Submitted:
25 January 2024
Posted:
26 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid construction and cell lines
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Flow cytometry
3. Results
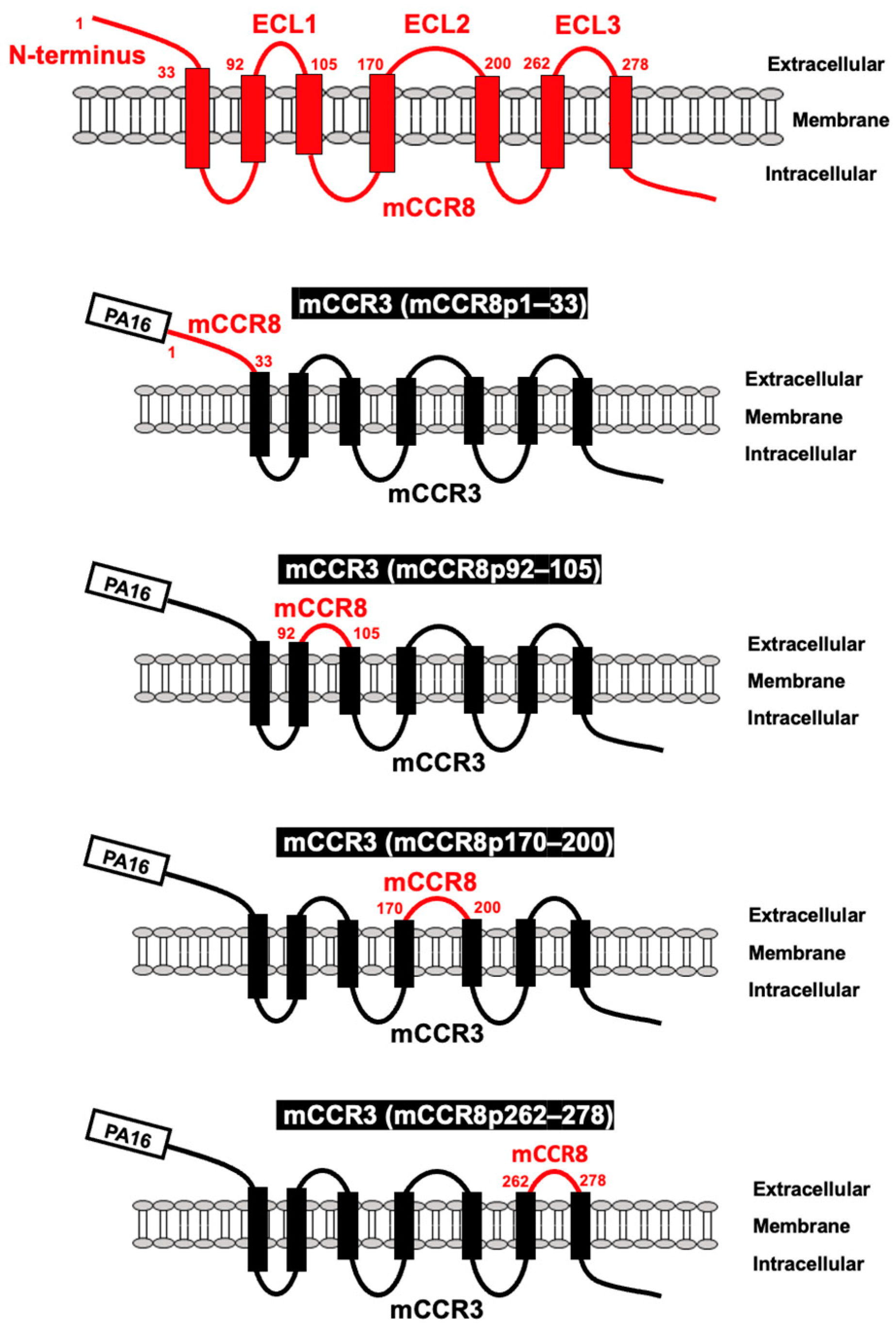
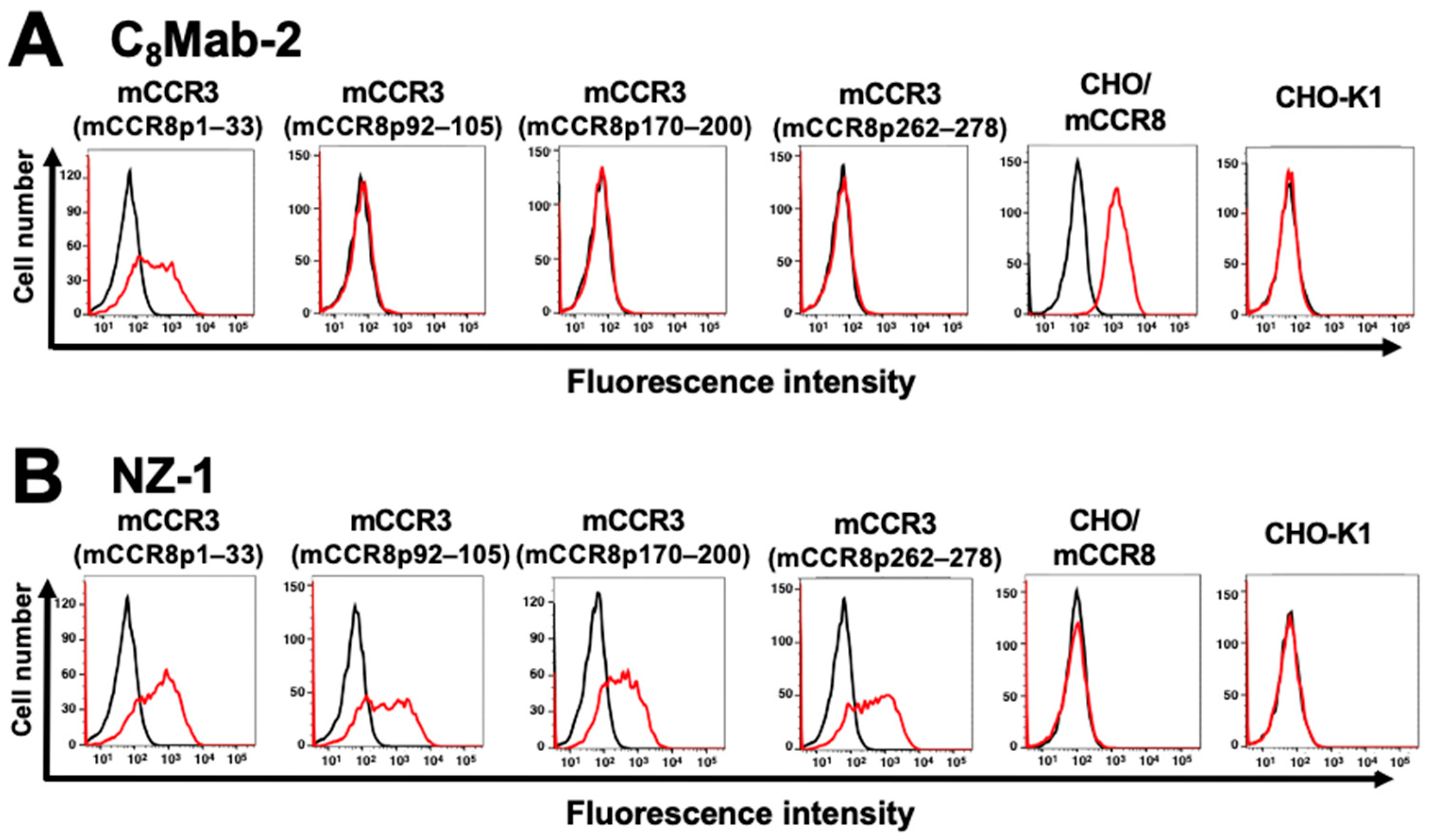
3.1. Determination of the epitope of an anti-mCCR8 mAb by flow cytometry using chimeric proteins
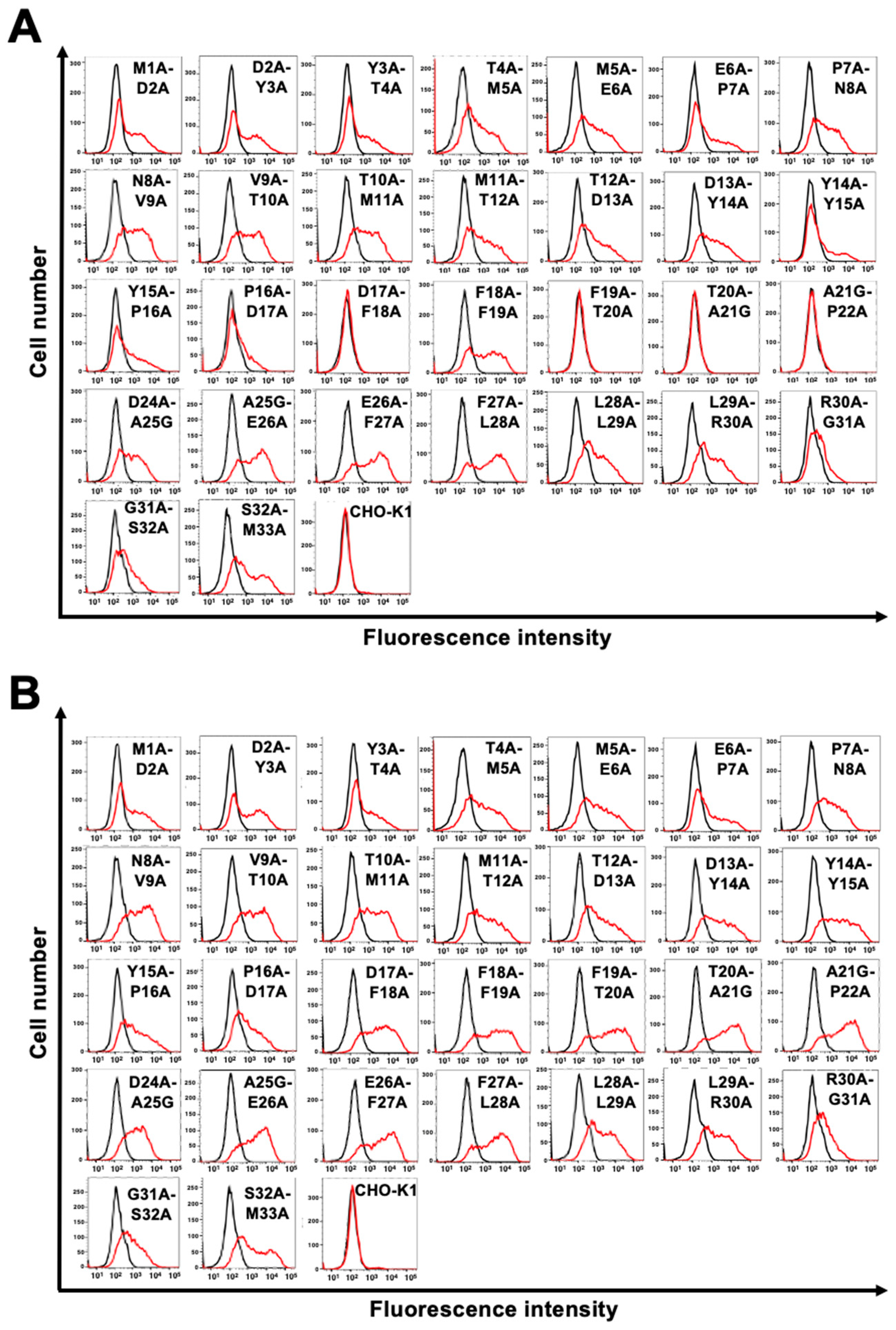
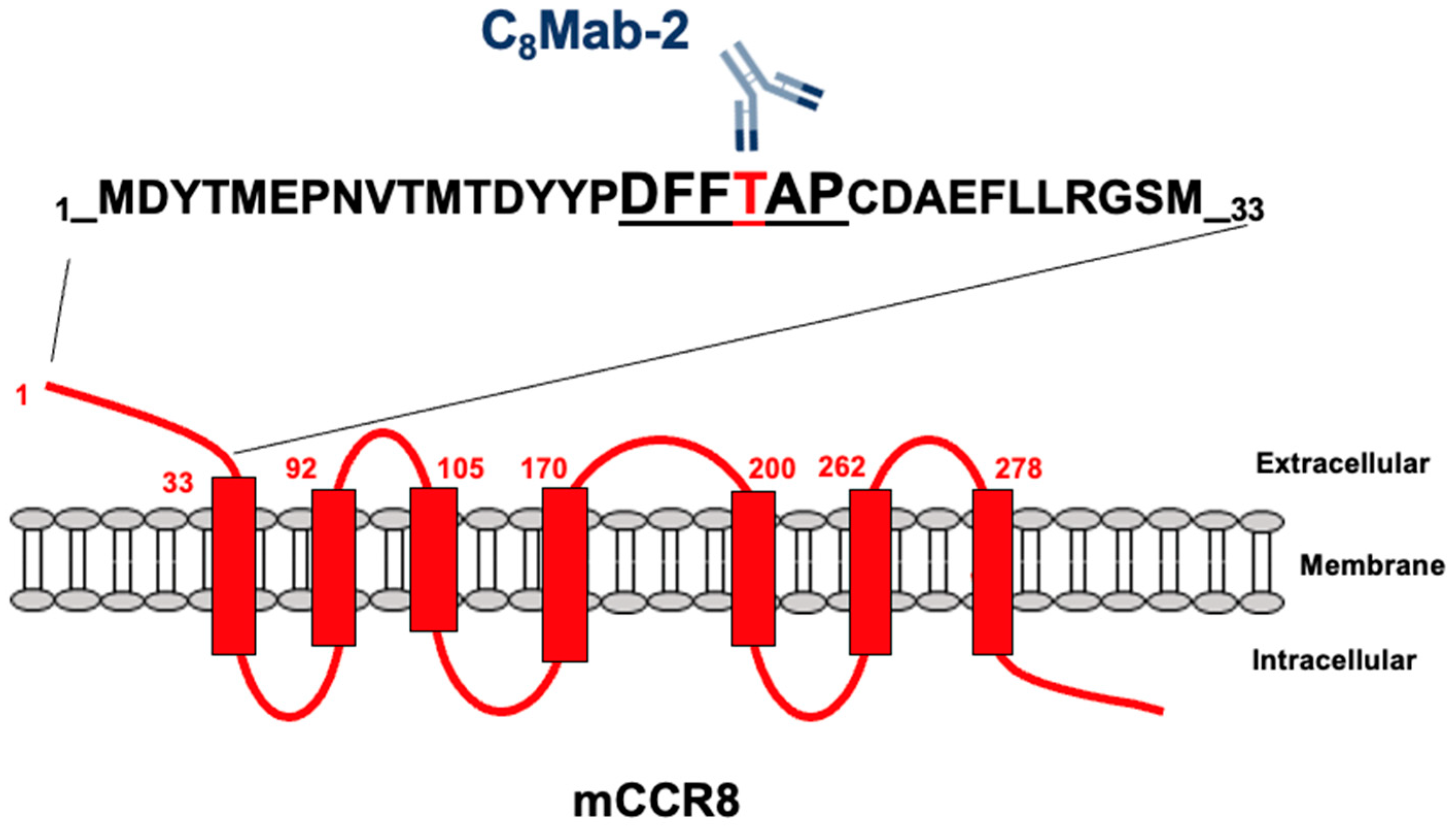
3.2. Determination of the C8Mab-2 epitope by flow cytometry using 1×alanine scanning
3.3. Determination of the C8Mab-2 epitope by flow cytometry using 2×alanine scanning
4. Discussion
References
- Roos, R.S.; Loetscher, M.; Legler, D.F.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. Identification of CCR8, the receptor for the human CC chemokine I-309. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 17251–17254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitas, G.; Konopacki, C.; Wu, K.; Bos, P.D.; Morrow, M.; Putintseva, E.V.; Chudakov, D.M.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer. Immunity 2016, 45, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsheshet, Y.; Wildbaum, G.; Levy, E.; Vitenshtein, A.; Akinseye, C.; Griggs, J.; Lira, S.A.; Karin, N. CCR8(+)FOXp3(+) T(reg) cells as master drivers of immune regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 6086–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohue, Y.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: Can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci 2019, 110, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Shitara, K.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression - implications for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019, 16, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraehenbuehl, L.; Weng, C.H.; Eghbali, S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Merghoub, T. Enhancing immunotherapy in cancer by targeting emerging immunomodulatory pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2022, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, A.; Nogami, W.; Nashiki, K.; Haruna, M.; Miwa, H.; Hagiwara, M.; Nagira, M.; Wada, H.; Nagira, Y. Immunotherapy Targeting CCR8+ Regulatory T Cells Induces Antitumor Effects via Dramatic Changes to the Intratumor CD8+ T Cell Profile. J Immunol 2023, 211, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidani, Y.; Nogami, W.; Yasumizu, Y.; Kawashima, A.; Tanaka, A.; Sonoda, Y.; Tona, Y.; Nashiki, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Hagiwara, M.; et al. CCR8-targeted specific depletion of clonally expanded Treg cells in tumor tissues evokes potent tumor immunity with long-lasting memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Tan, Y.; Shen, Q.; Hou, L.; Yao, B.; Qin, J.; Xu, P.; Mao, C.; Chen, L.N.; Zhang, H.; et al. Molecular insights into ligand recognition and activation of chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR3. Cell Discov 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaikina, P.; Tsai, C.J.; Dietz, N.; Pamula, F.; Grahl, A.; Goldie, K.N.; Guixà-González, R.; Branco, C.; Paolini-Bertrand, M.; Calo, N.; et al. Structural basis of the activation of the CC chemokine receptor 5 by a chemokine agonist. Sci Adv 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Qin, L.; Zacarías, N.V.; de Vries, H.; Han, G.W.; Gustavsson, M.; Dabros, M.; Zhao, C.; Cherney, R.J.; Carter, P.; et al. Structure of CC chemokine receptor 2 with orthosteric and allosteric antagonists. Nature 2016, 540, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Han, G.W.; Kufareva, I.; Li, T.; Ma, L.; Fenalti, G.; Li, J.; et al. Structure of the CCR5 chemokine receptor-HIV entry inhibitor maraviroc complex. Science 2013, 341, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Shen, Q.; Yao, B.; Mao, C.; Chen, L.N.; Zhang, H.; Shen, D.D.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Du, X.; et al. Identification and mechanism of G protein-biased ligands for chemokine receptor CCR1. Nat Chem Biol 2022, 18, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilko, D.J.; Johnson, Z.L.; Ammirati, M.; Che, Y.; Griffor, M.C.; Han, S.; Wu, H. Structural basis for chemokine receptor CCR6 activation by the endogenous protein ligand CCL20. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, K.; Bruenle, S.; Weinert, T.; Guba, W.; Muehle, J.; Miyazaki, T.; Weber, M.; Furrer, A.; Haenggi, N.; Tetaz, T.; et al. Structural Basis for Allosteric Ligand Recognition in the Human CC Chemokine Receptor 7. Cell 2019, 178, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, C.; Rappas, M.; Kean, J.; Doré, A.S.; Errey, J.C.; Bennett, K.; Deflorian, F.; Christopher, J.A.; Jazayeri, A.; Mason, J.S.; et al. Intracellular allosteric antagonism of the CCR9 receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Sun, Y.; Janezic, E.; Zhou, T.; Johnson, M.; Azumaya, C.; Noreng, S.; Chiu, C.; Seki, A.; Arenzana, T.L.; et al. Structural basis of antibody inhibition and chemokine activation of the human CC chemokine receptor 8. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchida, T.; Isoda, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Tanaka, T.; Handa, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a Novel Anti-Mouse CCR1 Monoclonal Antibody C(1)Mab-6. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, N.; Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Li, G.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry. Antibodies (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Harigae, Y.; Li, G.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. C(3)Mab-2: An Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibody for Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Saito, M.; Li, G.; Goto, N.; Nanamiya, R.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. C(3)Mab-3: A Monoclonal Antibody for Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 3 for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Saito, M.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kitamura, K.; Kudo, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. C(8)Mab-3: An Anti-Mouse CCR8 Monoclonal Antibody for Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Handa, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Harigae, Y.; Tateyama, N.; Nanamiya, R.; et al. C(8)Mab-2: An Anti-Mouse C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 8 Monoclonal Antibody for Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-Mouse CCR8 Monoclonal Antibody (C(8)Mab-1) for Flow Cytometry and Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Cx1Mab-1: A Novel Anti-mouse CXCR1 Monoclonal Antibody for Flow Cytometry. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchida, T.; Isoda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, Y. Cx(3)Mab-4: A Novel Anti-Mouse CXCR3 Monoclonal Antibody for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchida, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Cx(4)Mab-1: A Novel Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Amano, K.; Chiba, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirabayashi, J.; Narimatsu, H.; Mishima, K.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation using a novel anti-podoplanin antibody reacting with its platelet-aggregation-stimulating domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, N. Chemokines in the Landscape of Cancer Immunotherapy: How They and Their Receptors Can Be Used to Turn Cold Tumors into Hot Ones? Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, D.O.; L’Huillier, A.; Armington, S.; Mottershead, C.; Filippova, E.V.; Coder, B.D.; Petit, R.G.; Princiotta, M.F. Targeting CCR8 Induces Protective Antitumor Immunity and Enhances Vaccine-Induced Responses in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 5340–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagira, Y.; Nagira, M.; Nagai, R.; Nogami, W.; Hirata, M.; Ueyama, A.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Shinonome, S.; Yoshida, H.; et al. S-531011, a Novel Anti-Human CCR8 Antibody, Induces Potent Antitumor Responses through Depletion of Tumor-Infiltrating CCR8-Expressing Regulatory T Cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2023, 22, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




