Submitted:
11 January 2024
Posted:
12 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To our knowledge, DIH4RSID is the first to explicitly propose the use of deep information hiding technology to ensure the secure distribution of RSI. Therefore, our method not only opens a new way of thinking about RSI security distribution, but also enriches the research results in this field;
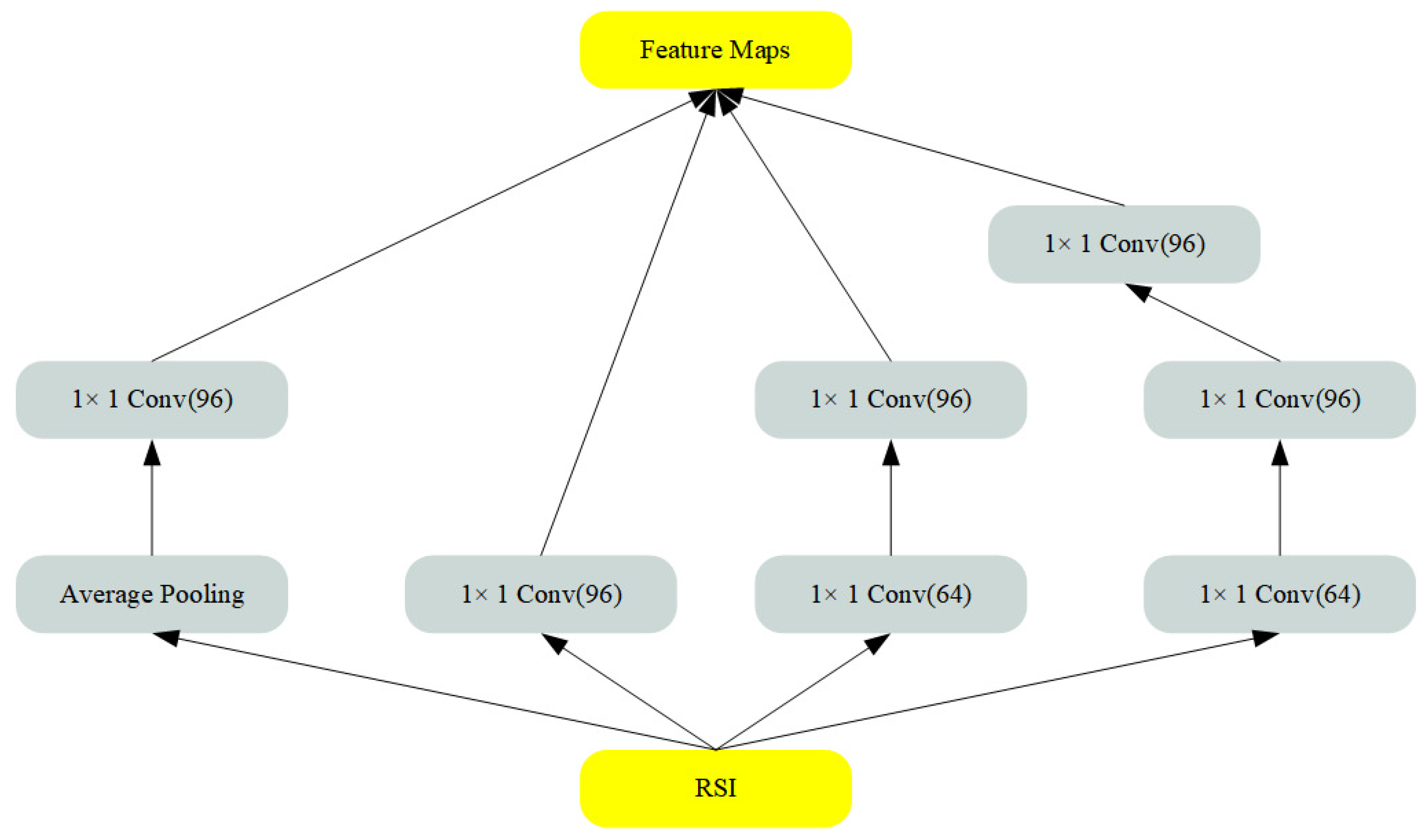
- Unlike the existing HIWI(Hiding images within images) framework, our study proposes a novel preprocessing network architecture, which is designed based on Inception networks and crafted to conform to the unique properties of remote sensing images, which can capture detailed information of objects at different scales.
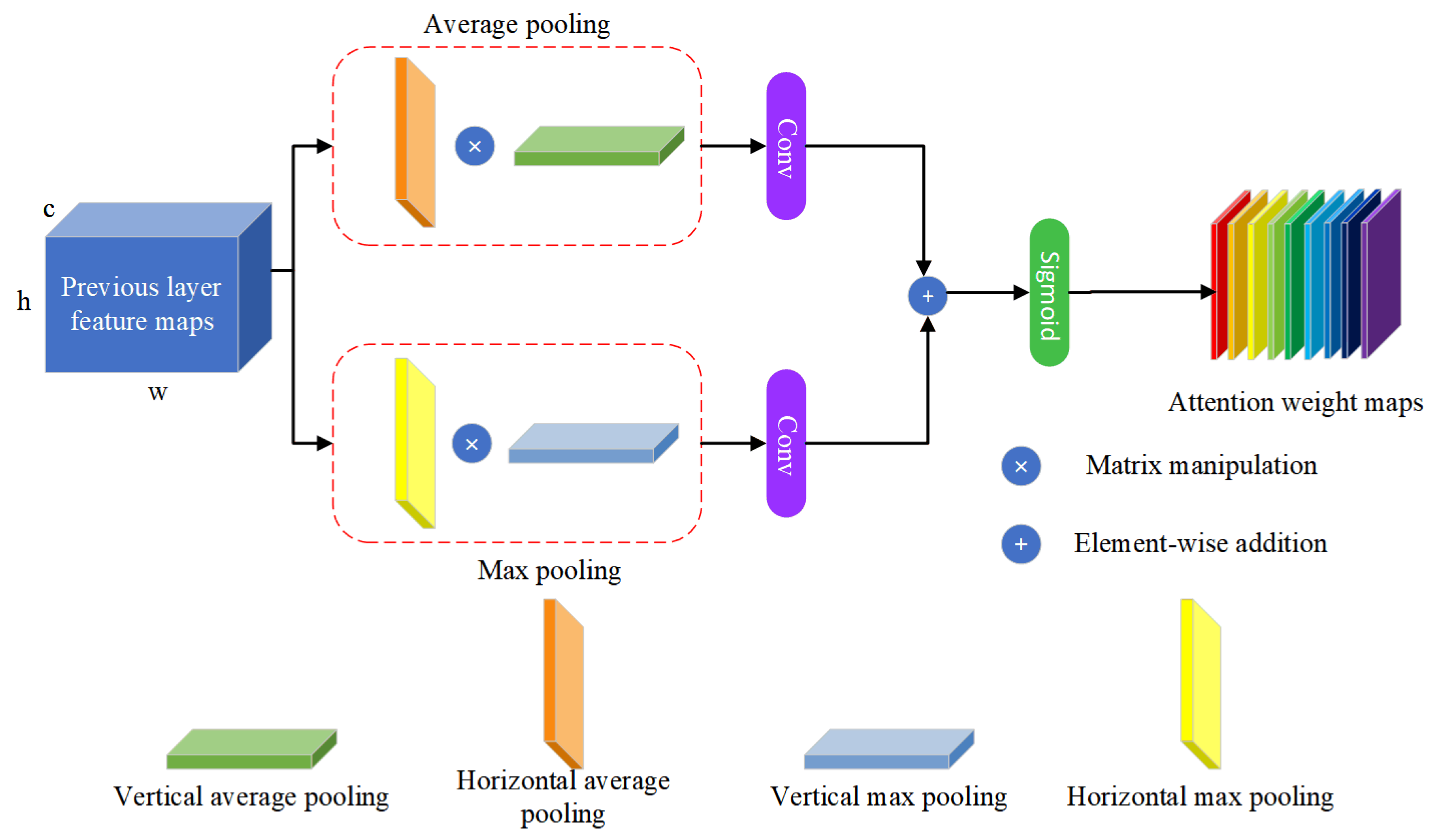
- According to the characteristics of our tasks and remote sensing images, a new attention mechanism PAM is designed in this paper, which carries out two kinds of pooling from two dimensions respectively. Convolution operations can then capture cross-channel relationships and spatial remote dependencies.
- A discriminator is added to the scheme, and iterative training is carried out by WGAN-GP, which improves the stability and correct convergence speed of the model.
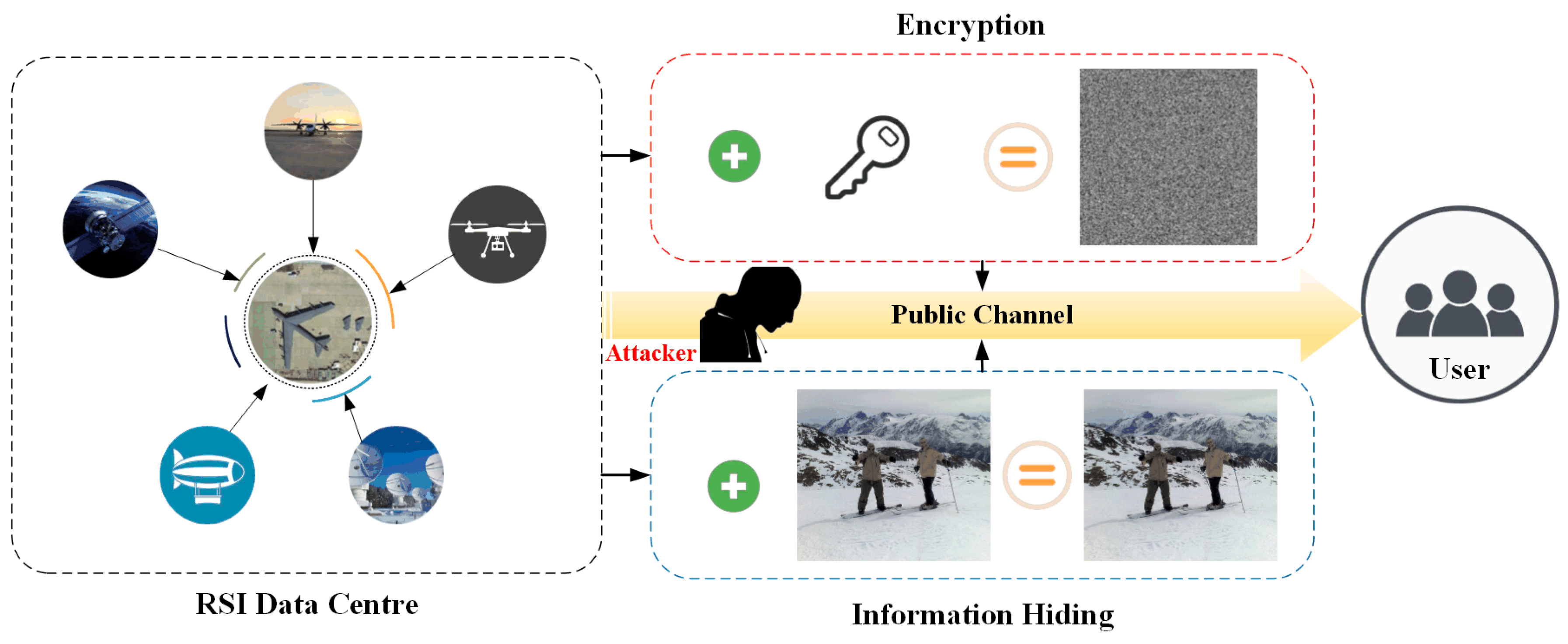
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Scheme
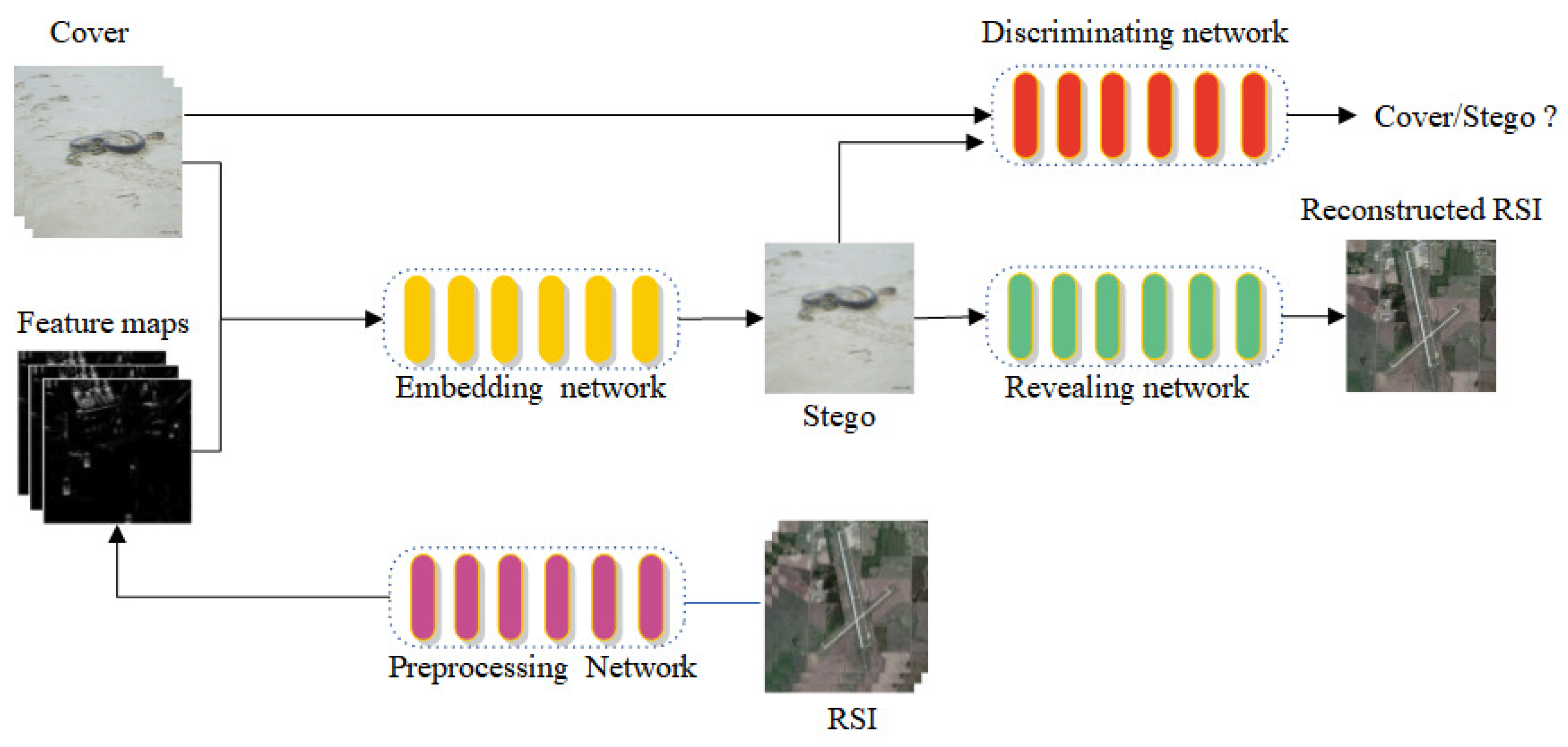
3.1. overview
3.2. Preprocessing network
3.3. Parallel Attention Mechanism
3.4. Embedding Network
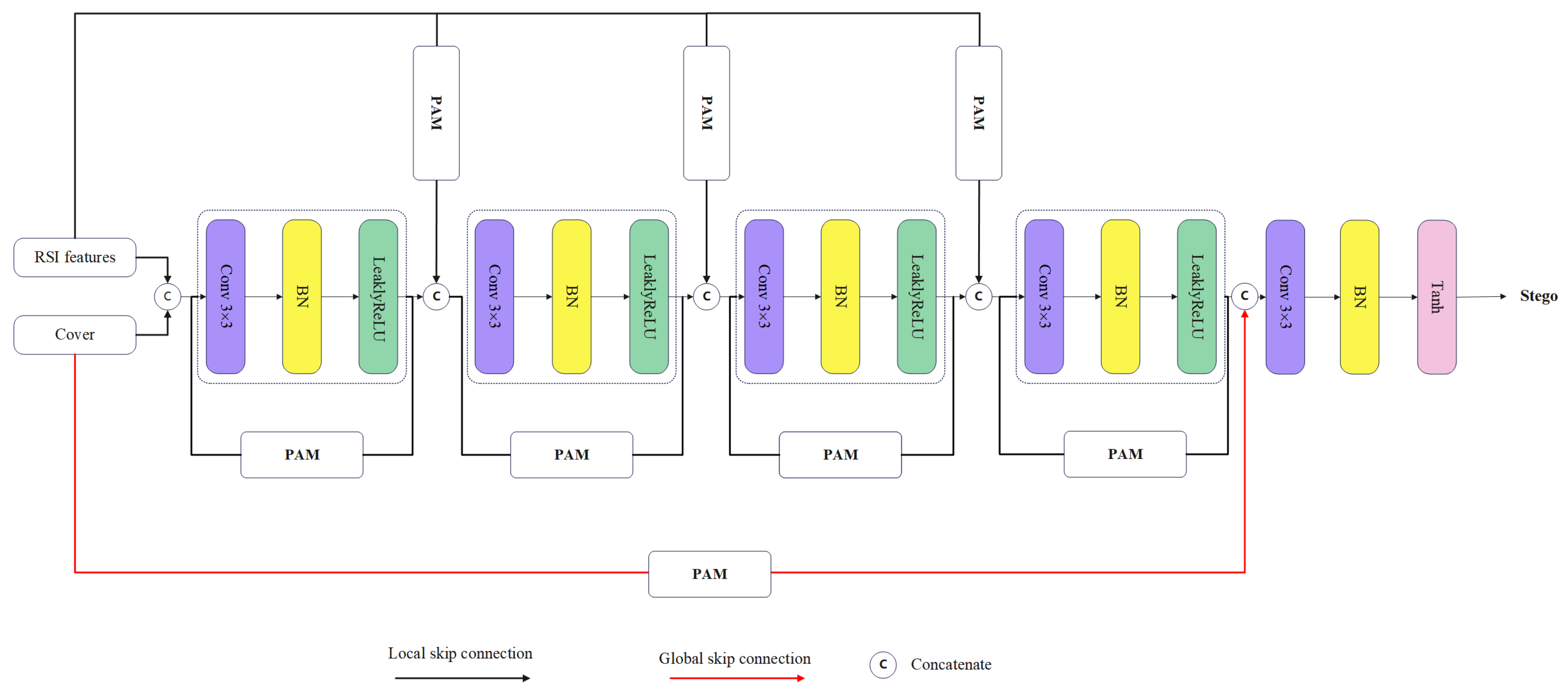
3.5. Revealing Network

3.6. Discriminating Network
3.7. Loss Function Design
3.8. Training Process
| Algorithm 1: Training DIH4RSID. We use default values of |
 |
4. Experiments Result and Analysis
4.1. Experiment Environment
4.2. Visual Quality Test

| The test pairs | Embedding | Revealing |
|---|---|---|
| PSNR/SSIM | PSNR/SSIM | |
| Row#1 | 46.8db/0.97 | 38.7db/0.86 |
| Row#2 | 47.1db/0.98 | 39.3db/0.84 |
| Row#3 | 46.9db/0.96 | 39.2db/0.86 |
| Row#4 | 46.8db/0.97 | 38.6db/0.88 |
| Row#5 | 47.2db/0.98 | 38.8db/0.86 |
| Row#6 | 46.9db/0.96 | 39.1db/0.85 |
4.3. Semantic Retention Capability Test
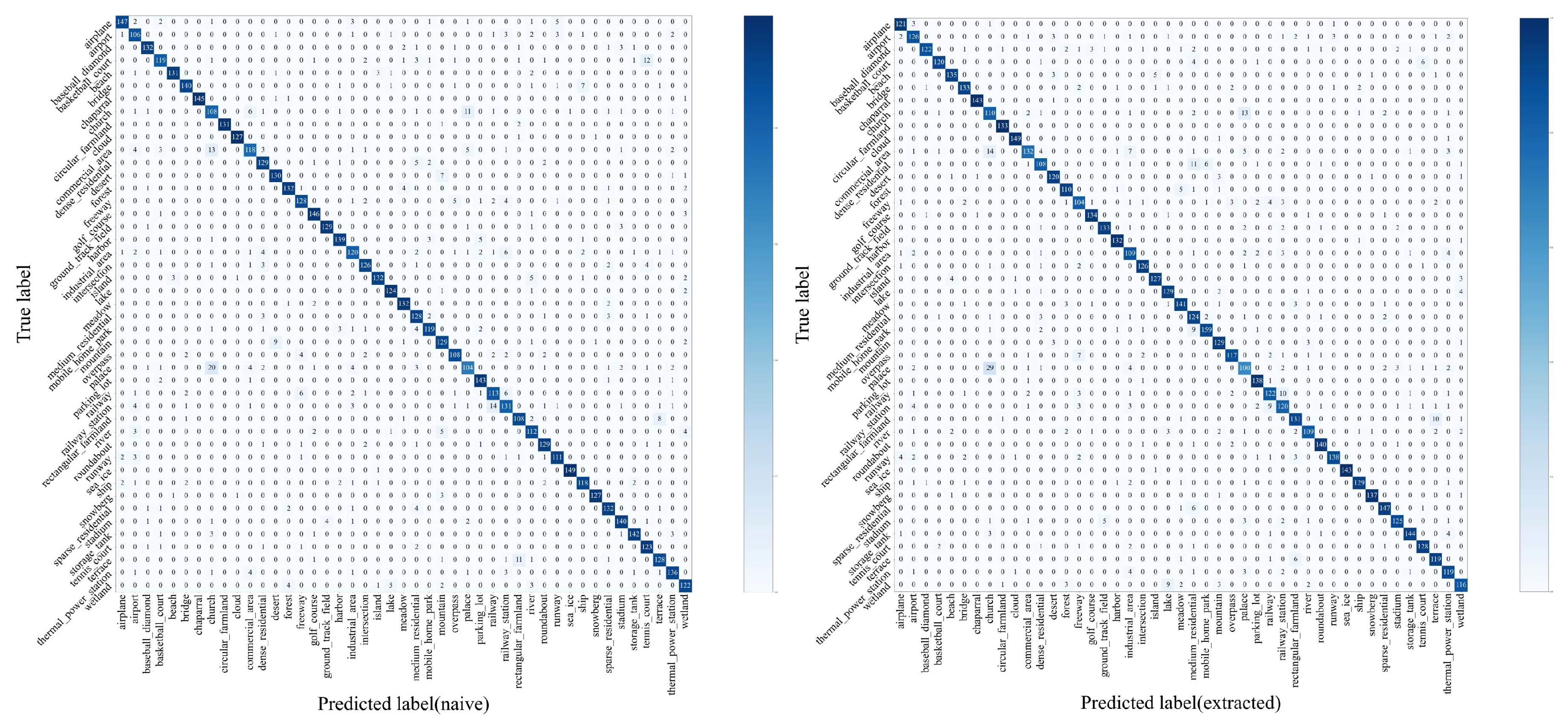
| Method based on CNN | 70% training ratio | 80% training ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Native/extracted | Native/extracted | |
| AlexNet | 91.5±0.18/91.3±0.17 | 92.7±0.12/92.6±0.11 |
| VGGNet16 | 90.5±0.19/90.6±0.15 | 92.6±0.20/92.6±0.19 |
| GoolgeLeNet | 91.8±0.13/92.1±0.12 | 92.3±0.13/92.2±0.15 |
| Fine-tuned AlexNet | 97.5±0.18/97.2±0.16 | 98.7±0.10/98.5±0.11 |
| Fine-tuned VGGNet16 | 97.6±0.18/96.9±0.19 | 98.9±0.09/98.3±0.08 |
| Fine-tuned GoolgeLeNet | 97.3±0.18/97.5±0.17 | 98.7±0.12/98.4±0.13 |
4.4. Security Test
4.5. Quantitative Comparison
4.6. Ablation Experiments
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Ren, L.; Shafiq, M.; Gu, Z. A Lightweight Privacy-Preserving System for the Security of Remote Sensing Images on IoT. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; Poslad, S. Granular Content Distribution for IoT Remote Sensing Data Supporting Privacy Preservation. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubaei, F.S.; Alneil, A.A.; Mohamed, A.; Mustafa Hilal, A. Block-Scrambling-Based Encryption with Deep-Learning-Driven Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naman, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Saha, T. Remote sensing and advanced encryption standard using 256-Bit key. In Proceedings of the Emerging Technology in Modelling and Graphics: Proceedings of IEM Graph 2018. Springer, 2020, pp. 181–190.
- He, R.; Sun, Q.; Thangasamy, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhou, M. Accelerate oxygen evolution reaction by adding chemical mediator and utilizing solar energy. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 8898–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhaee, M.A.; Marvasti, F. A Survey on Digital Data Hiding Schemes: Principals, Algorithms, and Applications. ISeCure 2013, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K. Data hiding: current trends, innovation and potential challenges. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 2020, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Rahim, R.; Nadeem, M.; Hussain, S. End-to-end trained CNN encode-decoder networks for image steganography. In Proceedings of the Proc. Comput. Vis.-ECCV 2018 Workshops, 2018, pp. 723–729.
- Zhang, K.A.; Cuesta-Infante, A.; Xu, L.; Veeramachaneni, K. SteganoGAN: High Capacity Image Steganography with GANs. arxiv 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C. Attention Based Data Hiding with Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2020, pp. 1120–1128.
- Chen, F.; Xing, Q.; Liu, F. Technology of hiding and protecting the secret image based on two-channel deep hiding network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 21966–21979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xing, Q.; Fan, C. Multilevel Strong Auxiliary Network for Enhancing Feature Representation to Protect Secret Images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 18, 4577–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielikainen, J. LSB matching revisited. IEEE signal processing letters 2006, 13, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, T.; Judas, J.; Fridrich, J. Minimizing Additive Distortion in Steganography Using Syndrome-Trellis Codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2011, 6, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevnỳ, T.; Filler, T.; Bas, P. Using high-dimensional image models to perform highly undetectable steganography. In Proceedings of the Information Hiding: 12th International Conference, IH 2010, Calgary, AB, Canada, June 28-30, 2010, Revised Selected Papers 12. Springer, 2010, pp. 161–177.
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J. Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), 2012, pp. 234–239. [CrossRef]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J. Digital image steganography using universal distortion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the first ACM workshop on Information hiding and multimedia security. ACM, 2013, pp. 59–68.
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Li, X. A new cost function for spatial image steganography. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2014, pp. 4206–4210.
- Zhu, J.; Kaplan, R.; Johnson, J.; Fei-Fei, L. Hidden: Hiding data with deep networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 657–672.
- Baluja, S. Hiding Images within Images. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 2020, 42, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Jia, K.; Li, B.; Guo, D.; Zhang, E.; Qin, C. Reversible image steganography scheme based on a U-Net structure. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 9314–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Luo, T.; Li, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.; Chang, C.C. ARWGAN: Attention-guided Robust Image Watermarking Model Based on GAN. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H. Channel attention image steganography with generative adversarial networks. IEEE transactions on network science and engineering 2021, 9, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xing, Q.; Sun, B.; Yan, X.; Cheng, J. An Enhanced Steganography Network for Concealing and Protecting Secret Image Data. Entropy 2022, 24, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, W.; Shan, H.; Li, E.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Remote Sensing Scene Classification Based on Multibranch Fusion Attention Network. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, H.Z.; Shi, Y.Q. Structural Design of Convolutional Neural Networks for Steganalysis. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2016, 23, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural information processing systems, 2014, Vol. 27.
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning-Volume 70. JMLR. org, 2017, pp. 214–223.
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs, 2017.
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. International journal of computer vision 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art. Proceedings of the IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohammad, A.; Ghinea, G. Stego image quality and the reliability of PSNR. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, 2010.
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Dong, S.; Liu, J. Invisible steganography via generative adversarial networks. Multimedia tools and applications 2019, 78, 8559–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inputs | modules | Kernal | Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stego() | HPF | Out1() | |
| Input1 | Conv-ABS-BN-Tanh—Average | Out2() | |
| Input2 | Conv-BN-Tanh—Average | Out3() | |
| Input3 | Conv-BN-Tanh—Average | Out4() | |
| Input4 | Conv-BN-Tanh—Average | Out5() | |
| Input5 | Conv-BN-Tanh—Average | Out5() | |
| Input6 | ASPP | Out5() | |
| Input7 | Fully Connection | - | Out5() |
| Input8 | SoftMax | - | Probabilities of classes () |
| Schemes | Embedding | Revealing | Acurracy of Detection |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR/SSIM | PSNR/SSIM | YeNet | |
| Literature [8] | 34.78db/0.92 | 31.5db/0.90 | 0.55/0.99 |
| Literature [21] | 34.6db/0.96 | 36.1db/0.94 | 0.53/0.98 |
| Literature [11] | 44.1db/0.97 | 39.8db/0.98 | 0.58/0.98 |
| Literature [20] | 41.3db/0.95 | 33.1db/0.97 | 0.52/0.98 |
| Literature [24] | 44.6db/0.97 | 38.6db/0.97 | 0.53/0.98 |
| Literature [12] | 42.3db/0.99 | 38.8db/0.96 | 0.52/0.96 |
| The proposed method | 43.8db/0.99 | 38.9db/0.99 | 0.51/0.90 |
| Variants | Embedding | Revealing | AD | ACA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR/SSIM | PSNR/SSIM | Stegexpose/YeNet | ||
| DIH4RSID-PAM-PN | 36.8db/0.80 | 29.6db/0.75 | 0.53/0.96 | 0.89 |
| DIH4RSID-PAM | 40.9db/0.83 | 30.1db/0.78 | 0.55/0.92 | 0.94 |
| DIH4RSID-PN | 42.1db/0.92 | 32.3db/0.80 | 0.52/0.90 | 0.93 |
| DIH4RSID | 47.1db/0.96 | 38.3db/0.84 | 0.53/0.85 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





