Submitted:
31 January 2024
Posted:
31 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
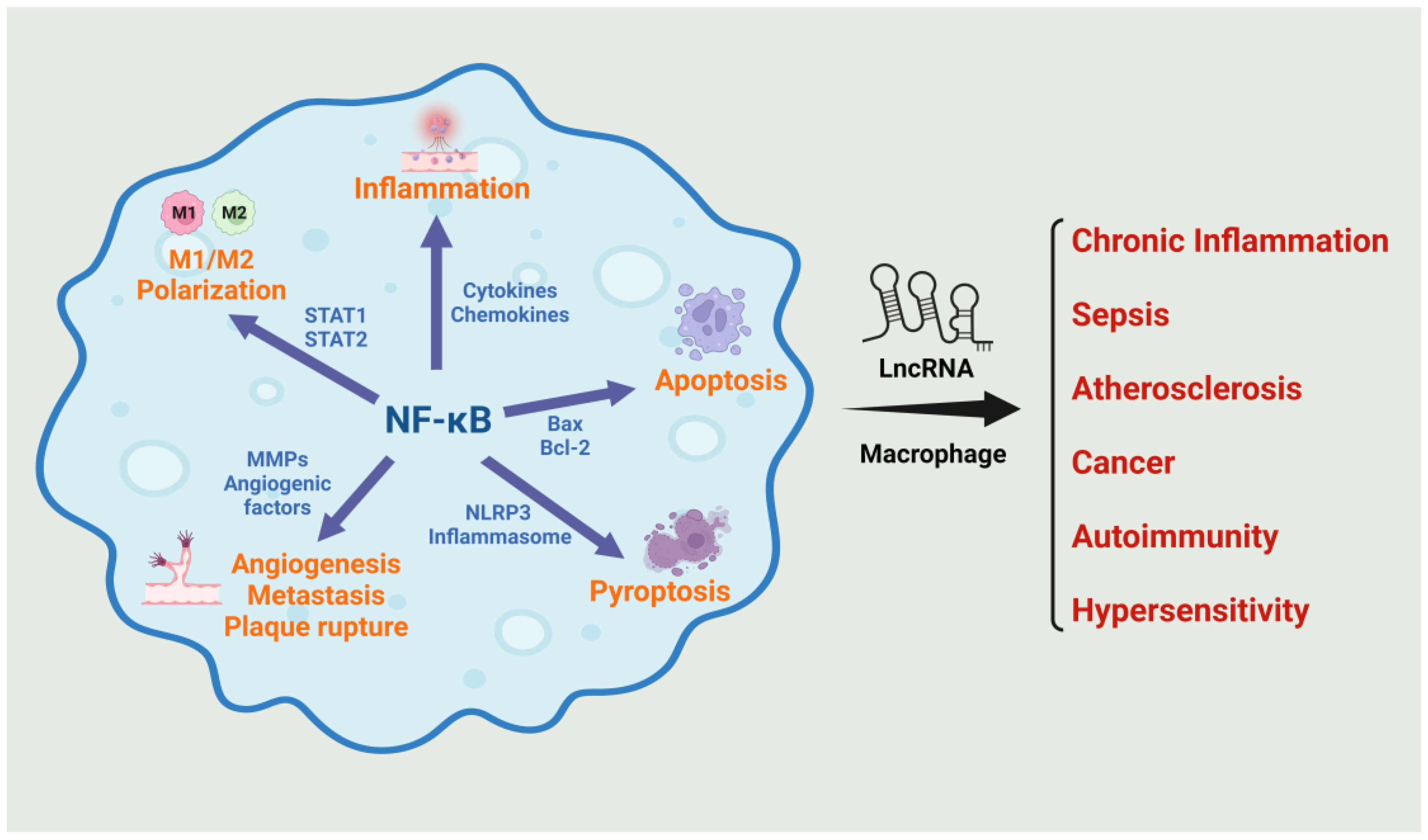
1. Introduction
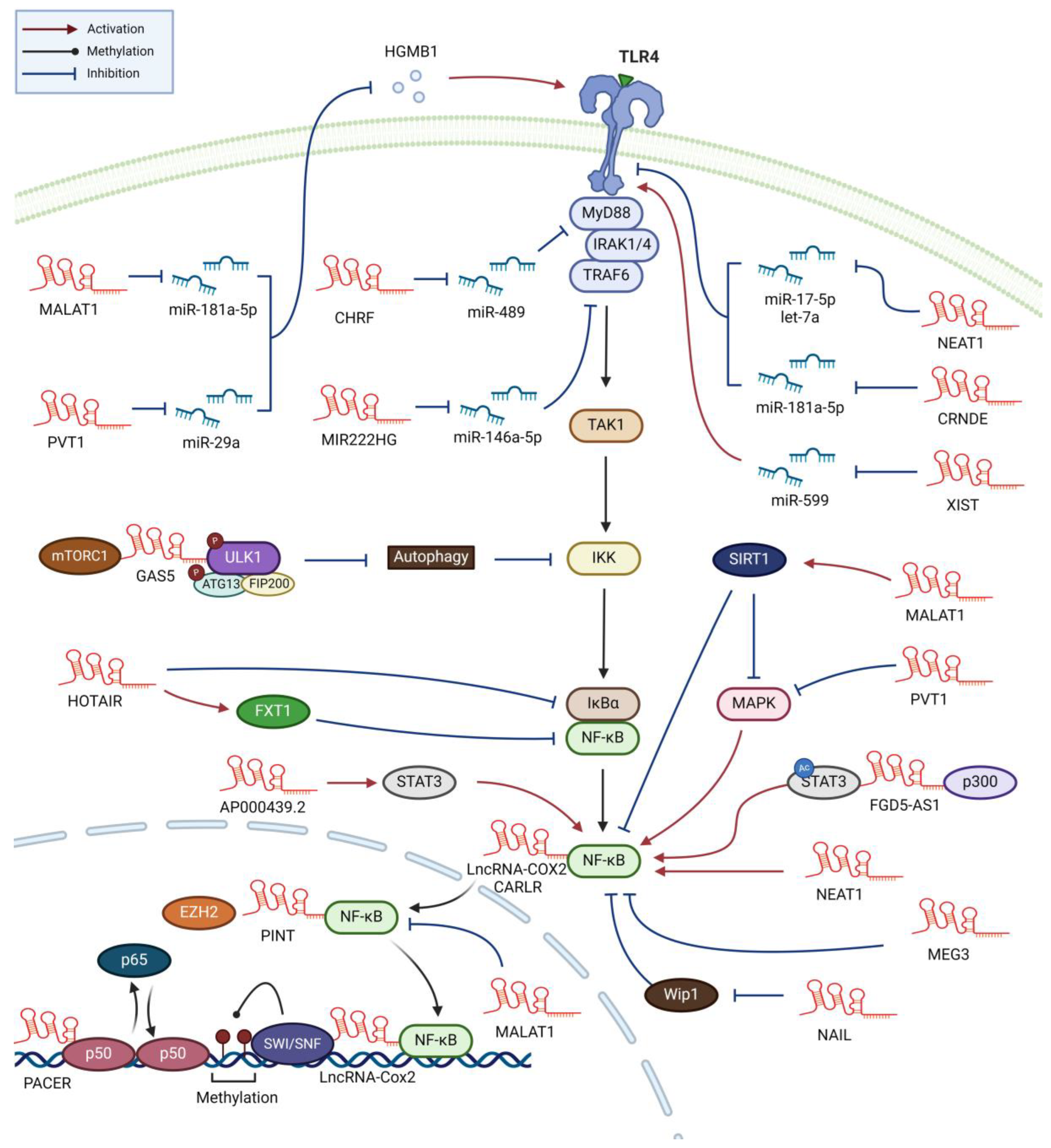
2. Sepsis
3. Atherosclerosis
| LncRNA | Disease | Target | Function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1. LncRNAs directly affecting NF-κB activity | ||||
| CARLR | Celiac disease | p65 | LPS-induced, regulates p65 translocation, promotes proinflammatory cytokines production | [103] |
| COX2 | Neuroinflammation | p65 | LPS-induced, promotes p65 translocation, enhances inflammasome formation, suppresses autophagy | [104] |
| COX2 | SLE | SWI/SNF/NF-κB | LPS-induced, enhances the expression of NF-κB-induced late inflammatory genes | [105] |
| MALAT1 | Sepsis | p65/p50 | LPS-induced, retrains NF-κB from promoter, regulates proinflammatory cytokine expression | [36] |
| PACER | Cancer | p50 | LPS-induced, sequesters p50 and promotes p300-mediated histone acetylation, enhances COX2 expression | [106] |
| PINT | Cancer | p65 and EZH2 | LPS-induced, bridges p65 and EZH2, activates TNFα transcription | [107] |
| Group 2. LncRNAs affecting pathways that regulate NF-κB activity | ||||
| CHRF | Cancer | miR-489/MyD88 | Silica-induced, promotes inflammatory responses and fibrosis. | [108] |
| CRNDE | Cancer | miR-181a-5p/TLR4 | LPS-induced, promotes inflammatory responses. Also increased in AML and IgA nephropathy | [41,44] |
| MALAT1 | Atherosclerosis | SIRT1/MAPK | ox-LDL-induced, promotes autophagy, reduces apoptosis | [93] |
| MIR222HG | Allergic rhinitis | miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 | Deceased in patients, causing the dominance of type 2 response. Promotes M1 and suppresses M2 polarization | [109] |
| NAIL | Ulcerative colitis | Wip1 | LPS-induced, promotes p65 phosphorylation by blocking Wip1 action, increases inflammatory response | [110] |
| NEAT1 | Osteolysis | miR-188-5p/ BTK KLF/BTK |
Induced by titanium particles, activates inflammasome and NF-κB, enhances M1 polarization | [68] |
| NEAT1 | Sepsis | miR-17-5p/TLR4 | LPS-induced, promotes inflammatory response by stabilizing TLR4 mRNA | [32] |
| NEAT1 | Sepsis | let-7a/TLR4 | LPS-induced, promotes inflammatory response by stabilizing TLR4 mRNA | [29] |
| NKILA | Asthma | IκB | Anti-inflammation by inhibiting IκB phosphorylation, induces M2 polarization | [111,112] |
| PVT1 | Sepsis | miR-29a/ HMGB1/TLR4 | LPS-induced, promotes inflammation and M1 polarization. Also increased in osteoarthritis patients | [48,50] |
| SNHG1 | Cancer/Sepsis | HMGB1/TLR4 | Enhances TLR4 signaling by interaction with HMGB1, promotes M1 polarization | [113] |
| XIST | Atherosclerosis | miR-599/TLR4 | OxLDL-induced in macrophages/vascular smooth muscle cells, promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis | [76] |
| Group 3. LncRNAs affecting NF-κB activity with unknown mechanism of action | ||||
| DCST1-AS1 | Cancer | p65 | Activates NF-κB signaling pathway in both cancer cells and macrophages. Promotes M2 polarization | [114] |
| FTX | Cirrhosis | NF-κB | Anti-inflammatory function. Decreased in patients, causing enhancement in inflammation | [115] |
| HOTAIR | Cancer | IκBα | LPS-induced, activates NF-κB by degrading IκB, regulates metabolic reprogramming by inducing GLUT1 | [116] |
| HOTAIR | Atherosclerosis | FXR1 | Anti-inflammation by inactivating NF-κB via FXR1. Decreased in patients and oxLDL-treated macrophages. | [101,102] |
| NEAT1 | Atherosclerosis | p65, ERK | ox-LDL-induced, regulates p65 and ERK phosphorylation, promotes TNF-α secretion. | [28,66] |
| MEG3 | Sepsis | p65 | Decreased in sepsis patients. LPS-induced, inhibits p65 phosphorylation. Downregulates inflammation and apoptosis. | [51] |
| SNHG16 | Atherosclerosis | miR-17-5p | ox-LDL-induced, promotes proliferation and inflammatory response. Also increased in cancer and diabetes | [73,74,75] |
| Group 4. LncRNAs transferred to macrophages via exosomes or EVs | ||||
| FGD5-AS1 | Cancer | P300/STAT3/NF-κB | Contained in exosomes from pancreatic cancer cells, activates STAT3/NF-κB, promotes M2 polarization | [117] |
| AP000439.2 | Cancer | STAT3, P65 | Contained in exosomes from cancer cells, promotes macrophage M2 polarization | [118] |
| GAS5 | Allergic rhinitis | mTORC1/ULK1/ATG13 | Activate NF-κB and promote M1 polarization by suppressing autophagy-dependent degradation of IKKa/b | [119] |
| HOTTIP | Cancer | - | Contained in M1-derived exosomes. Suppresses cancer growth via TLR5 activation. Promotes M1 polarization | [120] |
| MALAT1 | Acute pancreatitis | miR-181a-5p /HNGB1/TLR4 |
Carried by EVs originating from pancreatic cancer cells, promotes M1 polarization | [121] |
4. Cancer
5. Autoimmunity and hypersensitivity
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion and future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
Abbreviations
References
- Plytycz, B.; Seljelid, R. From inflammation to sickness: historical perspective. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2003, 51, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, L. From biological aging to functional decline: Insights into chronic inflammation and intrinsic capacity. Ageing Res Rev 2024, 93, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.B.; Storkus, W.J. Chronic inflammation and immunologic-based constraints in malignant disease. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motwani, M.P.; Gilroy, D.W. Macrophage development and polarization in chronic inflammation. Semin Immunol 2015, 27, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardito, S.; Martinelli, G.; Soldano, S.; Paolino, S.; Pacini, G.; Patane, M.; Alessandri, E.; Smith, V.; Cutolo, M. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 2019, 18, 102397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T.; Gilroy, D.W.; Colville-Nash, P.R.; Willoughby, D.A. Possible new role for NF-kappaB in the resolution of inflammation. Nat Med 2001, 7, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napetschnig, J.; Wu, H. Molecular basis of NF-kappaB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 2013, 42, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.B.; Tsitsipatis, D.; Gorospe, M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell 2022, 82, 2252–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, H.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Wang, D.O. LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2022, 41, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senmatsu, S.; Hirota, K. Roles of lncRNA transcription as a novel regulator of chromosomal function. Genes Genet Syst 2021, 95, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, L. LncRNA Structural Characteristics in Epigenetic Regulation. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, B. Mechanisms of lncRNA/microRNA interactions in angiogenesis. Life Sci 2020, 254, 116900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrè, F.; Colantoni, A.; Helmer-Citterich, M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform 2016, 17, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorkova, O.; Hsiao, J.; Wahlestedt, C. Basic biology and therapeutic implications of lncRNA. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015, 87, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, E.L.; Belhocine, M.; Dao, L.T.; Puthier, D.; Spicuglia, S. [Functions of lncRNA in development and diseases]. Med Sci (Paris) 2014, 30, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.X.; Koirala, P.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravda, J. Sepsis: Evidence-based pathogenesis and treatment. World J Crit Care Med 2021, 10, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofaro, P.; Opal, S.M. The Toll-like receptors and their role in septic shock. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2003, 7, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chousterman, B.G.; Swirski, F.K.; Weber, G.F. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin Immunopathol 2017, 39, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J.; Beutler, B.; Lowry, S.F.; Merryweather, J.; Wolpe, S.; Milsark, I.W.; Hariri, R.J.; Fahey, T.J., 3rd; Zentella, A.; Albert, J.D.; et al. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science 1986, 234, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shou, S.; Chai, Y. The roles of macrophage polarization in the host immune response to sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 96, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.F.; Malik, A.B. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006, 290, L622–L645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Tanigawa, A.; Sasaki, Y.F.; Goshima, N.; Hirose, T. Alternative 3'-end processing of long noncoding RNA initiates construction of nuclear paraspeckles. EMBO J 2012, 31, 4020–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Niu, F. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes inflammatory response in sepsis-induced liver injury via the Let-7a/TLR4 axis. Int Immunopharmacol 2019, 75, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yao, R.; Zhou, P.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Xu, S. LncRNA NEAT1 reversed the hindering effects of miR-495-3p/STAT3 axis and miR-211/PI3K/AKT axis on sepsis-relevant inflammation. Mol Immunol 2020, 117, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, F.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, Q.L. LncRNA NEAT1 facilitates the progression of sepsis through up-regulating TSP-1 via sponging miR-370-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020, 24, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Cai, Y. NEAT1 Promotes LPS-induced Inflammatory Injury in Macrophages by Regulating MiR-17-5p/TLR4. Open Med (Wars) 2020, 15, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Qin, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. LncRNA NEAT1 Promotes Inflammatory Response in Sepsis via the miR-31-5p/POU2F1 Axis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guo, Z.H. Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Promoting Macrophage M2 Polarization via miR-125a-5p/TRAF6/TAK1 Axis. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tang, S.; Ke, S.; Cai, J.J.; Osorio, D.; Golovko, A.; Morpurgo, B.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Winkle, M.; et al. Ablation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 activates antioxidant pathway and alleviates sepsis in mice. Redox Biol 2022, 54, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Su, Z.; Song, D.; Mao, Y.; Mao, X. The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through its interaction with NF-kappaB. FEBS Lett 2016, 590, 2884–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Jing, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Jiang, T.; et al. Knockdown of LncRNA MALAT1 contributes to the suppression of inflammatory responses by up-regulating miR-146a in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Connect Tissue Res 2018, 59, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.P.; Niu, G.H.; Zhang, X.Q. Influence of lncRNA MALAT1 on septic lung injury in mice through p38 MAPK/p65 NF-kappaB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019, 23, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Banerjee, S.; Guo, S.; Xie, N.; Ge, J.; Jiang, D.; Zornig, M.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates differential activation of macrophages and response to lung injury. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Cao, K.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J. Hsa-miR-346 plays a role in the development of sepsis by downregulating SMAD3 expression and is negatively regulated by lncRNA MALAT1. Mol Cell Probes 2019, 47, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yue, D.; Zeng, Z.; Yuan, W.; Xu, K. Linkage of lncRNA CRNDE sponging miR-181a-5p with aggravated inflammation underlying sepsis. Innate Immun 2020, 26, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, J.J. High expression of lnc-CRNDE presents as a biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia and promotes the malignant progression in acute myeloid leukemia cell line U937. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018, 22, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, B.; Shen, C.; Chu, X.; Luo, X.; Yu, L.; Ye, J.; Xiong, L.; Dan, W.; Li, J.; Zhong, L. [lncRNA CRNDE promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of U937 cells by downregulating miR-136-5p and upregulating MCM5]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 37, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Pan, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Pan, M.; Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, L. LncRNA CRNDE Exacerbates IgA Nephropathy Progression by Promoting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages. Immunol Invest 2022, 51, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ren, H.; Liu, B. Evaluating the potency of blood long noncoding RNA PVT1 as candidate biomarker reflecting inflammation, multiple organ dysfunction, and mortality risk in sepsis patients. J Clin Lab Anal 2022, 36, e24268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Xiong, X.; Du, J.; Fan, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. LncRNA PVT1 accelerates LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury through targeting miR-17-5p and regulating NF-kappaB pathway. Int Urol Nephrol 2021, 53, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Li, W.; Liao, W.; Huang, C.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zou, Z.; He, Z. Silencing of LncRNA-PVT1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in THP-1-derived macrophages via inhibition of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ann Palliat Med 2021, 10, 6410–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Lin, X.F.; Zhao, F.L.; Tu, H.T.; Wang, L.J.; Wen, M.Y.; Xian, S.X. Knockdown of lncRNA PVT1 attenuated macrophage M1 polarization and relieved sepsis induced myocardial injury via miR-29a/HMGB1 axis. Cytokine 2021, 143, 155509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreggvidsdottir, H.S.; Lundberg, A.M.; Aveberger, A.C.; Klevenvall, L.; Andersson, U.; Harris, H.E. High mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1)-partner molecule complexes enhance cytokine production by signaling through the partner molecule receptor. Mol Med 2012, 18, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Qiu, S.; Sun, L.; Zuo, J. Knockdown of exosome-mediated lnc-PVT1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by mediating the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway via miR-93-5p. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 5313–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; He, L. LncRNA MEG3 expression in sepsis and its effect on LPS-induced macrophage function. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2020, 66, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.S.; Domingues, N.; Vieira, O.V. Lipid and Non-lipid Factors Affecting Macrophage Dysfunction and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 14, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Atherosclerosis in Inflammation. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Sun, H.; Zhou, P.; Peng, Q.; Du, S.; Zheng, S.; Liu, X. Macrophage polarization states in atherosclerosis. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1185587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Abdollahi, E.; Nikfar, B.; Chaichian, S.; Ekhlasi-Hundrieser, M. Curcumin as a potential modulator of M1 and M2 macrophages: new insights in atherosclerosis therapy. Heart Fail Rev 2019, 24, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H. Regulation of Macrophage Activation and Differentiation in Atherosclerosis. J Lipid Atheroscler 2021, 10, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I. Macrophage death and defective inflammation resolution in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 2010, 10, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sahebkar, A.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Weng, J.; Ge, J. Mechanisms of Oxidized LDL-Mediated Endothelial Dysfunction and Its Consequences for the Development of Atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 925923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, U. Matrix metalloproteinases and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2004, 6, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.M. The intracellular signaling pathways governing macrophage activation and function in human atherosclerosis. Biochem Soc Trans 2022, 50, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, E.; Taheri, F.; Renani, P.G.; Reiner, Z.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage: A Key Therapeutic Target in Atherosclerosis? Curr Pharm Des 2019, 25, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, N.I.; Sachse, M.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Zormpas, E.; Bampatsias, D.; Delialis, D.; Bonini, F.; Galyfos, G.; Sigala, F.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; et al. Adenosine-to-inosine Alu RNA editing controls the stability of the pro-inflammatory long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2021, 160, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.B. Knockdown of NEAT1 mitigates ox-LDL-induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via miR-30c-5p/TCF7 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020, 24, 9633–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang-Fu, N.; Cheng, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, S.H. Neat1 regulates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammation and lipid uptake in macrophages via paraspeckle formation. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 3092–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, J.W.; Ke, Z.P.; Zhang, B.H. Blockade of NEAT1 represses inflammation response and lipid uptake via modulating miR-342-3p in human macrophages THP-1 cells. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 5319–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wen, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Lin, C.; Kuang, M.; Xue, C.; Ding, Y. LncRNA Neat1 promotes the macrophage inflammatory response and acts as a therapeutic target in titanium particle-induced osteolysis. Acta Biomater 2022, 142, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.D.; Hui, L.L.; Zhang, X.C.; Chang, Q. NEAT1 contributes to ox-LDL-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in macrophages through inhibiting miR-128. J Cell Biochem 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, M.; Rauch, B.H.; Haghikia, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Haas, J.; Stroux, A.; Schmidt, D.; Schumann, P.; Weiss, S.; Jensen, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 modulates immune cell functions and is suppressed in early onset myocardial infarction patients. Cardiovasc Res 2019, 115, 1886–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Qiao, L.; Shao, H.; Zhang, X. Small interfering RNA-induced silencing lncRNA PVT1 inhibits atherosclerosis via inactivating the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 24449–24463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, M.A.; Hazazi, A.; Khan, F.R.; Abdulaziz, O.; Alshaghdali, K.; Abalkhail, A.; Nassar, S.A.; Omar, B.I.A.; Almarshadi, F.; Gupta, G.; Binshaya, A.S. PVT1 lncRNA in lung cancer: A key player in tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities. Pathol Res Pract 2023, 253, 155019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Ma, Q.L.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Shi, F.W. LncRNA SNHG16 promoted proliferation and inflammatory response of macrophages through miR-17-5p/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in patients with atherosclerosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019, 23, 8665–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.L.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Su, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, H.; Mao, Q.S.; Xue, W.J. SNHG16/miR-605-3p/TRAF6/NF-kappaB feedback loop regulates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 7637–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiong, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. Silencing LncRNA SNHG16 suppresses the diabetic inflammatory response by targeting the miR-212-3p/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2023, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xue, Y.; Gao, X. LncRNA XIST Promotes Atherosclerosis by Regulating miR-599/TLR4 Axis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fu, Y.; Gu, X.; Xi, X.; Peng, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Qian, F.; Qin, Z.; et al. Macrophage-Enriched lncRNA RAPIA: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2020, 40, 1464–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, I.; Kudriashov, V.; Sufianov, A.; Begliarzade, S.; Ilyasova, T.; Liang, Y.; Beylerli, O. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the development of atherosclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res 2022, 7, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.; Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; He, R. H19 knockdown suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-148b/WNT/beta-catenin in ox-LDL -stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci 2018, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Chu, Y.; Tian, P. Knockdown of H19 Attenuates Ox-LDL-induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Regulating miR-599/PAPPA Axis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2021, 77, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, S.; Tahmasebi-Birgani, M.; Bijanzadeh, M.; Seyedian, S.M. Increased Expression Level of Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Plasma of Patients with Myocardial Infarction. Int J Mol Cell Med 2020, 9, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Long, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, D.C.; Yan, J.J.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, L.S. Increased plasma levels of lncRNA H19 and LIPCAR are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Silencing of H19 inhibits the adipogenesis and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated Raw264.7 cells by up-regulating miR-130b. Mol Immunol 2018, 93, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Y. LncRNA H19/miR-let-7 axis participates in the regulation of ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury via targeting periostin. Int Immunopharmacol 2019, 72, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Che, Y.; Wang, J.; Men, K. [Effects and mechanism of knocking down lncRNA H19 to inhibit lipid accumulation in human THP-1 cells-derived macrophages]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2023, 39, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.X. LncRNA H19 promotes atherosclerosis by regulating MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2017, 21, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Sun, J. lncRNA-MALAT1 expression in patients with coronary atherosclerosis and its predictive value for in-stent restenosis. Exp Ther Med 2020, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Tan, L.; Yao, J.; Yang, L. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates cholesterol accumulation in ox-LDL-induced macrophages via the microRNA-17-5p/ABCA1 axis. Mol Med Rep 2020, 21, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhu, H. LncRNA MALAT1 Suppression Protects Endothelium against oxLDL-Induced Inflammation via Inhibiting Expression of MiR-181b Target Gene TOX. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 8245810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, N.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X. LncRNA MALAT1 regulates oxLDL-induced CD36 expression via activating beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018, 495, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, X.; Ma, H. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Regulates the Progression of Atherosclerosis by miR-330-5p/NF-kappaB Signal Pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2021, 78, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Qu, Y.; Dong, H.; Dang, J.; Huo, Z.; Xu, G. LncRNA expression profile during autophagy and Malat1 function in macrophages. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0221104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 Enhances ox-LDL-Induced Autophagy through the SIRT1/MAPK/NF-kappaB Pathway in Macrophages. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2020, 18, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusetskaya, N.Y.; Loginova, N.Y.; Pokrovskaya, E.P.; Chesovskikh, Y.S.; Titova, L.E. Redox regulation of the NLRP3-mediated inflammation and pyroptosis. Biomed Khim 2023, 69, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Qiu, H.; Pei, X.; Fan, Y.; Tian, H.; Geng, J. Low-dose Sinapic Acid Abates the Pyroptosis of Macrophages by Downregulation of lncRNA-MALAT1 in Rats With Diabetic Atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2018, 71, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T. A Review of the Roles of Specialized Extracellular Vesicles, Migrasomes, and Exosomes in Normal Cell Physiology and Disease. Med Sci Monit 2023, 29, e940118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Luo, L.; Wei, X.; Gong, D.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Tang, W.; Jin, L. M1 Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Angiogenesis and Myocardial Regeneration Following Myocardial Infarction via the MALAT1/MicroRNA-25-3p/CDC42 Axis. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso Mda, S.; Castilho, G.; Lavrador, M.S.; Passarelli, M.; Nakandakare, E.R.; Lottenberg, S.A.; Lottenberg, A.M. The impact of dietary fatty acids on macrophage cholesterol homeostasis. J Nutr Biochem 2014, 25, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, M.; Rauch, B.H.; Nakagawa, S.; Haghikia, A.; Jasina, A.; Haas, J.; Nath, N.; Jensen, L.; Stroux, A.; Bohm, A.; et al. Immune system-mediated atherosclerosis caused by deficiency of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in ApoE-/-mice. Cardiovasc Res 2019, 115, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, W.; Zhu, J. Exosomal MALAT1 derived from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-treated endothelial cells promotes M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Med Rep 2018, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.L.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, P.Y.; Jiang, J.S.; Yu, C. HOTAIR alleviates ox-LDL-induced inflammatory response in Raw264.7 cells via inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018, 22, 6991–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanini, F.; Bontekoe, C.; Bakker, C.E.; van Unen, L.; Anar, B.; Willemsen, R.; Yoshida, M.; Galjaard, H.; Oostra, B.A.; Hoogeveen, A.T. Different targets for the fragile X-related proteins revealed by their distinct nuclear localizations. Hum Mol Genet 1999, 8, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Kratchmarov, R.; Sebastian, M.; Garcia-Etxebarria, K.; Garcia, L.; Irastorza, I.; Ghosh, S. Cytoplasmic Form of Carlr lncRNA Facilitates Inflammatory Gene Expression upon NF-kappaB Activation. J Immunol 2017, 199, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; et al. lincRNA-Cox2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy mediated neuroinflammation. Cell Death Differ 2019, 26, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Gong, A.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Su, C.J.; Shibata, A.; Strauss-Soukup, J.K.; Drescher, K.M.; Chen, X.M. LincRNA-Cox2 Promotes Late Inflammatory Gene Transcription in Macrophages through Modulating SWI/SNF-Mediated Chromatin Remodeling. J Immunol 2016, 196, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Emerson, B.M. p50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) activates COX-2 gene expression by occluding repressive NF-kappaB complexes. Elife 2014, 3, e01776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, P.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, R. An NF-kappaB-responsive long noncoding RNA, PINT, regulates TNF-alpha gene transcription by scaffolding p65 and EZH2. FASEB J 2021, 35, e21667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Han, L.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Ni, C. miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA CHRF. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 30921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Dong, L.; He, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tao, Z. MIR222HG attenuates macrophage M2 polarization and allergic inflammation in allergic rhinitis by targeting the miR146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-kappaB axis. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1168920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akincilar, S.C.; Wu, L.; Ng, Q.F.; Chua, J.Y.H.; Unal, B.; Noda, T.; Chor, W.H.J.; Ikawa, M.; Tergaonkar, V. NAIL: an evolutionarily conserved lncRNA essential for licensing coordinated activation of p38 and NFkappaB in colitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Lu, S. Long non-coding RNA NKILA alleviates airway inflammation in asthmatic mice by promoting M2 macrophage polarization and inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021, 571, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Yin, D.; Yang, X.; Tang, Q. lncRNA-NKILA/NF-kappaB feedback loop modulates laryngeal cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and radioresistance. Cancer Med 2018, 7, 2048–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, J.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, C.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.; Yao, M.; Lu, X.; Qiu, L.; Xing, L. Tanreqing Injection Attenuates Macrophage Activation and the Inflammatory Response via the lncRNA-SNHG1/HMGB1 Axis in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 820718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, H.; Wu, S.; Wei, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Zou, C. lncRNA DCST1-AS1 facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma by promoting M2 macrophage polarization through activating NF-κB signaling. Journal of Immunology Research 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Dou, C.; Yao, B.; Xu, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tu, K.; et al. Ftx non coding RNA-derived miR-545 promotes cell proliferation by targeting RIG-I in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25350–25365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, M.; Udden, S.M.N.; Alluri, P.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates glucose transporter Glut1 expression and glucose uptake in macrophages during inflammation. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. Exosome-derived FGD5-AS1 promotes tumor-associated macrophage M2 polarization-mediated pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett 2022, 548, 215751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Miao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, X.; Xue, S.; Du, B.; Tang, C.; Qu, L.; Fu, D.; Jia, R.; He, H. Exosomal AP000439.2 from clear cell renal cell carcinoma induces M2 macrophage polarization to promote tumor progression through activation of STAT3. Cell Commun Signal 2022, 20, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization in allergic rhinitis via restraining mTORC1/ULK1/ATG13-mediated autophagy and subsequently activating NF-small ka, CyrillicB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 121, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, L.; Shen, N.; Ning, X.; Wu, D.; Jiang, K.; Huang, X. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes and their key molecule lncRNA HOTTIP suppress head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating the TLR5/NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Pei, H.; Pan, L. MALAT1 shuttled by extracellular vesicles promotes M1 polarization of macrophages to induce acute pancreatitis via miR-181a-5p/HMGB1 axis. J Cell Mol Med 2021, 25, 9241–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Geng, X.; Hou, J.; Wu, G. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiani, P.; Boraschi, D. From Monocytes to M1/M2 Macrophages: Phenotypical vs. Functional Differentiation. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, G.; Germano, G.; Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) as major players of the cancer-related inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 2009, 86, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erreni, M.; Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P. Tumor-associated Macrophages (TAM) and Inflammation in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Microenviron 2011, 4, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cheng, D.; Ma, D.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Zhao, W.; Fang, C.; Ji, M. Mutual regulation of PD-L1 immunosuppression between tumor-associated macrophages and tumor cells: a critical role for exosomes. Cell Commun Signal 2024, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Ko, H.M.; Choi, J.H.; Jung, H.H.; Chun, Y.H.; Choi, I.W.; Lee, H.K.; Im, S.Y. Essential role for platelet-activating factor-induced NF-kappaB activation in macrophage-derived angiogenesis. Eur J Immunol 2004, 34, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, A.; Lawrence, T. Nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varney, M.L.; Olsen, K.J.; Mosley, R.L.; Bucana, C.D.; Talmadge, J.E.; Singh, R.K. Monocyte/macrophage recruitment, activation and differentiation modulate interleukin-8 production: a paracrine role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis. In Vivo 2002, 16, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Ji, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Shi, R.; Xiang, W.; Kang, X.; Zhang, D.; Yang, F.; et al. Macrophage ABHD5 Suppresses NFkappaB-Dependent Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression and Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 5513–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; An, Y. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate FAIM2 expression by sponging miR-1254 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond) 2019, 133, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X.; Wei, D.; Xu, X.; Yan, F. Long Noncoding RNA DCST1-AS1 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Triple-negative Breast Cancer by Forming a Positive Regulatory Loop with miR-873-5p and MYC. J Cancer 2020, 11, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X. Inhibition of lncRNA DCST1-AS1 suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by increasing miR-874-3p expression. J Gene Med 2021, 23, e3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lei, C.; Shi, P.; Teng, H.; Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, X. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 Promotes Endometrial Cancer Progression by Modulating the MiR-665/HOXB5 and MiR-873-5p/CADM1 Pathways. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 714652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Cui, M.F.; Du, J.; Song, B. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 regulated cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis in gastric cancer by targeting miR-605-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020, 24, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yao, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 downregulates miR-29b through methylation in glioblastoma (GBM) to promote cancer cell proliferation. Clin Transl Oncol 2020, 22, 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Dai, G. Long non-coding RNA DCST1-AS1/hsa-miR-582-5p/HMGB1 axis regulates colorectal cancer progression. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, S. Long Noncoding RNA FGD5-AS1 Knockdown Decrease Viability, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells by Regulating the MicroRNA-944/MACC1 Axis. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2021, 20, 1533033821990090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Ye, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ding, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Kuang, Y.; et al. CREPT/RPRD1B promotes tumorigenesis through STAT3-driven gene transcription in a p300-dependent manner. Br J Cancer 2021, 124, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, M.; Lei, W.; Yang, R.; Fu, S.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T. Advances in the role of STAT3 in macrophage polarization. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1160719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Du, X.; Xiao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Q. Activation of fgd5-as1 promotes progression of cervical cancer through regulating bst2 to inhibit macrophage m1 polarization. Journal of Immunology Research 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, S.J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. Tetherin inhibits retrovirus release and is antagonized by HIV-1 Vpu. Nature 2008, 451, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupzig, S.; Korolchuk, V.; Rollason, R.; Sugden, A.; Wilde, A.; Banting, G. Bst-2/HM1.24 is a raft-associated apical membrane protein with an unusual topology. Traffic 2003, 4, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Liu, D.; Liang, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X. A cluster of long non-coding RNAs exhibit diagnostic and prognostic values in renal cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 9597–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, K.; Tang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Cai, S.; Ye, J.; Xi, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Cai, C.; et al. Identification and experimental validation of a tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes-related long noncoding RNA signature for prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1046790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chureau, C.; Prissette, M.; Bourdet, A.; Barbe, V.; Cattolico, L.; Jones, L.; Eggen, A.; Avner, P.; Duret, L. Comparative sequence analysis of the X-inactivation center region in mouse, human, and bovine. Genome Res 2002, 12, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheykhi-Sabzehpoush, M.; Ghasemian, M.; Khojasteh Pour, F.; Mighani, M.; Moghanibashi, M.; Mohammad Jafari, R.; Zabel, M.; Dziegiel, P.; Farzaneh, M.; Kempisty, B. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA FTX in human disorders. Clin Transl Oncol 2023, 25, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, T.; Talluri, S.; Akshaya, R.L.; Dunna, N.R. HOTAIR LncRNA: A novel oncogenic propellant in human cancer. Clin Chim Acta 2020, 503, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Li, Q.; Fang, J.; Zhao, T. LncRNA HOTAIR: A Potential Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Target in Human Cancers. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 679244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Hu, P.; Gao, L.; Tian, S.; He, Z. Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR in Central Nervous System Disorders: New Insights in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Potential. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 949095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Gao, L.; Yu, Z.H.; Hong, S.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Qiu, Z.Z. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating Notch1 pathway via the modulation of miR-124. Nephrology (Carlton) 2019, 24, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. HOTAIR Epigenetically Modulates PTEN Expression via MicroRNA-29b: A Novel Mechanism in Regulation of Liver Fibrosis. Mol Ther 2017, 25, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, R.L.; Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. HOTAIR beyond repression: In protein degradation, inflammation, DNA damage response, and cell signaling. DNA Repair (Amst) 2021, 105, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, V.; Shyam, K.P.; Angelmary, A.; Kadalmani, B. Lauric acid epigenetically regulates lncRNA HOTAIR by remodeling chromatin H3K4 tri-methylation and modulates glucose transport in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells: Lipid switch in macrophage activation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2024, 1869, 159429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, M.; Udden, S.M.N.; Deb, P.; Shihabeddin, N.; Zaki, M.H.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine expression and inflammatory response in macrophages. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.F.; Li, L.J.; Ma, J.B. LncRNA HOTTIP promotes proliferation and cell cycle progression of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019, 23, 2908–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Dai, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. DDA1, a novel oncogene, promotes lung cancer progression through regulation of cell cycle. J Cell Mol Med 2017, 21, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesario, A.; Rocca, B.; Rutella, S. The interplay between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in chronic inflammation and cancer. Curr Med Chem 2011, 18, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Quan, J.C.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, M.; Liu, Z.; Guan, X.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, X.S. lncRNA-PACER upregulates COX-2 and PGE2 through the NF-kappaB pathway to promote the proliferation and invasion of colorectal-cancer cells. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2021, 9, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desind, S.Z.; Iacona, J.R.; Yu, C.Y.; Mitrofanova, A.; Lutz, C.S. PACER lncRNA regulates COX-2 expression in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2022, 13, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Song, D.; Yan, W.; Liu, T.; Wu, Z.; Kong, J.; Wei, H.; Xiao, J. P50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) overexpression promotes proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by activating COX-2 gene. Tumour Biol 2016, 37, 3879–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Deng, H.; Liu, F.; Zhao, D.; Tang, H.; Gu, H. Long Non-Coding RNA PACER Regulates Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced Inflammatory Response through Interaction with NF-kappaB. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2022, 52, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mola-Ali-Nejad, R.; Fakharianzadeh, S.; Maloum, Z.; Taheri, M.; Shirvani-Farsani, Z. A gene expression analysis of long non-coding RNAs NKILA and PACER as well as their target genes, NF-kappaB and cox-2 in bipolar disorder patients. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2023, 42, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhao, W.; Pang, J.; Xiong, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, L. Long non-coding RNA, CHRF, predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Oncol Lett 2018, 16, 6245–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.Y. Smad3 Signatures in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis. Int J Biol Sci 2022, 18, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Ding, X.; Zhao, S.; Mou, T.; Li, R.; Cao, X. Long non-coding RNA CHRF accelerates LPS-induced acute lung injury through microRNA-146a/Notch1 axis. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Zhou, S.; Cai, W.; Kang, M.; Zhang, P. LncRNA SNHG1: role in tumorigenesis of multiple human cancers. Cancer Cell Int 2023, 23, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Ren, K.; Han, X. The Interaction Between lncRNA SNHG1 and miR-140 in Regulating Growth and Tumorigenesis via the TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway in Cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Res 2019, 27, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. The regulatory network among CircHIPK3, LncGAS5, and miR-495 promotes Th2 differentiation in allergic rhinitis. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liechty, C.; Zgheib, C.; Hodges, M.M.; Liechty, K.W.; Xu, J. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Regulates Macrophage Polarization and Diabetic Wound Healing. J Invest Dermatol 2020, 140, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Ding, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization via miR-455-5p/SOCS3 pathway in childhood pneumonia. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 13242–13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yu, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, M.; Pu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Huang, A.; Xiang, Z.; et al. LncRNA GAS5 inhibits microglial M2 polarization and exacerbates demyelination. EMBO Rep 2017, 18, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, I.; Asai, A.; Suzuki, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F. M2b macrophage polarization accompanied with reduction of long noncoding RNA GAS5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017, 493, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, H.; Xu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Huang, C. LncRNA GAS5 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation-mediated pyroptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by targeting miR-34b-3p/AHR. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 3054–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wu, T.; Gao, X.; He, Z.; Nong, W. Research Progress of Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 in Malignant Tumors. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 846497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Lei, X.; Gan, R. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 in human cancer. Oncol Lett 2020, 20, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Gong, A.Y.; Zhang, X.T.; Lin, C.; Ma, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Chen, X.M. LincRNA-Cox2 modulates TNF-alpha-induced transcription of Il12b gene in intestinal epithelial cells through regulation of Mi-2/NuRD-mediated epigenetic histone modifications. FASEB J 2016, 30, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapicavoli, N.A.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Mikhail, M.; Laberge, R.M.; Chang, H.Y. A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2013, 2, e00762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, R.H.; Fouad, N.A.; Hefzy, E.M.; Shaker, O.G.; Ahmed, T.I.; Hussein, H.A.; Nasr, M.H.; Zaki, O.M.; Abdelghaffar, N.K.; Abdelaleem, O.O. The potential role of serum expression profile of long non coding RNAs, Cox2 and HOTAIR as novel diagnostic biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0268176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A long noncoding RNA mediates both activation and repression of immune response genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; He, Q.; Geng, Y.; Xu, J. LncRNA-Cox2 regulates macrophage polarization and inflammatory response through the CREB-C/EBPbeta signaling pathway in septic mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 101, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogulur, I.; Pat, Y.; Ardicli, O.; Barletta, E.; Cevhertas, L.; Fernandez-Santamaria, R.; Huang, M.; Bel Imam, M.; Koch, J.; Ma, S.; et al. Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases. Allergy 2021, 76, 3659–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Jimenez, N.; Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Plaza-Izurieta, L.; Irastorza, I.; Elcoroaristizabal, X.; Jauregi-Miguel, A.; Lopez-Euba, T.; Tutau, C.; de Pancorbo, M.M.; Vitoria, J.C.; Bilbao, J.R. Coregulation and modulation of NFkappaB-related genes in celiac disease: uncovered aspects of gut mucosal inflammation. Hum Mol Genet 2014, 23, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Verma, S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Gupta, S. EZH2 and NF-kappaB: A context-dependent crosstalk and transcriptional regulation in cancer. Cancer Lett 2023, 560, 216143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Wang, G.; Xu, L.; Fu, Y. CEBPB promotes gastrointestinal motility dysfunction after severe acute pancreatitis via the MALAT1/CIRBP/ERK axis. Mol Immunol 2023, 156, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fu, S.; Sun, D.; Xing, J.; Hou, T.; Wu, X. EPC-derived exosomes promote osteoclastogenesis through LncRNA-MALAT1. J Cell Mol Med 2019, 23, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, K.G.; Wang, B.W.; Fang, W.J.; Pan, C.M.; Lin, C.M. Exosomal MALAT1 Derived from High Glucose-Treated Macrophages Up-Regulates Resistin Expression via miR-150-5p Downregulation. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lai, Y.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, T. Long non-coding RNA cox-2 prevents immune evasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering M1/M2 macrophage polarization. J Cell Biochem 2018, 119, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA therapeutics - challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, I.; Park, J.; Shin, J.J.; Shin, H.S.; Suk, K.; Lee, W.H. Macrophage lncRNAs in cancer development: Long-awaited therapeutic targets. Biochem Pharmacol 2023, 218, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgna, V.; Villegas, J.; Burzio, V.A.; Belmar, S.; Araya, M.; Jeldes, E.; Lobos-Gonzalez, L.; Silva, V.; Villota, C.; Oliveira-Cruz, L.; et al. Mitochondrial ASncmtRNA-1 and ASncmtRNA-2 as potent targets to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in the RenCa murine renal adenocarcinoma model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43692–43708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





