Introduction
In the coal mining area, on the one hand, large-scale drainage of groundwater is required due to the exploitation of coal seams; on the other hand, a large amount of water is needed for mine production and mining area life (Liu et al. 2019; Acharya et al. 2020; Mardonova et al. 2023). However, the waste tailings produced by mining operations will affect the groundwater environment. Some ions in mine water exceed the standard and carry a large number of dust, rock powder, and other suspended solids. The water quality is poor. It is necessary to clearly understand the main ions in groundwater, so as to further understand the interaction and mechanism of groundwater pollution. Hydrogeochemical facies can not only be used to evaluate the quality of groundwater but also provide information for distinguishing different regions of anions and cations in groundwater (Refat et al. 2021; Dhaoui et al. 2022; Parisi et al. 2023).
Many analysis and evaluation studies on groundwater chemistry in mining areas have been carried out at home and abroad (Jiang et al. 2022; Abu et al. 2002; Sahoo et al. 2020a). To investigate the impact of abandoned mines on the water quality of surface water and groundwater, Zhang et al. (2020) analyzed the hydrochemical characteristics in the multi-aquifer system of a closed mine in Huainan by using the Euclidean distance and the Ward method and determined the genesis, evolutionary process and fate of the hydrogeochemistry of the area by combining the stable hydroxide isotopes and reverse geochemical simulation methods. Ewusi et al. (2022) appraised the hydrogeochemical characteristics and sources of heavy metals and the probable human health risks associated with the consumption of water contaminated with heavy metals in the mine pit water–surface water–groundwater system in the Nsuta manganese mining area in western Ghana. To find out the influence of mine water on water quality and hydrogeochemical processes, a large number of related studies have been carried out on mine water at home and abroad (Zhang et al. 2024; Wang et al. 2023; Tarasenko et al. 2022; Chudy et al. 2021). Hydrogeochemical methods have made great progress in the study of groundwater, especially the application of isotope and thermodynamic basic principles, which solves the practical problems of quantitative and semi-quantitative hydrogeochemistry, making the method of hydrogeochemistry to study groundwater more rigorous and perfect (Prakash et al. 2023; Ju et al. 2023; Weber et al. 2021; Akpataku et al. 2019). Multivariate statistical analysis methods, including linear regression analysis, discriminant analysis, cluster analysis, and principal component analysis, are widely used in hydrogeochemical analysis (Liu et al. 2019).
Taking the Hancheng mining area as an example, the recharge, runoff, and drainage system of groundwater in the Hancheng mining area has become an independent hydrogeological unit. Xue et al. (2014), based on the data of water quality analysis and rock chemical composition detection, analyzed the hydrogeological background of occurrence and distribution of Ordovician limestone water quality in Xiangshan Mine of Hancheng Mining Area and focused on the characteristics of water chemical components. Through the study, it is found that the mine water receives a large amount of recharge from shallow pore diving, and it is necessary to further identify the genesis and hydrogeochemical characteristics of shallow but shallow pore diving. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the hydrogeochemical process of shallow groundwater in the Hancheng mining area to help formulate appropriate groundwater management plans.
Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater includes groundwater hydrochemistry and variation, and groundwater environmental quality evaluation, which requires a lot of water quality monitoring data. In Hancheng, the observation data on shallow groundwater chemistry are scarce. This paper aims to study the hydrogeochemical behavior of shallow groundwater around the Hancheng mining area and clarify the causes of main anions and cations in groundwater. Taking Gibbs diagram as a reference, the hydrogeochemical survey was carried out by using pipeline diagram to determine the factors affecting groundwater composition. Therefore, the main objectives of this research are (1) to explain the main hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Hancheng mining area of Shaanxi Province ; (2) Hydrogeochemical processes are distinguished according to major ion chemistry, element ratio, and hydrogeochemical phases. This will contribute to the current water resources planning in the area and provide some basic data for the future evolution of mine water.
Study Area
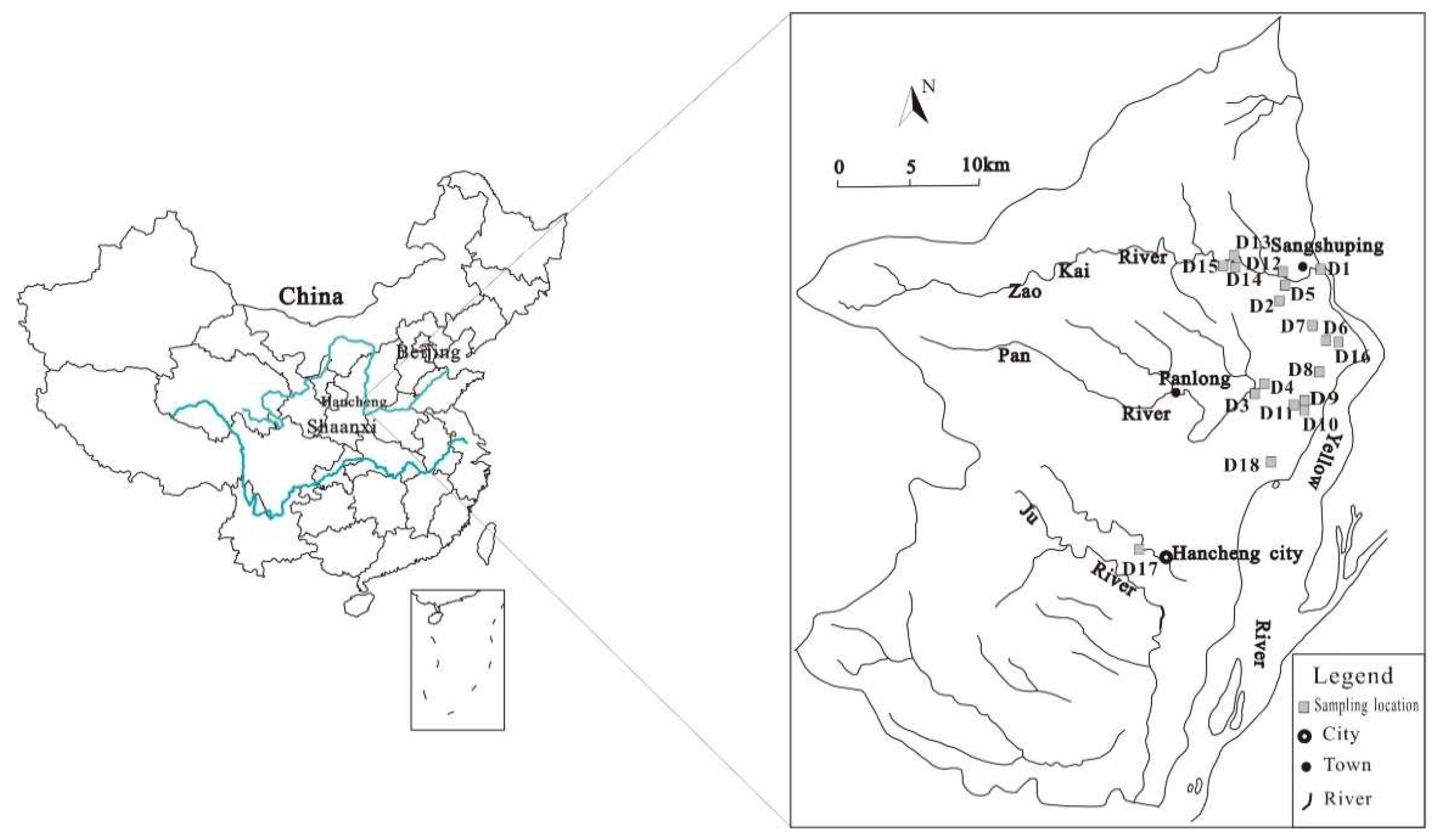
Hancheng mining area is located at the intersection of Jinxi fold belt and Weibei uplift in the southeastern margin of the Ordos block in Shaanxi Province. It is located at the west of the Yellow River, and extends between longitude110°07'19"-110°37'24" and latitude35°18'50"-35°52'08"(
Figure 1), Total area of about 1115.7 km
2.
The Hancheng mining area is located in arid and semi-arid areas of China, belonging to warm temperate semi-arid continental monsoon climate. The regional climate is dry, with an annual average temperature of 13.8 °C. The precipitation is small and uneven in time and space. The precipitation is mostly concentrated in July – September. The annual average precipitation is 559.7 mm, and the evaporation is strong. The annual evaporation is 1119.4~1679.1 mm, resulting in drought and water shortage in the region and fragile ecological environment. The study area flows through the largest river-cut river, with abundant water throughout the year, which is the main water source for residents around the mining area. The recharge, runoff, and drainage system of groundwater in the mining area is controlled by geographical and geological factors to form an independent hydrogeological unit. The structure of the mining area is divided into different regions. The structures in the southern and eastern regions are strongly developed, and the structures in the northern and western regions are relatively weak. The structures in the shallow and edge regions are complex, and the structures in other regions are relatively simple. The south area is mainly tensile structure, mainly fault; there are many extrusion structures in the north area, mainly fold. Hancheng mining area belongs to the Weibei Carboniferous-Permian coalfield. The surface is covered by Quaternary loess. Ordovician carbonate rock is the base. There are three types of groundwater in the area: pore water in the Quaternary loose layer, fissure water in the Permian and above-covered strata, and karst water in the Ordovician limestone fissure. Pore water mainly occurs in the Quaternary loess layer and alluvial diluvial layer on both sides of the valley. Under the control of topography, geomorphology, and recharge conditions, the groundwater level on the loess tableland is generally deep and the water quantity is poor. In the low-lying areas of the surface and on both sides of the valley, the groundwater level is shallow and the water is abundant. The thickness of the Quaternary loose layer is about 40m. The aquifer is composed mainly of silty sand, fine sand, and gravel. Groundwater capacity is abundant, with a permeability coefficient of 1.93-6.73 m/d. The phreatic water quality is relatively good, with mineralization degree ranging from 630-750 mg/L. The unconfined groundwater is recharged mainly by precipitation. It is discharged mainly as springs, human extraction, and mine water.
Fractured water occurs in the Permian and Triassic aquifer groups. The unit water inflow of sandstone formation is 0.0000113 ~ 0.360000 L/(s·m), and the permeability coefficient is 0.0000903 ~ 1.07 m/d. It is an aquifer with weak water abundance and medium permeability (Duan et al.2020). The fissure water hydrochemical type is HCO3·SO4-Ca·Mg (Tang et al.2000).
Karst water exists under the coal seam floor. The direct basement of the coal seam is a strong karst fissure aquifer section, which is composed of the second section of the middle Ordovician peak (O2f2), 0~75 m thick, and the main lithology is relatively single thick layered limestone. Drilling unit water inflow is 1.31~3.22 L/(s·m), the permeability coefficient is 9~15 m/d, the water-rich layer is uniform, belongs to a strong karst fissure aquifer. Hydrochemical types are mainly HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na, Ca, Mg or SO4·HCO3·Cl-Na, Mg, Ca.
Materials and Methods
A total of 18 groundwater samples were collected from the water samples collected by the research group from the Yellow River in the east, Yangshanzhuang in the west, Wangfeng in the north, and Guicun in the south. According to the sampling method, the samples were stored in white plastic bottles and numbered from D1 to D18 (
Figure 1). After the collection, the groundwater samples were sealed to the laboratory for physical and chemical analysis. Analyzed indices included pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), total hardness (TH), cations (Ca
2+, Mg
2+, Na
+, K
+), and anions (HCO
3-, CO
32-, SO
42-, Cl
-, F
-). The pH and EC were measured on-site, and the geographical coordinates and environmental conditions of the sampling points were recorded. The cations Na
+, K
+, Ca
2+, and Mg
2+ were determined by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICAP6300), F
-, Cl
- and SO
42- were determined by ion chromatography (ICS-2000), HCO
3- was determined by titration. In the sample test, the quality control uses 5% repeated samples, all repeated samples error is less than 5%.
Results and Discussion
Chemical Characteristics of Groundwater
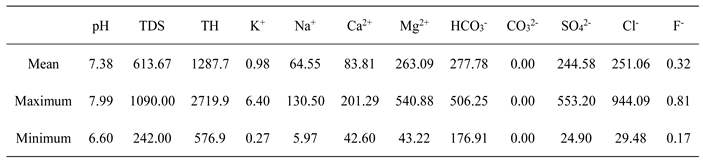
The pH value of groundwater in the study area ranged from 6.60 to 7.99, with an average of 7.38 (
Table 1).
The groundwater was neutral and weakly alkaline, which met the basic limits of groundwater quality standards and was higher than the pH value of acid mine drainage 5.88 (Tang et al. 2000; Lu et al. 2003; Duan et al. 2020). The F- of all groundwater samples is lower than 1.0 mg/L based on the classification of Chinese Standards for Drinking Water Quality (GB5749-2006). The average contents of cations K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in the river water around the mining area were 1.88 mg/L, 197.78 mg/L, 152.56 mg/L, and 275.11 mg/L, respectively. The overall performance was K+ < Ca2+ < Na+ < Mg2+; The average content of HCO3- was 187.75 mg/L, and the content of SO42- was between 34.58 mg/L and 207.330 mg/L. The average content of HCO3- was 359.51 mg/L, and the average content of Cl- was 44.811 mg/L. The overall performance was SO42- < Cl- < HCO3-. The main cation components in groundwater in the study area were Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+, and the anion components were HCO3-, Cl-, and SO42-. The results showed that the main cations and anions in groundwater in the study area were similar to those in the surrounding river water.
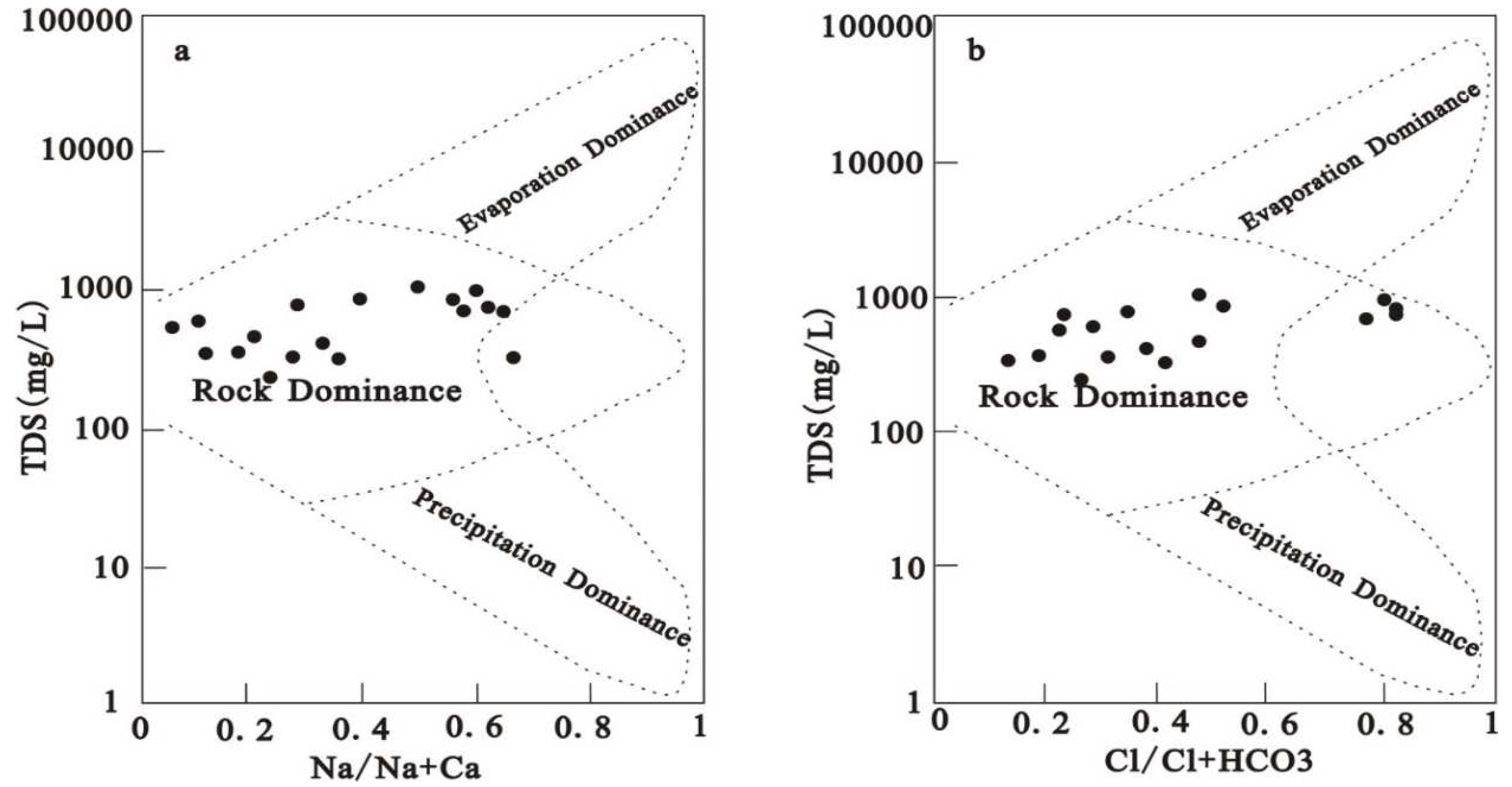
The groundwater TDS was between 242.00 mg/L and 1090.00 mg/L, with an average of 613.67 mg/L. Through the relationship map between conventional ions and TDS, it can be seen that with the runoff of the Hancheng mining area from south to north, the main ions such as calcium, magnesium, chlorine, and sulfate show an accelerated growth trend, that is, the slope of the relationship curve between ions and TDS gradually increases, which shows that the hydrodynamic conditions are poor, that is, the runoff is relatively slow. Shallow groundwater in mining area is the main drinking water source for local residents. Based on the classification of groundwater, 89% of groundwater samples are freshwater in this area (TDS<1000 mg/L). The TH value of water depends upon the total dissolved content of Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Aminiyan et al.,2020; Subba et al. 2022). The TH of groundwater in this area varies from 576.9 to 2719.9 mg/L with a mean of 1287.7 mg/L, suggesting hard water (TH>450 mg/L) based on the classification of Chinese Standards for Drinking Water Quality ( GB5749-2006). These TDS and TH values are close to those of Ordovician limestone water, indicating a similar recharge source (Tang et al. 2000; Lu et al. 2003; Xue et al. 2014).
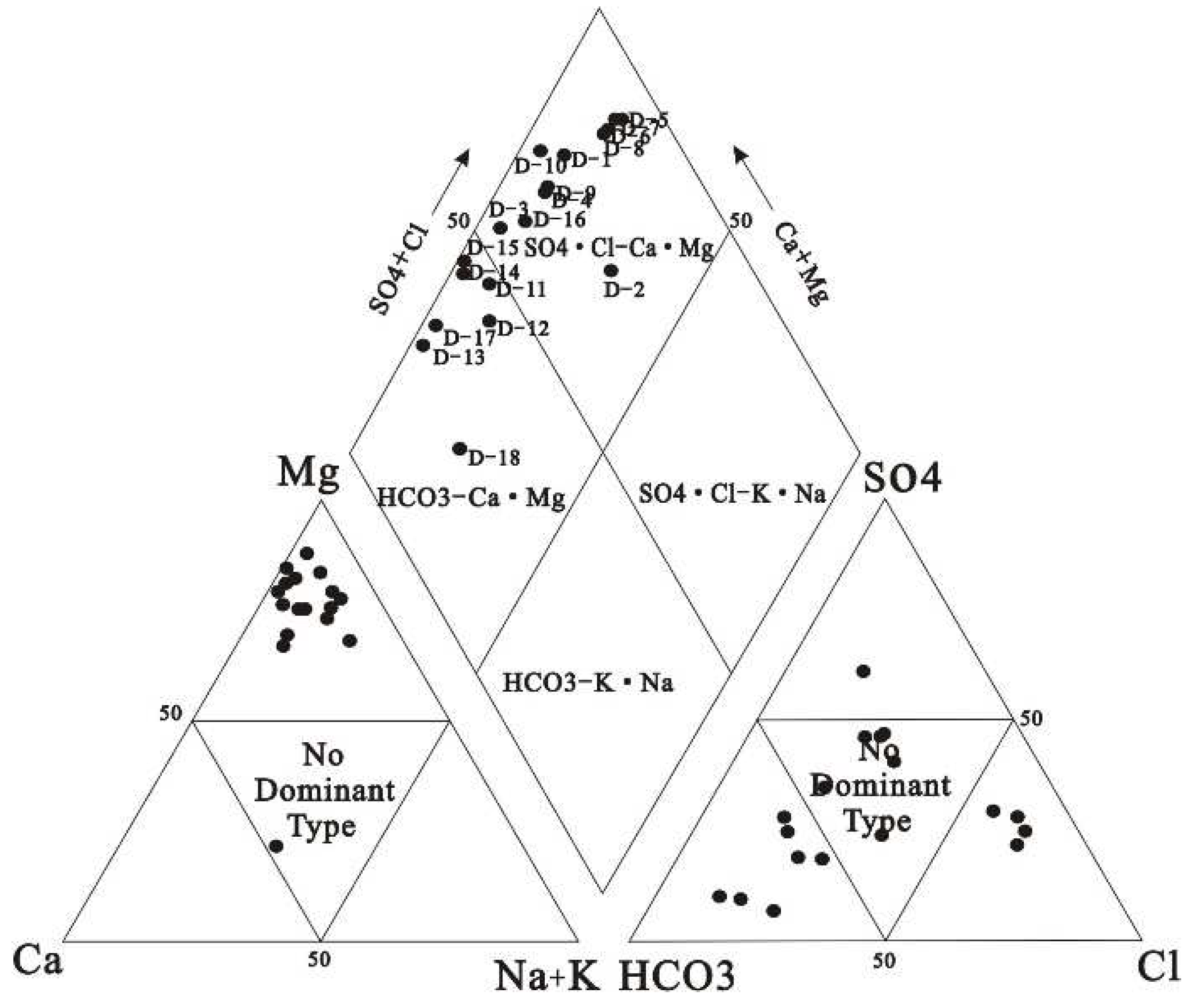
Hydrogeochemical Facies and Types
The salinity range of the collected water samples was 242.00~1090.00 mg/L, and the anion content was SO
42- < Cl
- < HCO
3-. The anion concentration ranges were 24.90~553.20 mg/L, 29.48~944.09 mg/L, and 176.91~506.25 mg/L, respectively. The average values were 277.78 mg/L, 251.06 mg/L, and 244.58 mg/L, respectively. Ca
2+ concentration is generally in the range of 42.6~201.29 mg/L, and Mg
2+ concentration is in the range of 43.22~540.88 mg/L (
Table 1). According to
Figure 2, the water quality types of different sampling points are different, the left lower triangular cation field reveals 94.4 % of groundwater samples belong to magnesium type. The lower right triangle anion field showed that 38.9 % of the groundwater samples fell into the carbonate field, about 33.3 % of the groundwater samples fell into the non-dominant field, and 22.2 % of the groundwater samples fell into the chloride ion field. The rhombus reveals that the groundwater samples belong to the type of alkaline earth metal exceeding alkaline metal in area 1, and shows that 38.9 % of the groundwater samples are HCO
3-Ca·Mg type and 61.1 % of the groundwater samples are SO
4·Cl-Ca·Mg type.
Effect of Natural Factors on Chemical Composition of Groundwater
Rock Weathering
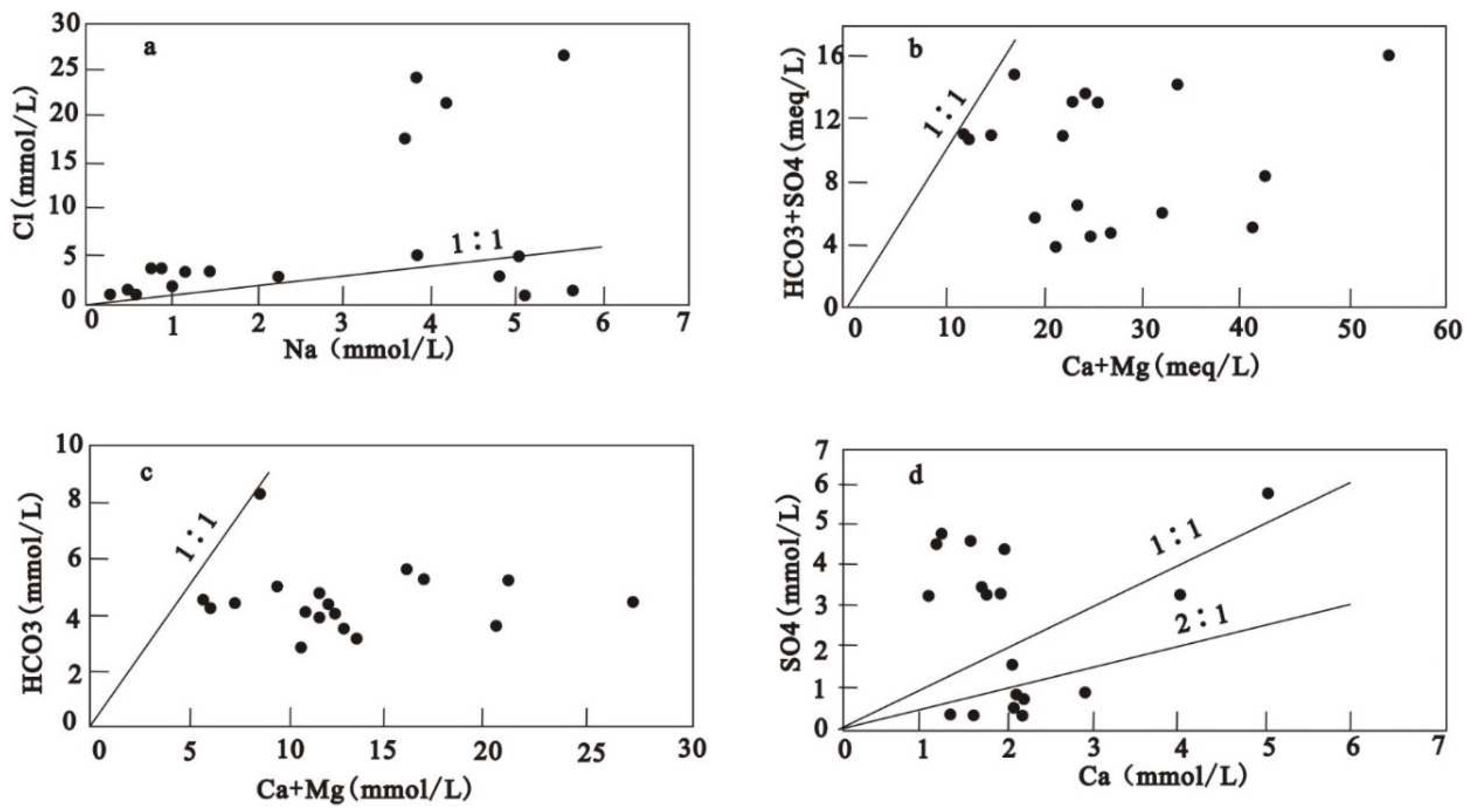
When Gibbs diagram (1970) is used to analyze the formation mechanism of dissolved chemical components in groundwater, the synchronous changes of Na
+ and Cl
- concentration indicate that they may be recharged by precipitation or concentrated by evaporation. However, in this study, except for a small number of sampling points, the equivalent concentration of Cl
- was higher than that of Na
+, and the equivalent concentration ratio of Cl
- and Na
+ gradually approached 1:1 on the whole (
Figure 4a), indicating that Na
+, Ca
2+, Mg
2+, SO
42-, Cl
- and HCO
3- may be added to by rock minerals during the initial hydrochemical erosion process. The good linear relationship between Cl
- and HCO
3- concentration can be verified when TDS≤1000 mg·L
-1 in
Figure 3 (b). The results of Gibbs diagram analysis showed that the Na/(Na+Ca) and Cl/(Cl+HCO
3) of most groundwater samples were less than 0.6 (
Figure 3). The relative ratio of ion concentration can reflect the source of main ions in groundwater ( Sahu et al. 2020, Mahlknecht et al. 2017 ). Most groundwater samples are in the rock weathering zone, indicating that rock weathering controls the main ionic chemistry of shallow groundwater in this area.
Mineral Dissolution or Precipitation
In the study of groundwater chemical process, the ion equivalent relationship between [(Ca
2++Mg
2+) -(SO
42-+HCO
3-)] and [(Na
++K
+)-Cl
-] is often used to explore the effect of water-rock interaction on groundwater chemical composition during exchange reaction and dissolution (Elango et al. 2007). Potential chemical reactions can be determined by calculating the chemical equilibrium between water and minerals for water-rock interactions (Samtio et al. 2022). Ca
2+ increased significantly with the increase of TDS in the Hancheng mining area, indicating that gypsum dissolution occurred in the Hancheng mining area because gypsum dissolution was not related to carbon dioxide content, but only related to water and time (Eang et al. 2018). The relationship between Ca
2+ and SO
42- in
Figure 4(d) was analyzed. Among the 18 groundwater samples collected, seven points fell below the 2:1 line, nine points fell above the 1:1 line, and two points fell between the 2:1 line and the 1:1. The analysis results show that one of the sources of Ca
2+ and SO
42- is the dissolution of gypsum, and Ca
2+ also has other sources. In
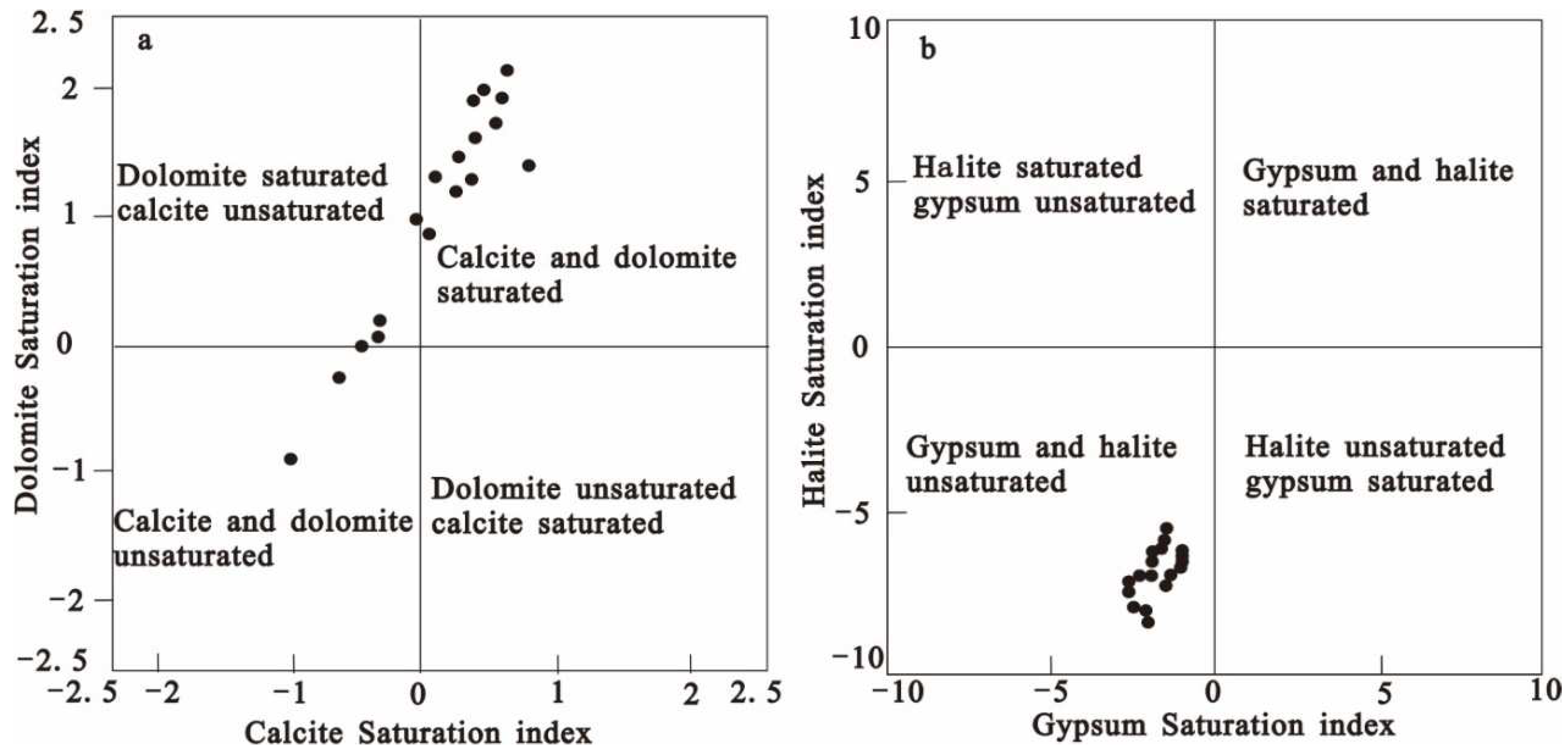
Figure 4(d), 50 % of the groundwater samples fall above the 1:1 line. Combined with the existing data, it is found that the groundwater in the study area is also affected by pyrite (Lin et al. 2019). Based on the previous analysis, the SI of calcite, dolomite, gypsum, and quartzite are calculated by the PHREEQC program. The SI diagrams of calcite and dolomite show that most groundwater samples are supersaturated (
Figure 5a). Supersaturation may lead to the precipitation of Ca or Ca-Mg carbonate under suitable physical and chemical conditions. About 33.3% of the water samples were calcite undersaturated and 16.7% were dolomite undersaturated. The SI diagram of gypsum and pyroxene shows that all groundwater samples are unsaturated (
Figure 5b), indicating that gypsum and pyroxene are more likely to dissolve in groundwater if gypsum and pyroxene are widespread in the study area.
Cation Exchange
The cation alternate adsorption is a common phenomenon in the hydrogeochemical process. In the long-term interaction between groundwater and rock strata, the adsorption plays an irreplaceable role in the chemical composition and change of groundwater. The common cation exchange process is sodium and calcium exchange (Priyadarshanee et al. 2022). The [Ca
2++Mg
2+-(HCO
3-+SO
42-)]/(Na
+-Cl
-) diagram is often used to analyze the cation exchange effect in water. [Ca
2++Mg
2+-(HCO
3-+SO
42-)] means the content of Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in water except for the dissolution of dolomite, calcite, and gypsum; Na
+ -Cl
- is expressed as the content of Na
+ after weathering and dissolution of salt rock in water. If [Ca
2++Mg
2+-(HCO
3-+SO
42-)]/(Na
+-Cl
-) showed a linear relationship and the slope was -1, it indicated that with the continuous increase of Na
+-Cl-, Ca
2++Mg
2+-(HCO
3-+SO
42-) showed a downward trend, indicating that there was a positive cation exchange effect in groundwater (Tang et al. 2020). If cation exchange does not occur and only depends on rock dissolution reaction, the scattered points should be concentrated near the (0, 0) origin in
Figure 5. When the slope between the two was close to -1, it indicated that the exchange adsorption reaction was an important factor for the change of cation concentration in water (Dedzo et al. 2019).
If the dissolution of calcite, dolomite, and gypsum is the main ion source of groundwater, the ratios of (Ca
2++Mg
2+) vs (HCO
3-+SO
42-) will close to the 1:1 line. In this study, the ratios of (Ca
2++Mg
2+) vs (HCO
3-+SO
42-) fall below the 1:1 line (
Figure 4b). The Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ were greater than HCO
3-+SO
42-, indicating that Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ either have other sources or that some reactions expend Ca
2+ and Mg
2+. (Ca
2++Mg
2+) vs (HCO
3-) of most groundwater samples from the aquifer fell below the 1:1 line (
Figure 4c). This indicates that Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ don’t originate completely from the dissolution of calcite and dolomite, and were balanced by some other anions like SO
42- (Bhardwaj et al. 2010; Singh et al. 2012).
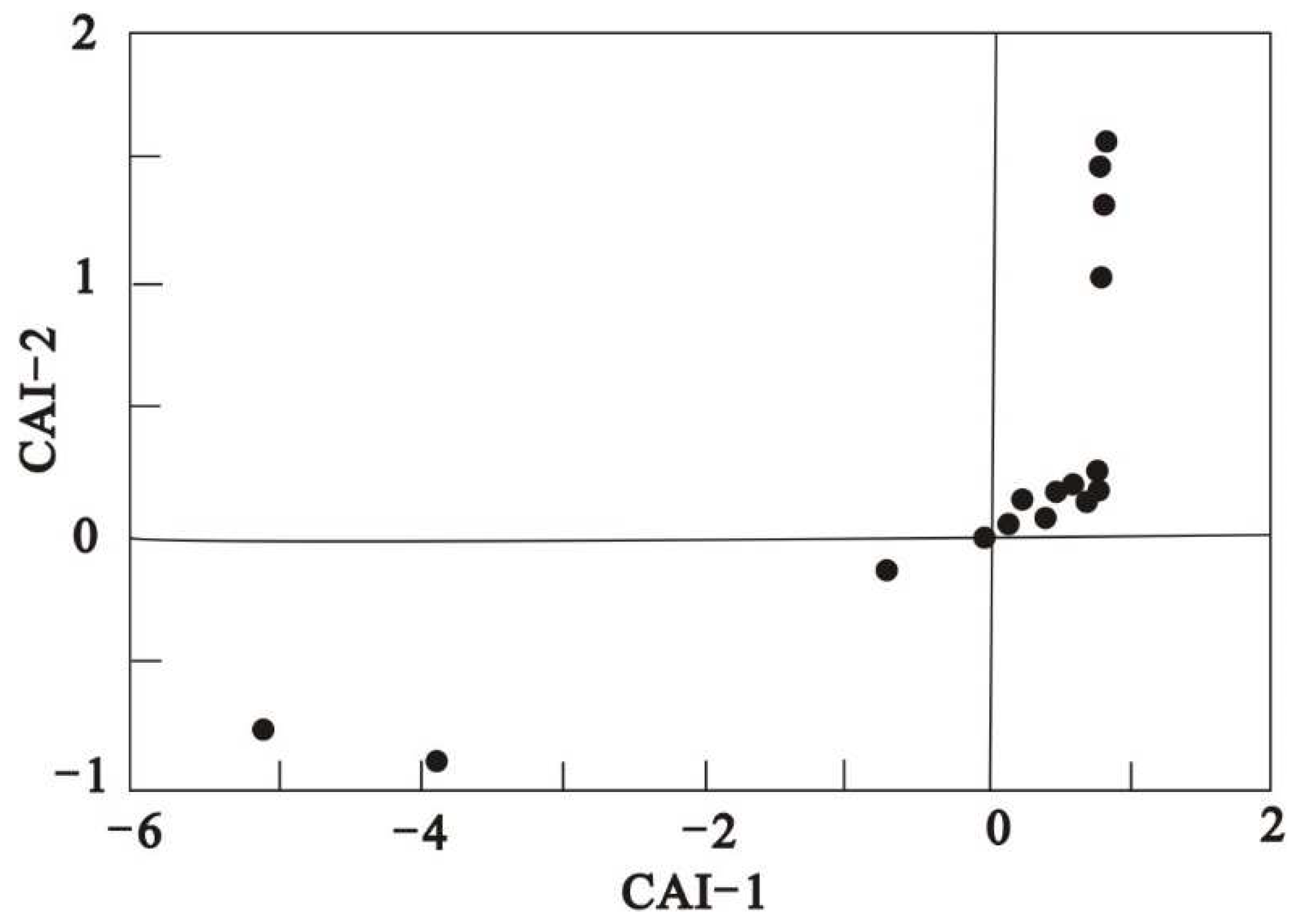
In the study of cation exchange in water, to better understand the process of positive and negative alternating adsorption of cations in water, the chloralkali index (CAI) (Schoeller 1965) is usually introduced:
If Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in groundwater are replaced by Na
+ in rock and soil, CAI-1 and CAI-2 > 0, reverse cation exchange occurs, that is, Na
+ in water is replaced by Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in rock and soil (Zakaria et al. 2021). According to the calculation statistics, about 83.3 % of the groundwater samples in this study had positive values indicating the exchange of Na
+ and K
+ in groundwater with Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in aquifer, and about 16.7 % had negative values indicating the ratio of anti-ion exchange (
Figure 6). Combined with
Figure 4(a) Na
+/Cl
- less than 1:1 and the relationship curve between groundwater samples (Ca
2++Mg
2+) and (HCO
3-+SO
42-), it is shown that all samples fall below the isoline, indicating that alkali exchange reaction and Ca
2++Mg
2+ occur at higher concentrations. It shows that Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in aquifer minerals have been exchanged by Na
+ in groundwater.
Effects of Human Activities on Chemical Composition of Groundwater
The relative ratio of ion concentration can reflect the source of main ions in groundwater (Sun et al. 2013). Na
+ vs Cl
-can reflect the source of Na
+ (Sami 1992). As shown in
Figure 4(a), 83.3 % of groundwater samples fall above the 1:1 line, indicating that Cl
- is greater than Na
+; coal gangue and coal in the study area contain a certain amount of Cl
-, and agricultural activities are frequent, indicating that coal gangue leaching water and agricultural irrigation runoff are the main sources of Cl
- in groundwater (Sun et al. 2014; Sun et al. 2016).
Conclusions
Based on the data of 18 groundwater samples collected in the field, this paper collects and summarizes the local topography, geomorphology, hydrogeology, and other data. Based on the basic theory of hydrology and geology, the hydrochemical evolution law of groundwater in the surrounding area of the Hancheng mining area in Shaanxi Province is explored by using the hydrochemical method. The conclusions are as follows:
(1) The main cation components in groundwater in the study area were Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+, and the anion components were HCO3-, Cl-, and SO42-. 89 % of the groundwater samples in this area were freshwater (TDS<1000 mg/L). The chemical types of groundwater were mainly SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg type, accounting for 61.1 %, followed by HCO3-Ca·Mg type, accounting for 38.9 %.
(2) The chemical components of groundwater in the study area are mainly affected by rock weathering, and there is cation exchange. Na++Cl- comes from the dissolution of halogen, Ca+ comes from the dissolution of gypsum, and SO42- concentration is affected by pyrite oxidation. Cl- and SO42- are not only controlled by natural factors but also affected by human input. According to the analysis of the saturation index, gypsum and salt rock in groundwater in the study area are in unsaturated state and will be dissolved continuously. Dolomite and calcite are generally in a saturated or quasi-equilibrium state, with a precipitation trend.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key research and development plan of Shaanxi Province (2020ZDLSF06-04, 2021ZDLSF05-05).
References
- Abu, M., et al., Groundwater characterization including prediction of the quality, fluoride, and nitrate occurrence in a typical artisanal mining area in Ghana: A hydrochemical and multivariate statistical approach. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2023. 23: p. 101041. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B. S., et al., Acid mine drainage from coal mining in the United States – an overview. Journal of Hydrology, 2020. 125061. [CrossRef]
- Akpataku, K.V., et al., Hydrochemical and isotopic characterization of groundwater in the southeastern part of the Plateaux Region, Togo. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2019. 64(8): p. 983-1000. [CrossRef]
- Aminiyan, M.M., et al., Comprehensive integrated index–based geochemistry and hydrochemical analyses of groundwater resources for multiple consumptions under coastal conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2020. 27, 21386–21406. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj V, Singh DS, Singh AK. Water quality of the Chhoti Gandak River using principal component analysis, Ganga Plain, India. J Earth Syst Sci, 2010. 119(1):117–127. [CrossRef]
- Chudy, K., et al., Chemical variations in mine water of abandoned pyrite mines exemplified by the Colorful Lakes in Wieściszowice, Sudetes Mountains, Poland. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 2021. 38: p. 100974. [CrossRef]
- Dedzo G., et al., Petrology and geochemistry of lavas from Gawar, Minawao and Zamay volcanoes of the northern segment of the Cameroon volcanic line (Central Africa): Constraints on mantle source and geochemical evolution. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2019. 153: p. 31-41. [CrossRef]
- Dhaoui O., et al., Hydrogeochemical processes on inland aquifer systems: A combined multivariate statistical technique and isotopic approach. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2023. 20: p. 100887. [CrossRef]
- Duan L., Sun Y., Mao M., Xiao K., Wang X., Tong X., Hydrochemical Characteristics and Influence Mechanism of River in Hancheng Mining Area. Water technical, 2020. 51(9):154-161.
- Eang, K.E., et al., Groundwater monitoring of an open-pit limestone quarry: Water-rock interaction and mixing estimation within the rock layers by geochemical and statistical analyses. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2018. 28(6): p. 849-857. [CrossRef]
- Elango, L. and R. Kannan, Chapter 11 Rock–water interaction and its control on chemical composition of groundwater, in Developments in Environmental Science, D. Sarkar, R. Datta and R. Hannigan, D. Sarkar, R. Datta and R. Hannigan^Editors. 2007, Elsevier. p. 229-243. [CrossRef]
- Ewusi, A., et al., Hydrogeochemical characteristics, sources and human health risk assessment of heavy metal dispersion in the mine pit water–surface water–groundwater system in the largest manganese mine in Ghana. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2022. 26: p. 102312. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C., et al., A hydrochemical and multi-isotopic study of groundwater sulfate origin and contribution in the coal mining area. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022. 248: p. 114286. [CrossRef]
- Ju, Q., et al., Multiple stable isotopes and geochemical approaches to elucidate groundwater reactive transport paths in mining cities: A case from the northern Anhui, China. Science of The Total Environment, 2024. 912: p. 169706. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y., et al. The evolution of hydrogeochemical characteristics of a typical piedmont karst groundwater system in a coal-mining area, Northern China. Environ Earth Sci 78, 557 2019. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., et al., Determining the factors controlling the chemical composition of groundwater using multivariate statistics and geochemical methods in the Xiqu coal mine, North China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019 78(12), 364.1-364.11. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. and W. Li, Zoning and management of phreatic water resource conservation impacted by underground coal mining: A case study in arid and semiarid areas. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019. 224: p. 677-685. [CrossRef]
- Lu GL., Cai D., Chen L., He B., Gao J., Probe into Chemical Properties and Forming Mechanism of Karst Water in Ordovician Limestone of Hancheng Mining Area. Coal Geology of China, 2003. 015(004):27-30.
- Mahlknecht, J., et al., Assessing seawater intrusion in an arid coastal aquifer under high anthropogenic influence using major constituents, Sr and B isotopes in groundwater. Science of The Total Environment, 2017. 587-588: p. 282-295. [CrossRef]
- Mardonova, M. and Y. Han, Environmental, hydrological, and social impacts of coal and nonmetal minerals mining operations. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023. 332: p. 117387. [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A., et al., Analyzing spatial and temporal evolution of groundwater salinization through Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Hydrogeochemical Facies Evolution-Diagram. Science of The Total Environment, 2023. 862: p. 160697. [CrossRef]
- Prakash Rai, S., et al., Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in northwestern part of the Indo-Gangetic Basin, India: A geochemical and isotopic approach. Geoscience Frontiers, 2023. 14(6): p. 101676. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshanee, K.S.G.S., et al., Deep groundwater recharge mechanism in the sedimentary and crystalline terrains of Sri Lanka: A study based on environmental isotope and chemical signatures. Applied Geochemistry, 2022. 136: p. 105174. [CrossRef]
- Refat Nasher, N.M. and M. Humayan Ahmed, Groundwater geochemistry and hydrogeochemical processes in the Lower Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna River Basin areas, Bangladesh. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences: X, 2021. 6: p. 100062. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S. and S. Khaoash, Impact assessment of coal mining on groundwater chemistry and its quality from Brajrajnagar coal mining area using indexing models. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020. 215: p. 106559. [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M., et al., Seasonal and geochemical variation of uranium and major ions in groundwater at Kanker district of Chhattisgarh, central India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2020. 10: p. 100330. [CrossRef]
- Sami K. Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J Hydrol, 1992. 139(1-4):27-48. [CrossRef]
- Samtio, M.S., et al., Impact of rock-water interaction on hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater: Using multivariate statistical, water quality index and irrigation indices of chachro sub-district, thar desert, sindh, Pakistan. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2023. 20: p. 100878. [CrossRef]
- Singh A., Mondal G., Singh T., Singh S, Tewary B., Hydrogeochemical processes and quality assessment of groundwater in Dumka and Jamtara districts, Jharkhand, India. Environ Earth Sci, 2012. 67(8):2175-2191. [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N., R. Das and S. Gugulothu, Understanding the factors contributing to groundwater salinity in the coastal region of Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2022. 250: p. 104053. [CrossRef]
- Sun L., Gui H., Chen L., Chen S., Groundwater quality and evolution in a deep limestone aquifer, northern Anhui province, China: evidence from hydrochemistry. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2013. 22(4a), 1126-1131.
- Sun Y., Shen Y., Duan L., Dou L., Effects of Weathering on the Release of Heavy Metals from Coal Gangue. Asian J Chem, 2014. 26(22):7532-7538. [CrossRef]
- Sun Y., Duan L., Yao M., Li W., The hydrogeochemical characteristic of different sulfide-containing gangue during leaching. Iop Conference, 2016. 39(1):012032. [CrossRef]
- Tang, L., et al., Hydrochemical analysis and groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation in an arid agricultural area of the Northwest China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2023. 259: p. 104256. [CrossRef]
- Tang Y., Ju T, Deng N., Chemical characteristics of the groundwater and the transformation from coal mine discharge to water resources in Hancheng coal field. Journal of Xi’an University of science&Technology, 2000. 20(1):39-42.
- Tarasenko, I., et al., Chemical composition of groundwater in abandoned coal mines: Evidence of hydrogeochemical evolution. Applied Geochemistry, 2022. 137: p. 105210. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., et al., The hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of high-fluoride mine water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023. 430: p. 139671. [CrossRef]
- Weber, N., et al., Hydrological and thermodynamic controls on late Holocene gypsum formation by mixing saline groundwater and Dead Sea brine. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022. 316: p. 363-383. [CrossRef]
- Xue W., Gao Y., Feng H., Karst water chemical characteristics in Xiangshan. Mine Coal Technology, 2014 33(4):273-274. [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N., et al., Evolution of groundwater hydrogeochemistry and assessment of groundwater quality in the Anayari catchment. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2021. 12: p. 100489. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A., et al., Reactive transport modelling of tailings hydrogeochemistry under a composite cover. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2024. 261: p. 104290. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., et al., Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and transport paths of a multi-aquifer system in closed mining regions. Journal of Hydrology, 2020. 589: p. 125344. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).