Submitted:
08 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers of AKI
2.1. Stress markers
2.2. Damage markers
2.3. Functional markers
3. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury
- In cases of renal hypoperfusion induced by hypovolemia, autoregulation and neurohumoral mechanisms are triggered to maintain GFR. Nevertheless, persistent renal hypoperfusion can lead to sustained inadequate oxygen delivery and depletion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), causing cellular injury to the epithelium [48]. This can subsequently activate inflammatory responses, induce endothelial injury, and ultimately result in renal damage [49,50].
- In sepsis, inflammatory cytokines can induce leukocyte activation, recruit neutrophils, and trigger endothelial injury and coagulation. Additionally, these inflammatory mediators may bind to specific receptors expressed by renal endothelial and tubule epithelial cells, causing direct injury [51]. The release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) by damaged cells further contributes to vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and a pro-thrombotic environment [52]. Furthermore, filtered DAMPs and Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) may activate Toll-like receptors 2 (TLR2) and Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR4) on proximal tubules, subsequently triggering interstitial inflammation. Vascular dysfunction, endothelial injury, immunological dysregulation, and abnormal cellular responses to injury collectively contribute to the development of AKI in sepsis [53].
- AKI resulting from major surgery can be attributed to fluid depletion, including blood loss and the extravasation of fluid into the third space [54]. Additionally, anesthetic agents may induce peripheral vasodilation and myocardial depression, thereby influencing renal perfusion. In case of AKI associated with cardiac surgery, ischemia–reperfusion injury (IRI) may occur due to extracorporeal circulation, leading to cell injury and death by increasing mitochondrial permeability [54,55]. Renal IRI stands as the primary cause of AKI, contributing to tubular epithelial apoptosis, necrosis, and inflammation during the peri-operative period [56].
- In individuals genetically predisposed to autoimmune activation, the renal consequences may involve glomerular inflammation and injury, such as rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis [58].
- Extrarenal or intrarenal obstruction has the potential to elevate intratubular pressure, compromise renal blood flow, and trigger inflammatory processes, ultimately leading to AKI [59].
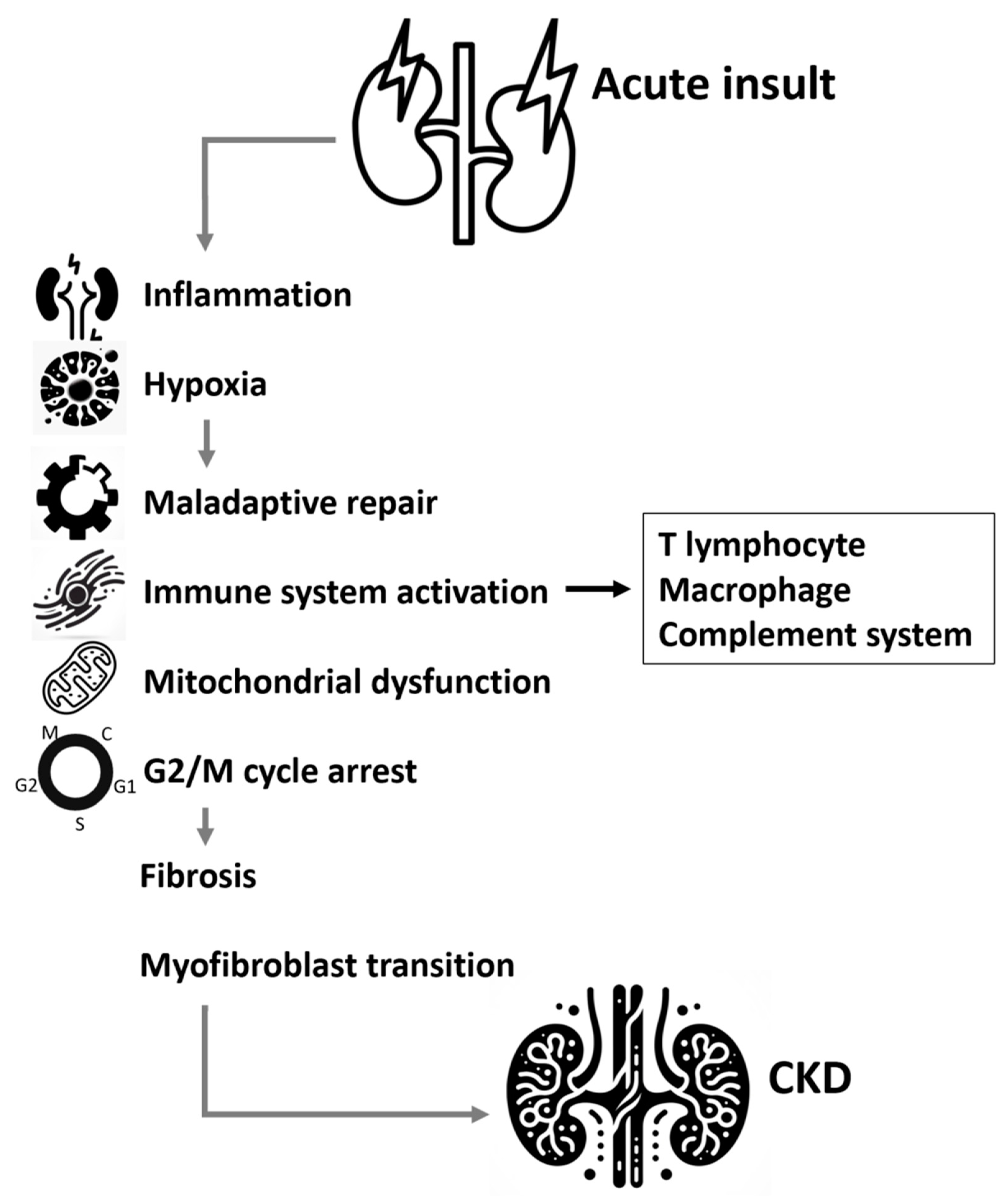
4. Molecular mechanism involved in AKI to CKD transition
4.1. Inflammation
4.2. Hypoxia
4.3. Signal pathways involved in the process of renal fibrosis
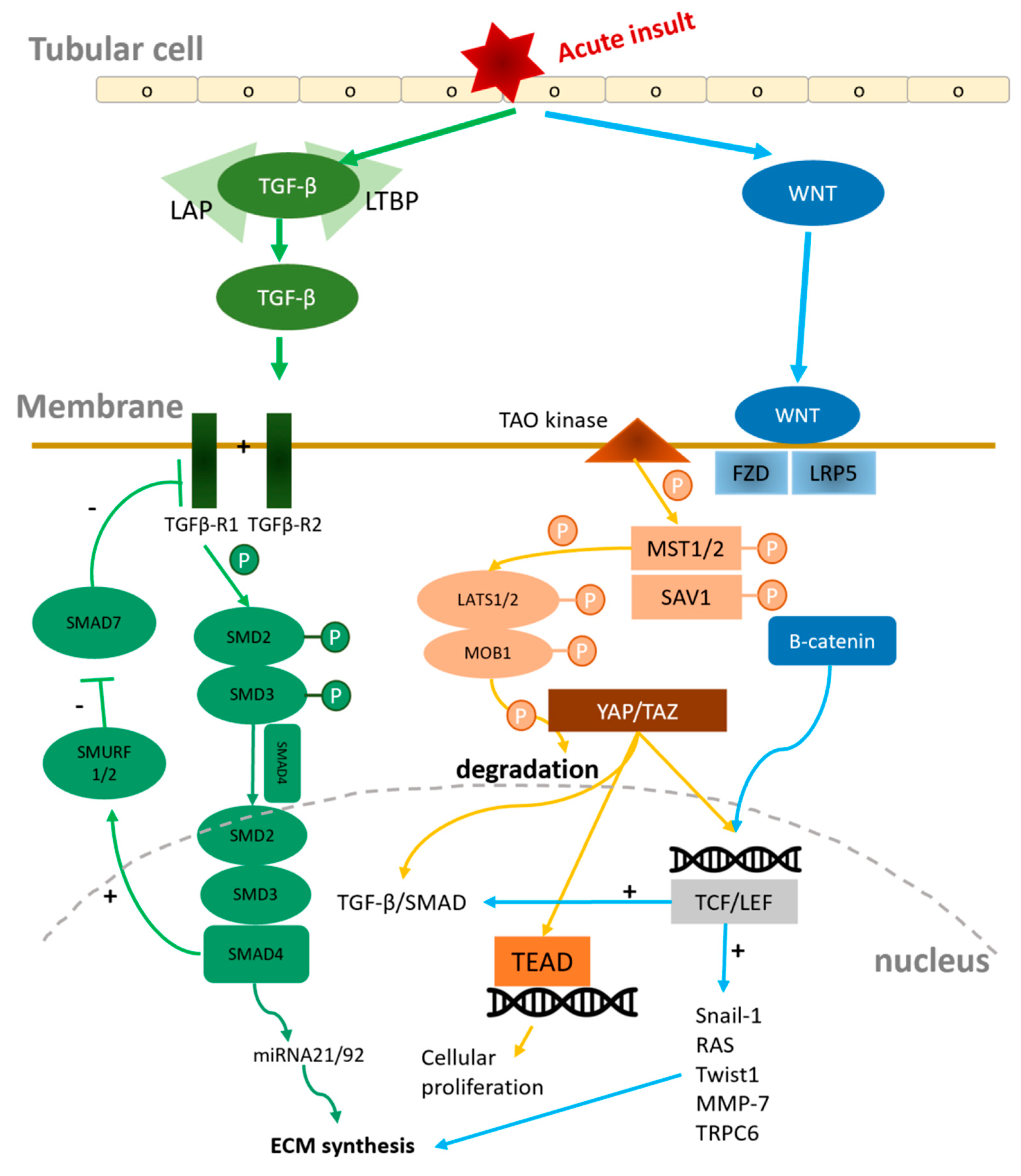
4.3.1. Wnt/β-Catenin signal pathway
4.3.2. TGF-β1/SMAD signal pathway
4.3.3. Hippo/ Yes-associated protein (YAP)/ Tafazzin (TAZ) Signaling
4.4. Innate and Adaptive Immunity
4.5. Mitochondria dysfunction
4.6. G2/M Arrest Pathway and cellular senescence
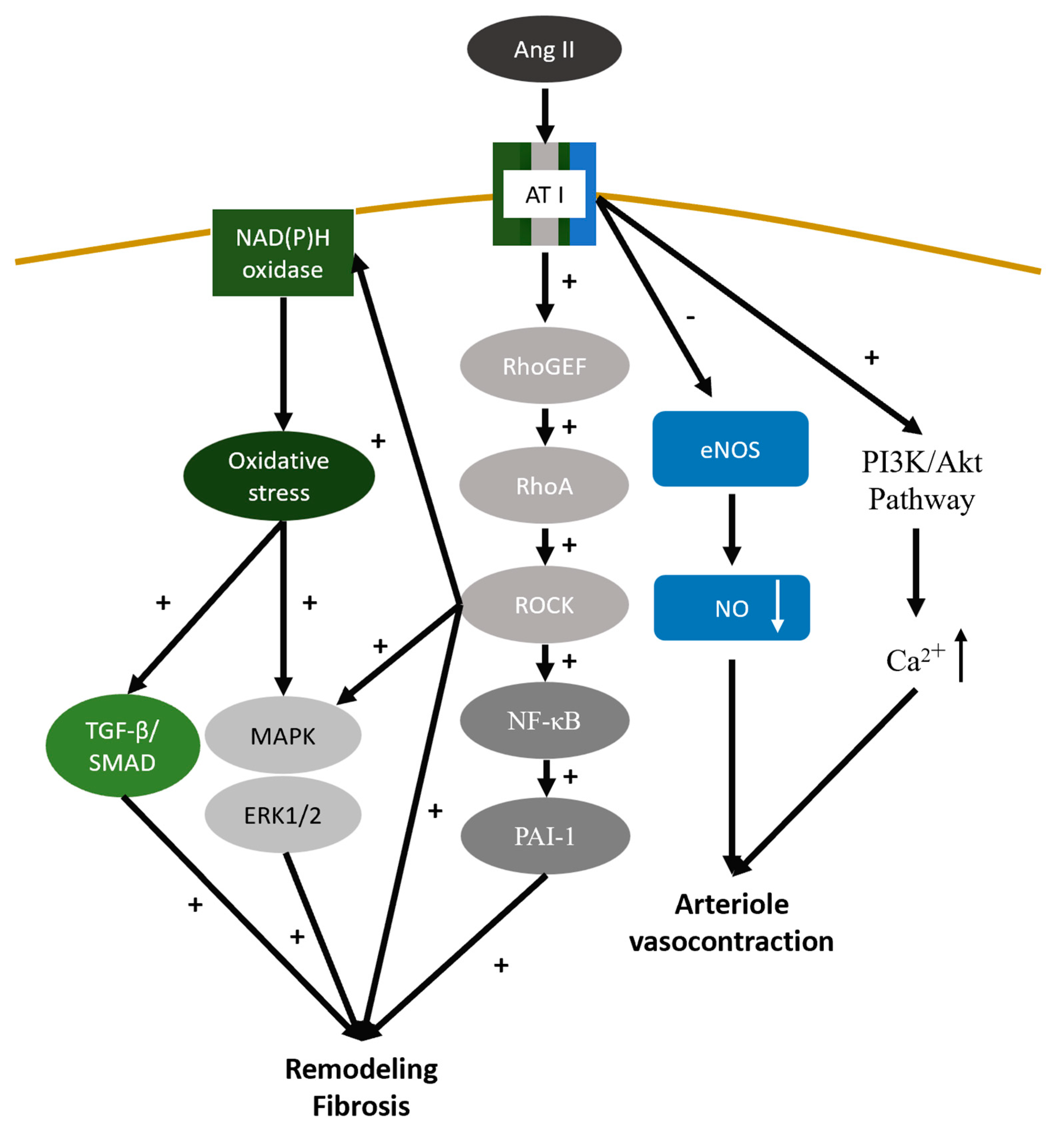
4.7. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kellum, J.A.; et al. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021. 7(1): p. 52.
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pr. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; Zeeuw, D.D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N.H.; Levin, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Cheung, M.; Jadoul, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Stevens, P.E.; Caskey, F.J.; Farmer, C.K.; Fuentes, A.F.; et al. Harmonizing acute and chronic kidney disease definition and classification: report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S. Defining AKD: The Spectrum of AKI, AKD, and CKD. Nephron 2021, 146, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkin, D.E., S. G. Coca, and K. Kalantar-Zadeh, Does AKI truly lead to CKD? J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012. 23(6): p. 979-84.
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, K.L.; Packington, R.; Monaghan, J.; Reilly, T.; Selby, N.M. Three-year outcomes after acute kidney injury: results of a prospective parallel group cohort study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.T.; Levey, A.S.; Tonelli, M.; Tan, Z.; Barry, R.; Pannu, N.; Ravani, P.; Klarenbach, S.W.; Manns, B.J.; Hemmelgarn, B.R. Incidence and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Diseases and Disorders Using an Integrated Approach to Laboratory Measurements in a Universal Health Care System. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e191795–e191795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Shiao, C.-C.; Neyra, J.A.; Matsuura, R.; Noiri, E.; See, E.; Chen, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-K.; et al. Outcomes associated with acute kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 55, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S.A.; Chertow, G.M. The Economic Consequences of Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2017, 137, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Parikh, C.R. Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S.J. and A.P. Kulkarni, Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury. Indian J Crit Care Med, 2020. 24(Suppl 3): p. S90-s93.
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Meersch, M.; Bell, M. Biomarker-guided management of acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yanagita, M. Pathophysiology of AKI to CKD progression. Semin. Nephrol. 2020, 40, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.-W.; Bonventre, J.V. Acute kidney injury and maladaptive tubular repair leading to renal fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers From the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement. JAMA Netw Open, 2020. 3(10): p. e2019209.
- Schunk, S.J.; Zarbock, A.; Meersch, M.; Küllmar, M.; A Kellum, J.; Schmit, D.; Wagner, M.; Triem, S.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Gröne, H.-J.; et al. Association between urinary dickkopf-3, acute kidney injury, and subsequent loss of kidney function in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: an observational cohort study. Lancet 2019, 394, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ardiles, T.; Artigas, A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bell, M.; Bihorac, A.; Birkhahn, R.; Cely, C.M.; Chawla, L.S.; et al. Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeong, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Acute Kidney Injury: Biomarker-Guided Diagnosis and Management. Medicina 2022, 58, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, S.; Yalavarthy, R.; Concato, J.; Parikh, C. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: A systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, J.R.; Portilla, D.; Okusa, M.D. A basic science view of acute kidney injury biomarkers. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, F.; Frischmann, S.; Grünbaum, M.; Zidek, W.; Westhoff, T.H. Urinary Calprotectin and the Distinction between Prerenal and Intrinsic Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E., et al., Identification and validation of biomarkers of persistent acute kidney injury: the RUBY study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 943–953. [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Tangri, N.; Komenda, P.; Kaushal, A.; Sood, M.; Brar, R.; Gill, K.; Walker, S.; MacDonald, K.; Hiebert, B.M.; et al. Urinary, Plasma, and Serum Biomarkers’ Utility for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Cardiac Surgery in Adults: A Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-C.; Yang, S.-Y.; Chiou, T.T.-Y.; Shiao, C.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Huang, C.-T.; Wang, T.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liao, H.-W.; Chen, S.-Y.; et al. Comparative accuracy of biomarkers for the prediction of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo-Ikemori, A.; Ichikawa, D.; Matsui, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Sugaya, T.; Kimura, K. [Urinary L-type fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) as a new urinary biomarker promulgated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan]. . 2013, 61, 635–40. [Google Scholar]
- Risch, L.; Blumberg, A.; Huber, A. Rapid and accurate assessment of glomerular filtration rate in patients with renal transplants using serum cystatin C. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; et al. Detection of decreased glomerular filtration rate in intensive care units: serum cystatin C versus serum creatinine. BMC Nephrol, 2014. 15: p. 9.
- Chen, S. Retooling the Creatinine Clearance Equation to Estimate Kinetic GFR when the Plasma Creatinine Is Changing Acutely. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, L.; Wan, J.; Li, X. Serum Cystatin C Predicts AKI and the Prognosis of Patients in Coronary Care Unit: a Prospective, Observational Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Hollinger, A.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; Dépret, F.; Cariou, A.; Deye, N.; Fournier, M.-C.; Jaber, S.; Damoisel, C.; Lu, Q.; et al. One-Year Prognosis of Kidney Injury at Discharge From the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e953–e961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Groote, T.; et al. Proenkephalin A 119-159 predicts early and successful liberation from renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a post hoc analysis of the ELAIN trial. Crit Care, 2022. 26(1): p. 333.
- Lin, L.-C.; Chuan, M.-H.; Liu, J.-H.; Liao, H.-W.; Ng, L.L.; Magnusson, M.; Jujic, A.; Pan, H.-C.; Wu, V.-C.; Forni, L.G. Proenkephalin as a biomarker correlates with acute kidney injury: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchewka, Z.; Długosz, A.; Kuźniar, J. Diagnostic application of AAP isoenzyme separation. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 1999, 31, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchewka, Z., J. Kuźniar, and A. Długosz, Enzymuria and beta2-mikroglobulinuria in the assessment of the influence of proteinuria on the progression of glomerulopathies. Int Urol Nephrol, 2001. 33(4): p. 673-6.
- Westenfelder, C. Earlier diagnosis of acute kidney injury awaits effective therapy. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-J. A long journey for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, F.S.; Rosenberger, C.; Mathia, S.; Arndt, R.; Arns, W.; Andrea, H.; Pagonas, N.; Bauer, F.; Zidek, W.; Westhoff, T.H. Urinary Calprotectin Differentiates Between Prerenal and Intrinsic Acute Renal Allograft Failure. Transplantation 2017, 101, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.A.; Galligan, M.; Redahan, L.; Martin, T.; Meaney, E.; Cotter, E.J.; Murphy, N.; Hannon, C.; Doran, P.; Marsh, B.; et al. Biomarker Predictors of Adverse Acute Kidney Injury Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: The Dublin Acute Biomarker Group Evaluation Study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 50, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Su, B. The value of kidney injury molecule 1 in predicting acute kidney injury in adult patients: a systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medić, B.; Rovčanin, B.; Jovanović, G.B.; Radojević-Škodrić, S.; Prostran, M. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Cardiovascular Diseases: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, K.; Kamihata, H.; Motohiro, M.; Senoo, T.; Yoshida, S.; Iwasaka, T. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein level as a predictive biomarker of contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 42, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Haneda, M.; Koya, D.; Sugimoto, T.; Isshiki, K.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Uzu, T.; Kashiwagi, A. Predictive impact of elevated serum level of IL-18 for early renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: an observational follow-up study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, F.; Awad, A.S.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C., R. Bellomo, and J.A. Kellum, Acute kidney injury. Lancet, 2019. 394(10212): p. 1949-1964.
- Xu, K.; Rosenstiel, P.; Paragas, N.; Hinze, C.; Gao, X.; Shen, T.H.; Werth, M.; Forster, C.; Deng, R.; Bruck, E.; et al. Unique Transcriptional Programs Identify Subtypes of AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, K.; Spanou, L. Acute Kidney Injury: Definition, Pathophysiology and Clinical Phenotypes. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Meola, M.; et al. Clinical Scenarios in Acute Kidney Injury: Post-Renal Acute Kidney Injury. Contrib Nephrol, 2016. 188: p. 64-8.
- Cantaluppi, V.; Quercia, A.D.; Dellepiane, S.; Ferrario, S.; Camussi, G.; Biancone, L. Interaction between systemic inflammation and renal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2004–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, U.; Martinelli, R.; Vollmann, E.H.; Best, K.; Therien, A.G. The impact of DAMP-mediated inflammation in severe COVID-19 and related disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 195, 114847–114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, H. and J.A. Kellum, Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2016. 22(6): p. 546-553.
- Wang, Y.; Bellomo, R. Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Neves, M.; Jorge, S.; Lopes, J.A. Acute kidney injury in major abdominal surgery: incidence, risk factors, pathogenesis and outcomes. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Han, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.; Cai, J.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Activation of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy protects against renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Breglia, A.; Brocca, A.; de Cal, M.; Bolin, C.; Vescovo, G.; Ronco, C. Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Damage Markers in Patients with Acute Heart Failure with and without Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalfino, L.; et al. Intra-abdominal hypertension and acute renal failure in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med, 2008. 34(4): p. 707-13.
- Praga, M. and E. González, Acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int, 2010. 77(11): p. 956-61.
- He, Z., H. Wang, and L. Yue, Endothelial progenitor cells-secreted extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-93-5p confer protection against sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via the KDM6B/H3K27me3/TNF-α axis. Exp Cell Res, 2020. 395(2): p. 112173.
- Roh, J.S.; Sohn, D.H. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial ROS promote mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic acute kidney injury by disrupting TFAM-mediated mtDNA maintenance. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1845–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, F.; Shi, C.; Pei, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z. TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and acute kidney injury. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yanagita, M. Immune cells and inflammation in AKI to CKD progression. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1501–F1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2009. 1(6): p. a001651.
- Oeckinghaus, A. M. S. Hayden, and S. Ghosh, Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol, 2011. 12(8): p. 695-708.
- Peasley, K.; Chiba, T.; Goetzman, E.; Sims-Lucas, S. Sirtuins play critical and diverse roles in acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; et al. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Embo j, 2004. 23(12): p. 2369-80.
- Honda, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Nangaku, M. The role of oxidative stress and hypoxia in renal disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2019, 38, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; et al. MicroRNA-493 targets STMN-1 and promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial cell cycle arrest in G(2)/M and renal fibrosis. Faseb j, 2019. 33(2): p. 1565-1577.
- Gunaratnam, L.; Bonventre, J.V. HIF in Kidney Disease and Development. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-inducible factor–prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in the treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2021, 11, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Guo, C.; Dong, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Hypoxia, HIF, and Associated Signaling Networks in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; et al. p53 upregulated by HIF-1α promotes hypoxia-induced G2/M arrest and renal fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Cell Biol, 2019. 11(5): p. 371-382.
- Li, L.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Q.; D’agati, V.D.; Al-Awqati, Q.; Lin, F. FoxO3 activation in hypoxic tubules prevents chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2374–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Navarro, A.; Mejía-Vilet, J.M.; Pérez-Villalva, R.; Carrillo-Pérez, D.L.; Marquina-Castillo, B.; Gamba, G.; Bobadilla, N.A. SerpinA3 in the Early Recognition of Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) transition in the rat and its Potentiality in the Recognition of Patients with CKD. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Soria, I.; Soto-Valadez, A.D.; Martínez-Rojas, M.A.; Ortega-Trejo, J.A.; Pérez-Villalva, R.; Gamba, G.; Sánchez-Navarro, A.; Bobadilla, N.A. SerpinA3K Deficiency Reduces Oxidative Stress in Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M., T. Tanaka, and M. Nangaku, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain Inhibitors to Treat Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib Nephrol, 2019. 198: p. 112-123.
- Matovinović, M.S. 1. Pathophysiology and Classification of Kidney Diseases. 2009, 20, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, I.; Duffield, J.S.; Humphreys, B.D. The origin of interstitial myofibroblasts in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 27, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Ke, X.; Qu, Y. Activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway for disease therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 196, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Miao, N.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, J.; Yin, F.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; et al. FoxM1 promotes Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation and renal fibrosis via transcriptionally regulating multi-Wnts expressions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1958–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S.J.; et al. WNT-β-catenin signalling - a versatile player in kidney injury and repair. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2021. 17(3): p. 172-184.
- Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhou, L.; Igarashi, P.; Liu, Y. Tubule-specific ablation of endogenous β-catenin aggravates acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-S.; Sun, Q.; Hua, M.-R.; Suo, P.; Chen, J.-R.; Yu, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; et al. TGF-β/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol, 2015. 6: p. 82.
- Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.-Y. Smad3 Signatures in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gersdorff, G.; et al. Smad3 and Smad4 mediate transcriptional activation of the human Smad7 promoter by transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem, 2000. 275(15): p. 11320-6.
- Nagarajan, R.P.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, Y. Regulation of Smad7 Promoter by Direct Association with Smad3 and Smad4. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33412–33418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.Y.; Chung, A.C.-K. TGF-β/Smad Signaling in Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2012, 32, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. and T. Imamura, Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases. Cancer Sci, 2008. 99(11): p. 2107-12.
- Lan, H.Y. Smad7 as a therapeutic agent for chronic kidney diseases. Front. Biosci. 2008, ume, 4984–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.M.-K.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.-Y. Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; et al. Macrophage-to-Myofibroblast Transition Contributes to Interstitial Fibrosis in Chronic Renal Allograft Injury. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017. 28(7): p. 2053-2067.
- Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Lin, X.; Feng, X.-H.; Wang, Y. Smad3 signaling activates bone marrow-derived fibroblasts in renal fibrosis. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 94, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, B.A. From Cell Structure to Transcription: Hippo Forges a New Path. Cell 2006, 124, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. Mechanisms of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-Y.; Lai, T.-C.; Hsiao, M.; Chang, Y.-C. The Diverse Roles of TAO Kinases in Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Chengcheng, L.; Xuan, Q.; Yibing, C.; Lei, W.; Hao, Y.; Xizhi, L.; Yuan, L.; Xiaoxing, Y.; Qian, L. Quercetin inhibited mesangial cell proliferation of early diabetic nephropathy through the Hippo pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, D.; Xue, J.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Lian, F. The critical role of the Hippo signaling pathway in kidney diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 988175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habshi, T.; Shelke, V.; Kale, A.; Lech, M.; Gaikwad, A.B. Hippo signaling in acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition: Current understandings and future targets. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, P.-X.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.-J.; Yin, M.-X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, D.-P.; Sun, H.-P.; Liu, Z.-B.; et al. Involvement of the Hippo pathway in regeneration and fibrogenesis after ischaemic acute kidney injury: YAP is the key effector. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Dissection of Key Events in Tubular Epithelial to Myofibroblast Transition and Its Implications in Renal Interstitial Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, T.; Fujigaki, Y.; Fujikura, T.; Tsuji, T.; Ohashi, N.; Kato, A.; Yasuda, H. Cytoresistance after acute kidney injury is limited to the recovery period of proximal tubule integrity and possibly involves Hippo-YAP signaling. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Huen, S.; Nishio, H.; Nishio, S.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, B.-S.; Ruhrberg, C.; Cantley, L.G. Distinct Macrophage Phenotypes Contribute to Kidney Injury and Repair. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. How Acute Kidney Injury Contributes to Renal Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019. 1165: p. 117-142.
- Feng, Y.; Ren, J.; Gui, Y.; Wei, W.; Shu, B.; Lu, Q.; Xue, X.; Sun, X.; He, W.; Yang, J.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin–Promoted Macrophage Alternative Activation Contributes to Kidney Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 29, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; et al. Fate alteration of bone marrow-derived macrophages ameliorates kidney fibrosis in murine model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 34, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Sahu, R.K.; Landes, S.G.; Yu, J.; Taylor, R.P.; Ayyadevara, S.; Megyesi, J.; Stallcup, W.B.; Duffield, J.S.; Reis, E.S.; et al. Pericytes and immune cells contribute to complement activation in tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2017, 312, F516–F532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, D.; Xavier, S. Role of intracellular complement activation in kidney fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boor, P.; Konieczny, A.; Villa, L.; Schult, A.-L.; Diaeresis]Cher, E.B.; Rong, S.; Kunter, U.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Polakowski, T.; Hawlisch, H.; et al. Complement C5 Mediates Experimental Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Sahu, R.K.; Bontha, S.V.; Mas, V.; Taylor, R.P.; Megyesi, J.; Thielens, N.M.; Portilla, D. Complement C1r serine protease contributes to kidney fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2019, 317, F1293–F1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Qian, Z.; Xue, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Cai, D.; Rui, J.; Zhang, L. Aristolochic acid I aggravates renal injury by activating the C3a/C3aR complement system. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 312, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Swaminathan, S.; Bachman, L.A.; Croatt, A.J.; Nath, K.A.; Griffin, M.D. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells in renal lymph nodes is linked to systemic and local injury to the kidney. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, G.R.; Sharma, R.; Okusa, M.D. Regulatory T Cells in AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kinsey, G.R. Regulatory T cells in acute and chronic kidney diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 314, F679–F698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Shou, S. The role of IL-10 in kidney disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Schnellmann, R.G. Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, D.L.; Green, N.H.; Danesh, F.R. The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Mitophagy in Acute Kidney Injury and Kidney Repair. Cells 2020, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Linn, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Mitophagy and mitochondrial integrity in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhu, T.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, C. PINK1 Deficiency Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced mitophagy protects against renal dysfunction via Drp1-dependent-pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 369, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Tam, D.; Bardia, A.; Bhasin, M.; Rowe, G.C.; Kher, A.; Zsengeller, Z.K.; Akhavan-Sharif, M.R.; Khankin, E.V.; Saintgeniez, M.; et al. PGC-1α promotes recovery after acute kidney injury during systemic inflammation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.T.; Zsengeller, Z.K.; Berg, A.H.; Khankin, E.V.; Bhasin, M.K.; Kim, W.; Clish, C.B.; Stillman, I.E.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. PGC1α drives NAD biosynthesis linking oxidative metabolism to renal protection. Nature 2016, 531, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyano, T.; Namba, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakakuni, K.; Nakano, D.; Fukushima, M.; Nishiyama, A.; Matsuyama, M. The p21 dependent G2 arrest of the cell cycle in epithelial tubular cells links to the early stage of renal fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, D.A.; Zhang, J.-M.; Ouyang, J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Genois, M.-M.; Zou, L. ATR Protects the Genome against R Loops through a MUS81-Triggered Feedback Loop. Mol. Cell 2019, 77, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; et al. Epithelial cell cycle arrest in G2/M mediates kidney fibrosis after injury. Nat Med, 2010. 16(5): p. 535-43, 1p following 143.
- Canaud, G.; Brooks, C.R.; Kishi, S.; Taguchi, K.; Nishimura, K.; Magassa, S.; Scott, A.; Hsiao, L.-L.; Ichimura, T.; Terzi, F.; et al. Cyclin G1 and TASCC regulate kidney epithelial cell G 2 -M arrest and fibrotic maladaptive repair. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, D.R.; McMurdo, M.; Karaca, G.; Wilflingseder, J.; Leaf, I.A.; Gupta, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Susa, K.; Johnson, B.G.; Soliman, K.; et al. Interleukin-1β Activates a MYC-Dependent Metabolic Switch in Kidney Stromal Cells Necessary for Progressive Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1690–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L., B. D. Humphreys, and J.V. Bonventre, Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease: maladaptive repair. Contrib Nephrol, 2011. 174: p. 149-155.
- Novitskaya, T.; McDermott, L.; Zhang, K.X.; Chiba, T.; Paueksakon, P.; Hukriede, N.A.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Skrypnyk, N.I.; Voziyan, P.; Yang, H.; et al. A PTBA small molecule enhances recovery and reduces postinjury fibrosis after aristolochic acid-induced kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 306, F496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Gong, A.Y.; Haller, S.T.; Dworkin, L.D.; Liu, Z.; Gong, R. The ageing kidney: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 63, 101151–101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabla, N.; et al. Mitigation of acute kidney injury by cell-cycle inhibitors that suppress both CDK4/6 and OCT2 functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2015. 112(16): p. 5231-6.
- Chou, Y.-H.; Huang, T.-M.; Chu, T.-S. Novel insights into acute kidney injury–chronic kidney disease continuum and the role of renin–angiotensin system. J. Formos. Med Assoc. 2017, 116, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, T.M.; Rigato, M.; Ravarotto, V.; Calò, L.A. ROCK (RhoA/Rho Kinase) in Cardiovascular–Renal Pathophysiology: A Review of New Advancements. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQudah, M.; Hale, T.M.; Czubryt, M.P. Targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2020, 91-92, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Progression of Renal Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravarotto, V.; Pagnin, E.; Fragasso, A.; Maiolino, G.; Calò, L.A. Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular-Renal Remodelling in Hypertension: Insights from a Human Model Opposite to Hypertension. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2015, 22, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A., R. C. Che, and A.H. Zhang, Role of Aldosterone in Renal Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019. 1165: p. 325-346.
- Brown, N.J. Aldosterone and end-organ damage. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2005, 14, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I.; et al. Renoprotective Effect of the Angiotensin-Receptor Antagonist Irbesartan in Patients with Nephropathy Due to Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, M.Z.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker use, and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2014. 63(7): p. 650-658.
- Chen, J.-Y.; Tsai, I.-J.; Pan, H.-C.; Liao, H.-W.; Neyra, J.A.; Wu, V.-C.; Chueh, J.S. The Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types of Markers | Markers | Clinical application |
|---|---|---|
| Stress marker | Urine | |
| DKK3 | Preoperative levels of urinary DKK3 have been identified as an independent predictor for the occurrence of postoperative AKI [19]. | |
| TIMP-2 IGFBP-7 |
These markers may show a rapid increase after cellular stress, typically within 4 to 12 hours, even before the occurrence of injury [20,21]. | |
| Damage marker | Urine | |
| Alanine aminopeptidase | Diagnostic relevance in nephrolithiasis [36]. Positive correlation between urinary Alanine aminopeptidase concentrations and glomerulonephritis [37]. |
|
| Alkaline phosphatase | Endre et al. took Alkaline phosphatase as biomarker of acute kidney biomarker in the EARLYARF trial [38]. | |
| γ-glutamyl transpeptidase | The Translational Research Investigating Biomarker Endpoints in AKI (TRIBE-AKI) study evaluated γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in AKI diagnosis [39]. | |
| Calprotectin | Calprotectin indicates primary intrinsic AKI causes [40]. | |
| CCL14 | predictive marker for persistent AKI in critically ill patients in the RUBY study [25]. | |
| NGAL | Elevated levels of urinary NGAL are useful for predicting AKI, differentiating intrinsic AKI from pre-renal AKI, predicting renal non-recovery, in-hospital mortality, long-term CKD progression [41]. | |
| KIM-1 | Indicator of renal tubular damage [42]. Elevated levels of KIM-1 in patients with AKI may manifest prior to histological changes [43]. |
|
| L-FABP | Indicator of ischemic or toxic insults that result in tubulointerstitial damage [44]. | |
| IL-18 | Indicators of severity of albuminuria, and deterioration of kidney function and associated with diabetic nephropathy [45]. | |
| Serum | ||
| NGAL | NGAL can be detected in ischemic or toxicity-induced damage to the kidney [22,23,26] and had the best predictive accuracy for the occurrence of AKI [27]. | |
| Functional marker | Serum | |
| Cystatin C | Better accuracy than serum creatinine in identifying individuals with reduced GFR [30] and increased level within 12–24 hours following renal injury [29]. | |
| Proenkephalin A | Proenkephalin A serves as a useful biomarker for early detection of AKI and predicting a shorter duration and successful liberation from renal replacement therapy [34,35]. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





