1. Introduction
Amid the Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), vaccines against variants of concern are currently being developed and licenced as boosters1,2. Recently, COVID-19 vaccines against XBB 1.5 variants were licensed as booster vaccine to effectively target the circulating variants of COVID-193,4. Additionally, new variants like JN.1 belonging to parent lineage of BA.2.86 (Pirola) and EG.5 (Eris) have been recently reported globally5,6. Global research map for COVID-19, stresses the need for continual global sero-survelliance to measure the level of infection and vaccine effectiveness7,8. Thus, monitoring of serological responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants will be a key to develop rational vaccination strategies to combat against disease9. The serological response to SARS-CoV-2 infection codes for multiple structural proteins including trimeric spike protein (S1, S2, RBD regions) and nucleocapsid (N) protein10. Antibody response (IgG, IgM, IgA) directed against S, S1-RBD proteins confer protective immune signatures of COVID-19, being key proteins in virus entry and assembly mechanism. Antibody response to nucleocapsid antigen during infection is shown to correlate with seropositivity9. Since the emergence of pandemic, 85 different serological test achieved authorization from FDA11. However, out of these 85 assays, majority of them are monoplex cut off assays and very few are fully quantitative assays. Multiplex Serology fully quantitative assays are best suited for establishing serological signatures as against mono-plex cut off antibody assays, because they allow; simultaneous estimation of serological response to a) multiple virus proteins (antigen) specific antibodies b) high throughput and c) allow easy calibration to international reference standards12.
Mesoscale Discovery (MSD’s) MULTI-ARRAY® electrochemiluminescence detection technology provides quantitative multiplex immunoassay platform for such applications. The V-PLEX product line of MSD provides MULTI-SPOT® (N=10), independents, electrically conductive, well-defined regions coated plates with specific capture antigens/antibodies13. MSD platform also offers opportunities for development of surrogate multiplex neutralization assay, which could simultaneously measure ACE blocking antibodies to multiple variants. Thus, a combination of MSD serology assay and surrogate neutralization assays will be the best tool to assess serological signatures 14,15.
We report here method validation and applicability of MSD assays (serology and surrogate neutralization assay; 9 PLEX assay measuring three SARS-CoV-2 antigens, spike (S), receptor binding domain (RBD) of S1 and nucleocapsid (N) and four different variants of spike protein and RBD-S1 protein i.e. Wuhan, B.1.351, P.1 and B.1.1.7 to study serological signatures following infection or vaccination and in breakthrough cases. The study involves use of a sera samples collected during 2021-22, following infection and/or vaccination. The evaluation also covered studies with NIBSC reference standard (NIBSC 20/268), WHO reference panel for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin 16. Assay demonstrated establishment of distinct serological signatures in different groups and thereby establishing the usefulness of multiplex assays in generation of robust data on seropositivity which will be useful during serosurveillance studies.
2. Method
2.1. Human Serum Samples for Method Validation
Serum samples used for method validation were collected from healthy volunteers aged > 18 years reported at SIIPL, India, after obtaining informed consent. The selected sera (n =19) samples used for the study are mentioned in
Table 1. The selected panel also includes WHO reference standards (20/268) panel members such as (NIBSC 20/150, 20/148, 20/140), negative standard 20/142, antibody depleted human sera and sera samples representative of negative, low, medium, high antibody concentrations. Haemolytic (Hb levels at 2.02 g/dL) and lipemic sera samples (cholesterol: 172 mg/dL; triglycerides (TG): 255 mg/dL) (Haemo Service Laboratories, Hyderabad), were also used during selectivity study. A total 16 samples [6 SARS-CoV-2 positive samples; 4 (High, mid, low, negative) NIBSC panel members; 6 SARS-CoV-2 negative samples] were assigned for IgG concentrations in AU/ml, by performing 6 consecutive runs. All serum samples were used in accordance with local regulations and guidelines and approved by the Independent Research Ethics Committee, Pune (IEC No. IRECP/004/2021).
2.2. MSD Serology Assay Procedure: Total IgG
V-PLEX MSD COVID-19 Panel 7 serology assay measures antibodies against nine SARS-CoV-2 antigens as N, S1 RBD, S1 RBD (B.1.1.7), S1 RBD (B.1.351), S1 RBD (P.1), Spike, Spike (B.1.1.7), Spike (B.1.351), Spike (P.1). V-PLEX COVID-19 serology assay was chosen by Operation Warp Speed (OWS), as the basis of its standard binding assays for immunogenicity assessments in all Phase III clinical trials of vaccines17. The V-PLEX COVID-19 serology assay was performed as per manufactures instruction18. Briefly, Blocker A solution was added to the pre-printed 10 spot 96-well plate at 150 µl/well. The plates were sealed and incubated at room temperature for 30 min on continuous shaking at 700 rpm for 30 mins. The plates were washed three times with 1X wash buffer (150ul/well). Sera samples were prepared with four different dilutions in MSD Diluent 100. The kits contain a serum-based standard, Reference Standard 1 (Lot No.: A0080286), which was used to establish a calibration curve in the assay. The reference standard was provided by MSD with arbitory assigned concentration (AU/mL) for each antigen. The calibration curve was used to calculate IgG concentration against multiple antigens. The calibrators were prepared for 7-point calibration curve with 10-fold diluted reference standard with a zero-calibrator blank on each assay plate. Each serum sample and blank were tested in duplicates. After addition of the sample, reference standard, serology assay controls (1.1, 1.2, 1.3), plates were sealed and further incubated at room temperature with continuous shaking at 300 rpm for 120 min. After incubation, plates were washed 3 times with 1X wash buffer. Then the detection antibody, SULFO-TAG (anti-human IgG 1X) concentration was added to the wells (50 µl/well). The plates were sealed and incubated at room temperature with continuous shaking at 300 rpm for 60 mins. After washing, 150 µl of a working solution of MSD GOLD Read buffer B, was added to each well and plates were read on MESO QUICKPLEX SQ 120 (MSD) reader, as per manufacturer’s instruction.
2.3. MSD Assay Procedure: ACE-2 Neutralization (Surrogate) Assay
For estimation of ACE-2 neutralization antibodies against nine antigens, plates were blocked with blocking buffer (MSD Blocker A) following incubation and washing with MSD wash buffer, reference standard (MSD Calibrator), and human sera samples were added
19. The human sera samples were analysed at 1:10, 1:25, 1:100 dilutions in dilution buffer (MSD Diluent-100). After incubation and washing with MSD wash buffer, ACE-2 detection antibody was added (MSD SULFO-TAG
TM Human ACE-2 Antibody). Further after incubation and washing, MSD GOLD
TM read Buffer B, was added and plates were read using an MSD plate imager Meso Quick Plex SQ 120. Percentage inhibition was calculated relative to the assay calibrator (maximum 100% inhibition) using the equation below.
2.4. Assay Validation
The assay was analytically validated according to ICH, EMA, and US FDA guidelines on bioanalytical methods and as per International Council for Harmonization (ICH) guideline Q2 (R1), and bioanalytical method validation guidelines20–22. Assays were tested in multiple runs, across multiple days, and by multiple analysts. Parameters such as robustness, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, specificity, recovery, linearity, and selectivity were optimized23.
2.5. Sera Panel for Method Validation Studies
A total of 19 samples [6 SARS-CoV-2 positive samples; 4 NIBSC samples (High, mid, low, negative); 6 SARS-CoV-2 negative samples; Haemolytic (Hb levels at 2.02 g/dL) sample; lipemic sera sample (cholesterol: 172 mg/dL; TG: 255 mg/dL); and antibody depleted human sera sample (Sigma)] (
Supplementary Table S1), were used for the validation of this assay method.
2.5.1. Specificity
Assay specificity was evaluated using panel of 5 sera samples. These samples were evaluated using a single dilution (1:5000) for inhibition specificity against Wuhan antigens by mixing a neat aliquot of virus with sera sample in a 1:1 ratio to demonstrate homologous antigen inhibition. Cross reacting material (CRM 197) having 10 µg/mL in a 1:1 ratio was used to demonstrate heterologous specificity. Specificity was determined based on % inhibition of IgG against homologous Wuhan variant and heterologous CRM197 antigen >75% and < 25% of value obtained in sample without any treatment respectively.
2.5.2. Selectivity
The method’s selectivity was evaluated using three human serum matrices: (i) matrix 1— Sera from healthy volunteers (samples 10–15), (ii) matrix 2—haemolytic and lipemic matrix (samples 16–17), and (iii) matrix 3—NIBSC negative sample (sample 18), and (iv) antibody-depleted human sera (sample 19) as mentioned in
Table 1. These matrices are representative of 10 negative or low concentration sera.
Matrices 1 - 4 were spiked with different concentrations of reference standard and tested at concentrations of 1:1000 (high), 1:5000 (medium), and 1:20000 (low). Recovery of spiked samples from the different matrices was calculated with the acceptance criteria within the range of 70%–130% of expected concentrations.
The % recovery at each level was calculated as follows:
2.5.3. Precision
The assay precision was evaluated over 3 days and six runs for different analysts, and days. Intra-assay precision refers to the variability observed for the same day. Inter-assay precision refers to the variability in experiments performed on different days by different analysts. The assay precision was reported in terms of the % CV.
2.5.4. Accuracy
Accuracy was assessed over 3 days and six runs using a panel of sera samples. These samples were tested at different concentrations in six assays spread over 3 days read by two analysts. The estimates were compared with the assigned values to determine the accuracy. The resulting IgG concentration of each serum sample was calculated and compared with the assigned values, with an acceptance criterion of percent agreement between 70 and 130 %.
2.5.5. Dilutional Linearity
Dilution linearity was evaluated in twelve different runs using panel of 9 samples. Assay dilutability was assessed in twelve independent runs, using four dilutions (1:500,1:5000, 1:25000 and 1:50000). Recovery was calculated as a percentage difference between the observed and assigned concentrations. Linearity was considered acceptable if said dilution complied with an acceptable % CV of duplicates (i.e., <20%) and if the dilution-corrected concentrations were within 70– 130% of the assigned values (
Figure 1).
2.5.6. Robustness
The robustness of the assay was evaluated using nine sera samples at single dilution i.e. 1:5000. Robustness data on samples concerning incubation time of Ag-Ab and sulfo tag (secondary antibody) was assessed. The % agreement of observed versus expected concentration was calculated for each sample. The following parameters were studied during the robustness assessment: assay sample incubation time and secondary antibody incubation time by (±)30 mins.
2.5.7. Assay Range
The reference standard for the determination of the assay range was evaluated in six runs by four-fold serial dilutions of the reference standard (
Supplementary Table S2). The assay range for each antigen was determined using estimates from precision, accuracy, and dilution linearity, after which the most stringent lower and upper concentration limits complying with acceptable accuracy (70–130%) and precision (< 20% CV) and dilutional accuracies of between 70 and 130 % were selected. The assay range was also supported by back-calculated concentrations of calibration standards. The back-calculated concentrations were to be within 70-130 %.
2.6. Calibration Curve
MSD kit provides reference standard and assay controls. Calibration curve was fitted using 7 point and 4-fold dilution series and a zero-calibrator blank of the reference standards on each assay plate, as specified by manufacturer.
2.7. Panel 7 Assay Calibration with WHO International Panel and MSD Reference Standard (20/268)
A series of six runs were performed to calibrate the MSD reference standard and Panel 7 assay to the first international WHO reference panel (NIBSC code: 20/268). The WHO reference panel consists of individual panel members denoted as; NIBSC 20/150 (high), 20/148 (mid), 20/140 (low), 20/142 (negative human plasma)24.
2.8. MSD Serology Applicability Study: Development of Serological Signatures
2.8.1. Study Samples
The study uses sera samples from subjects reported at Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd., (SIIPL), Pune, selected by Occupational Health Centre (SIIPL), with criteria of above 18 years during the period of year 2021-22. The sera samples were collected with written, informed consent for collection of demographic and clinical data. A total of forty-five sera samples were selected for this study. Study samples represent three groups representing Group 1: Breakthrough infection cases; Group 2: Convalescent and Group 3: Vaccinated with no infection. All vaccinated individuals are immunized with COVISHIELDTM vaccine manufactured by SIIPL, Pune25. Samples were collected within 4-6 months of vaccination. The breakthrough infection and convalescent group samples were collected within 4-6 weeks and 1-2 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection respectively. A confirmed case of COVID-19 was defined with positive result for real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay of nasal and nasopharyngeal swab specimens26. Blood samples were collected from the patients at the time of first visit after detection of symptomatic disease and later in accordance with routine biochemical tests27. For total IgG estimation against nine different antigens of SARS-CoV-2 similar MSD V-Plex COVID-19 serology assay procedure was used.
2.8.2. Ethics
The study compiled with the declaration of Helsinki, written informed consent was obtained from all participants and the study was approved by the Independent Research Ethics committee, Pune (IRECP/004/2021)28.
2.8.3. Method Applicability: Development of Serological Signatures
MSD assay provides sera profile with respect to IgG concentrations against nucleocapsid, RBD and spike protein of Wuhan and other variants. Such data can be used to develop serological signatures which can allow assessment of vaccine immunogenicity, breakthrough cases and seropositivity profiles during course of infection19,29. The assay offers quantitative read outs in AU/mL. The data in three different groups of infection, vaccinated and breakthrough cases was analysed with respect to ratios of spike protein and nucleocapsid IgG antibody concentration (S/N) and ratio of antibody concentration against variant/antibody concentration against vaccine strain25.
2.8.4. Statistical Analysis
The MSD assay provides a readout in units of mean luminescence intensity and all readouts were directly log transformed and interpolated using a 4-parameter logistic curve fit directly using MSD Discovery Workbench and GraphPad Prism version 7.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA)18. For analysis of disease severity various demographic, hematological and laboratory parameters were compared between convalescent group and breakthrough infected group by Student t-test. p values of <0.05 were considered as significant.
3. Results
3.1. MSD Assay Validation and Characterization
3.1.1. Sera Panel Establishment
Target values for sera panel were established using an average of six consecutive runs, which was further used during validation study. The established values for sera panel is provided in
Supplementary Table S3.
3.2. Reference Standard Curve
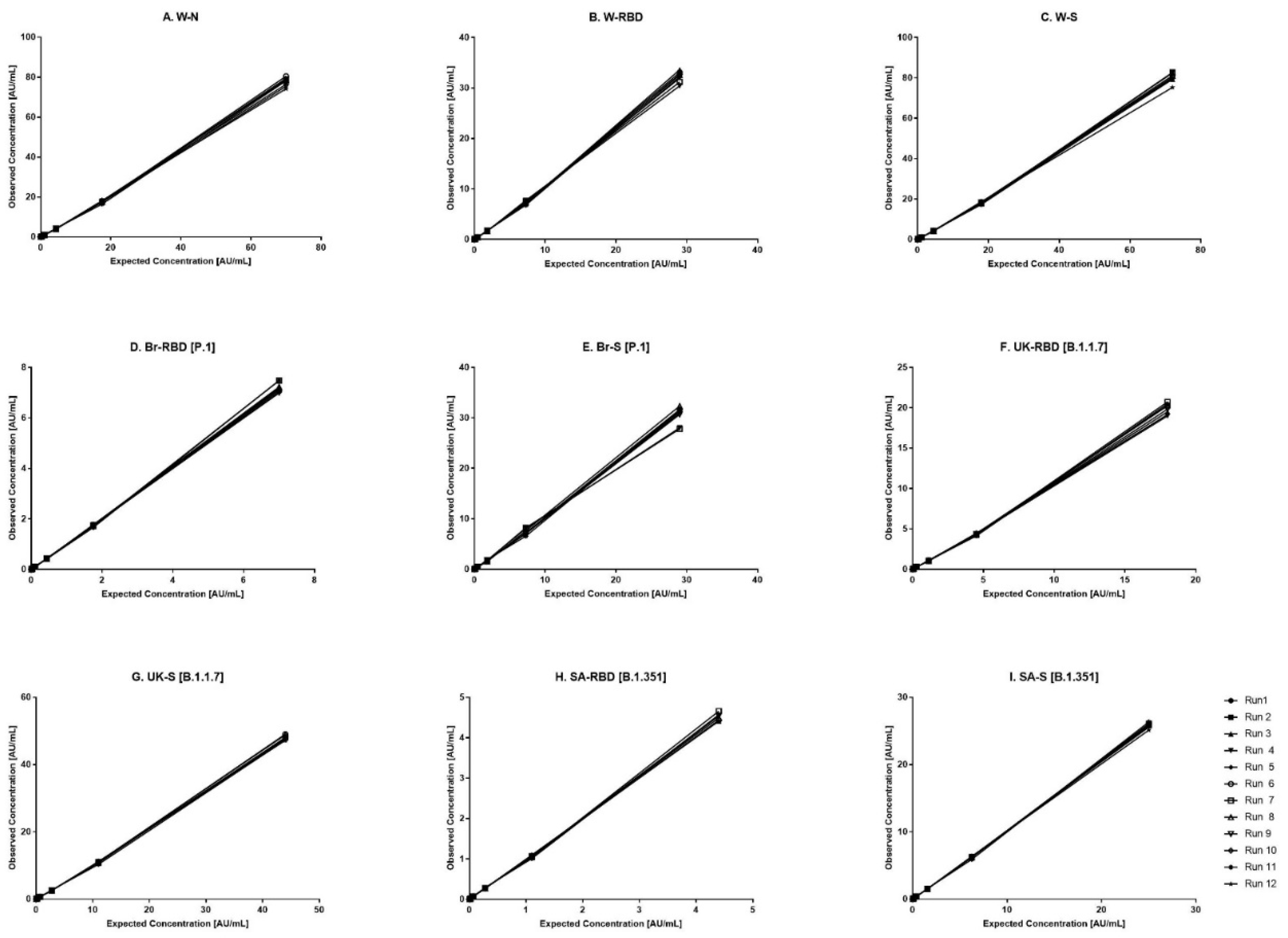
The kit-based Reference standard 1, was used to establish a calibration curve in the assay. The calibration curve was used to calculate concentration of human IgG against nine antigens. Reference standard 1 was diluted 10-fold to create highest calibrator point (CAL-01). Overall, seven separate four-fold dilutions of the reference standard were performed and were fitted using a 4-PL fit.
Figure 1 shows the reference standard dilutional profiles for each of the nine antigens. Linearity of response was demonstrated using back-fitted recoveries, all nine antigens showed 70-130% recoveries for all calibration levels. The lower limit (LL) and upper limit (UL) of the assay range were determined using estimates from accuracy, precision, and robustness analysis (
Table 2). The assigned values for the concentration of IgG antibodies to nine antigens in Reference Standard 1 is provided in
Supplementary Table S2.
3.3. Method Validation
The validation study was designed based on the FDA, EMA, and ICH M10 guidelines for bioanalytical methods. The SARS-CoV-2 serology assay (MSD) was validated for specificity, selectivity, precision, accuracy, dilutional linearity, LOQ and stability using sera samples (
Table 2).
3.3.1. Specificity
Specificity is demonstrated for SARS-CoV-2 serology assay in inhibition experiments using homologous and a heterologous competitor antigen. For inhibition experiments, the % inhibition of RFU of a positive serum sample following the addition of an individual antigen was assessed for all nine antigens. The addition of homologous and heterologous antigens, resulted in an >75% and <25% inhibition of signal for all 9 antigens respectively (
Table 3), indicating the high specificity of the assay in capturing the respective antibodies in the serum sample.
3.3.2. Precision
Precision analysis suggested that the assay was precise for different analysts on different days. The % CV for the combined precision of the two analysts was below 30 % for all nine antigens (
Table 4). Based on the data, the precision-based LLs and ULs ranged from 0.01914 to 86.1 AU/mL for W-N, 0.00777 to 35.4 AU/mL for W-RBD, 0.01960 to 82.7 AU/mL for W-S, 0.00119 to 7.9 AU/mL for Br-RBD (P.1), 0.00700 to 32.3 AU/mL for Br-S (P.1), 0.00337 to 23.0 AU/mL for UK-RBD (B.1.1.7), 0.01071 to 49.0 AU/mL for UK-S (B.1.1.7), 0.00077 to 4.8 AU/mL for SA-RBD (B.1.351), and 0.00682 to 26.3 AU/mL for SA-S (B.1.351) (
Table 2).
3.3.3. Accuracy
Acceptable recoveries were observed within the range of 70-130 % for all 9 antigens (
Table 4). The accuracy-based LLs and ULs ranged from 0.01914 to 86.1 AU/mL for W-N, 0.00777 to 35.4 AU/mL for W-RBD, 0.01960 to 82.7 AU/mL for W-S, 0.00119 to 7.9 AU/mL for Br-RBD (P.1), 0.00700 to 32.3 AU/mL for Br-S (P.1), 0.00337 to 23.0 AU/mL for UK-RBD (B.1.1.7), 0.01071 to 49.0 AU/mL for UK-S (B.1.1.7), 0.00077 to 4.8 AU/mL for SA-RBD (B.1.351), and 0.00682 to 26.3 AU/mL for SA-S (B.1.351) (
Table 2).
3.3.4. Selectivity
The selectivity of the method was evaluated with respect to the use of different serum matrices for SARS-CoV-2 negative samples, NIBSC negative, haemolytic sera, antibody depleted human sera, and lipemic sera. The assay showed high selectivity, as excellent spike recoveries (70-130%) were observed in all the matrices (
Table 5). No interference was observed in the assay for haemolytic and lipemic matrices covering up to 2.02 g/dL of haemoglobin and 275 mg/mL of total cholesterol respectively.
3.3.5. Robustness
The robustness of the assay was studied using sera samples covering the entire range. The critical assay parameters studied included Ag-Ab incubation time and sulfo tag (secondary antibody) incubation time. The % agreement of observed versus expected concentration was calculated for each sample. The results demonstrated that concentration of samples generated from the assays with deliberate variations were within the acceptable range of < 30% agreement for all the antigens (
Table 6).
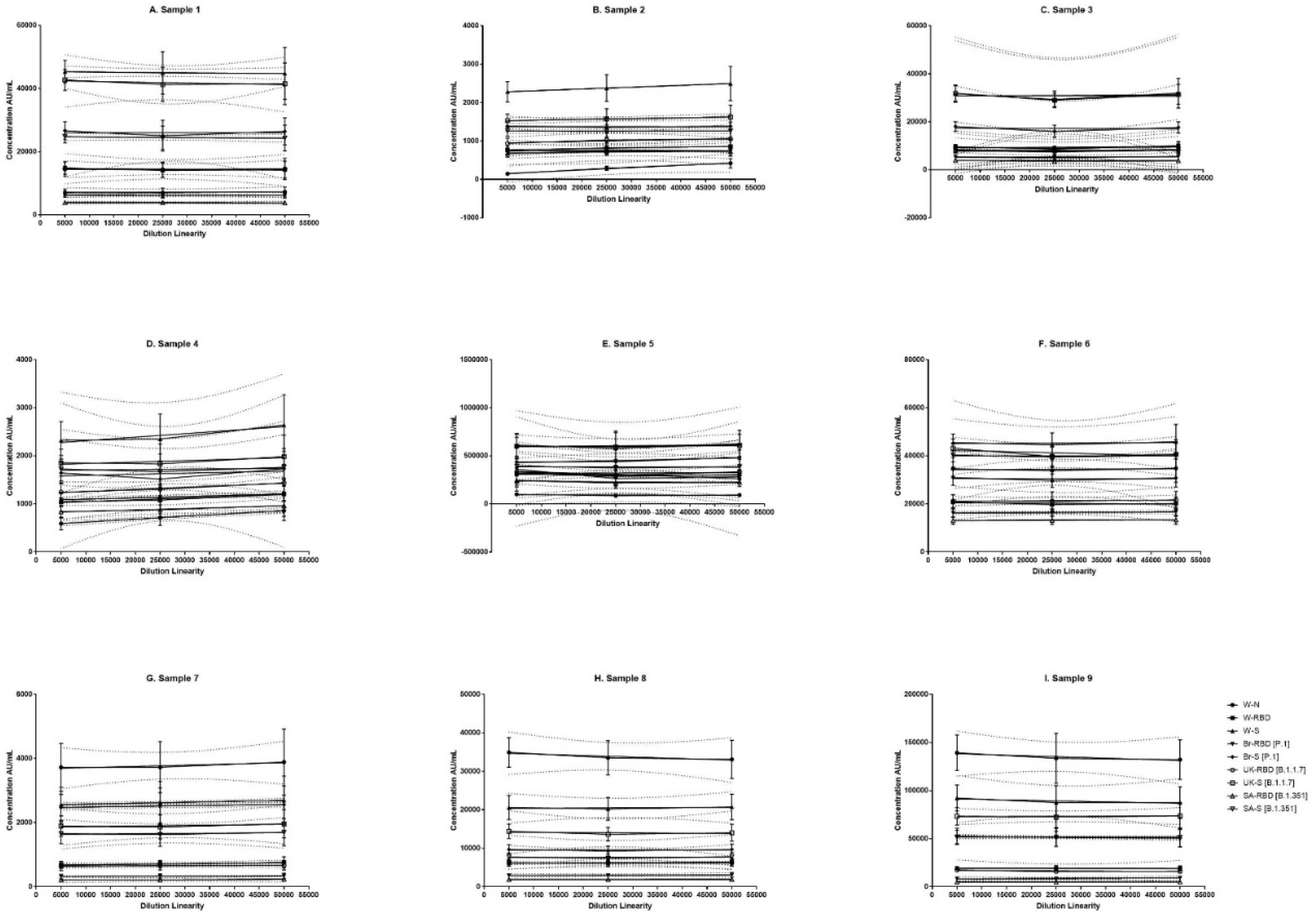
3.4. Dilution Linearity
The panel samples were tested in twelve independent runs across a series of sera samples ranging from a dilution of 1:500 to 1:50000. No loss in dilution integrity was observed with 1:5000, 1:25000 and 1: 50000 dilution range recorded for all antigens (
Figure 2).
3.5. Assay Range
The assay range was selected based on the estimates from precision, accuracy, and study sets. The LL and UL of the assay range were established as ranging from 0.01914 to 86.1 AU/mL for W-N, 0.00777 to 35.4 AU/mL for W-RBD, 0.01960 to 82.7 AU/mL for W-S, 0.00119 to 7.9 AU/mL for Br-RBD (P.1), 0.00700 to 32.3 AU/mL for Br-S (P.1), 0.00337 to 23.0 AU/mL for UK-RBD (B.1.1.7), 0.01071 to 49.0 AU/mL for UK-S (B.1.1.7), 0.00077 to 4.8 AU/mL for SA-RBD (B.1.351), and 0.00682 to 26.3 AU/mL for SA-S (B.1.351) (
Table 2).
3.6. Studies with WHO International Reference Panel (NIBSC/WHO)
We report here calibration factors (MSD reference standard to WHO international reference standard; NIBSC 20/268) which will be useful for harmonization of assays across different laboratories. NIBSC 20/268 reference panel is recommended by WHO for assessment and development of assays used in the detection and quantitation of antiSARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The panel provides the unitages for spike, RBD and Nucleocapsid antibodies. The reference panel was further characterized for values against different variants. We provide here factors against reference standard provided by MSD which can be used for harmonization of assay across different laboratories (
Table 7).
3.6.1. Method Applicability for Development of Serological Signatures with Respect to Nucleocapsid, RBD and Spike Protein of Ancestral Strain
A total of forty-five sera samples were analyzed for total IgG antibodies against N, S and S1 RBD antigens, using mesoscale discovery (MSD) COVID-19 Serology Assay panel 7. Total IgG antibodies concentration was evaluated using MSD COVID-19 Serology Assay kit provided reference standard (Calibrators) (
Supplementary Table S3). Assay reported significantly higher antibodies against N protein in convalescent patient cohort [68887 AU/mL (1088-455149 AU/mL)], as compared to the breakthrough infected group [568 AU/mL (47-2649 AU/mL)] and vaccinated non-infected group [361 AU/mL (160-1040 AU/mL)]
30. This is consistent to reports wherein antibody levels to nucleocapsid are shown to correlate with viral loads
29,31. Trend in vaccinated and non-vaccinated samples was found further consistent with RT-PCR predictions, wherein convalescent subjects showed positivity and virologic symptoms in other parameters (
Table 8).
Antibodies against spike protein and its subunits S1 RBD are reported to correlate with virus neutralization activities32,33. In vaccinated group, S1 RBD antibodies were found to be in the range of [1936 AU/mL (512-5426 AU/mL)]. These levels were on expected lines as these samples were collected 4-6 months post vaccination34. These levels are further consistent with reports wherein antibodies are known to wane with time35. Higher level of antibodies was observed against S1 RBD in breakthrough infection group [35780AU/mL (918-459708) AU/mL)] as compared to vaccinated group.
For Spike [S1 and S2] antigen too, a similar trend was observed wherein a significant increase in IgG antibodies were observed in vaccinated breakthrough infected patient cohort [94780 AU/mL (4515-1170950 AU/mL)] as compared to the convalescent group; [49670 AU/mL (585-1420159AU/mL)]36. This increase is further consistent to reports on robust recall responses in vaccinated subjects37. This is further continual with other virologic characterization, wherein the breakthrough subjects did not experience severe infection outcomes and hospitalization was limited.
3.6.2. Serological Signatures: Immune Responses to Different Variants- Total IgG
Multiplex assays such as MSD allows simultaneous measurement of IgG responses against parent and variant strains. Sera panel comprising of samples from convalescent, breakthrough and vaccinated subjects were evaluated for IgG concentrations against Brazil. SA and UK variant. It was noted that all the subjects received vaccine containing Wuhan variant38. The assay predicted immune response against the different variants in vaccinated subjected wherein the level of antibodies against Wuhan, Brazil, SA and UK variant of spike antigen was 7211 AU/mL (2433-15193 AU/mL), 3438 AU/mL (976-10680 AU/mL), 3517 AU/mL (1577-7598 AU/mL) and 5040 AU/mL (2045-14085 AU/mL) respectively. For RBD antigen, the level of antibodies against Wuhan, Brazil, SA and UK variant were 1936 AU/mL (512-5426 AU/mL), 1495 AU/mL (634-5440 AU/mL), 1117 AU/mL (287-3923 AU/mL) and 2083 AU/mL (596-6248 AU/mL) respectively 39.
The sera of breakthrough and convalescent subjects are representative of infections during second wave of pandemic. A significantly higher number of antibodies (median) against Brazil, SA and UK variants was observed in breakthrough group. The order of levels was UK>Brazil >SA. This trend is consistent with published reports wherein vaccination with Wuhan did provide protection against different variants40. This was further supported by reduced levels of nucleocapsid antibody levels in these groups.
The sera of convalescent groups showed the level of antibodies against different variants in the order of UK>Brazil >SA respectively (
Table 9).
3.6.3. Serological Signatures with Respect to Surrogate Neutralization Antibodies Using MSD COVID-19 ACE-2 Neutralization Assay
The V-plex panel 7 measures % inhibition of ACE-2 neutralizing antibodies against Wu-N, Wu-S, Br-S, UK-S, SA-S and Wu-S1 RBD, Br-S1 RBD, UK-S1 RBD, SA-S1 RBD antigens. A significantly higher % of ACE-2 inhibition against Brazil, SA and UK variants was observed in breakthrough group. The order of inhibition was UK>SA>Brazil for spike antigen and SA>UK>Br for RBD antigen. This trend is consistent with published reports wherein vaccination with Wuhan did provide protection against different variants31,41.
The sera of convalescent groups showed the % inhibition against RBD and spike antigen for different variants in the order of UK>Brazil >SA and UK>SA>Brazil respectively (
Table 10).
3.7. Method Applicability to Predict Distinct Signatures
3.7.1. Spike Protein: Nucleocapsid IgG Antibody Concentration Ratios Were Distinctive among Groups
Ratio of IgG concentration of the spike and nucleocapsid protein [S/N] and RBD and nucleocapsid protein [R/N] of the vaccinated and non-vaccinated infected groups were compared
42. These ratios were found distinctive among groups wherein highest ratios were observed in the ascending order of breakthrough > vaccinated > convalescent groups. These ratios were also monitored for RBD and Spike IgG concentrations of different variants and similar pattern was observed (
Table 9).
3.8. Method Applicability to Develop Profiles against Variants
All the subjects in vaccinated and breakthrough cases received the vaccine manufactured using Wuhan strain. Sera samples were profiled for total and functional IgG antibodies against different variants
12. Ratio of antibodies (antibody concentration against variant/antibody concentration against vaccine strain) were determined for each of the group. These ratios were found distinctive among groups wherein highest ratios were observed in the ascending order of breakthrough > convalescent >vaccinated groups. These ratios were also monitored for Spike IgG concentrations of different variants and similar pattern was observed for all variants except UK variant were highest ratios observed in the ascending order of convalescent > breakthrough > vaccinated groups. (
Table 11).
3.9. Hematological Parameters in Convalescent/Breakthrough Subjects
The study also collected the haematological data of convalescents (n=15), breakthrough (n=15) and vaccinated subjects (n=15) to study association with serological signatures if any. Haematological parameters included markers such as D-Dimer, CRP, Ferritin and LDH
43–45. The demographic and haematology for all samples are summarized in
Table 12. The results suggest significant differences in CRP, D-Dimer, Ferritin and LDH levels among groups of convalescent and breakthrough cases which is on expected lines (
Table 12). It was noted that breakthrough group values were significantly lower for all these parameters suggesting reduced severity of disease in vaccinated subjects
46. This is further consistent with trends observed in serology wherein breakthrough groups reported significantly reduced levels of nucleocapsid antibodies as compared to convalescent group
47.
4. Discussion
COVID-19 vaccine based on spike protein continues to provide protection against disease outcomes, even in presence of emerging variants48. Serological responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection is multi-targeted and therefore bring challenges in effective monitoring. Multiplex assays bring opportunities as it allows simultaneous estimation of antibody responses against multiple proteins of ancestral as well as variant strains. Such multi-dimensional data further offers opportunities in establishment of serological signatures. We report here the validation of multiplex MSD platform based serological assay and its applicability to establish serological signatures of SARS-CoV-2. The signatures were identified for total and functional IgG levels against parent and different variants. The functional IgG was determined using ACE receptor blocking antibodies on MSD platform. Neutralization assay is reported as surrogate neutralization assay for quantification of virus neutralizing antibodies49.
The performance of any multiplex assay depends on many factors12. MSD assay was therefore validated using a panel of sera samples. The validation parameters were designed based on guidelines of US FDA, EMA and ICH guidance on bioanalytical methods. This study for the very first time reports the performance evaluation of MSD assay with respect to different variants. The assay performance against different variants was slightly variable. It was noted that assay showed relatively high variability against Brazil and SA variants50. This could be due to multiple reasons as technology involves spotting and single detection antibody for all the variants. Additionally, the assay reports the values for all the variants against one reference serum. The binding of different variants can vary. It is recommended that each laboratory should perform validation and establish the performance metrics in their laboratories using international reference standards as this will allow pooling of data across the laboratories. We report here calibration factor of MSD assay reference standard international reference standard. The study here reports suitable calibration factors which could be used to report the estimated IgG concentration in international units for other emerging variants used in panel 7 assay.
Serological signatures involving multiple proteins of different variants offers comprehensive understanding of serologic responses against infection, vaccination and recall responses. For applicability to sero-signatures, results were reported from a pilot scale study using N=45 seropositive individuals representing vaccination, infection and vaccinated individuals following breakthrough infection. The vaccinated samples represent immunization with COVISHIELD™ vaccine. The vaccine is based on adeno-vector platform (ChAdOx1 ncov-19 Corona Virus particles) which is a recombinant, replication-deficient chimpanzee adenovirus vector encoding the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein of Wuhan variant38. The study uses sera samples collected during the duration, 2021- 22 and thus represent infections with Delta or Omicron variants of concern (VOCs). Method was able to clearly establish distinct serological signature between infection, vaccinated and breakthrough responses. Antibodies against nucleocapsid proteins were found to be highly indicative of infection wherein breakthrough and infection groups showed significantly higher antibodies against nucleocapsid protein. The diagnostic significance of antibodies against nucleocapsid protein is already reported and established10. An attempt was also made to study the ratios of antibodies against nucleocapsid and spike protein in these groups. It was noted ratios were also predictive of distinct signatures in the groups used in the study. Antibodies against S protein and the RBD of SARS-CoV-2, serve as a target for the development of vaccines and therapy51,52. The assay was able to predict different levels of reactivities to spike protein and S1-RBD in different groups. Vaccinated breakthrough cases showed significantly higher number of antibodies against spike protein and RBD supporting a strong recall response with vaccine. This is further consistent with reports on COVID vaccines wherein a robust recall response was reported in breakthrough cases53.
Several variants of concern (VOC) of SARS-CoV-2 have emerged54. There is an urgent need to quantify the breadth of immune responses generated by any vaccine against these variants35,55. Between the 3 groups, vaccinated breakthrough infection showed highest median antibody titre values of IgG followed by convalescent and vaccinate non-infected for all variants. This further supports the reports of robust recall responses with Covid vaccines. The assay reported antibodies against variants in the order of Wuhan > Br >UK > SA for both spike and RBD. Thereby supporting the reports on variable degrees of protection against variants of SARS-CoV-2.
Neutralizing or functional antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 virus were reported using different assay platforms including plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT), microneutralization test and pseudo neutralization test
56. However, all these tests are laborious and requires considerable amount of serum. Determination of functional IgG levels using surrogate neutralization tests such as MSD ACE receptor inhibition assay offers opportunities of high throughput, simultaneous estimation against different variants and most importantly uses minimal amount of serum sample. The study analyzed ACE2 binding inhibition within serum samples from vaccinated infected, non-infected and non-infected alone individuals. The percentage inhibition of ACE-2 receptor binding to all four variants for the vaccinated breakthrough infected cohort was significantly higher than the convalescent. Among recently emerged strains (alpha, beta, gamma), ACE2 binding inhibition compared to wild type was reduced for all
6. Although, all RBD mutants except wild type (Wuhan) showed slightly reduced ACE2 binding inhibition (
Table 10) in serum samples. This specific mutation has been reported in multiple studies as an escape mutation that enhances the RBD-ACE2 affinity which may also be confirmed from the study results
57. Additionally, results generated also showed positive correlation between ACE2 binding inhibition and S1/trimeric spike antibody production. Therefore, the signatures developed by assays were able to distinctively classify the groups of convalescent, breakthrough, and vaccinated groups.
The present study has limitations are with respect to number of samples in this study. The study reports result from N=45 subjects which is very limited. Nevertheless, the study provides sufficient evidence on capability of the multiplex methods to establish serological signatures. Another limitation of the study is that the study is done on a panel of sera samples available at occupational health center. Though, suitable care was taken to identify the best panel of samples for this study, however a time course study would have further helped to establish the kinetics of the immune responses. The study uses panel 7 MSD kits which was the most updated kits available during the study. It is noted that recently MSD also introduced kits with the most current XBB variant in panel. It will be further interesting to profile the sera samples against the XBB variant8,40. It is also noted that at the time of data analysis NIBSC also introduced a new reference standard for VoCs. It will be further helpful to develop calibration factors against the international standard for SARS-CoV-2 to allow reporting the results in international units.
Multiplex assays such as MSD will be essential in large scale serosurveillance and deciphering vaccination strategy12. By comparing the results of serologic assays that detect antibodies to either spike (S1), the spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain (RBD), or the nucleocapsid (N), it is possible to study vaccine effectiveness between previously SARS-CoV-2-infected (either infected alone or infected and then vaccinated), vaccinated and uninfected individuals. By comparing the titer of antibodies to either spike (S1), the spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain (RBD), or the nucleocapsid (N), it will be possible to distinguish between previously SARS-CoV-2-infected (either infected alone or infected and then vaccinated), vaccinated (with no evidence of prior infection), and uninfected individuals using MSD platforms. The study also demonstrated the usefulness of platform to profile the sera reactivity to different variants which will help in better understanding of impact of vaccines in real-world settings.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, findings presented here presents opportunities for multiplex SARS-CoV-2 serological diagnostics in sero-surveillance studies as it allows efficient classifications among different groups of vaccinated, infected and breakthrough cases. The precision and accuracy estimate of assay especially the range and sensitivity further support the use of multiplex assays in regions and studies where low seroprevalence is expected. The study suggests method suitability to establish serological signatures in different groups based on vaccination and infection status. The study further supports the concept and merits of serological signatures which will be helpful in better understanding of diversity of immune responses against SARS-CoV-2.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Supplementary Table S1. Antigen details used for specificity study, Supplementary Table S2. Values of Reference Standard 1 in MSD Arbitrary units (AU/ml), Supplementary Table S3 Assigned values (AU/ml) for sera panel.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Disclaimer
The conclusions of the paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Serum Institute of India, Pvt Ltd. Pune.
Acknowledgments
We thank Siddharth Lele and Amar Patil for their help with initial assay development and sample analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Li, M. et al. COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 146 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Burckhardt, R. M., Dennehy, J. J., Poon, L. L. M., Saif, L. J. & Enquist, L. W. Are COVID-19 Vaccine Boosters Needed? The Science behind Boosters. J. Virol. 96, e01973-21 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Zhu, Y. & Chu, M. Role of COVID-19 Vaccines in SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Front. Immunol. 13, 898192 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.-Y. et al. COVID-19 vaccine update: vaccine effectiveness, SARS-CoV-2 variants, boosters, adverse effects, and immune correlates of protection. J. Biomed. Sci. 29, 82 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Chenchula, S., Karunakaran, P., Sharma, S. & Chavan, M. Current evidence on efficacy of COVID-19 booster dose vaccination against the Omicron variant: A systematic review. J. Med. Virol. 94, 2969–2976 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Andre, M. et al. From Alpha to Omicron: How Different Variants of Concern of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 Impacted the World. Biology 12, 1267 (2023). [CrossRef]
- WHO: A coordinated Global Research Roadmap.2019 Novel Coronavirus.12 March (2020).
- Chakraborty, C. et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron recombinant subvariants XBB, XBB.1, and XBB.1.5 are expanding rapidly with unique mutations, antibody evasion, and immune escape properties – an alarming global threat of a surge in COVID-19 cases again? Int. J. Surg. 109, 1041–1043 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Mallano, A., Ascione, A. & Flego, M. Antibody Response against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Implications for Diagnosis, Treatment and Vaccine Development. Int. Rev. Immunol. 41, 393–413 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wu, W., Cheng, Y., Zhou, H., Sun, C. & Zhang, S. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: its role in the viral life cycle, structure and functions, and use as a potential target in the development of vaccines and diagnostics. Virol. J. 20, 6 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kenny, G. et al. Performance and validation of an adaptable multiplex assay for detection of serologic response to SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination. J. Immunol. Methods 510, 113345 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J. et al. Multiplex assays for the identification of serological signatures of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an antibody-based diagnostic and machine learning study. Lancet Microbe 2, e60–e69 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. et al. Evaluation of a novel multiplexed assay for determining IgG levels and functional activity to SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 130, 104572 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, D. et al. Validation and performance of a multiplex serology assay to quantify antibody responses following SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 11, e1385 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Sancilio, A. E. et al. A surrogate virus neutralization test to quantify antibody-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 in finger stick dried blood spot samples. Sci. Rep. 11, 15321 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Windsor, W. J. et al. Harmonization of Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Reference Materials Using the WHO IS (NIBSC 20/136): Results and Implications. Front. Microbiol. 13, 893801 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H. et al. Operation Warp Speed: implications for global vaccine security. Lancet Glob. Health 9, e1017–e1021 (2021). [CrossRef]
- MSD V-plex covid-19 serology assays insert.
- Grunau, B. et al. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Neutralizing Antibody Titers with Anti-Spike Antibodies and ACE-2 Inhibition among Vaccinated Individuals. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e01315-22 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. (2018).
- Kaza, M., Karaźniewicz-Łada, M., Kosicka, K., Siemiątkowska, A. & Rudzki, P. J. Bioanalytical method validation: new FDA guidance vs. EMA guideline. Better or worse? J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 165, 381–385 (2019). [CrossRef]
- ICH-guideline-m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-2021.
- Lee, J. W. et al. Fit-for-Purpose Method Development and Validation for Successful Biomarker Measurement. Pharm. Res. 23, 312–328 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Mattiuzzo, G. et al. Establishment of the WHO International Standard and Reference Panel for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody.
- Alter, G. et al. Immunogenicity of Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants in humans. Nature 596, 268–272 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Tombuloglu, H., Sabit, H., Al-Suhaimi, E., Al Jindan, R. & Alkharsah, K. R. Development of multiplex real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. PLOS ONE 16, e0250942 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Alfadda, A. A. et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics of people experiencing post-coronavirus disease 2019-related symptoms: A prospective follow-up investigation. Front. Med. 9, 1067082 (2022). [CrossRef]
- wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects.pdf.
- McGee, C. et al. Longitudinal Serological Surveillance for COVID-19 Antibodies after Infection and Vaccination. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e02026-22 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Henss, L. et al. Analysis of Humoral Immune Responses in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 223, 56–61 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Patil, R., Palkar, S., Mishra, A., Patil, R. & Arankalle, V. Variable neutralizing antibody responses to 10 SARS-CoV-2 variants in natural infection with wild- type (B.1) virus, Kappa (B.1.617.1), and Delta (B.1.617.2) variants and COVISHIELD vaccine immunization in India: utility of the MSD platform. Front. Immunol. 14, 1181991 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Dupont, L. et al. Neutralizing antibody activity in convalescent sera from infection in humans with SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Nat. Microbiol. 6, 1433–1442 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Yan, L. et al. Neutralizing Antibodies and Cellular Immune Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 Sustained One and a Half Years After Natural Infection. Front. Microbiol. 12, 803031 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Chia, W. N. et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody responses and duration of immunity: a longitudinal study. Lancet Microbe 2, e240–e249 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Bates, T. A. et al. Antibody Response and Variant Cross-Neutralization After SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection. JAMA 327, 179 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E. et al. Characterization of Quantiferon Sars-Cov-2 and Anti-Sars-Cov-2 Nucleocapsid and S1 Spike Protein Antibodies in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Covid-19 Patients. https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=4563163 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L. F. et al. Immune Profile and Clinical Outcome of Breakthrough Cases After Vaccination With an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 12, 742914 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P. M. et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 396, 467–478 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, S. et al. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 isolates, namely the Wuhan strain, Delta variant, and Omicron variant, identifies differential immune profiles. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e01256-23 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Wall, E. C. et al. Neutralising antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs B.1.617.2 and B.1.351 by BNT162b2 vaccination. The Lancet 397, 2331–2333 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Tan, C. W. et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2–spike protein–protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 1073–1078 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J. et al. Serological signatures of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Implications for antibody-baseddiagnostics. (2020). [CrossRef]
- Alsrhani, A., Alshomar, A., Elderdery, A. Y., Rasheed, Z. & Farhana, A. Diagnosis and Stratification of COVID-19 Infections Using Differential Plasma Levels of D-Dimer: A Two-Center Study from Saudi Arabia. Microbiol. Res. 14, 67–76 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Molins, B. et al. C-reactive protein isoforms as prognostic markers of COVID-19 severity. Front. Immunol. 13, 1105343 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Patil, S., Dhumal, U. & Acharya, A. Correlation of ferritin with the duration of illness, disease severity, oxygenation status, ventilatory requirement, and lung fibrosis in COVID-19 pneumonia: A single-center experience of 1000 cases in tertiary care setting in India. Adesh Univ. J. Med. Sci. Res. 4, 86–93 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Samprathi, M. & Jayashree, M. Biomarkers in COVID-19: An Up-To-Date Review. Front. Pediatr. 8, 607647 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M. et al. The magnitude and timing of recalled immunity after breakthrough infection is shaped by SARS-CoV-2 variants. Immunity 55, 1316-1326.e4 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Tang, P. et al. BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in Qatar. Nat. Med. 27, 2136–2143 (2021). [CrossRef]
- D’Apice, L. et al. Comparative analysis of the neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 strain and variants of concern: Performance evaluation of a pseudovirus-based neutralization assay. Front. Immunol. 13, 981693 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Shen, H., Huang, R., Tong, X. & Wu, C. Serum neutralising activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants elicited by CoronaVac. Lancet Infect. Dis. 21, 1071–1072 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Salvatori, G. et al. SARS-CoV-2 SPIKE PROTEIN: an optimal immunological target for vaccines. J. Transl. Med. 18, 222 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Min, L. & Sun, Q. Antibodies and Vaccines Target RBD of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8, 671633 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Becker, M. et al. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in vaccinated individuals. Nat. Commun. 12, 3109 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, F., Darvishi, M. & Bezmin Abadi, A. T. ‘The end’ – or is it? Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 EG.5 and BA.2.86 subvariants. Future Virol. fvl-2023-0150 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Brochot, E. et al. Anti-spike, Anti-nucleocapsid and Neutralizing Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Inpatients and Asymptomatic Individuals. Front. Microbiol. 11, 584251 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Bewley, K. R. et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by wild-type plaque reduction neutralization, microneutralization and pseudotyped virus neutralization assays. Nat. Protoc. 16, 3114–3140 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Naresh, G. K. R. S. & Guruprasad, L. Mutations in the receptor-binding domain of human SARS CoV-2 spike protein increases its affinity to bind human ACE-2 receptor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 41, 2368–2381 (2023). [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Dynamic range of reference standard for each antigen. (A–I) represents the assay range of reference standard for nine antigens. The X-axis represents expected concentration (AU/mL) whereas Y-axis represents obtained concentration (AU/mL.). Data is representative of 12 runs. W-N, Wuhan Nucleocapsid; W-RBD, Wuhan receptor binding domain (RBD); W-S, Wuhan Spike (S); Br-RBD [P.1], Brazil RBD; Br-S [P.1], Brazil S; UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom RBD; UK-S [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom S; SA-RBD [B.1.351], South Africa RBD; SA-S [B.1.351] South Africa S.
Figure 1.
Dynamic range of reference standard for each antigen. (A–I) represents the assay range of reference standard for nine antigens. The X-axis represents expected concentration (AU/mL) whereas Y-axis represents obtained concentration (AU/mL.). Data is representative of 12 runs. W-N, Wuhan Nucleocapsid; W-RBD, Wuhan receptor binding domain (RBD); W-S, Wuhan Spike (S); Br-RBD [P.1], Brazil RBD; Br-S [P.1], Brazil S; UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom RBD; UK-S [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom S; SA-RBD [B.1.351], South Africa RBD; SA-S [B.1.351] South Africa S.
Figure 2.
Dilution linearity of assay in SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples and NIBSC samples for W-N, W-RBD, W-S, Br-RBD [P.1], Br-S [P.1], UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], UK-S [B.1.1.7], SA-RBD [B.1.351], SA-S [B.1.351] antigens. The X-axis represents the sample's dilutions, and the Y-axis represents the concentration observed in (AU/ml). (A–F) represent dilution linearity graphs for SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples. (G-I) represents dilution linearity data for NIBSC samples. SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples and NIBSC samples shows no loss of dilution integrity 5000-50000 dilution range. The dotted line in the figure represents the 95% confidence interval. W-N, Wuhan Nucleocapsid; W-RBD, Wuhan receptor binding domain (RBD); W-S, Wuhan Spike (S); Br-RBD [P.1], Brazil RBD; Br-S [P.1], Brazil S; UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom RBD; UK-S [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom S; SA-RBD [B.1.351], South Africa RBD; SA-S [B.1.351] South Africa S.
Figure 2.
Dilution linearity of assay in SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples and NIBSC samples for W-N, W-RBD, W-S, Br-RBD [P.1], Br-S [P.1], UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], UK-S [B.1.1.7], SA-RBD [B.1.351], SA-S [B.1.351] antigens. The X-axis represents the sample's dilutions, and the Y-axis represents the concentration observed in (AU/ml). (A–F) represent dilution linearity graphs for SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples. (G-I) represents dilution linearity data for NIBSC samples. SARS-CoV-2 infected sera samples and NIBSC samples shows no loss of dilution integrity 5000-50000 dilution range. The dotted line in the figure represents the 95% confidence interval. W-N, Wuhan Nucleocapsid; W-RBD, Wuhan receptor binding domain (RBD); W-S, Wuhan Spike (S); Br-RBD [P.1], Brazil RBD; Br-S [P.1], Brazil S; UK-RBD [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom RBD; UK-S [B.1.1.7], United Kingdom S; SA-RBD [B.1.351], South Africa RBD; SA-S [B.1.351] South Africa S.
Table 1.
Sera sample panel used for assay validation.
Table 1.
Sera sample panel used for assay validation.
| Sr. No. |
Sample ID |
Sample Description |
Test Details |
| 1 |
Sample 1 |
SARS-CoV-2 positive samples |
Samples used for specificity, accuracy, precision, robustness, and stability study |
| 2 |
Sample 2 |
| 3 |
Sample 3 |
| 4 |
Sample 4 |
| 5 |
Sample 5 |
| 6 |
Sample 6 |
| 7 |
Sample 7 |
NIBSC samples |
| 8 |
Sample 8 |
| 9 |
Sample 9 |
| 10 |
Sample 10 |
SARS-CoV-2 negative samples |
Samples used for selectivity study |
| 11 |
Sample 11 |
| 12 |
Sample 12 |
| 13 |
Sample 13 |
| 14 |
Sample 14 |
| 15 |
Sample 15 |
| 16 |
Sample 16 |
Haemolytic and Lipemic samples |
| 17 |
Sample 17 |
| 18 |
Sample 18 |
NIBSC Negative sample |
| 19 |
Sample 19 |
Sigma ADHS |
Table 2.
Assay range with a lower and upper limit of quantification.
Table 2.
Assay range with a lower and upper limit of quantification.
| Antigen |
Calibration Curve range (AU/mL) |
Precision (AU/mL) |
Accuracy (AU/mL) |
Robustness (AU/mL) |
Selectivity (AU/mL) |
| Lower limit |
Upper limit |
Lower limit |
Upper limit |
Lower limit |
Upper limit |
Lower limit |
Upper limit |
Lower limit |
Upper limit |
| W-N |
0.01710 |
70 |
0.01914 |
86.1 |
0.01914 |
86.1 |
0.01957 |
80.8 |
0.02022 |
83.2 |
| W-RBD |
0.00708 |
29 |
0.00777 |
35.4 |
0.00777 |
35.4 |
0.00812 |
33.1 |
0.00813 |
35.6 |
| W-S |
0.01760 |
72 |
0.01960 |
82.7 |
0.01960 |
82.7 |
0.02110 |
82.1 |
0.02212 |
86.2 |
| Br-RBD (P.1) |
0.00171 |
7 |
0.00119 |
7.9 |
0.00119 |
7.9 |
0.00152 |
7.4 |
0.00210 |
7.6 |
| Br-Spike (P.1) |
0.00708 |
29 |
0.00700 |
32.3 |
0.00700 |
32.3 |
0.00417 |
31.0 |
0.00732 |
32.7 |
| UK-RBD (B.1.1.7) |
0.00439 |
18 |
0.00337 |
23.0 |
0.00337 |
23.0 |
0.00044 |
21.3 |
0.00453 |
21.8 |
| UK-S (B.1.1.7) |
0.01070 |
44 |
0.01071 |
49.0 |
0.01071 |
49.0 |
0.01300 |
50.2 |
0.01342 |
52.7 |
| SA-RBD (B.1.351) |
0.00107 |
4.4 |
0.00077 |
4.8 |
0.00077 |
4.8 |
0.00086 |
5.4 |
0.00108 |
4.6 |
| SA-S (B.1.351) |
0.00610 |
25 |
0.00682 |
26.3 |
0.00682 |
26.3 |
0.00629 |
26.3 |
0.00733 |
27.7 |
Table 3.
Specificity.
| Sample. |
% inhibition |
| W-N |
W-RBD |
W-S |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
Br-S
[P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
| Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
Ho |
He |
| Sample 1 |
89 |
1 |
88 |
2 |
89 |
1.3 |
89 |
2 |
89 |
4 |
88 |
1.6 |
88 |
2.3 |
88 |
1.3 |
89 |
2 |
| Sample 3 |
89 |
0.6 |
88 |
3.3 |
88 |
2 |
89 |
1.6 |
89 |
3.3 |
88 |
0.3 |
87 |
1 |
87 |
4 |
88 |
1 |
| Sample 6 |
89 |
0.6 |
88 |
1.3 |
89 |
0.6 |
89 |
2.6 |
89 |
2 |
88 |
1 |
89 |
0.6 |
88 |
1.3 |
88 |
0.3 |
| Sample 8 |
90 |
2 |
89 |
1 |
89 |
0 |
89 |
0 |
90 |
2.3 |
89 |
1.3 |
89 |
1.6 |
88 |
0.3 |
89 |
3.6 |
| Sample 9 |
90 |
1 |
90 |
1.3 |
90 |
1.3 |
89 |
0 |
90 |
3.6 |
89 |
2.3 |
89 |
2.3 |
88 |
0 |
89 |
0.6 |
Table 4.
Precision and accuracy estimates.
Table 4.
Precision and accuracy estimates.
| Precision |
*Analyst (% CV) |
**Days (% CV) |
| W-N |
W-RBD |
W-S |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
Br-S [P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
W-N |
W-RBD |
W-S |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
Br-S [P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
| Sample 1 |
15 |
6 |
6 |
5 |
10 |
6 |
5 |
6 |
6 |
15 |
12 |
10 |
8 |
9 |
15 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
| Sample 2 |
16 |
10 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
14 |
12 |
13 |
12 |
16 |
14 |
13 |
12 |
9 |
17 |
13 |
14 |
12 |
| Sample 3 |
11 |
6 |
8 |
7 |
19 |
7 |
6 |
9 |
8 |
11 |
11 |
13 |
11 |
18 |
14 |
10 |
14 |
11 |
| Sample 4 |
18 |
12 |
12 |
11 |
11 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
13 |
18 |
19 |
16 |
15 |
12 |
19 |
15 |
16 |
16 |
| Sample 5 |
13 |
19 |
15 |
12 |
15 |
14 |
15 |
15 |
16 |
13 |
17 |
16 |
19 |
15 |
18 |
20 |
15 |
16 |
| Sample 6 |
8 |
8 |
10 |
10 |
4 |
9 |
10 |
9 |
12 |
8 |
11 |
10 |
11 |
18 |
14 |
10 |
11 |
13 |
| Sample 7 |
20 |
15 |
16 |
13 |
18 |
16 |
17 |
15 |
15 |
20 |
19 |
20 |
17 |
17 |
19 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
| Sample 8 |
12 |
13 |
17 |
13 |
18 |
11 |
16 |
12 |
16 |
12 |
12 |
14 |
15 |
14 |
13 |
13 |
12 |
14 |
| Sample 9 |
15 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
16 |
15 |
14 |
17 |
14 |
16 |
15 |
16 |
13 |
16 |
| Accuracy |
*Analyst (% Recovery) |
**Days (% Recovery) |
| Sample 1 |
94 |
101 |
104 |
101 |
110 |
101 |
104 |
104 |
104 |
94 |
100 |
100 |
101 |
106 |
100 |
102 |
103 |
100 |
| Sample 2 |
105 |
100 |
95 |
105 |
93 |
112 |
97 |
116 |
93 |
105 |
93 |
88 |
102 |
89 |
105 |
90 |
110 |
88 |
| Sample 3 |
87 |
93 |
95 |
77 |
107 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
89 |
87 |
93 |
91 |
79 |
99 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
85 |
| Sample 4 |
75 |
97 |
90 |
104 |
87 |
110 |
92 |
115 |
89 |
75 |
91 |
84 |
100 |
84 |
103 |
86 |
109 |
84 |
| Sample 5 |
93 |
89 |
91 |
82 |
85 |
88 |
90 |
102 |
82 |
93 |
92 |
102 |
90 |
91 |
90 |
94 |
107 |
81 |
| Sample 6 |
88 |
97 |
92 |
95 |
89 |
100 |
94 |
94 |
88 |
88 |
96 |
88 |
99 |
98 |
99 |
91 |
95 |
86 |
| Sample 7 |
73 |
95 |
94 |
103 |
93 |
104 |
97 |
106 |
101 |
73 |
90 |
82 |
90 |
82 |
88 |
91 |
94 |
92 |
| Sample 8 |
84 |
87 |
85 |
90 |
91 |
114 |
87 |
90 |
88 |
84 |
86 |
81 |
89 |
87 |
112 |
83 |
89 |
84 |
| Sample 9 |
91 |
87 |
86 |
89 |
80 |
91 |
91 |
90 |
86 |
91 |
92 |
88 |
93 |
86 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
90 |
Table 5.
Selectivity.
| Samples |
Sample Description |
Reference Standard Spike Level |
% Recovery |
| W-N |
W-RBD |
W-S |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
Br-S [P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
| Sample 10 |
SARS-CoV-2 negative samples |
High |
90 |
88 |
87 |
87 |
92 |
98 |
85 |
98 |
95 |
| Mid |
103 |
107 |
105 |
92 |
109 |
130 |
106 |
120 |
118 |
| Low |
99 |
108 |
104 |
125 |
102 |
123 |
123 |
112 |
128 |
| Sample 11 |
High |
91 |
86 |
89 |
87 |
94 |
97 |
89 |
94 |
99 |
| Mid |
108 |
103 |
109 |
115 |
111 |
88 |
105 |
123 |
115 |
| Low |
120 |
110 |
82 |
105 |
75 |
95 |
80 |
107 |
74 |
| Sample 12 |
High |
92 |
89 |
94 |
89 |
91 |
113 |
105 |
96 |
104 |
| Mid |
114 |
113 |
116 |
127 |
97 |
125 |
86 |
81 |
83 |
| Low |
105 |
95 |
86 |
102 |
86 |
122 |
118 |
86 |
89 |
| Sample 13 |
High |
90 |
93 |
89 |
96 |
95 |
96 |
89 |
96 |
96 |
| Mid |
86 |
91 |
98 |
85 |
95 |
75 |
101 |
90 |
102 |
| Low |
95 |
97 |
81 |
82 |
84 |
80 |
73 |
83 |
104 |
| Sample 14 |
High |
91 |
91 |
88 |
90 |
93 |
99 |
88 |
103 |
96 |
| Mid |
102 |
98 |
97 |
111 |
106 |
104 |
103 |
130 |
114 |
| Low |
124 |
95 |
84 |
106 |
95 |
123 |
124 |
112 |
115 |
| Sample 15 |
High |
87 |
90 |
87 |
104 |
92 |
95 |
88 |
102 |
96 |
| Mid |
105 |
128 |
105 |
122 |
124 |
120 |
115 |
125 |
114 |
| Low |
97 |
109 |
121 |
108 |
118 |
73 |
85 |
123 |
115 |
| Sample 16 |
Haemolytic and Lipemic samples |
High |
116 |
83 |
103 |
127 |
97 |
86 |
80 |
70 |
90 |
| Mid |
105 |
86 |
108 |
115 |
90 |
82 |
76 |
75 |
96 |
| Low |
113 |
95 |
116 |
128 |
96 |
81 |
71 |
80 |
88 |
| Sample 17 |
High |
86 |
85 |
88 |
101 |
97 |
94 |
89 |
118 |
95 |
| Mid |
86 |
130 |
110 |
111 |
116 |
118 |
119 |
111 |
123 |
| Low |
86 |
70 |
111 |
125 |
75 |
78 |
118 |
120 |
73 |
| Sample 18 |
NIBSC Negative Sample |
High |
92 |
82 |
94 |
97 |
95 |
95 |
92 |
87 |
95 |
| Mid |
96 |
104 |
99 |
108 |
103 |
90 |
106 |
104 |
106 |
| Low |
82 |
71 |
104 |
112 |
101 |
82 |
89 |
125 |
90 |
| Sample 19 |
Sigma antibody depleted human serum |
High |
88 |
87 |
92 |
102 |
92 |
95 |
89 |
96 |
93 |
| Mid |
90 |
105 |
95 |
106 |
99 |
94 |
95 |
97 |
97 |
| Low |
89 |
100 |
94 |
112 |
105 |
102 |
91 |
96 |
94 |
Table 6.
Assay Robustness.
Table 6.
Assay Robustness.
| % Agreement Range |
|---|
| Antigen |
Ag-Ab incubation |
Sulfo Tag Incubation |
| 150 Minutes |
90 Minutes |
90 Minutes |
30 Minutes |
| W-N |
72 - 121 |
72 - 115 |
70 - 121 |
93 - 119 |
| W-RBD |
89 - 130 |
88 - 130 |
83 - 126 |
100 - 129 |
| W-Spike |
93 - 125 |
93 - 125 |
86 - 124 |
101 - 122 |
| Br-RBD [P.1] |
90 - 114 |
84 - 115 |
81 - 110 |
83 - 114 |
| Br-Spike [P.1] |
70 - 126 |
71 - 115 |
85 - 128 |
92 - 124 |
| UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
88 - 113 |
83 - 130 |
80 - 129 |
87 - 126 |
| UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
97 - 112 |
90 - 121 |
88 - 122 |
98 - 123 |
| SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
86 - 112 |
78 - 123 |
80 - 126 |
90 - 125 |
| SA-S [B.1.351] |
91 - 120 |
83 - 127 |
87 - 113 |
90 - 125 |
Table 7.
NIBSC Standards (20/268) values using Panel 7 in BAU/ml.
Table 7.
NIBSC Standards (20/268) values using Panel 7 in BAU/ml.
| |
NIBSC High |
NIBSC Mid |
NIBSC Low |
Conversion factor |
| |
AU/mL |
BAU/mL Assigned values |
BAU/mL |
AU/mL |
BAU/mL Assigned values |
BAU/mL |
AU/mL |
BAU/mL Assigned values |
BAU/mL |
| W-N |
130339 |
713 |
308 |
45344 |
295 |
107 |
4896 |
45 |
12 |
0.00236 |
| W-S |
94318 |
832 |
2047 |
27350 |
241 |
593 |
3297 |
53 |
72 |
0.0217 |
| W-RBD |
21859 |
817 |
509 |
7971 |
205 |
186 |
790 |
12 |
18 |
0.0233 |
| UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
79280 |
- |
1720 |
17918 |
- |
389 |
2334 |
- |
51 |
0.0217 |
| UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
20147 |
- |
469 |
5658 |
- |
132 |
694 |
- |
16 |
0.0233 |
| SA Spike [B.1.351] |
61017 |
- |
1324 |
9616 |
- |
209 |
1882 |
- |
41 |
0.0217 |
| SA RBD [B.1.351] |
5195 |
- |
121 |
2155 |
- |
50 |
233 |
- |
5 |
0.0233 |
| Br Spike [P.1] |
58047 |
- |
1260 |
11526 |
- |
250 |
2961 |
- |
64 |
0.0217 |
| Br RBD [P.1] |
9520 |
- |
222 |
3381 |
- |
79 |
352 |
- |
8 |
0.0233 |
Table 8.
Serological signatures (Total IgG) in convalescent, breakthrough infected and vaccinated non-infected groups.
Table 8.
Serological signatures (Total IgG) in convalescent, breakthrough infected and vaccinated non-infected groups.
| Sr. No. |
|
W-S |
Br-S [P.1] |
UK-S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
W-RBD |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
W-N |
| Convalescent |
Mean |
153142 |
96724 |
149779 |
107637 |
61700 |
44362 |
57755 |
41650 |
121550 |
| GM |
38340 |
24558 |
40571 |
25313 |
9846 |
6166 |
9344 |
4221 |
60727 |
| Min |
585 |
368 |
521 |
385 |
244 |
146 |
243 |
143 |
1088 |
| Max |
1420159 |
841413 |
1296289 |
892359 |
678787 |
484588 |
640622 |
537828 |
455149 |
| Median |
49670 |
31791 |
51075 |
25313 |
9846 |
6166 |
9344 |
3618 |
68887 |
| Breakthrough Infected |
Mean |
231286 |
204313 |
190332 |
137319 |
77452 |
79452 |
83267 |
118569 |
704 |
| GM |
71419 |
50328 |
57198 |
34032 |
23650 |
22385 |
25059 |
20413 |
380 |
| Min |
4515 |
1344 |
3651 |
1700 |
918 |
830 |
1047 |
618 |
47 |
| Max |
1170950 |
1031308 |
976125 |
680803 |
459708 |
483341 |
518697 |
874411 |
2649 |
| Median |
94780 |
68982 |
82654 |
54032 |
35780 |
35951 |
36734 |
29289 |
568 |
| Vaccinated and Non-Infected |
Mean |
8555 |
4303 |
6347 |
4131 |
2366 |
2097 |
2610 |
1504 |
365 |
| GM |
6707 |
3306 |
5056 |
3468 |
1813 |
1607 |
2020 |
1095 |
321 |
| Min |
2433 |
976 |
2045 |
1577 |
512 |
634 |
596 |
287 |
160 |
| Max |
15193 |
10680 |
14085 |
7598 |
5426 |
5440 |
6248 |
3923 |
1040 |
| Median |
7211 |
3438 |
5040 |
3517 |
1936 |
1495 |
2083 |
1117 |
361 |
Table 9.
Spike: Nucleocapsid IgG antibody ratios for developing serological signatures.
Table 9.
Spike: Nucleocapsid IgG antibody ratios for developing serological signatures.
| |
IgG [Median] |
| W-S: W-N |
Br-S [P.1]: W-N |
UK-S [B.1.1.7]: W-N |
SA-S [B.1.351]: W-N |
W-RBD: W-N |
Br-RBD [P.1]: W-N |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7]: W-N |
SA-RBD [B.1.351]: W-N |
| Convalescent |
0.72 |
0.46 |
0.74 |
0.37 |
0.14 |
0.09 |
0.14 |
0.05 |
| Breakthrough Infected |
166.97 |
121.52 |
145.61 |
95.19 |
63.03 |
63.33 |
64.71 |
51.6 |
| Vaccinated and Non-Infected |
20 |
9.54 |
13.98 |
9.75 |
5.37 |
4.15 |
5.78 |
3.1 |
Table 10.
Serological signatures (functional antibodies) in convalescent, breakthrough infected and vaccinated non-infected groups.
Table 10.
Serological signatures (functional antibodies) in convalescent, breakthrough infected and vaccinated non-infected groups.
| ACE-2 Neutralisation |
W-S |
Br-S [P.1] |
UK- S [B.1.1.7] |
SA-S [B.1.351] |
W-RBD |
Br-RBD [P.1] |
UK-RBD [B.1.1.7] |
SA-RBD [B.1.351] |
W-N |
|
| Convalescent |
93.9 |
68.1 |
83.5 |
70.7 |
93.6 |
62.7 |
86.4 |
52.0 |
56.5 |
|
| Breakthrough Infected |
99.0 |
92.8 |
95.9 |
93.8 |
98.5 |
93.0 |
95.8 |
97.1 |
58.0 |
|
| Vaccinated and Non-Infected |
30.5 |
12.0 |
19.6 |
10.8 |
21.3 |
22.4 |
17.4 |
54.0 |
52.8 |
|
Table 11.
Impact of vaccine on different variants.
Table 11.
Impact of vaccine on different variants.
| |
ACE-2 Neutralisation |
IgG |
| |
Br-S [P.1]: W-S |
UK-S [B.1.1.7]: W-S |
SA-S [B.1.351]: W-S |
Br-S [P.1]: W-S |
UK-S [B.1.1.7]: W-S |
SA-S [B.1.351]: W-S |
| Convalescent |
0.72 |
0.89 |
0.75 |
0.64 |
1.03 |
0.51 |
| Breakthrough Infected |
0.94 |
0.97 |
0.95 |
0.73 |
0.87 |
0.57 |
| Vaccinated and Non-Infected |
0.39 |
0.64 |
0.35 |
0.48 |
0.7 |
0.49 |
Table 12.
Demographic parameters of study groups.
Table 12.
Demographic parameters of study groups.
| Parameters |
Convalescent |
Breakthrough Infected |
Vaccinated Non-Infected |
| n= 15 |
n= 15 |
n= 15 |
| Age (years) |
33 (23-49) |
40 (23-57) |
42 (34-61) |
| Sex (Male/ Female) |
5/15 |
15/0 |
15/0 |
| Vaccination Status |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
| Parameter |
Convalescent |
Breakthrough Infected |
Vaccinated Non-Infected |
p value [Student t-test] |
| Ct Value |
23 |
18 |
- |
p<0.01 |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) |
12.02 |
14.9 |
- |
p<0.001 |
|
MCV (µm3)
|
90.21 |
88 |
- |
p<0.01 |
| WBC (/mm3) |
10600 |
7200 |
- |
p<0.001 |
| Neutrophils (%) |
70 |
60 |
- |
p<0.001 |
| Lymphocytes (%) |
28 |
34 |
- |
p<0.001 |
|
Platelet (/µL)
|
242000 |
286000 |
- |
NS |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) |
739.34 |
119 |
- |
p<0.001 |
| Ferritin(ng/ml) |
370.33 |
149 |
- |
p<0.001 |
| LDH (U/L) |
717.99 |
379 |
- |
p<0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) |
25 |
6.57 |
- |
p<0.01 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).