1. Introduction
Thermal infrared (IR) remote sensing is a passive technique to measure the temperatures of objects within the field of view of an optical imaging system at some distance from the scene. The amount of radiation that objects emit and absorb at thermal infrared wavelengths (8–14
m) depends on their temperature and emissivity, which depends on wavelength. The energy of the emitted photons can be collected using a suitable wavelength dependent detector, optical imaging system and digital electronics. Together these parts constitute an IR camera. For most terrestrial applications, where scene temperatures might vary between 180 K to 380 K, the detector wavelength of choice is 8–14
m as the radiance within this waveband is substantial and the strength of absorption by interfering gases is smaller. Wider bands allow more energy throughput, and it is possible to use narrower bands for selective detection of objects that disperse IR radiation in order to measure their brightness temperatures
1. IR imaging systems with fixed two dimensional fields-of-view or through scanning a one dimensional detector array or single detector element, have been used on space-based platforms since the 1970s to monitor emissions from the atmosphere, land and ocean surface. The principles of passive thermal remote sensing of the environment can be found in several texts, for example Kruse [
1], and so these are not discussed here in any detail. Rather our paper describes the principle operation of small, affordable and sensitive passive IR cameras based on the SEEK microbolometer technology (
https://www.thermal.com/). These small (< 50 mm x 50 mm) detectors are available as commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) packages that can be easily integrated into systems used in a host of environmental sensing applications including temperatures in agricultural applications, within the urban environment and for measuring atmospheric parameters such as clouds, plumes and sky temperatures. A recent review of the use of IR remote sensing of volcanic activity can be found in Blackett [
2].
The purpose of this paper is to introduce a new small camera system–the Imaging InfraRed camera (IIRc), that integrates the SEEK microbolometer and lens with a powerful single board (SBC) microprocessor to measure and log image scene temperatures. After a brief discussion of the operating principles of the microbolometer operation, the camera system is described, its calibration is detailed and some examples of its use provided.
2. The Imaging InfraRed Camera (IIRc) System
The theoretical and practical aspects of uncooled bolometers and their measurement capabilities are described in [
1]. The camera core has a fixed focus lens with a 56°x42° field of view and a nominal NE
T of 100 mK at 300 K. The camera is controlled by a Raspberry pi-4 microcomputer
https://www.raspberrypi.org and a visible camera is included in the package with a similar field of view as the IR camera. The camera (or earlier versions) has been used in applications to volcanic plumes [
3,
4] and in synergistic applications with other instruments, e.g. [
5,
6]. The IIRc system consists of a 320x240 microbolometer detector array
2 mounted on an aluminium bracket and with a USB connection that provides power and signal communication. The specifications of the camera are provided in
Table 1 and a photograph of the basic infrared component is shown in
Figure 1.
The IR camera forms one part of the camera system that also includes a visible camera, a microprocessor and software for acquisition, storage, display and analysis. On one model, aimed at estimating SO2 gas amounts, there is a second IR camera installed with a narrowband filter in front of the lens. In this study only the single IR camera system is described.
The visible camera is included to provide extra information on volcanic plume behaviour when acquiring data during the day. It is also possible to use data fusion to combine visible and IR data into a single image. The visible camera specification is provided in
Table 2.
The system is powered by a portable battery or from a mains power supply, if available. The microprocessor is a Raspberry pi Model 4 running the Raspian OS and custom open source software has been developed to acquire, display and analyse both IR and visible imagery. A 7" LED touch screen display allows the user to manage the data acquisition and display without the need for a keyboard and mouse and contributes to the portability of the system. As the system is built mostly on open source packages, other commercially available sensors can be added to the system. For example, accelerometers, digital attitude sensors, air and humidity sensors, and pressure sensors can all be easily included onto the Raspberry pi. An 8x8 pixel IR temperature monitor is included to display housing temperatures but this could also be used to assess sky temperature by mounting it onto the outer housing.
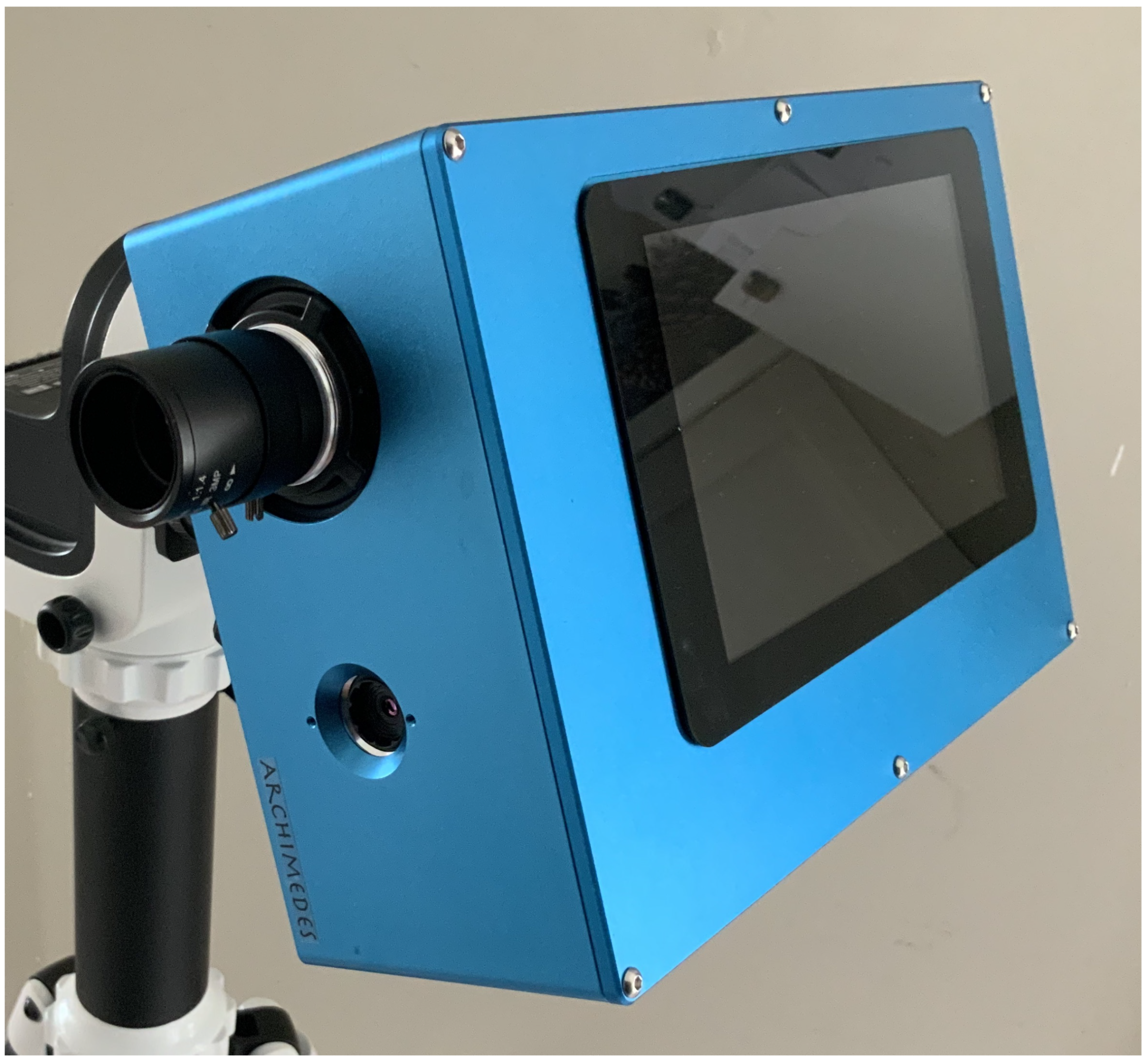
Figure 2 shows the IIRc assembly with a single IR and visible camera.
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Calibration
The IIRc systems return brightness temperatures in a 320x240 pixels image. The cameras were calibrated in the laboratory using a custom built blackbody plate of high emissivity (
> 0.98) which could be heated (to ∼320 K) and cooled (to ∼260 K) using a thermoelectric (Peltier) cooler that operates by applying a current to a semiconductor material. One side of the plate gets hot while the other cools. The blackbody was constructed by applying several coats of black paint to an aluminium plate and attaching it to a water cooled assembly to remove heat from the hot side, since the main desire was to calibrate at low temperatures. Typically the plate could be cooled to ∼260 K. By pointing the camera at the plate, temperatures from ∼270 K to room temperature could be obtained. The plate was simultaneously monitored with four contact temperature transducers and a small IR module. The manufacturers calibration was assumed for the monitoring sensors (AD592–see
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ad592.pdf) of 0.5 K at 288 K, with excellent linearity and an operating range of ∼250–350 K. The IR module was a D6T MEMS sensor with an accuracy of ±1.5 K and an operating range of 280–340 K (
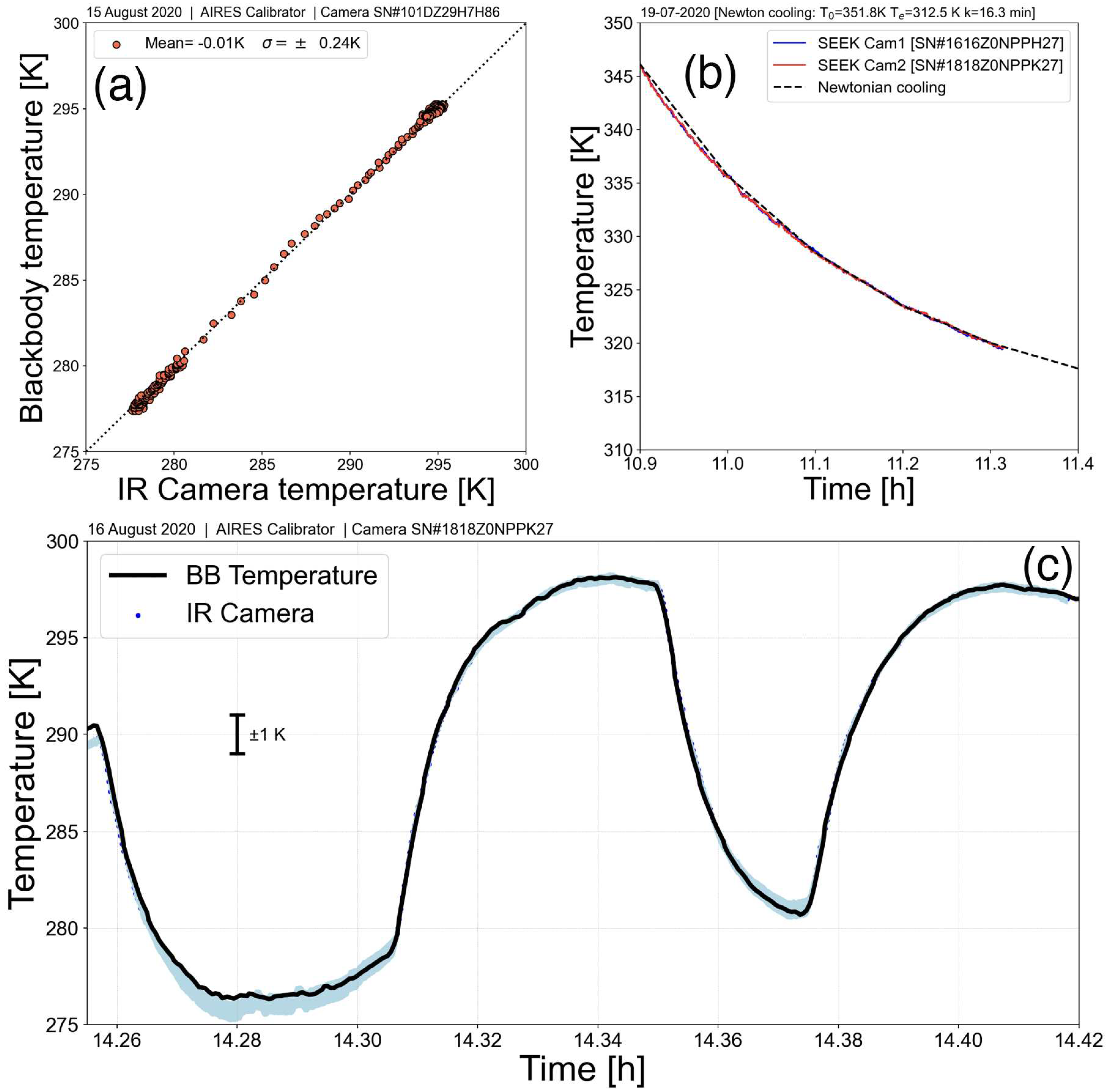
https://docs.rs-online.com/5d12/0900766b8139883c.pdf). As well as assessing the linear calibration of the IR cameras, their temporal behaviour was also analysed by measuring the rate of cooling of the plate and also by cycling the plate by turning off the current to the Peltier cooler so that it warmed rapidly. Typical results for these tests are shown in
Figure 3. The upper-left panel (
Figure 3(a)) shows the linearity of the system for one particular camera with a standard error of ∼±0.3 K and almost zero bias. The upper-right panel (
Figure 3(b)) shows measurements of the cooling rate of the blackbody for two different cameras compared with a theoretical (Newtonian cooling) estimate,
where
is the temperature of the environment,
is the blackbody temperature at time
t,
, the start time, and
k is an inverse time constant. Finally, the lower panel (
Figure 3(c)) shows the responsivity of one camera over a period of ∼30 min, illustrating there is no time lag in responding to temperature changes of the blackbody.
In order to ensure uniformity of the blackbody plate it needed to be small (0.04 m x 0.04 m) and to avoid radiation from the plate heating the camera assembly it was necessary to mount the camera at least 0.5 m from the plate. This configuration means that the plate does not fill the field of view of the camera and an assumption must be made about the uniformity of the response of each pixel.
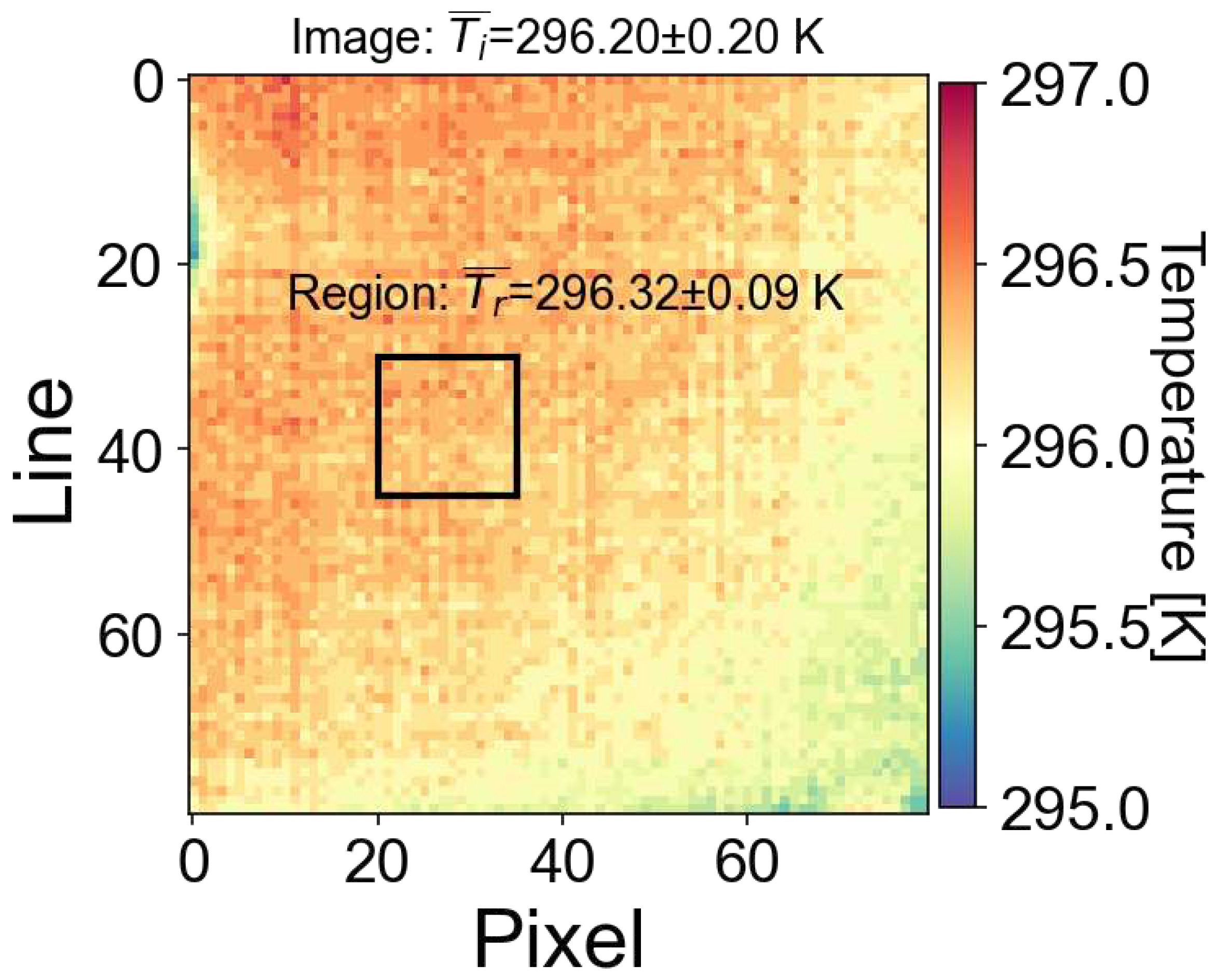
Figure 4 shows an 80x80 pixels portion of the image which includes only the blackbody plate. The mean and standard deviation over this region of the image is 296.20±0.20 K, while the mean and standard deviation of a subregion of 15x15 pixels is 296.32±0.09 K, suggesting that the uniformity is good and less than ±0.50 K. Similar statistics were obtained by rotating the camera and translating it so that different detector elements were impacted by radiation from the blackbody plate. It is likely also that some of the non-uniformity is due to imperfections in the blackbody plate.
3.2. Vignetting
All wide-field imagery contains a certain amount of optical vignetting which is manifested by the gradual dimming of light towards the edges of the image caused by optical components obstructing off-axis light [
7]. The degree of vignetting in image data is very difficult to predict and usually corrections are made by experimental measurements. To observe the degree of vignetting a blackbody plate can be used; but this plate must have very little temperature variation across the plate and must also be large enough to fill the entire field of view. The plate must be large because the field of view must include off-axis radiation at large angles. The actual temperature of the plate is not required as the correction is a geometrical one. An isothermal wall might be a suitable target to measure vignetting.
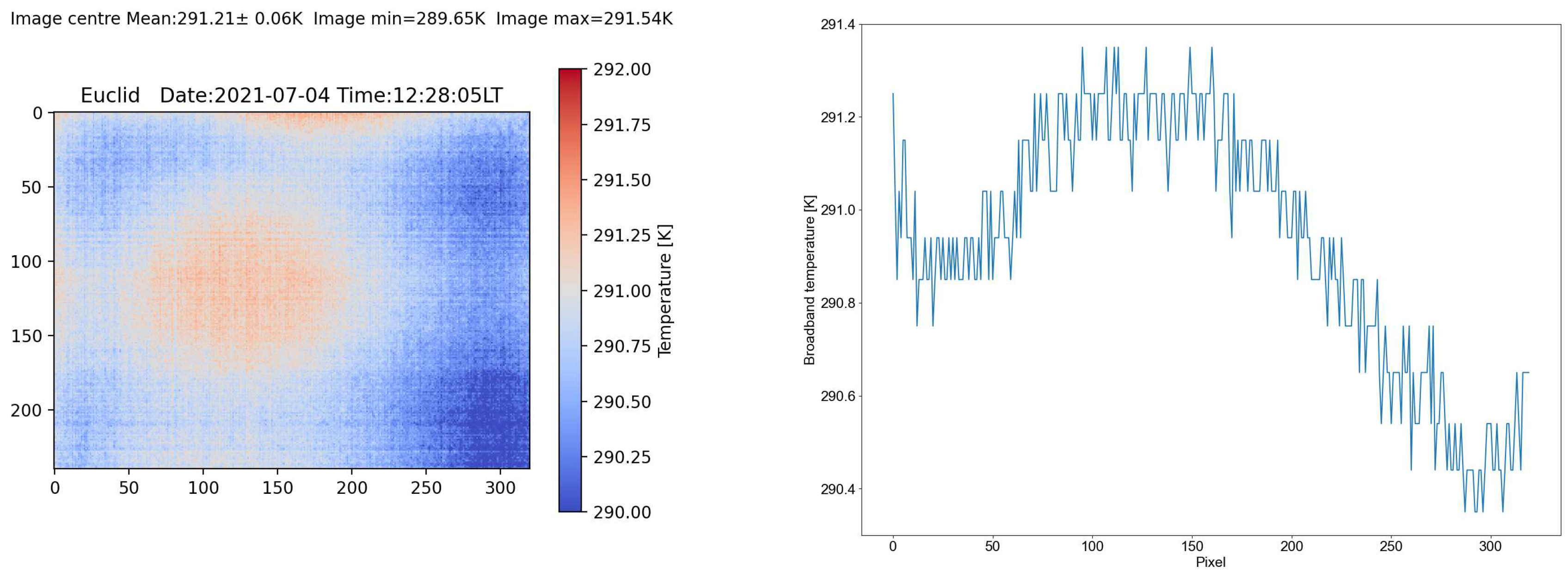
Figure 5 shows the vignetting pattern for the broadband channel when viewing a wall at a distance of 30 cm. The wall is not completely uniform but the expected circular vignetting pattern is discernible. A transect across the image reveals that the brightness temperature variation amounts to ∼0.4 K and is small enough that a correction is not warranted.
Apart from optical vignetting there may also be some mechanical vignetting caused by an obstruction within the field of view of the instrument. This, of course, should be avoided. In the case of some of the Etna field campaign data some mechanical vignetting was caused in the broadband channel by the visible telephoto lens that protruded into the field of view. This affects approximately 20 rows (or lines depending on the orientation of the camera) and the only way to correct this is to remove these 20 rows/lines from the analysis.
3.3. Imaging Clear and Cloudy Skies
Uncooled microbolometer IR cameras with detection sensitivity between 8–14
m are optimised for use at temperatures between 270–370 K, higher than most cloud temperatures. The expected noise temperature in this range is between 0.1–0.2 K but at lower temperatures this increases by a factor that depends on
, where
B is the Planck function,
T is (brightness) temperature and
is wavelength. At clear and cloudy sky temperatures of 240 K, the noise equivalent temperature difference (NEDT) is closer to ±0.5 K. These theoretical estimates need to be validated against real measurements. The camera calibration between 270–300 K was performed in the laboratory and it was found that the camera is linear and accurate within this temperature range. Below 270 K one way to assess the accuracy of the camera is to make clear sky measurements and compare these with radiative transfer calculations using a model driven by temperature and humidity profiles from a nearby radiosonde station. This has been done on several occasions and one example is shown in
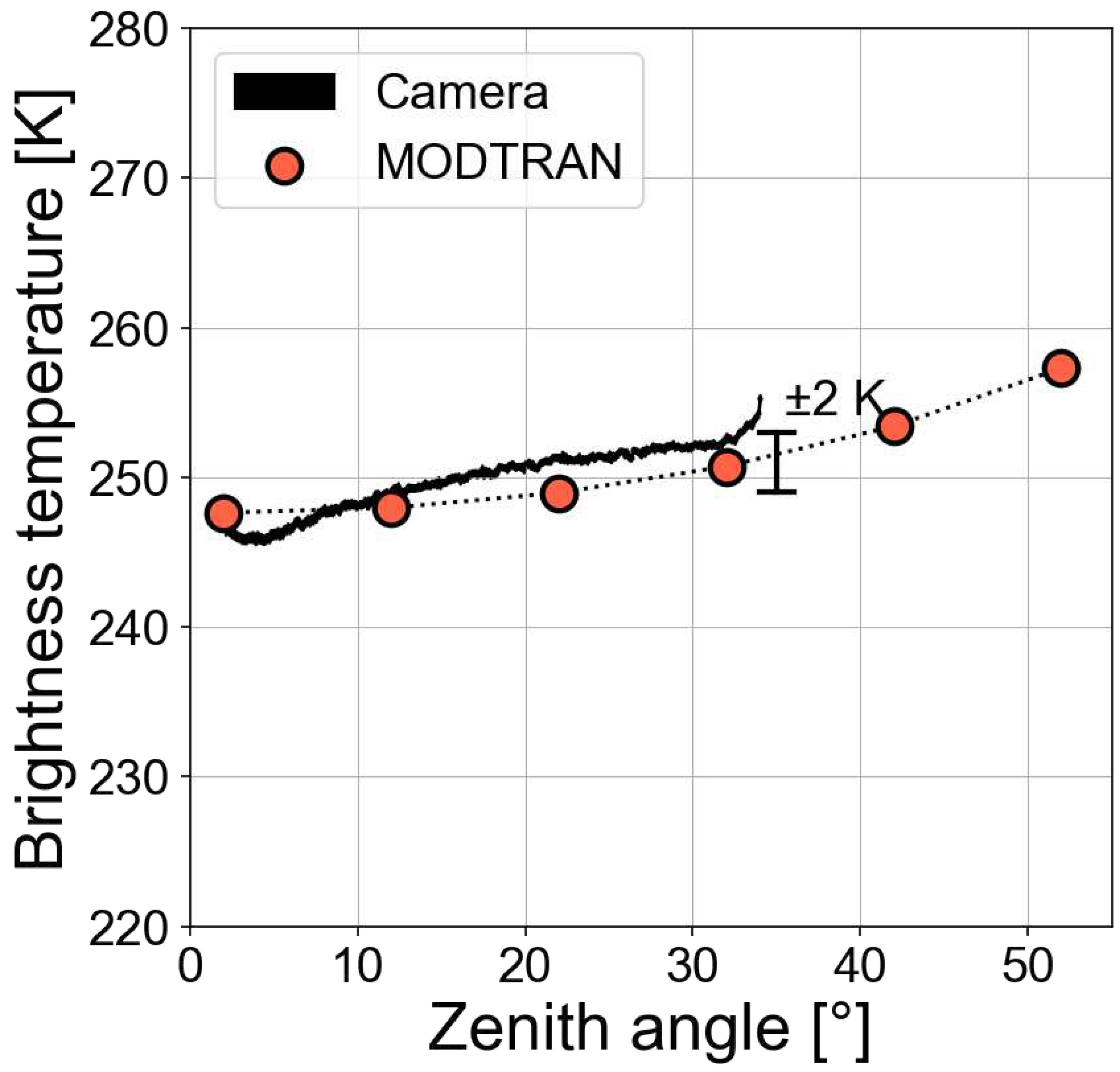
Figure 6 for a clear sky during the night. The radiosonde data was obtained from the University of Wyoming upper air sounding website (
https://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html) for Perth airport (94610) on 29 November 2021. The camera was tilted at ∼60° elevation so that the field of view covered zenith angles from 2–32°. The MODTRAN [
8] code was used to calculate the broadband radiance between 7.8–14
m and converted to brightness temperature at an equivalent wavelength (
≈ 10.2
m) that gives the same radiance as that obtained by integration over the filter function. The results shown in
Figure 6 compare the MODTRAN calculation with an average of 50 images, each averaged over 10 lines orthogonal to the angle of tilt around the centre of the image (keeping the camera fixed) and plotted against the zenith view angle of the camera. Results suggest that the camera agrees with the radiative transfer calculation within ±2 K for zenith angles less than 30 degrees. More data is required in order to investigate whether agreement at higher zenith angles agrees with radiative transfer calculations, where the atmospheric path is much longer and the sky temperature is more difficult to calculate accurately. It is also necessary that the sky is clear: clouds, particularly thin cirrus are difficult to model.
4. Radiative Transfer
We model the cloud (or plume) as a plane-parallel layer, of small geometric thickness, emissivity (
), uniform cloud temperature (
) at a height above the surface where water vapour absorption is small. An IR imaging instrument observing this cloud from the ground, measures a radiance of,
where
is measured radiance in a narrow (∼4
m, half-width half-maximum) wavelength interval represented by an equivalent wavelength (
) at pixel
i and line
j. Likewise
,
,
, are the radiances from the cloud (
c), from the atmosphere (
a) below the cloud and from space (
s) above the cloud layer, respectively.
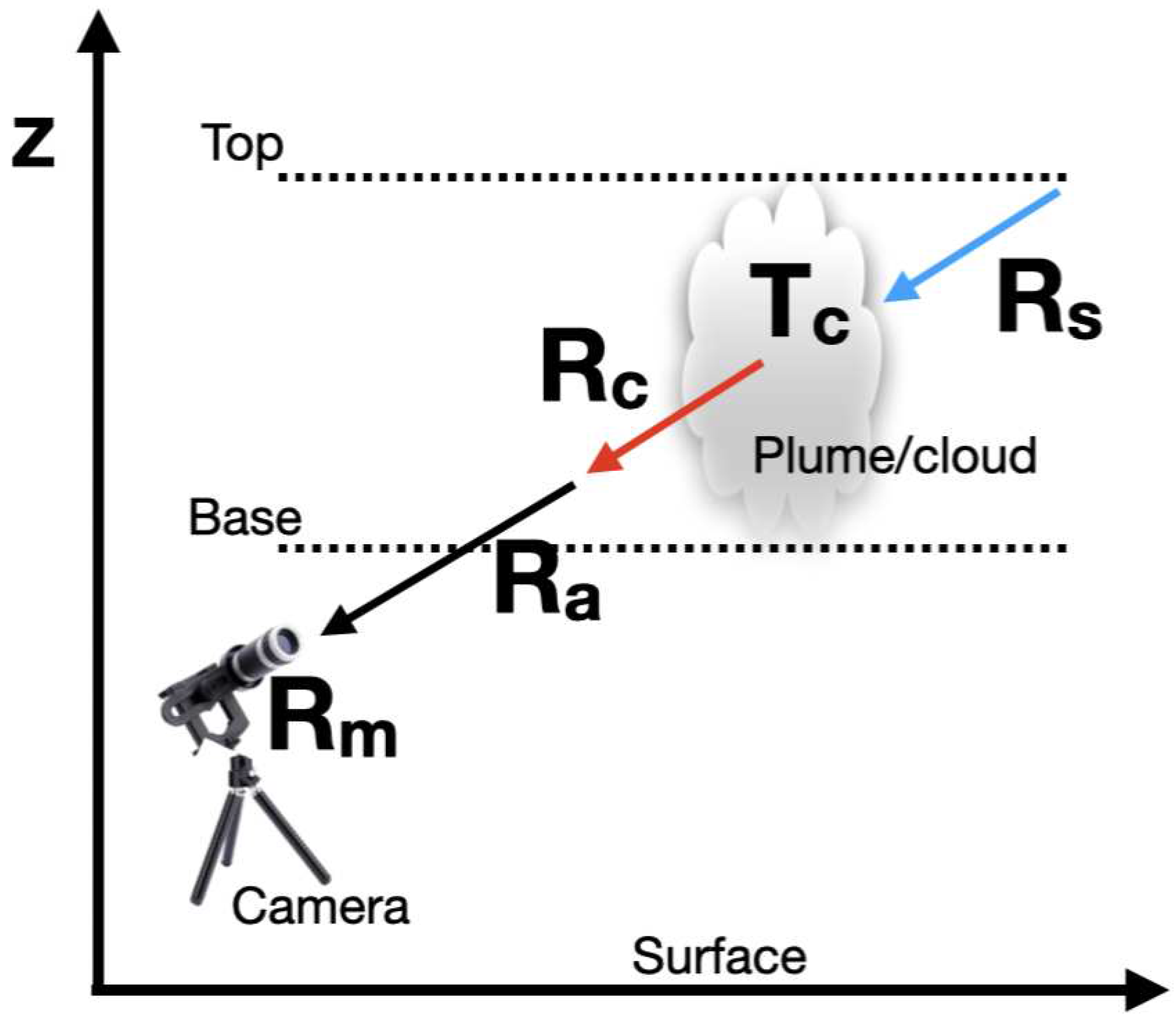
are pixel and line numbers within the image which can be converted to azimuth and zenith view angles. An illustration of the model is shown in
Figure 7.
In the following, for notational convenience, we drop the reference to
and
. The IR camera has a fairly broad (∼42-56°) total field of view and so it is reasonable to assume that some parts of the sky will be clear of cloud. For clear sky, the camera measurement is,
and
are assumed to not have changed from values under and above the cloudy regions, i.e. the atmosphere and space are assumed to be uniform over the region sampled. Evaluating the radiances in Eq. (1) using the Planck function,
where
is an atmospheric transmittance along the path between the camera and target. The Planck functions are evaluated at wavelength
and temperatures corresponding to the subscripts,
a for atmosphere,
c for cloud and
s for space (above the cloud). This equation has several unknowns, which are difficult to measure with the camera. By pointing the camera away from the cloud (or using a pixel in the image where there is no cloud), a new measurement,
can be made,
so that we may write,
The extra measurement helps, but does not alleviate the problem of estimating the cloud temperature as both
and
are not known. The path transmittance can be evaluated using a model and radiosonde data and it is reasonable to assume this is the same over the whole image. But
will vary from pixel to pixel and cannot be evaluated through modelling. A possible option then is to find the warmest pixel (
=
) in the image of the cloud/plume and assume that this is optically thick and
,
. Then a third measurement, gives,
hence,
where
is a relative emissivity,
. By design
and Eq. (7) will be well-posed. Once
has been determined, Eq. (5) can be used to estimate the cloud temperature.
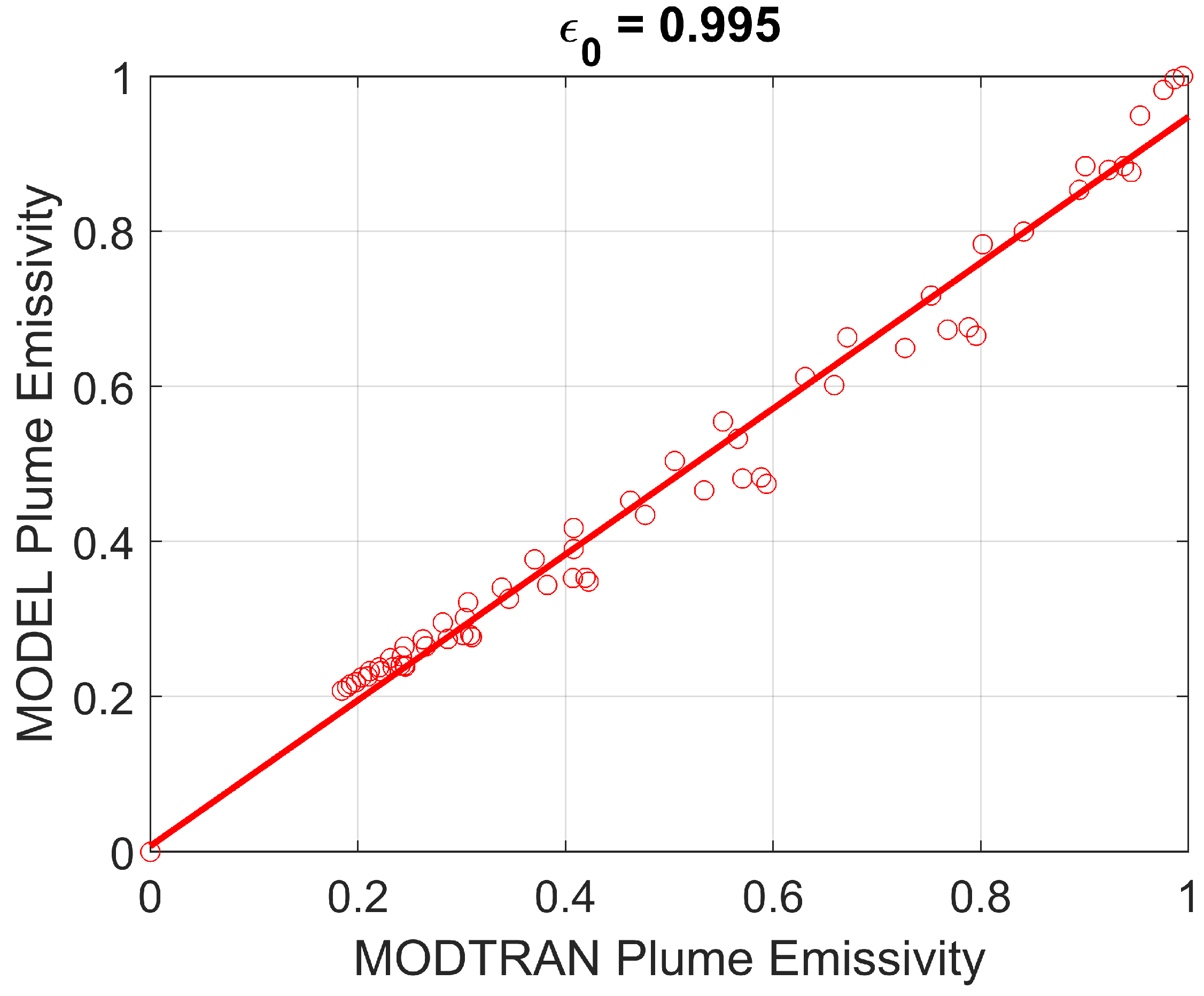
These equations are valid spectrally and therefore, in theory, they are not valid for a broadband sensor so it is worthwhile to check on the validity using simulations. This has been done, again using MODTRAN and the results are shown in
Figure 8, where the modelled emissivity, from Eq. (7), is plotted against the simulated (MODTRAN) emissivity for an ash cloud with thickness 0.5 km placed at 1.5 km above the surface, of uniform cloud temperature (293 K), variable optical depth and ash particle effective radii in the range (0–10
m).
5. Environmental Application: Volcanic Emissions
Monitoring volcanic eruptions in a safe manner is of paramount importance. Remote sensing is a natural choice as a measuring device for volcanic applications because, most of the time, the technology can be deployed at a safe distance from the source. Satellite-borne instruments are used routinely to remotely sense volcanoes and volcanic unrest. Many remote and inaccessible volcanoes would not be monitored at all without satellite measurements. These data need validation and verification and on occasions volcanic emissions can be obscured from the satellite view due to intervening clouds. Ground-based measurements can also be made from a safe distance using remote sensing technology. Indeed ground-based remote sensing using ultra-violet imaging cameras is a rapidly developing activity. Thermal remote sensing has largely be confined to measurements of the “hot" components of volcanic emissions, such as lava flows, lava lakes and eruption columns, although there are a few studies that make use of thermal cameras for studying ash and gas emissions. A reason why the technology has not received widespread interest and use is the cost of IR camera technology, often in the range of $1000s to $100,000s.
5.1. Cloud Temperature and Emissivity
Using the simple radiative transfer model developed earlier, data from measurements acquired on 25 July 2021 on Stromboli (769 m, a.s.l, 38.79565 °N, 15.21658 °E) were used as input to estimate
and
. The camera was quite close to the vent and so the atmospheric path was short (line-of-sight distance < 100 m), making the calculation less dependent on errors in calculation
.
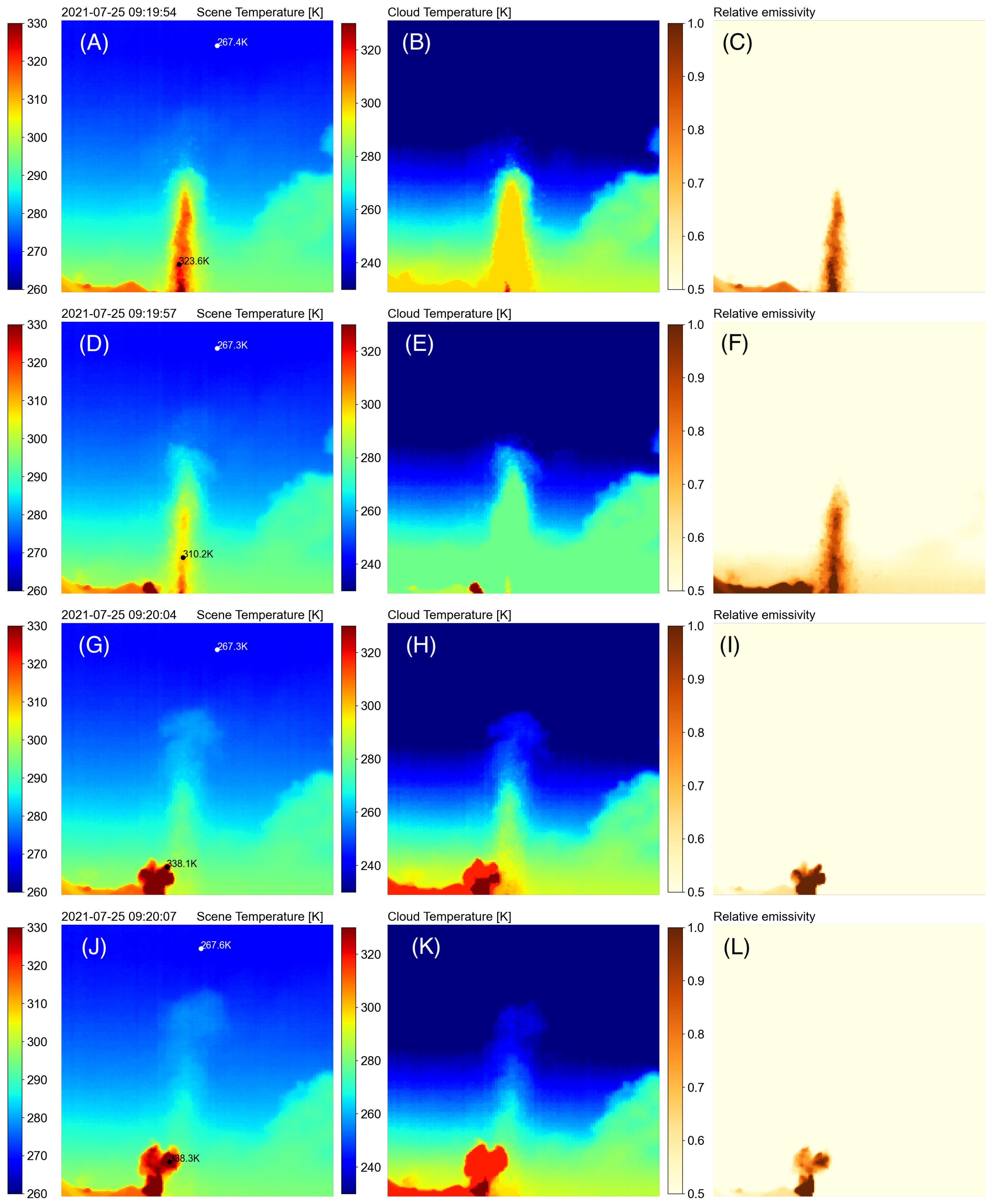
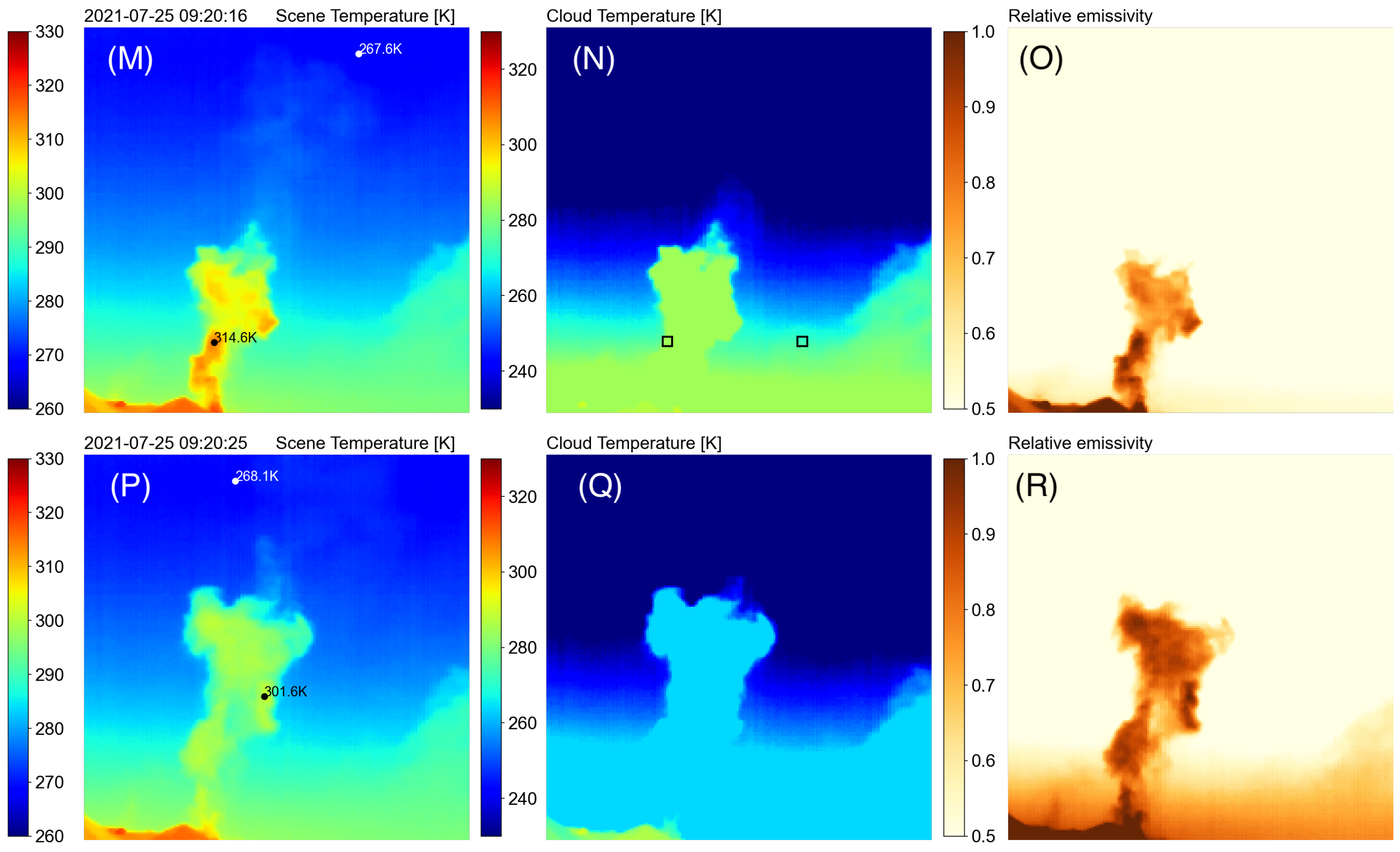
Figure 9 shows the scene temperature (left column), the retrieved cloud temperature (middle column) and the retrieved cloud emissivities (right column) obtained for a sequence of camera images collected during Stromboli activity on 25 July 2021.
The series of images shown in
Figure 9 in the middle panels shows how quickly the cloud reaches thermal equilibrium with the environment. The two right-most panels show the separation of the cloud temperature and emissivity components of the volcanic plume. Most of the structure is in the cloud emissivity, as this measures the transparency (in the IR) of the cloud, whereas the cloud temperature is quite uniform. At the start of an eruption the plume, composed mostly of gases, is much hotter than the surrounding atmosphere but cools rapidly to reach thermal equilibrium as the plume ascends. Consecutive images are separated in time by ∼3–9 s and the plume reaches thermal equilibrium within ∼2 min.
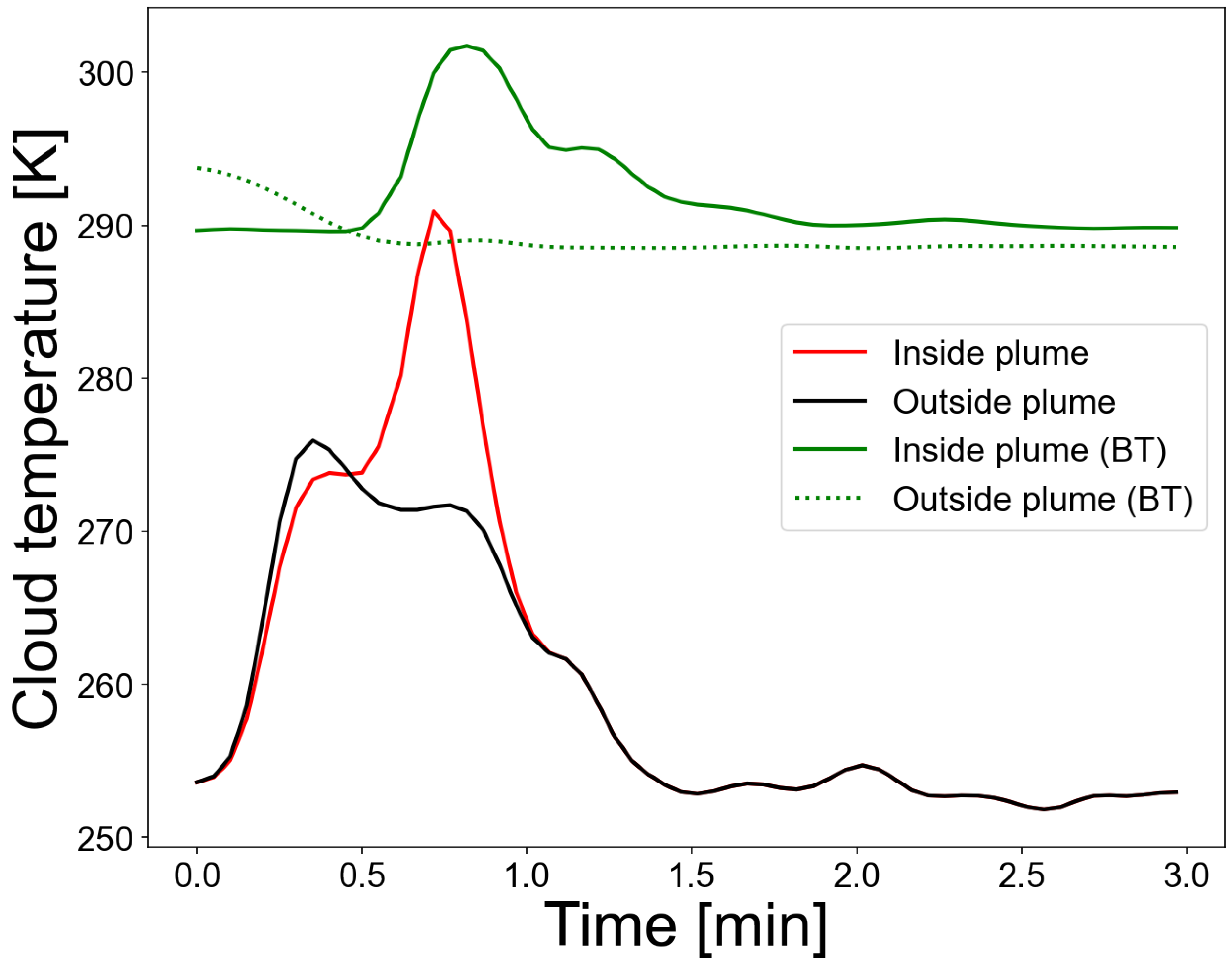
Figure 10 shows cloud temperature means of 5x5 pixels at two locations as a function of time. One location is inside the plume and the second outside the plume (see panel (N) in
Figure 9 for the locations). Also shown for reference are the scene brightness temperatures at the same locations, which include the effect of cloud opacity. The appearance of a sharp peak in cloud temperature at the location of the plume signifies the ascent of the plume with time and after ∼1.5 min the cloud temperature decays back to the background temperature (black coloured line). The difference between the two sets of curves (one set emissivity corrected, red- and black-coloured lines) illustrates the effects of plume opacity, where between ∼0.5–1 minutes the plume is up to ∼20 K warmer than its environment. Without corrections for cloud opacity (emissivity) the plume temperature appears to be ∼10 K warmer than its environment. The plume mostly consisted of H
2O and SO
2 gas; plumes dominated by ash may take longer to reach thermal equilibrium.
5.2. Optical Flow and Wind Speed
An advantage of the high acquisition rate of the IIRc (up to 1 Hz) is that energetic eruption columns can be imaged and eruption rates measured. For a fixed sampling rate, the fastest vertical ascent speed that can be measured depends on the object pixel size, which in turn depends on the line-of-sight distance to the object, and the total vertical distance imaged. At a range of 5 km the pixel size is ∼10 m and the total vertical distance imaged is ∼3.2 km (larger if the camera is tilted). Thus vertical speeds can be detected up to several 100 ms
−1. The ascent rates of the eruption columns of Stromboli and Etna volcanoes are typically <10 ms
−1 [
9], although fire-fountaining ascent velocities are typically much higher (100–300 ms
−1). The procedure to estimate ascent rates from IR imagery is relatively straightforward. With a stable camera viewing platform, the main parameters needed are geometric: the distance to the plume, the camera elevation angle, the altitude of the camera relative to the plume and the optical field of view parameters of the camera (see
Table 1). With these parameters, consecutive images are analysed to detect movement of features using well-known optical flow methods. In this case we use the Farneback [
10] algorithm, which is described in Thomas and Prata [
11] in applications using ground based camera images.
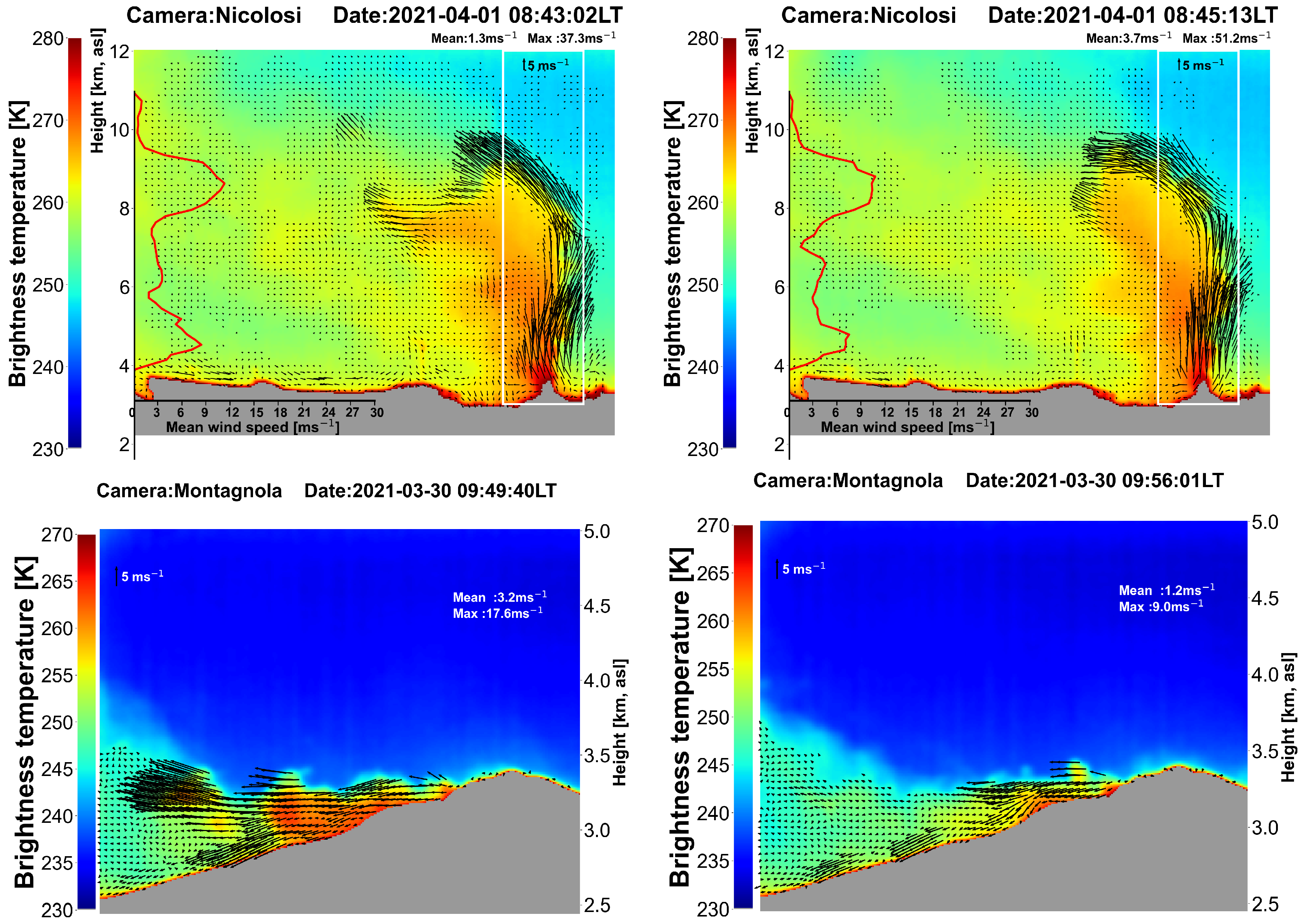
Optical flow measurements were made on several different days at Etna volcano and at Stromboli in March/April and July 2021 during periods of lava fountains and ordinary activities at the volcanoes. Examples for acquisitions at two sites at Etna are shown in
Figure 11.
The upper two panels of
Figure 11 show the evolution of the 25th Etna lava fountain [
12,
13], where the column is almost vertical and relatively unaffected by the background winds. A vertical cross-section through the column averaged over a portion of the data (shown by the white rectangular box), provides a measurement of the vertical variation of the ascent velocity, which peaks at 12 km. Measurements made over ∼ 2 hours indicate that the column winds fluctuated but maximum core wind speeds were found at two levels of ∼3-5 km and ∼8–10 km. Because the wind direction brings the plume towards the camera the estimation of the plume altitude will be affected, and the true altitude will differ from that derived here, where no correction for wind direction was made. The INGV-VONA bulletin issued at 07:42 UT indicates 9 km a.s.l., which is in reasonable agreement with our estimate. Not all eruptions of Etna produce tall columns: the two lower panels of
Figure 11 show ‘ground-hugging’ plumes from weak eruptions. These eruptions tend to follow the orography and can travel quite fast: 5–10 ms
−1, controlled principally by the low-level wind field. Again, the ‘true’ plume height will differ because of wind direction effects.
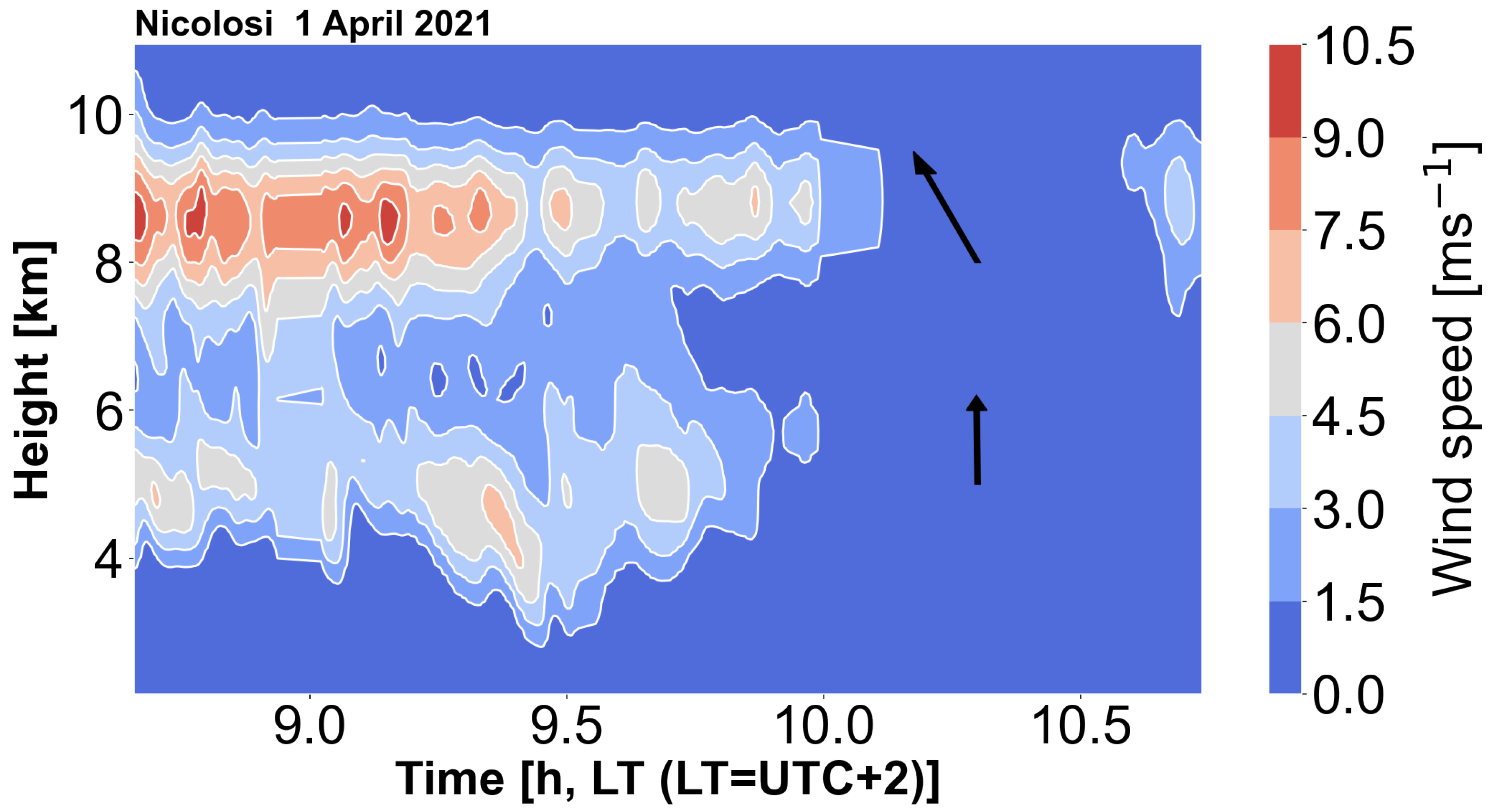
Figure 12 shows a contour plot of the smoothed time-height optical flow wind speeds for a period of about 2 hours on the morning of 1 April 2021. This is the magnitude of the wind but the directions at the two maxima were quite consistent and their directions are indicated by the arrows shown on the plot. This suggests that the lower core is due mostly to the force of the eruption, while the upper core is dominated by the prevailing meteorological winds at that level. In other words the resulting column is ‘bent over’. Visual analysis confirms this conclusion (
Figure 13). Analysis of the meteorological wind fields at this time and location (
https://earth.nullschool.net/#2021/03/31/2300Z/wind/isobaric/250hPa/orthographic=-346.38,38.65,1706/loc=15.189,37.614) suggest ∼20 ms
−1 speeds from the NE at ∼10 km, weakening substantially to ∼3 ms
−1 from NNW at ∼19 km.
5.3. Height and Ascent Rate
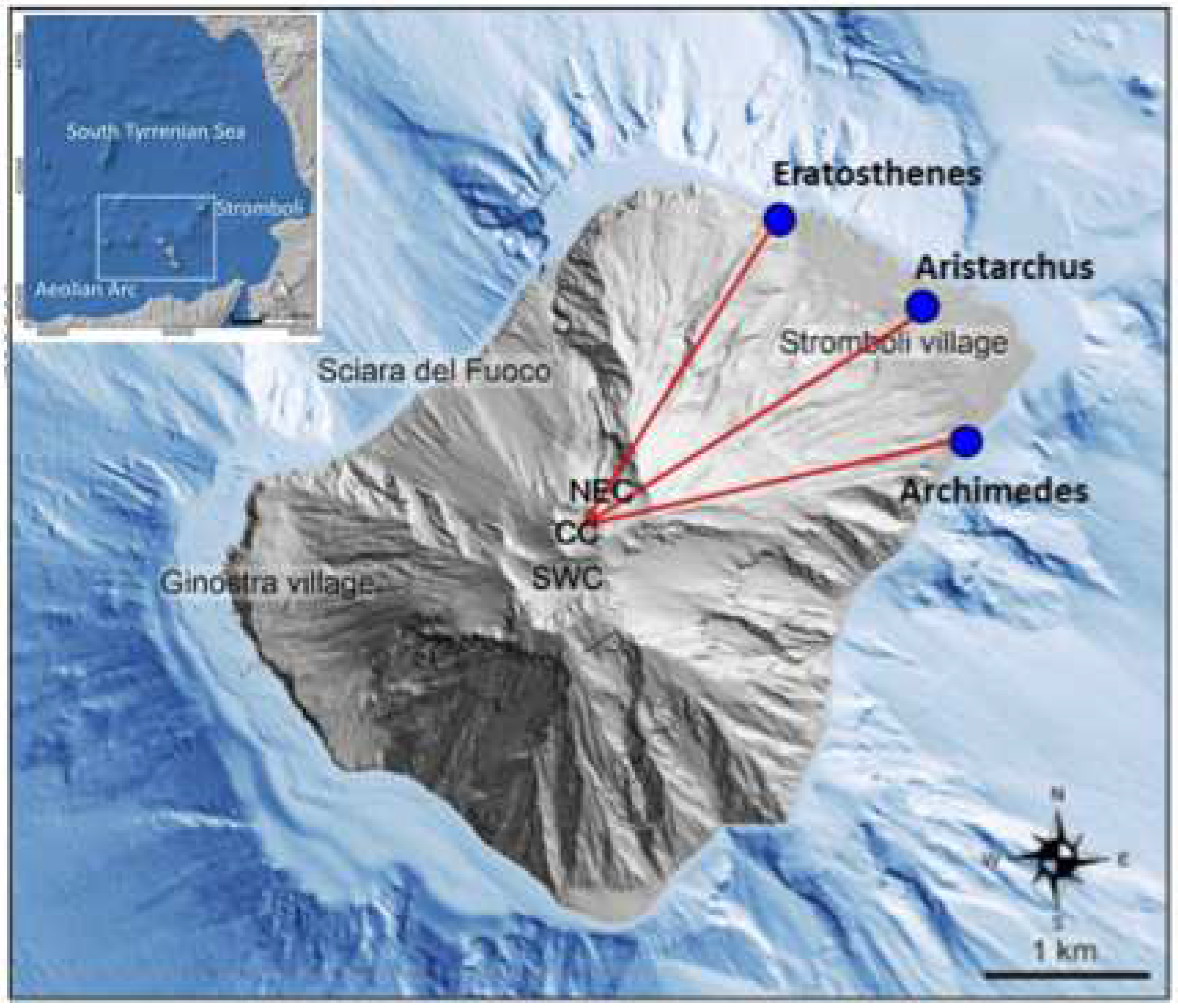
Three cameras were place in different locations on the island of Stromboli (see
Figure 14) but at approximately the same distance from the summit and at the same altitude to view the eruption column at the same elevation angle.
The main purpose was to obtain data for tomographic analysis but also to compare measurements using different cameras and to obtain ascent rates. Stromboli undergoes frequent, small (column heights < 1 km) eruptions [
15] and has been studied previously using thermal cameras [
16], and so is an ideal target for testing the cameras. Data were acquired from all three cameras at the maximum sampling rate of 1 Hz.
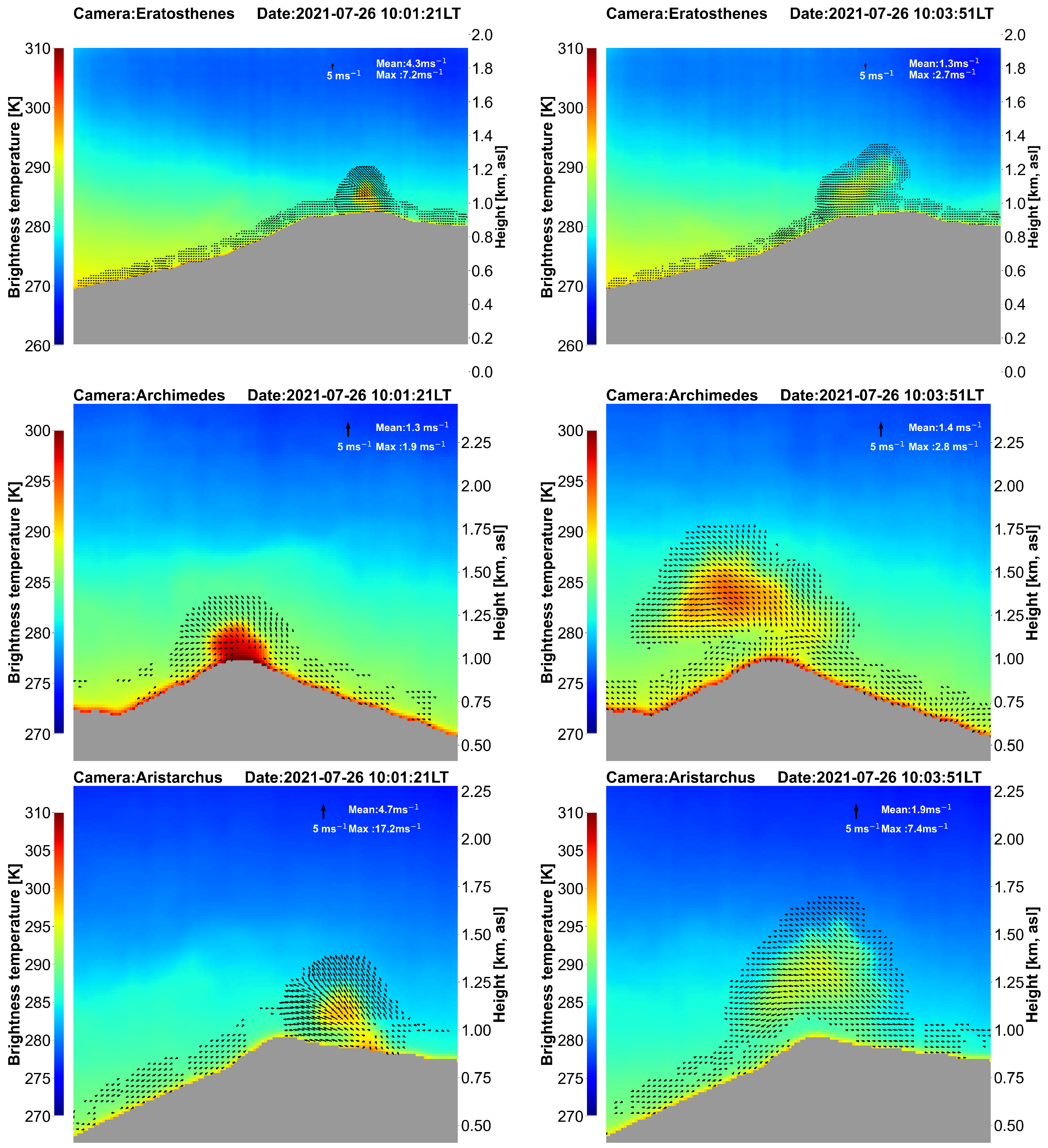
Figure 15 shows an example of the optical flow obtained from the cameras at two different times, separated by 2.5 minutes, illustrating the development of the eruption column. In these examples the means have been calculated for all wind vectors with speeds >0.5 ms
−1. At 10:01:21 LT (left-hand panels of
Figure 15), there is disparity between the estimates from the three cameras, whereas at 10:03:51 LT (right-hand panels of
Figure 15) the agreement is good. The reasons for disagreement may be due to wind direction, which is not accounted for in the calculations. In future work the wind direction will be taken into account to obtain an approximate three dimensional reconstruction of the plume behaviour. Even so, with three cameras all placed in one quadrant it will not be possible to get an accurate estimate of the wind field and the optimal number of cameras to utilise requires further field studies.
The main constituents of the Stromboli eruption column are water vapour, CO2 and SO2 gas with some ash particles. The IIRc is not able to distinguish the material properties of the cloud and detects the onset of the eruption by changes in opacity (increases in brightness temperature) against the colder background sky. Multi-spectral IR cameras can provide information on cloud properties (e.g. ash and SO2) and development of these cameras are in progress.
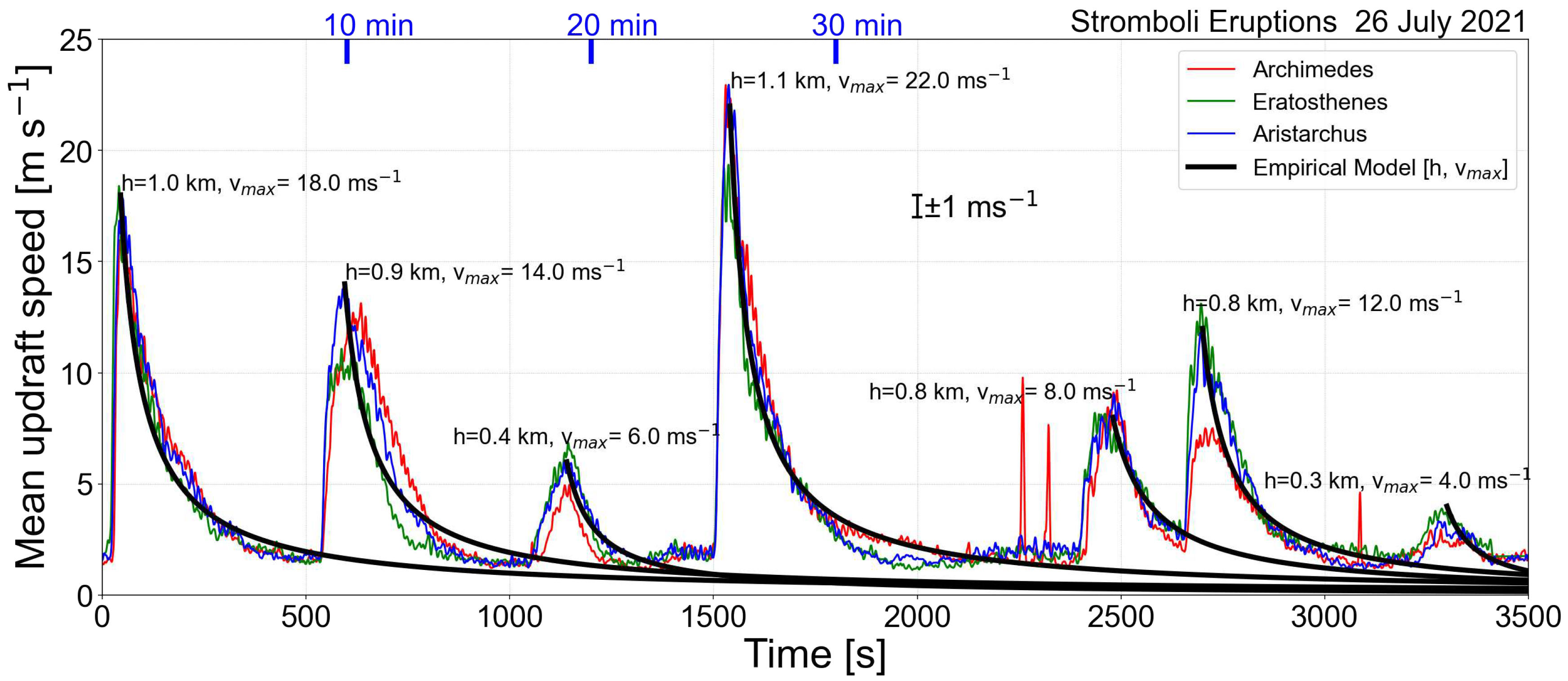
Figure 16 shows a time-series of several eruptions from Stromboli over a period of about 1 hour. Each eruption is marked by a rapid increase in the ascent rate (in ms
−1) followed by a gradual decay that appears to follow the relation,
where
is the maximum ascent velocity,
is the maximum height and
t is time.
The three cameras capture the eruptions in a consistent manner, with maximum heights (
) of ∼1 km and maximum ascent rates (updraft velocities,
) of ∼20 ms
−1. The two sharp peaks between 2300–2500 s and the one near 3100 s measured by Archimedes (red-coloured line in
Figure 16) are anomalies caused by failures in the optical flow algorithm. They can be removed using data filtering methods but this did not seem necessary since they are not detected by the other two cameras and hence can be inferred to be to algorithmic failure. Given estimates of
and
the model is a good indicator of the decay rate of the column. Such measurements are useful in the context of hazard assessment as they provide an estimate of the lifetime of each event, in this case ∼10 minutes. It is difficult to judge whether this timescale has any effect on the frequency of eruptions or whether the maximum height of subsequent eruptions are influenced by the height reached by an event immediately before, but these data in conjunction with other data, such as seismicity, might be useful to investigate this further. Longer series of measurements are required for such studies and this would require deployment of an IR camera permanently or semi-permanently at the volcano.
6. Conclusions
The use of infrared cameras at volcanoes is not widespread. In most cases where they are used, they tend to provide real-time infrared imagery of a mostly qualitative nature with a temperature scale showing scene temperatures. This can be very useful as they provide information on eruptive activity during the night when visible, webcam type cameras are less useful. In this study the development and deployment of portable infrared cameras at volcanoes for quantitative assessment of eruptive activity has been shown to be viable and useful. Measurements of the ascent rate of small to medium eruptive columns at Stromboli demonstrates the value of fast sampling (1 Hz) imagery and also provides a measure of the maximum height of these columns. In the case of Etna, columns higher than ∼8 km were measured. However, because of plume movement towards or away from the camera line-of-sight, height estimates measured this way can be erroneous. Use of indpendent wind data and/or three or more camera systems would alleviate this problem. A simple model for the decay of the ascent velocity is proposed that agrees well with the observations. The data were also used to determine the IR opacity of the eruptive columns and it was found that gas-dominated plumes reach thermal equilibrium with the environment within a few minutes.
The optical flow calculations were used to determine the vertical profile of the ascent velocity by analysing data through a vertical section of the eruption columns for Etna. These profiles reveal that at lower levels the plume speed dominates over the meteorological wind, whereas at higher levels, the background meteorology caused the plume to become bent over with maximum heights of 8–10 km.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P. and S.C.; methodology, F.P, S.C, R.B. and L.G.; software, F.P., L.G., L.M., D.S. and A.P.; validation, L.G.,S.C., L.M. and D.S.; formal analysis, F.P., A.P., L.G; investigation, .; resources, X.X.; data curation, L.G., D.S.,L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.P.; writing—review and editing, F.P., S.C., L.G., R.B. and A.P; visualization, F.P. and A.P.; supervision, S.C.; project administration, S.C..; funding acquisition, S.C and R.B.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The European Space Agency (ESA) provided funding to conduct the field work at Etna and Stromboli through the VISTA project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The camera data used in this study are available upon request. Contact: fred@aires.space
Acknowledgments
Dr Cirilo Bernardo contributed to the design of the infrared cameras used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results’.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| COTS |
Commerical-Off-The-Shelf |
| H2O |
Water Vapour |
| HFOV |
Horizontal Field Of View |
| IR |
InfraRed |
| IIRc |
Imaging InfraRed camera |
| LED |
Light Emitting Diode |
| MEMS |
Micro-ElectroMechanical System |
| MODTRAN |
MODerate resolution atmospheric TRANsmission |
| NEDT |
Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference |
| NUC |
Non-Uniformity Correction |
| SBC |
Single Board Computer |
| SO2
|
Sulfur Dioxide |
| VFOV |
Vertical Field Of View |
References
- Kruse, P.W. Uncooled thermal imaging: arrays, systems, and applications; SPIE press, 2001; Vol. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Blackett, M. An overview of infrared remote sensing of volcanic activity. Journal of Imaging 2017, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.; Bernardo, C. Retrieval of volcanic ash particle size, mass and optical depth from a ground-based thermal infrared camera. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 2009, 186, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.; Bernardo, C. Retrieval of sulfur dioxide from a ground-based thermal infrared imaging camera. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 2014, 7, 2807–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, T.; Thomas, H.; Prata, A.; Amigo, A.; Fee, D.; Moriano, D. Volcanic plume characteristics determined using an infrared imaging camera. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 2015, 300, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fee, D.; Izbekov, P.; Kim, K.; Yokoo, A.; Lopez, T.; Prata, F.; Kazahaya, R.; Nakamichi, H.; Iguchi, M. Eruption mass estimation using infrasound waveform inversion and ash and gas measurements: Evaluation at Sakurajima Volcano, Japan. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 2017, 480, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, M. Simulation of vignetting effect in thermal imaging system. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 2009, 7494, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Conforti, P.; Kennett, R.; Perkins, T.; Hawes, F.; Van Den Bosch, J. MODTRAN® 6: A major upgrade of the MODTRAN® radiative transfer code. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS); 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rizza, U.; Donnadieu, F.; Morichetti, M.; Avolio, E.; Castorina, G.; Semprebello, A.; Magazu, S.; Passerini, G.; Mancinelli, E.; Biensan, C. Airspace Contamination by Volcanic Ash from Sequences of Etna Paroxysms: Coupling the WRF-Chem Dispersion Model with Near-Source L-Band Radar Observations. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnebäck, G. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In Proceedings of the Image Analysis: 13th Scandinavian Conference, SCIA 2003, Halmstad, Sweden, 29 June–2 July 2003; Proceedings 13. Springer, 2003; pp. 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.E.; Prata, A. Computer vision for improved estimates of SO2 emission rates and plume dynamics. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2018, 39, 1285–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvari, S.; Nunnari, G. Comparison between automated and manual detection of lava fountains from fixed monitoring thermal cameras at Etna Volcano, Italy. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, L.; Corradini, S.; Theys, N.; Stelitano, D.; Merucci, L. Volcanic Clouds Characterization of the 2020–2022 Sequence of Mt. Etna Lava Fountains Using MSG-SEVIRI and Products’ Cross-Comparison. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Traglia, F.; Fornaciai, A.; Casalbore, D.; Favalli, M.; Manzella, I.; Romagnoli, C.; Chiocci, F.L.; Cole, P.; Nolesini, T.; Casagli, N. Subaerial-submarine morphological changes at Stromboli volcano (Italy) induced by the 2019–2020 eruptive activity. Geomorphology 2022, 400, 108093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Pistolesi, M.; Bertagnini, A.; Landi, P.; Pompilio, M.; Di Roberto, A. Chapter 14 Stromboli volcano, Aeolian Islands (Italy): present eruptive activity and hazards. Geological Society, London, Memoirs 2013, 37, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvari, S.; Lodato, L.; Steffke, A.; Cristaldi, A.; Harris, A.; Spampinato, L.; Boschi, E. The 2007 Stromboli eruption: Event chronology and effusion rates using thermal infrared data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 |
Brightness temperature is a wavelength-dependent quantity calculated by inverting the Planck function using the detected radiance over a wavelength interval. |
| 2 |
|
Figure 1.
Photographs of the SEEK camera module, showing the assembly and lens.
Figure 1.
Photographs of the SEEK camera module, showing the assembly and lens.
Figure 2.
The Imaging InfraRed Camera (IIRc).
Figure 2.
The Imaging InfraRed Camera (IIRc).
Figure 3.
Calibration plots for two different IIRc systems. Left: (a) Blackbody vs. camera temperature, Right: (b) Cooling curve compared to theoretical Newtonian cooling, Bottom: (c) Rapid recycling of the blackbody temperature showing degree of correspondence with the IIRc recorded temperatures.
Figure 3.
Calibration plots for two different IIRc systems. Left: (a) Blackbody vs. camera temperature, Right: (b) Cooling curve compared to theoretical Newtonian cooling, Bottom: (c) Rapid recycling of the blackbody temperature showing degree of correspondence with the IIRc recorded temperatures.
Figure 4.
Recorded temperature variation across a portion of the detector array when exposed to a uniform blackbody plate.
Figure 4.
Recorded temperature variation across a portion of the detector array when exposed to a uniform blackbody plate.
Figure 5.
Optical vignetting patterns for the broadband channel. Note that the drop in temperature beyond pixel ∼200 is due to wall temperature and is not part of the vignetting pattern. (This was established by rotating the camera through 90 degrees and observing the temperature pattern).
Figure 5.
Optical vignetting patterns for the broadband channel. Note that the drop in temperature beyond pixel ∼200 is due to wall temperature and is not part of the vignetting pattern. (This was established by rotating the camera through 90 degrees and observing the temperature pattern).
Figure 6.
MODTRAN-4 calculations for a clear-sky night when the IIRc was tilted at 60° elevation angle to view upwards. The camera measurements represent an average of 10 lines (around each camera zenith angle) in each of 50 images (about 10 minutes).
Figure 6.
MODTRAN-4 calculations for a clear-sky night when the IIRc was tilted at 60° elevation angle to view upwards. The camera measurements represent an average of 10 lines (around each camera zenith angle) in each of 50 images (about 10 minutes).
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of a plane-parallel cloud showing the radiances considered in the model. Rm is the radiance measured at the camera, Ra is the radiance from the atmosphere between the target (cloud) and camera, Rc is the radiance emitted by the target and Rs is the radiance from the atmosphere and space behind the target.
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of a plane-parallel cloud showing the radiances considered in the model. Rm is the radiance measured at the camera, Ra is the radiance from the atmosphere between the target (cloud) and camera, Rc is the radiance emitted by the target and Rs is the radiance from the atmosphere and space behind the target.
Figure 8.
Comparison of model (Eq. 7) and simulated (MODTRAN) emissivities for an ash plume placed at 1500 m a.s.l., thickness = 500 m, temperature = 293 K, relative humidity of 100%, optical depth (at 0.55 m) range of 0–5 and ash particle effective radii in the range 0–10 m.
Figure 8.
Comparison of model (Eq. 7) and simulated (MODTRAN) emissivities for an ash plume placed at 1500 m a.s.l., thickness = 500 m, temperature = 293 K, relative humidity of 100%, optical depth (at 0.55 m) range of 0–5 and ash particle effective radii in the range 0–10 m.
Figure 9.
Brightness temperature (scene temperature), retrieved cloud temperature and retrieved cloud emissivities for a sequence of images obtained during Stromboli activity on 25 July 2021. The black coloured rectangles in the panel (N) show locations inside and outside the plume where 5x5 means have been calculated to construct time-series. (see
Figure 10). Note that the images have been cropped to remove the hillside.
Figure 9.
Brightness temperature (scene temperature), retrieved cloud temperature and retrieved cloud emissivities for a sequence of images obtained during Stromboli activity on 25 July 2021. The black coloured rectangles in the panel (N) show locations inside and outside the plume where 5x5 means have been calculated to construct time-series. (see
Figure 10). Note that the images have been cropped to remove the hillside.
Figure 10.
Cloud temperatures as a function of time inside and outside a volcanic plume emitted from Stromboli. The scene brightness temperatures (not corrected for emissivity) at the same locations are also shown (green coloured lines). See
Figure 9, panel (N) for the locations.
Figure 10.
Cloud temperatures as a function of time inside and outside a volcanic plume emitted from Stromboli. The scene brightness temperatures (not corrected for emissivity) at the same locations are also shown (green coloured lines). See
Figure 9, panel (N) for the locations.
Figure 11.
Optical flow analyses for eruptions at Mt Etna volcano. Upper-panels: 1 April 2021, 08:43–08:45 LT (LT=UTC+2). Lower-panels: 30 March 2021, 09:49–09:56 LT.
Figure 11.
Optical flow analyses for eruptions at Mt Etna volcano. Upper-panels: 1 April 2021, 08:43–08:45 LT (LT=UTC+2). Lower-panels: 30 March 2021, 09:49–09:56 LT.
Figure 12.
Wind speed (ms−1) contours determined from optical flow for an eruption of Etna on 1 April 2021. Note that these are magnitudes only. The directions of the main cores at heights of ∼3–5 km and ∼8–10 km are indicated by the arrows.
Figure 12.
Wind speed (ms−1) contours determined from optical flow for an eruption of Etna on 1 April 2021. Note that these are magnitudes only. The directions of the main cores at heights of ∼3–5 km and ∼8–10 km are indicated by the arrows.
Figure 13.
Photograph taken by the IIRc on 1 April 2021 showing the bent over nature of the mostly gas plume.
Figure 13.
Photograph taken by the IIRc on 1 April 2021 showing the bent over nature of the mostly gas plume.
Figure 14.
Stromboli Island, and its position on Tyrrhenian Sea, with locations of villages, Sciara del Fuoco, main craters (NEC: North East Crater; CC: Central Crater; SWC: South West Crater) and the position of the three IIRc systems (Eratosthenes, Aristarchus and Archimedes). Modified from Di Traglia
et al. [
14].
Figure 14.
Stromboli Island, and its position on Tyrrhenian Sea, with locations of villages, Sciara del Fuoco, main craters (NEC: North East Crater; CC: Central Crater; SWC: South West Crater) and the position of the three IIRc systems (Eratosthenes, Aristarchus and Archimedes). Modified from Di Traglia
et al. [
14].
Figure 15.
Optical flow analyses for an eruption at Stromboli volcano using images from three different locations (see
Figure 14) at two different times 2.5 minutes apart.
Figure 15.
Optical flow analyses for an eruption at Stromboli volcano using images from three different locations (see
Figure 14) at two different times 2.5 minutes apart.
Figure 16.
Time-series of eruption rates for several small Stromboli eruptions from three different cameras. The black lines show the expected decay rate of the velocity according to Eq. 8.
Figure 16.
Time-series of eruption rates for several small Stromboli eruptions from three different cameras. The black lines show the expected decay rate of the velocity according to Eq. 8.
Table 1.
Specifications for the SEEK Thermal IR camera (MOSAIC Core C3 Series)
Table 1.
Specifications for the SEEK Thermal IR camera (MOSAIC Core C3 Series)
| Microbolomter |
Uncooled VOx
|
| Pixel pitch |
12 m |
| Spectral response |
7.8 – 14 m |
| Sensor resolution (HxV) |
320 x 240 |
| Frame rate |
< 9 Hz |
| Scene dynamic range |
–40°C to 330°C |
| NET |
100 mK 25°C |
| Non-uniformity correction (NUC) |
automatic shutter |
| Video interface |
USB |
| Supply voltage |
3.3V to 5.5V |
| Power (core only) |
<50 mW |
| Power (core+interface) |
300 mW |
| Output formats |
16-bit or 32-bit floating point |
| Optics |
|
| Focal length |
4 mm |
| Focus |
Fixed |
| HFOV |
56° |
| VFOV |
42° |
| Mechanical |
|
| Ingress protection |
IP67 |
| Operating temperature range |
–10°C to 60°C |
| Humidity |
10–95% (non-condensing) |
| Core dimensions (LxWxH) |
20 mm x 20 mm x 21 mm |
| Core weight |
12 g |
| Core material |
Chalcogenide |
Table 2.
Specifications for the ELP HD visible camera.
Table 2.
Specifications for the ELP HD visible camera.
| Brand Name |
ELP |
| Max. Resolution |
1260x960 (1.3 MP) |
| Model Number |
ELP-USB4KHDR01-MFV (2.8-12 mm) |
| Auto Focus |
No |
| Interface Type |
USB |
| Sensor Type |
1/2.5 sony IMX317 sensor |
| Lens |
2.8-12mm varifocal lens |
| High frame rate |
1260x960 MJPEG 30 fps |
| Output Formats |
MJPEG, YUY2 |
| Minimal illumination: 0.2 Lux |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).