1. Introduction
An effective strategy for reducing the cooling energy demand of buildings involves the implementation of external shading systems. However, many current technologies are intricate and necessitate centralized control. Retrofitting existing buildings with external shading systems typically requires substantial renovation measures. To address this challenge and facilitate straightforward retrofitting, the research project "smartskinreal" [
1,
2] has developed an innovative and automatic shading system. The key lies in harnessing the thermal shape memory effect (SME) [
3], enabling the development of a self-regulating solar shading actuator [
4]. This system is capable to operate automatically, eliminating the need for electricity, sensors, or electric motors. It implements a metal wire made from a tailor-made shape memory alloy (SMA) placed within a thermal solar collector as heat source driven by solar radiation. By utilizing the thermomechanical properties of the SMA-wire, the system actuates the slats of the shading system. It enables automatic adjustment of the shading depending on external factors such as the position of the sun and temperature.
In this article, we provide a detailed insight into the development and functionality of the self-regulating sunshade system. The system consists of various components: the sunshade construction, the actuator, the collector, and the SMA-wire. Initially, these components are examined and dimensioned separately. The design of the components is tailored to a temperate climate in Central Europe; however, it is fundamentally transferable to other climate zones and requirements. Subsequently, these components are assembled into a 1:1 demonstrator and tested under real conditions. The system is designed for an automatically adjustment based on solar radiation without electrical energy. We highlight the advantages of such a system for building climate control and discuss its significance for further future applications.
2. Concept of the Self-regulating Solar Shading Actuator
2.1. Sunshade Construction
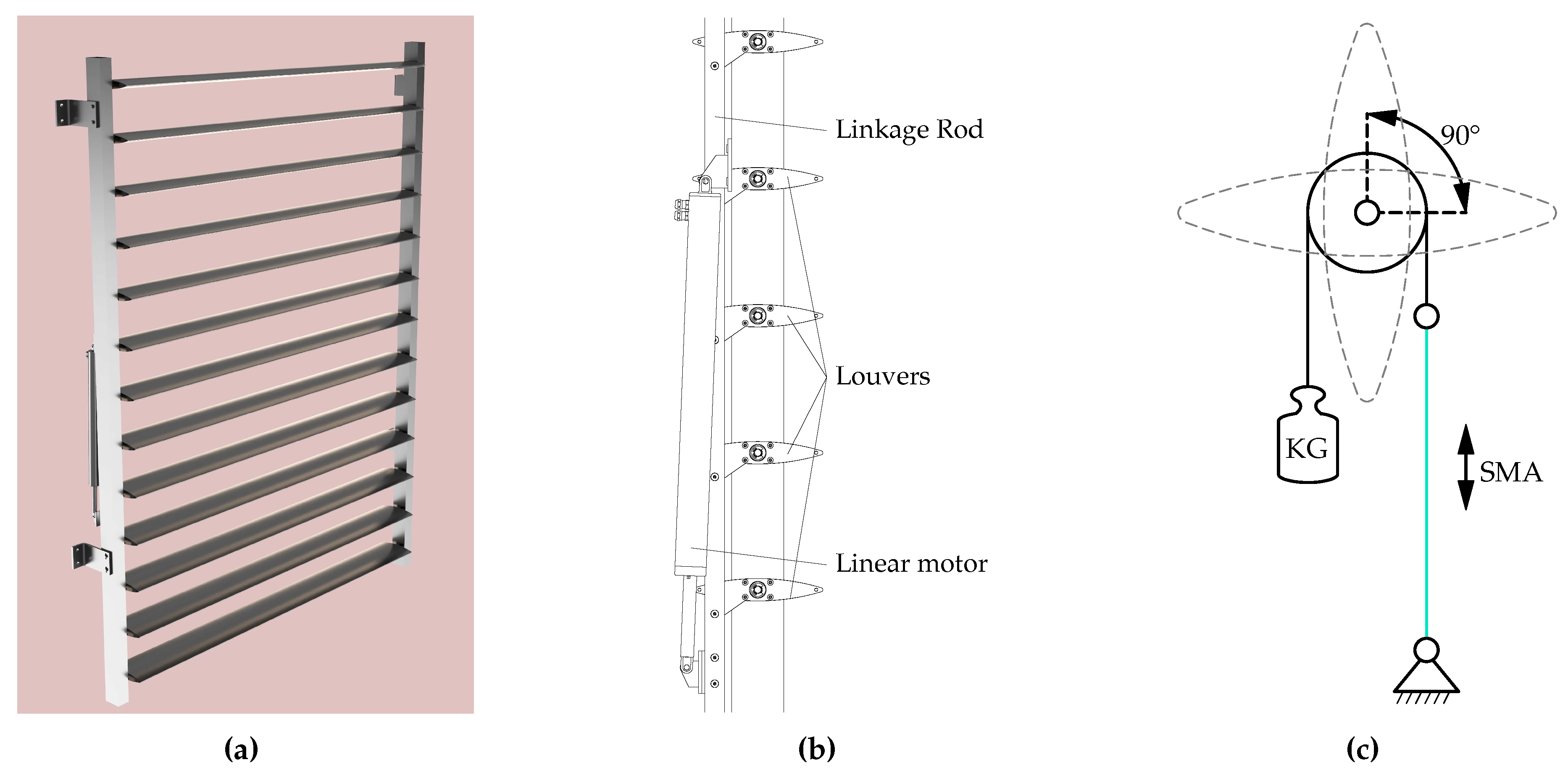
We utilize a standard sunshade construction system as the foundational structure, comprising large rotating aluminum louvers [
5].
Figure 1 (
a) depicts a 3D model, and (
b) presents a sectional view of the structure with its various standard components. The design is well-established and has been used for shading purposes, primarily for external facade shading, for many years. It is commonly installed in buildings and meets various static requirements according to EN 13659 [
6]. Typically, the system is divided into smaller segments that can be arranged to shade large areas. The system can be positioned vertically and horizontally. Alternatively, it can also be used for ceiling shading, such as in outdoor terraces. The mechanics are designed in such a way that a building-specific number of louvers securely connected together via a linkage rod. The louver angle is thus adjusted by a linear motor mounted on the linkage rod. Shifting the linkage rod causes a synchronized movement of connected louvers. Standard control is managed by a central control unit collecting and analyzing data from a weather station. Using relays, the individual louver segments are electrically controlled. Local user controls provide the flexibility to regulate individual or groups of shading units as required or to transfer control to an automatic system.
This chosen system allows louvers to rotate up to 90° for actuation, according to the intended application of the technology utilizing the thermal SME.
Figure 1 (
c) illustrates the mechanical principle underlying this integration. To connect the sunshade construction to the actuator, a louver was extended with a shaft. This extension enables system control through a 90° rotational movement using the designated mechanical principle.
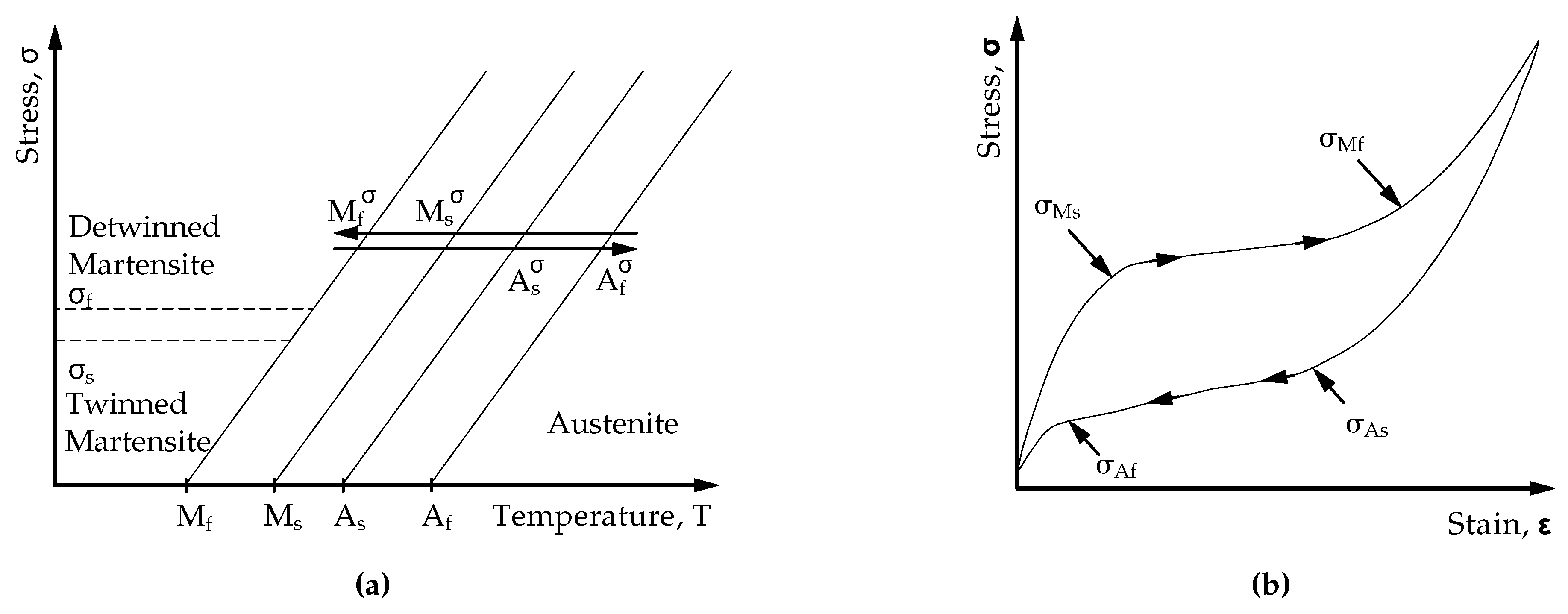
2.2. Shape Memory Effect
The shape memory effect describes the capability of some materials, such as shape memory alloys, to recover the initial shape after being apparently plastic deformed. The process can be thermal- and/or stress-induced. From an engineering point of view, SMAs present high actuation energy density [
3,
7]. SMAs can exhibit two different crystal structures: austenite (
A) or high-temperature structure phase and martensite (
M) or low-temperature phase. The transformation from one phase to the other is known as martensitic transformation. Each martensitic structure presents distinct orientation directions known as variants. The arrangement of these martensitic variants are manifested in two forms: twinned martensite (
), when the growth of the variants is self accomodated and detwinned or reoriented martensite (
), where a specific variant becomes dominant in one specific direction.
Under a mechanical load detwinned martensite can be induce from the twinned martensitic state [
8,
9]. This process involves reorienting a certain number of variants in the favourable direction. Detwinning leads also to a noticeable change in the material’s shape, which is almost retained even after the load is removed. However, the applied load must reach a certain threshold to initiate the detwinning process, known as the detwinning start stress
. If the load achieves a sufficiently high level, complete detwinning of the martensite occurs. This stress level is referred to as the detwinning finish stress
.
Figure 2 (
a) illustrates the various points and the material behavior schematically.
When the material is subjected to a mechanical load higher than
in the austenitic phase, the phase transformation during cooling leads directly to the formation of detwinned martensite, causing a change in shape. Upon heating the material under constant load, shape recovery occurs, and thus it is a revesible process [
3]. The phase transition from austenite to martensite is termed as forward transformation and back to austenite is called reverse transformation. The martensitic transformaton is characterised by four singular temperatures that are stress dependent. On the one hand, the forward transformation is determined by
and
as the martensite start and finish temperatures, respectively. On the other hand, the reverse transformation is illustrated respectively by
and
as the austente start and finish temperatures.
The pseudoelastic behavior of SMAs is associated to the stress-induced phase transformation. Above
, large reversible strains are feasible upon monotonic loading and unloading. A typical pseudoelastic thermomechanical loading path concerns a transformation between (stable) austenite and detweinned martensite.
Figure 2 (
b) shows an example of a stress-strain diagram during the pseudoelastic transformation between austenite and martensite.
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the material behaviour of SMAs with (
a): Temperature-induced phase transformation in the presence of applied load [
3] and (
b) a typical SMA pseudoelastic loading cycle [
3].
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the material behaviour of SMAs with (
a): Temperature-induced phase transformation in the presence of applied load [
3] and (
b) a typical SMA pseudoelastic loading cycle [
3].
2.3. Actuator Concept
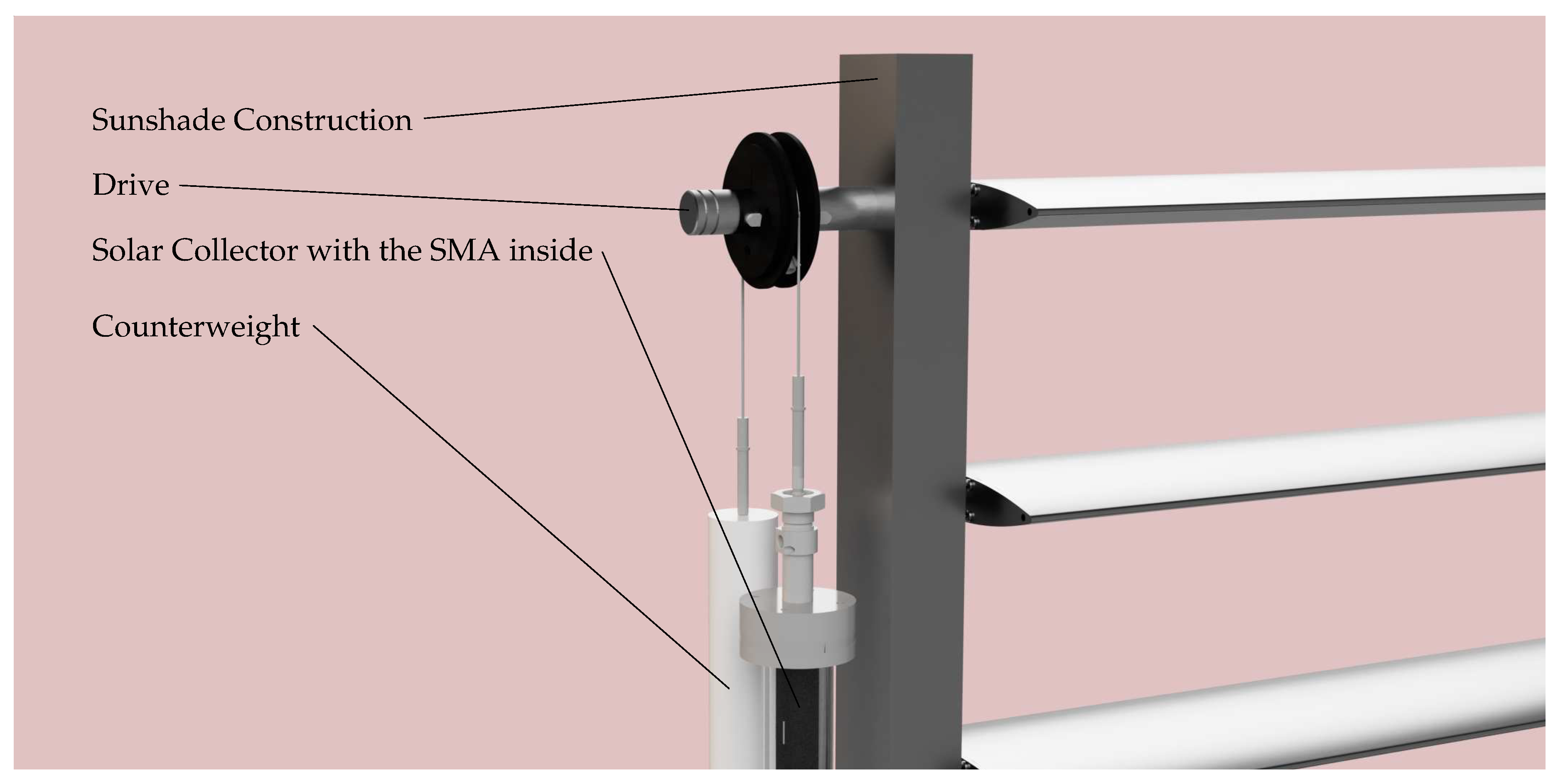
The developed actuator assembly consisted of several components: sunshade construction, drive, counterweight, SMA-wire, and solar collector (cf.
Figure 3). The sunshade construction has been modified with the linear motor being removed. The axis of the top louver is connected to an approximately 30
thick shaft, penetrated the two sheets of the outer aluminum support profile and extended approximately 10 to 20
. All louvers were still flexibly joined to the linkage rod, and by rotating the top shaft by 90°, the entire sunshade construction closed. The linkage rod was eccentrically positioned and, due to its weight, ensured the opening of the sunshade construction when the louvers were horizontally arrangedin absence of external forces.
The designed drive consisted of a pulley that guided a flexible wire rope. On one side of the wire rope, the SMA-wire was attached, while the other side was weighted. The weight provided stability to the sunshade construction and prevented the misalignment of the louver angle due to wind or user interference. Furthermore, the weight ensured a constant mechanical tension in the SMA-wire. This was particularly important for utilizing the detwinned martensite to austenite transformation, as it helped to maintain stable SMA characteristics. Otherwise, external forces such as wind loads on the louvers of the sunshade construction could shift the characteristic temperatures due to varying mechanical stresses in the SMA-wire. We expected this approach to yield reproducible results in the switching behavior of the actuator. In this study, we have utilize the thermal-induced phase transformation between detwinned martensite and austenite.
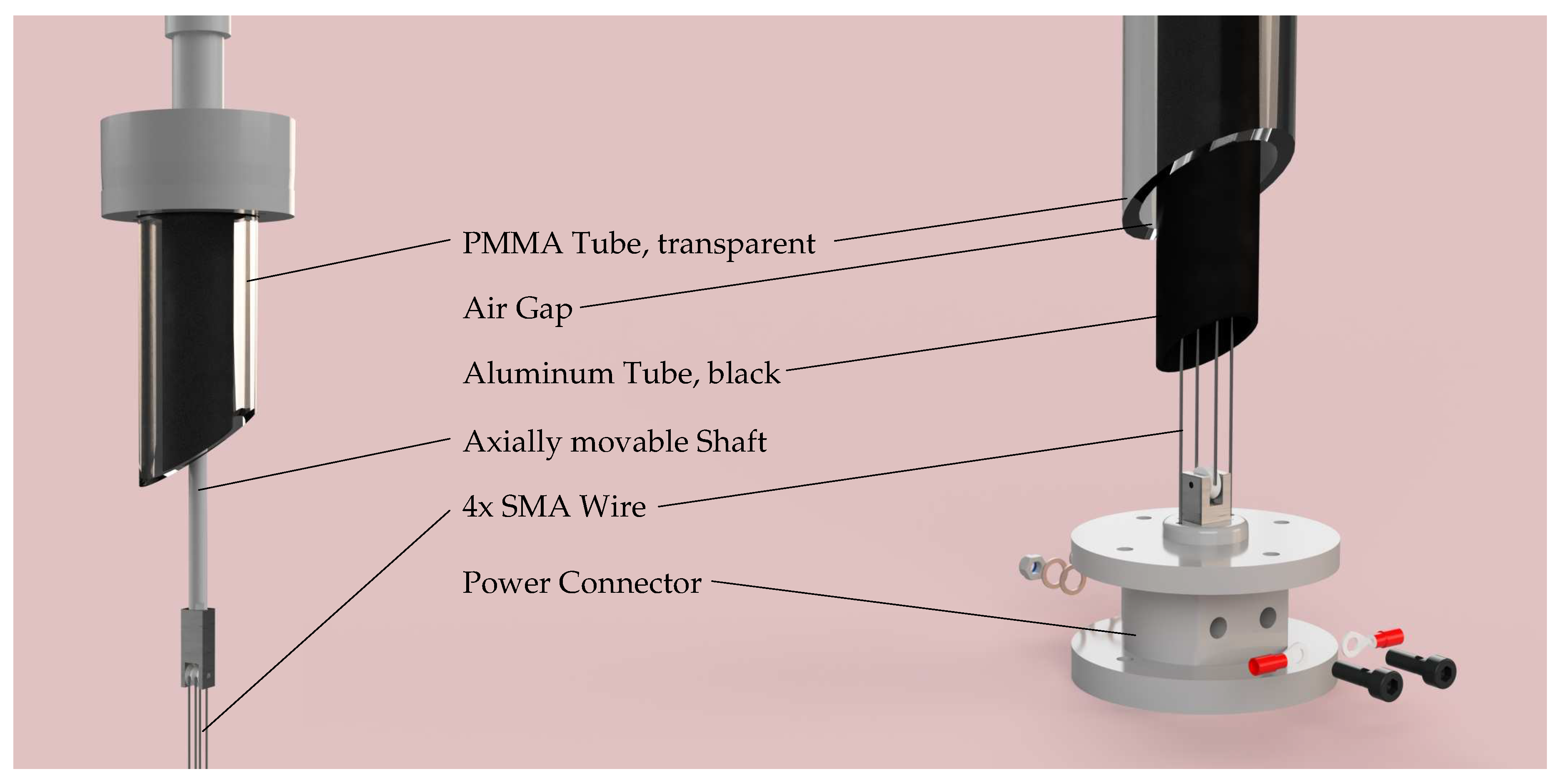
The SMA-wire was enclosed within a thermal solar collector for the thermal activation [
10]. Therewith, temperatures significantly higher than the outdoor ones could be achieved when the collector was directly exposed to solar radiation. Hence, the activation temperatures of the SMA-wire could be purposefully achieved. The selected heat transfer medium inside the solar collector was air. The heating of air within the solar collector is based on the greenhouse effect. It is similar to the process of a room being heated in summer by solar radiation passing through glass surfaces. The collector was thus used as a temperature controlling element triggered by the solar radiation. The solar collector consisted of a transparent PMMA tube and a concentrically located black-painted aluminum tube. The two tubes were connected by a shaft seal at each end, which hermetically sealed the air gap between them. The aluminum tube contained the SMA-wire and was hermetically sealed on both ends by special cover points.
Figure 4 depicts the cover points in a 3D-model of solar collector. The upper cover point included an axially movable shaft for transmitting the displacement of the SMA-wire to the actuator. The shaft was equipped with two shaft seals. At the lower connection point, the wire ends were permanently clamped using screws, and connections were provided for electrical contact.
The aim of the project was a solar shading actuator that was powered only by solar heating and without electrical energy. However, for the development phase we had integrated electrical connectors for joule heating into the system [
11,
12,
13]. This simplified testing of the actuator in terms of functionality, fatigue or demonstration. It was important that the system could still operate primarily without electrical energy. To apply efficiently electrical heating, we employed 4 SMA-wires within the solar collector. The wires were mechanically attached in parallel and electrically connected in series. The implemented configuration increased the electrical resistance while maintaining the same mechanical performance compared to a single thicker wire. This allowed for the electrical heating to operate with Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) according to IEC 61140:2016 [
14]. The long wire, as shown in
Figure 4, was tensioned using three ceramic rollers with a diameter of
.
In principle, the SMA-wire did not move over the rollers but remained constantly tensioned over them in a fixed position. Frequent movement of the SMA-wire over the rollers would leaded to bending of the wire. This would damaged the wire in the long term and should be avoided to ensure the functionality of the system. Additionally, the constant loading on the bent sections of the SMA-wire could cause long-term damage. Microcracks could form in the vicinity of the bending point due to the volume expansion associated with the martensitic transformation [
15,
16,
17]. To prevent fracture failure of the SMA at these locations, a low mechanical load was required.
Figure 4.
3D model of the solar collector, on the left is the upper cover and on the right is the lower cover.
Figure 4.
3D model of the solar collector, on the left is the upper cover and on the right is the lower cover.
3. Actuator Component Design
3.1. Actuator Parameters
The design of the actuator components and the selection of the SMA-wire depended on several factors. To calculate the resulting force on the SMA-wires
, a balance of forces was applied considering the system in mechanical equilibrium
1. Relevant factors were the wire cross-section
, the number of parallel SMA-wires as well as, the systems mechanical resistance and the restoring force of the counterweight
. While adjusting the mass of the counterweight was relatively straightforward, the system resistance was a dynamic factor that depended on the external conditions and the angular position. External conditions included wear or contamination of sliding bearing connections in the sunshade construction system, resulting in changes in friction coefficients. Additionally, physical effects, such as thermal expansion of the shading system components, and alterations in resistance forces
under summer and winter conditions, caused an impact on the required SMA-forces. Wind forces cloud exert an impact on the system. A detailed analysis of the external forces was not within the scope of this work and estimations were considered based on simulated tests.
Considering the mechanical equilibrium as:
then:
The weight force must been greater than the resistance force so that the counterweight cloud open the sun shading construction system
. A large actuation radius ractuator
led to a reduction of the SMA-forces to overcome the resistance forces. For this aim, a pulley was integrated as a standard component. The actuator radius
was calculated based on the dimensions of the pulley
and the wire rope diameter
as follows:
From the required rotation angle to close the shading system given by 90°, the length of the SMA-wire
could be dimensioned.
The effective functional length of the SMA-wire was limited by the system. The experimental setup of the actuator should not exceed the height of the shading system. With a maximum length of the collector of
m, the maximum length was limited to
m. According to the Clausius-Clapeyron relation, an increase on the mechanical stress causes a rise in the transformation temperatures
,
,
and
. The stress-temperature variation can be described by the Clausius-Clapeyron coefficient
C [
], which is SMA-specific. To calculate the transformation temperatures of the SMA, the setpoint switching temperatures determined in
Section 3.3.3 are used. Their calculation is done by equations
5 and
6.
where
and
are the Clausius-Clapeyron coefficients of the austenitic phase transformation and martensitic phase transformation. The selection of the appropriate SMA was based on the requirements and data from the literature [
18,
19,
20]. Equation
1–
6 were used to dimension the components of the actuator.
3.2. Definition of the Shading Requirement
The first step of the SMA-actuator design was to define and develope the automatic control of the solar colector. The system should primarily be automatically driven by the intensity of solar radiation. Therefore, the components should be designed to activate and deactivate the shading according to specific requirements. Initially, the open-close-criteria of the sunshade louvers should be determined. The purpose of a sunshade system is to control solar radiation and protect the building from direct sunlight. An effective sunshade system takes into account the specific requirements of the building, geographical conditions, and individual user preferences. It should provide a balanced combination of protection against overheating and utilization of natural daylight to ensure a pleasant indoor environment while maintaining high energy efficiency.
Typically, a sunshade system should be closed when the solar radiation is too intense and there is a risk of overheating the interior room, especially during the summer months and time periods of direct sunlight. The sunshade system should reopen when the solar radiation decreases. As reference values for possible criteria for sunshade operation, specifications from DIN 4108-2 [
21] were used. According to these specifications and in the absence of specific control parameters, a radiation-dependent control can be assumed. For windows oriented towards north, northeast, and northwest the irradiation limit value amount to 200
for residential buildings or 150
for non-residential buildings. For all other orientations, an irradiation limit value of 300
for residential buildings or 200
for non-residential buildings. The irradiation limit (
[
]) describes the solar radiation intensity as the sum of direct and diffuse radiation perpendicular to the window. The values specified in DIN 4108-2 for
define ranges in which the sunshade should be closed.
Instead of the irradition, there are sunshade controls that utilize the illuminance (
[
]) as a control parameter [
22,
23]. The main advantage of these control systems are the cost-effective sensors. However, it is generally accepted that the resulting global radiation on the window surface represents the relevant control parameter for sunshade systems. Consequently, the radiation was chosen as the relevant control variable. Numerous studies have already been conducted to define the irradiation limit as a control parameter [
24,
25,
26].
The sunshade construction system of this work shaded slightly the facade even in the open state. Therefore, the typical irradiation limit values for closing the shading tend to be slightly higher compared to systems that are completely open. The provided standard control system utilizes a simplified approach by measuring the illuminance in [] on a horizontal surface. By calculating the solar position based on location and time, the individual shading elements are activated or deactivated according to their orientation. Nevertheless, the conversion between illuminance and solar irradiation can not be done accurately. Therefore, assumptions regarding the as reference values were realized for the design of SMA-controlled solar shading actuator.
3.3. Determination of the Design Temperatures for the SMA Transformation
The temperature of the SMA-wire influences the angular position of the sunshade construction. The correlation between the thermo-mechanical properties of the SMA-wire, the mechanical wire tension, and the temperature in the solar collector defined the shading system’s switching operations. In order to open and close the system as per the requirements, thermal investigations have been conducted. In a thermal model, the temperatures of the SMA-wire within the solar collector were calculated based on the outdoor air temperature and solar radiation. The model was validated with measurement data. By using the model, switching threshold temperatures at which the SMA-wire should close () and open () were defined . These calculation results were used for selecting the appropriate SMA.
3.3.1. Model Approach for the Thermal Description of the SMA-wire
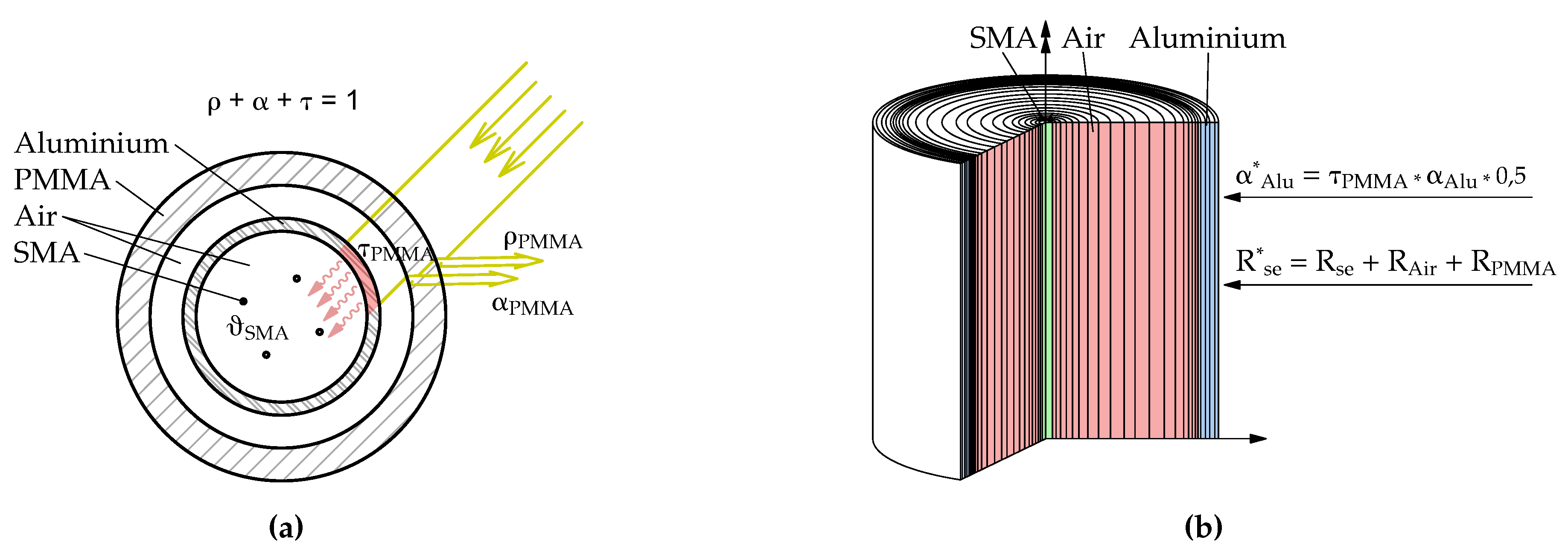
The employed model aimed to comprehensively describe the thermodynamic behavior of the developed system, know as smartskinreal system, particularly the heat transfer process within the system. Both the influence of conduction and thermal storage, as well as radiation were regarded to enable a precise prediction of the system’s thermal behavior. The conduction within the system was considered through the thermal properties of the materials, specifically for the materials of the solar collector and the SMA-wire. A material database was utilized for assigning thermal conductivities and specific heat capacities to the model. Enclosed air layers was treated as equivalent. Furthermore, radiation was contemplated as another significant heat transfer mechanism in the model. When radiation strikes a body, a part of it is reflected, a part is absorbed, and if the material is transparent, a part is transmitted. The fraction of incident radiation that is reflected is defined as the reflection coefficient
, the absorbed fraction as the absorption coefficient
, and the transmitted fraction as the transmission coefficient
. According to the first law of thermodynamics, these three components must sum one. Opaque bodies do not transmit radiation, and
[
27].
Figure 5 (
a) illustrates the basic solar model. A large part of the incident solar radiation energy is transmitted through the outer tube made of translucent PMMA. A significant part of this radiation is then absorbed by the absorber surface of the inner black-painted aluminum tube. This heat warms the enclosed air chamber within the inner tube. The SMA-wire is located inside the air chamber. To model the wire temperature in the collector, we utilized the hygrothermal simulation software Delphin 5.9 [
28]. The collector construction was simplified and transferred in a horizontal 1D roto-symmetric transport construction model. We assumed that the temperature inside the aluminum tube was largely uniformly distributed. Therefore, we cloud place the SMA-wire in the center of the tube in the model, as a metallic wire with a diameter of 1
. Adjacent to it, a stationary air layer was assumed with the corresponding radius of the aluminum tube, as well as an aluminum layer with the wall thickness of the inner tube (see model in
Figure 5 (
b)). Due to software-specific limitations for defining radiation transmission, the boundary conditions were directly applied to the inner black-coated aluminum tube. However, to account for the outer transparent acrylic glass tube, modifications were made to the heat transfer resistances and absorption coefficient. For the consideration of enclosing PMMA pipes, the external transition resistance was adjusted. The modified temperature transition resistance to the outside air
resulted in:
The temperature transition resistance was thus increased by the temperature transmission resistances of the stationary air layer and the PMMA tube. The modified emissivity of the surface of the aluminium tube
was obtained by multiplication with the total energy transmittance of the transparent acrylic glass tube
. Due to the symmetry conditions of the 1D roto-symmetric model, the incident direct and diffuse radiation fractions were each halved. This was because the incident direct radiation hits the absorber surface of the tube with only half of the surface:
By implementing the model, temperatures of the SMA-wire in the collector cloud be calculated as a function of the outdoor climate. With the thermo-mechanical properties of the SMA-wire, predictions about the switching behaviour could be conducted.
Figure 5.
Thermodynamic model used to calculate the SMA-temperature. (a): sectional view of the solar thermal collector with SMA-wire inside and illustration of the basic radiation model and (b): representation of the simulation model with definition of boundary conditions.
Figure 5.
Thermodynamic model used to calculate the SMA-temperature. (a): sectional view of the solar thermal collector with SMA-wire inside and illustration of the basic radiation model and (b): representation of the simulation model with definition of boundary conditions.
3.3.2. Experimental Validation of the Model
The model validation was realized through the comparison of simulated results with experimental data from real-world trials. Various scenarios and boundary conditions were considered over a continuous period of 14 days to ensure an accurate model. The experimental setup included the developed collector with a length of 1
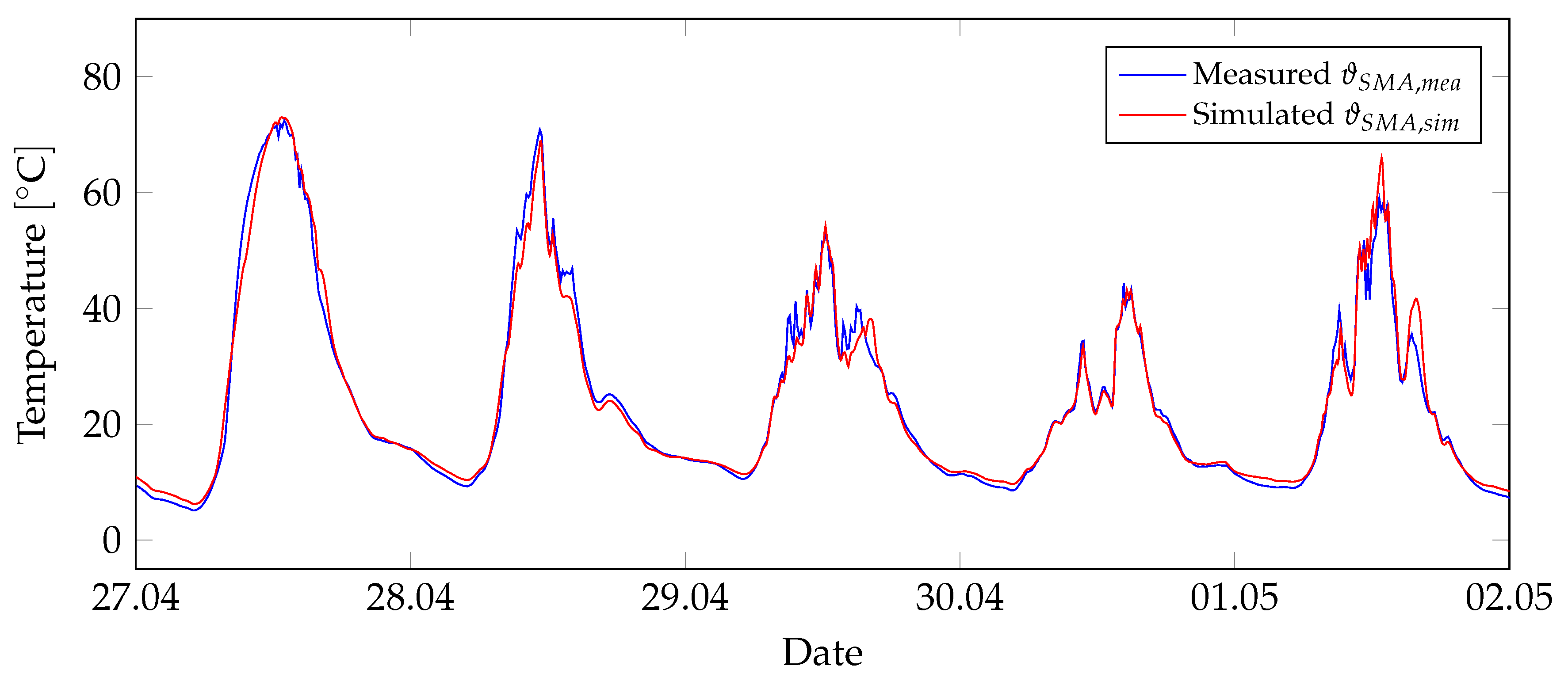
m. It was located on the roof of a three-story building in Leipzig, Germany, oriented to the south and not shaded by surrounding structures. The top and bottom openings were sealed against air and water. A temperature sensor was installed in the center of the inner air chamber of the collector. We assumed that the air temperature in the center of the solar collector corresponded to the temperature of the SMA-wire. This assumption was based on the fact that the sensor and sensor wiring was made of a metallic wire similar to the SMA-wire, and their properties were expected to be comparable. Furthermore, the recording of boundary conditions includes outdoor air temperature and south-facing solar radiation. With a measurement output at 10-minute intervals, data from April to May 2020 over a period of 14 days were available. The measured boundary conditions were also implemented as boundary conditions in the model. For the simulation period, the temperatures of the SMA-wire in the center of the collector was calculated and compared with the available measurement data. The measured and simulated data showed a high degree of agreement.
Figure 6 illustrates an exemplary comparison plot.
3.3.3. Defining SMA Setpoint Switching Temperatures
In the next step, we used the validated model to define the SMA setpoint switching temperatures. They described the theoretical SMA-temperatures at which the sunshade construction should start to close (
) and open (
). The martensitic transformation from austenite to martensite and vice versa does not occur at a specific temperature but within a temperature range. It was evident that this behavior also influences the switching dynamics of the sunshade construction. Therefore, the sunshade construction could not abruptly close upon reaching a specific temperature. The SMA setpoint switching temperatures should broadly define the martensitic transformation between
and
or
and
. These temperatures of the SMA-wire were reached when the solar irradiation of the facade surface overtook the limit values determined in Chapter
Section 3.2,
Table 1. For this purpose, SMA-temperatures
and irradiation of the vertical surface
were calculated with the model for different orientations. We used a climate dataset TRY-4 Potsdam, Germany [
29] as boundary conditions. The dataset included outdoor air temperature and radiation data, which was used for the validation of the data.
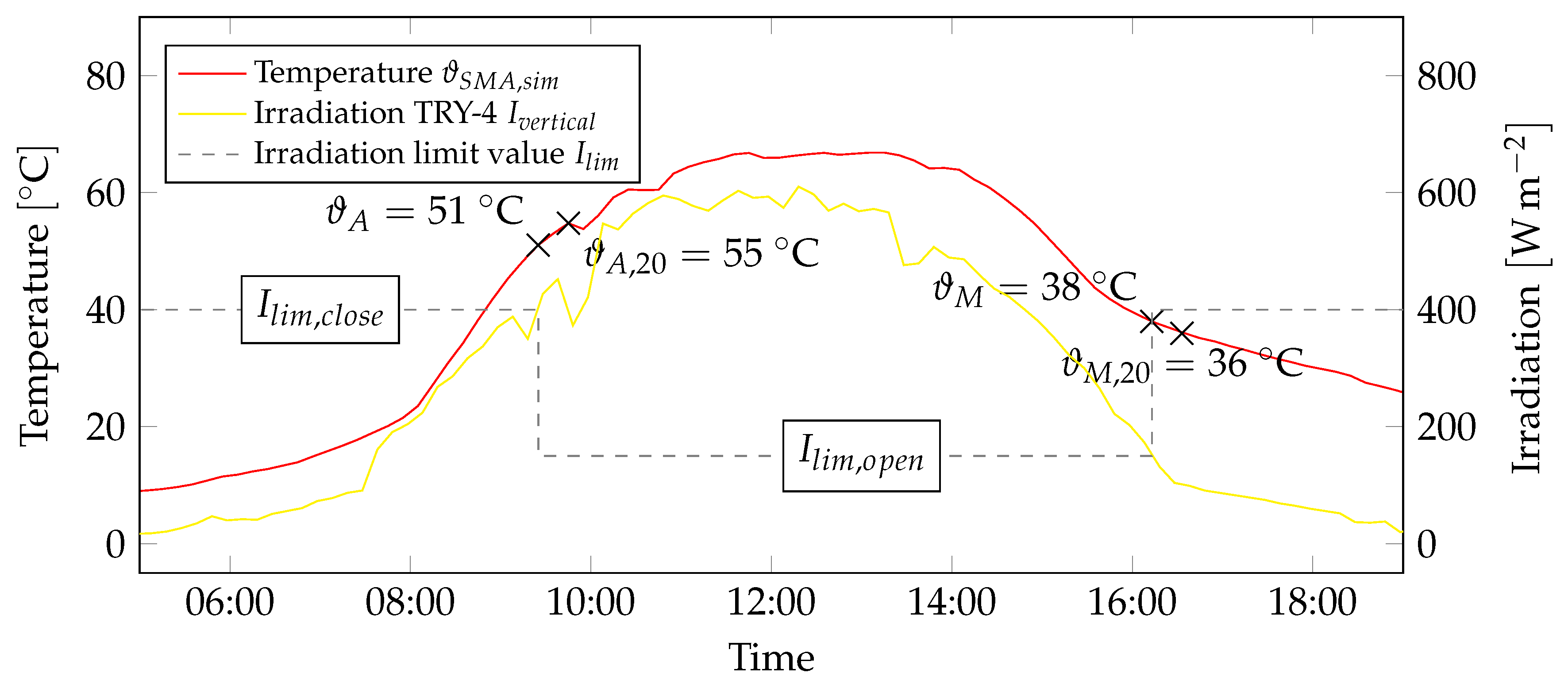
Figure 7 shows the simulation results on this topic using a single day in summer as an example. The irradiation limit values
to open and close the system are shown as a step curve. The model calculated the
based on the TRY-4 radiation data. Subsequently, the corresponding
, at which the sunshade construction system should open and close, were determined using
. These temperatures corresponded to the stages when
reached the respective
values. The
for opening and closing were provided for these time points. The smartskinreal sunshade construction system was designed to be generally react accordingly to the temperature variations with a desired gradual and uniform opening and closing of the louvers. The simulation data revealed that the differences between the
for opening and closing were sometimes very narrow. This was problematic for the selection of a fitting SMA-wire. We therefore collected the
from the simulation results. This dataset described the SMA-temperatures obtained 20 minutes after the solar irradiation reached the limit values
. We assumed that a delay of 20 minutes for the opening and closing of the louvers was an acceptable compromise.
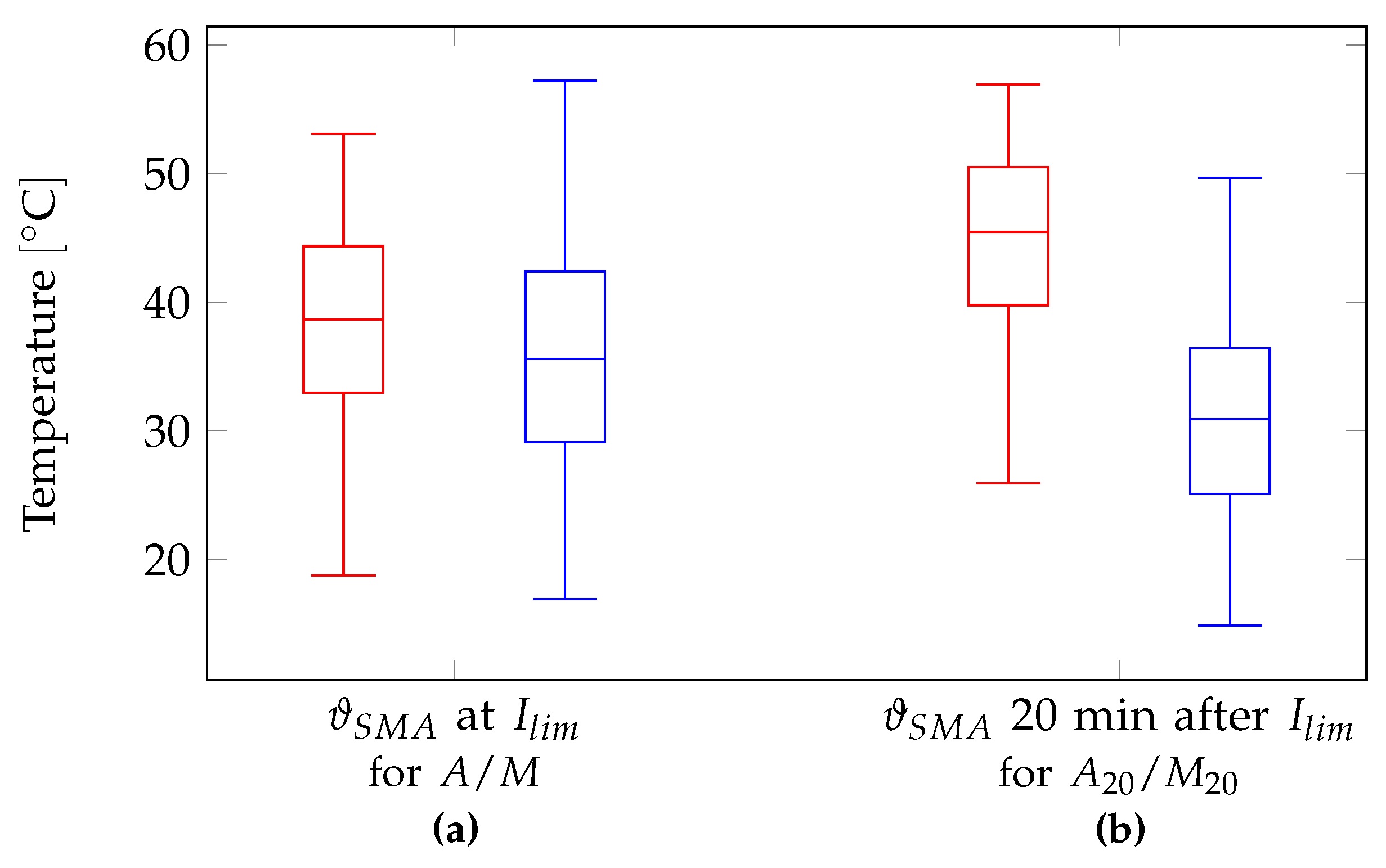
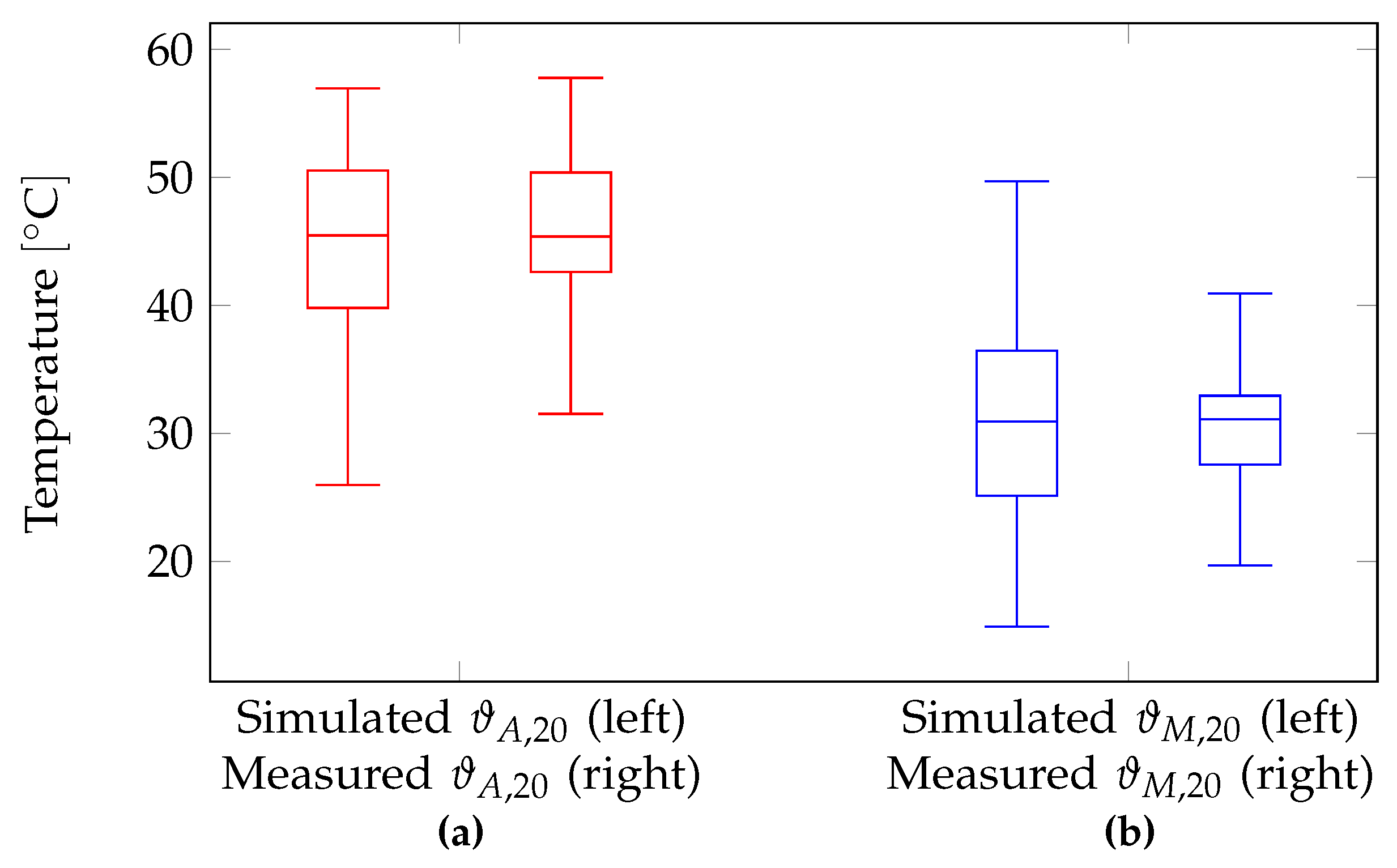
Figure 8 presents the results of the simulations for
for one summer period from April 1 to September 30. The data distinguishes between two variants: (
a) and (
b). In variant (
a), temperatures of the SMA-wire we provided at the time when solar irradiation
I reaches the threshold values
. In variant (
b), temperatures were calculated, 20 minutes after reaching the threshold values. We developed the second variant for better estimating of the dynamics of temperature trends in the solar collector. Both variants differentiated between the events for closing
(shown on the left in red) and opening
(shown on the right in blue) of the louvers. The data exhibited a significant scattering of values. This was due to the fact that during cloudy periods, irradiation values on the facade surface could rise and fall abruptly. In contrast, the data in
Figure 7 represents a mostly cloudless day, where solar irradiation
I varies smoothly over the course of the day. The high scattering was thus attributed to the inertia of the solar collector during heating and cooling. Furthermore, it cloud be possible that on a cloudy day,
could only be briefly exceeded or undershot. The sluggish behavior could help to avoid rapid the opening and closing of the louvers. Consequently, the differences in medians between
and
increased from
K in variant (
a) to
K in variant (
b). The simulation data covered a whole summer period. Particularly low temperatures in the solar collector along with high irradiation values could be attributed to cold outdoor air temperatures. This granted the utilization of solar gains during cold seasons. Despite the high variability in the simulation results, the heating of the solar collector could be compared to the solar heating of indoor spaces. The goal of the sunshade construction system was to avoid overheating in rooms during summer. This implies that the dynamics of solar heating in the solar collector may behave similarly to the heating patterns of the protected rooms.
In order for the sunshade construction to open fully again at low irradiation, the SMA-temperature had to decrease. In some cases, the solar collector heated the SMA wire well above the temperature of the ambient air. During the martensitic transformation from austenite to martensite, the temperature could only drop to the ambient air temperature. This means that the ambient air temperature significantly influenced the opening behavior. If the ambient air temperature remains consistently above throughout the night, the sunshade construction will not fully open during the night. This would clearly indicate a system malfunction. In the temperate Central European climate, tropical nights occur only occasionally. Tropical nights are weather events with air temperatures above 20 °C during the night. Therefore, an additional SMA setpoint is recommended defined by °C.
Based on the general considerations and the calculation results from the simulations, SMA setpoint switching temperatures are defined, see
Table 2.
3.4. Determination of the System Resistance
The resistance force
of the sunshade construction system was an essential input parameter for the drive design. It described the force required to move the louvers. Thus, it was the force that the actuator must apply to open and close the system. Since the force transmission of the actuator to the sunshade construction system tooks place through a 90° rotary motion, the resistance force
was described by a resistance torque
(Eq.
9).
was comprised of different components. Firstly, the friction of the plain bearings, in which the lamellas are supported. Secondly, the weight force of the eccentrically arranged push rod contributed to
. And finally, the environmental effects due to wind, snow and rain also influenced
. It must be emphasized that the components are particularly variable. For instance, the friction in the sliding bearings of the louvers are time and assembling dependent. Therefore,
cloud only be approximated.
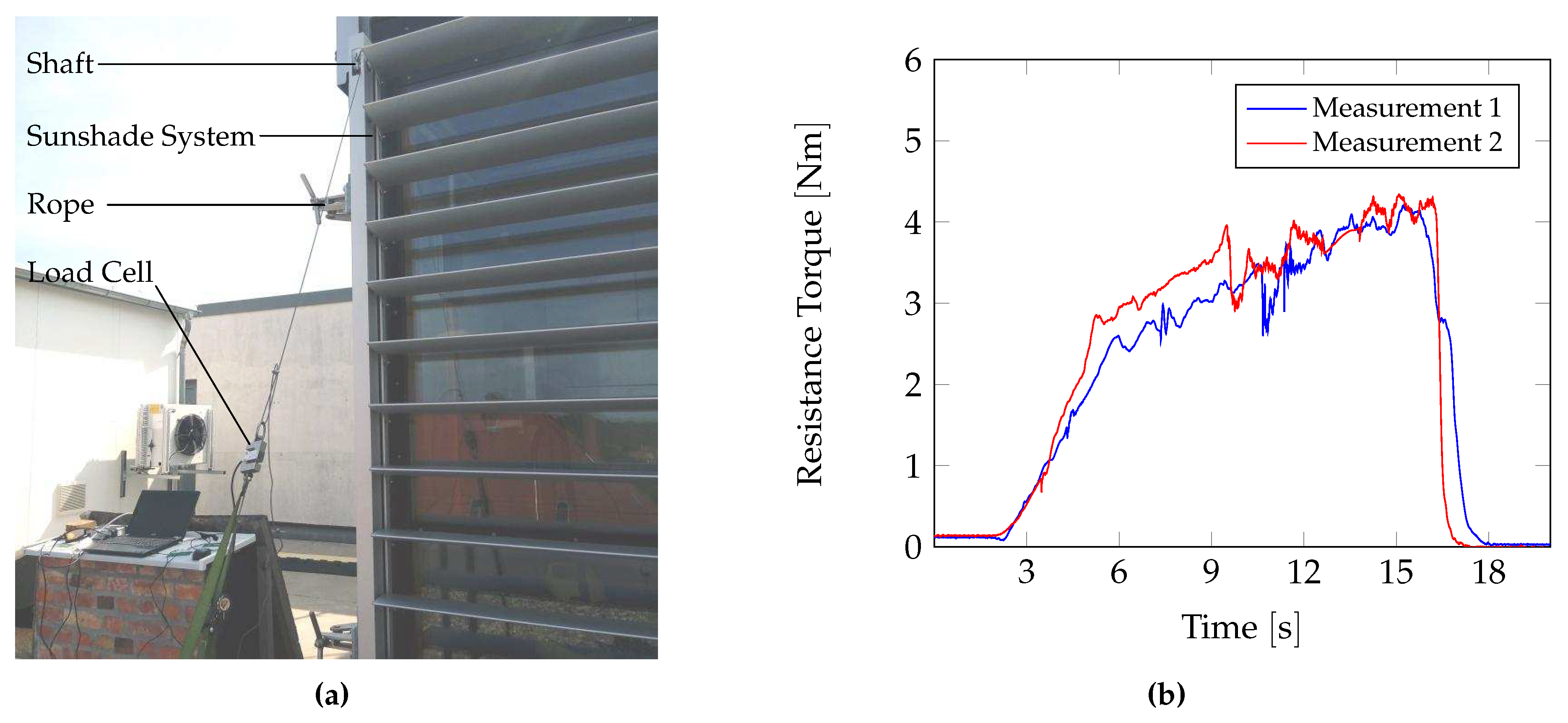
For a realistic estimation of
, we performed measurements on an existing sunshade construction system such as the smartskinreal system. As already stated in the actuator concept, the measurements were performed using the
rotary motion of a drive shaft. A pulley with a rope mounted on the drive shaft and attached to a load cell was employed for the measurements. In stationary mechanical state, the sunshade are open due to the weight of the push rod. Thus, the sunshade system could be closed by pulling on the rope with the load cell. For a good reproducibility, several trials were carried out ba pulling manually the rope to determine the
of the sunshade system.Finally, the forces determined by the load cell were multiplied by the radius of the pulley to obtain
(Eq.
9).
In
Figure 9, the experimental setup (
a) and the results (
b) of the measurements are depicted. The results for
are shown over the duration time of the experiment. The data trend presented a continuous increase in
. Approximately between 3 and 6
s, the breaking torque was being developed. It was reached at about 3
. Between seconds 6 and 15, the sunshade construction system was closed. During this period,
increased by about 1
. The latter increase cloud be attributed to the required force to raise the connecting push rod that links all the louvers. In the closed state,
attained a maximum of approximately
. The measurement data for
provided reference values for the actuator design. Additional factors such as wind or snow were not taken into consideration.
3.5. Selection of the Shape Memory Alloy
Based on the results of the preceding subchapters, the selection of a suitable and comercially available SMA was accomplished. NiTi alloys are the most widely used SMAs, finding extensive applications due to their excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and characteristics as both shape memory effect (SME) and superelastic SMAs [
3,
30]. Substituting portions of nickel with copper in the alloy composition reduces both the thermal hysteresis and the transformation stress of NiTi alloys. Although any modification in the composition of a binary NiTi alloy strongly influences the transformation temperatures, the addition of copper to binary NiTi alloys significantly diminishes the sensitivity of transformation temperatures [
30,
31]. The optimal composition range is found between 5
Cu and 10
Cu in the Ni-Ti-Cu alloys [
3]. Furthermore, the addition of chromium increases the yield stress, contributing to the overall strengthening of the alloy [
32]. The influence of mechanical stress on the selection of a suitable SMA alloy is of great importance. As stress increases, the transformation temperatures between states also change according to the Clausius-Clapeyron relation. The relationship can be described by the Clausius-Clapeyron coefficient
C [
]. For NiTi alloys, a wide range of values, from
to
, is reported in the literature [
33]. In
Section 3.1 to
Section 3.4, the fundamentals for the actuator design have been presented. These were applied to develop the self-regulating solar shading actuator. Equations (
1) to (
6) were computed to determine the actuator’s parameters and select a suitable SMA. The meaningful factor for the SMA-selection was the requirement from
Section 3.3.3 above
°C, so that, the sunshade construction opens reliably even on tropical nights. The design parameters are presented in
Table 3. For the intended application, a
SMA-wire with a diameter of
has been chosen.
4. Validation of the Full-scale Demonstrator
Considering the findings outlined in
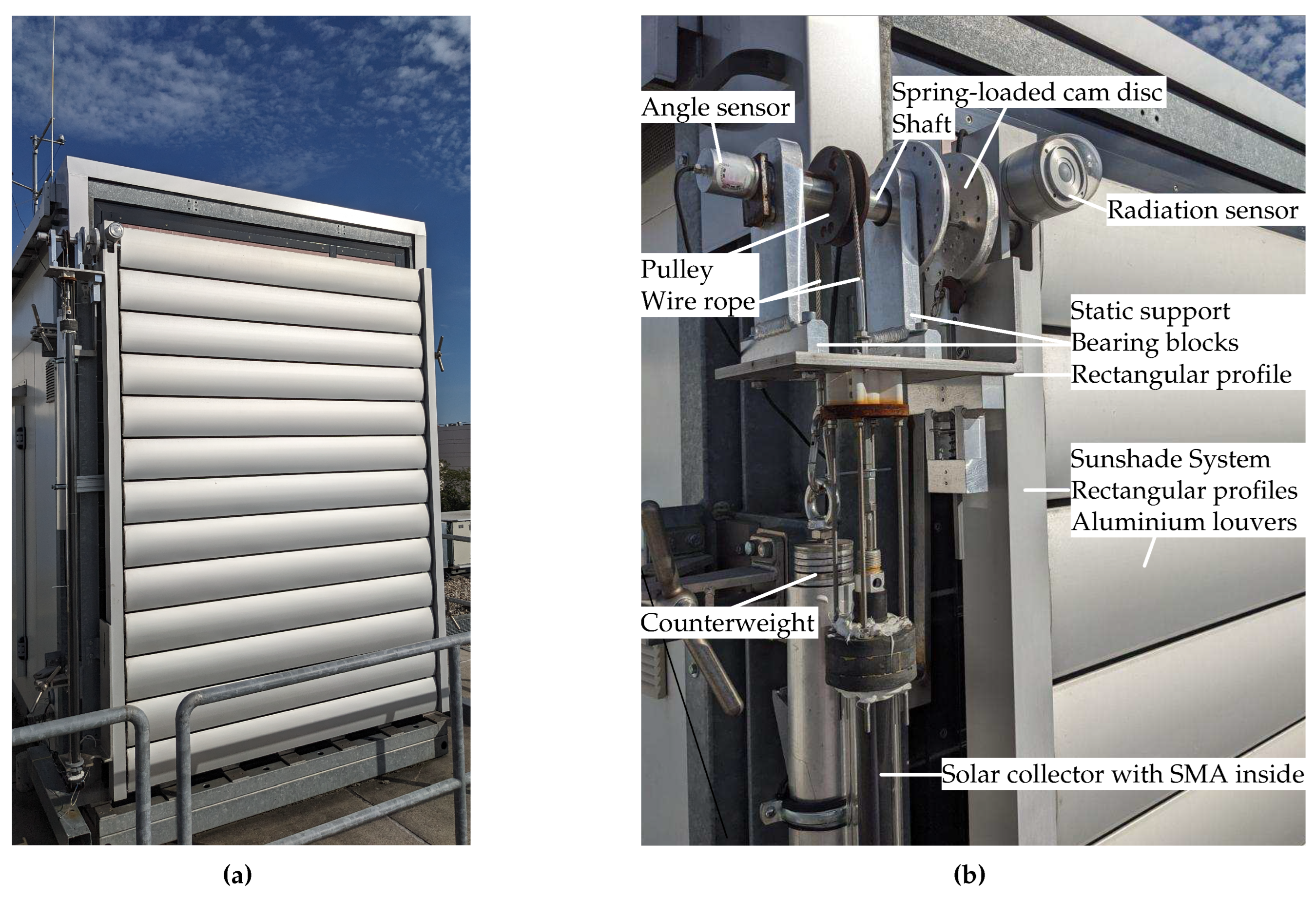
Section 3, a full-scale demonstrator was constructed with the primary objective of assessing the functionality. This entails the validation of theoretical models, assumptions, and outcomes within real-world conditions. The demonstrator was attached to a climate test cell, providing the capability to shade a fixed glazed section of a mullion-transom facade system. The internal climate within the test cell was subject to monitoring and control, enabling an analysis of the sunshade’s impact on indoor environmental conditions. The demonstrator is located in Leipzig, Germany, on the campus of the University of Applied Sciences. Situated in a westward orientation, the shaded facade area was supported by a static structure designed for the seamless connection of diverse components and efficient low-friction force transmission. To facilitate a comprehensive assessment, an array of sensors were strategically incorporated for monitoring purposes. Subsequent to data collection, an analysis was conducted, drawing comparisons between the observed data and the theoretical models developed.
4.1. The Demonstrator Setup
The implementation of the full-scale demonstrator required a static structure that provided seamlessly the assembly of the components. Consequently, we designed a prototype where the actuator components were positioned externally to the conventional components of the sunshade construction system. This strategic arrangement conferred the advantages of simplified component replacement and increased adaptability for the integration and substitution of sensors. The components constituting the sunshade construction system were predominantly preserved in their original configuration.
For the sunshade construction, a total of 13 aluminum louvers, each with a depth of 20 cm and a width of 195 cm, were systematically arranged. This arrangement resulted in a shaded area of 270 cm in height and 195 cm in width. The louvers were securely affixed on both the left and right sides within aluminum rectangular profiles through sliding bearings. A linkage rod joined all the louvers. The coupling to the actuator was established through a shaft positioned within the topmost louver. The shaft traversed the left rectangular profile and was supported by sliding bearings. On the left side of the sunshade construction, two angle profiles (top and bottom) made from 10 mm thick stainless steel sheets, were steadfastly mounted. These profiles provided robust support for the the actuator components. At the upper profile, the shaft was additionaly supported by two bearing blocks. The shaft was mounted with minimal friction through double ball bearings. A pulley, as the actuator drive, was securely fixed to the shaft. Enclosed within the pulley was a wire rope that linked the counterweight on one side and the solar collector with SMA-wire on the other side. To ensure stability and mitigate the rattling of louvers during windy conditions, a spring-loaded cam disc was coupled to the shaft. This disc was designed to maintain the louver positions at
,
, and
. Integrated sensors enabled the monitoring. A solar irradiation sensor, positioned at a
, precisely measured the solar irradiation on the facade surface. It also was capable to record simultaneously the ambient air’s temperature and relative humidity. Additionally, measurements of the louver angle and the temperature at the center of the solar collector were systematically acquired. The installed monitoring system collected data diligently over an extensive period of time, concretely from June 1 to August 31, 2023. Data retrieval from the sensors was facilitated by a data logger operating at a rate of 3 values per second.
Figure 10 visually represents the components of the full-scale demonstrator.
4.2. Sunshade Function
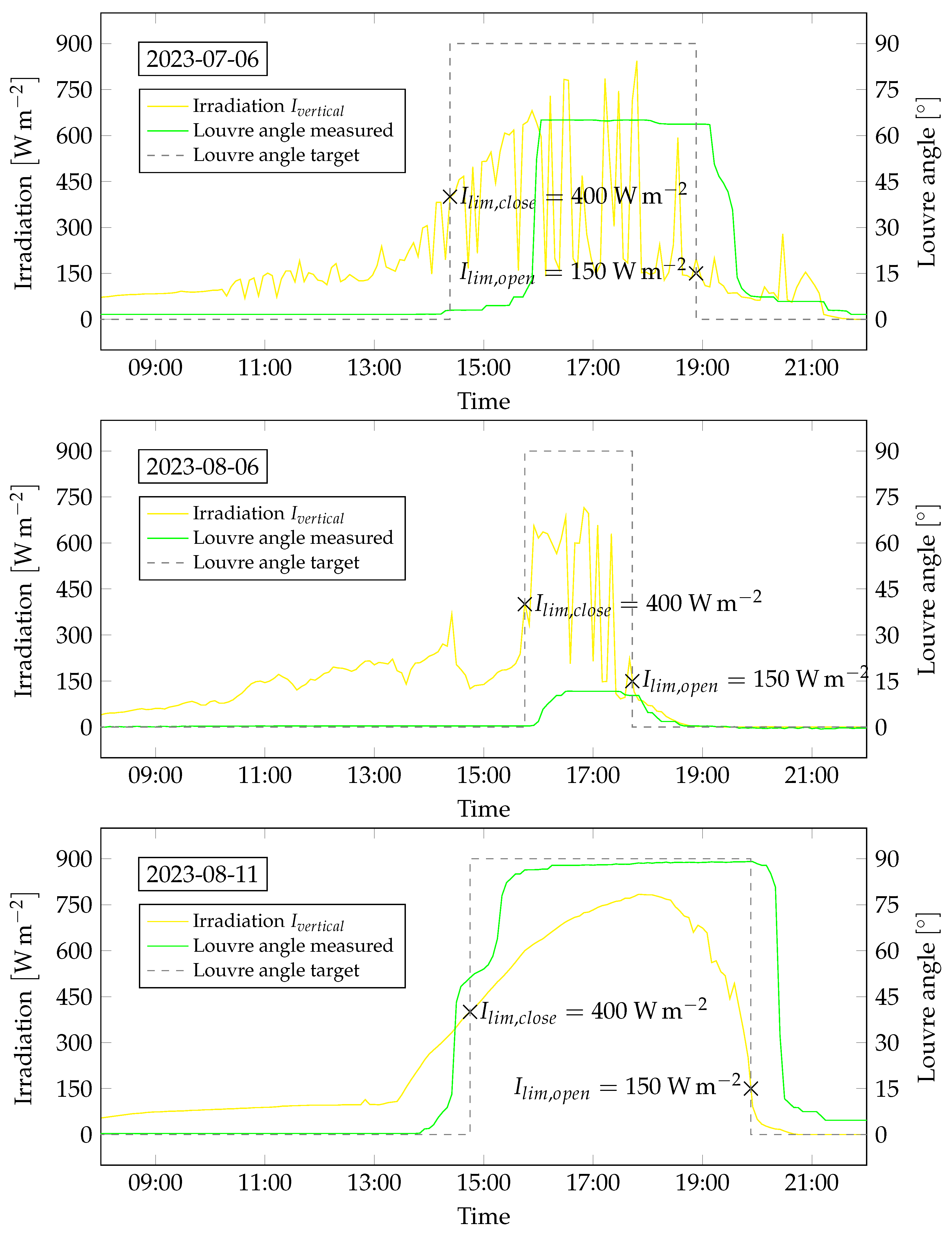
The shading function of the system was firstly ascertained. The operating points for the opening and closing operation were determined. In
Section 3.2, the irradiation on the facade was defined as the primary requirement for louver activation.
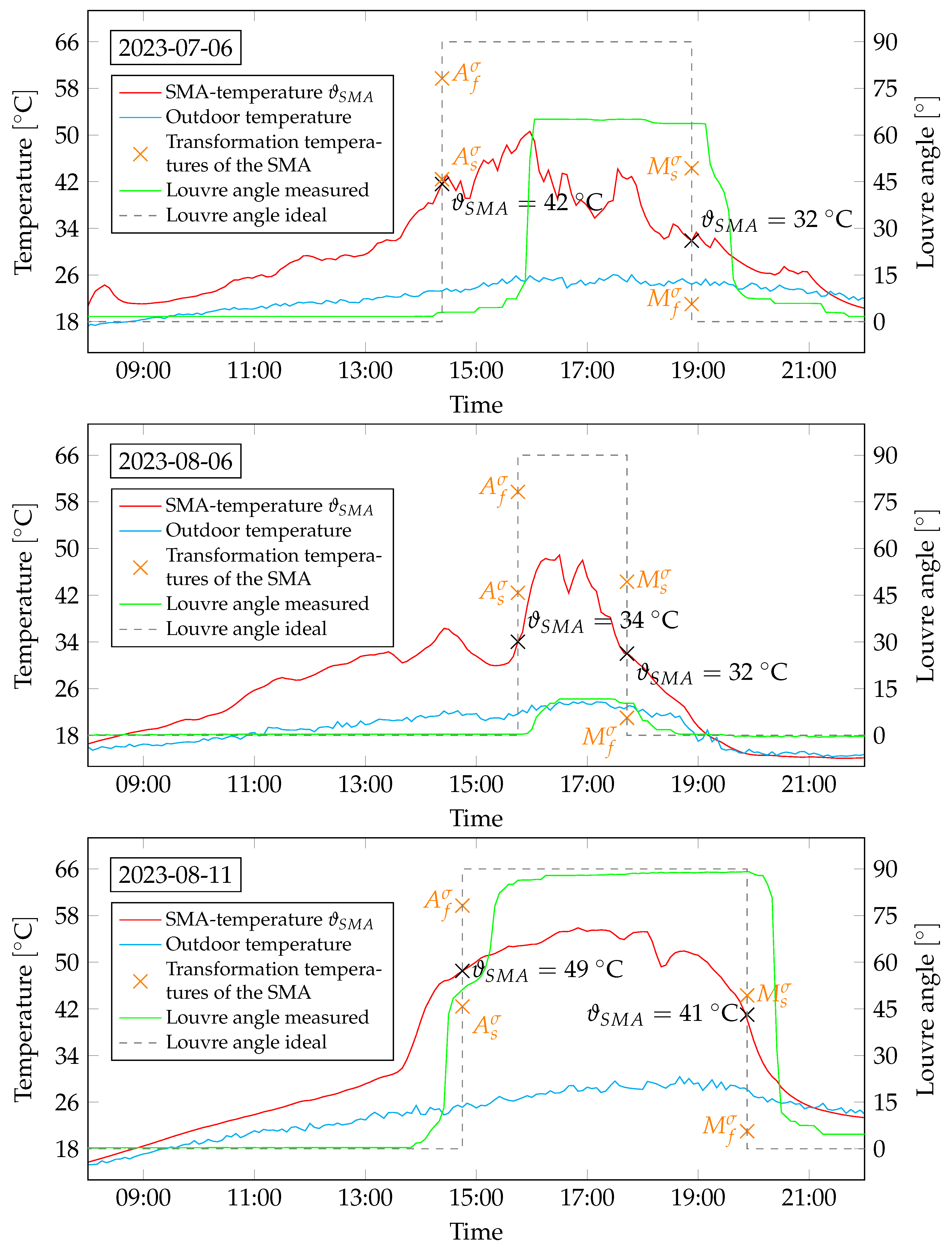
Figure 11 presents irradiation data for three exemplary days. In the year 2023, July 6 represents a lightly cloudy summer day, August 6 was more overcast, and August 11 was a cloudless summer day. The measured irradiation data and the threshold values from
Table 1 were utilized to calculate the ideal louver angles. These data are also depicted in
Figure 11 and are superimposed to the measured louver angles. Calculation and measurement exhibit high correlation on the cloudless summer day. On cloudy days, the louvers either did not close or a partial and delayed closure was monitored. The louver closing started partly before and after reaching the irradiation threshold of
. The louver opening began as estimated, completing shortly below the irradiation threshold of
. In general, the switching process (closing and opening) proveed to be markedly sluggish, extending over an hour in some instances. On August 11, 2023, a deviation in the louver angle of approximately
was recorded, which closely corresponds to the intended rotation of
.
Principally, the functionality of the system was validated. Particularly on clear summer days, the system fulfilled the specifications and requirements. On overcast days, the system either partially closed or did not close at all. This outcomes seemed reasonable, as the primary purpose for shading was not as demanded or given under such sky conditions. The issue arised when the louvers either closed with a significant time delay or, in some cases, did not close at all during partially cloudy conditions or sudden high irradiation on the facade. This delay was likely attributed to a certain inertia in the heating of the solar collector.
4.3. Solar Collector
An essential issue of the system was the coordination between the solar collector and the SMA-wire. The SMA-wire was located in the inner air chamber of the solar collector. Solar radiation hit the solar collector, and the inner air chamber heated up. As solar radiation on the collector decreased due to transmission heat losses to the surroundings and minor air leaked in the solar collector, the inner air chamber’s temperature droped. In the monitoring process, we measured the temperature in the inner air chamber, assuming that the temperature of the SMA-wire was almost similar. Data from
Section 4.2 indicated that the closing process of the louvers could be time-expensive. This suggests that the heating of the SMA-wire within the inner air chamber of the solar collector occurred slowly. In
Figure 12 we compare the measured SMA-temperatures with the material characteristics of the selected SMA. To illustrate the heating of the solar collector, we utilize the three exemplary summer days from
Section 4.2 and
Figure 11 (July 6, 2023, August 6, 2023, and August 11, 2023). In
Figure 12, we present the outdoor temperature alongside the SMA-temperature inside the solar collector. Also depicted are the martensitic transformation temperatures of the integrated SMA-wire at the ideal time of each switching event (
,
,
, and
). For a reliable operation of the sunshade construction, the SMA-temperature should follow a steep rise and fall within the range between the start and the finish temperatures. During the martensitic transformation, the SMA-temperature on all three exemplary days correlated with the desired switching time within the setpoint temperatures
and
. Consequently, the switching process for opening the sunshade construction was fulfilled. The austenitic transformation only corresponded with the desired switching time within the setpoint temperatures
and
on August 11, 2023. For July 6 and August 6, 2023, the SMA-temperature at the appropriated switching time was below
. The closing process of the sunshade construction was significantly delayed on July 6, 2023, and on August 6, 2023, the louvers were only rotated by a few degrees. The developed system accomplished the criteria with limitations. To ensure a stable opening function of the system on particularly hot nights,
°C was chosen. As a consequence, the austenite transformation temperatures,
°C and
°C, were slightly raised, leading to a delay in closing the sunshade construction under less intense solar irradiation.
The setpoint switching temperatures as detailed in
Section 3.3.3 were established to achieve specific temperatures at particular irradiation levels. These temperature thresholds (refer to
Table 2) corresponded to the conditions prevailing within the solar collector when the facade’s irradiation surpassed predefined thresholds (refer to
Table 1). In
Section 3.3, a thermal model for the solar collector was developed and validated. The theoretical model was applied to the measurement data from the full-scale demonstrator. In the simulation, climate data were utilized as boundary conditions for defining the SMA setpoint switching temperatures. The aim was to ascertain whether comparable results for the SMA setpoint switching temperatures were obtained under real-world conditions. In
Figure 13, we presented a comparative analysis, contrasting previously calculated data with measurements acquired from the full-scale demonstrator. The data underscored a agreement between simulated and real-world measurements. In particular, the measured data akin to our simulations exhibited a noteworthy range of variability. The model of the solar collector were therewith validated for the full-scale demonstrator, too.
Figure 12.
Measurement data of the full-scale demonstrator with the irradiation and the louvre angle (measured and calculated from the irradiation threshold values). Data are shown over the course of three exemplary days (July 6 2023, August 6 2023 and August 11 2023).
Figure 12.
Measurement data of the full-scale demonstrator with the irradiation and the louvre angle (measured and calculated from the irradiation threshold values). Data are shown over the course of three exemplary days (July 6 2023, August 6 2023 and August 11 2023).
4.4. Analysis of SMA Characteristics
The material properties of the selected SMA should be identified in the collected monitoring data. Throughout the actuator’s operation, the SMA-wire was consistently subjected to a constant mechanical stress of
. As a result, the SMA transformation temperatures underwent alterations influenced by the Clausius-Clapeyron coefficient
C. This coefficient slightly varies for each transformation temperature; however, we used an average value
to evaluate the SMA-properties. We compare temperature data in the inner chamber of the solar collector with the louver angular positions. The SMA-temperature could not be measured accurately with the full-scale demonstrator setup. We assumed that temperature changes in the solar collector were gradual, and the temperature differences between the SMA-wire and the air inside the solar collector were negligible. In addition, the temperature sensor used in the solar collector consisted of two thin metallic wires with an NTC-probe. These wires ran parallel to the SMA-wire and entailed similar thermal properties. Therefore, we equate the temperature in the solar collector with the SMA-temperature.
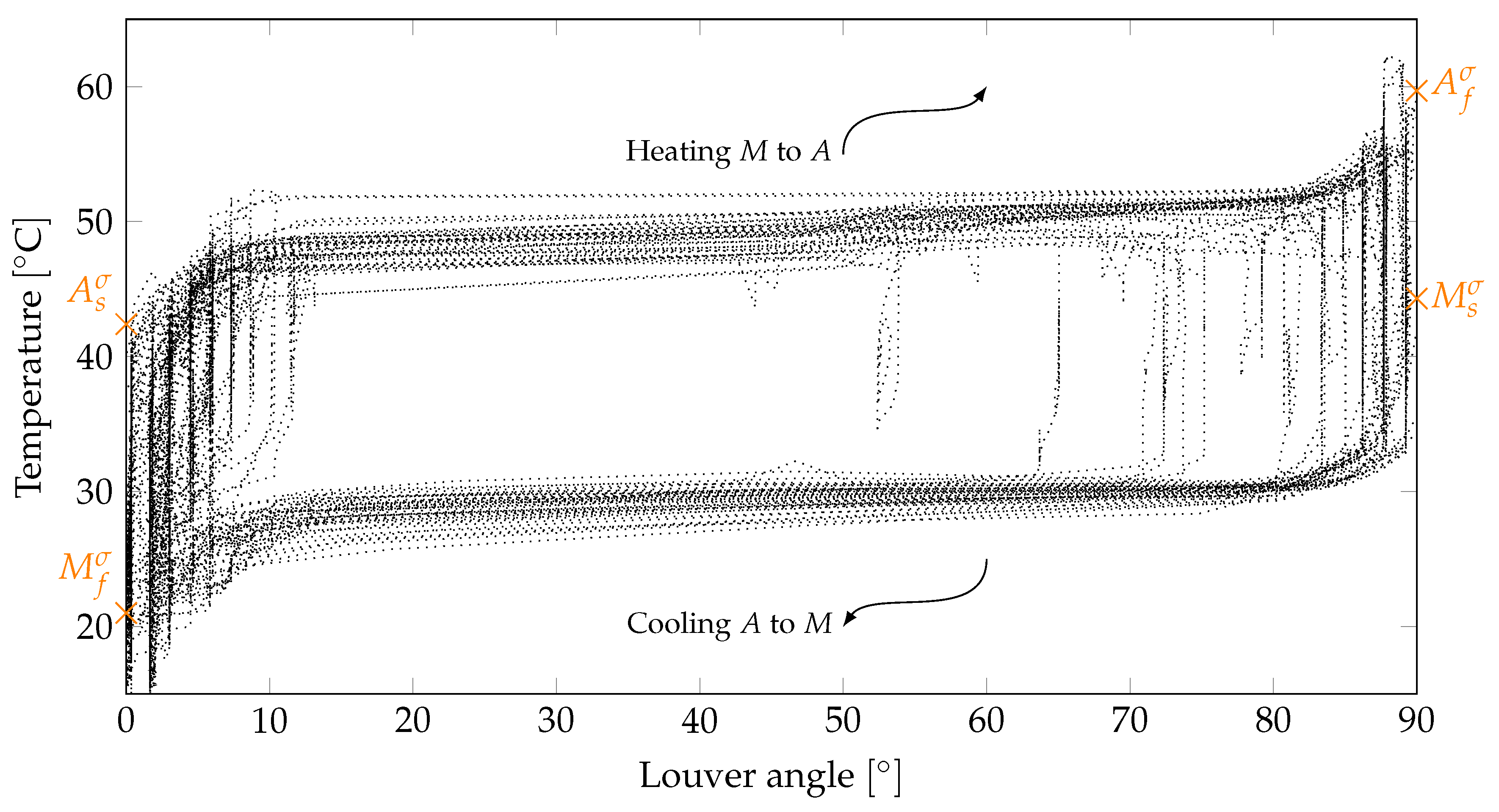
Figure 14 illustrates SMA-temperatures across louver angular positions. We deployed data from a representative period spanning from June 1 to August 24, 2023. Also shown are the martensitic transformation temperatures when the SMA-wire is subjected to tensile stress (
,
,
and
). They are plotted at the corresponding louvre angles of
or
. In
Figure 14, 5-minute averages are presented as a curve set over many days. Certainly, the resolution of the monitoring was too low to depict the relationship between SMA-temperature and louver angle at each acquired point. The switching process should occur significantly faster than can be recovered with a 5-minute measurement interval. However, measurement and setup errors could also lead to inaccuracies in the diagramms. For exmaple, the assumption of the same temperatures in the collector and on the SMA-wires. Particularly the trends in the angular ranges between approx.
and
seemed to scatter. In regions below
there is a partial spread. These corresponded to data from days by which the solar irradiation was not sufficient to close the louvers completely (cf. August 6, 2023, in
Figure 11 and
Figure 12). Similarly, data were distributed as point clouds in the angle ranges between approx.
and
, where the louvres were only partially closed (cf. July 6, 2023, in
Figure 11 and
Figure 12). Taking these points into account, a recurring pattern could be discerned from the data. The course from
to
described the forward martensitic transformation, and from
to
described the reverse martensitic transformation. The theoretically computed transformation temperatures (in orange in
Figure 14) could be validated, but for a few measurements the were located slightly higher than acquired measurement data.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the development of a self-regulating solar shading actuator by means of the thermal shape memory effect set a further milestone in applications driven by SMA. The actuator’s primary function as a sunshade has been demonstrated and validated. Particularly, the requirements were fulfilled on clear summer days.
However, future work should optimise the shading operation under varying sky conditions or on overcast days to avoid partial closure delays or even non-closure. This phenomenon was attributed to the thermal inertia in the solar collector, which impinged on the dynamic performance response of the SMA-wire.
The monitoring of SMA-temperatures revealed a gradual closing process of louvers could last, indicating a sluggish heating of the SMA-wire. While the system generally fulfilled the criteria, adjustments in SMA setpoint switching temperatures could enhance its dynamic response, especially in conditions of sudden high irradiation or partially cloudy situations. Lowering the SMA transformation temperatures, for example by lowering the tensile stress in the SMA-wire or changing the alloy composition, could improve the closing process but impair the opening process, particularly on warm nights. Anther potential solution to this issue could be to increase the efficiency of the solar collector.
The validation of simulation data with real-world measurements verified the thermal model for the developed solar collector. The system’s performance in the full-scale demonstrator validated its functionality, despite inherent variability in real-world conditions.
Despite challenges in directly measuring SMA-temperatures, the study outlines the correlation between the temperature data in the solar collector and louver positions. The observed patterns align well with theoretical results, validating the function of the SMA in driving the sunshade construction.
Lastly, the developed system showcases commendable performance under optimal conditions. Further investigations of the solar collector and SMA-wire, as well as adjustments in setpoint temperatures, can enhance the reliability and operational response across a broader range of environmental scenarios. The findings gained from this study to a contribute valuable knowledge to the field of adaptive building systems, emphasizing the importance of real-world validation for smart and responsive technical solutions. The outcomes and results gathered with the developed components under real boundary conditions can be used in future works for the development of new actuator systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Video S1: smartskinreal.mp4. Time lapse of the full-scale demonstrator at July 5 - 10, 2023.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; methodology, M.S. and I.N.; validation, M.S. and F.Z.; investigation, M.S., F.Z. and A.N.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, I.N.; visualization, M.S. and F.Z.; project administration, A.K., B.M. and W.D.; funding acquisition, I.N., B.M., A.K. and W.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung grant number FKZ: 03ZZ1042G. The APC was funded by Hochschulbibliothek of Leipzig University of Applied Sciences.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and supplementary materials.
Acknowledgments
In this section you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stelzmann, M.; Schreier, M.; Navarro de Sosa, I.; Schurig, M.; Syga, K.; Nemati, A. , Schlussbericht smartskinreal: Zwanzig20 – smart3 - Verbundvorhaben – SmertSkinReal – Entwicklung und Monitoring eines Verschattungssystems mit FGL-Steuerung; TP1: Ermittlung von Einflüssen auf Schalttemperaturen, Report, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro de Sosa, I., Smartskin - Entwicklung von selbstregulierenden Sonnenschutzkomponenten für die Gebäudehülle auf Basis des thermischen Formgedächtniseffektes : Teilprojekt: FGL-Aktorsystem : Akronym: S3-smartskin-VI : Schlussbericht, Report, 2017.
- Lagoudas, D.C. Shape memory alloys. Modeling and engineering applications; Springer: New York, NY, 2008; pp. 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro de Sosa, I.; Ruff, M.; Kirmse, S.; Kahnt, A.; Drossel, W.-G. Self-regulating Solar Shading System for the Building Envelope Based on Thermal Shape Memory Effect. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR 2018: 16th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 25–27. June 2018; pp. 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Großlamellen aus Aluminim für den Sonnenschutz Colt Solarfin – Colt. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.colt-info.de/grosslamellensystem-solarfin.html (accessed on 27. June 2023).
- EN 13659 Shutters and external venetian blinds – Performance requirements including safety, 2015.
- Duerig, T.W.; Melton, K.N.; Stöckel, D.; Wayman, C.M. Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 115–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Stalmans, R.; Delaey, L. Some aspects of the properties of NiTi shape memory alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 1997, 1-2, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghavani, J.; Auricchio, F.; Naghdabadi, R.; Sohrabpour, S. A 3-D phenomenological constitutive model for shape memory alloys under multiaxial loadings. International Journal of Plasticity 2010, 26, 976–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, V.; Hans, V. S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, R.; Pathak, S. K.; Singla, M.; Saini, R. P. A comprehensive study on the progressive development and applications of solar air heaters. Solar Energy 2021, 229, 112–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Leal, M. Jr.; Pino, L.; Barati, M.; Saint-Sulpice, L.; Daniel, L.; Chirani, S. A. Modeling of functional fatigue of SMA-based actuators under thermomechanical loading and Joule heating. International Journal of Fatigue 2024, 179, 108055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kang, S.; Lim, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Nam, T. emperature profiles in a Ti–45Ni–5Cu (at%) shape memory alloy developed by the Joule heating. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2010, 490(1-2), L28–L32.
- Song, H.; Kubica, E.; Gorbet, R. Resistance modelling of SMA wire actuators. In International Workshop Smart Materials Structures and NDT in Aerospace, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, November 2nd to 4th (2011). [NDT].
- IEC 61140 Protection against electric shock - Common aspects for installation and equipment, 2016.
- Carl, M.; Zhang, B.; Young, M.L. Texture and Strain Measurements from Bending of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Wires. Shape Memory and Superelasticity 2016, 2, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.V.; Choi, E.; Park, S.J. Investigating stress distribution of crimped SMA fibers during pullout behavior using experimental testing and a finite element model. Composite Structures 2021, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeifar, R.; DesRoches, R.; Yavari, A.; Gall, K. On superelastic bending of shape memory alloy beams. International Journal of Solids and Structures 2013, 50, 1664–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Transformation Temperature Predictions Through Computational Intelligence for NiTi-Based Shape Memory Alloys. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 2020, 6, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, K.; Mercier, O. The mechanical properties of NiTi-based shape memory alloys. Acta Metallurgica 1981, 2, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaissi, A.; Radhi, N.S.; Morad, K.F.; Hafiz, K.F.; Atiyah, A.A. Optimization of nickel content on some properties of (niti) shape memory alloy. Knowledge-Based Engineering and Sciences 2020 1 (1), 40-47.
- DIN 4108-2 Thermal protection and energy economy in buildings - Part 2: Minimum requirements to thermal insulation 2013.
- Da Silva, P. C.; Leal, V.; Andersen, M. Influence of shading control patterns on the energy assessment of office spaces. Energy and Buildings 2012, 50, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, L.; Heiselberg, P.; Bryn, I.; Johra, H. Solar shading control strategy for office buildings in cold climate. Energy and Buildings 2016 118, 316-328.
- Yun, G.; Park, D. Y.; Kim, K. S. Appropriate activation threshold of the external blind for visual comfort and lighting energy saving in different climate conditions. Building and Environment 2017, 113, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabadkani, A.; Roetzel, A.; Li, H. X.; Tsangrassoulis, A.; Attia, S. Analysis of the impact of automatic shading control scenarios on occupant’s comfort and energy load. Applied energy 2021, 294, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabadkani, A.; Roetzel, A.; Li, H. X.; Tsangrassoulis, A. A review of automatic control strategies based on simulations for adaptive facades. Building and Environment 2020, 175, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D. Y. Solar Thermal Collectors. In Principles of solar engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, 2022; pp. 119–204. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolai, A.; Scheffler, G.A.; Grunewald, J.; Plagge, R. An Efficient Numerical Solution Method and lmplementation for Coupled Heat, Moisture, and Salt Transport: The DELPHIN Simulation Program. In: Simulation of time dependent degradation of porous materials, Final report on Priority Program 1122, funded by the German Research Foundation DFG Franke, L., Deckelmann, G., Espinosa-Marzal, R., Eds., Cuvillier, Göttingen, Germany, 2009. pp. 85–100.
- Spekat, A. 2011: Aktualisierte und erweiterte Testreferenzjahre von Deutschland für mittlere, extreme und zukünftige Witterungsverhältnisse. Bundesamt für Bauwesen und Raumordnung (BBR) self-published, Offenbach, Germany, 2011; pp. 16–18.
- Karakoc, O.; Yegin, Y.; Ozdogan, M.; Salman, M.; Nagabandi, N.; Yegin, C.; Yurukcu, M.; Murat Sari, M. Smart and state-of-the-art materials in oil and gas industry. Sustainable Materials for Transitional and Alternative Energy 2021, 2, pp. 1–51.
- Nam, T. H.; Saburi, T.; Shimizu, K. Cu-Content Dependence of Shape Memory Characteristics in Ti–Ni–Cu Alloys. Materials Transactions, JIM 1990, 31, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frotscher, M.; Burow, J.; Schön, P.; Neuking, K.; Böckmann, R.; Eggeler, G. Characterization of the mechanical properties of ultra-fine grained NiTiCr-wires. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 2009, 40, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isalgue, A.; Torra, V.; Yawny, A.; Lovey, F. C. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2008, 91, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
A standard sunshade system was utilized in this development. The angular position of all louvers was coupled through a linkage rod. (a) depicts a 3D model of the sunshade construction system. (b) presents a sectional drawing with the labeling of various components. The illustration in (c) schematically demonstrates the intended application of the SMA.
Figure 1.
A standard sunshade system was utilized in this development. The angular position of all louvers was coupled through a linkage rod. (a) depicts a 3D model of the sunshade construction system. (b) presents a sectional drawing with the labeling of various components. The illustration in (c) schematically demonstrates the intended application of the SMA.
Figure 3.
3D model of the actuator concept.
Figure 3.
3D model of the actuator concept.
Figure 6.
Comparison of measured and simulated data of SMA-temperature. The measurements were made under outdoor climatic conditions on a full-scale thermal solar collector. The measured boundary conditions (outdoor temperature and solar radiation data) were implemented in the simulation model.
Figure 6.
Comparison of measured and simulated data of SMA-temperature. The measurements were made under outdoor climatic conditions on a full-scale thermal solar collector. The measured boundary conditions (outdoor temperature and solar radiation data) were implemented in the simulation model.
Figure 7.
The validated simulation model was used to calculate SMA-temperatures using climate data sets. Based on the vertical irradiation of the façade surface, the SMA-temperatures, at which the sunshade construction system should close or open, were calculated. The diagram shows the evaluation of these variables for a single day.
Figure 7.
The validated simulation model was used to calculate SMA-temperatures using climate data sets. Based on the vertical irradiation of the façade surface, the SMA-temperatures, at which the sunshade construction system should close or open, were calculated. The diagram shows the evaluation of these variables for a single day.
Figure 8.
Evaluation of the calculated SMA-temperatures as boxplot. Shown are data for temperatures at which the sunshade construction system should close (red) and reopen (blue). Two variants are compared: (a) the SMA wire temperatures at the time when the irradiation limit values are reached and (b) with a delay of 20 minutes after the values are reached.
Figure 8.
Evaluation of the calculated SMA-temperatures as boxplot. Shown are data for temperatures at which the sunshade construction system should close (red) and reopen (blue). Two variants are compared: (a) the SMA wire temperatures at the time when the irradiation limit values are reached and (b) with a delay of 20 minutes after the values are reached.
Figure 9.
Measurements to determine the resistance force for the closing of the sunshade construction system. In (a) the experimental setup with the connection of the load cell is presented. (b) shows an exemplary measurement data for the required torque to shift the louvers through the shaft by .
Figure 9.
Measurements to determine the resistance force for the closing of the sunshade construction system. In (a) the experimental setup with the connection of the load cell is presented. (b) shows an exemplary measurement data for the required torque to shift the louvers through the shaft by .
Figure 10.
Full-scale demonstrator of the self-regulating sun shading actuator, complete view (a) and detailed view with labeling of various components (b).
Figure 10.
Full-scale demonstrator of the self-regulating sun shading actuator, complete view (a) and detailed view with labeling of various components (b).
Figure 11.
Measurement data of the full-scale demonstrator with the irradiation and the louvre angle (measured and calculated from the irradiation threshold values). Data are shown over the course of three exemplary days (July 6 2023, August 6 2023 and August 11 2023).
Figure 11.
Measurement data of the full-scale demonstrator with the irradiation and the louvre angle (measured and calculated from the irradiation threshold values). Data are shown over the course of three exemplary days (July 6 2023, August 6 2023 and August 11 2023).
Figure 13.
Comparison of simulated SMA setpoint switching temperatures 20 min after reaching irradiation limits from the
Section 3.3 (left) and measured values from monitoring (right) of
(
a) and
(
b).
Figure 13.
Comparison of simulated SMA setpoint switching temperatures 20 min after reaching irradiation limits from the
Section 3.3 (left) and measured values from monitoring (right) of
(
a) and
(
b).
Figure 14.
Measured data of the temperature in the solar collector drawn over the louver angle in the warm period from June 1 to August 24, 2023.
Figure 14.
Measured data of the temperature in the solar collector drawn over the louver angle in the warm period from June 1 to August 24, 2023.
Table 1.
Defined irradiation limit values as variables for the control of the sunshade construction system.
Table 1.
Defined irradiation limit values as variables for the control of the sunshade construction system.
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
| Solar irradiation during the sunshade should close |
|
400 |
|
| Solar irradiation during the sunshade should open |
|
150 |
|
Table 2.
Defined SMA setpoint switching temperatures for the selection of the SMA.
Table 2.
Defined SMA setpoint switching temperatures for the selection of the SMA.
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
| Sunshade during the closing process |
|
45.7 |
°C |
| Sunshade during the opening process |
|
31.1 |
°C |
| Sunshade opening process is complete |
|
>20.0 |
°C |
Table 3.
Design parameters for the control of the sunshade construction system.
Table 3.
Design parameters for the control of the sunshade construction system.
| Parameter |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
| Length of the SMA-wire |
|
1.92 |
m |
| Actuator radius |
|
0.0343 |
m |
| SMA cross sectional |
|
1.81 |
|
| Weight force |
|
147.0 |
N |
| Resistance torque |
|
4.5 |
|
| Resistance force |
|
131.0 |
N |
| SMA tension |
|
71.4 |
|
| SMA strain |
|
2.9 |
% |
| SMA stress influence coefficient |
C |
0.226 |
|
| Martensite start temperature |
|
28.2 |
°C |
| Martensite finish temperature |
|
4.9 |
°C |
| Austenite start temperature |
|
26.3 |
°C |
| Austenite finish temperature |
|
43.6 |
°C |
| Martensite start temperature under tensile stress
|
|
44.3 |
°C |
| Martensite finish temperature under tensile stress
|
|
21.0 |
°C |
| Austenite start temperature under tensile stress
|
|
42.4 |
°C |
| Austenite finish temperature under tensile stress
|
|
59.7 |
° |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).