Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of bacteria
2.2. Adhesion of bacteria to orthodontic archwires
2.3. Antibacterial action of antiseptics
2.4. Anti-adhesive effects of antiseptics
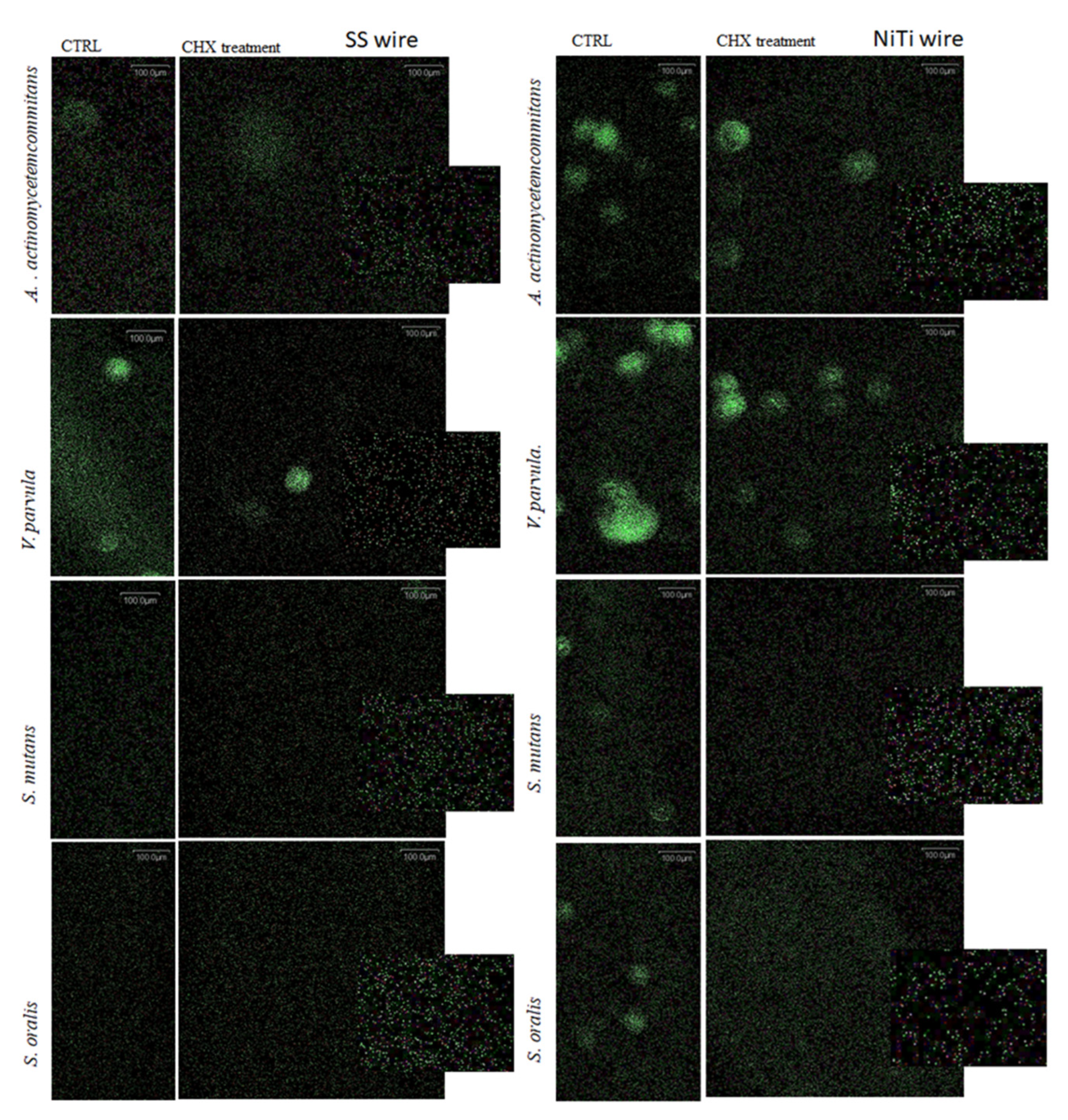
2.5. Visualization of adherent bacteria on archwires by fluorescence microscopy
2.6. Statistical methods
3. Results
3.1. Minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC)
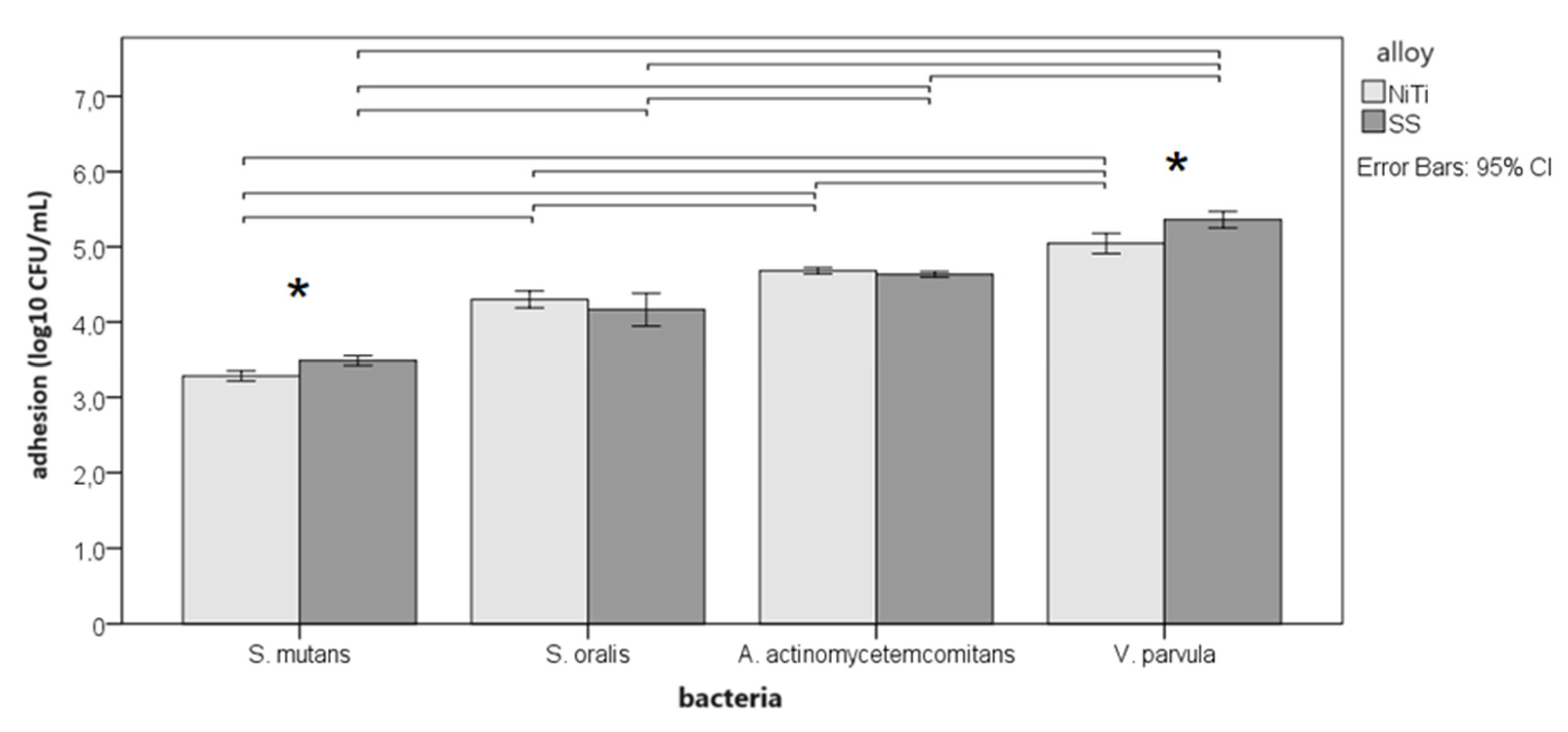
3.2. Adherence to alloys
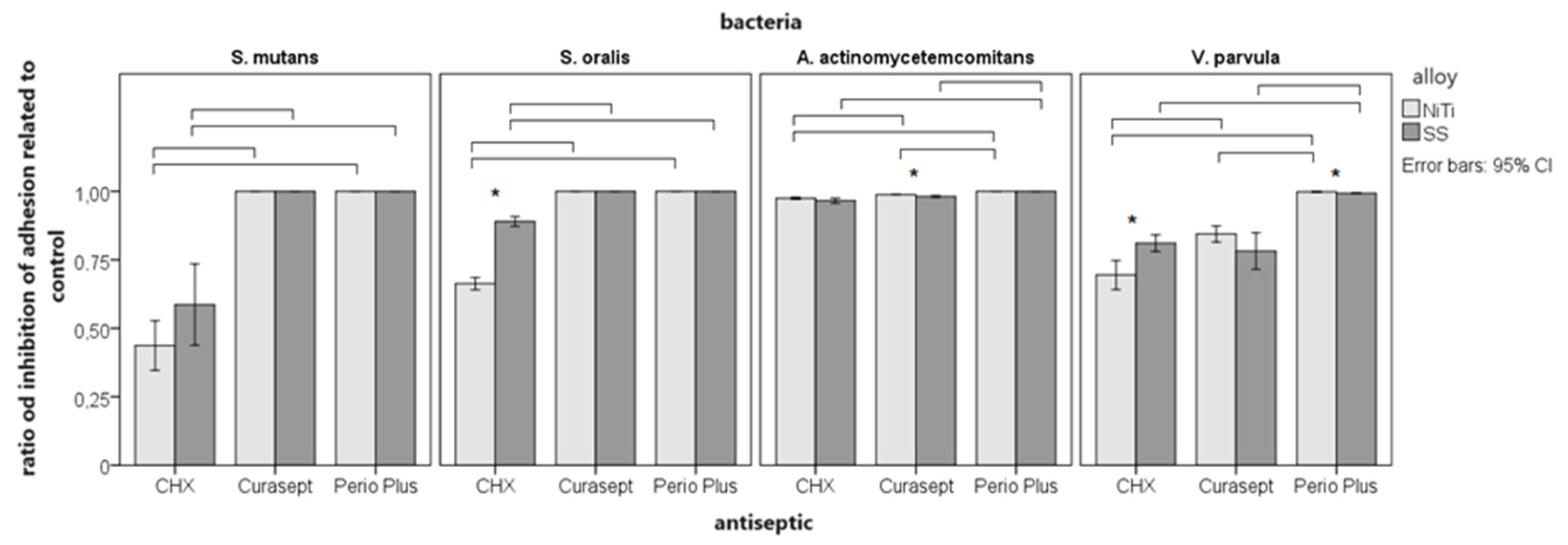
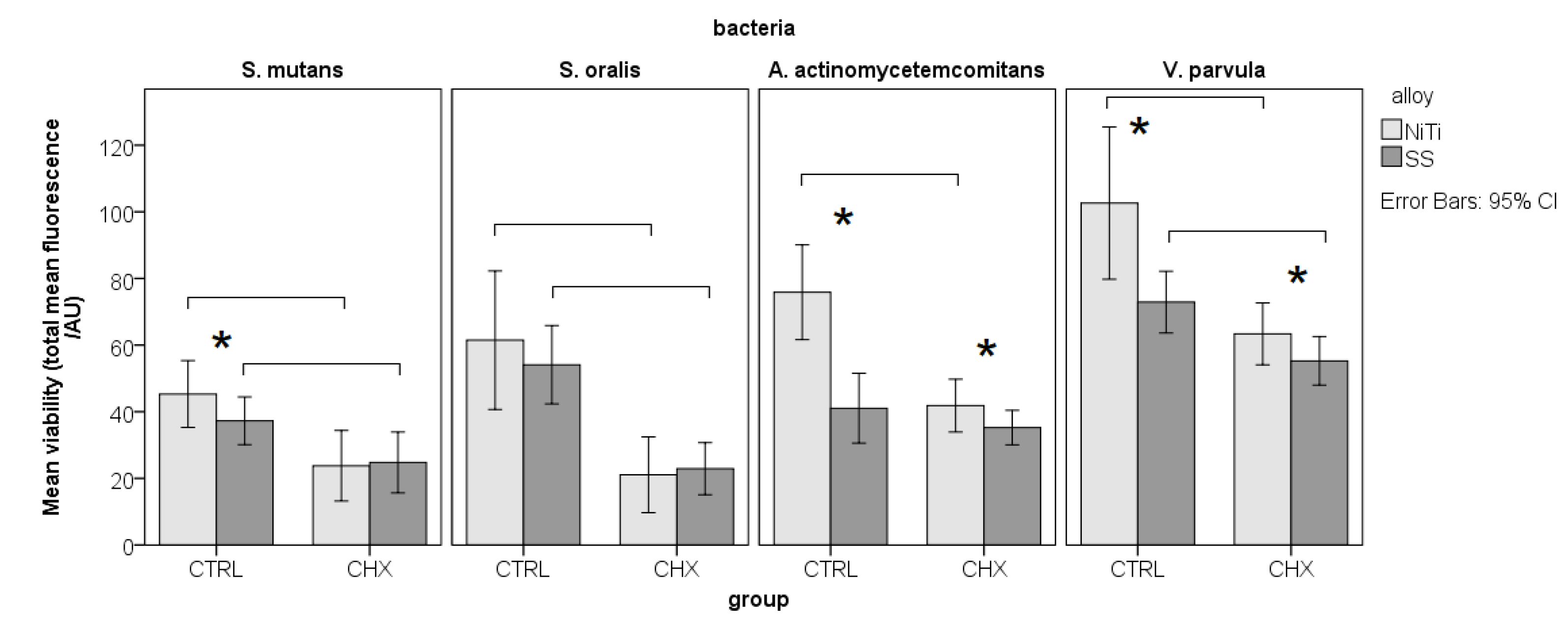
3.3. Inhibition of adhesion
3.4. Differences between alloys
3.5. Differences between solutions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.; Lamster, I.B.; Levin, L. Current concepts in the management of periodontitis. Int. Dent. J. 2021, 71, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, A.O.A.; Marquezan, M.; Nojima, M.D.C.G.; Alviano, D.S.; Maia, L.C. The influence of orthodontic fixed appliances on the oral microbiota: A systematic review. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijnge, V.; van Leeuwen, M.B.M.; Degener, J.E.; Abbas, F.; Thurnheer, T.; Gmür, R.; et al. Oral biofilm architecture on natural teeth. PLoS ONE. 2010, 5, e9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhou, H.; Hansen, B.F.; et al. Periodontal health and relative quantity of subgingival porphyromonas gingivalis during orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod. 2011, 81, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapila, S.; Sachdeva, R. Mechanical properties and clinical applications of orthodontic wires. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1989, 96, 100–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chieng, J.; Wong, C.; Benic, G.; Farella, M. Factors affecting dental biofilm in patients wearing fixed orthodontic appliances. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, Y.; Lindhe, J.; Ramberg, P.; Volpe, A.R. Patterns of de novo plaque formation in the human dentition. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1992, 19, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, A.S.; Suzuki, S.S.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Mada, E.Y.; Freitas, A.Z.; Suzuki, H. Biofilm retention by 3 methods of ligation on orthodontic brackets: A microbiologic and optical coherence tomography analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2011, 140, e193–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, P.; Dutra, C.S.; Lisboa, M.R.; Gondim, D.V.; Leitão, R.; Brito, G.A.; et al. Clinical efficacy of a 1% Matricaria chamomile L. mouthwash and 0.12% chlorhexidine for gingivitis control in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 58, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleter, G.A. Discoloration of dental carious lesions (a review) Arch. Oral Biol. 1998, 43, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yunxia, Y.; Jiuhui Cuiying, L. Effects of motivational methods on oral hygiene of orthodontic patients A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018, 97, e13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shqaidef, A.J.; Saleh, M.Y.N.; Kussad, J.; Khambay, B.S. Do parents of adolescent patients undergoing fixed appliance treatment recall more information using written material or an animated video? A randomized controlled trial. Saudi Dent. J. 2023, 35, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, F.; Krasse, B. Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli frequency in orthodontic patients; the effect of chlorhexidine treatments. Eur. J. Orthod. 1987, 9, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattousch, T.J.; van der Veen, M.H.; Zentner, A. Caries lesions after orthodontic treatment followed by quantitative light-induced fluorescence: A 2-year follow-up. Eur. J. Orthod. 2007, 29, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, M.; Berry, C.W.; Bennet, C.L.; Israelson, H. Changes in gingival and gingival flora with bonding and banding. Angle Orthod. 1987, 57, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.J.; Campbell, P.M.; Rees, T.D.; Buschang, P.H. A randomized controlled trial evaluating antioxidant-essential oil gel as a treatment for gingivitis in orthodontic patients. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeturu, S.K.; Acharya, S.; Urala, A.S.; Pentapati, K.C. Effect of Aloe vera, chlorine dioxide, and chlorhexidine mouth rinses on plaque and gingivitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, M. Chlorhexidine compared with other locally delivered anti-microbials. A short review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1986, 13, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenseifen, J.W.; Madonia, J.V. Study of dental plaque in orthodontic patients. J. Dent. Res. 1970, 49, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliades, T.; Eliades, G.; Brantley, W.A. Microbial attachment on orthodontic appliances. I. Wettability and early pellicle formation on bracket materials. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1995, 108, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazola Filho, J.; Leal Vizoto, N.; de Aguiar Loesch, M.L.; Dias de Sena, M.; Mendes da Camara, D.; Sampaio Caiaffa, K.; de Oliveira Mattos-Graner, R.; Duque, C. Genetic and physiological effects of subinhibitory concentrations of oral antimicrobial agents on Streptococcus mutans biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovic, R.; Begic, G.; Lucic Blagojevic, S.; Karleusa, L.J.; Spalj, S.; Gobin, I. Temporal dynamics of adhesion of oral bacteria to orthodontic appliances. Dent. Mater. J. 2023, 42, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Balani, K. Adhesion force of staphylococcus aureus on various biomaterial surfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhra, S.S.; Littlewood, S.J.; Houghton, N.; Luther, F.; Prabhu, J.; Munyombwe, T.; et al. Do we need primer for orthodontic bonding? A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 37, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.S.; Kim, K.; Cho, S.; Lim, B.S.; Ahn, S.J. Compositional differences in multi-species biofilms formed on various orthodontic adhesives. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, D.M.; An, J.S.; Lim, B.S.; Ahn, S.J. Orthodontic bonding procedure influence biofilm composition. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulewicz, M.; Gronostajski, Z.; Wielgus, A.; Chojnacka, K. Transparent orthodontic archwires: A systematic literature review. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, M.P.; Hellemann, C.F.; Grade, S.; Heuer, W.; Stiesch, M.; Schwestka-Polly, R.; et al. Comparative three-dimensional analysis of initial biofilm formation on three orthodontic bracket materials. Head Face Med. 2015, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.C.; Thomson, J.J.; Alhabeil, J.A.; Toma, J.M.; Plecha, S.C.; Pacheco, R.R.; et al. In vitro Streptococcus mutans adhesion and biofilm formation on different esthetic orthodontic archwires. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.S.; Jagdish, N.; Kailasam, V.; Padmanabhan, S. Streptococcus mutans adhesion on nickel titanium (NiTi) and copper-NiTi archwires: A comparative prospective clinical study. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszewski, Z.; Nowakowska-Toporowska, A.; Wezgowiec, J.; Nowakowska, D. Design and characteristics of new experimental chlorhexidine dental gels with anti-staining properties. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppolo Deus, F.; Ouanounou, A. Chlorhexidine in dentistry: Pharmacology, uses, and adverse effect. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukomska-Szymańska, M.; Sokołowski, J.; Łapińska, B. Chlorhexidine – mechanism of action and its application to dentistry. J. Stomatol. 2017, 70, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solderer, A.; Kaufmann, M.; Hofer, D.; Wiedemeier, D.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R. Efficacy of chlorhexidine rinses after periodontal or implant surgery: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesvoll, P.; Lökken, P.; Rölla, G.; Paus, P.N. Retention of chlorhexidine in the human oral cavity after mouth rinses. Arch. Oral Biol. 1974, 19, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppolo Deus, F.; Ouanounou, A.; Mouthwashes and their use in dentistry: A review. Oral Health. 2021. Available online: https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/mouthwashes-and-their-use-in-dentistry-a-review/ (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Laugisch, O.; Ramseier, C.A.; Salvi, G.E.; Hägi, T.T.; Bürgin, W.; Eick, S.; et al. Effects of two different post-surgical protocols including either 0.05 % chlorhexidine herbal extract or 0.1 % chlorhexidine on post-surgical plaque control, early wound healing and patient acceptance following standard periodontal surgery and implant placement. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duss, C.; Lang, N.P.; Cosyn, J.; Persson, G.R. A randomized, controlled clinical trial on the clinical, microbiological, and staining effects of a novel 0.05% chlorhexidine/herbal extract and a 0.1% chlorhexidine mouthrinse adjunct to periodontal surgery. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, P.; Labriola, A.; Zambelli, R.; Prato, G.P.; Nieri, M.; Tonetti, M.S. Chlorhexidine with an anti-discoloration system after periodontal flap surgery: A cross-over, randomized, triple-blind clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, A.; Kaspar, S.; Kathirvelu, R.; Srinivasan, B.; Srinivasan, S.; Sundram, R. Chlorhexidine: An elixir for periodontics. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohefer, S.A.; Levon, J.A.; Gregory, R.L.; Eckert, G.J.; Lippert, F. Caries lesion remineralization with fluoride toothpastes and chlorhexidine - effects of application timing and toothpaste surfactant. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2018, 26, e20170499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, Z.L.S.; Bescos, R.; Belfield, L.A.; Ali, K.; Roberts, A. Current uses of chlorhexidine for management of oral disease: A narrative review. J. Dent. 2020, 103, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, P.J.; Singh, D.K.; Jalaluddin, M.; Mandal, A. Comparative evaluation of antiplaque efficacy between essential oils with alcohol-based and chlorhexidine with nonalcohol-based mouthrinses. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7 (Suppl 1), S36–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bescos, R.; Ashworth, A.; Cutler, C.; Brookes, Z.L.; Belfield, L.; Rodiles, A.; et al. Effects of Chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacteria | CHX DG solution (µg/mL) | Curasept (%) | Perio Plus (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. mutans | 12.5 | 1.56 | 9.98 x 10(-2) |
| S. oralis | 25 | 3.13 | 9.98 x 10(-2) |
| V. parvula | 12.5 | 0.78 | 0.195 |
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | 6.25 | 3.13 | 0.195 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





