Submitted:
24 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Search Strategies
3. Search Outcomes
4. Synthesis of Evidence
5. Critical Appraisal for Quality of Evidence
6. Results
7. Overview of Evaluation Process
8. Studied Population
9. Healthcare Settings
10. Process Implementation Interventions
11. Epidemiology and Surveillance
12. Efficacy and Safety
13. Influencing Prescribing Behavior
14. Quantifying Metrics
15. Role of Pharmacy
16. Evaluation of Outcome Measures
16.1. Interface of ASP and Its Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance
16.2. Economic Impact and Cost Effectiveness
16.3. Quality Assessment and Development of ASPs
17. Role of Modern Information Technology
18. Limitations
19. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Approval: Data Availability and Management
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloland P, Simone P, Burkholder B, Slutsker L, De Cock KM. The role of public health institutions in global health system strengthening efforts: the US CDC's perspective. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayberry, R.M.; Nicewander, D.A.; Qin, H.; Ballard, D.J. Improving Quality and Reducing Inequities: A Challenge in Achieving Best Care. Bayl. Univ. Med Cent. Proc. 2006, 19, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, A.; Breton, E.; Guichard, A.; Ridde, V. The concept of mechanism from a realist approach: a scoping review to facilitate its operationalization in public health program evaluation. Implement. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilford, R.J.; A Brown, C.; Nicholl, J. Use of process measures to monitor the quality of clinical practice. BMJ 2007, 335, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon-Woods M, McNicol S, Martin G. Ten challenges in improving quality in healthcare: lessons from the Health Foundation's programme evaluations and relevant literature. BMJ Qual Saf. 2012, 21, 876–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Program Evaluation 2022 [cited 2022. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/evaluation/index.htm.
- Dyar OJ, Huttner B, Schouten J, Pulcini C. What is antimicrobial stewardship? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 793–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE. Antimicrobial stewardship: systems and processes for effective antimicrobial medicine use. 2015.
- Mendelson, M.; Morris, A.M.; Thursky, K.; Pulcini, C. How to start an antimicrobial stewardship programme in a hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 26, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathwani, D.; Varghese, D.; Stephens, J.; Ansari, W.; Martin, S.; Charbonneau, C. Value of hospital antimicrobial stewardship programs [ASPs]: a systematic review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, J.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Schellack, N.; Cornistein, W.; Al Maani, A.; Adnan, S.; Stevens, M.P. Global Antimicrobial Stewardship with a Focus on Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A position statement for the international society for infectious diseases. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kraker, M.E.; Abbas, M.; Huttner, B.; Harbarth, S. Good epidemiological practice: a narrative review of appropriate scientific methods to evaluate the impact of antimicrobial stewardship interventions. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; A Cataldo, M.; Paul, M.; Leibovici, L.; Kluytmans, J.; Schröder, W.; Foschi, F.; De Angelis, G.; De Waure, C.; Cadeddu, C.; et al. STROBE-AMS: recommendations to optimise reporting of epidemiological studies on antimicrobial resistance and informing improvement in antimicrobial stewardship. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, M.A.; Nasser, S.A.; Rababa’h, A.M. A systematic review of Antimicrobial Stewardship Program implementation in Middle Eastern countries. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Ohmagari, N.; Tokuda, Y.; Mattar, C.; Warren, D.K. Antimicrobial Stewardship in Inpatient Settings in the Asia Pacific Region: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S119–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losier, M.; Ramsey, T.D.; Wilby, K.J.; Black, E.K. A Systematic Review of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions in the Emergency Department. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooda, K.; Canterbury, E.; Bellolio, F. Impact of Pharmacist-Led Antimicrobial Stewardship on Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2022, 79, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.M.M.; Daniel, R.; Hughes, K.; Wootton, M.; Hood, K.; Gillespie, D. A systematic review investigating the use of microbiology outcome measures in randomized controlled trials evaluating antimicrobial stewardship interventions published between 2011 and 2021. JAC-Antimicrobial Resist. 2022, 4, dlac013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey P, Brown E, Charani E, Fenelon L, Gould IM, Holmes A, et al. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013, Cd003543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, P.J.; Rohailla, S.; Taggart, L.R.; Lightfoot, D.; Havey, T.; Daneman, N.; Lowe, C.; Muller, M.P. Antimicrobial Stewardship and Intensive Care Unit Mortality: A Systematic Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, D.; Sato, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kamada, M.; Moriwaki, N.; Nakano, T.; Shiotsuka, S.; Tokushige, C.; Toh, H.; Kamimura, H.; et al. The impact of earlier intervention by an antimicrobial stewardship team for specific antimicrobials in a single weekly intervention. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 77, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandan, M.; Thapa, P.; Maharjan, P.; Bhandari, B. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship program on antimicrobial-resistance and prescribing in nursing homes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 29, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusef, D.; A Hayajneh, W.; Issa, A.B.; Haddad, R.; Al-Azzam, S.; A Lattyak, E.; Lattyak, W.J.; Gould, I.; Conway, B.R.; Bond, S.; et al. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship programme on reducing broad-spectrum antibiotic use and its effect on carbapenem-resistantAcinetobacter baumannii(CRAb) in hospitals in Jordan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 76, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, P.; Marwick, C.A.; Scott, C.L.; Charani, E.; McNeil, K.; Brown, E.; Gould, I.M.; Ramsay, C.R.; Michie, S. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients (updated protocol). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014, 2, CD003543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuts, E.C.; Boyd, A.; E Muller, A.; Mouton, J.W.; Prins, J.M. The Effect of Antibiotic Restriction Programs on Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dik, J.-W.H.; Vemer, P.; Friedrich, A.W.; Hendrix, R.; Lo-Ten-Foe, J.R.; Sinha, B.; Postma, M.J. Financial evaluations of antibiotic stewardship programs—a systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 317–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysari, M.T.; Lehnbom, E.C.; Li, L.; Hargreaves, A.; Day, R.O.; Westbrook, J.I. The effectiveness of information technology to improve antimicrobial prescribing in hospitals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2016, 92, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helou, R.I.; Foudraine, D.E.; Catho, G.; Latif, A.P.; Verkaik, N.J.; Verbon, A. Use of stewardship smartphone applications by physicians and prescribing of antimicrobials in hospitals: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanika, S.; Paudel, S.; Grigoras, C.; Kalbasi, A.; Mylonakis, E. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical and Economic Outcomes from the Implementation of Hospital-Based Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4840–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Van Dort, B.; Penm, J.; Ritchie, A.; Baysari, M.T. The impact of digital interventions on antimicrobial stewardship in hospitals: a qualitative synthesis of systematic reviews. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO regions 2023 [Available from: https://www.who.int/about/who-we-are/regional-offices.
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajar, P.; Saugstad, O.D.; Berild, D.; Dutta, A.; Greisen, G.; Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Mande, S.S.; Nangia, S.; Petersen, F.C.; Dahle, U.R.; et al. Antibiotic Stewardship in Premature Infants: A Systematic Review. Neonatology 2020, 117, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donà D, Barbieri E, Daverio M, Lundin R, Giaquinto C, Zaoutis T, et al. Implementation and impact of pediatric antimicrobial stewardship programs: a systematic scoping review. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Gerber, J.S.; Hersh, A.L. Inpatient Antimicrobial Stewardship in Pediatrics: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, e127–e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenehjem, E.; Hyun, D.Y.; Septimus, E.; Yu, K.C.; Meyer, M.; Raj, D.; Srinivasan, A. Antibiotic Stewardship in Small Hospitals: Barriers and Potential Solutions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, M.R.; Isemin, N.U.; Udoh, A.E.; Ashiru-Oredope, D. Implementation of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in African countries: a systematic literature review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorafa, E.M.; Komatsiouli, V.P.; Iosifidis, E.; Kourti, M.; Sdougka, M.; Roilides, E. Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in PICU Settings: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 24, e20–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollo, L.G.; Lutkemeyer, D.S.; Levin, A.S. Are antimicrobial stewardship programs effective strategies for preventing antibiotic resistance? A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2018, 46, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzani, M.D.; Mazzaferri, F.; Compri, M.; Galia, L.; Mutters, N.T.; Kahlmeter, G.; E Zaoutis, T.; Schwaber, M.J.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Harbarth, S.; et al. Linking antimicrobial resistance surveillance to antibiotic policy in healthcare settings: the COMBACTE-Magnet EPI-Net COACH project. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, ii2–ii19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo da Silva AR, Albernaz de Almeida Dias DC, Marques AF, Biscaia di Biase C, Murni IK, Dramowski A, et al. Role of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in children: a systematic review. J Hosp Infect. 2018, 99, 117–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, D.; Sneddon, J.; Malcolm, W.; Wiuff, C.; Patton, A.; Hurding, S.; Eastaway, A.; Seaton, R.A.; Watson, E.; Gillies, E.; et al. Scottish Antimicrobial Prescribing Group (SAPG): development and impact of the Scottish National Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabah, A.; Cotta, M.O.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Schouten, J.; Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J.; Tacey, M.; Timsit, J.-F.; Leone, M.; Zahar, J.R.; et al. A Systematic Review of the Definitions, Determinants, and Clinical Outcomes of Antimicrobial De-escalation in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 62, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, A.; Medisauskaite, A.; Potts, H.W.W.; Griffin, A. A theory-based study of doctors’ intentions to engage in professional behaviours. BMC Med. Educ. 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warremana, E.; Lambregtsa, M.; Wouters, R.; Visser, L.; Staats, H.; van Dijk, E.; de Boer, M. Determinants of in-hospital antibiotic prescription behaviour: a systematic review and formation of a comprehensive framework. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 25, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, G.J.; Owens, S.; Breckons, M. A systematic review of qualitative literature on antimicrobial stewardship in Sub-Saharan Africa. Glob. Health Res. Policy 2021, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotherton, A.L. Metrics of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterman, R.; Hussein, K.; Leibovici, L.; Carmeli, Y.; Paul, M. Systematic review of antibiotic consumption in acute care hospitals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 561–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benić, M.S.; Milanič, R.; A Monnier, A.; Gyssens, I.C.; Adriaenssens, N.; Versporten, A.; Zanichelli, V.; Huttner, B.; Tebano, G.; E Hulscher, M.; et al. Metrics for quantifying antibiotic use in the hospital setting: results from a systematic review and international multidisciplinary consensus procedure. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, vi50–vi58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanichelli, V.; A Monnier, A.; Gyssens, I.C.; Adriaenssens, N.; Versporten, A.; Pulcini, C.; Le Maréchal, M.; Tebano, G.; Vlahović-Palčevski, V.; Benić, M.S.; et al. Variation in antibiotic use among and within different settings: a systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, vi17–vi29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin. ; Fontela, P.S.; Manges, A.R.; Platt, R.W.; Buckeridge, D.L.; Quach, C. Measuring antimicrobial use in hospitalized patients: a systematic review of available measures applicable to paediatrics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmaturapoj, T.; Scott, J.; Smith, P.; Abutheraa, N.; Watson, M. Pharmacist-led education-based antimicrobial stewardship interventions and their effect on antimicrobial use in hospital inpatients: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 115, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Morey, P.; Valle, M. A systematic review of inpatient antimicrobial stewardship programmes involving clinical pharmacists in small-to-medium-sized hospitals. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2017, 25, e69–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, L.M.; Weber, D.J. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing at hospital discharge: A systematic review. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 42, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–55. [CrossRef]
- Naylor, N.R.; Atun, R.; Zhu, N.; Kulasabanathan, K.; Silva, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Knight, G.M.; Robotham, J.V. Estimating the burden of antimicrobial resistance: a systematic literature review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2018, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, D.; Gladstone, B.P.; Burkert, F.; Carrara, E.; Foschi, F.; Döbele, S.; Tacconelli, E. Effect of antibiotic stewardship on the incidence of infection and colonisation with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulou, M.; Reynolds, L. Role of antimicrobial restrictions in bacterial resistance control: a systematic literature review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 104, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Modarai, M.; Naylor, N.R.; E Boyd, S.; Atun, R.; Barlow, J.; Holmes, A.H.; Johnson, A.; Robotham, J.V. Quantifying drivers of antibiotic resistance in humans: a systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e368–e378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Beiersmann, C.; Neuhann, F.; Moazen, B.; Lu, G.; Müller, O. Risk factors for antibiotic resistance development in healthcare settings in China: a systematic review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 149, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan JE, Gerding DN. Does antibiotic restriction prevent resistance? New horizons (Baltimore, Md). 1996, 4, 370–6.
- Huebner, C.; Flessa, S.; Huebner, N.-O. The economic impact of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in hospitals: a systematic literature review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 102, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, V.A.; van Heijl, I.; van Werkhoven, C.H.; Islam, J.; Hendriks-Spoor, K.D.; Bielicki, J.; Bonte, M.J.; Walker, A.S.; Llewelyn, M.J.; Harbarth, S.; et al. The quality of studies evaluating antimicrobial stewardship interventions: a systematic review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 25, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.H.; Maruan, K.; Khairy, H.A.M.; Hong, Y.H.; Dali, A.F.; Neoh, C.F. Economic Evaluations on Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme: A Systematic Review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 20, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, J.C.; Fitzpatrick, M.A.; Suda, K.J. Expanding Antimicrobial Stewardship Through Quality Improvement. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e211072–e211072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Monnier, A.; Schouten, J.; Tebano, G.; Benić, M.S.; Milanič, R.; Adriaenssens, N.; Versporten, A.; Huttner, B.; Zanichelli, V.; E Hulscher, M.; et al. Quality indicators for responsible antibiotic use in the inpatient setting: a systematic review followed by an international multidisciplinary consensus procedure. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, vi30–vi39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmer, D.N.; Trienski, T.L.; Walsh, T.L.; Moffa, M.A. Role of Technology in Antimicrobial Stewardship. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson TM, Moore LSP, Hernandez B, Charani E, Castro-Sanchez E, Herrero P, et al. A systematic review of clinical decision support systems for antimicrobial management: are we failing to investigate these interventions appropriately? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 524–32. [CrossRef]
- Micallef, C.; Chaudhry, N.T.; Holmes, A.H.; Hopkins, S.; Benn, J.; Franklin, B.D. Secondary use of data from hospital electronic prescribing and pharmacy systems to support the quality and safety of antimicrobial use: a systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulou, M.; Reynolds, L. Systematic review of the effects of antimicrobial cycling on bacterial resistance rates within hospital settings. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, P.; Peden, C.; Charani, E.; Marwick, C.; Michie, S. Time for action—Improving the design and reporting of behaviour change interventions for antimicrobial stewardship in hospitals: Early findings from a systematic review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, M.C.; Prins, J.M. A Systematic Review of Quality Indicators for Appropriate Antibiotic Use in Hospitalized Adult Patients. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’riordan, F.; Shiely, F.; Byrne, S.; Fleming, A. Quality indicators for hospital antimicrobial stewardship programmes: a systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouly, E.; Coppry, M.; Rogues, A.-M.; Dumartin, C. Systematic review of factors promoting behaviour change toward antibiotic use in hospitals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzewuska, M.; Duncan, E.M.; Francis, J.J.; Morris, A.M.; Suh, K.N.; Davey, P.G.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Ramsay, C.R. Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation of Antibiotic Stewardship Programmes in Hospitals in Developed Countries: Insights From Transnational Studies. Front. Sociol. 2020, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuts, E.C.; Hulscher, M.E.J.L.; Mouton, J.W.; Verduin, C.M.; Stuart, J.W.T.C.; Overdiek, H.W.P.M.; van der Linden, P.D.; Natsch, S.; Hertogh, C.M.P.M.; Wolfs, T.F.W.; et al. Current evidence on hospital antimicrobial stewardship objectives: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck C, Vlieghe E, Cox JA. Antibiotic stewardship interventions in hospitals in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 266–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feazel, L.M.; Malhotra, A.; Perencevich, E.N.; Kaboli, P.; Diekema, D.J.; Schweizer, M.L. Effect of antibiotic stewardship programmes on Clostridium difficile incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.T.; Beauchemin, M.P.; Neu, N.; Larson, E.L. Prior antibiotic use and acquisition of multidrug-resistant organisms in hospitalized children: A systematic review. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert-May, E.; Chew, D.S.; Conly, J.; Guirguis, M.; Slobodan, J.; Fryters, S.; Bresee, L. Clinical practice guidelines for creating an acute care hospital-based antimicrobial stewardship program: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2019, 47, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.; Stevens, M.P. Clinical Decision Support Systems and Their Role in Antibiotic Stewardship: a Systematic Review. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, T.; Heneghan, C.; Roberts, N.; Curtis, D.; Williams, V.; Onakpoya, I. Healthcare-associated infections and the prescribing of antibiotics in hospitalized patients of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) states: a mixed-methods systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 110, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner B, Filice GA, Drekonja D, Greer N, MacDonald R, Rutks I, et al. Antimicrobial stewardship programs in inpatient hospital settings: a systematic review. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 1209–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo YN, Freyne B, Kululanga D, Bryant PA. The Impact of Antimicrobial Stewardship in Children in Low- and Middle-income Countries: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2022, 41, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.F.; Cowling, B.J.; Feng, S.; Aso, H.; Wu, P.; Fukuda, K.; Seto, W.H. Impact of antibiotic stewardship programmes in Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim JM, Singh SR, Duong MC, Legido-Quigley H, Hsu LY, Tam CC. Impact of national interventions to promote responsible antibiotic use: a systematic review. J. Antimicrob Chemother. 2020, 75, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, C.; Edwards, G.; Dooley, M.; Mitra, B. Roles of the emergency medicine pharmacist: A systematic review. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2018, 75, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siachalinga, L.; Mufwambi, W.; Lee, I.-H. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing for hospital inpatients in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2022, 129, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamna-Mawassi, H.; Huberman-Samuel, M.; Hershcovitz, S.; Karny-Epstein, N.; Kola, A.; Cortés, L.E.L.; Leibovici, L.; Yahav, D. Interventions to reduce infections caused by multidrug resistant Enterobacteriaceae (MDR-E): A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garwan, Y.M.; Alsalloum, M.A.; Thabit, A.K.; Jose, J.; Eljaaly, K. Effectiveness of antimicrobial stewardship interventions on early switch from intravenous-to-oral antimicrobials in hospitalized adults: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2023, 51, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashad, N.; Perumal, D.; Stewart, D.; Tonna, A. Mapping hospital antimicrobial stewardship programmes in the Gulf Cooperation Council states against international standards: a systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keikha, M.; Kamali, H.; Ghazvini, K.; Karbalaei, M. Conceptual framework of antibiotic stewardship programs in reducing ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Chemother. 2022, 34, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, Z.; Paravattil, B.; Wilby, K. the impact of antimicrobial stewardship strategies on antibiotic appropriateness and prescribing behaviours in selected countries in the Middle East: a systematic review. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2017, 23, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teerawattanapong, N.; Kengkla, K.; Dilokthornsakul, P.; Saokaew, S.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Prevention and Control of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in Adult Intensive Care Units: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S51–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
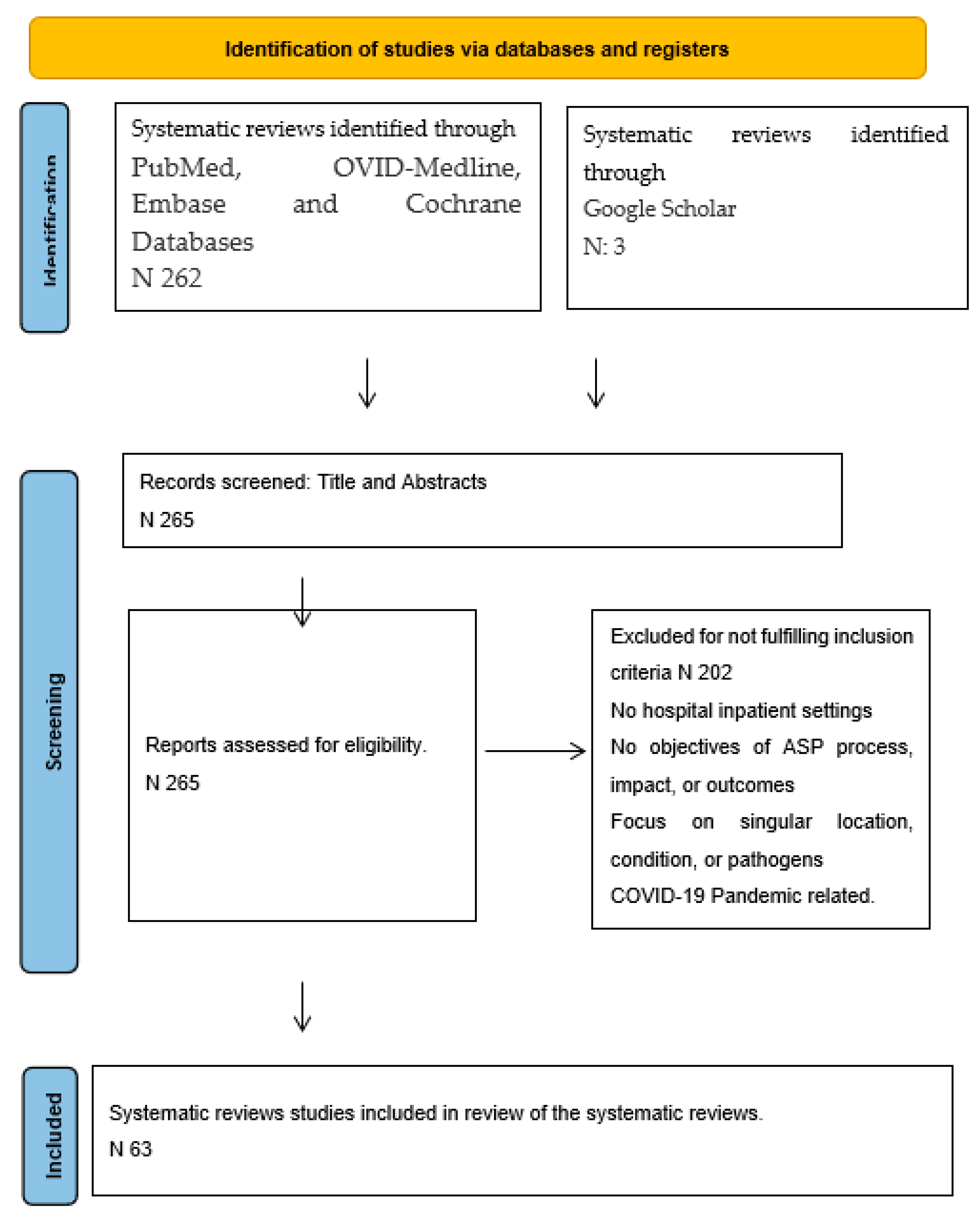
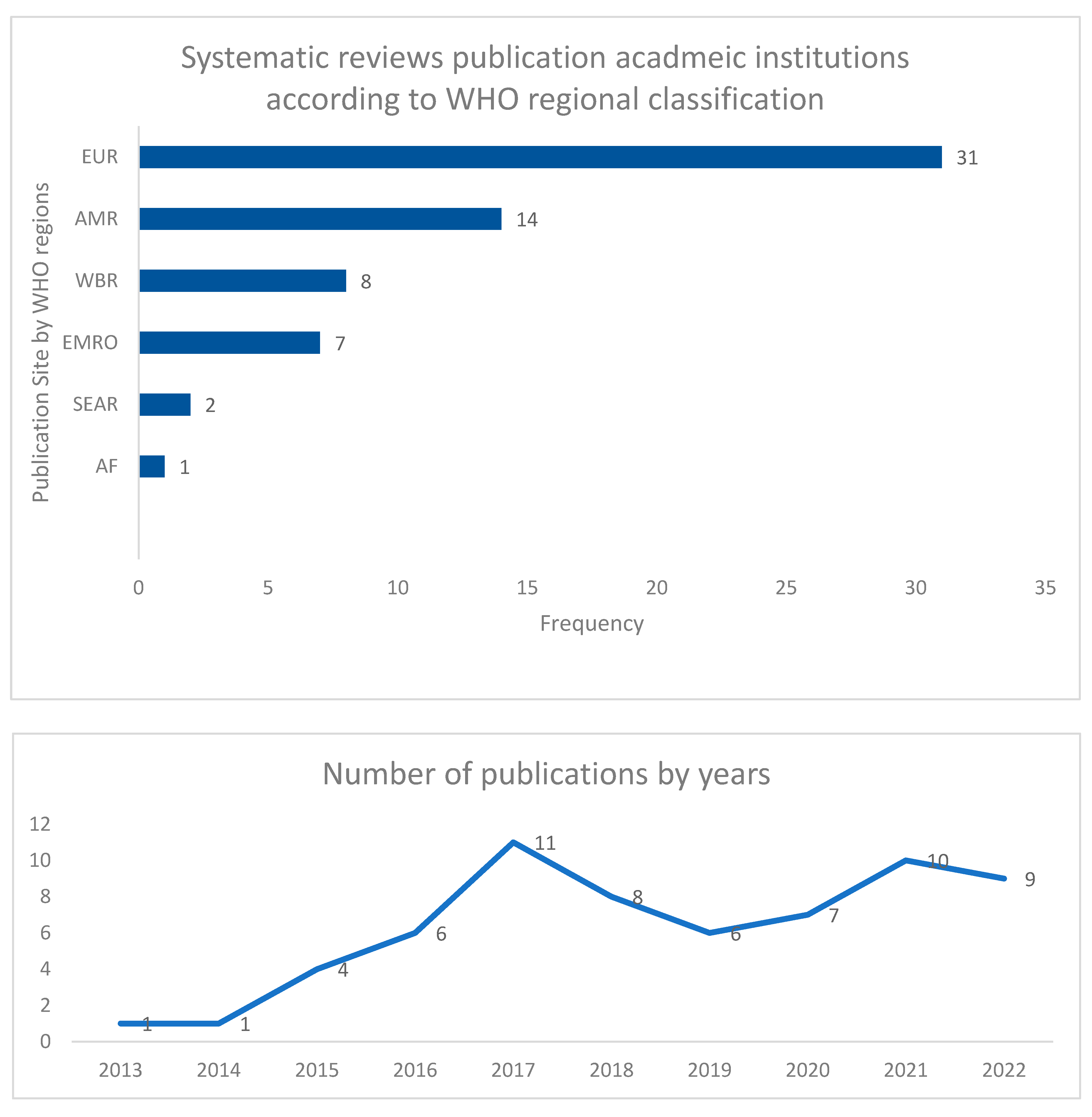
| Regions | Systematic reviews/year | Approach | Primary concept | Reviewed studies | Process measures | Outcome measures | *AMSTAR-2 Quality | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe (EUR) | Baur 2017 Chatzopoulou 2020 Chatzopoulou 2022 Corafa 2022 Davey 2013 Davey 2015 Davey 2017 Donà 2020 Dik 2015 Helou 2020 Huebner 2019 Kallen 2017 Lau 2022 Mas-Morey 2018 Micallef 2017 Monmaturapoj 2021 Monnier 2018 Nathwani 2019 O'Riordan 2021 Porter 2021 Pouly 2022 Rajar 2021 Rawson 2017 Rzewuska 2020 Schuts 2016 Schuts 2021 Schweitzer 2019 Stanic 2018 Tacconelli 2016 Van Dijck 2018 Warreman 2019 |
Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Regional Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global |
Adverse Events Antimicrobial Resistance Antimicrobial Resistance Critical Care Effectiveness Behaviour Safety and efficacy Efficacy Economic impact Information Technology Economic Impact Quality Indicators Microbiological outcomes Role of Pharmacy Information Technology Role of Pharmacy Quality Indicators Clinical and Economic outcomes Quality Indicators Behavioural Factors Behavioural Factors Safety Information Technology Implementation Efficacy Antimicrobial Resistance Quality of studies Metrics Surveillance Middle- and low-income countries Behavioural Factors |
32 15 29 13 89 116 221 113 95 13 16 14 117 28 14 52 70 164 16 14 124 12 58 145 15 145 825 168 78 27 9 |
No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes No Yes No Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes No No Yes Yes No No Yes Yes No |
CL CL CL CL L CL H CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL H CL CL CL L CL CL CL CL CL |
[58] [59] [71] [39] [19] [72] [24] [35] [26] [28] [63] [73] [18] [54] [70] [53] [67] [43] [74] [47] [75] [34] [69] [76] [77] [25] [64] [50] [13] [78] [46] |
| Americas (AMR) | Araujo da Silva 2018 Bertollo 2018 Daniels 2021 Feazel 2014 Karanika 2016 Kooda 2022 Lindsay 2019 Losier 2017 Murray 2021 Rennert-May 2017 Rittmann 2019 Smith 2015 Wade 2021 Wagner 2014 |
Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Global Regional Regional |
Effectiveness Antimicrobial Resistance Discharge medications Adverse Events Economic Impact Role of Pharmacy Critical care Emergency Department Antimicrobial Resistance Guidelines Information Technology Efficacy Healthcare Associated infections. Efficacy |
9 26 6 78 26 24 1143 29 5 45 9 21 37 |
Yes No Yes No No Yes No Yes No Yes Yes No Yes Yes |
Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes |
L CL CL L CL L CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL |
[42] [40] [55] [79] [29] [17] [20] [16] [80] [81] [82] [36] [83] [84] |
| West Pacific Region (WPR) | Abo 2020 Baysari 2016 Honda 2017 Lee 2018 Lim 2020 Roman 2018 Siachalinga 2022 Tabah 2016 |
Global Global Regional Regional Global Global Global Regional |
Efficacy Information Technology Safety and efficacy Safety and efficacy National Interventions Role of Pharmacy Efficacy Critical Care |
34 45 46 77 34 15 28 14 |
Yes Yes No No Yes Yes Yes Yes |
Yes No Yes Yes No No No Yes |
L CL CL CL CL CL L CL |
[85] [27] [15] [86] [87] [88] [89] [44] |
| East Mediterranean (EMRO) | Ababneh 2021 Atamna-Mawassi 2021 Bitterman 2016 Garwan 2022 Hashad 2020 Keikha 22 Nasr 2017 |
Regional Global Global Global Regional Global Regional |
Implementation Antimicrobial Resistance Antimicrobial consumption Antimicrobial Switch Effectiveness Antimicrobial Resistance Behavioural factors |
20 63 80 36 17 17 20 |
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes |
Yes Yes No Yes No Yes No |
CL CL CL CL CL L CL |
[14] [90] [49] [91] [92] [93] [94] |
| Southeast Asia (SEAR) | Ibrahim 2017 Teerawattanapong 2017 |
Global Global |
Economic Impact Antimicrobial Resistance |
5 42 |
No Yes |
Yes Yes |
CL CL |
[65] [95] |
| Africa (AF) | Akpan 2020 | Regional | Implementation | 13 | Yes | Yes | CL | [38] |
| Primary focus | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial Resistance | 8 | 12.7 |
| Efficacy | 6 | 9.52 |
| Behaviour | 5 | 7.94 |
| Information technology | 5 | 7.94 |
| Economic impact | 4 | 6.35 |
| Quality | 4 | 6.35 |
| Role of Pharmacy | 4 | 6.35 |
| Critical Care | 3 | 4.76 |
| Effectiveness | 3 | 4.76 |
| Efficacy and Safety | 3 | 4.76 |
| Implementation | 3 | 4.76 |
| Adverse Events | 2 | 3.17 |
| Antimicrobial Switch | 1 | 1.59 |
| Antimicrobial consumption | 1 | 1.59 |
| Clinical and economic outcomes | 1 | 1.59 |
| Discharge medications | 1 | 1.59 |
| Emergency department | 1 | 1.59 |
| Guidelines | 1 | 1.59 |
| Healthcare Associated infections | 1 | 1.59 |
| Metrics | 1 | 1.59 |
| Microbiological outcomes | 1 | 1.59 |
| Middle- and low-income countries | 1 | 1.59 |
| National interventions | 1 | 1.59 |
| Safety | 1 | 1.59 |
| Surveillance | 1 | 1.59 |
| Total | 63 | 100 % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





