1. Limitation of anti-VEGF therapies.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the elderly. The number of people with AMD in 2020 was 196 million, projected to be 288 million in 2040, representing a substantial global burden on healthcare systems [
1]. Neovascular AMD (nAMD) or choroidal neovascularization (CNV), which accounts for 10-20% of AMD, is responsible for 80-90% of AMD blindness [
2]. The current first-line therapy targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a potent angiogenic factor that stimulates vessel growth and augments vascular permeability. It is estimated that up to 50% of patients have incomplete responses to current anti-VEGF treatment (persistent fluid, unresolved or new hemorrhage) and the long-term outcomes are suboptimal even among responders [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. For example, 67.4% of patients treated with bevacizumab and 51.5% of patients treated with ranibizumab showed persistent retinal fluid accumulation even after 2 years of treatment in the CATT study [
3]. In the VIEW 1 and VIEW 2 trials, 19.7%–36.6% of patients had active exudation after one year of regular 2.0 mg aflibercept treatments [
6]. In patients exiting the MARINA or ANCHOR trials (SEVEN-UP Study), the mean visual acuity gradually decreased during long-term follow-up with a pro re nata retreatment [
7]. Even patients who respond well initially can develop resistance over time (i.e., tachyphylaxis) [
4,
15,
16,
17]. nAMD patients treated with bevacizumab showed a gradual declining response over time, which was not alleviated by increased dosage [
18,
19,
20]. Patients treated with ranibizumab exhibited recurrence in 66% to 76% of cases following 12-24 months of repeated treatment [
21,
22].
Various strategies including high-dose treatment [
19,
23,
24,
25] or switching between anti-VEGF biologics [
26,
27] have been explored in small studies to resolve anti-VEGF resistance with some success over limited follow-up periods. However, early anatomic gains from conversion to higher dose therapy gradually plateau over time with only moderate improvements of central retinal thickness (CRT) and absent or negligible gains in visual acuity [
25,
28]. The improvement on central retinal thickness (CRT) was mild with no or small gains in visual acuity [
26,
28]. A recent NIH sponsored trial comparing high dose bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and aflibercept for treatment-resistant nAMD showed no significant benefit of any group, and no alleviation of injection frequency (one injection per 5.7-6.4 weeks) [
29]. Given this lack of response and the theoretical risks of higher volume injection, further research is recommended before advocating for using even higher dosages of these anti-VEGF agents delivered via standard formulations. Intriguingly, there is considerable similarity between the response to higher dosage of the same therapy and anti-VEGF switching, suggesting additional common mechanisms contribute to anti-VEGF resistance that are not resolved by targeting VEGF alone.
Combination therapies that simultaneously target VEGF and alternate pro-angiogenic signaling pathways have been explored in clinical trials. Combining ranibizumab with pegpleranib (Fovista) or nesvacumab as the antagonist of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) or angiopoietin 2 (Ang2), respectively, failed to achieve endpoints [
30,
31]. Faricimab (Vabysmo), a bispecific antibody that targets both VEGF-A and Ang2, delivered at extended treatment intervals (every 16 weeks) was found to be clinically equivalent (i.e., “no inferiority”) to aflibercept given at 8-week intervals for neovascular AMD, thereby reducing treatment burden in patients [
32]. However, there is no evidence showing that faricimab provided significantly improved benefits in treating anti-VEGF resistant patients. The VEGF pathway remains the exclusive target of most ongoing clinical trials [
33]. Thus, the development of an effective therapy that address anti-VEGF resistance represents an important unmet clinical need.
2. Animal Models of Anti-VEGF Resistance.
Multiple pivotal clinical trials (ANCHOR, MARINA, CATT) have shown that patients of advanced age with larger baseline CNV lesions are less responsive to anti-VEGF treatment and have worse outcomes [
13,
34,
35,
36]
. Importantly, anti-VEGF resistance in CNV patients is frequently associated with arteriolar CNV, characterized by large-caliber branching arterioles, vascular loops, and anastomotic connections (
Figure 1A-F) [
9]. Persistent fluid leakage in arteriolar CNV most likely involves increased exudation from poorly formed tight junctions at arteriovenous anastomotic loops, especially during high rates of blood flow. On the other hand, anti-VEGF responders are characterized by capillary CNV, in which VEGF-mediated permeability is responsible for the leakage (
Figure 1G-J). Furthermore, recurrent anti-VEGF treatment can cause vessel abnormalization, arteriolar CNV formation, and anti-VEGF resistance [
14,
37]. The observed abnormalization of the vessels may be explained by periodic pruning of angiogenic vascular sprouts by VEGF withdrawal in the face of unimpeded arteriogenesis [
14], suggesting a mechanism for acquired anti-VEGF resistance.
We found that laser photocoagulation produces larger CNV lesions in aged mice that are markedly more resistant to anti-VEGF treatment compared with young mice [
38,
39,
40]. Importantly, laser-induced CNV in young and old mice, respectively, mimics capillary and arteriolar CNV (
Figure 2) [
9,
39]. We propose that laser-induced CNV in aged mice is a clinically relevant model of anti-VEGF resistance [
38,
39]. Although this model uses aging as the pathological driver [
39,
40], we do not mean to suggest that age is the only factor dictating experimental or clinical CNV or the response to anti-VEGF therapy. In fact, previous studies have shown that cigarette smoking, environmental co-factors (e.g., viral infection), and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) stimulation increase the extent and severity of experimental CNV with increased arteriolar CNV formation [
41,
42,
43]. The common underlying theme is macrophage activation, which is consistent with our hypothesis that macrophages play a key role in anti-VEGF resistance (see below) [
38,
39]. Several main differences exist between mouse models and human AMD patients. Firstly, C57Bl6/J mice are on an inbred homogeneous genetic background whereas human AMD patients carry a wide range of diverse genetic risk factors. It is known that genetic risk factors (e.g., risk alleles in CFH and ARMS2/HTRA1) influence the response to anti-VEGF therapies [
44,
45,
46]. Secondly, laboratory mice inhabit strictly controlled germ-free environments such as diet and lighting, etc. This is different from human patients in which environmental factors including cigarette smoking and diet contribute to AMD severity. However, age is also an important risk factor as multiple pivotal clinical trials have shown that patients of advanced age and larger baseline CNV lesions are less responsive to anti-VEGF treatment and have worse outcomes [
13,
34,
35,
36]
. This is consistent with our data that laser photocoagulation produces larger CNV lesions in aged mice and these mice are markedly more resistant to anti-VEGF treatment than young mice [
38,
39]. Clearly, multiple genetic and environmental factors confound the age effect in human AMD. This explains why aged individuals with nAMD include both responders and non-responders. The important aspect is that laser-induced CNV in aged mice mimics the arteriolar CNV that is resistant to anti-VEGF treatment in human patients, which is invaluable for translational studies. A parallel example is laser-induced CNV, which is the most widely used model of wet AMD (e.g., in rodents, pigs, nonhuman primates) not only for mechanistic studies, but also for most preclinical treatment evaluation experiments. Although the laser injury model does not have the age-related progressive pathology of nAMD, it captures many of the important features of the human condition, such as newly formed neovascular vessels that project into the subretinal space through defects in Bruch’s membrane, and leukocytes infiltration near CNV lesions [
47,
48,
49]. However, this does not imply laser injury is a risk factor for AMD.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines require that the efficacy of a pharmaceutical product must be demonstrated in two different animal species (one rodent and one non-rodent). Rabbit eyes have been used as a longstanding retinal model due to their relatively large size, sharing physiologic parameters similar to those seen in humans. These similarities include eye size, internal eye structure, eye optical system, eye biomechanics, and eye biochemical features. The rabbit eye axial length is 18.1 mm, nearly 80% that of humans (approximately 23 mm), whereas mice have an axial length of 3.2 mm, only 13% that of humans, and rats have an axial length of 5.98 mm. Various physiologic manipulation technologies and equipment developed for human eyes can be applied to rabbits with minimal modification [
50,
51,
52]. Much is known about the rabbit choroidal vasculature, which shares many similarities to human vasculature [
53,
54]. Therefore, we developed a rabbit CNV model of anti-VEGF resistance for drug development. Consistent with mouse studies, Matrigel and VEGF-induced CNV in aged rabbits is resistant to anti-VEGF treatments (i.e., bevacizumab) [
55]. Matrigel-induced CNV in rabbits is considered a closer model of human CNV compared to laser-induced models, in part because Matrigel mimics sub-RPE deposits associated with human CNV [
53,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60]. The much larger eye size, longer half-time, and residence time of therapeutics makes the rabbit model ideal for efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and toxicology studies. We believe that the two animal models of CNV we developed, resistant to anti-VEGF therapies, are valid models for anti-VEGF resistance in AMD to test new therapies. Currently, no other animal models are available for this purpose. As no animal models fully recapitulate all features of neovascular AMD, successful strategies that have demonstrated promise in alleviating anti-VEGF resistance in aged animals must be evaluated in clinical trials.
3. Role of Macrophages in Anti-VEGF Resistance.
Several lines of evidence suggest that the accumulation of intracellular lipids in old macrophages plays a critical role in anti-VEGF resistance. Firstly, decreased efficacy of anti-VEGF therapy with age correlates inversely with age-dependent increase of intracellular lipids in macrophages [
38]. Secondly, macrophage depletion in old mice converts arteriolar CNV to capillary CNV [
9] and restores CNV sensitivity to anti-VEGF treatment [
38]. Thirdly, macrophages in surgically excised human CNV membranes following bevacizumab treatment have increased density and proliferative activity [
61], and the proportion of circulating CD11b+ monocytes correlates with the number of anti-VEGF injections in patients with neovascular AMD and PCV [
62]. Actions of lipid laden macrophages are also consistent with the well-established roles of monocytes and macrophages in promoting arteriogenesis by releasing growth factors, proteases and chemokines that mediate structural remodeling of the extracellular matrices, cell proliferation, and migration [
63,
64,
65,
66]. Both preclinical and clinical studies are consistent with an involvement of neovascular remodeling, in which macrophages are known to play important roles in anti-VEGF resistance [
9,
14,
64].
Consistent with contributions of lipid-laden macrophages in human arteriolar CNV formation, Lutty et al., identified a high frequency of activated HLA-DR
+ macrophages associated with arteriolar CNV in human postmortem CNV specimens (Figures 9 and 10 in Ref [
67]). In addition to lipid-containing microglial cells found in type 3 neovascularization [
68], hyperreflective lipid-filled cells of monocyte origin (i.e., macrophages) have been detected in neovascularization AMD [
69]. Curcio and colleagues suggest that these monocyte-derived cells filled with lipid droplets resemble foam cells in coronary artery plaques [
69], which is well-known to promote inflammation in association with atherosclerosis.
Oxidized lipoproteins and macrophages were colocalized with CNV lesions and most macrophages in the CNV membranes expressed oxidized lipoprotein-specific scavenger receptors, suggesting a close link between oxidized lipoproteins and macrophages in AMD [
70]
. Transcriptomic profiling showed that
impaired cholesterol homeostasis is perturbed in aged macrophages, and that oxysterol signatures in patient samples distinguish AMD from physiologic aging [
71]
. Expression of ABCA1 and cholesterol efflux are reduced in aged macrophages in mice and humans (old people and AMD) [
72]
, and ABCA1 polymorphisms are associated with advanced AMD [
73]
. Multiple studies confirm the involvement of dysregulated lipid metabolism, macrophages, and inflammation in CNV [
59,
61,
71,
72,
74,
75,
76,
77,
78,
79,
80,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85], as well as beneficial roles of lipid lowering medications in reducing the risk of CNV, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic macular edema [
86,
87,
88,
89]. It should be stressed that it can be difficult to definitively distinguish between microglia and macrophages by in vivo imaging of human patients. Although our macrophage depletion experiments suggests that blood-derived macrophages contribute to anti-VEGF resistance [
38], retinal microglia may also be involved in anti-VEGF resistance.
Positive and negative roles have been assigned to macrophages in the progression of CNV pathogenesis. Macrophages may play a beneficial role in eliminating drusen and waste products, potentially reducing the formation of CNV [
90,
91]. Macrophages from young but not old mice inhibit experimental CNV [
72,
78]. Nevertheless, substantial evidence using multiple criteria including histology and genetics in both animal models and human patients supports the involvement of macrophages in CNV pathogenesis, particularly evident in their consistent presence within CNV lesions expressing elevated VEGF [
59,
62,
72,
74,
75,
78,
79,
80,
81,
82,
83,
92]. Macrophage activation is also associated with CNV [
92]. Notably, during subretinal neovascularization, endothelial cells migrate through defects in Bruch’s membrane, primarily composed of elastin and collagen. Macrophages, expressing matrix metalloproteinases, contribute to the breakdown of Bruch’s membrane. Our data suggest that cholesterol dysregulation, inflammation, and macrophage activation underline the pathological role of aged macrophages in anti-VEGF resistance. Thus, we propose a strategic approach to manage anti-VEGF resistance by selectively targeting activated inflammatory macrophages. This can be achieved by normalizing the lipid rafts of activated macrophages, referred to as “inflammarafts [
93,
94],” in CNV lesions (refer to “treatment strategies” below). This approach ensures the targeted intervention of the pathology without compromising the protective functions of macrophages at various stages of lesion progression.
4. Treatment Strategies for Anti-VEGF Resistance by Simultaneously Targeting Capillary and Arteriolar CNV.
Our results suggest that while VEGF-dependent capillary angiogenesis is dominant in CNV pathogenesis of young mice, inflammation-dependent neovascular remodeling and arteriolar CNV formation involving macrophages becomes dominant in aged mice and contributes to anti-VEGF resistance. Therefore, an effective treatment strategy requires the targeting of both capillary and arteriolar CNV. Because CNV is driven by abnormal levels of angiogenesis and inflammation with critical roles for VEGF-A, endothelial cells, and macrophages, we explored a new treatment strategy that targets each of these central elements to address the limitations of current anti-VEGF [
38,
39].
Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts harboring activated receptors (e.g., VEGFR2, TLR4) serve as the organizing platform to initiate angiogenic and inflammatory signaling [
93,
95,
96,
97]. Extracellular apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) binding protein (AIBP) regulates lipid rafts via augmenting cholesterol efflux from endothelial cells, macrophages, and T cells, resulting in inhibition of angiogenesis and atherosclerosis, etc. [
38,
98,
99,
100,
101,
102,
103,
104,
105]. AIBP binds its partner apoA-I or high-density lipoprotein (HDL) to enhance cholesterol efflux and inhibit lipid raft-anchored VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells [
38,
98]. By binding to the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), AIBP/apoA-I augments cholesterol efflux from macrophages and microglia, normalizes plasma lipid rafts, and suppresses inflammation [
94,
99,
100,
106]. The ability of AIBP to target both hyperactive endothelial cells and cholesterol-laden macrophages makes it an ideal candidate to address the challenge of anti-VEGF resistance in CNV treatment. We found that a combination of AIBP/apoA-I and anti-VEGF treatment ameliorated anti-VEGF resistance to aflibercept in experimental CNV in old mice by robustly inhibiting arteriolar CNV (
Figure 3) [
39]. Despite sharing endothelial VEGFR2 signaling as a common target, combined AIBP and anti-VEGF provides synergistic therapeutic benefit for CNV. This is because macrophages that are recruited by VEGF to lesion sites of inflammation secrete additional VEGF and other pro-angiogenic factors thereby creating strong positive feedback loops [
76,
77,
107]. Thus, both anti-VEGF agents and AIBP are required to interrupt the vicious cycle of events initiated by the reciprocal causal nexus of VEGF and inflammation.
Whereas the precise mechanism for arteriolar CNV formation is unknown, our results indicate that it shares features with arteriogenesis while capillary CNV forms via angiogenesis, in which new capillary blood vessels sprout from a preexisting blood vessel. Although angiogenesis is highly VEGF dependent, arteriogenesis is not VEGF dependent [
108,
109,
110]. In support of this hypothesis, we found that capillary CNV in young mice is highly responsive to aflibercept while arteriolar CNV in old mice is resistant [
39]. These findings are consistent with clinical findings that anti-VEGF resistance in CNV patients is frequently associated with arteriolar CNV while anti-VEGF responders are associated with capillary CNV [
9]. Yet despite this, current nAMD drugs only target angiogenesis with minimal or no effects on arteriogenesis. AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy resolves this issue by simultaneously targeting VEGF-dependent angiogenesis and VEGF-independent arteriogenesis (
Figure 4).
As discussed above, macrophages may have varying roles in CNV. How can we ensure the proposed combination therapy only targets pathological macrophages? This is achieved through the selectivity and normalization properties of AIBP on lipid rafts of activated target cells. Previous studies have shown that AIBP selectively targets lipid rafts of activated macrophages/microglia and inhibits inflammatory signaling by binding to activated (e.g., dimerized) TLR4 [
93,
94,
106]. AIBP normalizes lipid rafts of activated macrophages/microglia (i.e.,
inflammarafts [
93]
) [
94]
, reducing the proinflammatory and proangiogenic
subtypes (i.e., pathogenic) without affecting normal macrophage function including their protective functions.
Out of the three components, infusion of HDL/apoA-I had been tested in clinical trials in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Whereas HDL/apoA-1 targeted therapies successfully ameliorate plaque in atherosclerosis mouse models, clinical trials failed to show significant reduction of human atheroma (reviewed in Ref [
111]). Multiple possible reasons may account for the different responses of humans versus animal models to HDL/apoA-1 replacement therapy. One study reported that raising apoA-1 had striking stage-specific atheroprotective effects [
112]. When initiated at early stages of disease, apoA-I markedly inhibited atheroma progression and systemic inflammation, but these benefits were attenuated when treatment was initiated at later times in mice with advanced atheroma. Most preclinical studies reporting such benefits were performed in young mice with early-stage lesions [
113,
114,
115] whereas large-scale HDL-raising clinical trials in elderly patients with established plaque failed to show benefit. This is antiparallel to our studies that demonstrate efficacy of combination AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF therapy in old mice with severe arteriolar CNV lesions that resemble arteriolar CNV in anti-VEGF resistant AMD patients [
39]. In addition, we have shown that: 1) apoA-I alone is insufficient to treat laser-induced CNV (Figure 6a,b in Ref. [
38]); and 2) AIBP/apoA-I is insufficient to treat arteriolar CNV in old mice (Figure 6e in Ref. [
38]). The likely reason is that AIBP can significantly enhance apoA-I’s ability to remove cholesterol from target cells (e.g., macrophages and endothelial cells) [
38,
94,
98,
99,
100,
106]. That is why we propose to develop the AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy.
5. How Does the Combination Therapy Compare with Anti-VEGF Gene Therapy and Higher Dose Anti-VEGF Regimen Currently in Development?
AMD is a complex multi-factorial disease. It is unrealistic to expect that targeting one factor or one pathway will solve all the problems. The anti-VEGF gene therapy and higher dose regimen that are currently in development only target VEGF-dependent angiogenesis without targeting arteriogenesis, which are unlikely to resolve resistance (see Discussion regarding high dose regimen in 1. Limitation of anti-VEGF therapies). In the HARBOR trial, high dose ranibizumab (2.0 mg) did not increase efficacy in treatment-naïve patients [
116]. In the recently completed PULSAR trial, 8 mg aflibercept sustained improvements of visual acuity and retinal anatomy at 22 months with 36% fewer injections relative to the standard 2-mg dose, suggesting the potential to reduce treatment burdens. However, there is no evidence that the high-dose aflibercept eliminates anti-VEGF resistance. Rather, there is evidence that this unbalanced treatment targeting VEGF-dependent angiogenesis alone can cause vessel abnormalization, arteriolar CNV formation, and anti-VEGF resistance [
14,
37] (
Figure 4). Combination therapy has an advantage by targeting both angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. A possible analogy is anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) “cocktail” therapy that slows the progression of HIV markedly better than any monotherapy.
6. Perspectives
Because long-term efficacy of anti-VEGF therapy is suboptimal and repeated anti-VEGF treatment can lead to arteriolar CNV and anti-VEGF resistance [
14,
37], we predict that combination therapy with AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF not only overcomes anti-VEGF resistance for monotherapy non-responders, but also improves therapeutic efficacy at all levels of anti-VEGF response in the treatment of nAMD. Combination therapy has the potential to replace current anti-VEGF monotherapies and become a new first-line therapy. The global anti-VEGF therapeutics market size was valued at USD 12.3 billion in 2022 and is estimated to reach USD 13.7 billion by 2031, representing a significant portion of global healthcare cost. Our objective is to generate preclinical efficacy and safety data to support an Investigational New Drug (IND) application for AIBP/apoA-I/aflibercept therapy and advance to a
first-in-human Phase I clinical trial that will ultimately benefit a wide range of nAMD patients including anti-VEGF non-responders and responders with sub-optimal long-term efficacy.
Patent
Fu Y, Fang L, Parker M, Shen M, Yan Q, and Enemchukwu N (2020). Patent Title: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING NEOVASCULARIZATION AND ISHEMIC RETINOPATHIES BY TARGETING ANGIOGENESIS AND CHOLESTEROL TRANSPORT. WO2021240488A1 WIPO(PCT). PCT Patent Application No.: PCT/IB2021/055463. PCT pending.
Authors contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F.; Investigation, Z. Z.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Y. F.; Writing—Review & Editing, K.W. and Y. M. P.; Funding Acquisition, Y. F. and Y. M. P.
Conflict of interest’s statement
YF has a pending patent on the AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy. All other authors, None.
References
- Wong, W. L. et al. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2, e106–e116 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Bressler, N. M., Bressler, S. B. & Fine, S. L. Age-related macular degeneration. Surv. Ophthalmol. 32, 375–413 (1988). [CrossRef]
- Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials (CATT) Research Group et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The Comparison of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials. Ophthalmology 123, 1751–1761 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., Zhao, J. & Sun, X. Resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a comprehensive review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 10, 1857–1867 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Ehlken, C. et al. Switch of anti-VEGF agents is an option for nonresponders in the treatment of AMD. Eye Lond. Engl. 28, 538–545 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Heier, J. S. et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 119, 2537–2548 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Rofagha, S. et al. Seven-year outcomes in ranibizumab-treated patients in ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON: a multicenter cohort study (SEVEN-UP). Ophthalmology 120, 2292–2299 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Krebs, I. et al. Non-responders to treatment with antagonists of vascular endothelial growth factor in age-related macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 97, 1443–1446 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Mettu, P. S., Allingham, M. J. & Cousins, S. W. Incomplete response to Anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular AMD: Exploring disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 100906 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Otsuji, T. et al. Initial non-responders to ranibizumab in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 7, 1487–1490 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Cobos, E. et al. Association between CFH, CFB, ARMS2, SERPINF1, VEGFR1 and VEGF polymorphisms and anatomical and functional response to ranibizumab treatment in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol. (Copenh.) 96, e201–e212 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Kitchens, J. W. et al. A pharmacogenetics study to predict outcome in patients receiving anti-VEGF therapy in age related macular degeneration. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 7, 1987–1993 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, P. J. et al. Characteristics of Patients Losing Vision after 2 Years of Monthly Dosing in the Phase III Ranibizumab Clinical Trials. Ophthalmology 118, 523–530 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Spaide, R. F. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Signs of Vascular Abnormalization With Antiangiogenic Therapy for Choroidal Neovascularization. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 160, 6–16 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D., Zachary, I. & Jia, H. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Anti-VEGF Therapy for Neovascular Eye Diseases. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 64, 28 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Zuber-Laskawiec, K., Kubicka-Trzaska, A., Karska-Basta, I., Pociej-Marciak, W. & Romanowska-Dixon, B. Non-responsiveness and tachyphylaxis to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment in naive patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 70, (2019).
- Hara, C. et al. Tachyphylaxis during treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration with aflibercept. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 257, 2559–2569 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Schaal, S., Kaplan, H. J. & Tezel, T. H. Is there tachyphylaxis to intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor pharmacotherapy in age-related macular degeneration? Ophthalmology 115, 2199–2205 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Forooghian, F., Cukras, C., Meyerle, C. B., Chew, E. Y. & Wong, W. T. Tachyphylaxis after intravitreal bevacizumab for exudative age-related macular degeneration. Retina Phila. Pa 29, 723–731 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R. Y., Santos, D. & Oliver, S. C. N. RATES OF EXUDATIVE RECURRENCE FOR EYES WITH INACTIVATED WET AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION ON 12-WEEK INTERVAL DOSING WITH BEVACIZUMAB THERAPY. Retina Phila. Pa 40, 679–685 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y. et al. Factors Associated with Recurrence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration after Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ophthalmology 122, 2303–2310 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H., Chang, Y. S., Kim, J. W., Kim, C. G. & Lee, D. W. RECURRENCE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 3 NEOVASCULARIZATION (RETINAL ANGIOMATOUS PROLIFERATION) AFTER INTRAVITREAL RANIBIZUMAB. Retina Phila. Pa 37, 1508–1515 (2017). [CrossRef]
- You, Q. S. et al. HIGH-DOSE HIGH-FREQUENCY AFLIBERCEPT FOR RECALCITRANT NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION. Retina Phila. Pa 38, 1156–1165 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. M., Chen, E., Mariani, A., Major, J. C., & SAVE Study Group. Super-dose anti-VEGF (SAVE) trial: 2.0 mg intravitreal ranibizumab for recalcitrant neovascular macular degeneration-primary end point. Ophthalmology 120, 349–354 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Fung, A. T. et al. Pilot study to evaluate the role of high-dose ranibizumab 2.0 mg in the management of neovascular age-related macular degeneration in patients with persistent/recurrent macular fluid <30 days following treatment with intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy (the LAST Study). Eye Lond. Engl. 26, 1181–1187 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Chang, A. A. et al. Intravitreal aflibercept for treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 121, 188–192 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Marquis, L.-M. & Mantel, I. Beneficial switch from aflibercept to ranibizumab for the treatment of refractory neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 258, 1591–1596 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Spooner, K. et al. Long-term outcomes of switching to aflibercept for treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol. (Copenh.) 97, e706–e712 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Broadhead, G. K., Keenan, T. D. L., Chew, E. Y., Wiley, H. E. & Cukras, C. A. Comparison of agents using higher dose anti-VEGF therapy for treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 260, 2239–2247 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Dunn, E. N., Hariprasad, S. M. & Sheth, V. S. An Overview of the Fovista and Rinucumab Trials and the Fate of Anti-PDGF Medications. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retina 48, 100–104 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Apte, R. S., Chen, D. S. & Ferrara, N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell 176, 1248–1264 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Heier, J. S. et al. Efficacy, durability, and safety of intravitreal faricimab up to every 16 weeks for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (TENAYA and LUCERNE): two randomised, double-masked, phase 3, non-inferiority trials. The Lancet 399, 729–740 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Khachigian, L. M., Liew, G., Teo, K. Y. C., Wong, T. Y. & Mitchell, P. Emerging therapeutic strategies for unmet need in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J. Transl. Med. 21, 133 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P. K. et al. Ranibizumab for predominantly classic neovascular age-related macular degeneration: subgroup analysis of first-year ANCHOR results. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 144, 850–857 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Finger, R. P., Wickremasinghe, S. S., Baird, P. N. & Guymer, R. H. Predictors of anti-VEGF treatment response in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Surv. Ophthalmol. 59, 1–18 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Boyer, D. S. et al. Subgroup analysis of the MARINA study of ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 114, 246–252 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Lumbroso, B. et al. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Study of Choroidal Neovascularization Early Response after Treatment. Dev. Ophthalmol. 56, 77–85 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. et al. Combination of apolipoprotein-A-I/apolipoprotein-A-I binding protein and anti-VEGF treatment overcomes anti-VEGF resistance in choroidal neovascularization in mice. Commun. Biol. 3, 386 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Shen, M. M. & Fu, Y. Combination of AIBP, apoA-I, and Aflibercept Overcomes Anti-VEGF Resistance in Neovascular AMD by Inhibiting Arteriolar Choroidal Neovascularization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 63, 2 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Attarde, A., Riad, T. S., Zhang, Z., Ahir, M. & Fu, Y. Characterization of Vascular Morphology of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration by Indocyanine Green Angiography. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. e65682 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Suñer, I. J. et al. Nicotine increases size and severity of experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 45, 311–317 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Cousins, S. W. et al. Macrophage Activation Associated with Chronic Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection Results in More Severe Experimental Choroidal Neovascularization. PLOS Pathog. 8, e1002671 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Mettu, P. S., Saloupis, P. & Cousins, S. W. PAMP Stimulation of Macrophages Promotes Neovascular Remodeling in Experimental Choroidal Neovascularization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55, 1198 (2014).
- Wang, Z. et al. Genetic associations of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy response in age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Ophthalmol. (Copenh.) 100, e669–e680 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., Liu, Z., Hu, S. & Qi, J. Meta-Analysis of the Pharmacogenetics of ARMS2 A69S Polymorphism and the Response to Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmic Res. 64, 192–204 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Gourgouli, K. et al. Investigation of genetic base in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Int. Ophthalmol. 40, 985–997 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Grossniklaus, H. E. et al. Correlation of histologic 2-dimensional reconstruction and confocal scanning laser microscopic imaging of choroidal neovascularization in eyes with age-related maculopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960 118, 625–629 (2000). [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T., Goodnight, R., Prendergast, R. A. & Ryan, S. J. Activated macrophages in experimental subretinal neovascularization. Ophthalmol. J. Int. Ophtalmol. Int. J. Ophthalmol. Z. Augenheilkd. 200, 39–44 (1990). [CrossRef]
- Oh, H. et al. The potential angiogenic role of macrophages in the formation of choroidal neovascular membranes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 40, 1891–1898 (1999).
- Ahn, S. J. et al. Use of Rabbit Eyes in Pharmacokinetic Studies of Intraocular Drugs. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. e53878 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Del Amo, E. M. & Urtti, A. Rabbit as an animal model for intravitreal pharmacokinetics: Clinical predictability and quality of the published data. Exp. Eye Res. 137, 111–124 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Hasumura, T., Yonemura, N., Hirata, A., Murata, Y. & Negi, A. Retinal damage by air infusion during vitrectomy in rabbit eyes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41, 4300–4304 (2000).
- Qiu, G. et al. A new model of experimental subretinal neovascularization in the rabbit. Exp. Eye Res. 83, 141–152 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. et al. Real-time OCT guidance and multimodal imaging monitoring of subretinal injection induced choroidal neovascularization in rabbit eyes. Exp. Eye Res. 186, 107714 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V. P. et al. Age differential response to bevacizumab therapy in choroidal neovascularization in rabbits. Exp. Eye Res. 223, 109215 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. et al. A subretinal matrigel rat choroidal neovascularization (CNV) model and inhibition of CNV and associated inflammation and fibrosis by VEGF trap. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51, 6009–6017 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Lima, L. H., Farah, M. E., Gum, G., Ko, P. & de Carvalho, R. A. P. Sustained and targeted episcleral delivery of celecoxib in a rabbit model of retinal and choroidal neovascularization. Int. J. Retina Vitr. 4, 31 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Green, W. R. & Enger, C. Age-related macular degeneration histopathologic studies. The 1992 Lorenz E. Zimmerman Lecture. Ophthalmology 100, 1519–1535 (1993). [CrossRef]
- Sarks, J. P., Sarks, S. H. & Killingsworth, M. C. Morphology of early choroidal neovascularisation in age-related macular degeneration: correlation with activity. Eye Lond. Engl. 11 ( Pt 4), 515–522 (1997). [CrossRef]
- Sarks, S. H. New vessel formation beneath the retinal pigment epithelium in senile eyes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 57, 951–965 (1973). [CrossRef]
- Tatar, O. et al. Effect of bevacizumab on inflammation and proliferation in human choroidal neovascularization. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960 126, 782–790 (2008). 2008. [CrossRef]
- Subhi, Y. et al. Association of CD11b+ Monocytes and Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Injections in Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 137, 515–522 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, I. & Schaper, W. Arteriogenesis Versus Angiogenesis: Two Mechanisms of Vessel Growth. News Physiol. Sci. Int. J. Physiol. Prod. Jointly Int. Union Physiol. Sci. Am. Physiol. Soc. 14, 121–125 (1999). [CrossRef]
- Heil, M., Eitenmüller, I., Schmitz-Rixen, T. & Schaper, W. Arteriogenesis versus angiogenesis: similarities and differences. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 10, 45–55 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Arras, M. et al. Monocyte activation in angiogenesis and collateral growth in the rabbit hindlimb. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 40–50 (1998). [CrossRef]
- la Sala, A., Pontecorvo, L., Agresta, A., Rosano, G. & Stabile, E. Regulation of collateral blood vessel development by the innate and adaptive immune system. Trends Mol. Med. 18, 494–501 (2012). [CrossRef]
- McLeod, D. S. et al. Distribution and Quantification of Choroidal Macrophages in Human Eyes With Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 57, 5843–5855 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Li, M. et al. Clinicopathologic Correlation of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Treated Type 3 Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 125, 276–287 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Pang, C. E., Messinger, J. D., Zanzottera, E. C., Freund, K. B. & Curcio, C. A. The Onion Sign in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Represents Cholesterol Crystals. Ophthalmology 122, 2316–2326 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Kamei, M. et al. Scavenger receptors for oxidized lipoprotein in age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 48, 1801–1807 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. B. et al. Oxysterol Signatures Distinguish Age-Related Macular Degeneration from Physiologic Aging. EBioMedicine 32, 9–20 (2018. [CrossRef]
- Impaired cholesterol efflux in senescent macrophages promotesSene, A. et al. Impaired cholesterol efflux in senescent macrophages promotes age-related macular degeneration. Cell Metab. 17, 549–561 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Neale, B. M. et al. Genome-wide association study of advanced age-related macular degeneration identifies a role of the hepatic lipase gene (LIPC). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 7395–7400 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Heidmann, D. G. et al. Macrophage depletion diminishes lesion size and severity in experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44, 3586–3592 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, E., Anand, A., Ambati, B. K., van Rooijen, N. & Ambati, J. Macrophage depletion inhibits experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44, 3578–85 (2003). 2003. [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S. et al. VEGF164-mediated inflammation is required for pathological, but not physiological, ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. J Exp Med 198, 483–9 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Nagineni, C. N., Kommineni, V. K., William, A., Detrick, B. & Hooks, J. J. Regulation of VEGF expression in human retinal cells by cytokines: implications for the role of inflammation in age-related macular degeneration. J. Cell. Physiol. 227, 116–126 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Apte, R. S., Richter, J., Herndon, J. & Ferguson, T. A. Macrophages inhibit neovascularization in a murine model of age-related macular degeneration. PLoS Med. 3, e310 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Cherepanoff, S., McMenamin, P., Gillies, M. C., Kettle, E. & Sarks, S. H. Bruch’s membrane and choroidal macrophages in early and advanced age-related macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 94, 918–925 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Grossniklaus, H. E. et al. Macrophage and retinal pigment epithelium expression of angiogenic cytokines in choroidal neovascularization. Mol. Vis. 8, 119–126 (2002).
- Hagbi-Levi, S. et al. Proangiogenic characteristics of activated macrophages from patients with age-related macular degeneration. Neurobiol. Aging 51, 71–82 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Killingsworth, M. C., Sarks, J. P. & Sarks, S. H. Macrophages related to Bruch’s membrane in age-related macular degeneration. Eye Lond. Engl. 4 ( Pt 4), 613–621 (1990). [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P. F., Lambert, H. M., Grossniklaus, H. E. & Sternberg, P. Well-defined subfoveal choroidal neovascular membranes in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 100, 415–422 (1993). [CrossRef]
- Campa, C. et al. Inflammatory mediators and angiogenic factors in choroidal neovascularization: pathogenetic interactions and therapeutic implications. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, (2010). [CrossRef]
- Chen, M., Chan, C.-C. & Xu, H. Cholesterol homeostasis, macrophage malfunction and age-related macular degeneration. Ann. Transl. Med. 6, S55 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Kang, E. Y.-C. et al. Association of Statin Therapy With Prevention of Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 137, 363–371 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-R. et al. Association of statin use and hypertriglyceridemia with diabetic macular edema in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 16, 4 (2017). . [CrossRef]
- Vail, D., Callaway, N. F., Ludwig, C. A., Saroj, N. & Moshfeghi, D. M. Lipid-Lowering Medications Are Associated with Lower Risk of Retinopathy and Ophthalmic Interventions among United States Patients with Diabetes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 207, 378–384 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Vavvas, D. G. et al. Regression of Some High-risk Features of Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) in Patients Receiving Intensive Statin Treatment. EBioMedicine 5, 198–203 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Duvall, J. & Tso, M. O. Cellular mechanisms of resolution of drusen after laser coagulation. An experimental study. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960 103, 694–703 (1985). [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J. V. Macrophages eyed in macular degeneration. Nat. Med. 9, 1350–1351 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Cousins, S. W., Espinosa-Heidmann, D. G. & Csaky, K. G. Monocyte activation in patients with age-related macular degeneration: a biomarker of risk for choroidal neovascularization? Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960 122, 1013–1018 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y. I., Navia-Pelaez, J. M., Corr, M. & Yaksh, T. L. Lipid rafts in glial cells: role in neuroinflammation and pain processing. J. Lipid Res. 61, 655–666 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Navia-Pelaez, J. M. et al. Normalization of cholesterol metabolism in spinal microglia alleviates neuropathic pain. J. Exp. Med. 218, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, L. et al. Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 Activity by Caveolin-1 and Plasma Membrane Cholesterol. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 334–347 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Laurenzana, A. et al. Lipid rafts: integrated platforms for vascular organization offering therapeutic opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 72, 1537–1557 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, M. et al. Endothelium in Spots – High-Content Imaging of Lipid Rafts Clusters in db/db Mice. PLOS ONE 9, e106065 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Fang, L. et al. Control of angiogenesis by AIBP-mediated cholesterol efflux. Nature 498, 118–122 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D. A. et al. AIBP protects against metabolic abnormalities and atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. (2018). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. et al. AIBP reduces atherosclerosis by promoting reverse cholesterol transport and ameliorating inflammation in apoE-/-mice. Atherosclerosis (2018). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. et al. Apolipoprotein A-1 binding protein promotes macrophage cholesterol efflux by facilitating apolipoprotein A-1 binding to ABCA1 and preventing ABCA1 degradation. Atherosclerosis 248, 149–159 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Dubrovsky, L. et al. Inhibition of HIV Replication by Apolipoprotein A-I Binding Protein Targeting the Lipid Rafts. mBio 11, (2020). [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q. et al. AIBP-mediated cholesterol efflux instructs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell fate. Science 363, 1085–1088 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H. et al. AIBP augments cholesterol efflux from alveolar macrophages to surfactant and reduces acute lung inflammation. JCI Insight 3, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X., Luo, J. & Fang, L. AIBP, Angiogenesis, Hematopoiesis, and Atherogenesis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 23, 1 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Woller, S. A. et al. Inhibition of Neuroinflammation by AIBP: Spinal Effects upon Facilitated Pain States. Cell Rep. 23, 2667–2677 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Corliss, B. A., Azimi, M. S., Munson, J. M., Peirce, S. M. & Murfee, W. L. Macrophages: An Inflammatory Link Between Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Microcirc. N. Y. N 1994 23, 95–121 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Deindl, E. et al. Role of ischemia and of hypoxia-inducible genes in arteriogenesis after femoral artery occlusion in the rabbit. Circ. Res. 89, 779–786 (2001). [CrossRef]
- Schierling, W. et al. The role of angiogenic growth factors in arteriogenesis. J. Vasc. Res. 46, 365–374 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. et al. Immunohistochemical study of the growth factors, aFGF, bFGF, PDGF-AB, VEGF-A and its receptor (Flk-1) during arteriogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 343, 223–229 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Abudukeremu, A. et al. Efficacy and Safety of High-Density Lipoprotein/Apolipoprotein A1 Replacement Therapy in Humans and Mice With Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Morton, J. et al. Strikingly Different Atheroprotective Effects of Apolipoprotein A-I in Early- Versus Late-Stage Atherosclerosis. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 3, 187–199 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Shah, P. K. et al. High-dose recombinant apolipoprotein A-I(milano) mobilizes tissue cholesterol and rapidly reduces plaque lipid and macrophage content in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Potential implications for acute plaque stabilization. Circulation 103, 3047–3050 (2001). [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A. et al. Intravenous injection of rabbit apolipoprotein A-I inhibits the progression of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15, 1882–1888 (1995). [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, R. K. et al. Regression of atherosclerosis induced by liver-directed gene transfer of apolipoprotein A-I in mice. Circulation 100, 1816–1822 (1999). [CrossRef]
- Busbee, B. G. et al. Twelve-month efficacy and safety of 0.5 mg or 2.0 mg ranibizumab in patients with subfoveal neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 120, 1046–1056 (2013). [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Clinical examples of treatment responses in arteriolar CNV and capillary CNV. (A-F) Arteriolar CNV. At baseline, (A) fundus photography and (B) fluorescein angiography (FA) demonstrate evidence of serous pigment epithelial detachment, (C) indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) demonstrates an arteriolar predominant lesion, with feeder artery (red arrowhead), arteriole (orange arrow), ill-defined marginal rim of vessels (yellow-dotted region, probable capillaries), and draining vein (green arrowhead). Post-loading dose with three anti-VEGF treatments, (D) there is large submacular hemorrhage in the macula by clinical exam and fundus photography, (E) FA demonstrates blockage of fluorescence from the hemorrhage but increased late hyperfluorescence at the margin with expanding, blurry margins consistent with leakage from CNV, and (F) ICGA demonstrates growth of the CNV lesion, with increased vessel caliber of choroidal feeder artery (red arrowhead), growth of new branching arterioles (orange arrow), extension of arterioles with vascular loops without visible capillaries into the macula (yellow-dotted region), and draining venule (green arrowhead). (G-J) Capillary CNV. At baseline, (G) FA demonstrates a Type 2 CNV pattern and (H) ICGA demonstrates capillary CNV morphology (red arrows). Post-treatment with a single anti-VEGF, (I) FA shows clearance of the CNV and (J) ICGA shows regression of the capillary microvascular structure (red arrows). Used with permission of Elsevier Science & Technology Journals, from Incomplete response to Anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular AMD: Exploring disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities by Mettu, P. S., Allingham, M. J. & Cousins, S., Prog. Retin. Eye Res. (2021) 82:100906.
Figure 1.
Clinical examples of treatment responses in arteriolar CNV and capillary CNV. (A-F) Arteriolar CNV. At baseline, (A) fundus photography and (B) fluorescein angiography (FA) demonstrate evidence of serous pigment epithelial detachment, (C) indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) demonstrates an arteriolar predominant lesion, with feeder artery (red arrowhead), arteriole (orange arrow), ill-defined marginal rim of vessels (yellow-dotted region, probable capillaries), and draining vein (green arrowhead). Post-loading dose with three anti-VEGF treatments, (D) there is large submacular hemorrhage in the macula by clinical exam and fundus photography, (E) FA demonstrates blockage of fluorescence from the hemorrhage but increased late hyperfluorescence at the margin with expanding, blurry margins consistent with leakage from CNV, and (F) ICGA demonstrates growth of the CNV lesion, with increased vessel caliber of choroidal feeder artery (red arrowhead), growth of new branching arterioles (orange arrow), extension of arterioles with vascular loops without visible capillaries into the macula (yellow-dotted region), and draining venule (green arrowhead). (G-J) Capillary CNV. At baseline, (G) FA demonstrates a Type 2 CNV pattern and (H) ICGA demonstrates capillary CNV morphology (red arrows). Post-treatment with a single anti-VEGF, (I) FA shows clearance of the CNV and (J) ICGA shows regression of the capillary microvascular structure (red arrows). Used with permission of Elsevier Science & Technology Journals, from Incomplete response to Anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular AMD: Exploring disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities by Mettu, P. S., Allingham, M. J. & Cousins, S., Prog. Retin. Eye Res. (2021) 82:100906.
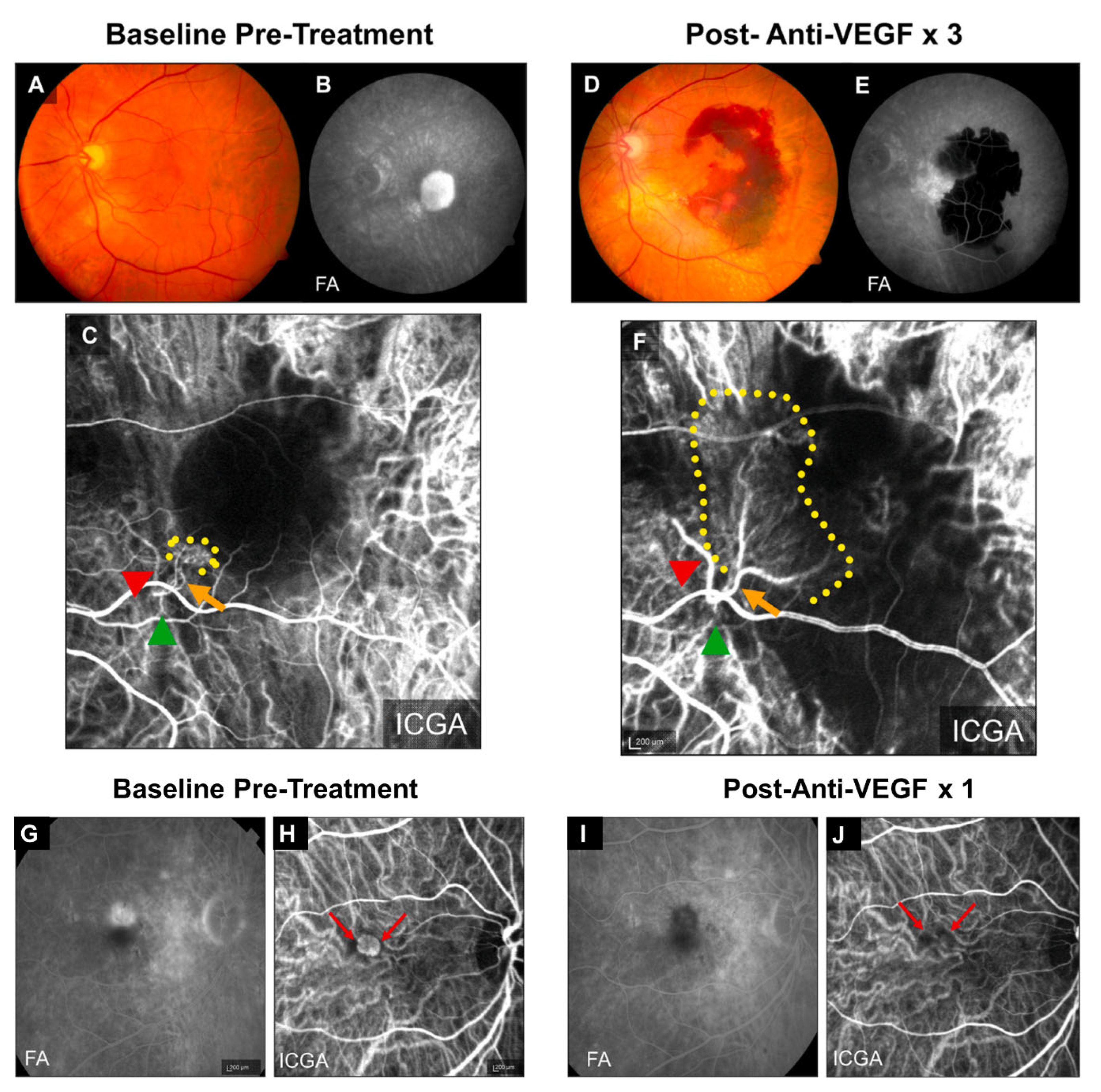
Figure 2.
Vascular morphology of laser-induced CNV in young and old mice. (A) ICGA of laser-induced CNV in young and old mice. White arrows and arrowheads indicate vascular loops and branching arterioles in old mice, respectively. Red arrows indicate a large caliber feeder vessel. (B) Representative images of CNV lesions labeled by Alexa 568 isolectin on RPE/choroid flatmounts in young and old mice. White arrowheads and arrows indicate branching arterioles and vascular loops in old mice, respectively. Scale bar = 40 μm. (C) Distribution of capillary and arteriolar CNV in young versus old mice based on ICGA. The numbers inside the bars indicate the number of CNV laser spots. (D) Quantitative results of normalized CNV area in young and old mice. CNV areas were measured from Alexa 568 isolectin labeled RPE/choroid flatmounts. N = 32 and 40 laser spots in young and old mice, respectively. Bars represent mean ± SD. ****, P < 0.0001. (E) Early and late phase FA show that laser-induced CNV in old mice exhibits significantly increased hyperpermeability compared with that in young mice. (F) The percentage increase of fluorescent area of CNV between the early and late phases of FA. Bars represent mean ± SD. ****, P < 0.0001. Adapted from Zhang, Z., Shen, M. M. & Fu, Y. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. (2022) 63(12):2.
Figure 2.
Vascular morphology of laser-induced CNV in young and old mice. (A) ICGA of laser-induced CNV in young and old mice. White arrows and arrowheads indicate vascular loops and branching arterioles in old mice, respectively. Red arrows indicate a large caliber feeder vessel. (B) Representative images of CNV lesions labeled by Alexa 568 isolectin on RPE/choroid flatmounts in young and old mice. White arrowheads and arrows indicate branching arterioles and vascular loops in old mice, respectively. Scale bar = 40 μm. (C) Distribution of capillary and arteriolar CNV in young versus old mice based on ICGA. The numbers inside the bars indicate the number of CNV laser spots. (D) Quantitative results of normalized CNV area in young and old mice. CNV areas were measured from Alexa 568 isolectin labeled RPE/choroid flatmounts. N = 32 and 40 laser spots in young and old mice, respectively. Bars represent mean ± SD. ****, P < 0.0001. (E) Early and late phase FA show that laser-induced CNV in old mice exhibits significantly increased hyperpermeability compared with that in young mice. (F) The percentage increase of fluorescent area of CNV between the early and late phases of FA. Bars represent mean ± SD. ****, P < 0.0001. Adapted from Zhang, Z., Shen, M. M. & Fu, Y. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. (2022) 63(12):2.
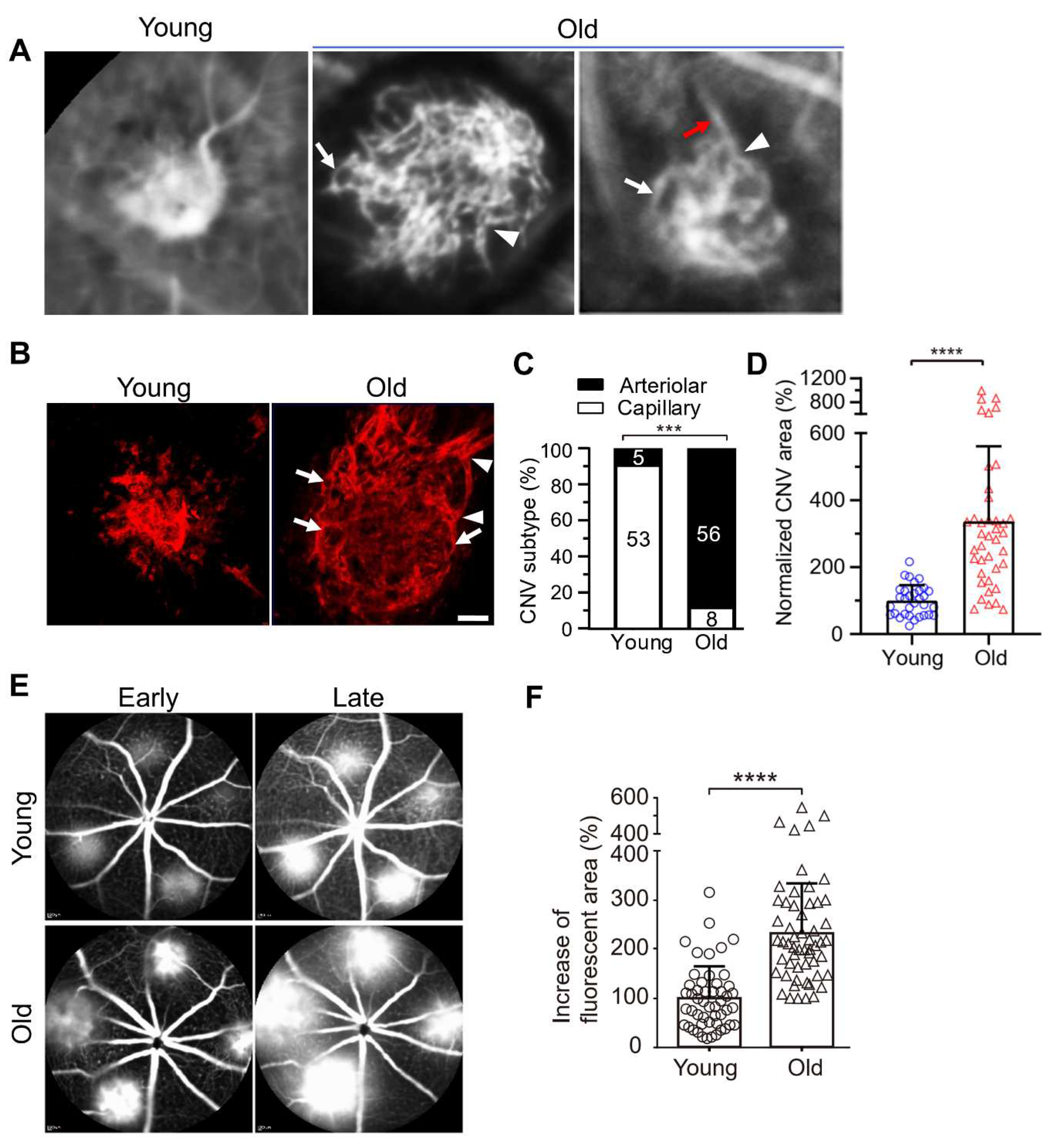
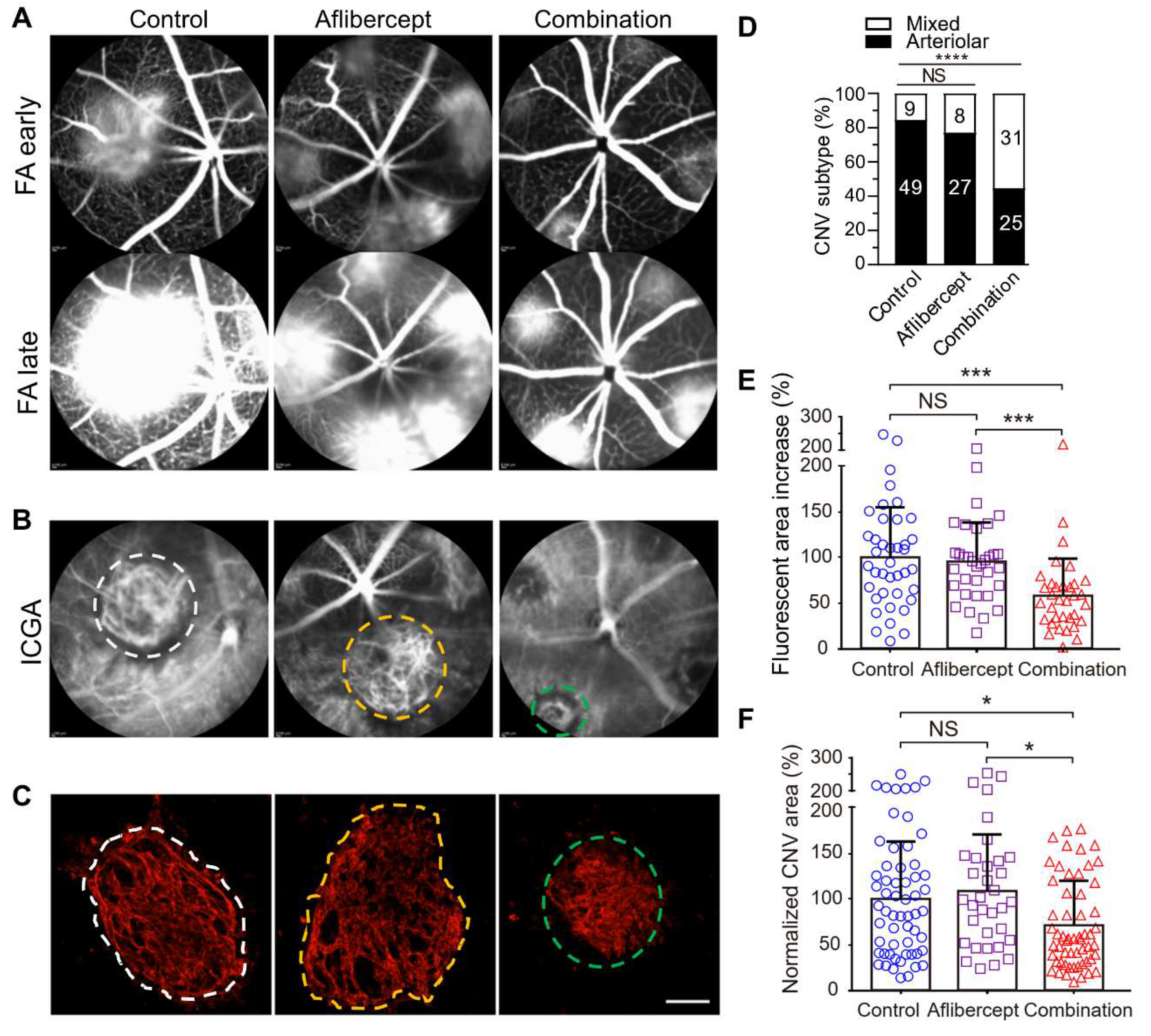
Figure 3.
Comparison between aflibercept and combination therapy (AIBP, apoA-I, and aflibercept) in suppressing laser-induced CNV in old mice. Representative (A) FA, (B) ICGA, and (C) Alexa 568 isolectin labeled RPE/choroid flatmounts of CNV lesions after treatments. (D) CNV vessel type quantification based on isolectin-B4 staining. The numbers inside the bars indicate the number of CNV laser spots. (E) Quantitative results of the percentage increase of fluorescent area in CNV lesions between the early and late phases of FA. (F) Quantitative results of normalized CNV area. Old mice were treated on day 2 (A-E) and were analyzed at day 7 post laser injury. Mice treated on day 4 showed similar results. Bars represent mean ± SD. NS, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; *, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Adapted from Zhang, Z., Shen, M. M. & Fu, Y. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. (2022) 63(12):2.
Figure 3.
Comparison between aflibercept and combination therapy (AIBP, apoA-I, and aflibercept) in suppressing laser-induced CNV in old mice. Representative (A) FA, (B) ICGA, and (C) Alexa 568 isolectin labeled RPE/choroid flatmounts of CNV lesions after treatments. (D) CNV vessel type quantification based on isolectin-B4 staining. The numbers inside the bars indicate the number of CNV laser spots. (E) Quantitative results of the percentage increase of fluorescent area in CNV lesions between the early and late phases of FA. (F) Quantitative results of normalized CNV area. Old mice were treated on day 2 (A-E) and were analyzed at day 7 post laser injury. Mice treated on day 4 showed similar results. Bars represent mean ± SD. NS, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; *, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Adapted from Zhang, Z., Shen, M. M. & Fu, Y. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. (2022) 63(12):2.
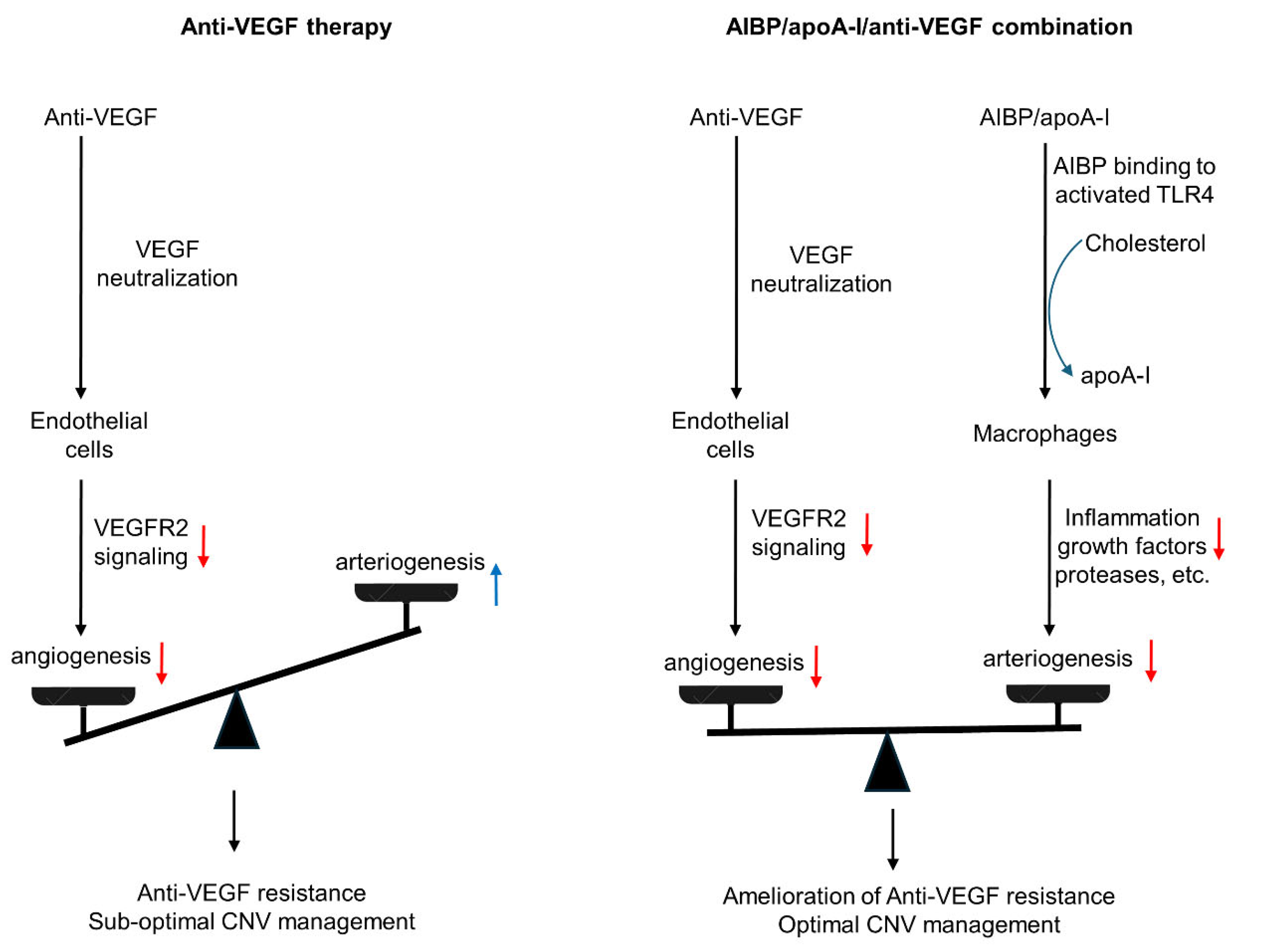
Figure 4.
Comparison of anti-VEGF monotherapy with AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy in the treatment of CNV. Anti-VEGF therapies neutralize VEGF, inhibit VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells, and thereby inhibit angiogenesis and capillary CNV. However, this treatment results in unchecked arteriogenesis, vessel abnormalization, and arteriolar CNV formation, leading to anti-VEGF resistance and sub-optimal CNV management. In AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy, AIBP binds to activated TLR4 and augments cholesterol efflux from macrophages and microglia to apoA-I, normalizing plasma lipid rafts and suppressing inflammation, which inhibits arteriolar CNV. Simultaneously, anti-VEGF therapies inhibit VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells, thereby suppressing angiogenesis and capillary CNV. Thus, the combination therapy leads to the amelioration of anti-VEGF resistance and optimal CNV management.
Figure 4.
Comparison of anti-VEGF monotherapy with AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy in the treatment of CNV. Anti-VEGF therapies neutralize VEGF, inhibit VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells, and thereby inhibit angiogenesis and capillary CNV. However, this treatment results in unchecked arteriogenesis, vessel abnormalization, and arteriolar CNV formation, leading to anti-VEGF resistance and sub-optimal CNV management. In AIBP/apoA-I/anti-VEGF combination therapy, AIBP binds to activated TLR4 and augments cholesterol efflux from macrophages and microglia to apoA-I, normalizing plasma lipid rafts and suppressing inflammation, which inhibits arteriolar CNV. Simultaneously, anti-VEGF therapies inhibit VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells, thereby suppressing angiogenesis and capillary CNV. Thus, the combination therapy leads to the amelioration of anti-VEGF resistance and optimal CNV management.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).