Submitted:
05 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
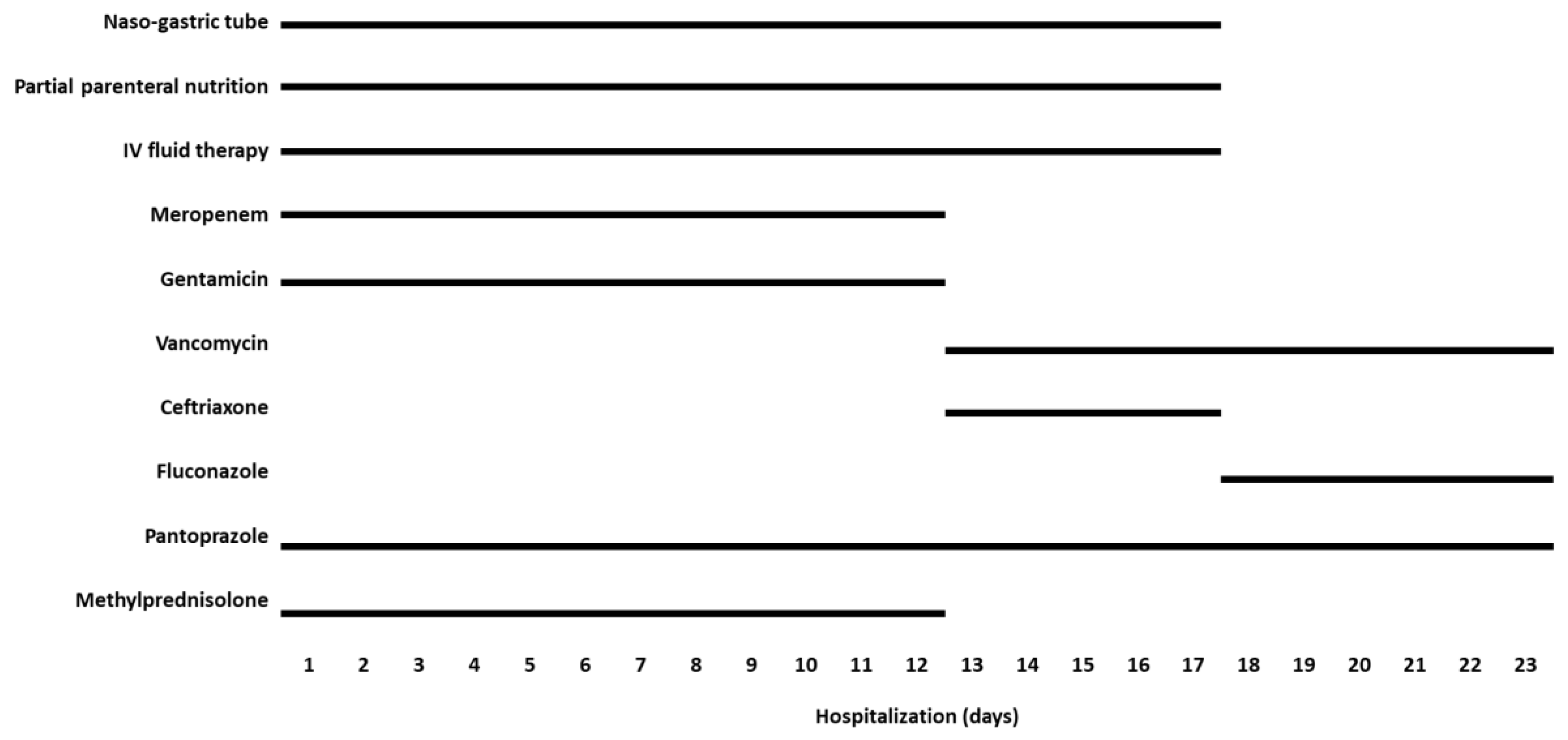
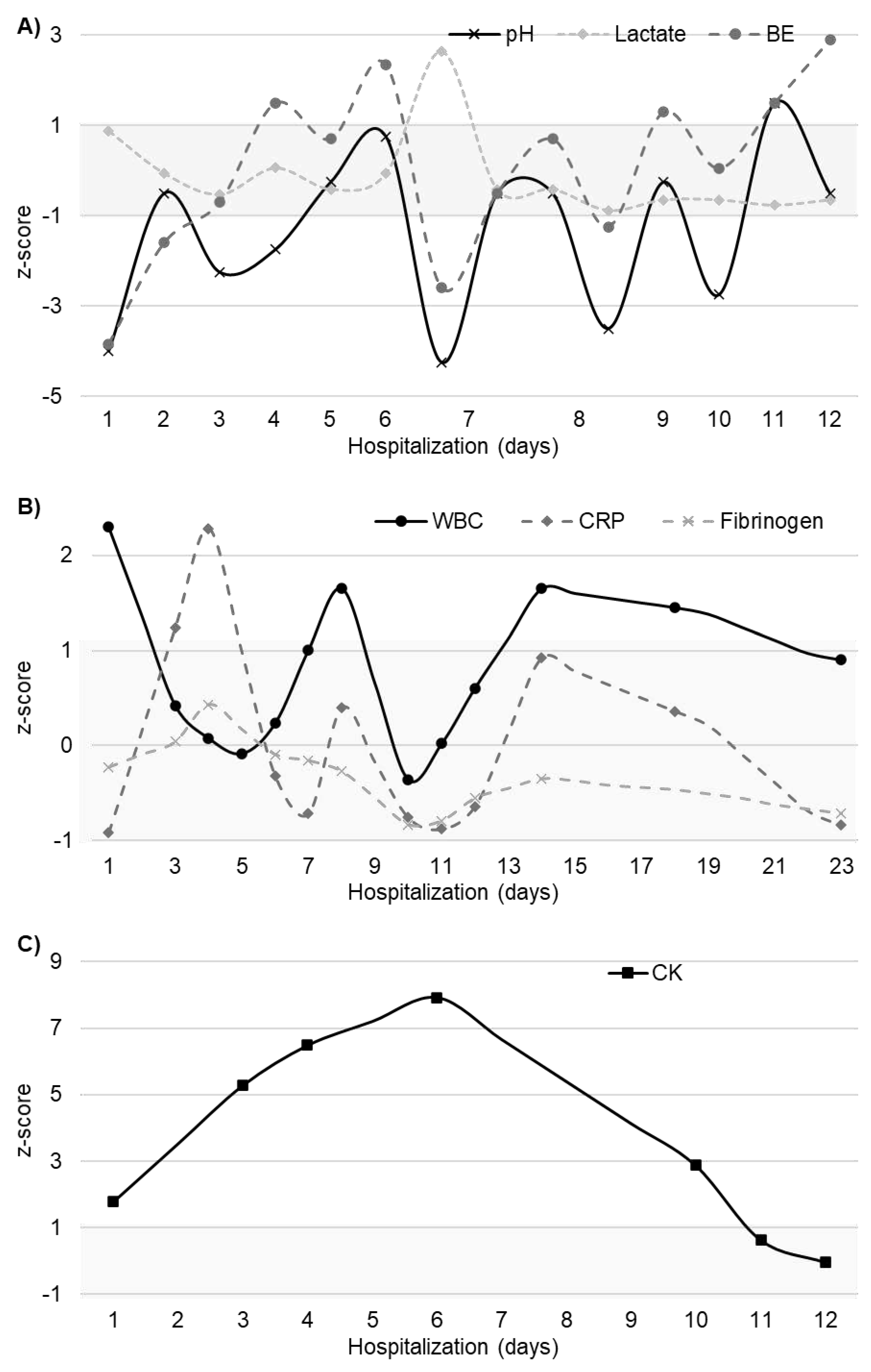
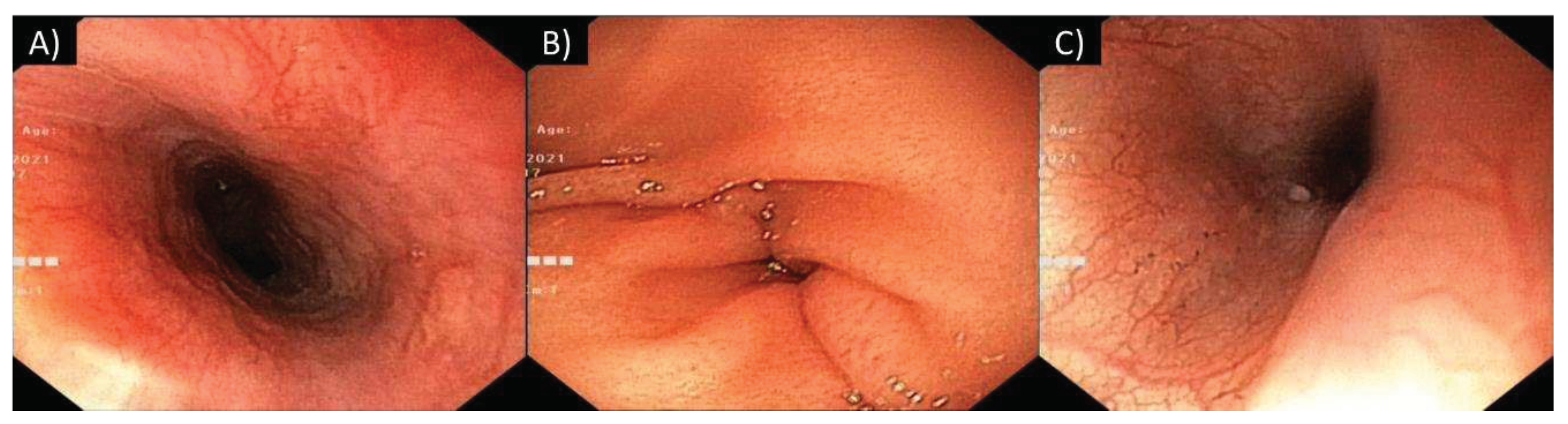
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
3.1. General considerations
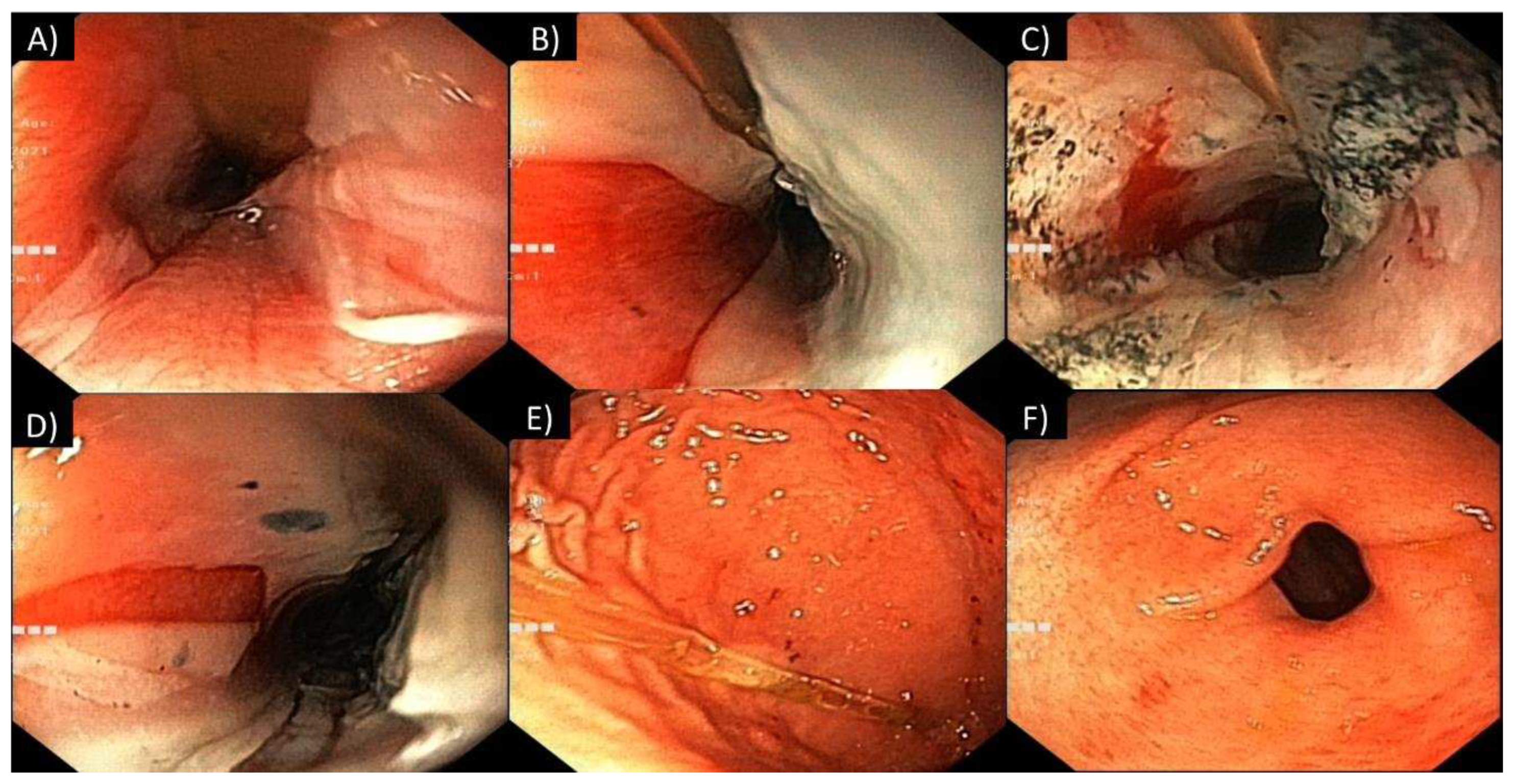
3.2. Gastrointestinal tract involvement
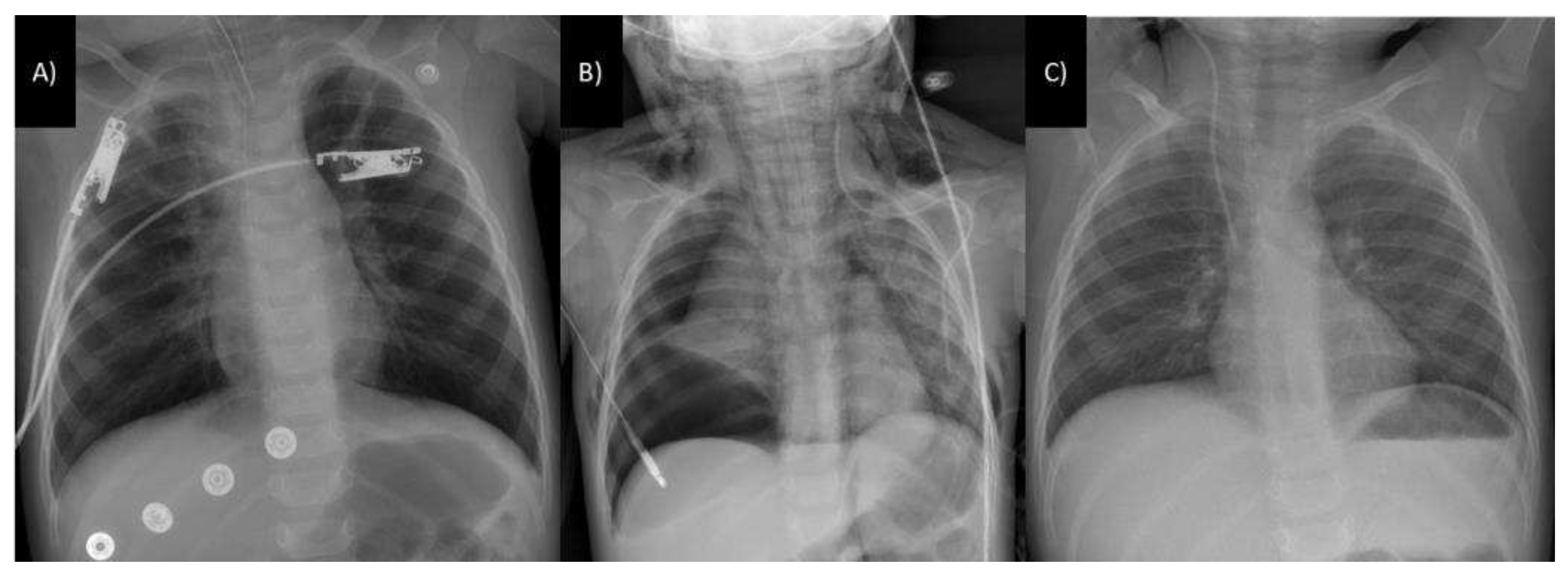
3.3. Respiratory tract involvement
3.4. Other complications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenman, K. D.; Reilly, M. J.; Wang, L. Calls to a State Poison Center Concerning Cleaners and Disinfectants From the Onset of the COVID-19 Pandemic Through April 2020; 2021; Vol. 136. [CrossRef]
- Hrubec, T. C.; Seguin, R. P.; Xu, L.; Cortopassi, G. A.; Datta, S.; Hanlon, A. L.; Lozano, A. J.; McDonald, V. A.; Healy, C. A.; Anderson, T. C.; Musse, N. A.; Williams, R. T. Altered Toxicological Endpoints in Humans from Common Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectant Exposure. Toxicol Rep 2021, 8, 646–656. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sangion, A.; Li, L. Evaluating Consumer Exposure to Disinfecting Chemicals against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Associated Health Risks. Environ Int 2020, 145, 106108. [CrossRef]
- Osimitz, T. G.; Droege, W. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: Perspectives on Benefits, Hazards, and Risk. Toxicology Research and Application 2021, 5, 239784732110490. [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Ji, P.; Zhang, W.; Jing, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, C.; Xu, P.; Huang, M. From Disinfectants to Antibiotics: Enhanced Biosafety of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds by Chemical Modification. J Hazard Mater 2023, 460, 132454. [CrossRef]
- Sapozhnikov, S. V.; Sabirova, A. E.; Shtyrlin, N. V.; Druk, A. Y.; Agafonova, M. N.; Chirkova, M. N.; Kazakova, R. R.; Grishaev, D. Y.; Nikishova, T. V.; Krylova, E. S.; Nikitina, E. V.; Kayumov, A. R.; Shtyrlin, Y. G. Design, Synthesis, Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity of Novel Quaternary Ammonium Compounds Based on Pyridoxine and Fatty Acids. Eur J Med Chem 2021, 211. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. H.; Kwon, D.; Lee, S.; Son, S. W.; Kwon, J. T.; Kim, P. J.; Lee, Y. H.; Jung, Y. S. Concentration-and Time-Dependent Effects of Benzalkonium Chloride in Human Lung Epithelial Cells: Necrosis, Apoptosis, or Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Toxics 2020, 8 (1). [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B. M. P.; Tagkopoulos, I. Benzalkonium Chlorides: Uses, Regulatory Status, and Microbial Resistance. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. American Society for Microbiology 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mishima-Kimura, S.; Yonemitsu, K.; Ohtsu, Y.; Sasao, A.; Tsutsumi, H.; Furukawa, S.; Nishitani, Y. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Detection of Benzalkonium Chloride (BZK) in a Forensic Autopsy Case with Survival for 18 days Post BZK Ingestion. Leg Med 2018, 32, 48–51. [CrossRef]
- Tambuzzi, S.; Gentile, G.; Andreola, S.; Migliorini, A. S.; Zoja, R. Visceral Microscopic Pattern From Suicidal Ingestion of Professional Lysoform® With Delayed Death. Acad Forensic Pathol 2022, 12 (3), 118–125. [CrossRef]
- Karaman, I.; Koç, O.; Karaman, A.; Erdogan, D.; Çavusoglu, Y. H.; Afsarlar, Ç. E.; Yilmaz, E.; Ertürk, A.; Balci, Ö.; Özgüner, I. F. Evaluation of 968 Children with Corrosive Substance Ingestion. Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2015, 19 (12), 714–718. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, K. Acute Toxicity of Benzalkonium Chloride in Balb/c Mice Following Intratracheal Instillation and Oral Administration. Environ Anal Health Toxicol 2019, 34 (3), e2019009. [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, A. B.; Yiannias, J. A.; Davis, M. D. P.; Killian, J. M. Benzalkonium Chloride: A Known Irritant and Novel Allergen. Dermatitis 2016, 27 (1), 14–20. [CrossRef]
- Peyneau, M.; de Chaisemartin, L.; Gigant, N.; Chollet-Martin, S.; Kerdine-Römer, S. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds in Hypersensitivity Reactions. Frontiers in Toxicology 2022, 4. [CrossRef]
- Migueres, N.; Debaille, C.; Walusiak-Skorupa, J.; Lipińska-Ojrzanowska, A.; Munoz, X.; van Kampen, V.; Suojalehto, H.; Suuronen, K.; Seed, M.; Lee, S.; Rifflart, C.; Godet, J.; de Blay, F.; Vandenplas, O. Occupational Asthma Caused by Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: A Multicenter Cohort Study. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021, 9 (9), 3387–3395. [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J. R.; Costa De Araujo, P.; De Marrez, L. G.; Halloy, J.-L.; Khalife, M.; Saussez, S. Contact Allergy to Benzalkonium Chloride in Patients Using a Steroid Nasal Spray: A Report of 3 Cases; 2018. https://www.entjournal.com/print/article/contact-allergy-benzalkonium-chloride-patients-using-steroid-nasal-spray-report-3-cases.
- Gigasept® instru AF Product Information Sheet. Available online: https://www.schuelke.com/media/products/docs/en/PRI_gigasept_instru_AF_664_EN_062023_06.pdf (first accessed on November 26, 2021, most recent date of access was December 27, 2023).
- Obarski, P.; Włodarczyk, J. Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Chemical Burns and Post-Burn Oesophageal Stenosis. Kardiochirurgia i Torakochirurgia Polska. Termedia Publishing House Ltd. 2021, pp 252–259. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. J.; Seak, C. J.; Kang, S. C.; Chen, T. H.; Chen, C. C.; Ng, C. J.; Lee, C. W.; Su, M. Y.; Huang, H. C.; Chen, P. C.; Ooyang, C. H.; Hsieh, S. Y.; Cheng, H. T. A New Perspective of the Risk of Caustic Substance Ingestion: The Outcomes of 468 Patients in One North Taiwan Medical Center within 20 Years. Clin Toxicol 2021, 59 (5), 409–417. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A. Acute Caustic Ingestion: State of Art and New Trends. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Res 2015, 4 (3), 1501–1506. [CrossRef]
- Meena, B. L.; Narayan, K. S.; Goyal, G.; Sultania, S.; Nijhawan, S. Corrosive Injuries of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Journal of Digestive Endoscopy 2017, 08 (04), 165–169. [CrossRef]
- Chirica, M.; Bonavina, L.; Kelly, M. D.; Sarfati, E.; Cattan, P. Caustic Ingestion. The Lancet. Lancet Publishing Group May 20, 2017, pp 2041–2052. [CrossRef]
- Caganova, B.; Foltanova, T.; Plackova, S.; Placha, K.; Bibza, J.; Puchon, E.; Ondriasova, E.; Batora, I. Caustic Effects of Chemicals: Risk Factors for Complications and Mortality in Acute Poisoning. Monatsh Chem 2017, 148 (3), 497–503. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A. F.; Gameel, D. E. G. El; Abdo, S. A. E.-F.; Elgebally, E. I.; Fayed, M. M. Evaluation of Pediatric Early Warning System and Drooling Reluctance Oropharynx Others Leukocytosis Scores as Prognostic Tools for Pediatric Caustic Ingestion: A Two-Center, Cross-Sectional Study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 29 (4), 5378–5395. [CrossRef]
- Hall, A. H.; Jacquemin, D.; Henny, D.; Mathieu, L.; Josset, P.; Meyer, B. Corrosive Substances Ingestion: A Review. Critical Reviews in Toxicology. Taylor and Francis Ltd September 14, 2019, pp 637–669. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, S.; Romano, C.; De Angelis, P.; Isoldi, S.; Mantegazza, C.; Felici, E.; Dabizzi, E.; Fava, G.; Renzo, S.; Strisciuglio, C.; Quitadamo, P.; Saccomani, M. D.; Bramuzzo, M.; Orizio, P.; Nardo, G. Di; Bortoluzzi, F.; Pellegrino, M.; Illiceto, M. T.; Torroni, F.; Cisarò, F.; Zullo, A.; Macchini, F.; Gaiani, F.; Raffaele, A.; Bizzarri, B.; Arrigo, S.; de’ Angelis, G. L.; Martinelli, M.; Norsa, L. Foreign Body and Caustic Ingestions in Children: A Clinical Practice Guideline: Foreign Bodies and Caustic Ingestions in Children. Digestive and Liver Disease 2020, 52 (11), 1266–1281. [CrossRef]
- Usta, M.; Erkan, T.; Cokugras, F. C.; Urganci, N.; Onal, Z.; Gulcan, M.; Kutlu, T. High Doses of Methylprednisolone in the Management of Caustic Esophageal Burns. Pediatrics 2014, 133 (6). [CrossRef]
- Tringali, A.; Thomson, M.; Dumonceau, J. M.; Tavares, M.; Tabbers, M. M.; Furlano, R.; Spaander, M.; Hassan, C.; Tzvinikos, C.; Ijsselstijn, H.; Viala, J.; Dall’Oglio, L.; Benninga, M.; Orel, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Keil, R.; Romano, C.; Brownstone, E.; Hlava, Š.; Gerner, P.; Dolak, W.; Landi, R.; Huber, W. D.; Everett, S.; Vecsei, A.; Aabakken, L.; Amil-Dias, J.; Zambelli, A. Pediatric Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Guideline Executive Summary. Endoscopy. Georg Thieme Verlag January 1, 2017, pp 83–91. [CrossRef]
- Ali Zargar, S.; Kochhar, R.; Mehta, S.; Kumar Mehta, S. The Role of Fiberoptic Endoscopy in the Management of Corrosive Ingestion and Modified Endoscopic Classification of Burns. Gastrointest Endosc 1991, 37 (2), 165–169. [CrossRef]
- Mantho, P.; Engbang, J. P.; Ndzana Awono, C. D.; Essola, B.; Kamguep, T.; Noah Noah, D.; Ngowe Ngowe, M. Caustic Esophageal Strictures in Children: Diagnosis, Treatment and Evolution in the City of Douala. J Surg Res (Houst) 2022, 05 (03). [CrossRef]
- Demirören, K.; Kocamaz, H.; Doğan, Y. Gastrointestinal System Lesions in Children Due to the Ingestion of Alkali and Acid Corrosive Substances. Turk J Med Sci 2015, 45 (1), 184–190. [CrossRef]
- Ollandzobo, L. C. A.-I. I.; Ahoui-Apendi, C.; Mimiesse-Monamou, J. F.; Babela, J. R. M.; D.-G.; Ibara, B. I. A.; Ibara, J.-R. Ingestion of Caustics by Children in Brazzaville (CONGO). Open J Pediatr 2018, 08 (03), 283–291. [CrossRef]
- Alser, O.; Hamouri, S.; Novotny, N. M. Esophageal Caustic Injuries in Pediatrics: A Sobering Global Health Issue. Asian Cardiovascular and Thoracic Annals. SAGE Publications Inc. July 1, 2019, pp 431–435. [CrossRef]
- Niedzielski, A.; Schwartz, S. G.; Partycka-Pietrzyk, K.; Mielnik-Niedzielska, G. Caustic Agents Ingestion in Children: A 51-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. Ear Nose Throat J 2020, 99 (1), 52–57. [CrossRef]
- Nardo, G. Di; Betalli, P.; Illiceto, M. T.; Giulia, G.; Martemucci, L.; Caruso, F.; Lisi, G.; Romano, G.; Villa, M. P.; Ziparo, C.; Pensabene, L.; Vassallo, F.; Quitadamo, P. Caustic Ingestion in Children: 1 Year Experience in 3 Italian Referral Centers. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2020, 71 (1), 19–22. [CrossRef]
- Spiller, H. A. A Case of Fatal Ingestion of a 10% Benzalkonium Chloride Solution. Journal of Forensic Toxicology and Pharmacology 2014, 03 (01). [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J. T. Benzalkonium Chloride Poisoning in Infant Twins. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1975, 129 (10), 1208. [CrossRef]
- Elkaramany, M. An Overview of Corrosive Injury of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: Discussion of Types, Clinical Evaluation, and Management Procedures. Advances in Digestive Medicine 2018, 5 (4), 115–120. [CrossRef]
- Amit Kumar; Rajesh Chetiwal; Priyank Rastogi; Shweta Tanwar; Saurabh Gupta; Rajesh Patnaik; Maduri Vankayalapati; Sudhish Gupta; Alok Arya. Severe Esophagitis and Chemical Pneumonitis as a Consequence of Dilute Benzalkonium Chloride Ingestion: A Case Report. International Journal of Medical Students 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bekdas, M.; Ozturk, S.; Kara, B.; Acar, S.; Ozturk, H. An Unpleasant Result of Imprecision: Esophageal Corrosive Injury Due to the Oral Intake of 10% Benzalkonium Chloride. Br J Med Med Res 2016, 14 (4), 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Civan, H. A.; Gulcu, D.; Erkan, T. Corrosive Esophagitis with Benzalkonium Chloride in a Two Days Old Neonate. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016, 19 (3), 207–209. [CrossRef]
- Turan, C.; Özkan, U.; Özokutan, B. H.; Özdemir, M.; Okur, H.; Küçükayd&#x, M. Corrosive Injuries of the Esophagus in Newborns. Pediatr Surg Int 2000, 16 (7), 483–484. [CrossRef]
- Okan, F.; Coban, A.; Ince, Z.; Can, G. A Rare and Preventable Cause of Respiratory Insufficiency Ingestion of Benzalkonium Chloride; 2007. [CrossRef]
- Amigoni, M.; Bellani, G.; Zambelli, V.; Scanziani, M.; Farina, F.; Fagnani, L.; Latini, R.; Fumagalli, R.; Pesenti, A. Unilateral Acid Aspiration Augments the Effects of Ventilator Lung Injury in the Contralateral Lung. Anesthesiology 2013, 119 (3), 642–651. [CrossRef]
- Chirica, M.; Kelly, M. D.; Siboni, S.; Aiolfi, A.; Riva, C. G.; Asti, E.; Ferrari, D.; Leppäniemi, A.; Ten Broek, R. P. G.; Brichon, P. Y.; Kluger, Y.; Fraga, G. P.; Frey, G.; Andreollo, N. A.; Coccolini, F.; Frattini, C.; Moore, E. E.; Chiara, O.; Di Saverio, S.; Sartelli, M.; Weber, D.; Ansaloni, L.; Biffl, W.; Corte, H.; Wani, I.; Baiocchi, G.; Cattan, P.; Catena, F.; Bonavina, L. Esophageal Emergencies: WSES Guidelines. World Journal of Emergency Surgery. BioMed Central Ltd. May 31, 2019. [CrossRef]
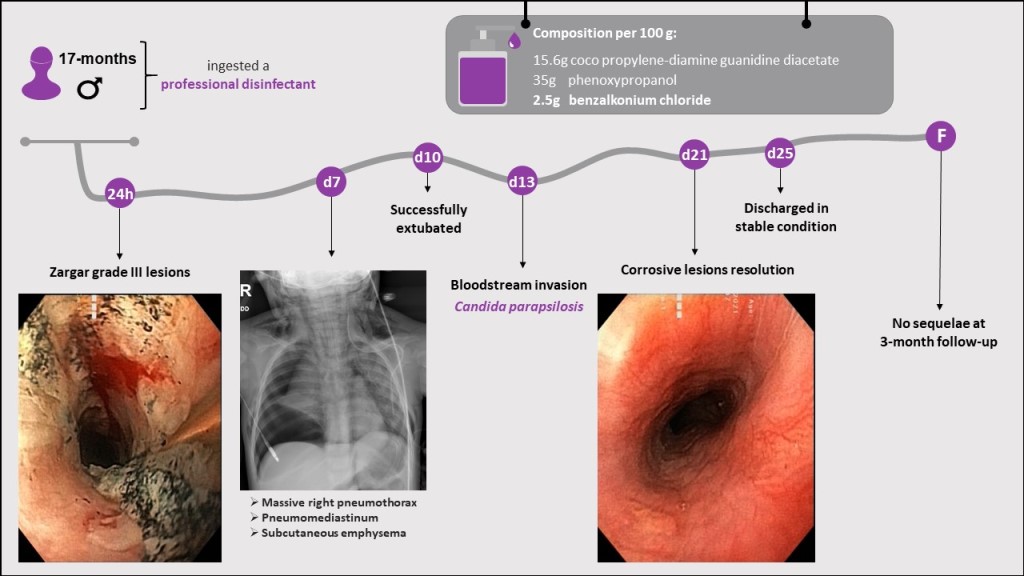
| Activeingredients: | 15.6% Cocos propylene diamine-guanidine diacetate |
| 35% Phenoxypropanols | |
| 2.5% Benzalkonium chloride | |
| pH: | 9.1—9.5 |
| Density: | 0.99 g/cm3 |
| Viscosity: | 30 mPa*s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




