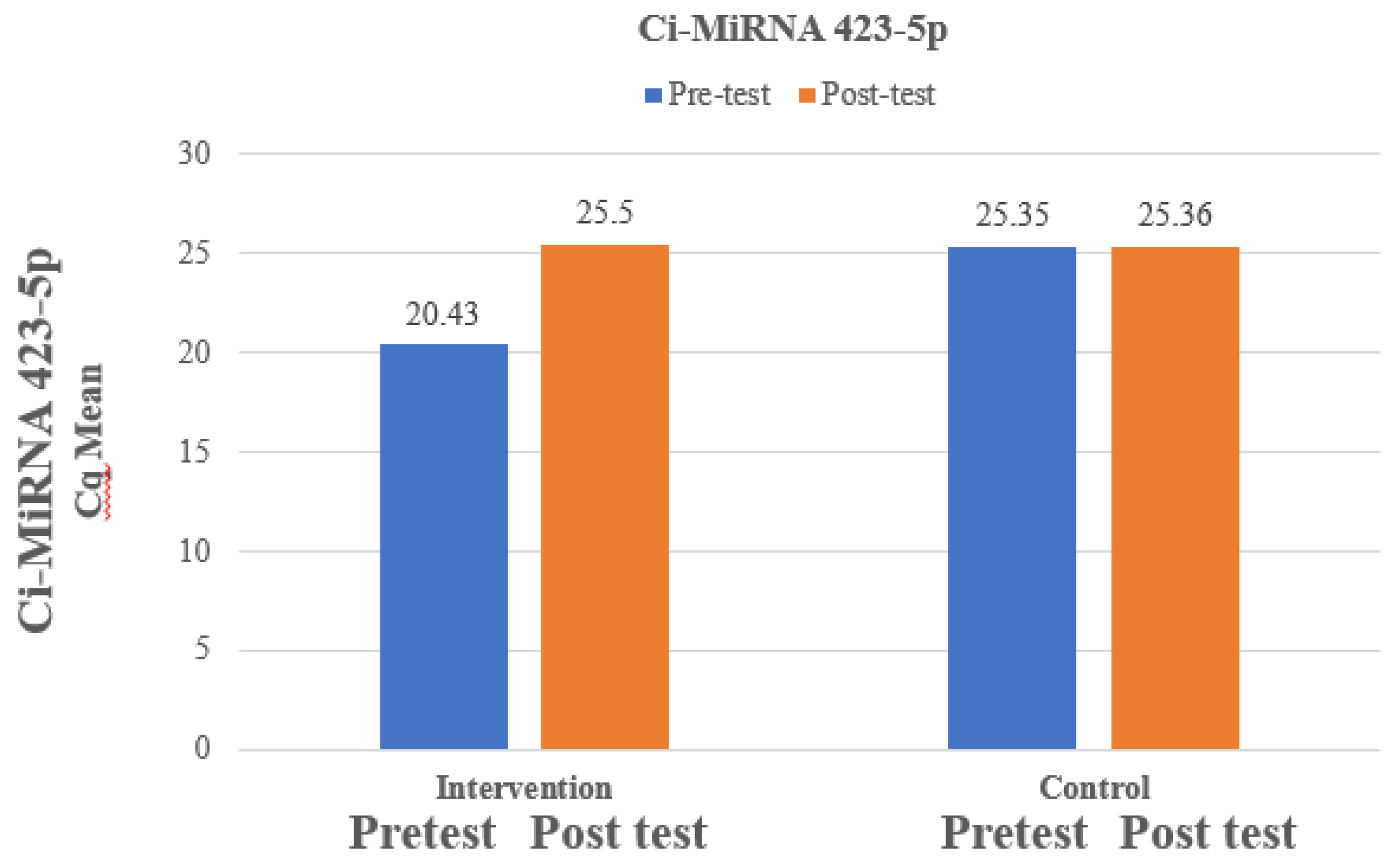
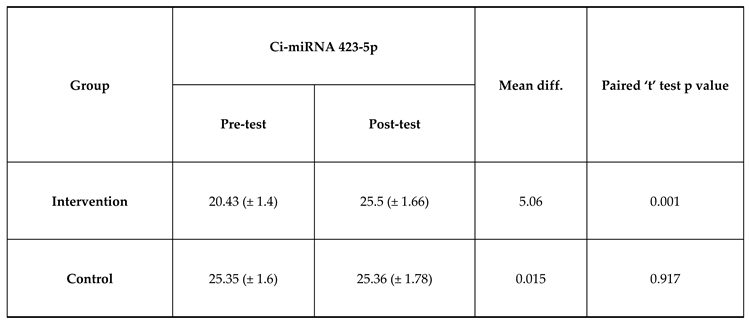
The mean Ci-miRNA 423-5p at pre-test was 20.43 which is lower than mean Ci-miRNA 423-5p at post-test which was 25.5 and the difference between Ci-miRNA 423-5p at pre-test and Ci-miRNA 423-5p at post-test was statistically significant among intervention group. The mean Ci-miRNA 423-5p at pre-test was 20.43 which is lower than mean Ci-miRNA 423-5p at post-test which was 25.5 and the difference between Ci-miRNA 423-5p at pre-test and Ci-miRNA 423-5p at post-test was not statistically significant among control group. The paired t-test for comparison of the analysis was exhibited in
Table 2 and expressed in
Figure 1 and the comparison of analysis of cytokines between the pre and post-test was exhibited in
Figure 2.
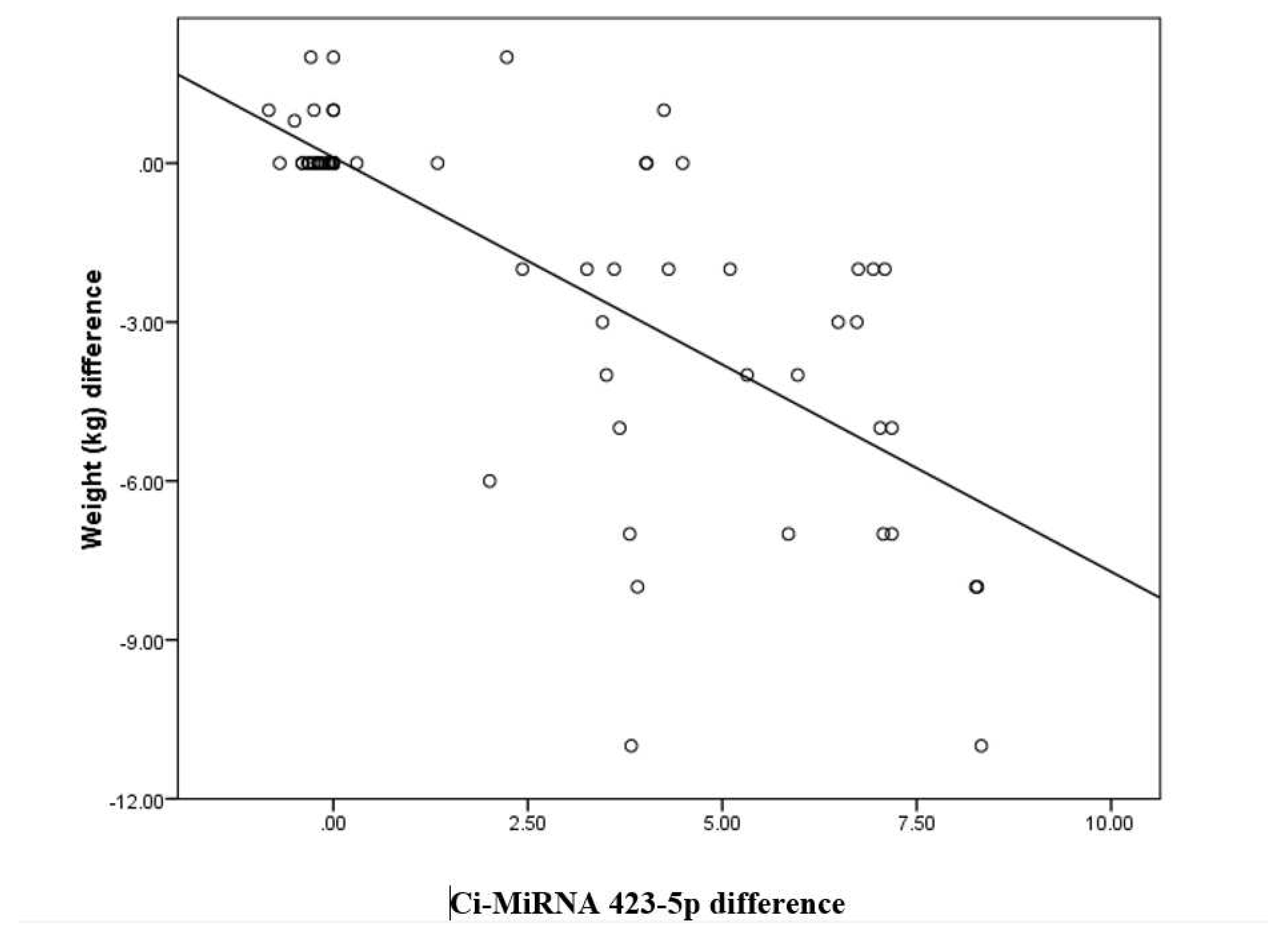
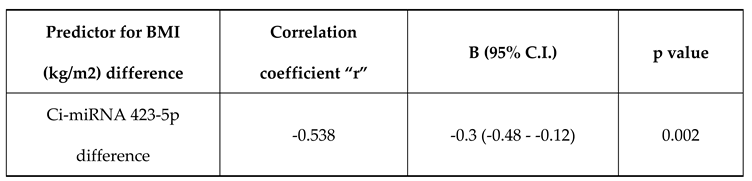
Ci-miRNA423 difference has a negative correlation with BMI (kg/m2) difference with a correlation coefficient of -0.54. BMI (kg/m2) difference decreases by -0.3 times for each unit increase in CimRNA423 difference. The correlation between BMI (kg/m2) difference and Ci-mRNA423 difference was statistically significant (
Table 3).
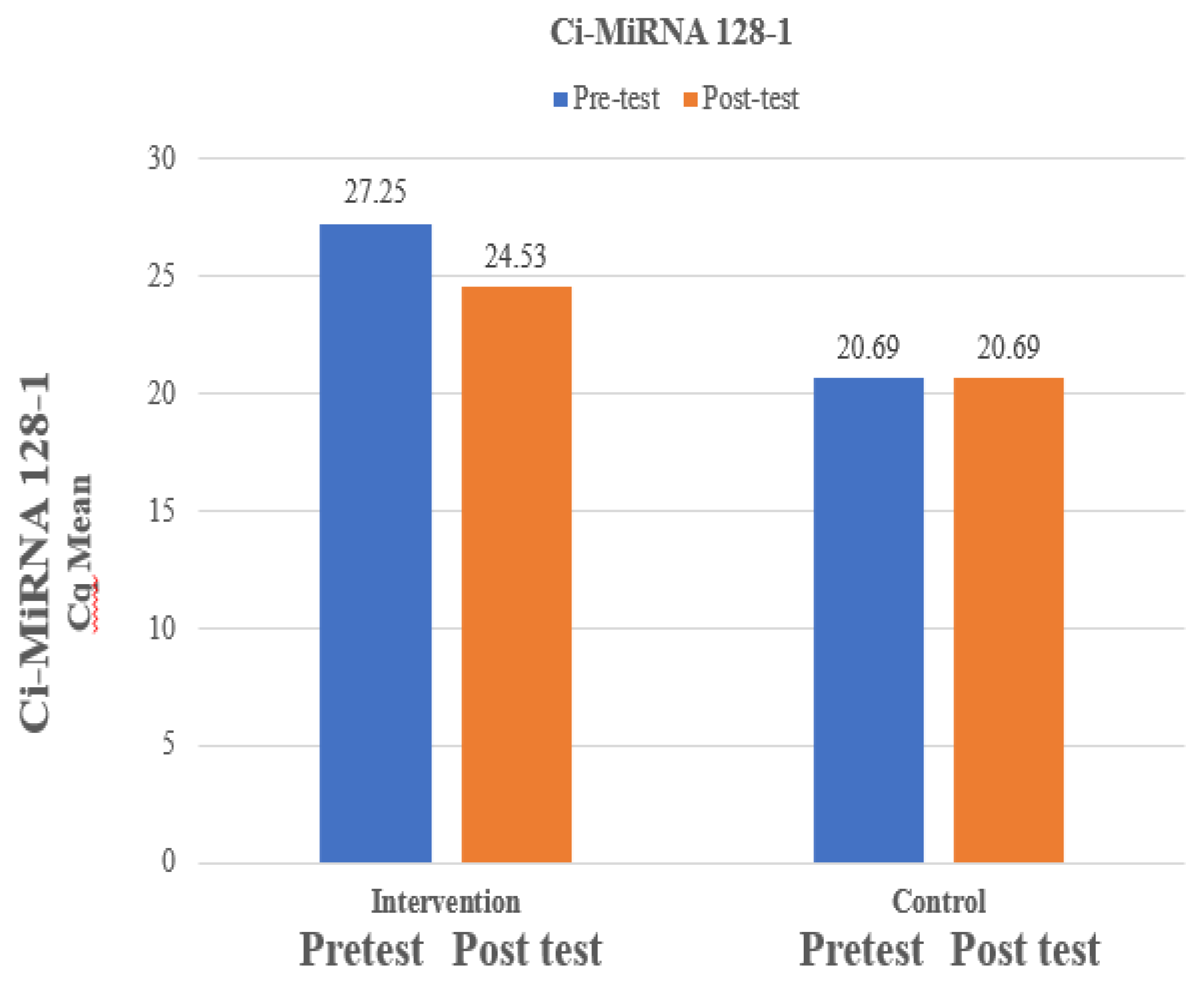
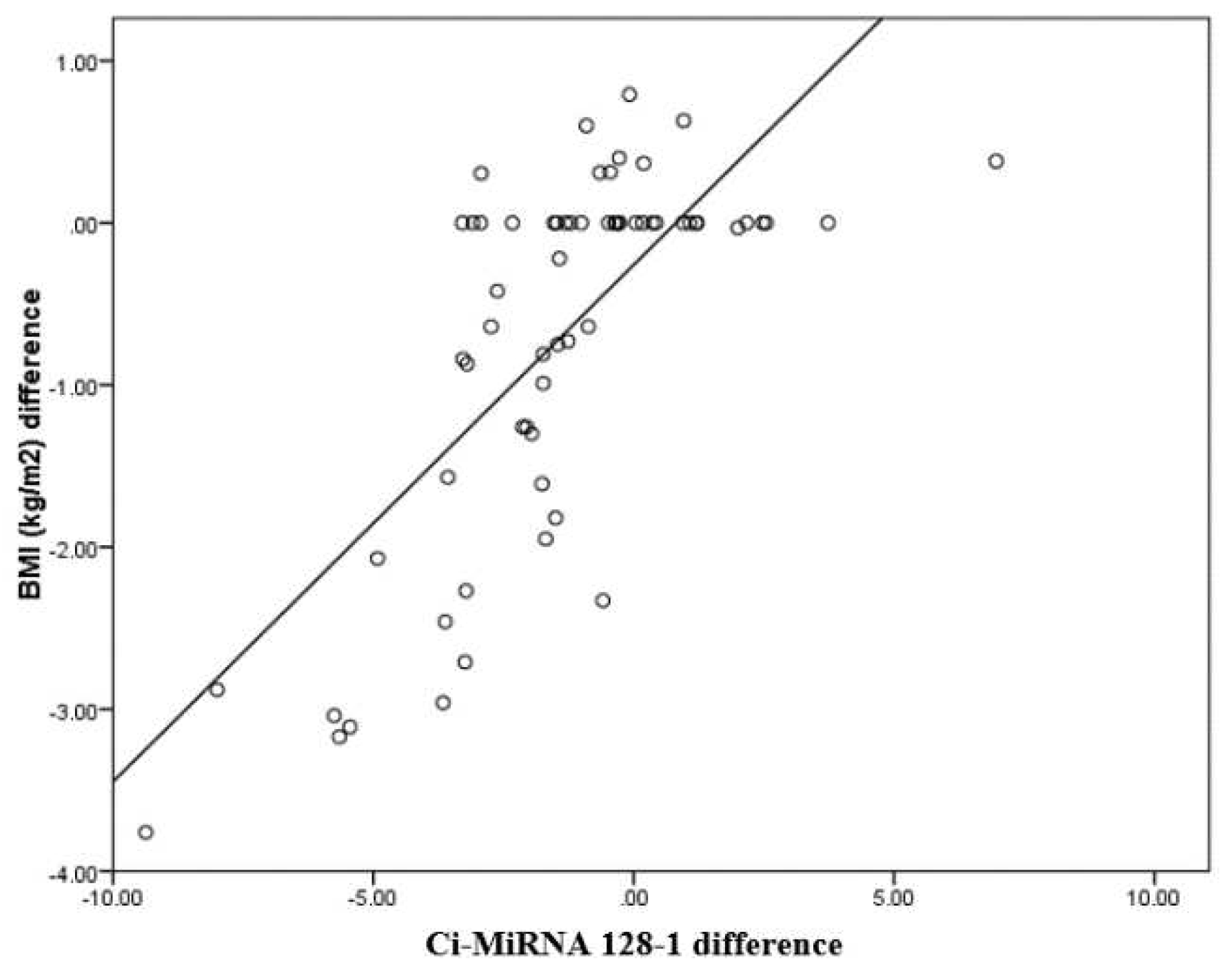
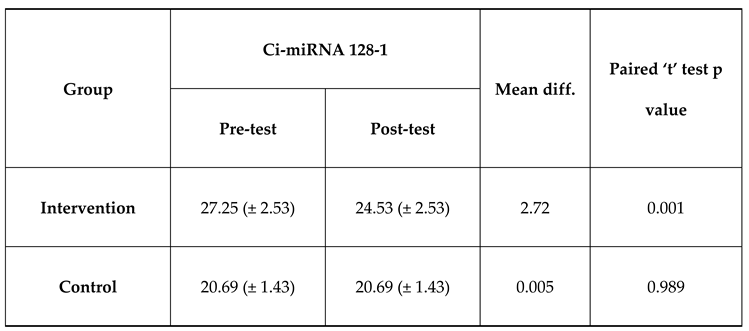
The mean Ci-miRNA 128-1 at pre-test was 27.25 which is higher than mean Ci-miRNA 128-1 at post-test which was 24.53 and the difference between Ci-miRNA 128-1 at pre-test and Ci-miRNA 128-1 at post-test was statistically significant among intervention group. The mean Ci-miRNA 128-1 at pre-test was 27.25 which is higher than mean Ci-miRNA 128-1 at post-test which was 24.53 and the difference between Ci-miRNA 128-1 at pre-test and Ci-miRNA 128-1 at post-test was not statistically significant among control group which was expressed in
Table 4 and
Figure 3.
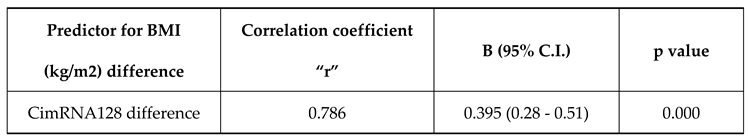
CimRNA128 difference has a positive correlation with BMI (kg/m2) difference with a correlation coefficient of 0.79. BMI (kg/m2) difference increases by 0.39 times for each unit increase in CimRNA128 difference. The correlation between BMI (kg/m2) difference and CimRNA128 difference was statistically significant (
Table 5).
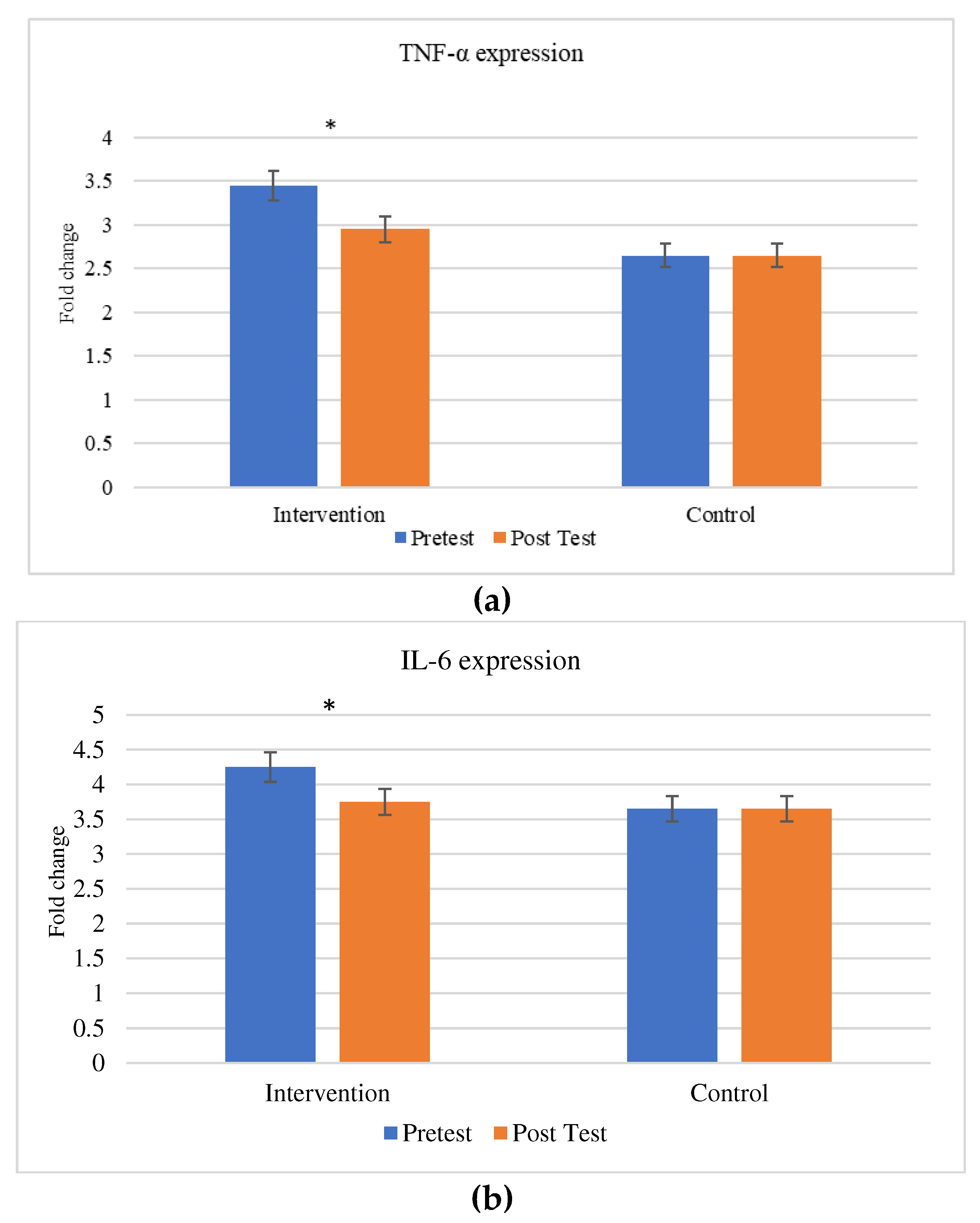
The comparison between the gene expression of cytokines (TNF-α & IL-6) were exhibited in
Figure 5. There is a significant change in the expression in cytokines between the individuals before and after the aerobic exercise training.
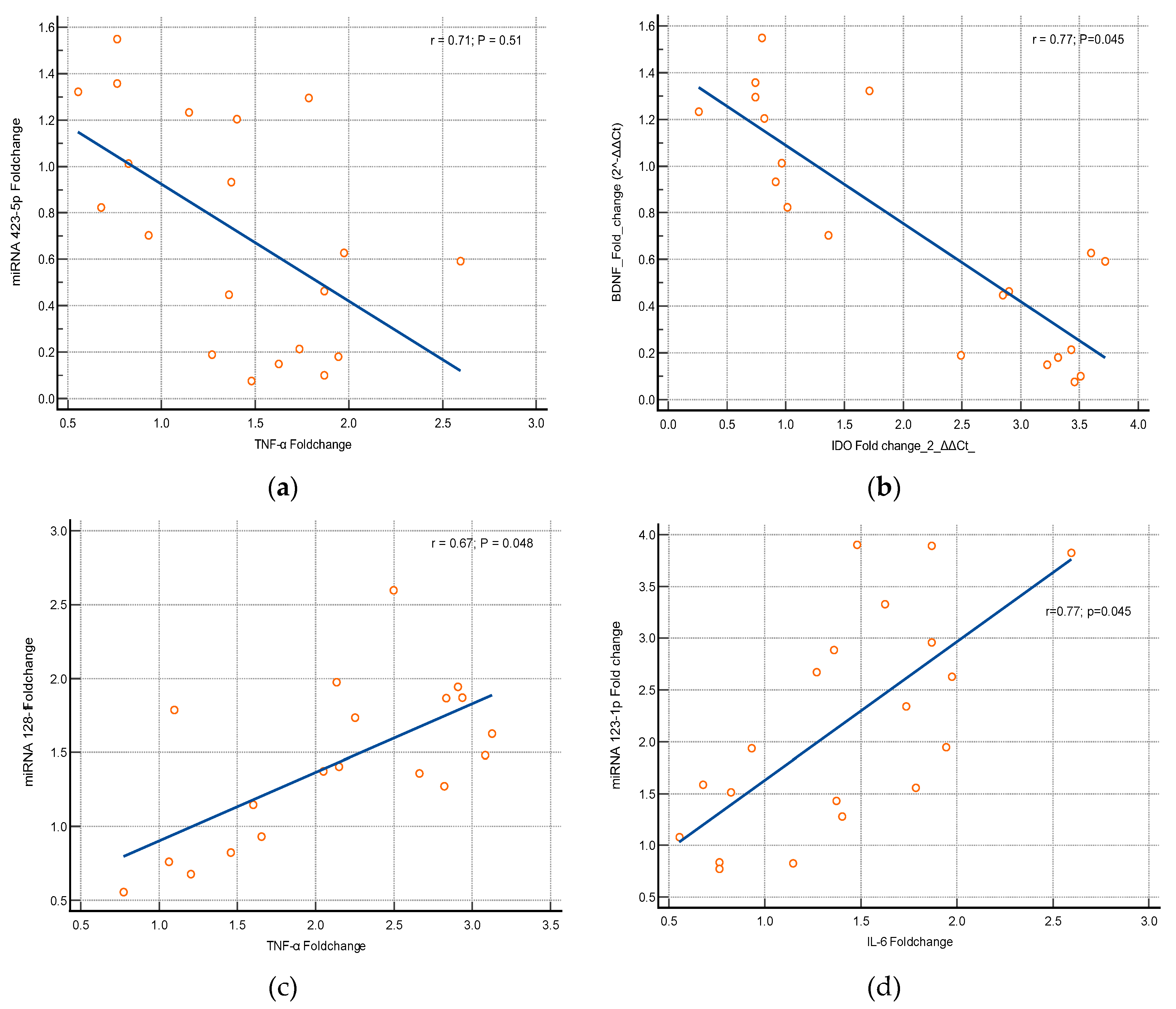
Association between the Expression of Cytokines and miRNA Genes
miRNAs 423-5p and 128-1 are usually stimulated by the inflammatory responses. Our study results found that there is a significant alteration in the expression of miRNAs 423-5p and 128-1 genes related to cytokines (TNF-α & IL-6). Logistic regression statistics proves that the elevation in the expression of miRNAs genes has a strong significant association with elevation of the cytokines [miRNA-423-5p with TNF-α (p=0.051, r=0.71) & miRNA-423-5p with IL-6 (p=0.045, r=0.77); miRNA-128-1p with TNF-α (p=0.051, r=0.71) & miRNA 128-1p with IL-6 (p=0.045, r=0.77)] were depicted in
Figure 5.
5. Discussion
The purpose of the study was to analyse the Ci-miRNAs 423-5p & Ci-miRNA 128 levels before intervention with obese and lean adults and to evaluate the effect of exercise training on Ci-miRNA 423-5p & Ci-miRNA -128-1 in obese adults. The current study shows expression levels of circulating microRNAs 423-5p & 128-1 were significantly differed before and after exercise in study population (P<0.001). Circulating miRNA 423-5p increased and correlated significantly with BMI while Circulating miRNA 128-1 decreased and correlated significantly with BMI after 6-month aerobic exercise program.
According to a study by Al-Rawaf HA, at least 10 circulating miRNAs, including elevated levels of miR-142-3p, miR-140-5p, miR-222, miR-143, and miR-130 and decreased levels of miR532-5p, miR-423-5p, miR-520c-3p, miR-146a, and miR-15a, were found in overweight and obese adolescents. These miRNAs were strongly correlated with measures of body mass index (BMI), Waist- hip ratio (WHtR), adipokines, adiponectin, leptin, and Fasting blood sugar levels (FBS), insulin, HOMA-IR, Triglycerides (TG), HDL-C, C-peptide, and LDL-Cholesterol [
23]. Prepubertal obesity was found to have a significant deregulation of 15 distinct circulating miRNAs, including lower levels of miR-221 and miR-28-3p and elevated plasma concentrations of miR-486-5p, miR-486-3p, miR-142-3p, miR-130b, and miR-423-5p (all P <.0001). In accordance with anthropometric associations, the circulating concentration of these miRNAs was significantly correlated with body mass index and other measures of obesity, including percent fat mass, waist, and regional fat distribution, as well as with laboratory parameters, including high-molecular-weight adiponectin, C-reactive protein, and circulating lipids [
24]. In plasma, obese and morbidly obese males differed from the control group in 18 unique circulating miRNAs (p<0.05). Among these, there were differences in how they were expressed in morbidly obese patients, including increased expression of miR-142-3p, miR-140-5p, and miR-222 and lower circulating concentrations of miR-221, miR-15a, miR-520c-3p, miR-423-5p, and miR-130b. BMI and other measures of obesity were strongly correlated with plasma concentrations of these miRNAs (P< 0.0001). Recently, MicroRNA 128-1 (miR-128-1) was discovered as a thrifty microRNA that regulates energy expenditure, causing obesity and faulty glucose metabolism [
25].
According to studies, miR-128-1 is crucial for maintaining the balance of lipid and energy levels. MiR-128-1 is continuously inhibited in hyperlipidemic Apoe / mice results in a significant reduction of hepatic steatosis, VLDL-associated TAGs, and circulating VLDL-C/LDL-C. By specifically targeting the 3′UTR of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and the ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1), miR-128-1 also regulates the circulating lipoprotein metabolism. Additionally, miR-128-1 antagonism increases hepatic insulin sensitivity, which increases glucose clearance. Along with controlling lipoprotein metabolism, miR-128-1 also controls ABCA-1 expression in macrophages. When miR-128-1 is inhibited, ABCA1 expression and macrophage cholesterol efflux are both increased. Although these results point to miR-148 and miR-128-1 antagonism as potential therapeutic strategies for treating dyslipidemia, obesity, and CVD [
26]. Obesity is a heritable trait in humans. The mir-128-1 gene is situated at the human 2q21.3 locus, as well as syntenic loci in dogs and cattle, which encourage the accumulation of fat in these animals. Adipose tissue, muscle, and the liver are three tissues where miR-128-1 is widely expressed and controls the homeostasis of circulating lipoproteins. Together with other regulators of fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial energy expenditure, and inflammation, it also controls the expression of genes encoding PPAR transcription factors. PPAR transcription factors are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that regulates the activity of several genes involved in metabolic balance, lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism, adipogenesis, and inflammation. Free fatty acids, eicosanoids, and vitamin B3 are all endogenous ligands for peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs). Overall, miR-128-1 inhibits gene expression control energy expenditure in a variety of metabolically active organs and tissues. Loss of miR-128-1 consequently lowered weight gain and fat deposition in mice fed a calorie-rich diet, which was connected with improved insulin sensitivity. Therefore, people with the 2q21.3 variation have higher levels of miR-128-1 expression and more accessible chromatin at the mir-128-1 gene. They may be predisposed to obesity due to increased expression of the miRNA miR-128-1, which makes this miRNA a promising target for the treatment of obesity [
27].
There is an increasing body of literature that highlights the potential of miRNAs as valuable clinical instruments, specifically in the context of identifying “circulating” miRNAs as biomarkers. Optimal blood glucose levels are maintained through the precise regulation of insulin release. Recently recognized as “ribo-regulators” of glucose homeostasis, microRNAs (miRNAs) influence the sensitivity or resistance of its target tissues while playing a crucial role in the production and secretion of insulin [
28,
29,
30,
31]. In most cases, an imbalance between energy intake and energy output leads to obesity and overweight conditions. They result from the interaction of numerous factors, including an individual’s metabolism, caloric and food consumption, and lack of physical activity. Omics methodologies have intriguingly suggested a correlation between obesity or metabolic diseases and the expression of multiple microRNAs in various tissues (e.g., adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas). Additionally, the expression of miRNAs was found to be directly correlated with diet and lifestyle, according to multiple studies. Several studies indicate that the miR-17/20/93 family, miR-21/590-5p family, miR-200b/c family, miR-221/222 family, let-7/miR-98 family, and miR-203 are the most dysregulated in this context, despite the importance of the list of miRNAs associated with diet [
32]. The outcomes of our research are consistent with the theoretical and empirical findings mentioned earlier. The gene expression levels of the circulating 128-1 and 423-5p microRNAs were significantly elevated in obese adolescents relative to healthy individuals. Additionally, obese adolescents exhibited beneficial outcomes as a result of engaging in aerobic exercise training. Embryos undergoing aerobic exercise for six months exhibit a reduction in miRNA expression. The results of this study suggest that circulating microRNAs carrying the sequences 423-5p and 128-1 might possess diagnostic potential in relation to obesity.
Logistic regression statistics proves that the elevation in the expression of miRNA-128-1p has a strong significant association with elevation of the cytokines (TNF-α & IL-6). The results of Zhang et al., express that serum miRNA-128 had a greater clarification of their clinical significance are importing for improving the diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, the results of Zhang et al., the correlation analysis indicated that the serum miR-128 levels were positively correlated with the serum IL-1β levels and the TNF-α levels in neurological disorder patients [
33]. The research results of Arcidiacono et al., states that pro-inflammatory factors, including CRP, and cytokines, such as IL-6, TNF-α, and INF-γ, which contribute to insulin resistance in obese individuals [
34]. The combined results of Zhang et al., Arcidiacono et al., and our research express that miRNA-128 family have a strong positive correlation with the cytokines concluding miRNA-128 to be potential diagnostic marker in diseased conditions.
The effective application of logistic regression statistics provides evidence that there exists a robust and significant correlation between the upregulation of miRNA-423-5p and the increase in cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6). The research conducted by Yang et al. indicates that the expression level of miRNA-423-5p was significantly increased in an inflammatory environment and decreased in a treated animal model. The results of the study demonstrate a clear and indirect association between the levels of IL-6 and miRNA-423-5p in conditions associated with disease [
35]. The review results of Ibarra et al., states that miRNA expression had a direct correlation with inflammation and obesity. The review also proposed that miRNAs as biological markers of different diseases, and also as potential therapeutic targets [
36]. The integration of previous research, review findings, and our own study results demonstrates a robust association between miRNA-423-5p and cytokines. This suggests that miRNA-423-5p could serve as a promising diagnostic and therapeutic indicator in pathological states.