Submitted:
17 January 2024
Posted:
18 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
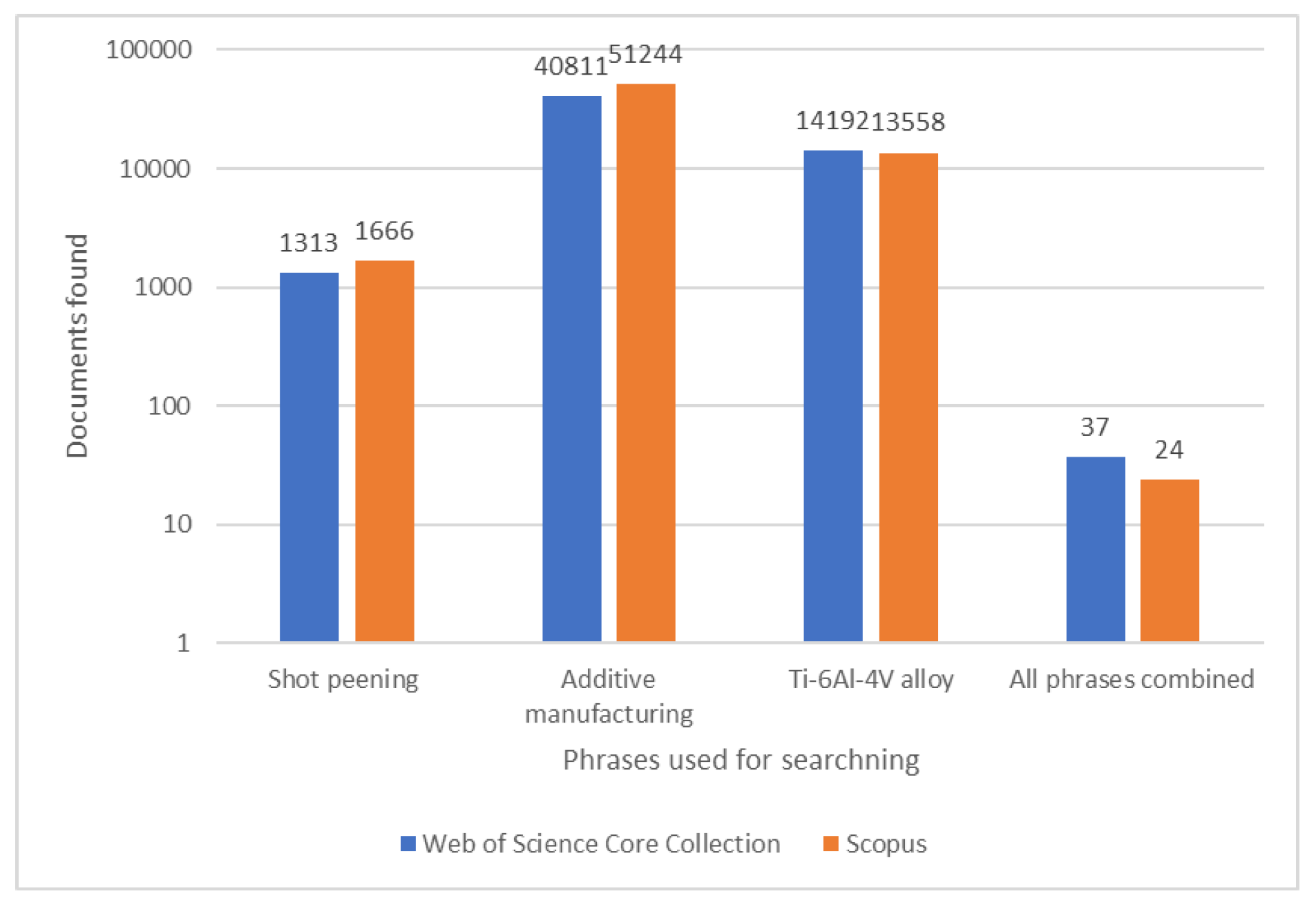
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Ti6Al4V Manufactured Using Conventional Methods and Additive Manufacturing Methods
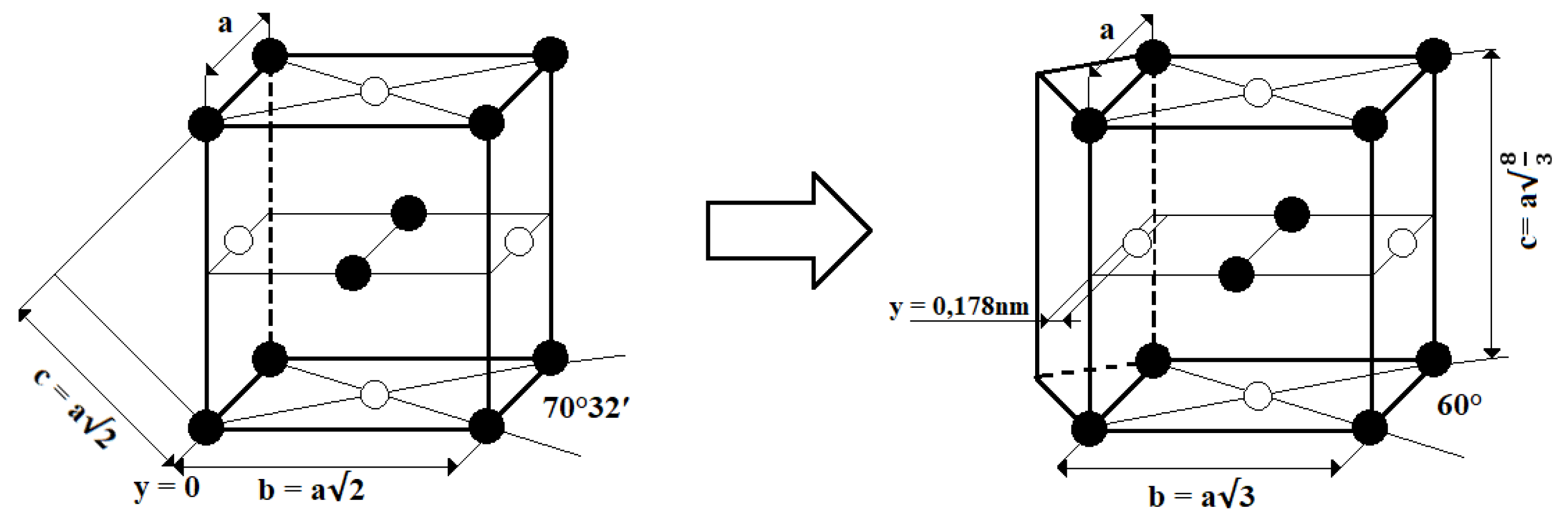
2.1. Microstructural Phases
2.2. Manufacturing Methods of Ti6Al4V Martensitic Structure
2.2.1. Subtractive Manufacturing
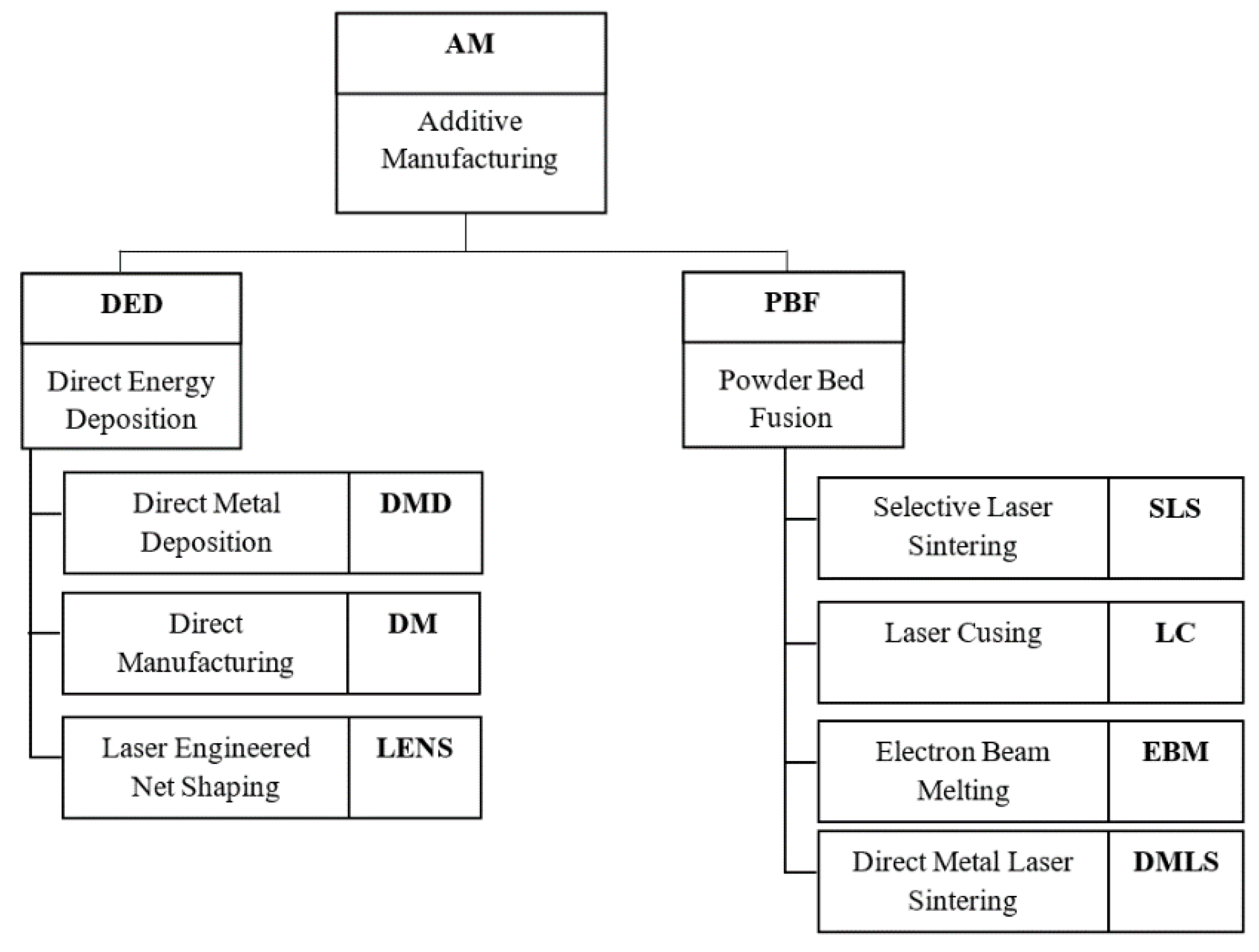
2.2.2. Additive Manufacturing
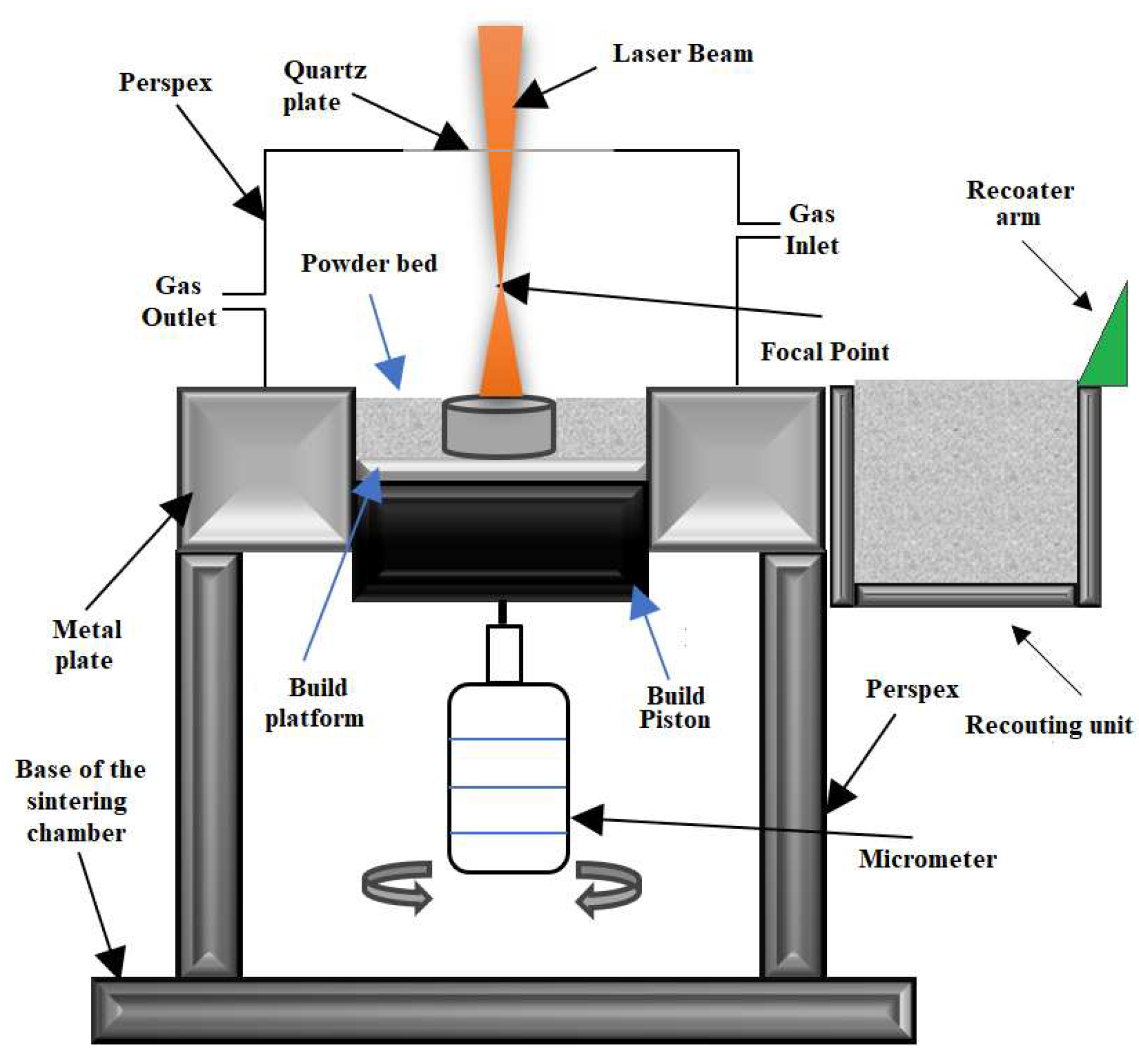
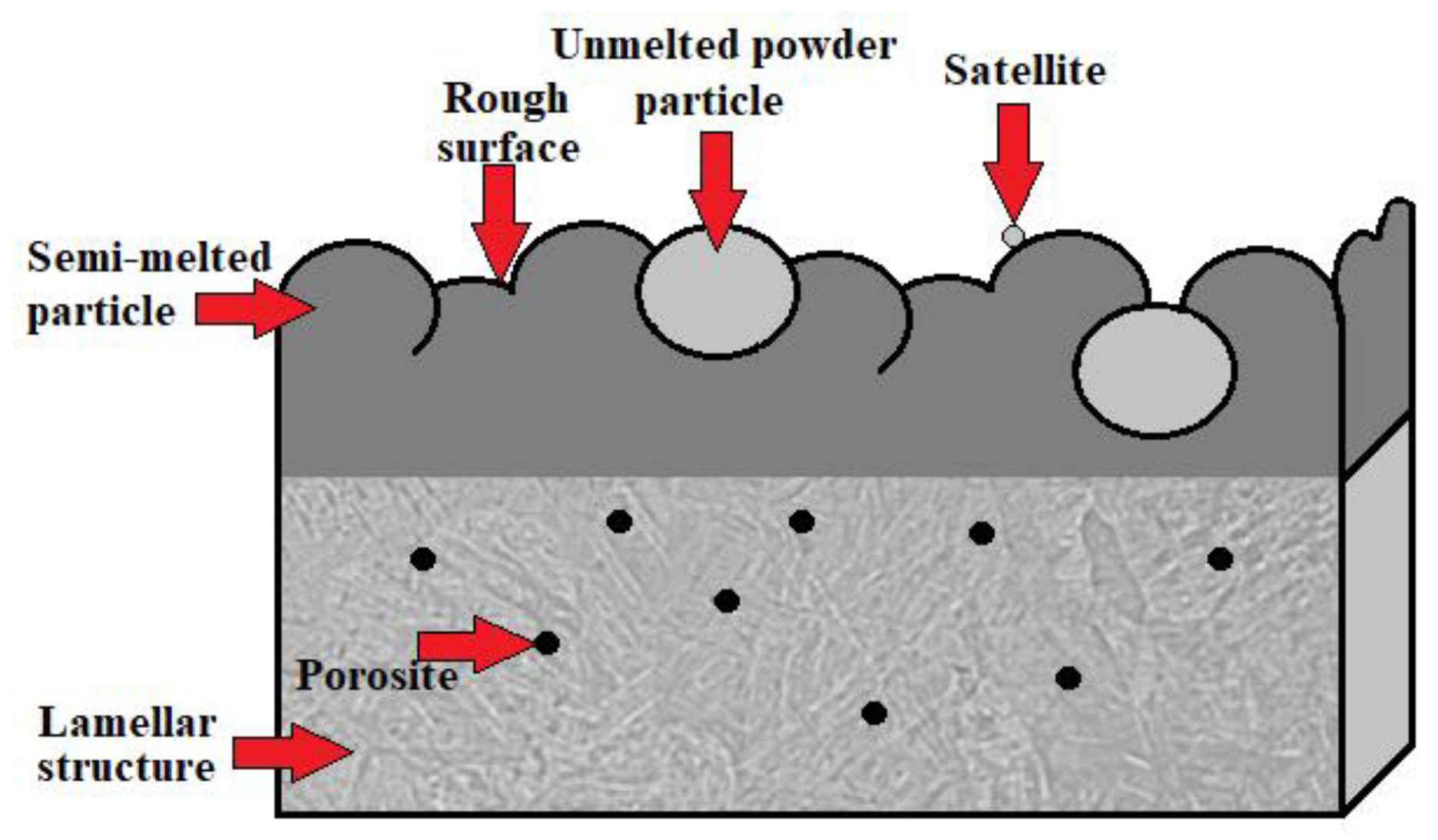
2.2.3. SLM—Selective Laser Melting
2.2.4. DMLS—Directive Metal Laser Sintering
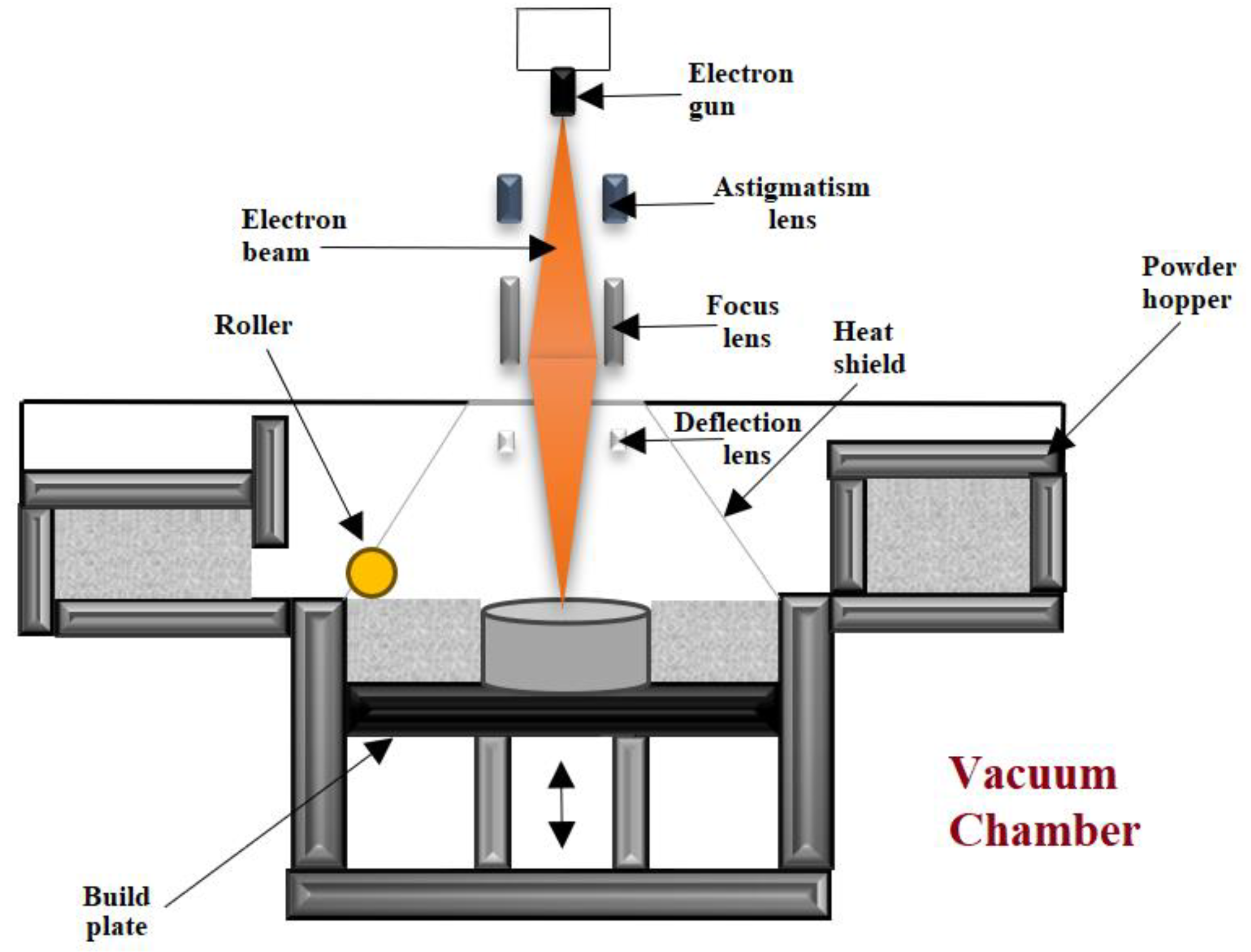
2.2.5. EBM—Electron Beam Melting
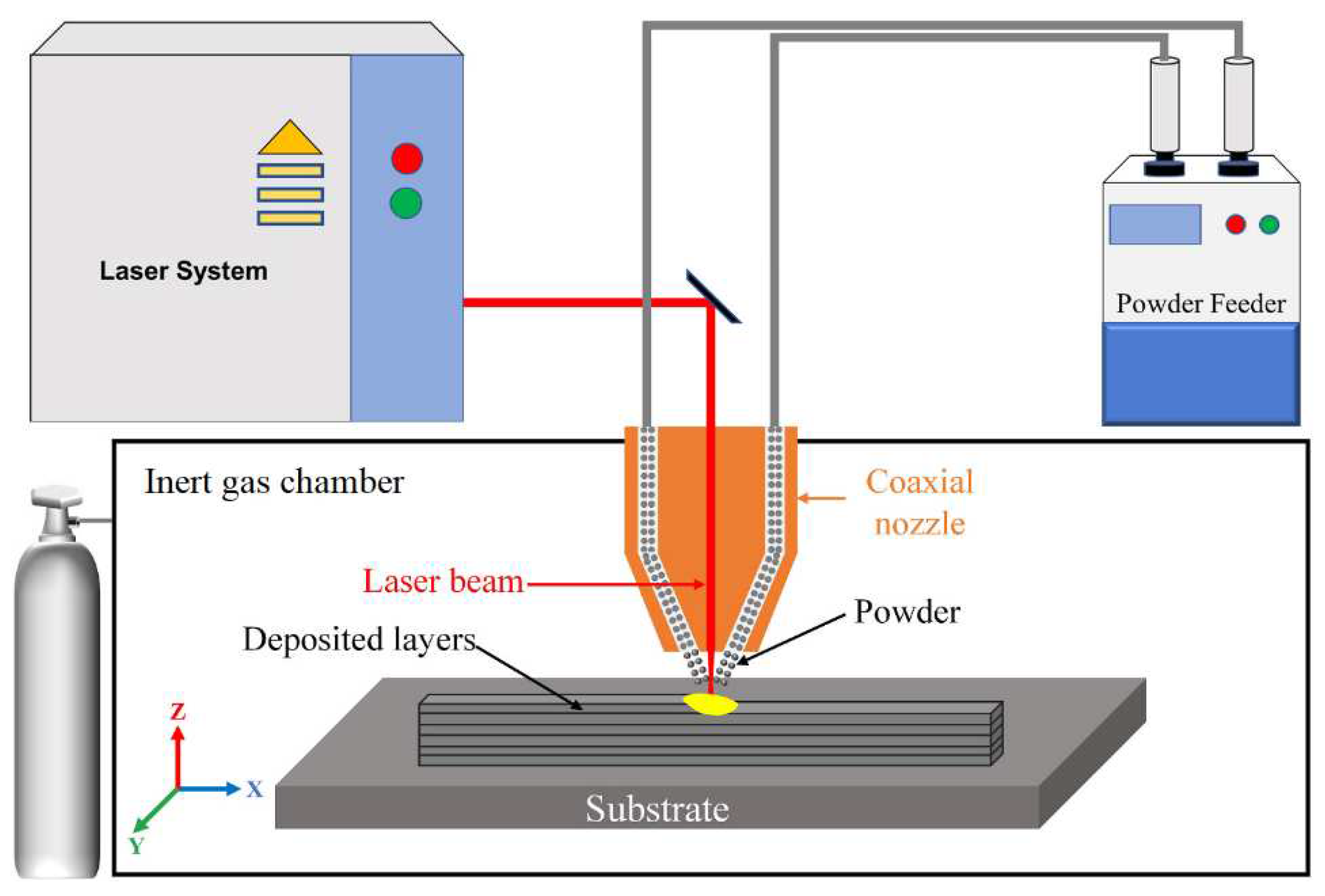
2.2.6. DED—Direct Energy Deposition Processes
3. Post-Process Surface Treatment Methods Applied to Modifying Ti6Al4V Surface Layer
3.1. Post-Processing after Additive Manufacturing
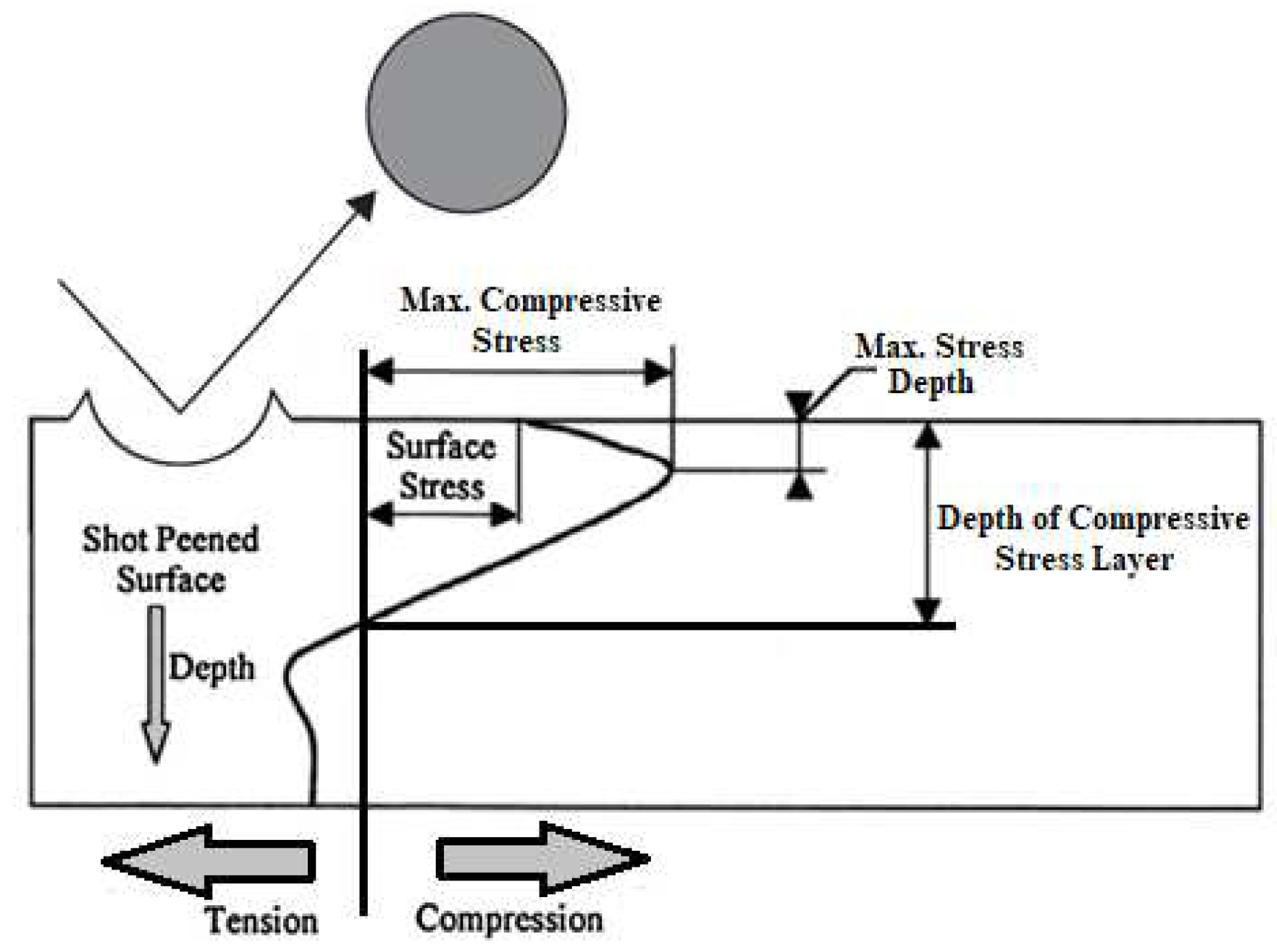
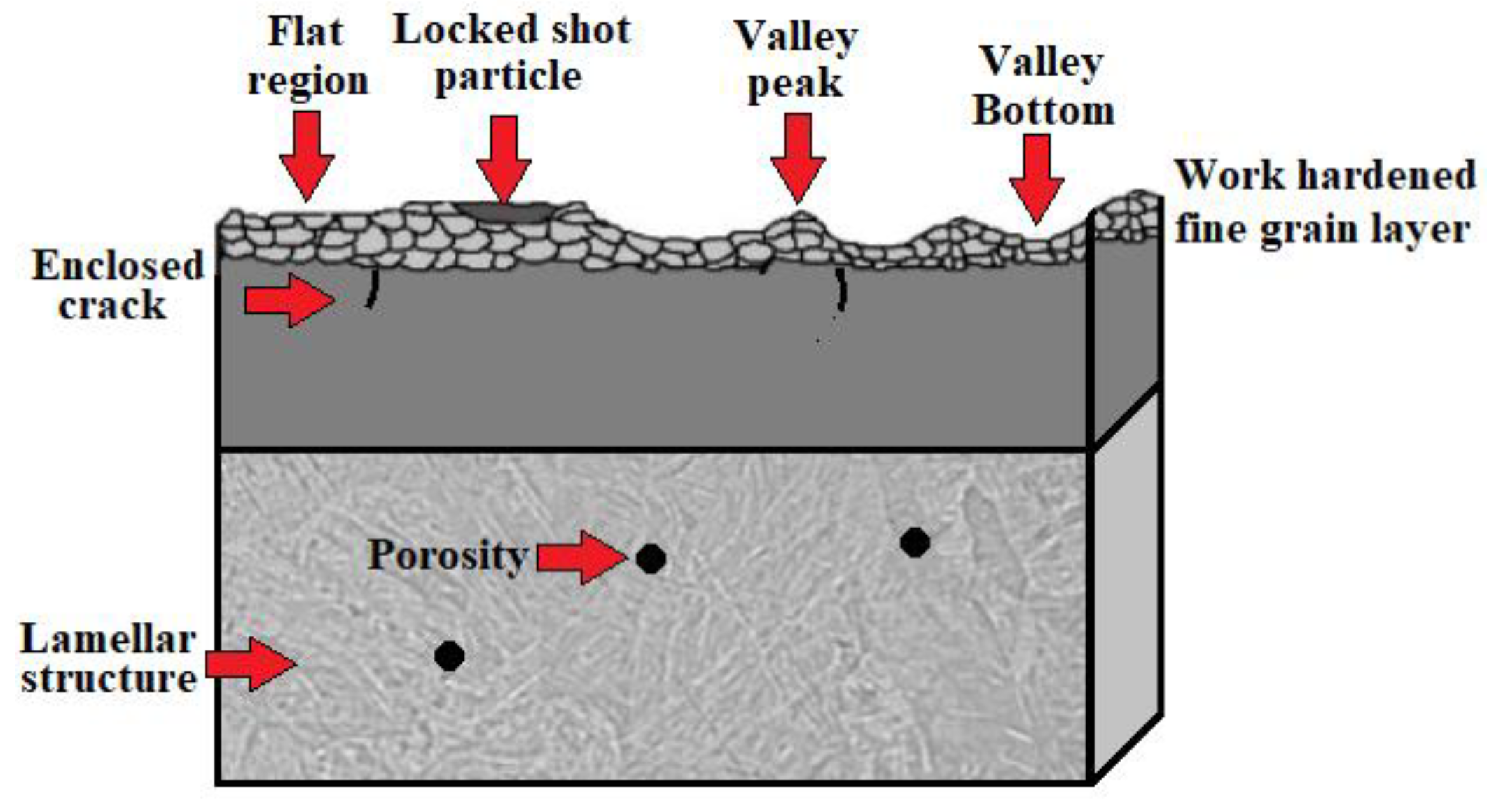
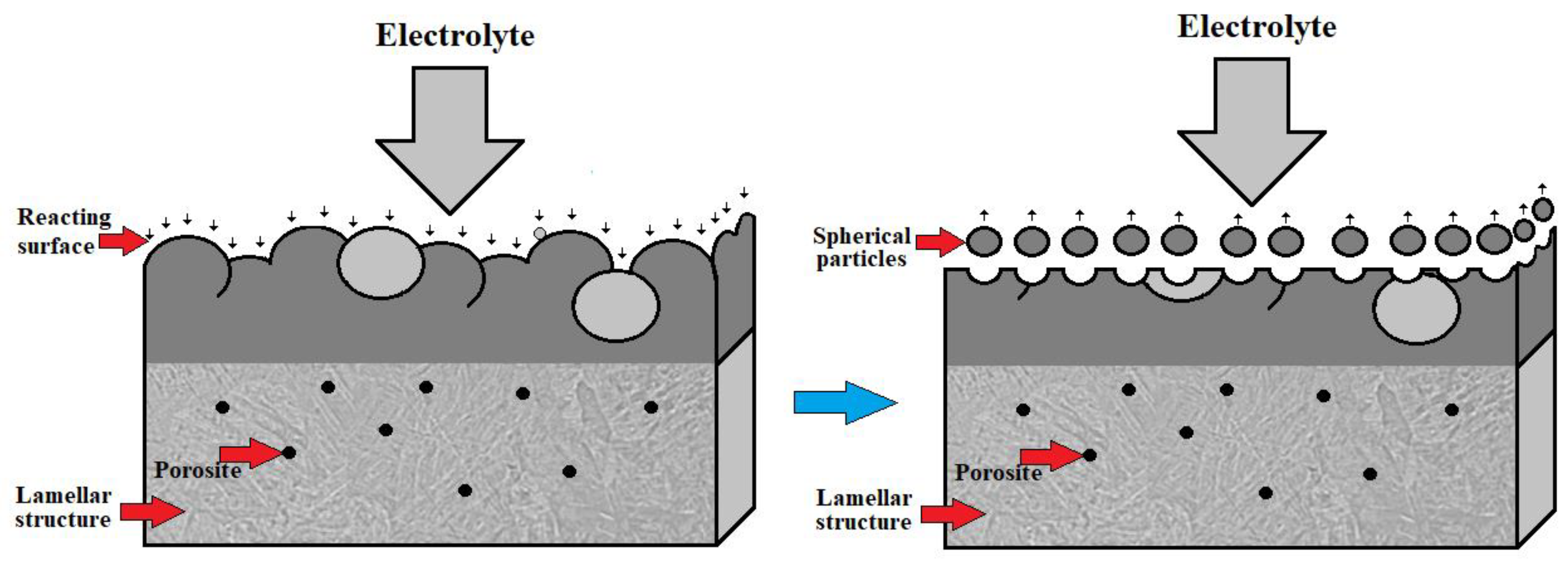
3.2. Shot Peening
- Grain refinement
- Increase in dislocation density
- Formation of passive layer
- Decrease in porosity
- Formation of compressive residual stresses
| Conditions | Current density, Icorr (mA/cm2) | Potential, Ecorr (mV) |
Polarization resistance Rp (kΩcm2) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 0,064 | -318,6 | 2291 | |
| Untreated mechanically polished |
0,067 | -141,1 | 328,5 | |
| Steel CrNi | 0.2 MPa | 0,421 | -173,5 | 210,5 |
| 0.3 MPa | 0,561 | -207,4 | 138,8 | |
| 0.4 MPa | 0,682 | -337,1 | 81,2 | |
| Nuts | 0.2 MPa | 0,124 | -106,6 | 346,5 |
| 0.3 MPa | 0,275 | -228,5 | 367,4 | |
| 0.4 MPa | 1,469 | -279,2 | 349,5 | |
| Ceramic Beads | 0.2 MPa | 0,026 | -123,8 | 170,8 |
| 0.3 MPa | 0,045 | -151,4 | 206,2 | |
| 0.4 MPa | 0,063 | -174,3 | 432,8 | |
3.3. Electropolishing
| Conditions | Current density of treatment (mA·cm-2) | Ra (nm) | Pit diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | - | 321 | - |
| Electrochemically etched |
5 | 651 | 25 |
| 10 | 967 | 24 | |
| 15 | 504 | 27 |
| Roughness | Microstructure at various cooling medium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Electropolishing 100s | Electropolishing 200s | Electropolishing 300s | Mechanical #1000SiC |
Mechanical #1500SiC |
|
| Micro [nm] | 120,05 ± 7,89 | 58,72 ± 3,68 | 12,63 ± 0,81 0,75 ± 0,05 |
10,33 ± 1,14 | 98,30 ± 3,79 | 86,42 ± 2,05 |
| Macro [µm] | 2,34 ± 0,07 | 1,68 ± 0,02 | 0,68 ± 0,03 | 2,04 ± 0,03 | 1,82 ± 0,09 | |
| Temperature | Roughness | ||
| Ra (nm) | Rms (nm) | Rz (nm) | |
| 7°C | 7,4 | 10,0 | 39,7 |
| 18°C | 6,1 | 8,1 | 27,5 |
| 25°C | 6,4 | 8,1 | 26,6 |
4. Properties of Ti6Al4V Manufactured Using Conventional Methods and Additive Manufacturing Methods
| Surface treatment processes |
Ecorr [mV] | Icorr [µA·cm-2] | Rp [kΩ·cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shot peening, sandblasting | -266 | 0,047 | 551 |
| Shot peening, electropolishing | -95 | 0,053 | 489 |
| Shot peening, mechanical polishing, electropolishing | -172 | 0,069 | 377,15 |
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, C.; Hu, B.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S. Titanium Alloy Production Technology, Market Prospects and Industry Development. Materials & Design 2011, 32, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y.C. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Review. Materials & Design 2019, 164, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushp, P.; Dasharath, S.M.; Arati, C. Classification and Applications of Titanium and Its Alloys. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, R.; Reinders, J.; Gibmeier, J.; Kretzer, J.P. Fatigue Strengthening of an Orthopedic Ti6Al4V Alloy: What Is the Potential of a Final Shot Peening Process? In Biomaterials and Medical Tribology; Elsevier, 2013; pp. 217–237. ISBN 978-0-85709-017-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.; Barrack, R.; Clemow, A. Corrosion and Wear at the Modular Interface of Uncemented Femoral Stems. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume 1994, 76-B, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzer, J.P.; Jakubowitz, E.; Krachler, M.; Thomsen, M.; Heisel, C. Metal Release and Corrosion Effects of Modular Neck Total Hip Arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 2009, 33, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lan, P.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Li, X.-K.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, C.-F.; Zheng, X.-B.; Guo, Z. Surface Characterization and in Vivo Performance of Plasma-Sprayed Hydroxyapatite-Coated Porous Ti6Al4V Implants Generated by Electron Beam Melting. Surface and Coatings Technology 2015, 283, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čapek, J.; Machová, M.; Fousová, M.; Kubásek, J.; Vojtěch, D.; Fojt, J.; Jablonská, E.; Lipov, J.; Ruml, T. Highly Porous, Low Elastic Modulus 316L Stainless Steel Scaffold Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 69, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Rack, H.J. Titanium Alloys in Total Joint Replacement—a Materials Science Perspective. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, G.; Araújo, A.; Bartolomeu, F.; Buciumeanu, M.; Carvalho, O.; Souza, J.C.M.; Silva, F.S.; Henriques, B. Design of Ti6Al4V-HA Composites Produced by Hot Pressing for Biomedical Applications. Materials & Design 2016, 108, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, D.; Luo, S.N.; Xiao, L.; Lu, W.; Zhang, S. Effect of Rotationally Accelerated Shot Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of a Metastable β Titanium Alloy. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2021, 75, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Torresani, E.; Leoni, M.; Fontanari, V.; Bandini, M.; Pederzolli, C.; Potrich, C. The Effect of Post-Sintering Treatments on the Fatigue and Biological Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V ELI Parts Made by Selective Laser Melting. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2017, 71, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, T.; Jaskari, M.; Järvenpää, A. Surface Roughness Improvement of Pbf-Lb Manufactured 316l with Dry Electropolishing. KEM 2023, 972, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Shim, H.-S.; Seo, M.J.; Hur, D.H. Corrosion Control of Alloy 690 by Shot Peening and Electropolishing under Simulated Primary Water Condition of PWRs. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Xin, R.; Jin, X.; Gao, S.; He, B.; Rong, Y.; Min, N. Effects of Laser Shock Peening on Microstructure and Properties of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy Fabricated via Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2020, 13, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gao, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, X. Effect of Solid-State Phase Transformation on Residual Stress of Selective Laser Melting Ti6Al4V. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2021, 819, 141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.; Huynh, T.; Zhou, L.; Hyer, H.; Mehta, A.; Imholte, D.D.; Woolstenhulme, N.E.; Wachs, D.M.; Sohn, Y. Mechanical Behavior Assessment of Ti-6Al-4V ELI Alloy Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2021, 11, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, M.; Baran-Sadleja, A.; Sieniawski, J.; Wierzbinska, M.; Gancarczyk, K. Decomposition of Deformed α ′( α ″) Martensitic Phase in Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Materials Science and Technology 2019, 35, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Singh, Y.P. Additive Manufacturing Techniques Used for Preparation of Scaffolds in Bone Repair and Regeneration. In Advances in Additive Manufacturing Artificial Intelligence, Nature-Inspired, and Biomanufacturing; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 103–127. ISBN 978-0-323-91834-3. [Google Scholar]
- Walczak, M.; Pasierbiewicz, K.; Szala, M. Effect of Ti6Al4V Substrate Manufacturing Technology on the Properties of PVD Nitride Coatings. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2022, 142, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Rack, H.J. Phase Transformations during Cooling in A+β Titanium Alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A 1998, 243, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoniyi, P.O.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Mahamood, R.M. Heat Treatments of Ti6Al4V Alloys for Industrial Applications: An Overview. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1107, 012094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, S.; Avcu, E.; Karakulak, E.; Yamanoglu, R.; Zeren, M.; Sinmazcelik, T. Effect of Heat Treatment on Erosive Wear Behaviour of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Materials Science and Technology 2013, 29, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan Soundararajan, S.; Vishnu, J.; Manivasagam, G.; Rao Muktinutalapati, N. Processing of Beta Titanium Alloys for Aerospace and Biomedical Applications. In Titanium Alloys - Novel Aspects of Their Processing [Working Title]; IntechOpen, 2018.
- Vrancken, B.; Thijs, L.; Kruth, J.-P.; Van Humbeeck, J. Heat Treatment of Ti6Al4V Produced by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2012, 541, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.D.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D. Effect of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Ti–6Al–4V ELI Alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2009, 506, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Galarraga, H.; Lados, D.A. Microstructure, Static Properties, and Fatigue Crack Growth Mechanisms in Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing: LENS and EBM. Engineering Failure Analysis 2016, 69, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, M.; Greer, P.; Owen, K.; Lilly, G.; Murr, L.E.; Gaytan, S.M.; Martinez, E.; Okabe, T. Evaluation of Titanium Alloys Fabricated Using Rapid Prototyping Technologies—Electron Beam Melting and Laser Beam Melting. Materials 2011, 4, 1776–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaro, T.; Colin, C.; Bartout, J.D. As-Fabricated and Heat-Treated Microstructures of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting. Metall Mater Trans A 2011, 42, 3190–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zou, J.; Yang, H. Wear Performance of Metal Parts Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: A Literature Review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2018, 19, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, J.; Herzog, D.; Emmelmann, C. Design Guidelines for Laser Additive Manufacturing of Lightweight Structures in TiAl6V4. Journal of Laser Applications 2015, 27, S14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.K.; Banerjee, M.; Sharma, A.; Singh, J.; Bansal, A.; Gupta, M.K.; Khanna, N.; Shahi, A.S.; Goyal, D.K. Selective Laser Melting of Ti6Al4V Alloy: Process Parameters, Defects and Post-Treatments. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2021, 64, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, D.; Palanisamy, S.; Liu, Q.; Dargusch, M.S. Mechanical Properties and Deformation Mechanisms of Martensitic Ti6Al4V Alloy Processed by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Water Quenching. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2022, 839, 142817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yin, Q.; Liu, W.; Shen, S. Dynamics of the Laser–Powder Interaction in the Ti6Al4V Powder Feeding Process of Laser-Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2023, 27, 6376–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Zou, J.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Qi, H. Influence of Laser Post-Processing on Pore Evolution of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2020, 818, 152845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Zhang, T.; Ryder, M.A.; Lados, D.A. A Review of the Fatigue Properties of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. JOM 2018, 70, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, W.S.W.; Kamariah, M.S.I.N.; Muhamad, N.; Ghani, S.A.C.; Ahmad, F.; Mohamed, Z. A Review of Powder Additive Manufacturing Processes for Metallic Biomaterials. Powder Technology 2018, 327, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcisto, J.; Enriquez, A.; Garcia, H.; Hinkson, S.; Steelman, T.; Silverman, E.; Valdovino, P.; Gigerenzer, H.; Foyos, J.; Ogren, J.; et al. Tensile Properties and Microstructures of Laser-Formed Ti-6Al-4V. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 2011, 20, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, M.; Salem, A.; Beuth, J.; Harrysson, O.; Lewandowski, J.J. Overview of Materials Qualification Needs for Metal Additive Manufacturing. JOM 2016, 68, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, M.; Tse, Y.Y.; Tuck, C. Effect of the Build Orientation on the Mechanical Properties and Fracture Modes of SLM Ti–6Al–4V. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2014, 616, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, L.; Gaur, V. On Study of Process Induced Defects-Based Fatigue Performance of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy. Additive Manufacturing 2022, 60, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, B.; Maj, P.; Sitek, R.; Buhagiar, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.; Święszkowski, W. Laser and Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing Methods of Fabricating Titanium Bone Implants. Applied Sciences 2017, 7, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, K. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V/ B4C Titanium Matrix Composite Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2023, 23, 1934–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Magalini, E.; Robotti, P.; Molinari, A.; Höges, S.; Wissenbach, K. Ductility of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting of Prealloyed Powders. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2010, 16, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, A.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A.; Bucciotti, F.; Facchini, L. Comparison between Wrought and EBM Ti6Al4V Machinability Characteristics. KEM 2014, 611–612, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, K.; Abdullah, M.; Mahmood, M.A. A State-of-the-Art Direct Metal Laser Sintering of Ti6Al4V and AlSi10Mg Alloys: Surface Roughness, Tensile Strength, Fatigue Strength and Microstructure. Optics & Laser Technology 2021, 143, 107366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolewska, K.; Ligaj, B.; Boroński, D. Strain Analysis of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Samples Using Digital Image Correlation. Materials 2020, 13, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzanová, A.; Ižaríková, G.; Brezinová, J.; Živčák, J.; Draganovská, D.; Hudák, R. Influence of Build Orientation, Heat Treatment, and Laser Power on the Hardness of Ti6Al4V Manufactured Using the DMLS Process. Metals 2017, 7, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Soni, M. Direct Metal Laser Sintering of TI6Al4V Alloy for Patient-Specific Temporo Mandibular Joint Prosthesis and Implant. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 38, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzejewska, Ż.A. Effect of Laser Energy Density, Internal Porosity and Heat Treatment on Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Ti6Al4V Alloy Obtained with DMLS Technology. Materials 2019, 12, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, L.; Verhaeghe, F.; Craeghs, T.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Kruth, J.-P. A Study of the Microstructural Evolution during Selective Laser Melting of Ti–6Al–4V. Acta Materialia 2010, 58, 3303–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, M. Martensite Formation and Decomposition during Traditional and AM Processing of Two-Phase Titanium Alloys—An Overview. Metals 2021, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeu, F.; Gasik, M.; Silva, F.S.; Miranda, G. Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A Review Focused on the Processing and Microstructural Parameters Influence on the Final Properties. Metals 2022, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancken, B.; Buls, S.; Kruth, J.; Humbeeck, J.V. Preheating of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium; Venkatesh, V., Pilchak, A.L., Allison, J.E., Ankem, S., Boyer, R., Christodoulou, J., Fraser, H.L., Imam, M.A., Kosaka, Y., Rack, H.J., Chatterjee, A., Woodfield, A., Eds.; Wiley, 2016; pp. 1269–1277. ISBN 978-1-119-28326-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kogo, B.; Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Chizari, M.; Reza Kashyzadeh, K.; Ghorbani, S. An Experimental Analysis to Determine the Load-Bearing Capacity of 3D Printed Metals. Materials 2022, 15, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.H.; Moylan, S.P. Literature Review of Metal Additive Manufacturing Defects; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, 2018; p. NIST AMS 100-16. [Google Scholar]
- Polozov, I.; Gracheva, A.; Popovich, A. Interface Characterization of Bimetallic Ti-6Al-4V/Ti2AlNb Structures Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2022, 15, 8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, V.; Doquet, V.; Persent, E.; Mareau, C.; Roguet, E.; Kittel, J. Surface versus Internal Fatigue Crack Initiation in Steel: Influence of Mean Stress. International Journal of Fatigue 2016, 82, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzkermani, A.; Sadowski, M.; Ladani, L. Direct Metal Laser Melting of Inconel 718: Process Impact on Grain Formation and Orientation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2018, 736, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Finite Element Simulation and Experimental Validation of Distortion and Cracking Failure Phenomena in Direct Metal Laser Sintering Fabricated Component. Additive Manufacturing 2017, 16, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Iyer, A.; Promoppatum, P.; Yao, S.-C. Numerical Modeling of the Thermal Behavior and Residual Stress in the Direct Metal Laser Sintering Process of Titanium Alloy Products. Additive Manufacturing 2017, 14, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Das, A.K. Issues in Fabrication of 3D Components through DMLS Technique: A Review. Optics & Laser Technology 2021, 139, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.G. Rapid Manufacturing and Tooling. In Design and Manufacturing of Plastics Products; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 381–456. ISBN 978-0-12-819775-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Mandal, V.; Kumar, V.; Das, A.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Development of TiN Particulates Reinforced SS316 Based Metal Matrix Composite by Direct Metal Laser Sintering Technique and Its Characterization. Optics & Laser Technology 2017, 97, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Deng, X. Melting and Resolidification of Direct Metal Laser Sintering with Multiscale Nonequilibrium Model. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer 2019, 33, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzejewska, Ż.A.; Hudák, R.; Sidun, J. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of DMLS Ti6Al4V Alloy Dedicated to Biomedical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebianian, M.; Aghaie, S.; Razavi Jafari, N.; Elmi Hosseini, S.; Pereira, A.; Fernandes, F.; Farbakhti, M.; Chen, C.; Huo, Y. A Review of the Metal Additive Manufacturing Processes. Materials 2023, 16, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Yildiz, M.; Secer, R.O.; Sen, C.; Bilgin, G.M.; Orhangul, A.; Akbulut, G.; Javidrad, H.; Koc, B. Fabrication of Electron Beam Melted Titanium Aluminide: The Effects of Machining Parameters and Heat Treatment on Surface Roughness and Hardness. Metals 2023, 13, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K. Application of Electron Beam Melting (EBM) in Additive Manufacturing of an Impeller. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Progress in Additive Manufacturing; Research Publishing Services, 2014; pp. 327–332.
- Cho, K.; Kawabata, H.; Hayashi, T.; Yasuda, H.Y.; Nakashima, H.; Takeyama, M.; Nakano, T. Peculiar Microstructural Evolution and Tensile Properties of β-Containing γ-TiAl Alloys Fabricated by Electron Beam Melting. Additive Manufacturing 2021, 46, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.A.; Khanna, V.; Gupta, P. Metal Matrix Composites: Fabrication, Production, and 3D Printing (Vol. 1), 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2022; ISBN 978-1-00-319489-7. [Google Scholar]
- Trevisan, F.; Calignano, F.; Aversa, A.; Marchese, G.; Lombardi, M.; Biamino, S.; Ugues, D.; Manfredi, D. Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys in the Biomedical Field: Processes, Properties and Applications. Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials 2018, 16, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, N.; Fatemi, A. Defects in Additive Manufactured Metals and Their Effect on Fatigue Performance: A State-of-the-Art Review. Progress in Materials Science 2021, 117, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G.K.L.; Jarfors, A.E.W.; Bi, G.; Zheng, H.Y. Porosity Formation and Gas Bubble Retention in Laser Metal Deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 97, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabe, N.; Quinn, T. Effects of Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) Fabricated Using Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Part 1: Distance from Build Plate and Part Size. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2013, 573, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, R.; Narra, S.P.; Montgomery, C.; Beuth, J.; Rollett, A.D. Synchrotron-Based X-Ray Microtomography Characterization of the Effect of Processing Variables on Porosity Formation in Laser Power-Bed Additive Manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V. JOM 2017, 69, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjatzadeh, S.M.H.; Parab, N.D.; Guo, Q.; Qu, M.; Xiong, L.; Zhao, C.; Escano, L.I.; Fezzaa, K.; Everhart, W.; Sun, T.; et al. Direct Observation of Pore Formation Mechanisms during LPBF Additive Manufacturing Process and High Energy Density Laser Welding. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 2020, 153, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabe, N.; Gnäupel-Herold, T.; Quinn, T. Fatigue Properties of a Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) Fabricated via Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Effects of Internal Defects and Residual Stress. International Journal of Fatigue 2017, 94, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandell, V.; Hansson, T.; Roychowdhury, S.; Månsson, T.; Delin, M.; Åkerfeldt, P.; Antti, M.-L. Defects in Electron Beam Melted Ti-6Al-4V: Fatigue Life Prediction Using Experimental Data and Extreme Value Statistics. Materials 2021, 14, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.S.; Zaman, S.; Dantzler, J.Z.R.; Leyva, D.H.; Mahmud, M.S.; Ramirez, J.M.; Gomez, S.G.; Lin, Y. 3D Printed Integrated Sensors: From Fabrication to Applications—A Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biserova-Tahchieva, A.; Biezma-Moraleda, M.V.; Llorca-Isern, N.; Gonzalez-Lavin, J.; Linhardt, P. Additive Manufacturing Processes in Selected Corrosion Resistant Materials: A State of Knowledge Review. Materials 2023, 16, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Mazumder, S.; Jin, Y.; Squires, B.; Sofield, M.; Pantawane, M.V.; Dahotre, N.B.; Neogi, A. A Review of Diagnostics Methodologies for Metal Additive Manufacturing Processes and Products. Materials 2021, 14, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, B.; Babu, S.; Jared, B. Additive Manufacturing Technology. In Science, Technology and Applications of Metals in Additive Manufacturing; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 11–53. ISBN 978-0-12-816634-5. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, M.; Mehrabi, H.; Naveed, N. An Overview of Modern Metal Additive Manufacturing Technology. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2022, 84, 1001–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, A.; Moridi, A. State of the Art in Directed Energy Deposition: From Additive Manufacturing to Materials Design. Coatings 2019, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Froes, F.H. The Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys. In Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys; Elsevier, 2016; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0-12-804782-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ye, Z.; Cao, W.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, F. Microstructure and Properties of (Diamond + TiC) Reinforced Ti6Al4V Titanium Matrix Composites Manufactured by Directed Energy Deposition. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2024, 28, 3110–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, B.E.; Palmer, T.A.; Beese, A.M. Anisotropic Tensile Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Components Fabricated with Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing. Acta Materialia 2015, 87, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Ravi, G.A.; Dance, C.; Ranson, A.; Dilworth, S.; Attallah, M.M. Fabrication of Large Ti–6Al–4V Structures by Direct Laser Deposition. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2015, 629, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, N.; Bordonaro, G.; Ferro, P.; Torgersen, J.; Berto, F. Porosity Effect on Tensile Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Specimens Produced by Laser Engineered Net Shaping Technology. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science 2021, 235, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, Y.; Lee, S.; Seo, S.-M.; Yeom, J.; Kim, S.E.; Kang, N.; Hong, J. Effects of Cr and Fe Addition on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Ti–6Al–4V Prepared by Direct Energy Deposition. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlizky, D.; Das, M.; Zheng, B.; Vyatskikh, A.L.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Schoenung, J.M.; Lavernia, E.J.; Eliaz, N. Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Additive Manufacturing: Physical Characteristics, Defects, Challenges and Applications. Materials Today 2021, 49, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Qin, P.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhang, L.C. Advances in Additively Manufactured Titanium Alloys by Powder Bed Fusion and Directed Energy Deposition: Microstructure, Defects, and Mechanical Behavior. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2024, 183, 32–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, S. Effect of Defects on Environment-Assisted Fracture (EAF) Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Fabricated by Direct Energy Deposition (DED). Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2022, 20, 4365–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleh, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Revilla, R.I.; Chao, Q.; Haghdadi, N.; Hughes, A.E.; Xu, W.; De Graeve, I.; Qian, M.; Gibson, I.; et al. Heat Treatment for Metal Additive Manufacturing. Progress in Materials Science 2023, 133, 101051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Zhao, C.; He, Y.; Reza Ghiaasiaan, S.; Shi, B.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N.; Wu, Z.; Kouraytem, N.; Sun, T.; et al. Defects and Anomalies in Powder Bed Fusion Metal Additive Manufacturing. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2022, 26, 100974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świetlicki, A.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Shot Peening on Corrosion Resistance of Additive Manufactured 17-4PH Steel. Materials Science-Poland 2022, 40, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M.; Korga, A.; Iwan, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Shot Peening on the Mechanical Properties and Cytotoxicity Behaviour of Titanium Implants Produced by 3D Printing Technology. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E.; Abakay, E.; Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Çalım, E.; Gökalp, İ.; Iakovakis, E.; Koç, F.G.; Yamanoglu, R.; Akıncı, A.; Guney, M. Corrosion Behavior of Shot-Peened Ti6Al4V Alloy Produced via Pressure-Assisted Sintering. Coatings 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M. Effect of the shot peening on surface properties and tribological performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by means of DMLS technology. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.K.C.; Sha, W.; Ramanaiah, N.; Krishnaiah, A. Effect of Shotpeening on Sliding Wear and Tensile Behavior of Titanium Implant Alloys. Materials & Design (1980-2015) 2014, 56, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.N.; Xu, H. The Effect of Nanostructured Surface Layer on the Fatigue Behaviors of a Carbon Steel. Applied Surface Science 2009, 255, 3811–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lei, L.; Sun, L. Effect of Shot Peening on the Fatigue Resistance of Laser Surface Melted 20CrMnTi Steel Gear. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2015, 629, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lei, L.; Sun, L. Influence of Different Combined Severe Shot Peening and Laser Surface Melting Treatments on the Fatigue Performance of 20CrMnTi Steel Gear. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2016, 658, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, V.; Hashemi, B.; Rezaee Yazdi, M. The Effect of Shot Peening on Fatigue and Corrosion Behavior of 316L Stainless Steel in Ringer’s Solution. Surface and Coatings Technology 2010, 204, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Gao, K. Research Progress of Surface Treatment Technologies on Titanium Alloys: A Mini Review. Coatings 2023, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, C.; Lu, W. The Influence of Shot Peening on the Surface Properties of (TiB+TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V. Applied Surface Science 2013, 280, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, C.; Lu, W.; Zhan, K.; Chen, Y. Investigation on the Residual Stress and Microstructure of (TiB+TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V Composite after Shot Peening. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2011, 528, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit-Renaud, F. Optimization of the Shot Peening Parameters. In Shot Peening; Wagner, L., Ed.; Wiley, 2003; pp. 119–129. ISBN 978-3-527-60658-0. [Google Scholar]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M.; Klepka, T.; Pasierbiewicz, K. Effect of the Shot Peening on Surface Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Produced by Means of DMLS Technology. Eksploatacja i Niezawodność – Maintenance and Reliability 2019, 21, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M. The Effect of Shot Peening on the Corrosion Behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Made by DMLS. Advances in Materials Science 2018, 18, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongtrakulkij, G.; Khantachawana, A.; Kondoh, K. Effects of Media Parameters on Enhance Ability of Hardness and Residual Stress of Ti6Al4V by Fine Shot Peening. Surfaces and Interfaces 2020, 18, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelliti, S.; Richard, C.; Retraint, D.; Roland, T.; Chemkhi, M.; Demangel, C. Effect of Surface Nanocrystallization on the Corrosion Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy. Surface and Coatings Technology 2013, 224, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, Y.; Komotori, J. Effect of Micro Ploughing during Fine Particle Peening Process on the Microstructure of Metallic Materials. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2009, 209, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Yetik, O.; Guney, M.; Iakovakis, E.; Sınmazçelik, T.; Avcu, E. Surface, Subsurface and Tribological Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Shot Peened under Different Parameters. Materials 2020, 13, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.C.L.; Rodrigues, R.C.S.; Claro, A.P.R.A.; De Mattos, M.D.G.C.; Ribeiro, R.F. Wear Resistance of Experimental Titanium Alloys for Dental Applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2011, 4, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airao, J.; Kishore, H.; Nirala, C.K. Comparative Analysis of Tool Wear in Micro-Milling of Wrought and Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V. Wear 2023, 523, 204788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S.; Choe, H.-C. Electrochemical Behavior of Co-Cr and Ni-Cr Dental Cast Alloys. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 2009, 19, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S.; Choe, H.C. Preferential Dissolution Behaviour in Ni-Cr Dental Cast Alloy. Bull Mater Sci 2010, 33, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.B.; Kossman, S.; Mejias, A.; Noirfalise, X.; Montagne, A.; Van Gorp, A.; Poorteman, M.; Olivier, M.-G. Mechanical and Corrosion Characterization of Industrially Treated 316L Stainless Steel Surfaces. Surface and Coatings Technology 2020, 382, 125175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Mhaede, M.; Wollmann, M.; Wagner, L. Effect of Micro Shot Peening on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Two Microstructure Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Applied Surface Science 2016, 363, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Surface Roughness Generated by Shot Peening. Applied Surface Science 2012, 258, 6831–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Ji, J.; Zhan, Z.; Deng, H. Mechanism Study of Electropolishing from the Perspective of Etching Isotropy. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2022, 305, 117599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, D. Fundamental Aspects of Electropolishing. Electrochimica Acta 1987, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, M.; Landolt, D. Fundamental Aspects and Applications of Electrochemical Microfabrication. Electrochimica Acta 2000, 45, 2535–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K. Development of Electropolishing Technology for Superconducting Cavities. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2003 Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37440); IEEE: Portland, OR, USA, 2003; pp. 462–466.
- Hensel, K.B. Electropolishing. Metal Finishing 1999, 97, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynick, G.L.; Boehlert, C.J. Use of Electropolishing for Enhanced Metallic Specimen Preparation for Electron Backscatter Diffraction Analysis. Materials Characterization 2005, 55, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Z.; Jing, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, C. Surface Performance and Optimization of Nickel Titanium Alloy Electropolishing Parameters. International Journal of Electrochemical Science 2021, 16, 210745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, B.; Tawfiq, K.; Wei, H.; Zhou, S.; Chen, G. Electropolishing of Surfaces: Theory and Applications. Surface Engineering 2017, 33, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jianzhong, L.I.; Che, S. Electropolishing Mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. International Journal of Electrochemical Science 2018, 13, 4792–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, J.B.; Landolt, D. Electropolishing of Titanium in Perchloric Acid-Acetic Acid Solution: II. Polarization Behavior and Stoichiometry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1978, 125, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, N.-S.; Nasirpouri, F. Electropolishing Behaviour of Pure Titanium in Perchloric Acid–Methanol–Ethylene Glycol Mixed Solution. Transactions of the IMF 2014, 92, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, O.; Madore, C.; Landolt, D. The Mechanism of Electropolishing of Titanium in Methanol-Sulfuric Acid Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 2362–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Son, K.; Sung, D.; Kim, Y.; Chung, W. Effect of Added Ethanol in Ethylene Glycol–NaCl Electrolyte on Titanium Electropolishing. Corrosion Science 2015, 98, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holze, R. Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids. F. Endres, A. P. Abbott, and D. R. MacFarlane (Eds). WILEY-VCH, Weinheim, 2008: 387 + XXII p., 105 €; ISBN 978-3-52731565-9. J Solid State Electrochem 2009, 13, 1633–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhong, Y.-T.; Chao, C.-Y.; Hung, W.-C.; Du, J.-K. Effects of Various Polishing Techniques on the Surface Characteristics of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and on Bacterial Adhesion. Coatings 2020, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Tong, X.; Ma, X. Surface Modification Techniques of Titanium and Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Orthopaedics Applications: A Review. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2023, 227, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kityk, A.; Švec, P.; Šoltys, J.; Pavlik, V.; Hnatko, M. Deep inside of the Mechanism of Electrochemical Surface Etching of α + β Ti6Al4V Alloy in Room-Temperature Deep Eutectic Solvent Ethaline. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2023, 375, 121316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, L.M.; Mielczarski, R.G.; Pigatto, C.; Müller, I.L.; Malfatti, C.D.F. The Influence of the Operating Parameters of Titanium Electropolishing to Obtain Nanostructured Titanium Surfaces. MSF 2012, 727–728, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Hong, Q. The Effect of Microstructure on the Mechanical Properties of TC4-DT Titanium Alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2013, 563, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, C.; Senthilkumar, V.; Sarala, S.; Arivarasan, J. Low Temperature Diffusion Bonding of Ti-6Al-4V and Duplex Stainless Steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2016, 234, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, A.; Bonnici, M.; Mhaede, M.; Wan, R.; Wagner, L. Shot Peening of Austempered Ductile Iron Gears. Surface Engineering 2017, 33, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsec, K.; Jenko, M.; Conradi, M.; Kocijan, A.; Vesel, A.; Kovač, J.; Godec, M.; Belič, I.; Šetina Batič, B.; Donik, Č.; et al. Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy. Coatings 2019, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ruiz, P.; Garcia-Blanco, M.B.; Vara, G.; Fernández-Pariente, I.; Guagliano, M.; Bagherifard, S. Obtaining Tailored Surface Characteristics by Combining Shot Peening and Electropolishing on 316L Stainless Steel. Applied Surface Science 2019, 492, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, M.; Szewczenko, J.; Marciniak, J.; Nowińska, K. Electrochemical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI Alloy after Anodization. In Information Technologies in Biomedicine; Piętka, E., Kawa, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; Volume 7339, pp. 369–378. ISBN 978-3-642-31195-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kiel-Jamrozik, M.; Szewczenko, J.; Basiaga, M.; Nowińska, K. Technological Capabilities of Surface Layers Formation on Implant Made of Ti-6Al-4V Eli Alloy. Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics; 01/2015; ISSN 1509-409X 2015. [CrossRef]
- Pochrząst, M.; Marciniak, J.; Szewczenko, J.; Walke, W. Application of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Comparison Analysis of Surface Modified Ti-6Al-4V ELI and Ti-6Al-7Nb Alloys. In Information Technologies in Biomedicine; Piętka, E., Kawa, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; Volume 7339, pp. 379–388. ISBN 978-3-642-31195-6. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczenko, J.; Walke, W.; Nowinska, K.; Marciniak, J. Corrosion Resistance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy after Diverse Surface Treatments. Materialwissenschaft Werkst 2010, 41, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
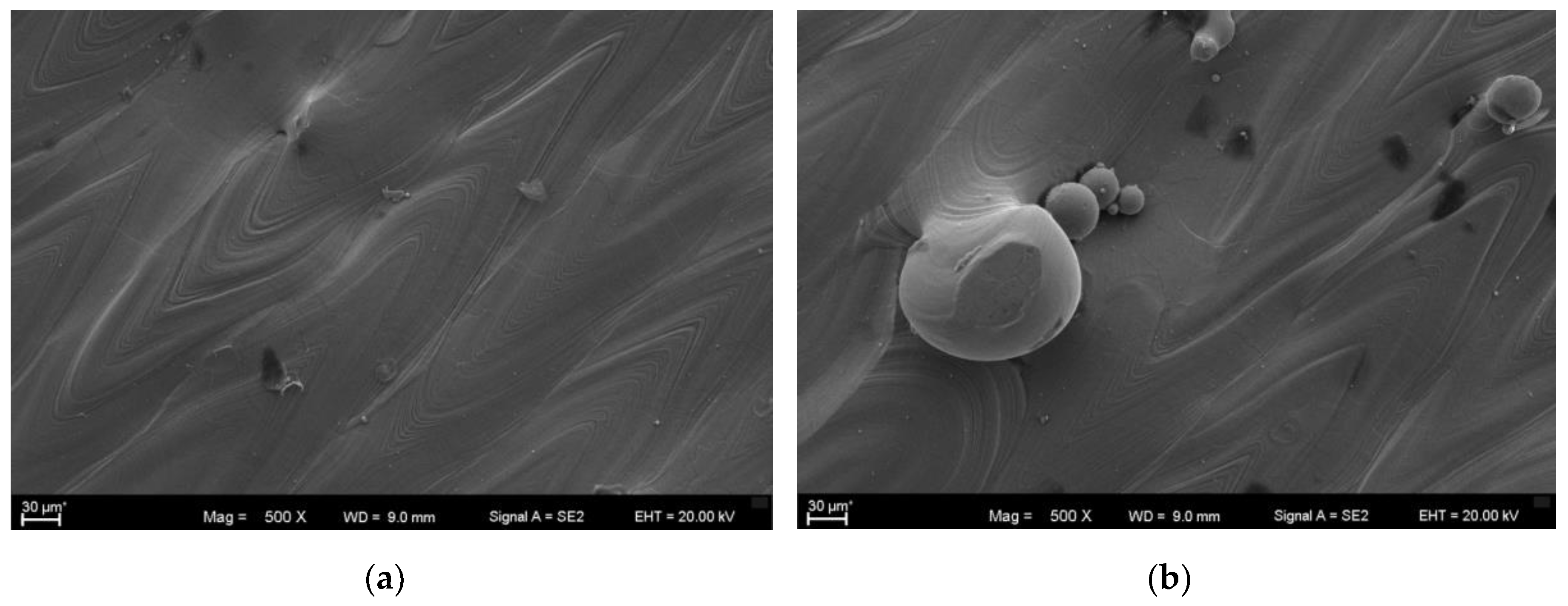
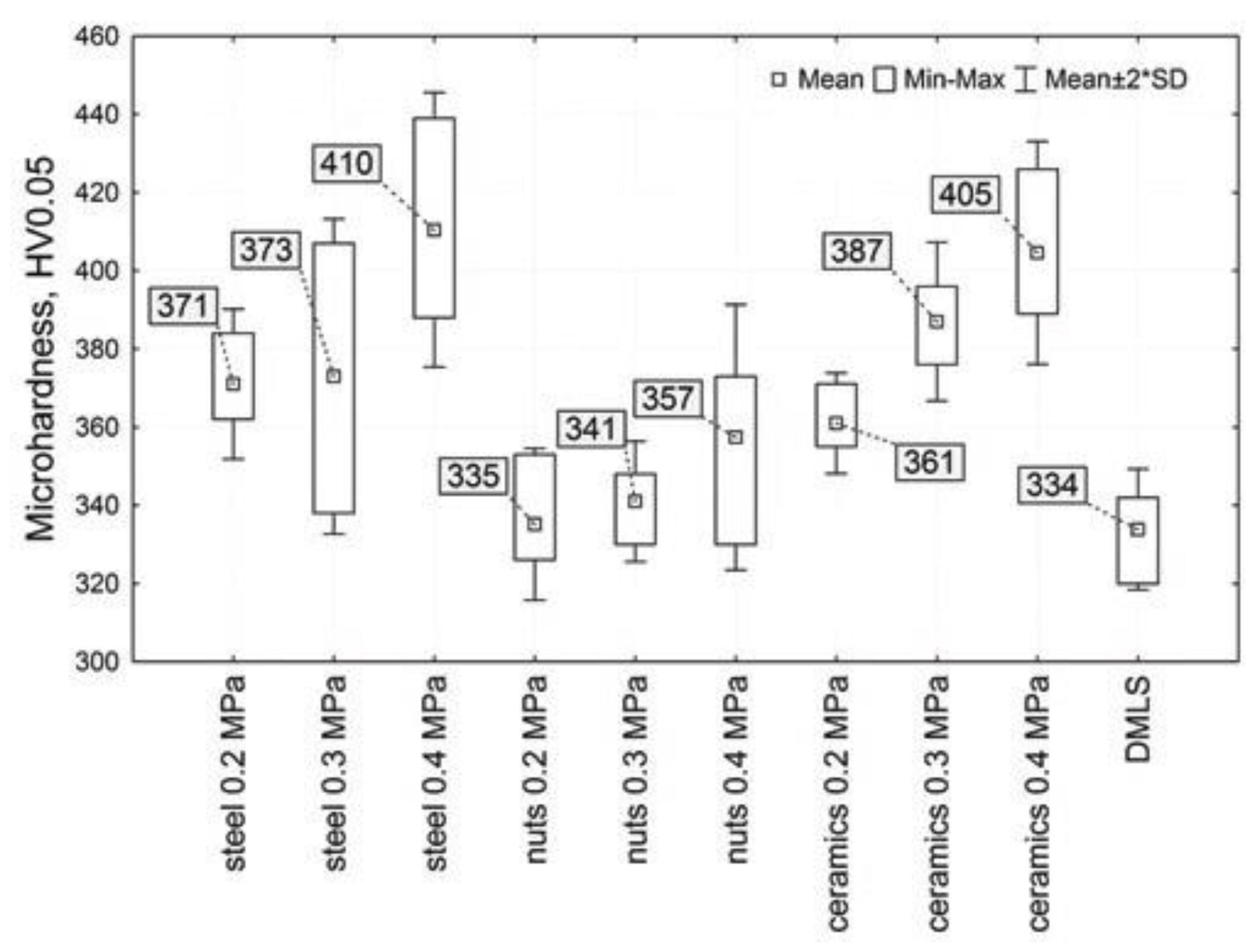
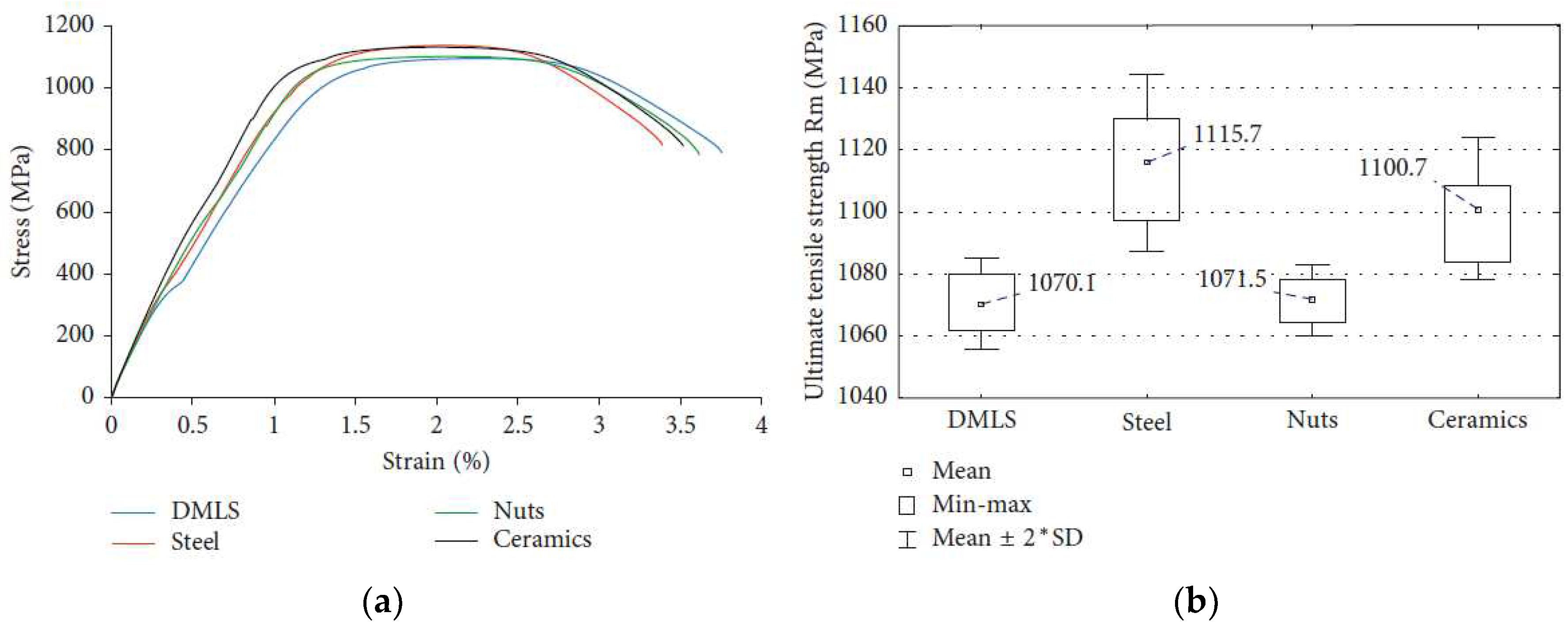
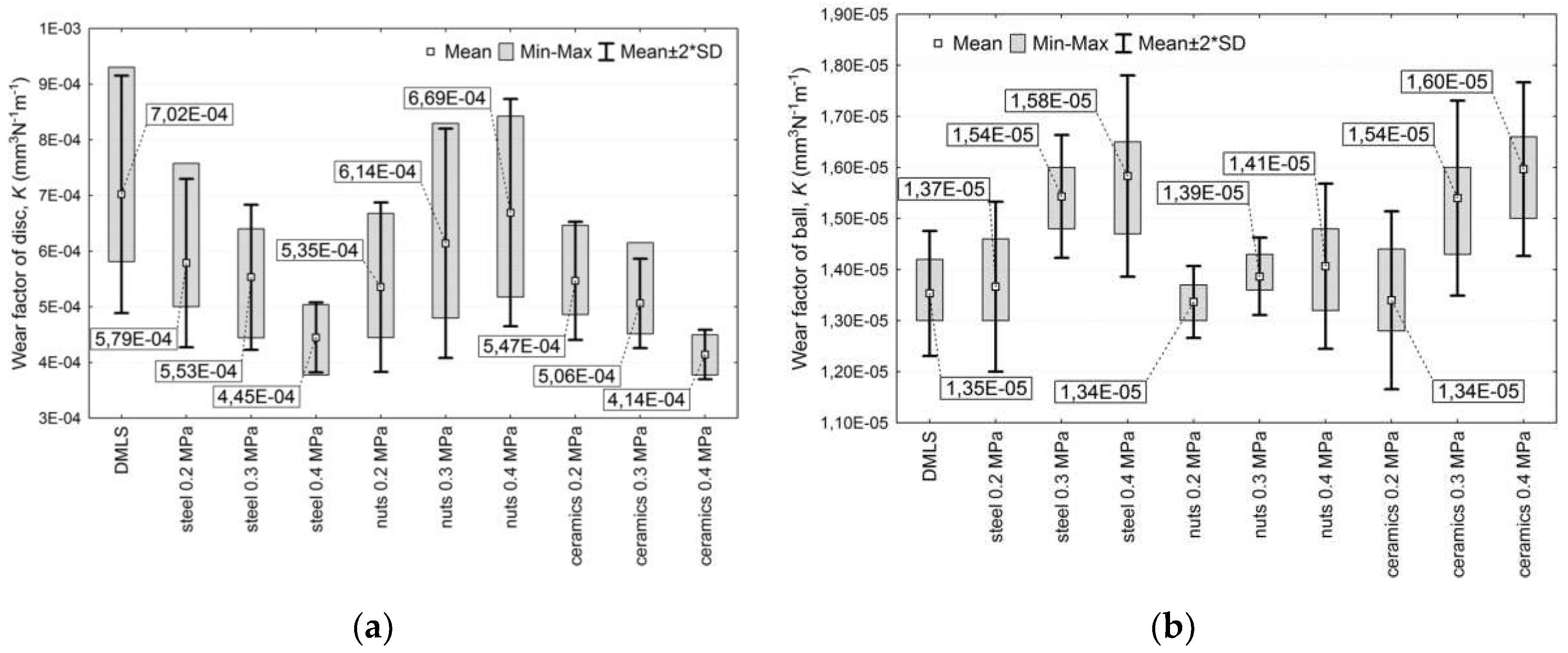
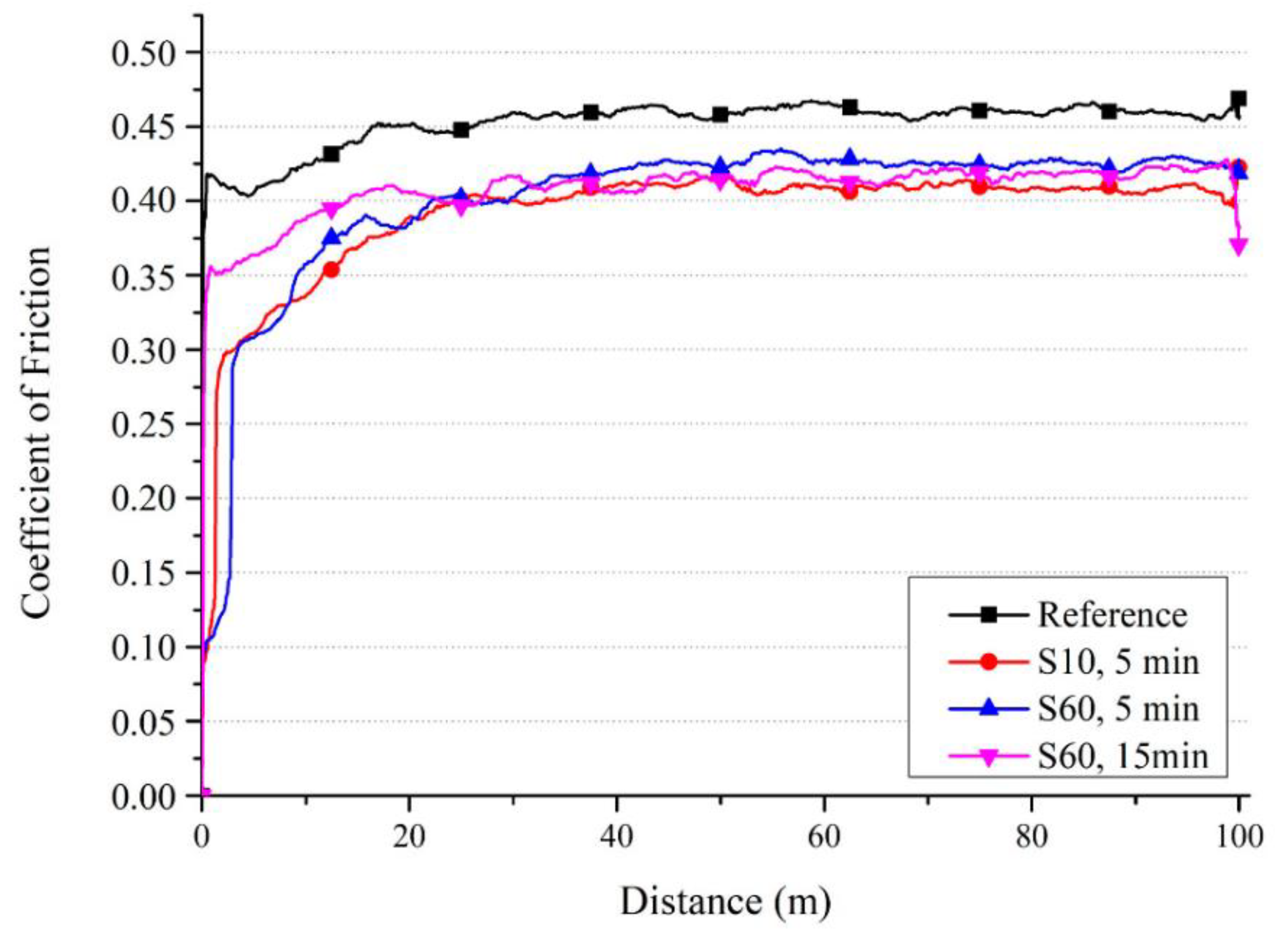

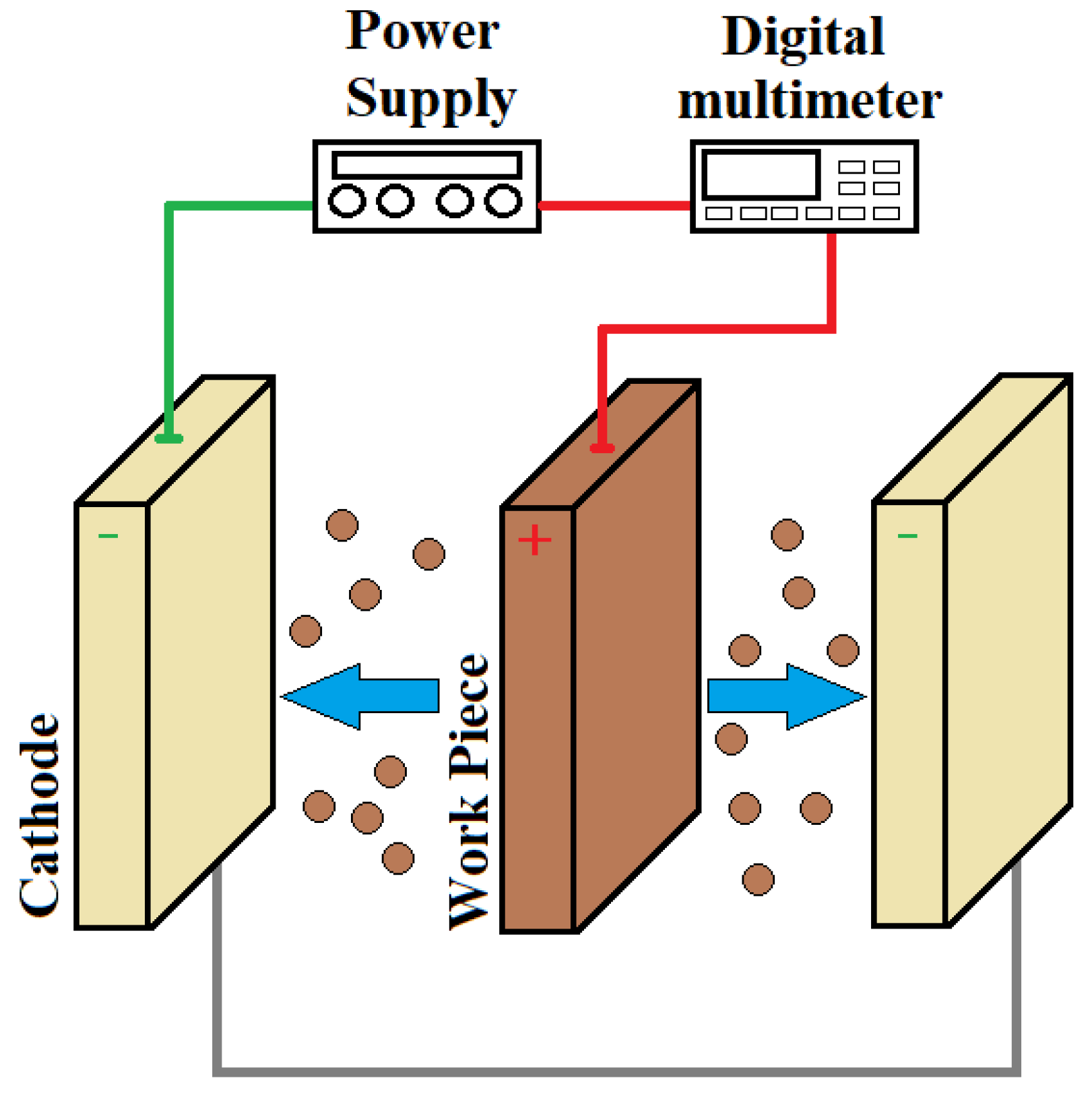
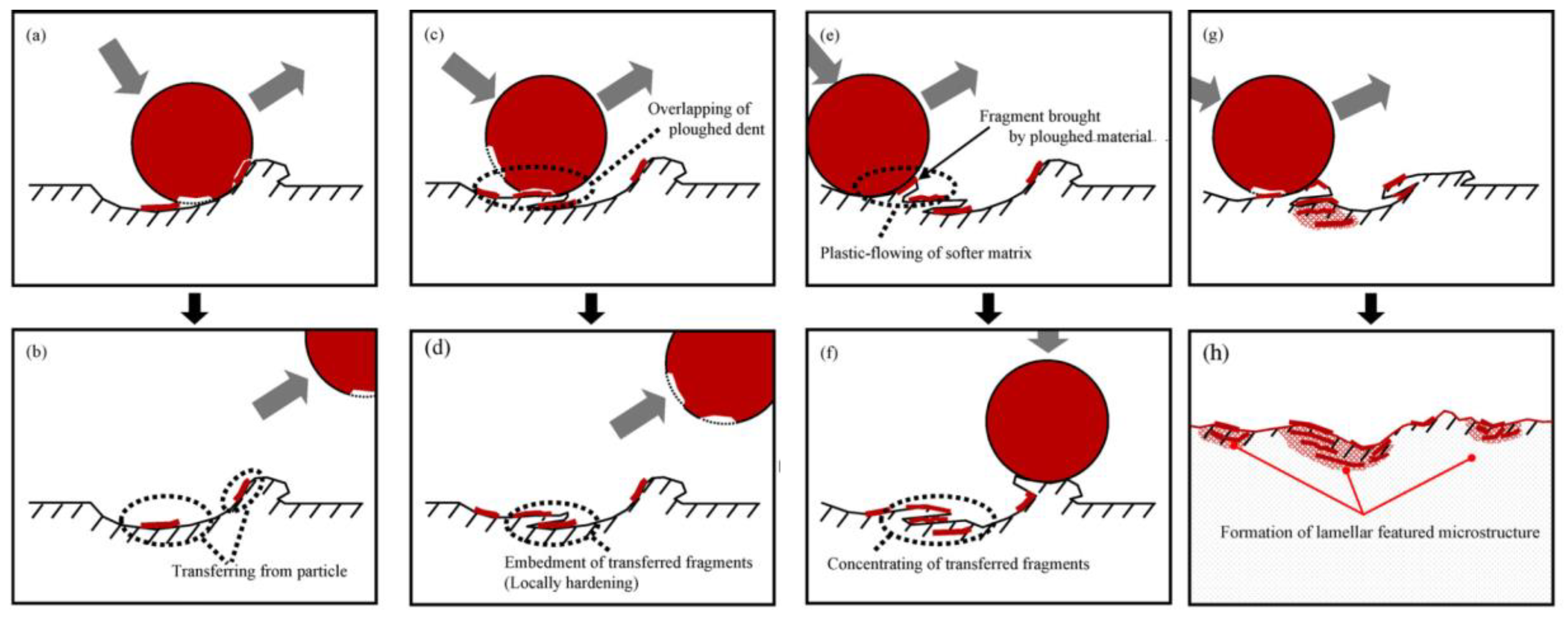
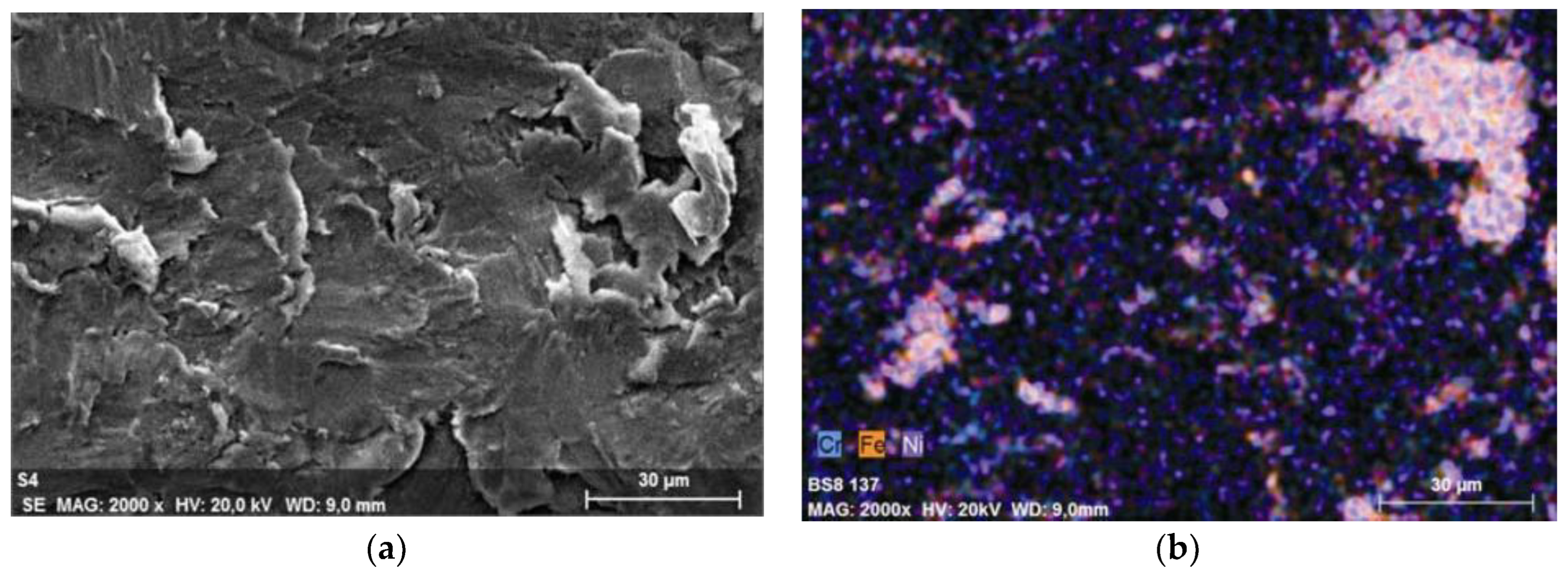
| Properties | Natural Human Bone |
Ti6Al4V Alloy (wrought) |
316L Stainless Steel (cast) | F75CoCrMo Alloy (cast) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.5-2 | 4.4 | 8.0 | 8.8 |
| Tensile modulus of elasticity (GPa) | - | 830-1070 | 205 | 500-1500 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 130-190 | 920-1140 | 515 | 900-1800 |
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 10-30 | 100-110 | 195-205 | 200-230 |
| Elongation (%) | - | 10-15 | 10-40 | 4-13 |
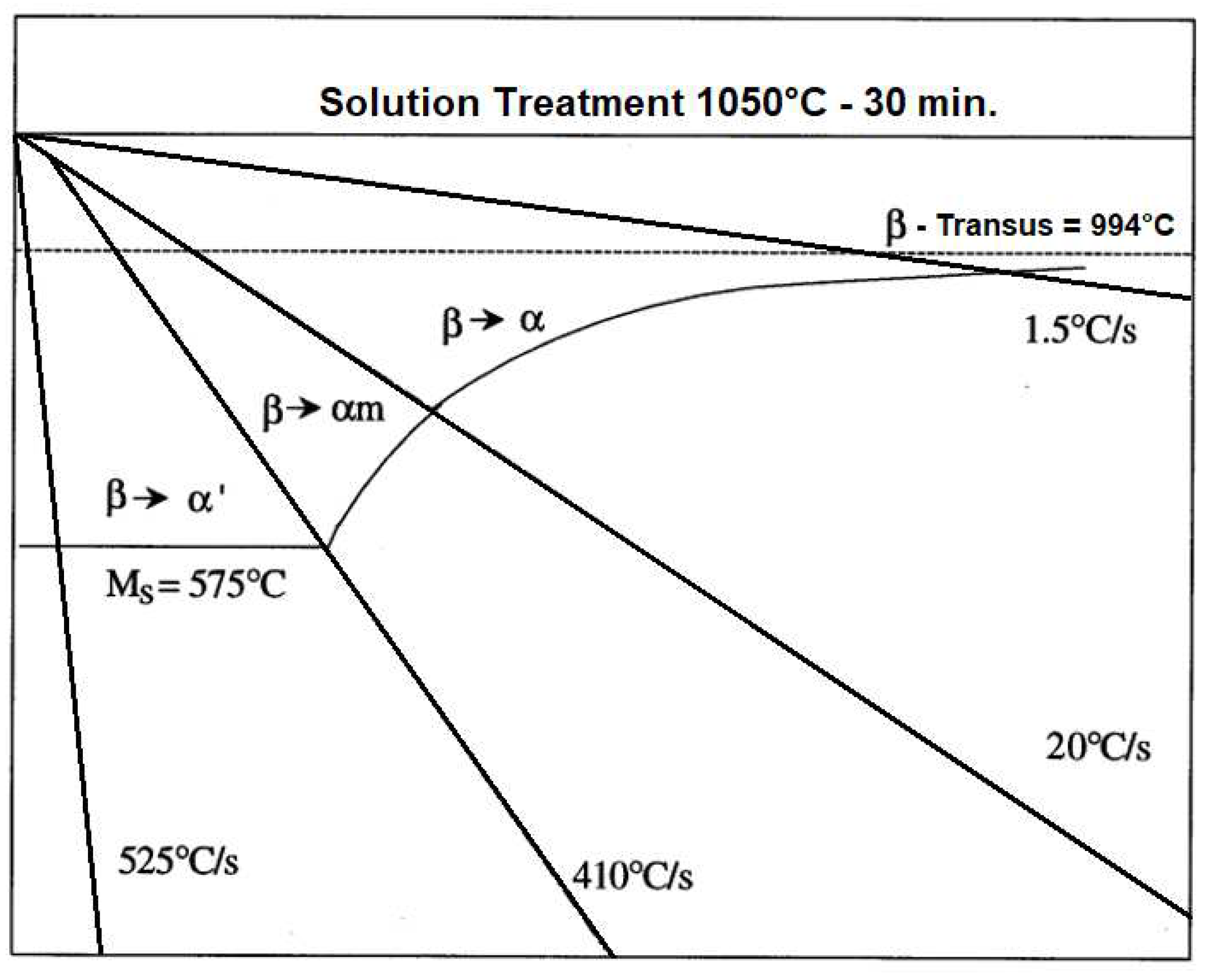
| Phase Transformation Region | Temperature Range (°C) | Microstructure at various cooling medium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Air | Furnace | ||
| α + β | 700-950 | A mixture of α and β structures, with more volume of α structures |
Primary α, with grains having α + β lamellar structure |
Primary α phase with intergranular β phase observed for all temperatures α phase on the phase boundary and a transition from β to α on the grain boundary. The grains were observed to have α/ β lamellar |
| β | 950-1100 | Martensite microstructure consist of a fine acicular α phase with grain boundaries consisting of β phase | Partial martensitic microstructure, there exists an incomplete transition from β to α phase on grain boundaries | |
| Process | Heat Treatment of Ti6Al4V alloy | Microstructure at various cooling medium | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microhardness | Yield Strength [MPa] | Ultimate Tensile Strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] | |||
| Wrought | Untreated | 325 HV | 880 | 960 910 |
14 | [25] |
| Untreated Ti6Al4V | 190 HK | 880 | 18 | [26] | ||
| water quenching + aging | 320 HK | 1110 | 1170 | 6,5 | [26] | |
| Ti6Al4V air cooling+aging |
210 HK | 910 | 980 | 12,5 | [26] | |
| Forged | Mill annealed | - | 1030 | 970 | 16 | [27] |
| Mill annealed | - | 960 | 1006 | 18,37 | [25] | |
| Cast | - | 330 HV | 750 | 875 | 4,5 | [28] |
| - | - | 865 | 980 | 13,5 | [29] | |
| AM Technology |
Specimen Orientation and Ref. |
Mechanical Properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young Modulus [MPa] | Microhardness | Yield Strength [MPa] | Ultimate Tensile Strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] | |||
| DED | XZ | [38] | - | - | 522 | 797 | 1,7 |
| XY | [38] | - | - | 892 | 911 | 6,4 | |
| XZ | [27] | - | - | 945 | 1041 | 14,5 | |
| XZ | [27] | - | - | 970 | 1087 | 13,6 | |
| XY | [39] | - | - | 960 | 1063 | 10,9 | |
| SLM | XZ | [40] | 115 | - | 978 | 1143 | 11,8 |
| ZX | [40] | 119 | - | 967 | 1117 | 8,9 | |
| XY | [40] | 113 | - | 1075 | 1199 | 7,6 | |
| XY | [41] | - | 394 HV | 1052 | 1136 | 2,92 | |
| XY | [42] | - | 370 HV0.3 | 1273 | 1421 | 3,2 | |
| XZ | [42] | - | 390 HV0.3 | 1150 | 1246 | 1,4 | |
| XY | [43] | - | 350 HV | - | 1137 | 9,10 | |
| EBM | XY | [44] | 118 | 321 HV | 830 | 915 | 13,1 |
| XY | [45] | 114 | 35 HRC | 830 | 914 | 13,1 | |
| XY | [42] | - | 315 HV0.3 | 846 | 976 | 15,0 | |
| XZ | [42] | - | 340 HV0.3 | 845 | 972 | 14,2 | |
| ZX | [46] | - | - | 869 | 965 | - | |
| DMLS | ZX | [46] | - | 380 HV | 1017 | 1096 | 16 |
| ZX | [47] | 111,9 | 871 HV10 | 1086 | 1121 | 16,9 | |
| XY | [48] | 110 | 400-430 HV | 1140 | 1290 | 7 | |
| XY | [49] | - | - | 990 | 1045 | 14 | |
| ZX | [50] | 108,0 | - | 982 | 1080 | 14,3 | |
| XZ | [50] | 108,7 | - | 980 | 1072 | 14,1 | |
| Name of shot peening media (type of media) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | SUS100 (SUS304) | SUS400 (SUS304) | FHB 80 (SiO2) | |
| Peening pressure | - | 0.5 MPa | ||
| Hardness | 371 HV | 420 HV | 440 HV | 470 HV |
|
Substrate: Ti6Al4V |
Coating | |||||
| - | AlTiN | TiAlN | ||||
| DMLS | Conv. | DMLS | Conv. | DMLS | Conv. | |
| Sa [µm] | 0,014 | 0,040 | 0,027 | 0,038 | 0,028 | 0,053 |
| HIT | 5,7 ± 0,2 | 4,8 ± 0,4 | 25,0 ± 4,6 | 26,1 ± 4,3 | 23,6 ± 3,4 | 23,2 ± 3,3 |
| EIT | 137,0 ± 4,1 | 114,5 ± 4,7 | 518,7 ± 129,1 | 559,2 ± 117,3 | 411,4 ± 45,8 | 503,5 ± 99,4 |
| Hcoating/Ecoating | - | - | 0,048 | 0,047 | 0,057 | 0,046 |
| H3coating/E2coating | - | - | 0,059 | 0,057 | 0,078 | 0,049 |
| Ecoating/Esubstrate | - | - | 3,79 | 4,88 | 3,00 | 4,40 |
| Sample No. | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polishing time (min.) | untreated | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Weight loss [%] | - | 5,98 | 10,82 | 14,76 | 16,29 |
| Ra [µm] | 6,33 | 2,01 | 1,63 | 1,132 | 1,72 |
| RL (Ω·cm2) | - | 20,69 | 16,44 | 21,49 | 23,29 |
| Qc (F·cm-2) | - | 2,016e-2 | 2,507e-5 | 5,625e-5 | 4,656e-5 |
| Rc (Ω·cm2) | - | 758,40 | 8,56 | 12,72 | 23,26 |
| Qd (F·cm-2) | - | - | 2,663e-6 | 3,724e-6 | 2,051e-6 |
| Rt (Ω·cm2) | - | - | -7,152e5 | 1,014e6 | 5,128e5 |
| Chi-squared (X2) | - | 2,02e-3 | 1,48e-3 | 7,97e-4 | 1,59e-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).