Introduction
In the past decades, advances in hyperspectral remote sensing imaging have provided new approaches of monitoring vegetation canopy structure changes, predicting plant growth and estimating crop yield and productivity [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Compared with broadband indices, hyperspectral technology, which dealt with narrowband based vegetation indices of canopy reflectance, could provide more accurate estimation of crop parameters [
5,
6,
7]. Hyperspectral remote sensing serves not only to enhance the recognition of crop and vegetation types but also to monitor crop growth, retrieve physiochemical characteristics, diagnose nutrition status, extract crop canopy information, and estimate agronomic parameters and chemical components [
8]. Thus, the hyperspectral technology holds unique application potential in regional and global crop yield estimation, precision regulation of water and fertilizer usage, and monitoring of diseases and insect pests [
9].
Vegetation canopy structural properties are important variables related to the exchange of energy, water and CO
2 between atmosphere and land surface [
10]. Among the parameters describing the vertical profile of plant canopy, leaf area index (LAI) plays a key role in plant ecological and biophysical processes [
11] and has been widely used for estimate foliage cover, crop growth and yield [
12]. The Leaf Area Index (LAI) serves as a crucial indicator, reflecting crop canopy structure and growth [
13,
14]. Monitoring changes in LAI offers a foundation for adapting cotton fertilization strategies [
15]. Consequently, the swift, accurate, and non-destructive monitoring of cotton LAI holds immense importance in guiding crop fertilization. Hyperspectral vegetation indices (HVIs) have been developed for estimating LAI by establishing statistical relationships between HVIs and measured LAI for various vegetation types. The most known and widely used vegetation index is the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and it has been recognized as the cornerstone of the vegetation indices (VIs) used to estimate LAI variations [
16].Cotton holds significant economic importance as a cash crop and serves as a major contributor to the global natural fiber supply. China, being one of the leading cotton producers, plays a substantial role, accounting for 25.6% of the world’s total cotton output [
17]. Cotton stands out as China’s primary cash crop [
18], and varying levels of the canopy structure significantly influence cotton growth. In 2020, Xinjiang’s cotton output constitutes a substantial portion, contributing 87.3% to the national output and 22.3% to the global output.
Remote sensing technology enables timely, dynamic, and macroscopic monitoring, establishing itself as a crucial method for tracking crop growth information. Over recent years, numerous studies, both domestic and international, have employed remote sensing technology to investigate crop biomass [
11,
15,
19]. Hyperspectral remote sensing serves not only to enhance the recognition of crop and vegetation types but also to monitor crop growth, retrieve physiochemical characteristics, diagnose nutrition status, extract crop canopy information, and estimate agronomic parameters and chemical components [
8]. The technology also holds unique application potential in areas such as yield estimation, precision regulation of water and fertilizer usage, and monitoring of diseases and insect pests. It constitutes a significant approach in advancing precision agriculture and promoting sustainable development in the future [
20].
In our research, we employ hyperspectral resolution techniques to achieve swift, efficient, non-contact, and non-destructive collection and processing of field information for the cotton canopy. Our investigation focuses on examining the relationship between the canopy’s reflecting spectra and canopy structure indices, aiming to establish a spectral cognition retrieval model. This model encompasses key indices such as Leaf Area Index (LAI) and biomass across various growth stages. The results underscore the advancement in the application of this technique for cotton remote sensing diagnosis, the accelerated progress in remote sensing quantitative research, and the establishment of a theoretical foundation for precision cotton cultivation.
1. Material and Method
The experiment was conducted at the Field Experimental Station of Shihezi University, Xinjing, China(44
0 20’ N,86
0 3’ E). The region is characterized by low mountain and hill terrain, with elevations ranging from 46 m to 114 m above sea level and slopes varying from 5° to 20°. The study area has a typical monsoon subtropical climate, with an mean annual temperature of 17.2 °C. The lowest monthly mean air temperature occurs in January at 4.7 °C, while the highest is recorded in July at 29.4 °C. The annual mean rainfall is 1422 mm, with the majority occurring between April and August. Annual mean relative humidity averages above 80%. The study site has a loam soil, with medium-fertility containing 1.29% organic matter, 33.8 mg•kg
-1 available nitrogen, 84 mg•kg
-1 available phosphorus and 300 mg•kg
-1 available potassium [
21].
The main cotton varieties included Xinluzao 9, Xinluzao 10, Xinluzao 13, Xinluzao 19, Paotai 1 and Zhongmiansuo 36. The experiment started in 2010. The date for dibbling of sowing was April 23, seedling transplantation on April 29, and topping on July 10th. Field management practices including film drip irrigation, diseases and pests control and herbicides application are consistent with those applied in larger-scale fields.
1.1. Measuring Methods
1.1.1. Spectral Measuring Method.
The cotton canopy spectra were measured using an ASD Field Spec Pro VNIR 2500 spectrometer (Analytical Spectral Devices, Boulder, CO, USA). The spectra range covered 350 to 2500 nm. The resolution for spectra within 350 to 1000 nm was 3 nm and was 10 nm between 1000 to 2500 nm. Measurements were conducted during sunny and cloudless mornings, specifically between 11:30am and 14:00pm, at various growth stages of cotton, including early budding, full budding, early blooming, full blooming, full-boll, and boll opening. The measurements were taken in sample fields selected for their representativeness, uniformity, and absence of diseases and insect pests in the cotton canopy. The field angle was fixed at 25°, with the detector head positioned vertically downward. The distance between the detector head and the canopy was maintained at 100 cm, and each treatment involved measuring 10 to 15 curves, with the average value serving as the spectra reflectance for the specified small area. The scanning time for each spectra curve was set at 0.2 seconds. Whiteboard proofreading was performed both before and after the measurement process.
1.1.2. Measuring of LAI.
In alignment with the positions of the measured canopy spectra, samples were collected and the American CI-110 digital plant canopy structure analyzer was employed for Leaf Area Index (LAI) measurements.
1.1.3. Biomass Measurements
In the biomass measurement process, samples were collected, and their fresh weights were determined based on organ types. The total fresh weight (g•m-2) for a 1 m2 area was calculated. Subsequently, the samples underwent enzyme deactivation in a 105℃ oven for 30 minutes and were dried at a constant temperature of 80℃. The measurement of dry biomass was conducted when the difference between two measurements, taken one hour apart, was ≤ 5%.
1.2. Hyper-spectral Analysis and Technique Method
1.2.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
This technique, as highlighted by [
22], stands among the most widely used methods for investigating vegetation and crop hyper-spectra. The independent variables encompass hyper-spectral statistics or their variations, including original spectra reflectance, first-order and higher-order derivative spectra, logarithmic transformations of original spectral reflectance, various vegetation indices, and logarithmic transformations of reflectance reciprocal. Dependent variables consist of biophysical and biochemical indices such as Leaf Area Index (LAI), biomass, and others associated with crops or vegetation. These variables serve as the basis for establishing multivariate regression estimation (predicting) models [
23]. The analysis usually involves two distinct phases: the creation of a statistical regression model and the subsequent evaluation of its precision. Generally, a portion of the collected experimental samples is designated for establishing the statistical regression model, while the remaining samples are dedicated to testing the precision of the model. In our research, the statistical data from the year 2009 was utilized both for constructing the model and assessing its precision.
1.2.2. Hyper-spectral Vegetation Indices.
Vegetation indices play a crucial role in estimating and measuring various biophysical and biochemical indices of vegetation. These include but are not limited to Leaf Area Index (LAI), vegetation coverage, biomass, photosynthetic effective radiation absorption index, chlorophyll content, and plant nutrition elements content. [
24]. In hyperspectral remote sensing, the approximate continuity of the spectrum allows for the construction of hyper-spectral vegetation indices. Notably, indices such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and the Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) at a wavelength λ0 can be represented as follows:
In the above equations, Near Infra-red (NIR) refers to the near-infrared region, specifically the reflectance of a wavelength between 760 to 1056 nm. Similarly, “Red (R)” denotes red light, representing the reflectance of a wavelength between 680 to 780 nm.
2. Results
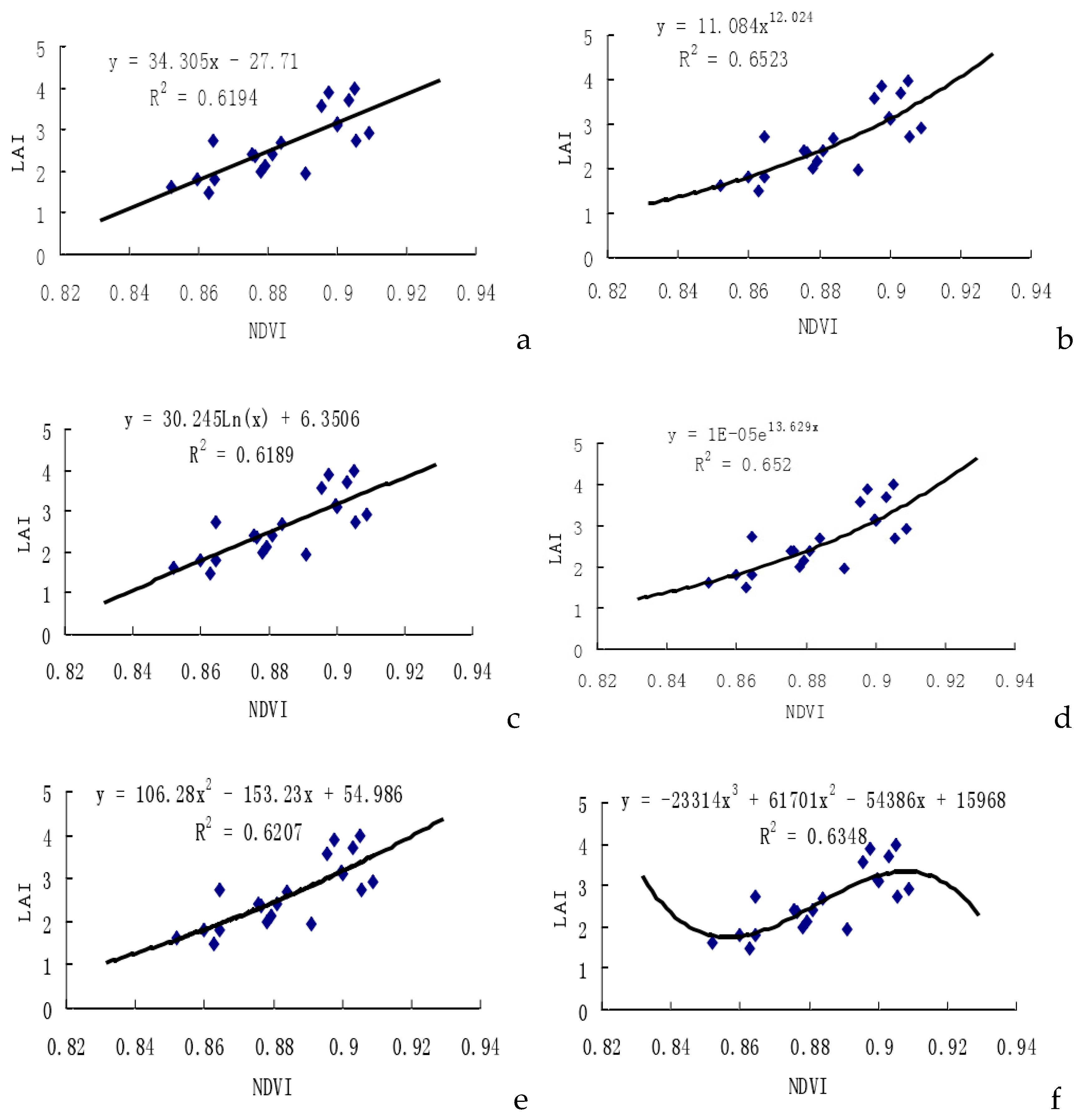
2.1. Research of NDVI in Retrieval of LAI
As presented in Table 1, when using NDVI to predict LAI across the six models, the correlation coefficient (r) consistently reaches an extremely remarkable level at α = 0.01. Among these models, the power function exhibits the highest multiple correlation coefficient (r2=0.6523), accompanied by the lowest root mean square difference, indicating a high estimation precision. This power function model emerges as the most suitable for hyper-spectral statistics and the mathematical relation between NDVI and LAI.
Notably, these findings align with results from prior research [
25]. Additionally, the results reveal a relatively high multiple correlation coefficient for the exponential function model (
r2=0.6520), with a total root mean square difference of 0.3634. Conversely, the multiple correlation coefficient for the logarithmic function model is the lowest (
r2=0.6189). This analysis affirms the feasibility of using NDVI to predict LAI in cotton, underscoring strong relationships with both power and exponential functions. In our research, we selected composite NDVI value of LAI and the reflectance of NIR and R ranges for experimental cotton samples. NDVI was considered as the independent variable, and LAI as the dependent variable, leading to the establishment of six linear and non-linear prediction models. As presented in
Figure 1, when using NDVI to predict LAI across the six models, the correlation coefficient (r) consistently reaches an extremely remarkable level at α=0.01. Among these models, the power function exhibits the highest multiple correlation coefficient (
r2=0.6523), accompanied by the lowest root mean square difference, indicating a high estimation precision. This power function model emerges as the most suitable for hyper-spectral statistics and the mathematical relation between NDVI and LAI.
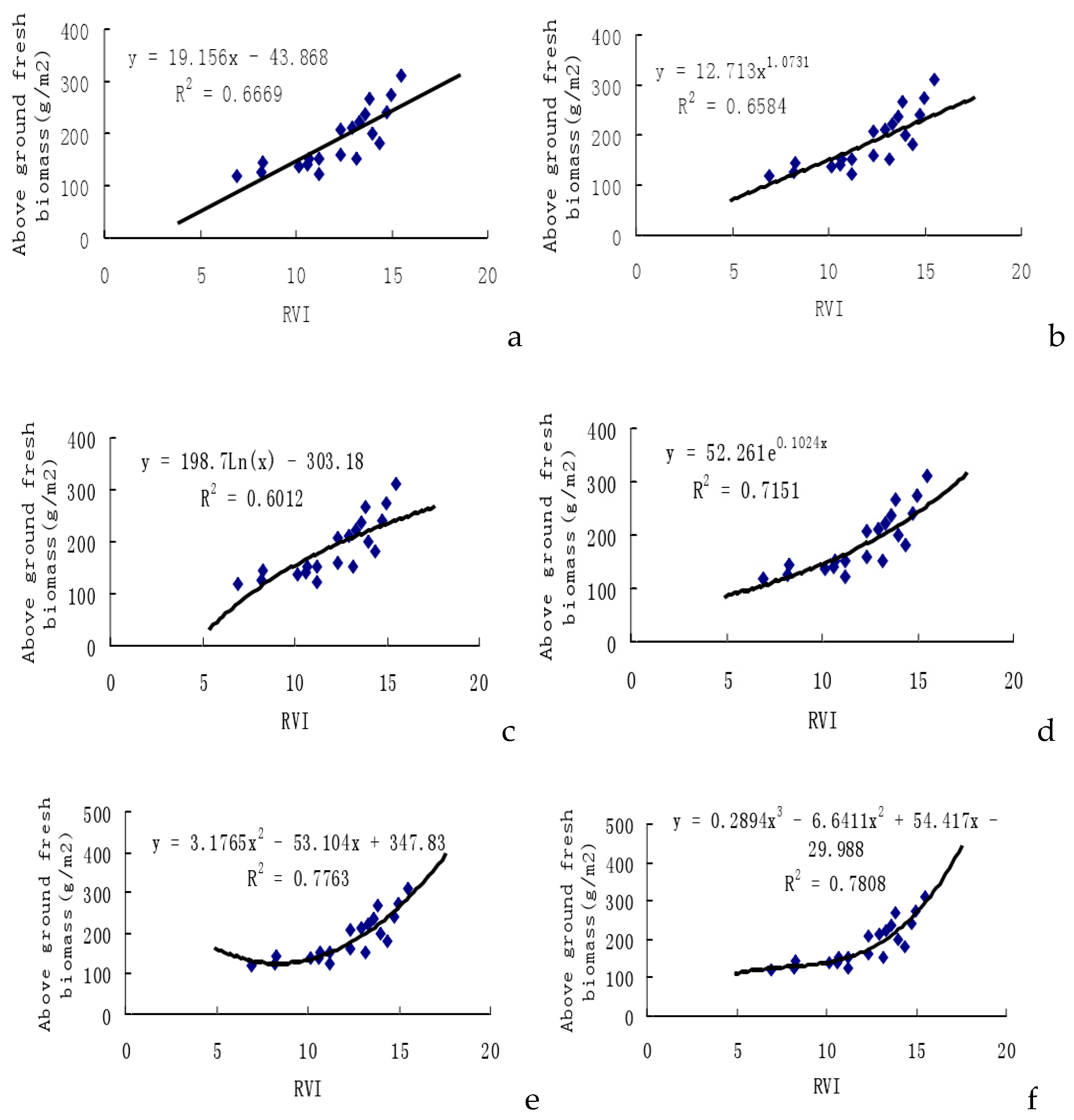
2.2. Remote Sensing Testing Model of RVI to Above-ground Biomass
In our research, we developed a remote sensing testing model utilizing the Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) to estimate above-ground dry biomass. The model incorporates the relationship between RVI and the weight of above-ground dry biomass. The Vegetation Index (VI) serves as a crucial indicator in the estimation of biomass. Numerous research studies have substantiated the relationships between VI and Leaf Area Index (LAI), as well as between VI and biomass. The majority of these investigations characterize the relationship between vegetation and biomass as either linearly correlated or exponentially correlated.[
26].
In our research, w used the Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) of experimental cotton samples to establish six prediction model equations for cotton unit area above-ground fresh biomass weights. As is shown in
Figure 2, among the estimation models, the cubic function model exhibits the highest multiple correlation coefficient (
r2=0.7808), followed by the quadratic function model (
r2=0.7763). However, their total root mean square differences are are larger than the REMS values of other models, standing at 0.4473 and 0.4824, respectively. Interestingly, the exponential function model demonstrates a rather high correlation coefficient, and notably, its root mean square difference is the lowest at 0.2895. This indicates that the estimation precision for the exponential function model is the highest, rendering it the best estimation model. These findings consistent with results obtained by previous researchers [
27]. Interestingly, the exponential function model demonstrates a rather high correlation coefficient, and notably, its root mean square difference is the lowest at 0.2895. This indicates that the estimation precision for the exponential function model is the highest, rendering it the best estimation model. These findings align with results obtained by previous researchers.
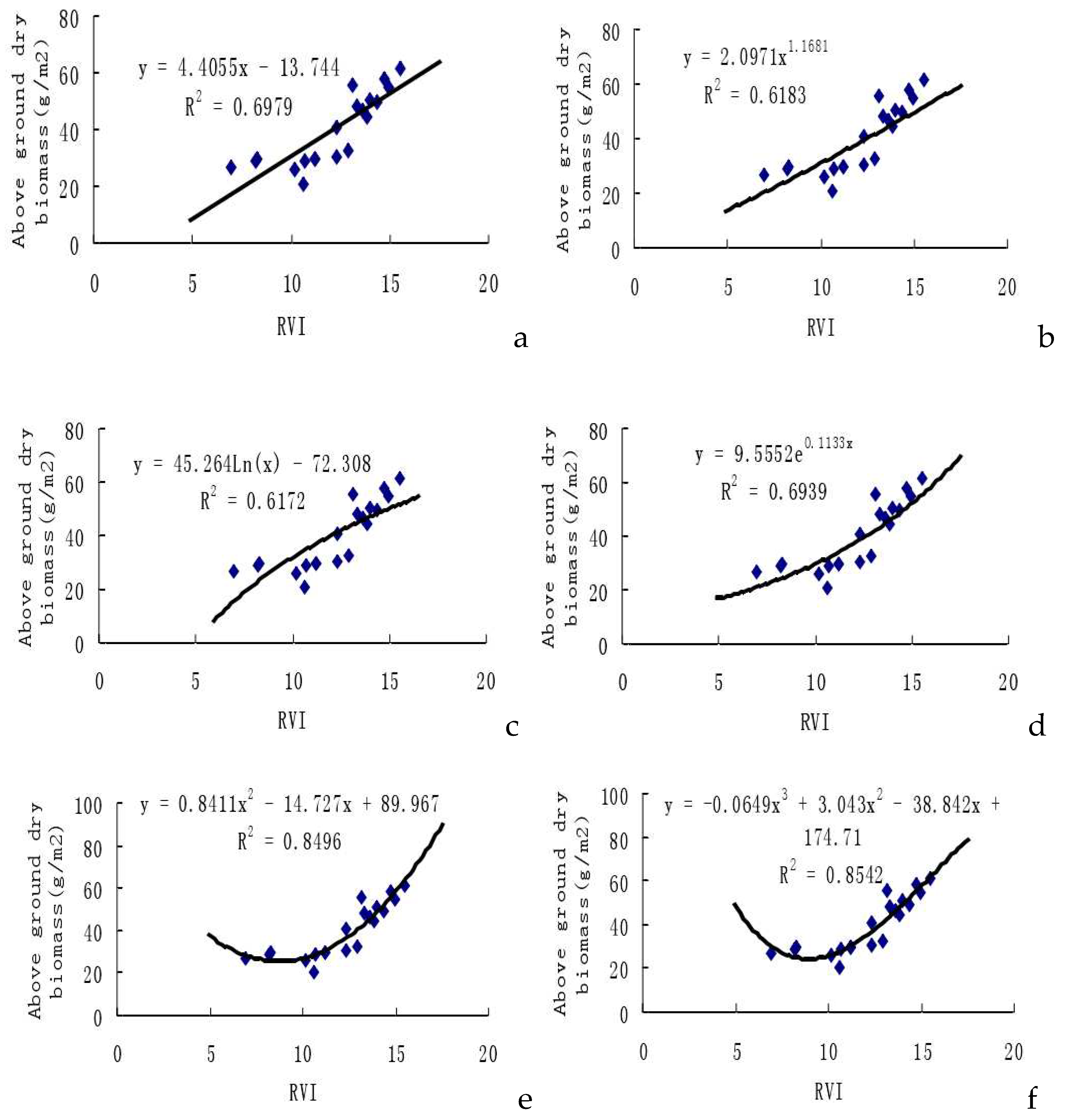
2.3. Remote Sensing Testing Model of RVI to Above-ground Dry Biomass
In our study, we selected the Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) from experimental cotton samples (n=20) to establish six prediction model equations for cotton unit area above-ground dry biomass weights. As presented in
Figure 3, among the estimation models, the cubic function model stands out with the highest multiple correlation coefficient (
r2=0.8542), followed by the quadratic function model (
r2=0.8496).
In the assessment of the estimation models for cotton unit area above-ground dry biomass weights based on RVI (as shown in Table 3), the cubic function model and the quadratic function model exhibit total root mean square differences of 0.3924 and 0.3932, respectively. These values are larger than the corresponding REMS values of other models. Notably, the exponential function model, represented by y=9.5552·exp (0.1133x), demonstrates a rather high correlation coefficient, and remarkably, its root mean square difference is the lowest at 0.3117. This signifies that the estimation precision for the exponential function model is the highest among the considered models, making it a superior choice for estimating cotton unit area above-ground dry biomass compared to other models.
3. Discussion
In our study, the primary focus was on leveraging hyper-spectral vegetation indices to establish remote sensing monitoring models for leaf area indices (LAI) and biomass. Leaf area index (LAI) is an important characteristic of plant canopies directly linked to energy acceptance, water exchange and primary production in plant ecosystem. It is essential for monitoring changes in ecosystem carbon stocks and other ecosystem level fluxes [
28]. In order to estimate LAI in a large area (such as a regional scale), empirical relationships between LAI and spectral vegetation indices (VIs) retrieved from remotely sensed data were proposed. The regression models describing these relationships vary in mathematical forms (linear, exponential, power, inverse of exponential, etc.) [
16,
29]. In the present study, we found the best fit empirical relationships between LAI and VIs was both the power and the exponential function models, with coefficients of determination (r
2) exceeding 0.65. The results were in agreement with the findings from other studies. For instances, the exponential functions were found as the best suitable model to describe empirical relationships between LAI and spectral indices in different crops (corn, wheat, soybean) [
16,
30].
The six fitting models utilizing the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to predict Leaf Area Index (LAI) in cotton all achieved a significance level of α=0.01. Furthermore, all correlation coefficients surpassed 0.7. The best-performing model is the power function model (y=11.084x12.024, r=0.8076**), and the second-best is the exponential model. When comparing the six fitting models based on using the Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) to predict cotton unit area above-ground fresh biomass weights with the corresponding models for dry biomass weights, it is evident that the correlation in the former models is superior to that in the latter models. Among the former six models, the exponential function model stands out as the best (y=52.261·exp(0.1024x), r= 0.8114**). Similarly, in the latter six models, the exponential function model is also identified as the best (y=9.5552·exp(0.1133x), r= 0.8330**). Therefore, adopting the mathematical model based on the exponential function correlation to predict biomass in cotton yields a higher estimation precision. This finding regarding a stronger exponential relation between Vegetation Index (VI) and biomass is consistent with results obtained by previous researchers [
31].
Despite being in its initial stages, the application of hyper-spectral remote sensing in cotton research in Xinjiang holds significant potential for diverse applications in the future. Firstly, there is an opportunity for further research on models based on remote sensing and Vegetation Indices (VIs) to achieve comprehensive monitoring of cotton’s growth. This includes diagnosing the nutrition status in cotton, providing guidance for cotton field irrigation to enhance water resource usage, improving cotton management and fertilization techniques, forecasting cotton diseases and insect pests, and enabling quick predictions of growing areas and production levels.
Application of VIs to estimate crop biomass has been recognized as an effective approach to obtain crop biomass with simplicity and availability, especially at different stages of plant growth and development [
2,
32]. Several previous studies found there were significant variations in estimating crop biophysical parameters by using VIs at different growth stage [
33]. For example,[
32] reported that different VIs exhibited various importance for maize biomass estimation at different growth stages. The differences of crop biomass estimated by using VIs at various plant growth stages were mainly attributed to the potential saturation of spectral indices after plant canopy closure and the influence of the soils at early plant growth stages [
33]. Thus, VIs derived from hyperspectral images were employed in the current study to estimate cotton biomass at different plant growth stages, including early budding, full budding, early blooming, full blooming, full-boll, and boll opening stages. Actually, LAI and RVI were changes along plant growth stages. As a result, plant growth stage should be considered when using plant canopy structure indexes as the variables for biomass estimation. Introducing spectral VIs information at different plant growth stage into traditional VIs-based models could improve the estimation accuracy of rice yields [
33].
In this study, six mathematical models were employed to estimate cotton biomass and they were simple linear regression, power regression, logarithmic regression, exponential regression, quadratic regression and cubic regression. We found that the exponential regression model was the most suitable model for estimating cotton above-ground biomass. Our results were in line with findings from other previous studies [
34]. It was reported that the non-linear models had high prediction accuracy in aboveground biomass estimation of maize, compared the linear regression models [
32]. In a multiple crops study including cotton, potato, soybeans and corn, they found the most relationships between crop biophysical variables and spectral indices were nonlinear. The overwhelming proportions of the best nonlinear models were exponential function [
6].
Conclusions: This study primarily concentrated on cotton canopy remote sensing monitoring. Through a systematic regression analysis of physical parameters and spectral characteristic parameters in the cotton canopy, correlative mathematical models were established for monitoring cotton growth. The prediction of Leaf Area Index (LAI) and biomass in cotton was achieved by analyzing spectral Vegetation Indices (VI). The research findings demonstrate that remote sensing models based on spectral variables are effective in monitoring the dynamic changes of LAI and biomass throughout various growth stages of cotton [
28]. This study results provided a scientific foundation for the precise monitoring of crop growth in the future.
Additionally, the exploration of hyper-spectral remote sensing lays the groundwork for future applications in aerospace hyper-spectral remote sensing. This involves building upon experiences from ground and aerospace remote sensing to advance vegetation monitoring capabilities. The envisioned applications underscore the transformative potential of hyper-spectral remote sensing in shaping the future of cotton research and agricultural practices in Xinjiang.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, Y.Q, methodology, Y.Q, data curation, X.C, and Y.Q, resources, B.C, Q.W and T.J, original draft preparation, Y.Q., review and editing, Y.P and Y.Q, supervision, X.Z, and C.S., project administration, Z.C., and H.Z.
Funding
Special Project for Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (NCG202311);XPCC Agricultural Innovation Project Special Fund Project:Cotton field information intelligent acquisition and intelligent management innovation team(NCG202304)
References
- Pena, M.; Brenning, A.; Sagredo, A. Constructing satellite-derived hyperspectral indices sensitive to canopy structure variables of a Cordilleran Cypress (Austrocedrus chilensis) forest. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. 2012, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kross, A.; McNairn, H.; Lapen, D.; Sunohara, M.; Champagne, C. Assessment of RapidEye vegetation indices for estimation of leaf area index and biomass in corn and soybean crops. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 34, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xiao, J.; Hou, J.; Duan, B. Rape yields estimation research based on spectral analysis for UAV image. J. Geomat. 2017, 42, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A. J., Köhler, P., Magney, T. S., Frankenberg, C., Fung, I., Cohen, R. C. A double peak in the seasonality of California’s photosynthesis as observed from space. Biogeosciences, 2020,17, 405-422. [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A. Reflectance wavebands and indices for remote estimation of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance in pine canopies - a promising technique to rapidly determine nitrogen and cholophyll content. Remote Sensing of Environment. 1998, 63, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Smith, R.B.; De Pauw, E. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000,71:158–182.
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, J. Estimating biomass of winter oilseed rape using vegetation indices and texture metrics derived from UAV multispectral images. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2019, 166, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Chen, Y.; Sui, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. Mechanism analysis of leaf biochemical concentration by high spectral remote Sensing. Journal of Remote Sensing. 2000, 4, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.K.; Chai, L.; Singh, R.P. Crop yield estimation model for Iowa using remote sensing and surface parameters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Long, S.P. Simultaneous improvement in productivity, water use, and albedo through crop structural modification. Global Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revill, A.; Myrgiotis, V.; Florence, A.; Hoad, S.; Rees, R.; MacArthur, A.; Williams, M. Combining process modelling and LAI observations to diagnose winter wheat nitrogen status and forecast yield. Agronomy. 2021, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Long, S. Bernacchi, C.; Liang, X.; Sivapalan, M. Ecohydrological responses of dense canopies to environmental variability: 1. Interplay between vertical structure and photosynthetic pathway. J. Geophys. Res., 2010,115, G04022-G04025. [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Feng, H.; Xu, L.; Miao, M.; Long, H.; Yue, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; Fan, L. Estimation of Crop Growth Parameters Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Sensors.2020,20,1296. [Green Version]. [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Xing, W.; Han, Y.; Bai, Q.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wei, Z.; Wu, W. The Optimal Soil Water Content Models Based on Crop-LAI and Hyperspectral Data of Winter Wheat. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 39, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Q. Rice Nitrogen Nutrition Estimation with RGB Images and Machine Learning Methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengju Z, Dengwei W, Chunyan H. Estimating of cotton canopy fraction of Photosyn The tically active radiation and leaf area index based on hyperspectral remote sensing data. Cotton Science, 2009,21(5):388-393.
- Khan, M.A.; Wahid, A.; Ahmad, M.; Tahir, M.T.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Hasanuzzaman, M. World Cotton Production and Consumption: An Overview. In Cotton Production and Uses: Agronomy, Crop Protection, and Postharvest Technologies; Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–7. ISBN 9789811514722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, G.; Han, L.; Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Xu, B.; Wu, J.; Lei, L. Estimation of Maize Above-Ground Biomass Based on Stem-Leaf Separation Strategy Integrated with LiDAR and Optical Remote Sensing Data. Peer J. 2019, 7, e7593. [PubMed][Green Version]. [CrossRef]
- Weidong F; Shaomin L; Jingfeng H. Resarch of remote sensing monitoring model for winter wheat Biomass. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment. 1997 ,11(1):84-89.
-
https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%9F%B3%E6%B2%B3%E5%AD%90%E5%B8%82/4776421?fromtitle=%E7%9F%B3%E6%B2%B3%E5%AD%90&fromid=348362 .
- RuiLiang P; Peng G. Hyperspectral remote sensing and its application. Beijing: Higher Education Press. 2000.
- Qinxi T; Lanfen Z; Jinnian W. Study on imaging spectrometer remote sensing information for wetland vegetation. Journal of Remote Sensing. 1997, 1 (1):50-57.
- Qianguang X; Weiying C; Peng D. Monitoring the ecological transect in east Asia monsoon region by meteor logical satellite remote sensing. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1997,39(9):826-830.
- Zhiyuan P; Bangjie Y. Analysis of multi-temporal and multi-spatial character of NDVI and crop Condition models development. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering.2000,16 (5):20-22.
- Casanova D; Epema G F; Goudriaan J. Monitoring rice reflectance at field level for estimating biomass and LAI.Field Crops Research.1998,55:83-92. [CrossRef]
- Renchao W; Jingfeng H. Rice yield estimation. Beijing: China Agriculture Press.2002,5.:21-23.
- Brantley, S.T.; Zinnert, J.C. Young, D.R. Application of hyperspectral vegetation indices to detect variations in high leaf area index temperate shrub thicket canopies. Remote Sensing of Environment. 2011, 115, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pavlic, G.; Brown, L.; Cihlar, J.; Leblanc, S.G.; White, P.H.; Hall, R.J.Peddle, D.R.; King, D.J.; Trofymow, J.A.; Swift, E.; Van der Sanden, J.; Pellikka, P.K.E. Derivation and validation of Canada-wide coarse-resolution leaf area index maps using high-resolution satellite imagery and ground measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002,55, 153-162.
- Broge, N.H.; Leblanc, E. Comparing prediction power and stability of broadband and hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimation of green leaf area index and canopy chlorophyll density. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 76, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanrong W. Correlation analysis between vegetation near-ground reflectance spectral characteristics and biomass for inner-mongolia steppe. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2004,28(2):178-185. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q. Estimating the maize biomass by crop height and narrowband vegetation indices derived from UAV-based hyperspectral images. Ecological Indicators. 2021,129, 107985. [CrossRef]
- Gnyp, M.L., Miao, Y.X., Yuan, F., Ustin, S.L., Yu, K., Yao, Y.K., Huang, S.Y., Bareth, G., Hyperspectral canopy sensing of paddy rice aboveground biomass at different growth stages. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 42–55. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, X.; Xie, L.; Zheng, J. Xu, T. Rice Yield Estimation Florescence Spectral Information from UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).