1. Introduction
Auger-emitting radionuclides have potential for the therapy of cancer due to their high level of cytotoxicity and short-range biological effectiveness [
1]. As a result of the decay processes of these radionuclides, a series of low energy electrons are ejected in what is referred to as the Auger effect [
2], which has already been explored as a potential source for targeted radiotherapy. The Auger effect is based on the emission of an electron following various excitation processes such as electron capture (EC), internal conversion (IC), or photoelectric X-rays absorption [
3]. The unique properties of Auger electrons make them an attractive choice for pin-point accuracy in internal radiotherapy. Auger electrons have a very short range, typically less than 100 nm, due to their high stopping power (linear energy transfer - LET) qualities [
4]. This makes them capable of inducing double-stranded DNA breaks [
5], a critical mechanism in the context of their therapeutic impact. Further, the short ranges of Auger electrons of less than a cell diameter makes it theoretically possible to effectively irradiate targeted cells, while largely sparing surrounding healthy tissues. For these reasons, Auger radiotherapy is considered a promising emerging field in nuclear medicine, especially for targeting very small tumor masses such as metastases.
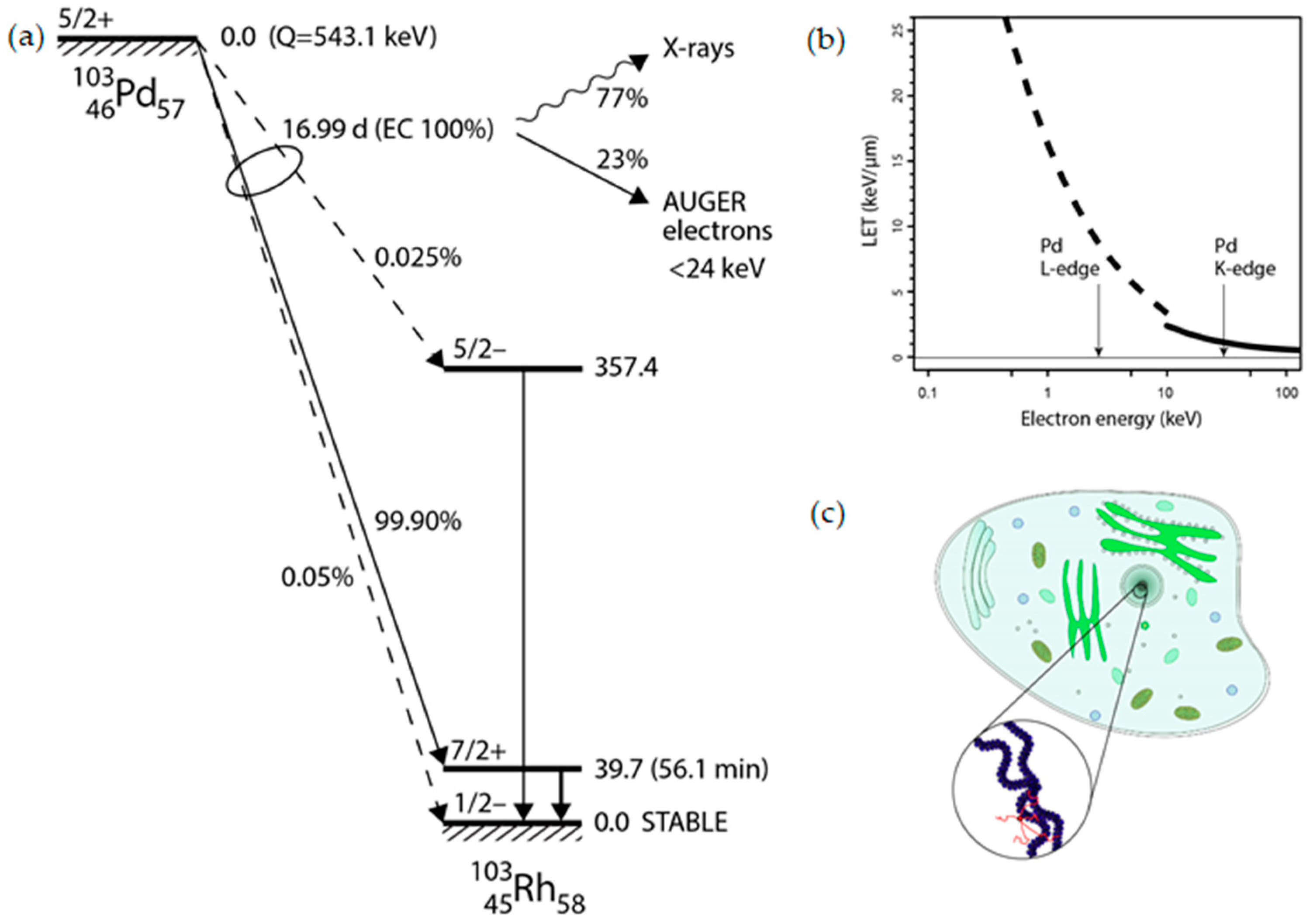
Palladium-103 (Pd-103) decays to rhodium-103m (Rh-103m) via electron capture (EC) with a half-life of 16.99 days (
Figure 1a). This process leaves a core-hole state that recombines by deexcitation cascades emitting characteristic X-rays (K-edge at 24.37 keV) and Auger electrons with a branching ratio of 77% and 23%, respectively [
6]. From technical point of view the relatively low energy of X-ray photons allows for fairly non-problematic shielding, handling, storage and elution of a Pd-103 based generator [
4]. Furthermore, Pd-103 already enjoys widespread medical use by virtue of its X-ray emissions, utilized in brachytherapy [
7].
The stopping range of KLL and KLM Auger electrons in the energy range of 20-24 keV can be calculated in organic media (
Figure 1b), which was found typically 30-50 nm being comparable with the average diameter of chromatin strands (~30 nm) as illustrated in
Figure 1c.
Production of Pd-103 from stable rhodium-103 (Rh-103) using a cyclotron has been reported, mainly through the
103Rh(p,n)
103Pd reaction [
9,
10]. Furthermore, an Auger electron emitter should be produced by a low-cost process while maximizing specific activity and purity in order to present therapeutic potential [
11,
12]. However, the separation process of the Pd-103 from the target material remains challenging and usually carrying out by the wet chemistry [
13], which is a very complicated and laborious process due to the extreme chemical inertness of these elements. Additionally, it involves the use of hazardous chemicals, resulting in a lower rhodium recovery rate and the generation of radioactive waste [
14], knowing that, the cost of rhodium material proves prohibitively expensive for any chemical processing.
In our study, we propose a more feasible method to address this challenge by employing diffusion-driven extraction for the separation of Pd-103 radionuclides generated by irradiating natural Rh-103 target with protons at the cyclotron facility of ATOMKI. We have designed and constructed a radionuclide separation equipment (RSE) based on the dry distillation method, which relies on the differences in partial vapor pressures between the target and the resulting radioactive materials. In practice, this principle of operation only holds for the case when the radionuclide material has at least 2 orders of magnitude higher vapor pressure than the target material. The experimental validation of the proof-of-principle and the determination of operational characteristics of the expected new separation method via thermo-diffusion [
15] have been conducted. Additionally, a technical design is proposed by calculating thermally-driven processes of atomic diffusion, evaporation, and deposition.
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of elemental interdiffusion at the Pd-Rh interface
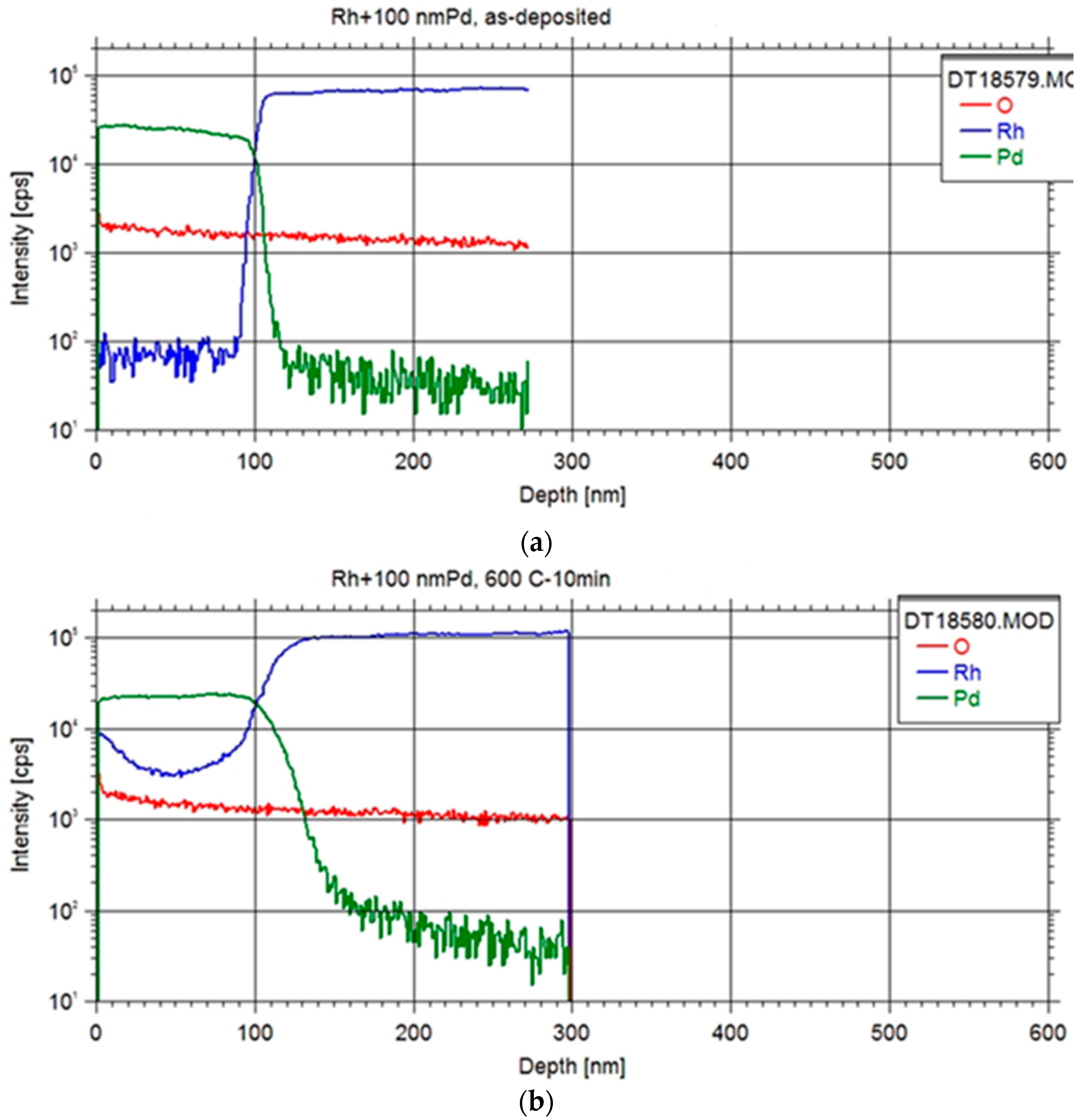
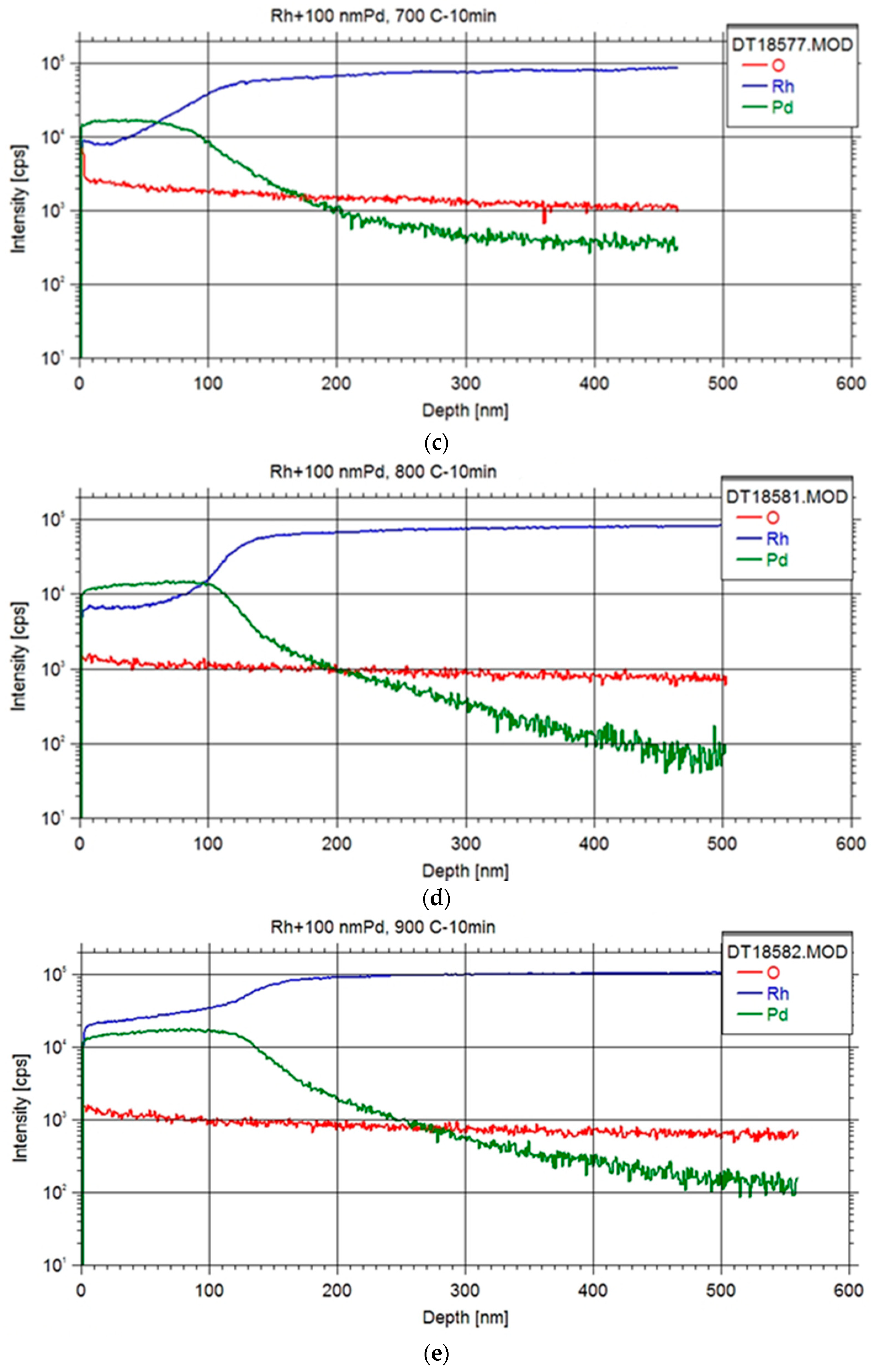
The examination of the Pd-Rh interface in all specimens entailed conducting depth profiling measurements with Secondary Neutral Mass Spectrometry (SNMS) technique as illustrated in
Figure 2. The equipment was operated in direct bombardment mode by using Ar+ ions with a fairly low energy for sputtering (E = 350 eV) and with a current density of ~1 mA/cm
2. The erosion area was confined to a circle of 2 mm in diameter by means of a Ta mask. The lateral homogeneity of the ion bombardment was checked by a profilometer (Ampbios XP I) to analyze the depth of the crater sputtered and to convert the sputtering time to depth scale.
Initial findings revealed a noteworthy degree of elemental interdiffusion between the two constituents, yielding valuable insights for the formulation of subsequent systematic measurements. The obtained depth profile exhibited characteristics indicative of an ideal depth profile, with observations indicating that samples featuring thinner foils displayed reduced surface roughness.
Upon annealing at 600 °C, a discernible accumulation of Rh at the surface was evident, suggesting the plausibility of Rh diffusion through the Pd layer via a grain boundary diffusion mechanism [
16], which occurred at a faster rate than the diffusion of Pd into the Rh foil. Subsequent annealing at higher temperatures further substantiated this phenomenon, revealing a temperature-dependent increase in Rh content within the Pd layer. Ultimately, this led to the attainment of a Pd layer fully impregnated with Rh, coinciding with concurrent diffusion of Pd into the Rh foil.
A preliminary value for the lattice diffusion constant of Pd in Rd matrix at the annealing temperatures could be obtained by fitting the Pd profiles with the formulation based on the Fick’s second law [
17] yielding 1.5-2 ∙ 10
-14 cm
2/s. This value indicates considerable diffusion rates at higher temperatures (e.g. >1200 °C), which may enhance extraction rates even on a minute scale of equipment operation. However, a systematic measurement of depth profiles over a wider temperature range and interdiffusion corrections will be needed for the accurate determination of absolute extraction rates.
2.2. Purity analysis of Pd separation
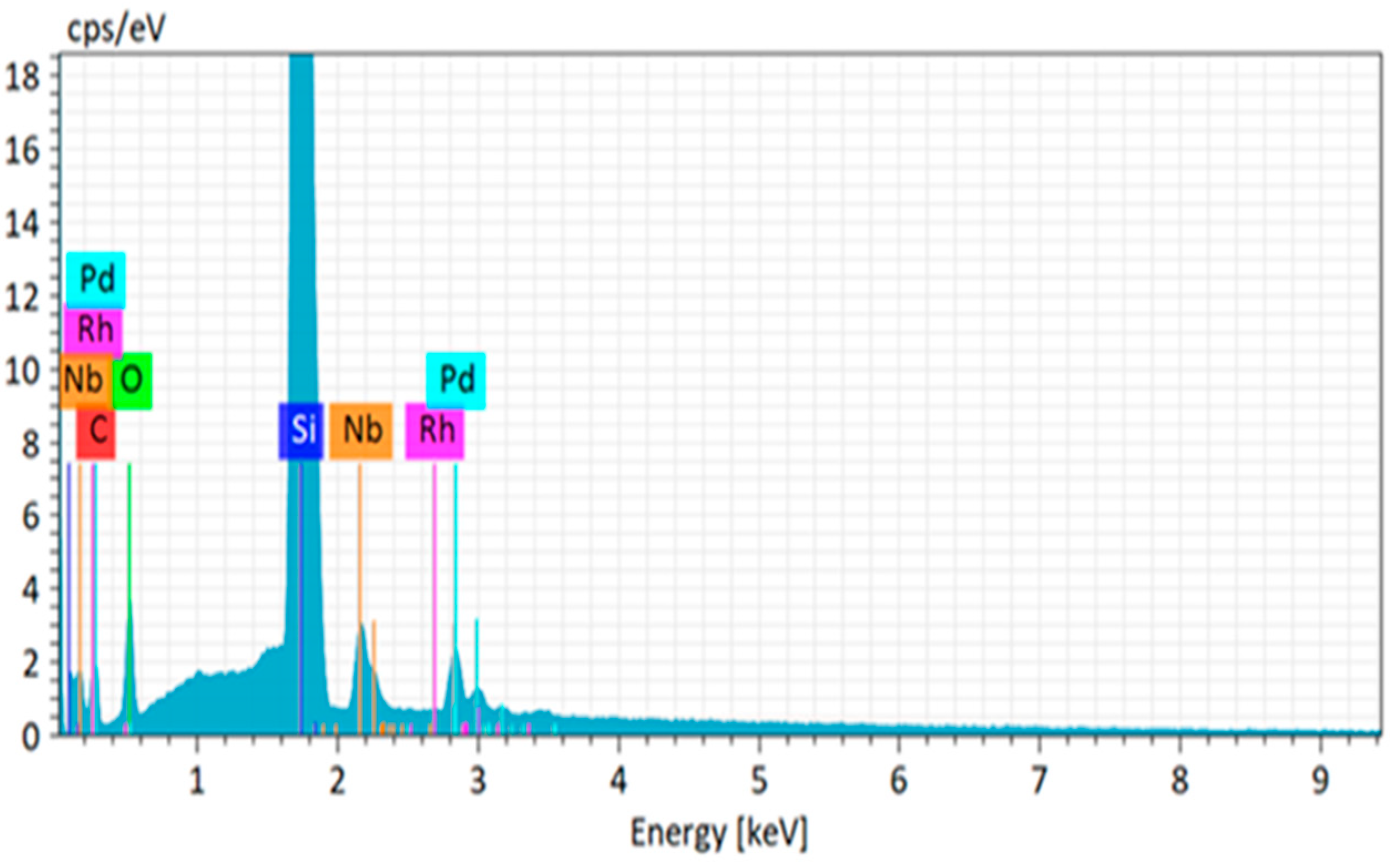
In order to verify the separation power of the dry-distillation method proposed for Pd-103, an evaporation probe was performed with a powder mixture of natural (inactive) Pd and Rh with 1:1 stochiometric ratio. The substrate used for probing the deposition was a niobium foil with a thickness of 50 µm (
Figure 3). The compositional purity of the deposited palladium layer was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The elemental analysis revealed the presence of Pd, while the Rh content did not exceed the sensitivity threshold of the instrument as shown in
Figure 4.
2.3. Quantitative analysis of Pd-103 with γ-spectroscopy
The quantification of Pd-103 activity was performed by the utilization of a High Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector. The specimens subjected to measurement encompassed the rhodium foil subsequent to each irradiation and separation test, the niobium substrate post-separation test and subsequent treatments with hydrochloric acid, the ZnO-covered W disk after separation test, and subsequent treatments with hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, along with the rinsed liquid containing the Pd-103 isolated in vials post each dissolution. Gamma peak areas were efficiency corrected and the Pd-103 activity of the samples was determined from the following well-known low yield γ line of Pd-103: 357.45 keV (0.0221 %) [
18]. Calculations were executed to assess the generated activity (
Table 1).
2.4. Separation efficiency of Pd-103 from the irradiated metal Rh foil
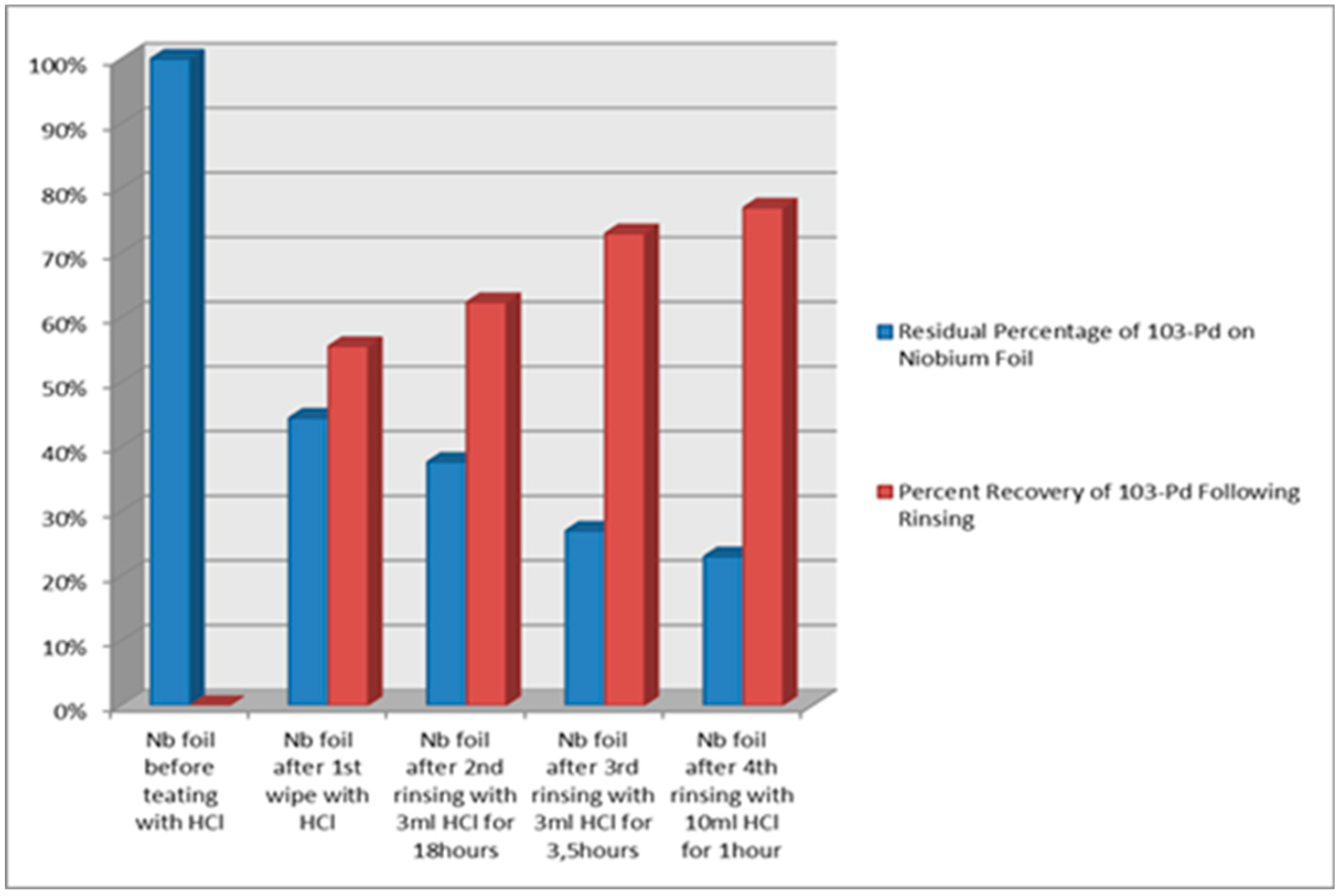
The experimental results substantiate a separation efficiency of 19% from the bulk of Rh foil under a heating regime of 10 minutes at 1500 °C, facilitated by the utilization of our separation equipment. The collection of evaporated Pd-103 involved deposition onto the "cold" surface of the Niobium (Nb) foil substrate. An amount of 77% ± 2% of the radioactivity was recovered from the substrate through the rinsing of the Nb foil in cc of HCl solution.
A comparative investigation was executed to ascertain the Residual Percentage of Pd-103 on the niobium foil, along with the Rinsed Pd-103 Yield, as illustrated in the
Figure 5.
For the following pilot, a study was conducted at a temperature of 1200 °C for duration of 20 minutes, resulting in an evaporation yield of up to 14%. The ZnO-covered W disk served as the designated collecting trap or deposition surface throughout the evaporation experiment. A recovery yield of 49% ± 2% was achieved from the ZnO substrate following treatment with cc of HCl and HNO3.
3. Discussion
We have systematically examined the operational parameters of the separation equipment in correlation with the extraction efficiency of Pd-103. We have concluded from the Pd/Rh interdiffusion measurements that significant Pd-extraction rates can be achieved at lower temperature with respect to the melting point of Pd (1552 °C). At selected value of operational temperature (1200 °C) and duration (20 min). The Pd-103 separation yielded an activity of 31 MBq measured for the γ line at 357.45 keV in Pd-103, while a slowly increasing activity from Rh-103m (39.7 keV) was also observable. This quantity is deemed notably substantial and suitable for conducting pre-clinical investigations involving approximately 10 adult rat models [
19]. The chemical purity of the deposited layer was not able to be measured with the surface analytical instruments; instead, we relied on the systematic measurements performed on inactive samples, which revealed that significant presence of Rh was not observed in the deposited layer.
Two main concerns must be discussed in order to reconsider technical steps that are essential for the maximization of the extraction efficiency. One is the thickness of the Rh foil, which was chosen 6 µm in our pilot experiments. A higher thickness, optimally around 100 µm, can be adjusted to the wide cross section peak of 103Rh(p,n)103Pd reaction, which may boost production rates. In contrast, the extraction rates governed by the diffusion do not favor thick layers; however, long operation times might compensate the low evaporation rates. In our case the 6-µm thick target was nearly optimal to produce well measurable trace amount of radioactivity by a few hour irradiation. The second concern is related to the deposition efficiency in terms of adequate material selection for the deposition surface adapted to the subsequent dissolution process. During the engineering phase of our separation equipment preliminary tests were performed to determine the ratio of the dissolvable Pd-103 content with respect to the total amount of deposited Pd-103. Since the deposition surface is also heated up by thermal radiation from the crucible side, an elevated rate of diffusion increases the amount of buried Pd-103 that cannot be recovered even by hard acidic digestion. The deposition surface in our studies was first a Nb foil without any surface treatment, then a W disk, which was covered with an intuitively selected ZnO layer to accumulate Pd-103 atoms and to prevent their penetration to the W surface, as well as an appropriate substrate for both high temperature operation and acidic dissolution. As a result, 23% of the deposited Pd-103 remained on the Nb foil, while 51% on the W disk. In the former case, the higher recovery ratio can be attributed to the highly polished surface of the Nb foil. In comparison with the case of the W disc, first disregarding the effect of the ZnO layer, we may conclude that the recovery ratio is highly sensitive on the material choice, surface morphology, as well as the temperature. However, this pilot experiment also evidenced the expected role of the ZnO layer as a diffusion barrier in contrast to the apparently insufficient thickness of 100 nm. To identify the benefit of employing metal-oxides as Pd-103 accumulator layer on the deposition substrates systematic investigations are recommended.
4. Materials and Methods
The rhodium foil with 125 μm and 6 μm thicknesses, the niobium foil with 50 µm thick, the boron nitride (BN) ceramic, and the tungsten (W) metal, were purchased from Goodfellow. The rhodium and palladium powders were purchased from Koch-Light Laboratories Limited, UK. The zinc oxide (ZnO) layer with 100 nm thick was fabricated at ATOMKI by Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) technique in a Beneq TFS-200 reactor [
20]. The ZnO layer was prepared by applying diethyl-zinc (DEZ) and water (HO) precursors (purchased from Sigma-Aldrich) at 100 °C reactor temperature. The consecutive pulse times were: 0.3 seconds for DEZ followed by 10 seconds nitrogen purge and 0.2 seconds for HO followed by 10 seconds nitrogen purge. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO₃) solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, and utilized without further purification.
All material characterization and experiments have been carried out at ATOMKI. Measurements of radioactive rhodium were conducted utilizing a High Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector Canberra type 2002 CSL, USA. The γ-spectra were analyzed with Genie-2000 software package. The deposition of palladium onto the rhodium foil was accomplished through the magnetron sputtering deposition technique using magnetron heads made by Kurt J. Lesker. The base pressure of the sputtering chamber was lower than 2∙10-7 mbar. Circular Pa target (purchased from Kurt J. Lesker), 5 cm diameter, were used as sputtering sources. During the layer deposition the Ar (99.999%) pressure (under dynamic flow) and the sputtering power were 5∙10-3 mbar and 40W, respectively. The sputtering rate was calculated from the layer thickness measured by an AMBIOS XP-1 profilometer. Annealing procedures were executed using a vacuum furnace at base pressure 7.5∙10-7 mbar. Depth profiling measurements were performed employing Secondary Neutral Mass Spectrometry (SNMS), made by SPECS GmbH, type INA-X. Surface morphology of the as-prepared and annealed samples were performed with a dual beam scanning electron microscopy type Thermo Fisher Scientific-Scios 2 (FIB-SEM, Waltham, MA, USA), equipped with Bruker type Quantax Energy Dispersive X-ray system (EDS) for composition analysis.
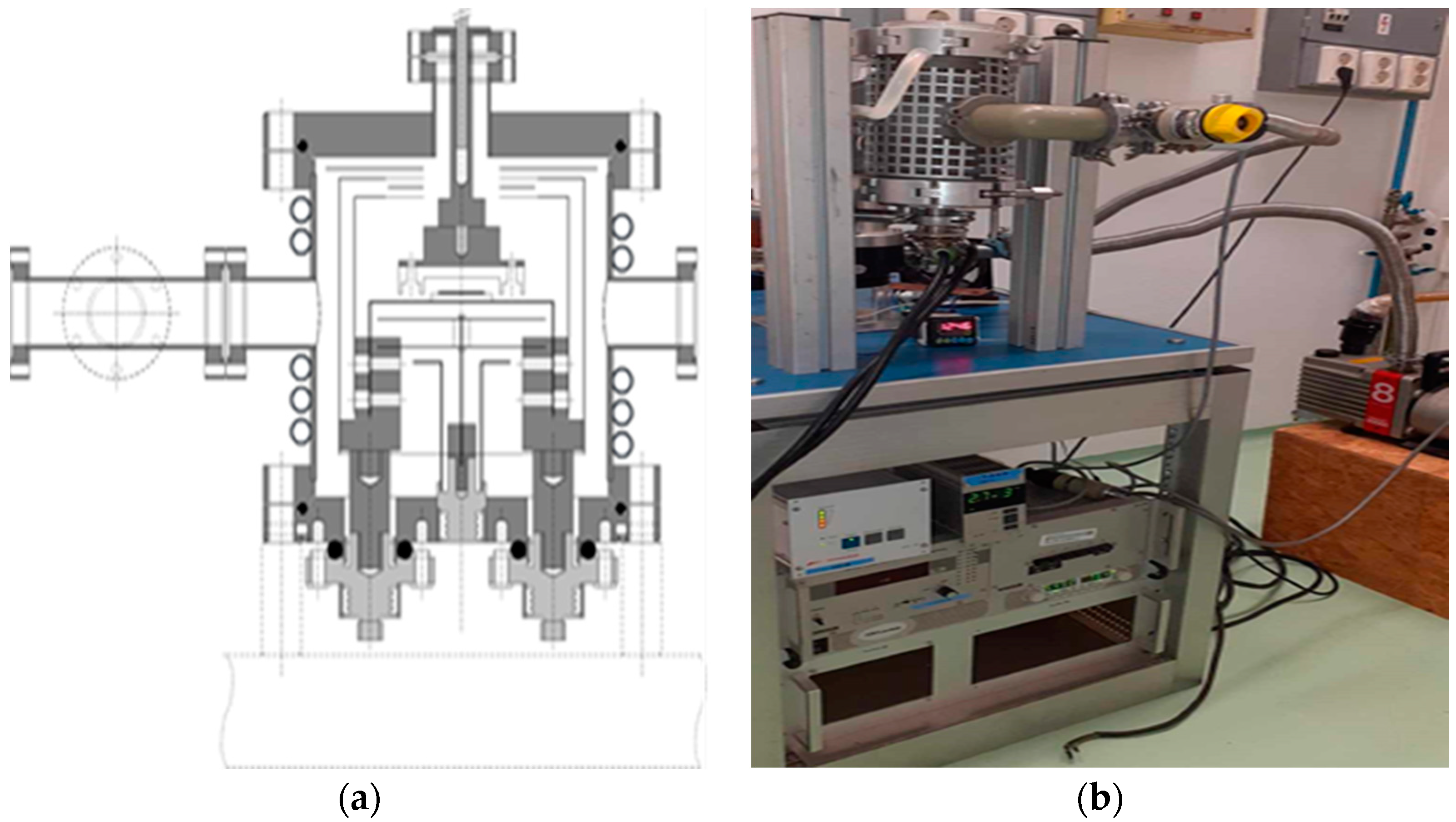
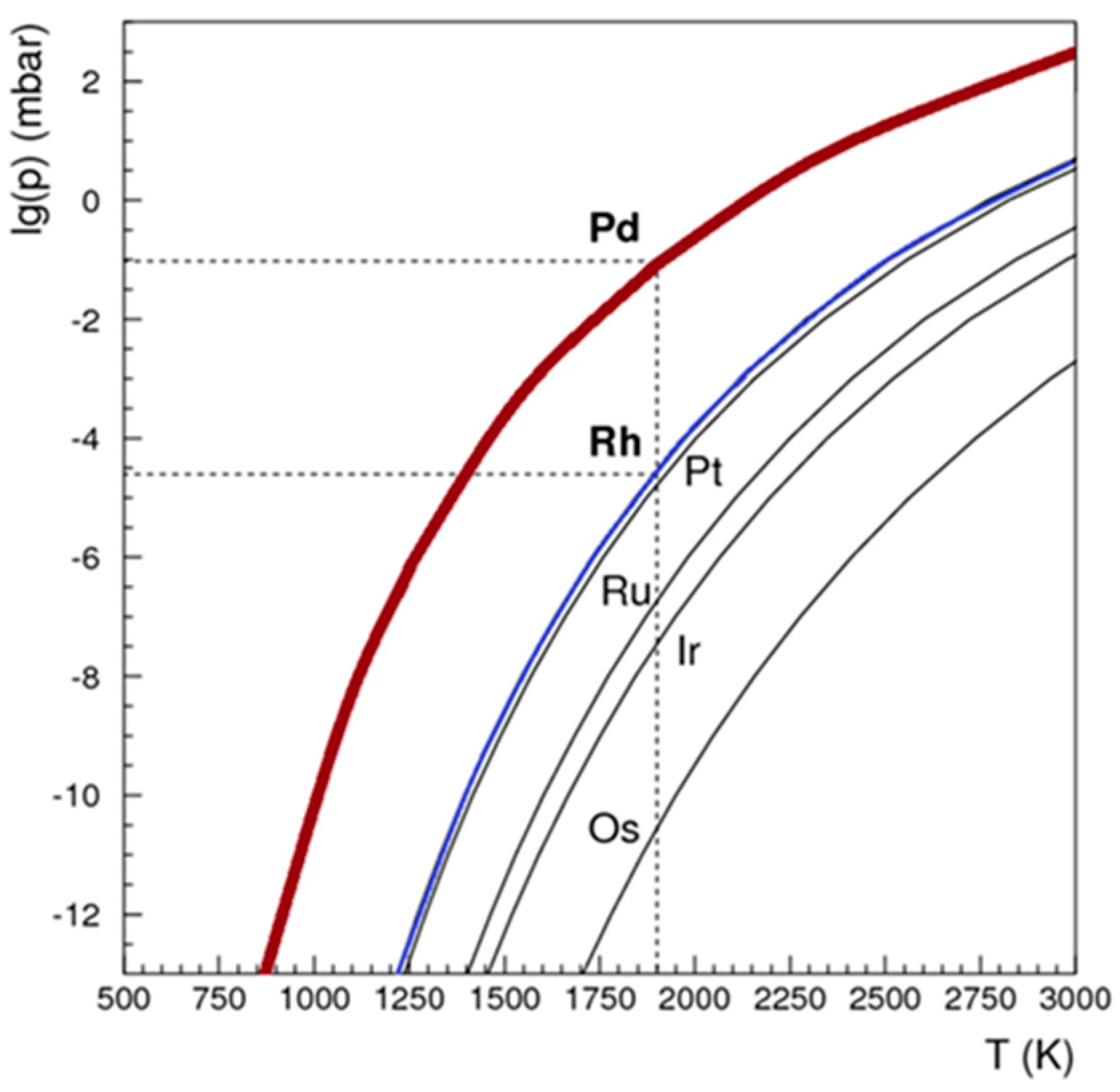
4.1. Engineering and optimization of the thermoregulation system for the RSE
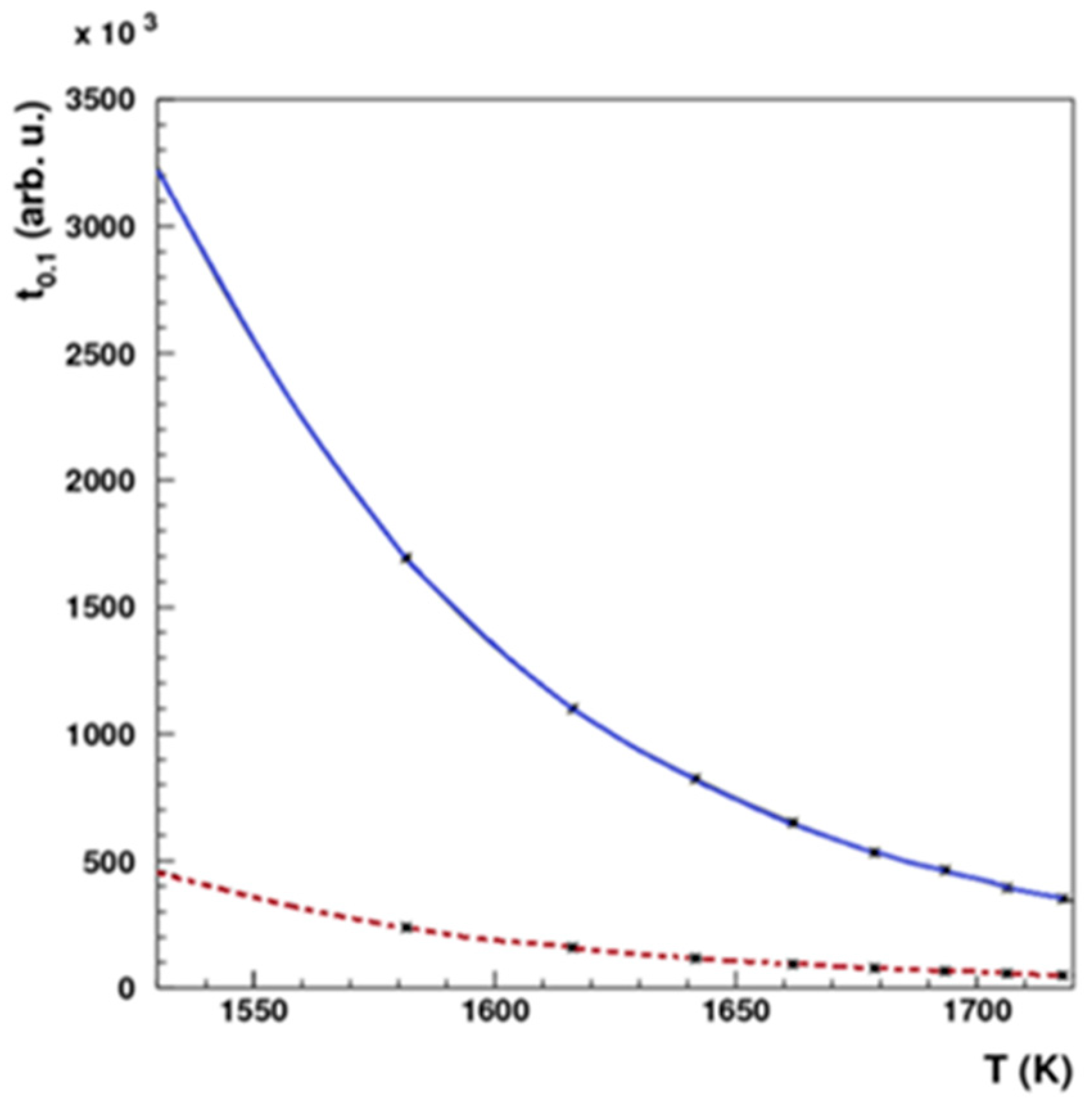
A dedicated system was engineered and constructed, as illustrated in
Figure 6. In the pursuit of isolating Pd-103 from the irradiated rhodium foil, a controlled temperature range of 1200 to 1750 °C and a vacuum pressure of 10
-4 mbar were selected. The theoretically optimal temperature and vacuum conditions were determined based on the insights provided in
Figure 7. Simulations were then undertaken to evaluate the requisite heating duration necessary for the efficient removal of Pd-103, considering two distinct thicknesses of Rhodium foil, as depicted in
Figure 8.
4.2. Production of Pd-103 via proton irradiation of Rh-103
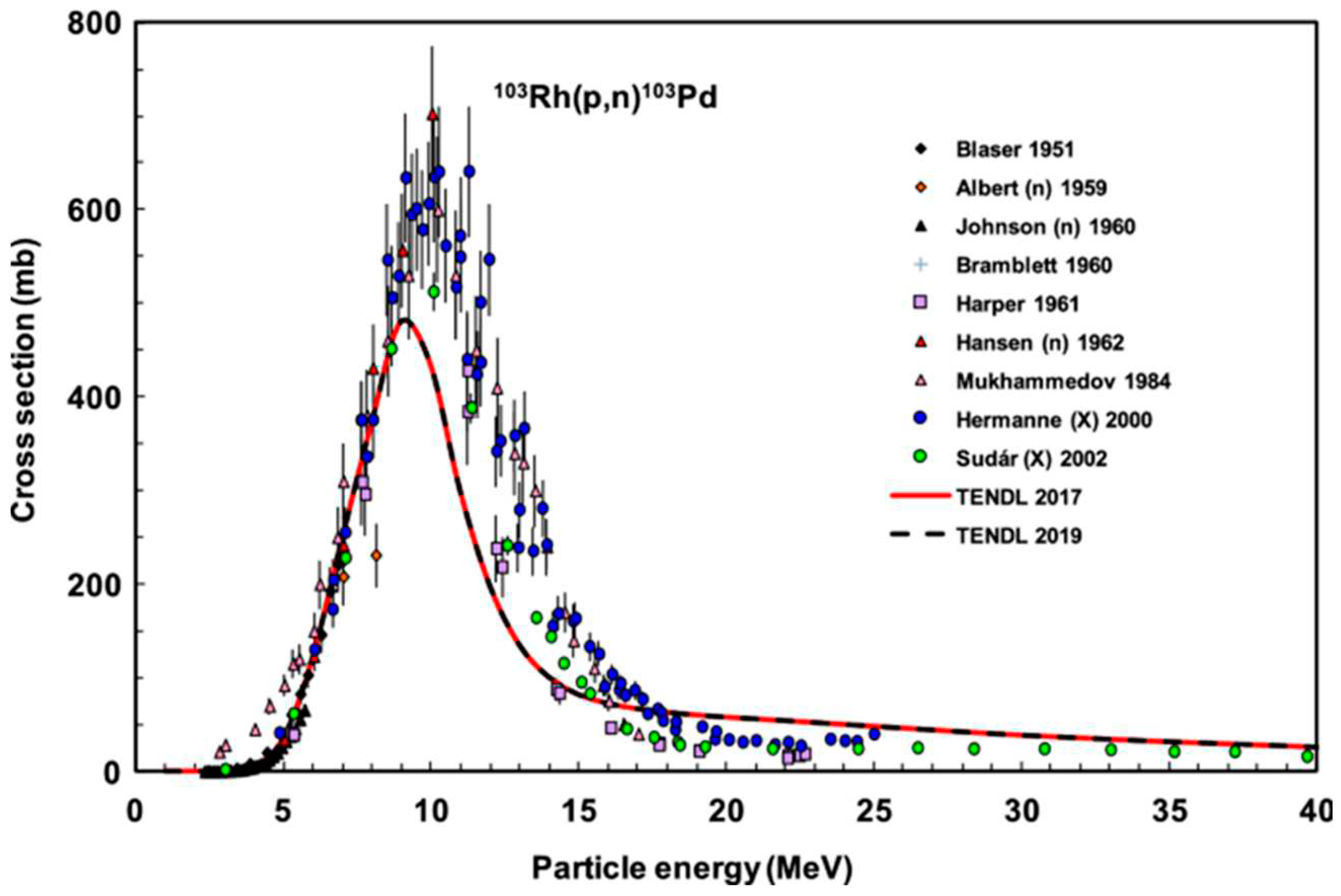
The
103Rh(p,n)
103Pd nuclear reaction was induced with a proton beam utilizing the MGC-20 cyclotron at ATOMKI. An optimal beam energy of 10 MeV and an intensity of 20 μA, was selected for this purpose. To achieve a desired activity of 10 MBq for each experimental iteration, the duration of irradiation in preliminary trials was meticulously determined by considering parameters such as rhodium foil thickness and cross-sectional data, as illustrated in
Figure 9. The first irradiation involved 2 hours with an energy of 14.5 MeV and an intensity of 10 μA, the second irradiation extended to 5 hours and 30 minutes with an energy of 10 MeV and an intensity of 10 μA, while the third irradiation spanned 8 hours with an energy of 11 MeV and an intensity of 20 μA.
4.3. Synthesis and diffusivity characterization of Pd/Rh alloy samples
To predict the intrinsic diffusion coefficient, rhodium foils were employed as substrates for sample preparation with the magnetron sputtering vapor deposition technique, depositing a 100 nm-thick layer of palladium onto their surfaces. Seven distinct sample sets were systematically prepared using rhodium foils of two different thicknesses. Two of these sets were designated as untreated controls, one with a thickness of 125 μm and the other with a thickness of 6 μm. The remaining sets underwent annealing processes at different temperatures: 700°C for 10 minutes, 800°C for one hour with a thickness of 125 μm, and at 600°C, 800°C, and 900°C for 10 minutes each with a thickness of 6 μm. These annealing processes were conducted within a vacuum furnace.
4.4. Separation of Pd-103 from irradiated Rh-103: A process of isolation
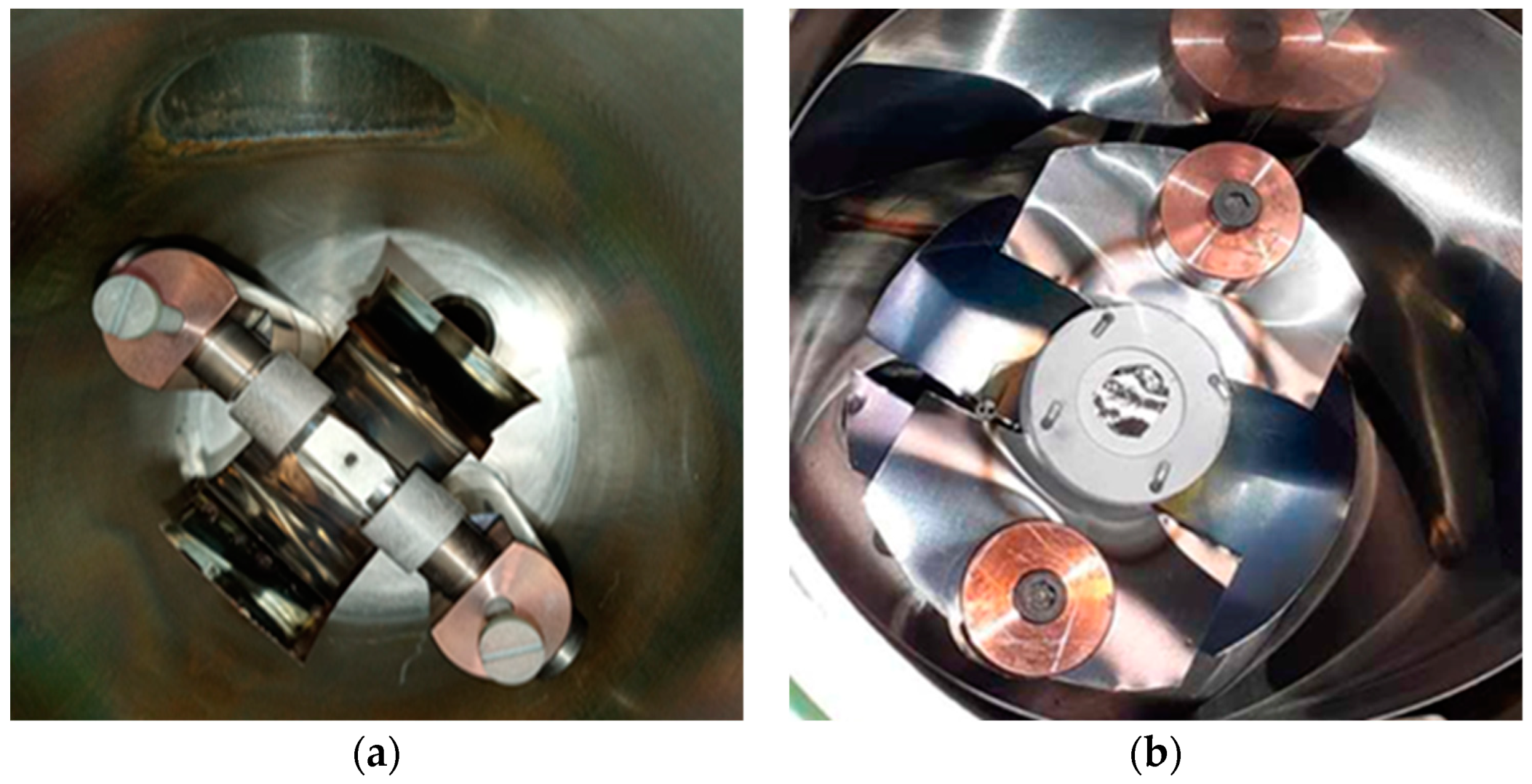
Initial experimentation focused on optimizing parameters for the RSE. This included fine-tuning vacuum pressure, electrical resistance, thermal conductance of electrode components, and calibrating heating power in correlation with temperature. Based on the output of the preliminary experimental tests, some functional elements of the equipment had to be redesigned, which included thermal-radiation shielding, thermocouple (D-type) fixing, material choice BN of crucible avoiding metallic contacts with the rhodium foil, and improvement of electrode contacts. The subsequent phase involved probing the ideal temperature conditions for the efficient isolation of the two metallic elements to avoid the rhodium contamination in the deposition material. A test material consisting of equimolar masses of rhodium and palladium powders was loaded into a BN crucible of the RSE as illustrated in
Figure 10. This composite underwent controlled heating within a temperature range of 1500 to 1700 °C.
Following the comprehensive optimization of parameters and the identification of the optimal temperature range for effective separation, the separation equipment was employed to execute dual separations of palladium-103 from irradiated rhodium-103. These separation processes occurred subsequent to both the second and third irradiation events.
4.5. Pd-103 retrieval from deposition surfaces through enhanced recovery processes
Two distinct substrates were employed as deposition surfaces for Pd-103, isolated using our separation equipment, as part of an optimization investigation. In the first case, a 50-µm thick Nb foil served as the deposition substrate for evaporated Pd-103. The Pd-103-coated Nb foil underwent treatment with concentrated HCl to facilitate rinsing and the harvest of separated Pd-103. Varied volumes of HCl were applied to the Nb foil for different durations. Subsequently, the rinsed material was collected in vials and subjected to quantitative analysis.
Following the initial pilot experiment involving untreated Nb foil, the subsequent experiment was dedicated to maximizing the recovery efficiency of Pd-103. Therefore, a tungsten (W) disk, measuring 2 mm in thickness and 30 mm in diameter, and covered with a 100-nm thick ZnO layer, was employed as the deposition substrate in order to accumulate Pd-103 atoms, with the ZnO layer serving as a diffusion barrier to minimize the penetration of Pd-103 into the W substrate. The deposition substrate underwent treatment with concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) followed by nitric acid (HNO₃), utilizing the same methodology as previously described, and was subsequently analyzed for quantitative measurements.
5. Conclusions
The outcomes of our investigation have instigated a pioneering concept: the exploitation of diffusion-driven extraction to isolate radionuclides, stemming from the irradiation of Rh-103 at the cyclotron. This innovative approach presents itself as a credible alternative to conventional wet chemistry techniques for the separation of Pd-103. Following the successful separation of Pd-103 from the bulk irradiated Rh material, a challenge emerged pertaining to the collection of the evaporated radioisotope and the need to avoid or minimize alloy formation between the trapped Pd-103 and the substrate. Subsequent optimization studies will be conducted in the future to address and resolve this challenge.
Author Contributions
Conduction of experimental procedures and manuscript authorship, Aicha Nour Laouameria.; Undertaking technical design, execution of experimental procedures and contribution editorial support to the manuscript, Mátyás Hunyadi.; Partaking in sample preparation, measurement methodologies, result interpretation and contribution editorial support to the manuscript, Attila Csík.; Supervision of experimental protocols, providing assistance in their execution, and contribution editorial support to the manuscript, Zoltán Szűcs. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the project TKP2021-NKTA-42 financed by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology, Hungary.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The scientific research has been supported by the Stipendium Hungaricum Scholarship Program of the Hungarian government. The research has been prepared with the professional support of the Chemical Doctoral School of the University of Debrecen, Hungary.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- O'donoghue, J. and T. Wheldon, Targeted radiotherapy using Auger electron emitters. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 1996. 41(10): p. 1973. [CrossRef]
- Ku, A., et al., Auger electrons for cancer therapy–a review. EJNMMI radiopharmacy and chemistry, 2019. 4(1): p. 1-36. [CrossRef]
- Pirovano, G., T.C. Wilson, and T. Reiner, Auger: The future of precision medicine. Nuclear medicine and biology, 2021. 96: p. 50-53. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.I., et al., A solid support generator of the Auger electron emitter rhodium-103m from [103Pd] palladium. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2020. 156: p. 108985. [CrossRef]
- Reissig, F., et al., Direct and Auger electron-induced, single-and double-strand breaks on plasmid DNA caused by 99mTc-labeled pyrene derivatives and the effect of bonding distance. PLoS One, 2016. 11(9): p. e0161973.
- Khan, F.M., The physics of radiation therapy. 2010: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Ferro, A., et al., Reductions in prostatic doses are associated with less acute morbidity in patients undergoing Pd-103 brachytherapy: Substantiation of the rationale for focal therapy. Brachytherapy, 2018. 17(2): p. 313-318. [CrossRef]
- Tung, C., J. Ashley, and R. Ritchie, Electron inelastic mean free paths and energy losses in solids II: Electron gas statistical model. Surface Science, 1979. 81(2): p. 427-439. [CrossRef]
- Sudár, S., F. Cserpák, and S. Qaim, Measurements and nuclear model calculations on proton-induced reactions on 103Rh up to 40 MeV: evaluation of the excitation function of the 103Rh (p, n) 103Pd reaction relevant to the production of the therapeutic radionuclide 103Pd. Applied radiation and isotopes, 2002. 56(6): p. 821-831.
- AC07607271, A., Cyclotron produced radionuclides-physical characteristics and production methods. 2009: Internat. Atomic Energy Agency.
- Tavares, A.A.S. and J.M.R. Tavares, 99mTc Auger electrons for targeted tumour therapy: A review. International journal of radiation biology, 2010. 86(4): p. 261-270. [CrossRef]
- Unak, P., Targeted tumor radiotherapy. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 2002. 45: p. 97-110.
- Nikoloski, A.N., K.-L. Ang, and D. Li, Recovery of platinum, palladium and rhodium from acidic chloride leach solution using ion exchange resins. Hydrometallurgy, 2015. 152: p. 20-32. [CrossRef]
- Szucs, Z., et al., The metal rhodium does not have allotropes. Journal of radioanalytical and nuclear chemistry, 2010. 284: p. 239-243.
- Alekseev, I., Diffusion-thermal methods for radionuclides isolation from solid-state reactor and cyclotron targets: possible prospects; Diffuzionno-termicheskie metody vydeleniya radionuklidov iz tverdotel'nykh reaktornykh i tsiklotronykh mishenej: vozmozhnye perspektivy. Radiokhimiya, 2003. 45.
- Mehrer, H., Continuum theory of diffusion. Diffusion in Solids: Fundamentals, Methods, Materials, Diffusion-Controlled Processes, 2007: p. 27-36.
- López-Salazar, P., et al., Determination of Diffusion Coefficient of Copper in ZnO (001) Single Crystals at 1000° C. Crystals, 2019. 9(3): p. 131. [CrossRef]
- IAEA Database: https://www-nds.iaea.org/relnsd/vcharthtml/VChartHTML.html.
- RADIOISOTOPES, I. and R. SERIES, Guidance for preclinical studies with radiopharmaceuticals. 2021.
- Johnson, R.W., A. Hultqvist, and S.F. Bent, A brief review of atomic layer deposition: from fundamentals to applications. Materials today, 2014. 17(5): p. 236-246. [CrossRef]
- Tárkányi, F., et al., Upgrade of recommended nuclear cross section data base for production of therapeutic radionuclides. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2022. 331(3): p. 1163-1206. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).