1. Introduction
Vaginal infections is a global public health issue affecting worldwide up to 70% of women at the reproductive age [
1,
2]. The symptoms or clinical manifestations are itching, irritation, abnormal vaginal discharge, and discomfort when urinating and during sexual activity. In some cases, the infections may be asymptomatic or show mild symptoms, The most common infections are caused by bacteria, fungus and protozoa are bacterial vaginosis, vulvovaginal candidiasis, and trichomoniasis [
3,
4]. Bacterial vaginosis is caused by the species
Staphylococcus and
Peptostreptococcus, Enterobacteriaceae,
Gardnerella vaginalis, and
Mycoplasma hominis. Vulvovaginal candidiasis is caused by
Candida albicans,
Candida tropicalis,
Candida parapsilosos,
Candida crusei,
Candida glabrata,
Candida stellatoidea, and
Candida lusitaniae. Trichomoniasis is caused by human protozoan pathogen
Trichomonas vaginalis.
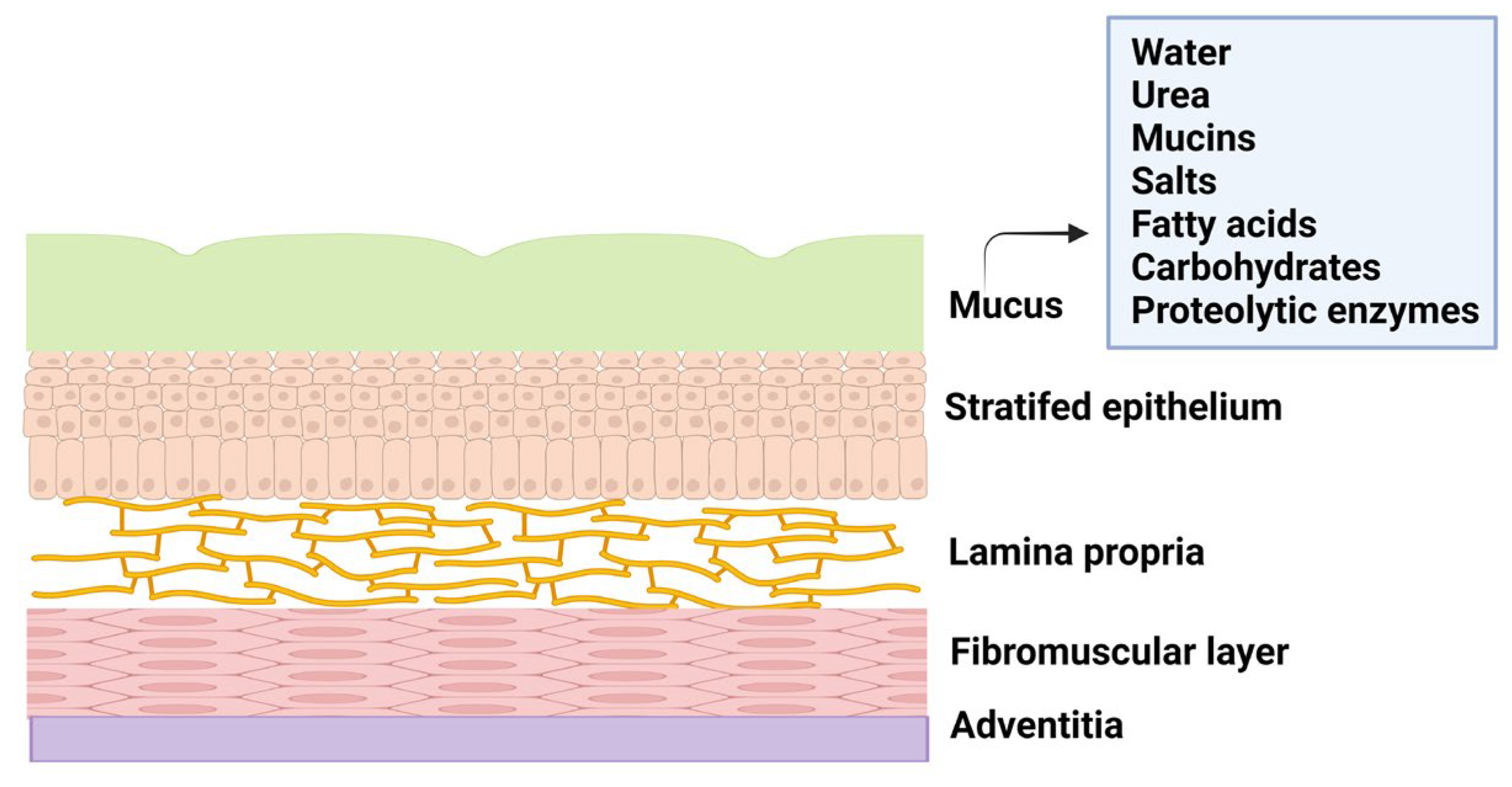
The female reproductive system is composed of fallopian tubes, ovary, cervix, ectocervix and vagina. The vagina is a distensible organ (~ 9 cm in length) which is characterized by stratified epithelium, fibromuscular layer, lamina propria and adventitia. The vagina is covered with cervical mucus which is composed of water (90 %), urea, carbohydrates, mucins, fatty acids, proteolytic enzymes, and salts [
5]. The consistency of cervical mucus and the thickness of the vaginal epithelium vary throughout the menstrual cycle and are regulated by hormones such as estrogen. The main functions of the mucus are to provide lubrication and protection against infections. The layers of vaginal tissue and compositions of mucus are illustrated in
Figure 1.
Various factors such as age, menstrual cycle, hormone level etc. influence the physiology of the vagina, and these factors affect natural vaginal flora or microbiota and the amount of vaginal fluids. The Lactobacillus species is the predominant microorganism that protects the vagina from the invasion of pathogens by producing lactic acid which provides the acidic environment of the vagina. When this normal symbiotic mutual relationship becomes imbalanced, the natural vaginal flora is heavily disturbed, leading to the onset of vaginal infections promoting colonization of pathogens.
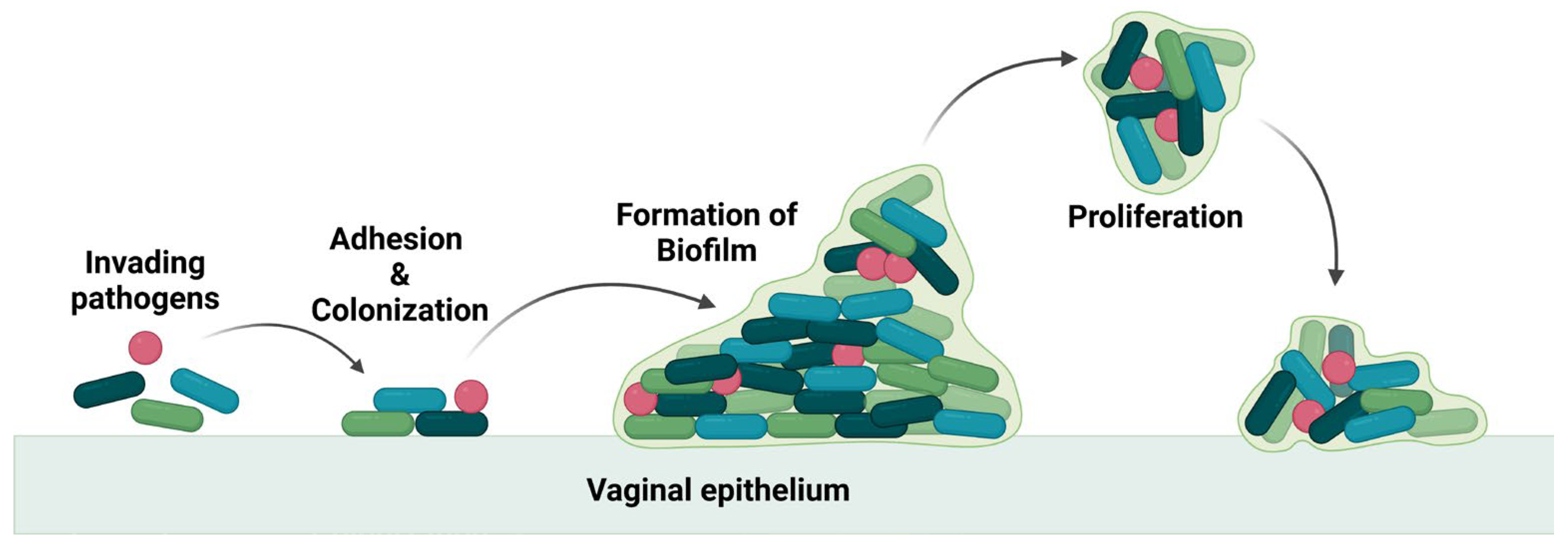
These pathogens thrive in the vagina by producing a biofilm which leads to the recurrence of the infection even after treatment [
6,
7], as the biofilm is an adaptation of the bacteria to resists any applied drugs and to evade the immune system. The biofilm is composed of a group of pathogenic microbes adhered to one another on a surface that is by extracellular polymeric substances that are produced by the microbes. The formation of biofilm is illustrated in
Figure 2. Biofilm is a physical barrier that limits the accessibility of drug molecules and enhances the thriving of pathogens. In this aspect, any drug formulation for vaginal delivery should not be harmful to the vaginal flora and its environment.
The vaginal infections, particularly bacterial vaginosis are comparatively higher in non-pregnant women than in pregnant woman, and in women at the age of 40 and above. This difference in rate of infection is attributed to the imbalance of estrogen which affects the viability of
Lactobacillus species in the vagina. In the management of vaginal infections, oral administration of drugs and topical applications are some of the current therapeutic approaches. However, both forms of drug delivery approaches suffers from numerous systemic adverse effects [
8]. Oral administration of the antibiotic metronidazole causes nausea, insomnia, dizziness, and dry mouth. The long-term oral administration of this antibiotic may lead to leukopenia and neutropenia [
9]. Oral administration of miconazole nitrate, an antifungal drug leads to thrombocytopenic purpura, a blood disorder [
10]. Apart from these, oral administration of such drugs may have serious side-effects in pregnant women and women suffering from gastrointestinal disorders.
Given the high exposure contact surface and dense vascularization the vagina is an alternative site for local and systemic drug delivery. The main advantage is the avoidance of the acidic gastrointestinal environment, less side-effects and by-pass the hepatic first-phase effect. Several conventional formulations in the form of capsules, creams, solutions, gels, and vaginal suppositories are used in the treatment of vaginal infections. These pharmaceutical products for vaginal drug delivery also suffer from a few limitations such as poor adhesion, short-retention or residence time, and poor release of the drug [
10,
11]. To address these limitations, formulations based on hydrogels have been developed. Hydrogels are well-suited for controlled delivery of biologically active therapeutics owing to their biocompatibility, high porosity, and high-water retention properties.
In this manuscript, hydrogel-based formulations for the treatment of vaginal infections and important considerations on the choice of materials is reviewed. The criteria of hydrogels for vaginal drug delivery and the different types of hydrogels used are presented in this review.
2. Important Considerations on Hydrogel-Based Approaches to Vaginal Drug Delivery
Vaginal suppositories are often used in gynaecological treatments to locally deliver the drug with minimal systemic toxicity. Due to insufficient retention time of the drug in the suppository, the drug tends to leach out making this type of drug delivery less effective. As a result of this, frequent drug administration becomes necessary. Treatments that are ineffective could lead to various health related issues such as development of bacterial resistance, inflammations, miscarriage, and infertility [
12]. To overcome the issues, a variety of drug delivery approaches have been developed for effective delivery of therapeutic agents to the vagina. In principle, an ideal vaginal drug delivery system (VDDS), should be safe and release the drug in a sustained manner.
For improved vaginal drug delivery, formulations based on hydrogels have been developed. Hydrogels are three-dimensionally crosslinked hydrophilic polymer networks that can absorb a large amount of water or physiological fluids without being dissolved [
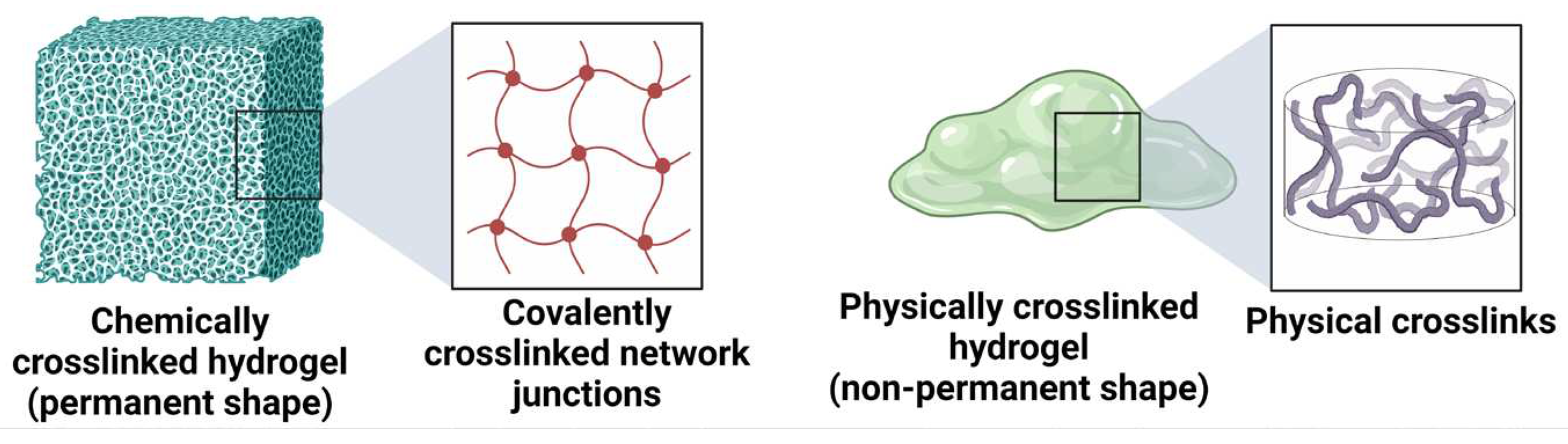
13]. The soft and rubber nature of fully swollen hydrogels resembles the nature of many soft biological tissues, making these materials a good choice for drug delivery applications. Depending on the nature of constituting polymers, hydrogels are classified as natural, synthetic, and hybrid (containing more than one type of polymer or components). The hydrogels are further classified into two main categories based on crosslinking, (i) chemically crosslinked hydrogels, and (ii) physically crosslinked hydrogels.
The chemically crosslinked hydrogels have permanent crosslink junctions through the formation of covalent bonds, while the physically crosslinked hydrogels have non-permanent crosslink junctions that arises due to physical or secondary interactions. These interactions include polymer entanglements, ionic interactions, hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions [
14]. The two types of hydrogels are illustrated in
Figure 3.
For any gynecological treatment, the most suitable hydrogel system would be the one with good shape-conforming properties. This property allows for higher retention time of therapeutics in the vaginal mucosa, and uniform distribution of the hydrogel over the area. Based on this criterion, chemically crosslinked hydrogels with defined and permanent shapes are not well-suited for vaginal drug delivery. Physically crosslinked hydrogels with non-permanent or reversible crosslinks are the most suitable systems for VDDS. The reversible crosslink interactions can be modulated by in-situ physical interactions, stereo complexation, inclusion complexation, and supramolecular interactions [
15].
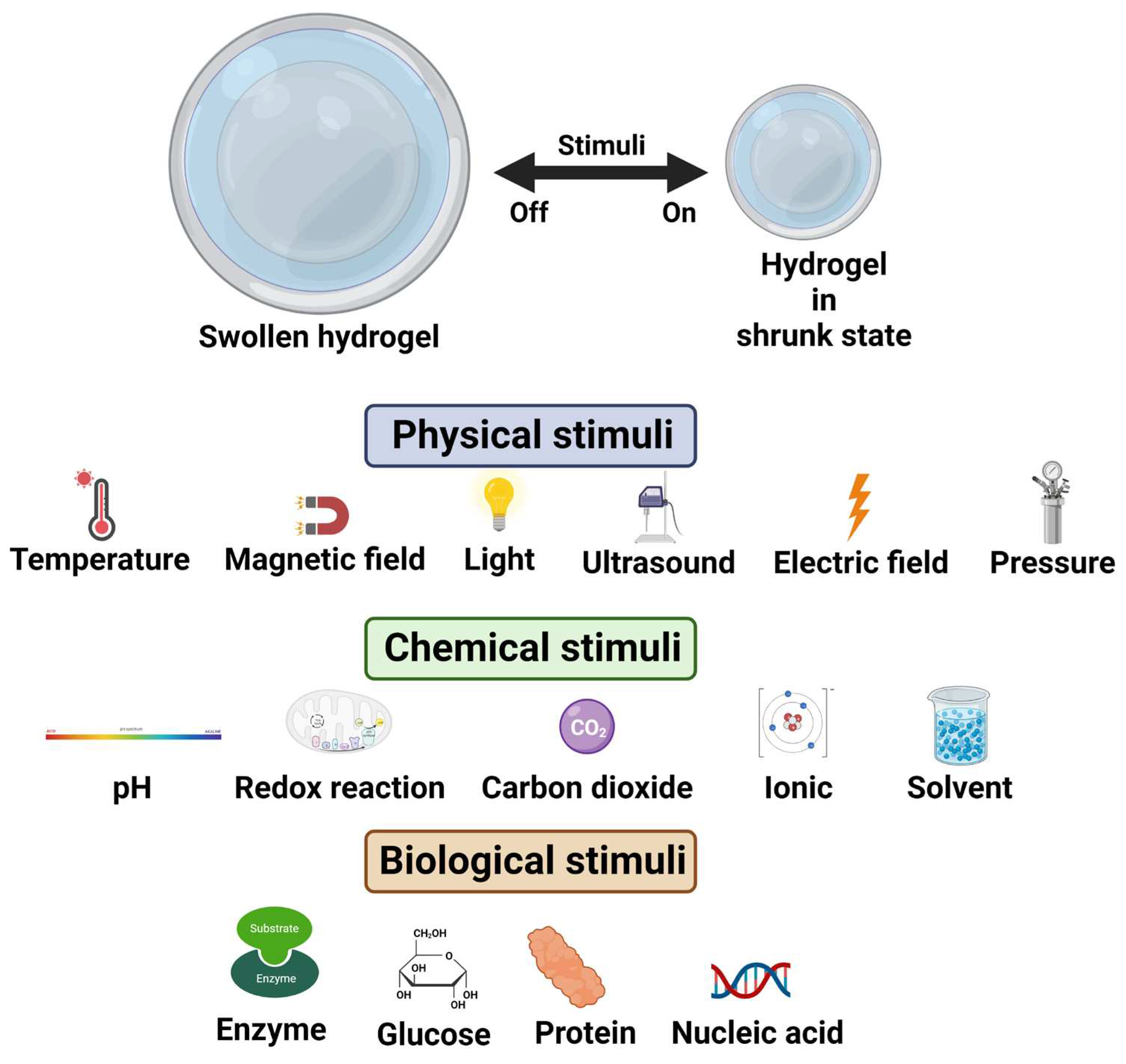
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels are an interesting class of hydrogels which responds to changes in external stimuli such as pH, temperature, ionic strength, surfactants, light intensity, biomolecules, and magnetic field [
16]. Upon the application of the stimuli, specific events such as in situ gel formation and drug release are evoked, and this property has made these materials very attractive for various types of drug delivery systems. Further, hydrogels that responds to multiple stimuli or trigger have been developed to achieve better control over the responsive behavior in target-specific drug delivery systems [
16]. The behavior of stimuli-responsive hydrogels under external stimuli and drug release profile is illustrated in
Figure 4.
Stimuli-responsive dynamic hydrogels with reversible crosslink interactions and desirable rheological properties are well-suited for vaginal drug delivery of therapeutic agents. The nature of the hydrogel matrix allows for the controlled encapsulation and administration of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs, and greatly limits toxicity and side-effects associated with the drug. In addition, the rheological properties should facilitate the convenient administration and even distribution of the gel (containing the therapeutics) on the mucosal tissue of the vagina.
2.1. Injectable Dynamic Hydrogels and Rheological Considerations
Injectable hydrogels are polymer systems that are liquid at room temperature but forms a solid gel (through physical crosslinking) at the site of administration. Stimuli-responsive polymers undergo sol-gel transition in response to environmental triggers. Such injectable hydrogels containing therapeutics are most suited for intravaginal applications. However, kinetics of gelation may be a disadvantage, i.e., if the gelation is very quick, the hydrogel can solidify within the syringe, or if the gelation is very slow, the therapeutics may be released prematurely [
17]. The problem associated with gelation kinetics is overcome by injectable hydrogels that show dynamic properties.
Injectable dynamic hydrogels allows easy and reversible transition between the sol-gel states due to their unique rheological properties such as shear-thinning and self-healing. The clinical applications of such dynamic hydrogels are limitless, with new therapeutic platforms. The rheological modifications required for each clinical application needs to be considered in relation to the constraints involved in injectability. In addition, thixotropic behavior (transient recovery of viscosity after the flow of material had stopped) needs to be evaluated.
For intravaginal applications, which requires high spreadability and strong mucoadhesion, the thixotropy evaluation provides valuable information which determines the efficacy of the treatment. The thixotropic property is strongly dependent on the chemical functional groups of the polymers that are involved in physical crosslinking (sol-gel transition). This property provides important information on the time scale of gelation or erosion of material after the administration process [
18].
2.2. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels
For gynecological treatments of vaginal infections, the vaginal drug delivery route is the most preferred method as it avoids first-pass metabolism and provides effective delivery of therapeutics at the site of infection. The vaginal secretions along with the self-cleansing actions of the vagina could potentially dilute the formulation leading to less efficacy of the therapeutics. Among several polymeric materials, polymers with mucoadhesive and thermos-responsive properties have attracted great attention for vaginal drug delivery. As discussed in the earlier section, stimuli-responsive polymers and hydrogels are well suited to overcome the limitations of other drug delivery systems.
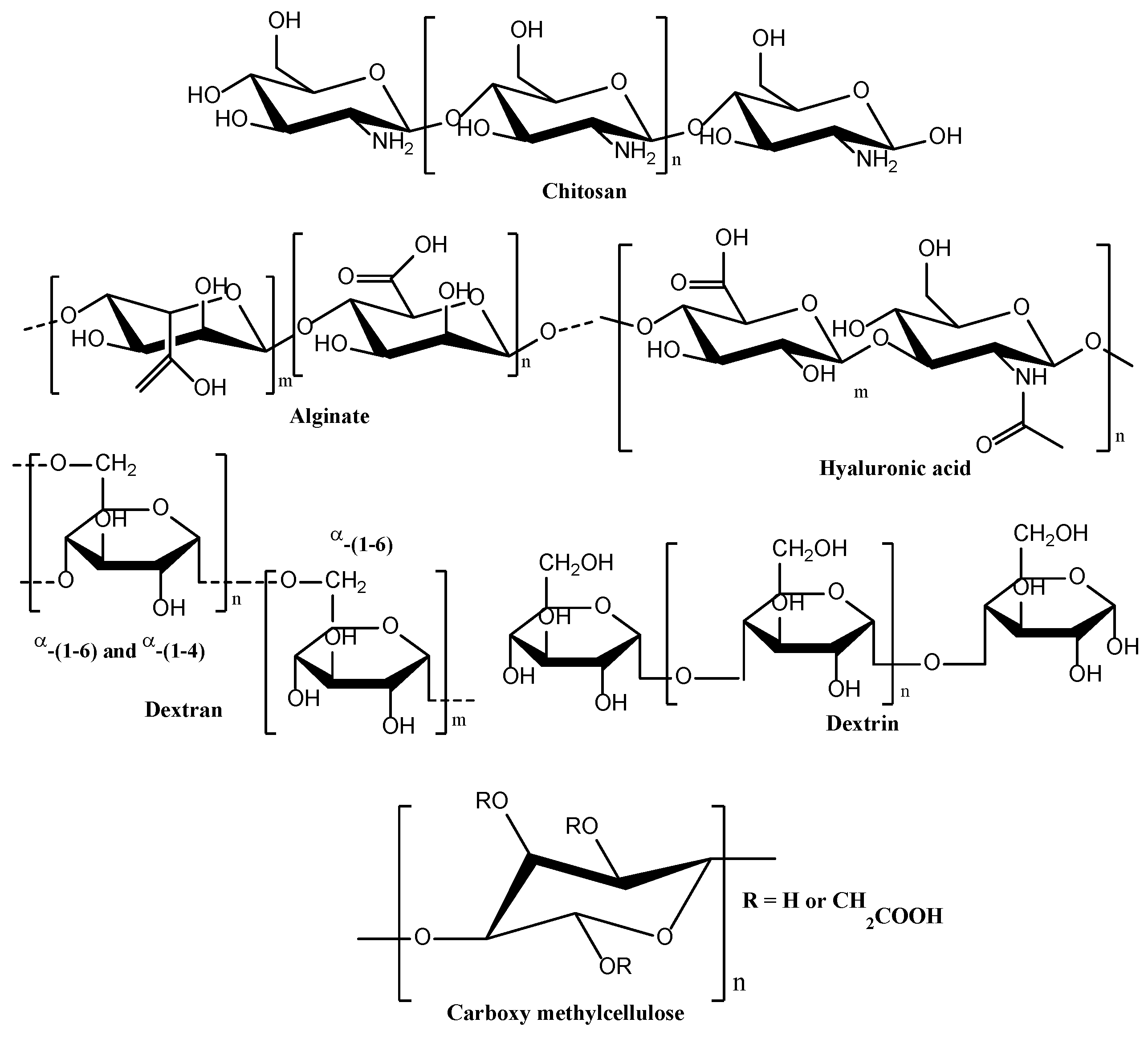
These materials sharply respond to slight changes in external stimuli due to changes in interactions between the polymer chains leading to changes in macroscopic properties. The molecular structures of a few important natural polymers used in hydrogels for gynecological treatment is shown in
Figure 6 [
14,
15,
16,
17].
2.3. Temperature-Responsive Hydrogels (Thermogelling Systems)
Hydrogels that undergo sol-gel transition in response to changes in external temperature are classified as temperature-responsive hydrogels or thermogelling hydrogels. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels based on natural and synthetic polymers with thermo-sensitive properties are widely used in vaginal drug delivery of therapeutics.
For formulations that are of low viscosity, they can be applied in the form of aerosols using a propellant such as propane: butane in the ratio 80:20 v/v. Thermogelling aerosol gels containing Carbopol, and triblock polymers such as Pluronic F68, and poloxamer 407 have been used in the treatment of cervical erosion and vaginitis [
19]. The formation of aerogel foam improved the penetration efficiency of the formulation increasing the strength of mucoadhesion of the gel, leading to initial rapid release of the drug followed by sustained release.
Chitosan-based hydrogels in combination with b-glycerol phosphate have been used widely in gynecological antimicrobial treatment [
20]. Chitosan is a polysaccharide obtained from chitin found in the shells of crustaceans and is composed of b(1,4)-linked glucosamine and
N-acetyl glucosamine subunits. This natural polymer is widely used in biomedical applications, due to its excellent properties such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and anti-microbial effects. The thermo-responsive gelation of chitosan with b-glycerol phosphate arises due to increased hydrophobic interactions (due to neutralization of chitosan) in response to changes in external temperature. Thermo-responsive hydrogels based on chitosan and b-glycerol phosphate, containing the drug auranofin has shown positive effect in the treatment of vaginal infections caused by
Trichomonas vaginalis.
Hydrogels based on chitosan (high concentration) and poloxamer 407 had been developed for the treatment of vaginitis. This highly viscous formulation provided high mucoadhesion providing sustained release of the drug thereby decreasing the drug administration frequency. Formulations of high viscosity improves the mechanical properties of the hydrogel and these are features that are required for effective vaginal gels as it allows for localization of antimicrobial drugs. Upon administration, the high viscosity of the chitosan promoted intermolecular interactions through polymer entanglements and dispersion forces which leads to in situ formation of gels with good compressibility, cohesiveness, elasticity, and adhesiveness.
Chitosan on its own forms a gel under acidic pH conditions (pH = 5) with non-Newtonian fluid behavior. Chitosan-based hydrogels containing extracts of the plant
Mitracarpus frigidus (Rubiaceae family) have been used in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. The active chemical ingredients in the plant extract such as kaempferol, kaempferol-
O-rutenoside, methyl ursolate, ursolic acid, scopoletin, and psychorubin have been recently identified as the main ingredients with antimicrobial properties []. Chitosan-based formulation containing an essential oil from the plant
Pelarognium graveoleus (geraneus oil) has also been effective in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis [
21].
Thermogelling hydrogels based on hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC), and poloxamer 407, containing the drug tinidazole has shown promising application in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. The improved mechanical property of the gel allowed good spreadability and high mucoadhesion which provided longer residence time for the drug with sustained release. However, this formulation promoted little irritation as confirmed by chorioallantoic membrane test (Hen’s Egg Test). Hydrogel formulation based on mixture of polymers such as Pluronic F127, Pluronic F68 and polycarbophil, containing the drug clotrimazole was effective in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). The combination of different polymers promoted good spreadability, mucoadhesion, and gelation at various temperatures due to the different gelation points of the individual polymers. Increase in concentration of polycarbophil in the formulation enhanced the mucoadhesive properties of the gels through various physical interactions between the carboxyl groups (-COOH) of polycarbophil and glycoproteins present on the mucous of the vaginal epithelium [
22].
Thermogelling formulation based on Pluronic F47 loaded with amphotericin-B was effective in the treatment of VVC due to enhanced permeation of the drug [
23]. The formation of polymeric micelles at the sol-gel temperature increased the viscosity allowing the formation of a porous gel. The encapsulation of the drug within the micelle favored local administration and sustained release. The formulation had low minimum inhibitory values (MIC) against many fungi including
Candida albicans,
Candida parapsilosis, and
Candida glabrata. Thermogelling formulations containing nanoparticles have also been developed for the treatment of VVC. Tenofovir loaded chitosan nanoparticles containing formulations released the drug in two phases with good residence time on the vaginal mucus. The Pluronic based formulations with natural polymers have been widely used for gynecological therapies for the controlled delivery of antimicrobial drugs such as metronidazole, amoxicillin, amphotericin, and clotrimazole [
21,
22,
23,
24].
2.4. pH-Responsive Hydrogels
Hydrogels that responds reversibly to slight variations in external pH conditions have been used in various drug delivery systems. The normal pH range of vagina is between 3.8 to 5.0, and variation is pH can significantly affect the vaginal drug delivery system. Bacterial infections is one factor that can significantly affect the pH of the vagina. Apart from the commercially available vaginal films and membranes, new pH-responsive hydrogels and organogels have been developed. A pH-responsive multicomponent formulation based on hydrogels and organogels containing the drug Tenofovir, have been developed for prophylaxis of HIV infection [
24]. The heteropolysaccharide, pectin in the hydrogel component provides a porous structure with dense polymeric matrix which aids in increasing the mucoadhesive property of the formulation and rapid release of the drug. The esterification reaction of carboxylic acid groups of pectin and glycoproteins present in the vaginal mucous leads to the formation of more hydrogen bonds. This type of intermolecular structure is responsible for the formation of dense polymer matrix in response to external pH changes.
Non-toxic and highly flexible pH responsive vaginal films based on chitosan citrate and polymethylmethacrylate have been developed by layer-by-layer techniques for improved pH-responsive properties. The amount of crosslinker present in the film modulated the swelling behavior and water penetration. The release of the drug Tenofovir was rapid in the simulated vaginal fluid. Polyurethane-based hydrogels and polyurethane membranes in the form of a reservoir-intravaginal ring have also been developed for the on-demand delivery of small interfering RNA in the treatment of HIV infections.
Hydrogel nanofibers containing polyurethane and 1,4-bis (2-hydroxyethyl) piperazine showed good pH-responsive properties due to protonation of amino nitrogen of piperazine under acidic pH conditions [
25]. To prevent the proliferation and migration of virions in the vagina, a pH-responsive biologically inspired synthetic mucin-like polymer system was developed. This polymer system based on phenylboronic acid and salicyl hydroxamic acid, showed both shear-thinning and shear-thickening behavior. The interaction of polymer components and the vaginal mucin resulted in good mucoadhesion and impeded the migration of virion in the vagina.
2.5. Ion-Responsive Hydrogels
Polymers that forms physically crosslinked gels in the presence of certain ions are called as ion-responsive or ion-sensitive polymers. The presence of charged chemical functional groups in the polymer facilitates the reversible crosslinking process. The vaginal fluid contains ions of sodium (Na
+), potassium (K
+), calcium (Ca
2+) and chloride (Cl
-). These ions can crosslink in situ with certain types of polymers such as alginate, chitosan, and gellan gum (polysaccharides) and form a solid gel. These types of materials are used in VDDS to improve bioadhesion and drug efficacy. Gellan gum is a natural polysaccharide (anionic) with repeating units of a-L-rhamnose, b-D-glucose, and b-D-glucoronate. The mole ratio of the three glucose units are 1:2:1. The carboxylic groups of the of b-D-glucoronate is responsible for electrostatic interactions with the ions leading to the formation of a gel [
26].
Vaginal gels based on chitosan (1 % w/v) and gellan gum (1 % w/v), containing the model drug clindamycin is used in the treatment of BV. This type of gel formulation has good adhesion on the vaginal mucous and has improved retention of the drug. Gellan gum and sodium carboxy methylcellulose-based formulations have been successful in the delivery of secnidazole for the treatment of vaginal trichomoniasis. The ion-responsive gelation process after administration was enhanced by the addition of calcium chloride (CaCl
2) and sodium citrate (Na
3C
6H
5O
7) in the formulation [
27].
Ion-responsive hydrogels based on cationic copolymers of methyl methacrylate, ethyl acrylate, and low content of methacrylic acid ester with quaternary ammonium groups (Eudragit
® RS-100) in the form of nanocapsules have been used to deliver the drug indole-3-carbinol for the treatment of vaginal trichomoniasis [
26]. Ionic crosslinking through thiol functional groups (-SH) have also been exploited in hydrogel formulations for gynecological treatments. A multicomponent system consisting of 8-arm poly(ethylene glycol) with terminal thiol groups and dendrimer based on 4-poly(amidoamine) functionalized with thiopyridyl end groups have been used in the delivery of the antibiotic amoxicillin. The sol-gel transition is facilitated by intramolecular disulphide crosslinks which provides long residence time for the therapeutics. Interestingly, this hydrogel formulation has been found to be suited for intravaginal treatment in pregnant women. This is because, the gel formed due to disulphide crosslinks of the dendrimer prevents diffusion across the membrane of the foetus [
28].
The synthetic polymer, Carbopol has also been used as ion-responsive materials in gynecological hydrogel formulation in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Carbopol is a high molar mass poly(acrylic acid) which is crosslinked with pentaerythritol allyl esters. The sol-gel transition is modulated by change of external pH conditions and presence of ions. Star shaped polymers, polyethylene glycol, thiolated carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid, and poly(ethylene glycol)-bis bromoacrylate have all been used in VDDS as ion-responsive systems, some in the form of dry films and vaginal in situ gel [
29].
2.6. Multi-Stimuli Responsive Hydrogels
Polymers that responds reversibly to more than one external stimulus are termed a multi-stimuli responsive polymer, and these materials open new avenues for smart and targeted vaginal drug delivery. Multi-stimuli responsive polymers are synthesized either by combing two or more polymers with desired effects or incorporating the required functional groups in the same molecule. A critical balance of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups is necessary to achieve the multi-stimuli responsive effect. When two polymers are combined for multiple sensitivity, the effect can be very synergistic. Natural polymers in combination with synthetic polymers provide better multi-stimuli properties and such systems are widely used in drug delivery systems.
Chitosan in combination with poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) provides pH and temperature responsive properties. By varying the composition of the two polymers the properties can be easily tuned for intended applications. Ion and temperature-responsive physically crosslinked gels based on Pluronic PF-127/68 and gellan gum has been developed for vaginal delivery of clindamycin. This system when combined with carrageenan improved the mucoadhesive property and prolonged the vaginal residence time of the drug for up to 9 hours.
Temperature and pH-responsive gels based on sodium alginate and PNIPAM with high swelling ratio has been developed for sustained release of the antibiotic oxytetracycline. The high swelling of the gel is due to ionic interactions between the carboxylate groups of sodium alginate. Ketoconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat vaginal infections. This drug however that has poor water solubility and the solubility can be improved through inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins.
Chitosan and gellan gum-based hydrogel encapsulated with ketoconazole and b-cyclodextrin was effective in the delivery of the drug. The gel was developed in the form of flakes for better penetration and sustained release of the drug over 6 hours through the vaginal mucosa. Gels consisting of pH and temperature-sensitive chitosan-graft-PNIPAM and polyvinyl alcohol has been developed for the safe delivery of voriconazole to the vaginal mucosa. The presence of PVA in the gel provided non-Newtonian properties and increased the viscosity for better adhesion over the mucus of the vagina.
Temperature and enzyme responsive organogels based on hyaluronic acid and palm oil has been developed for the delivery of anti-retroviral drug maraviroc. Organogels has a hydrophobic interior which is helpful to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs like maraviroc. The release of the drug in the presence of the enzyme hyaluronidase, the release of the drug was more than 2.5-fold due to enzymatic backdown of glucuronic acid units of the polymer. The organogels gel preserves the viability of the vaginal microbiome
Lactobacillus crispatus making this gel a good vehicle for mucoadhesion for vaginal microbicides [
30].
pH-responsive osmotic pump tablets for vaginal delivery of an antiretroviral drug IQP-0528 has been developed based on cellulose-acetate phthalate. The polymer core undergoes swelling when in contact with simulated vaginal fluid and extrudes into the vaginal canal. When in contact with simulated seminal fluid the coating of the tablet dissolved slowly giving a burst release of the encapsulated drug. In comparison to conventional vaginal tablets, the osmotic pump tablets provided a stable drug concentration in the vaginal mucosa and fluid for a period up to 10 days, allowing sustained release of vaginal microbicides. pH and temperature-responsive liposomes based on methoxy polyethylene glycol 2000-hydrazone-cholesteryl hemi succinate has been developed for vaginal administration of arctigenin in the form of liposomal gel or lipogel.
The sol-gel transition of the gel was induced by temperature changes and drug release was achieved due to polymer degradation under acidic pH conditions. During vaginal delivery of arctigenin, the poloxamers of the liposomes greatly reduced its toxicity and improved the drug release efficacy.
2.6. Liquid Crystalline Hydrogels
Hydrogels based on liquid crystal systems have been explored in vaginal administration of therapeutics due to their low viscosity and ability to form in situ crystalline phases in liquids. When in contact with the vaginal mucous the polymer undergoes phase transition with changes in flow behavior due to the formation of self-assembled structures. A liquid crystal system containing the extract of Syngonanthus nitens (grass-like plant species) has been studied in the treatment of vaginal infections caused by Candida krusei and Candida albicans. The extract loaded system on contact with vaginal mucous forms semi solid crystalline structures with increases cell permeability. This promotes the uptake of the extract or drug leading to inhibition of the vaginal pathogens. Liquid gels based on phytantriol that forms liquid crystalline gels even in small amounts of vaginal fluid has been developed for sustained delivery of sinomenine hydrochloride. The formation of cubic liquid crystalline structure adheres strongly to the vaginal mucosa and prevents vaginal cleansing action. This type of material is being investigated for vaginal topical applications due to its mild irritation and inflammatory properties.
Vaginal mucoadhesive systems based on liquid crystal precursors containing poloxamers such as Carbopol974P and polycarbophil have been developed for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. These materials had strong mucoadhesion force up to 13 mN with MIC values in the range 31.2-62.5 mg ml
-1. Mucoadhesive gels containing P407 and the drug hypericin has been investigated for therapeutic potential in the treatment of vaginal bacterial infections and gynaecological cancer. This gel, even after dilution exhibited very high mucoadhesion on the vagina with a force of 26 mN and showed high cell viability [
31].
2.7. Astrodimer Gel and Metronidazole in the Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
The astrodimer gel is a dendrimer- based mucoadhesive gel that was used in a phase 3, placebo controlled, double-blinded study to compare the efficacy and safety of a placebo against the astrodimer 1% gel. The study comprised of administering 5g of the gel vaginally for 7 days. The endpoint of the study was indicated by the absence of vaginal discharge, less than 20% clue cells as well as a negative whiff test which was is related to the absence of a bacterial vaginosis (BV) infection. The adverse effects that were reported during the study were considered mild to moderate as well as being tolerable, which resulted in the conclusion that supported the statement regarding the astrodimer gel being safe, effective, and beneficial towards the treatment of BV infections.
Metronidazole (MZT) is known to be a standard treatment towards BV infections. The limitations of this treatment include potential toxicity and the ability of the MZT to restrict the growth of normal, beneficial flora in the vagina. Shaaban et al. conducted a randomized controlled trial (RCT) that looked into the analysis of the efficacy in the use of an in-situ formulation of the MZT vaginal gel once every day and the use of a conventional formulation of the gel twice every day [
32].
The results were collected at the end of the first and fourth week to analyze the cure rates: with regards to the in-situ gel, in the first week there was a 74.5% cure rate, and in the fourth week a 66.7% cure rate was seen. When the results of the conventionally administered MTZ gel were analyzed, it was observe that in the first week a 63% cure rate was seen and in the fourth week, 40% of the cases involved with BV infections were cured. At the end of this RCT, it was concluded that the in-situ MTZ gel was more effective when it came to identifying a persistent, reliable cure in the treatment of BV. The reasons for this could be due to the demonstrated muco-adhesive properties and the ability of the thermos-responsive formulation to convert the solution into a gel which would allow it to have an increased ability to stay in contact with the vaginal surface.
3. Nanocarriers: Liposomes, Polymer Nanoparticles, Fibers, and Gels
In view of their appealing properties such as controlled release, precise targeting, and mucus adhesion, nanomaterials such as liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles have been used in VDDS. Azithromycin liposomes with different bilayer elasticity has been developed by Vanić et al. for the treatment of cervicovaginal infections [
33]. The rigid bilayer properties allowed slow release of azithromycin and prevented the formation of biofilms with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC
50). A significant inhibitory effect on biofilms was observed with deformable propylene glycol liposomes that contained propylene glycol and monoacyl phosphatidylcholine. Pregnant women are highly vulnerable to vaginal infections caused by human simplex virus (HSV).
This is due to reduced activities of T-helper cell type 1 to protect the growing foetus [
34]. The current anti-microbial therapy is not beneficial in controlling the infection due to resistance from the pathogen. Mucoadhesive liposomes decorated with chitosan and encapsulated with resveratrol has been developed to improve the bioavailability of the drug in the treatment of vaginal inflammation and infections. Mucin binding studies of these liposomes in both normal (healthy) vaginal conditions and infected vaginal conditions showed enhanced mucin binding properties at low chitosan concentration [
35].
Polymeric nanoparticles have been widely investigated as VDDS to enhance the residence time and delivery of therapeutics in the vagina. Chitosan is a cationic natural polymer that can easily form polyelectrolyte assemblies, and this feature has been widely exploited in various drug delivery systems. Polymeric nanoparticles based on PLGA with modified surface containing chitosan was developed to deliver clotrimazole in the vagina. The mucoadhesion was enhanced due to the presence of chitosan on the surface of the polymeric nanoparticles that allowed the formation of polyelectrolyte complexes when in contact with mucin of the vaginal mucus.
The modified polymeric nanoparticles exhibited higher biphasic drug release profile for up to 18 days, antibacterial and antifungal effects. Chitosan based nanoparticles containing miconazole nitrate have been effective in reducing the colony forming unit levels, and cellular infiltrate. This effect was achieved with a significantly lower concentration of the drug relative to the conventional formulation [
36].
Chitosan nanoparticles containing econazole were effective in the sustained relea7e of the drug relative to the free drug solutions. The formulation was non cytotoxic and exhibited a low minimum inhibitory concentration value against Candida albicans [
37]. The nanoparticles also showed excellent time-to-kill profile for the complete eradication of C. albicans culture in just three days. The results suggest that formulations containing drug loaded chitosan nanoparticles could be effective for the local treatment of vaginal candidiasis. Patient compliance and enhanced therapeutic delivery can be improved in the future by incorporating polymeric nanoparticles in films or spray gels [
38].
Gels containing liposomes (pectin coated sertaconazole-loaded liposomes) was effective in reducing the drug penetration through vaginal mucosa than the conventional gel without the pectin coating. Pectin coated liposomes showed higher adsorption of mucin with more retained in the vaginal tissues [
39,
40]. Similarly, mucoadhesive gel containing benzylamide hydrochloride loaded liposomes exhibited high mucoadhesion. The polymers present in the liposome gel (lipogel) such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and Carbopol
®974P further enhanced the mucoadhesion properties of the formulation.
Polymeric films containing therapeutics have been widely explored in the treatment of vaginal infections. Polymer films with desired properties and containing the pharmaceuticals can be achieved easily. Polymer films of chitosan and poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) containing ciprofloxacin has been developed for the treatment of vaginal infections. Polymer membranes containing alginate, chitosan, and metronidazole adhered strongly to the vaginal tissue and was effective against E. coli, S. aureus, and G. vaginalis [
41]. Antimicrobial vaginal films of thiolated gellan gum loaded with metronidazole showed strong mucoadhesion and prolonged residence time of the drug.
The composition of polymer in the greatly affects the adhesive properties of the films due to variation is swelling index in response to the composition of vaginal mucus. The bilayer vaginal films based on ethyl cellulose, tragacanth gum, and xanthan gum containing tenofovir has been explored for pre-exposure prophylaxis of HIV in women [
42]. Films containing a high concentration of xanthan gum was highly mucoadhesive, and non-toxic with long drug residence time. The choice of polymers is an important criterion for vaginal film platforms and affects the efficacy of the loaded therapeutics.
Polymers with strong mucoadhesive properties have also been exploited in VDDS, as it improves adhesion of formulation and retains the therapeutics for a longer time. The healthy vaginal mucosa consist of a squamous epithelium that is stratified and multilayered. In response to hormonal and environmental conditions the epithelium undergoes changes throughout the lifetime of a woman. The structure of the epithelium also varies according to the age of the individual [
43].
The stratum corneum of the vagina is enriched with mucins which are mainly composed of water, proteins, and lipids, and forms a gel-like lining on the mucosal tissues. Delivery of therapeutics in the vagina by means of non-mucoadhesive formulations remains a challenge due to poor adhesion, non-uniform surface coverage, and poor adsorption. Mucoadhesive polymers interact with the vaginal mucosa to improve the adhesion and delivery of therapeutics.
Mucoadhesive formulation based on microgels containing polycarbophil and miconazole nitrate loaded solid lipid particles exhibited high mucoadhesive strength and sustained drug release profile. Apart from being a non-irritant formulation, it was more effective in the eradication of C. albicans than the commercially available Daktarin
® cream [
44]. Nanocapsules containing Eudragil
® RS100 encapsulated with indole-3-carbinol was effective in controlling the reactive oxygen species through its anti-inflammatory effect. The addition of gellan gum to the formulation resulted in higher mucoadhesion and it is considered as a safe alternative therapy for vaginal trichomoniasis [
45].
Nanoemulsions containing oxiconazole nitrate, carboxymethyl cellulose, xanthan gum, and Carbopol 934 adhered strongly to the mucus and was effective in the penetration of the fungal cell wall. The formulation exhibited long drug resident time and controlled release profile and was effective against vaginal candidiasis [
46]. The different types of mucoadhesive polymeric materials and formulations are present in
Table 1.
3. Conclusions
To overcome the issues that arise with the most common vaginal infections such as bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis, drug delivery through the vagina has established itself as a promising site to administer drugs through a muco-adhesive system which has been used for systemic and local effects. It involves the addition of mucoadhesive polymers such as chitosan, gellan gum, HPMC and xanthan gum, these polymers have shown great biocompatibility, non-toxic effects and are safe. This system can be applied in a variety of forms, including vaginal tablets, gels, films and microparticles.
Stimuli-responsive systems have been of great interest in this field and the associated features of these systems allow them to have maximal surface coverage as they are administered as a low viscosity liquid over the mucosal area and transform into in-situ gels in response to environmental stimuli. Their mode of administration allows a prolonged formulation residence time in the lumen of the vagina which plays a significant role in patient adherence and compliance. The literature has shown that pH-responsive systems as well as thermal-responsive systems play a role in improving efficacy as the drug is applied locally through the vaginal route. Ion-responsive systems are considered a relatively new branch of stimuli-responsive systems as only a limited number of studies have been conducted on this drug delivery system. The safety concerns and clinical applications need to be investigated to further observe and explore the roles of this system and the polymers involved.
Multi-responsive systems which have a characteristic feature of undergoing chemical and/or physical changes as they respond to environmental stimuli have gained considerable interest and attention as a drug delivery system. It involves the synthesis of formulations that are not considered feasible and can be challenging. An obstacle that is faced is the variety of vaginal environments during the life span of a woman which needs to be further researched to allow for a personalized regimen to provide better treatment for vaginal infections and disorders. The effectiveness and tolerability of formulations for these drug delivery systems require further experimental studies to be able to achieve the goal of treating the various vaginal conditions at all stages.