1. Introduction
Since their discovery about 45 years ago, fullerenes and their physiochemical properties and applications have attracted the attention of researchers. This carbon based nanomaterial, and particularly fullerene C
60 captures the extra attention of scientists due to its symmetry and physicochemical properties. The C
60, as molecular crystal, was predict by Osawa [
1], synthesized and identificatified with mass spectroscopy by Kroto et.al. [
2], produced in gram quantities by Huffman et.al. [
3] and viewed with atomic resolution using the Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) by Koruga et.al. [
4]. It has a high icosahedral symmetry arrangement of carbon atoms and their eigenvalues T
1g, T
2g, T
1u and T
2u have four Fibonacci valuves 1/2
,
,
and
, respectively Φ,-Φ,-φ,φ (
Supplementary Materials S1: Supplementary Table S1). Rotation-vibration spectra of icosahedral molecule C
60 was investigated [
5] and its dual particle-wave properties were experimentaly discovered [
6]. Also, some biomolecules such as clathrin, microtubules, etc. have icosahedral symmetry properties [
7,
8] as well. As the electronic and vibrational states of biomolecules are determined by their symmetry, the vibrational modes of C
60 can be resonantly transmitted to biomolecules and have influence on them. The C
60 is a spherical molecular crystal with 60 carbon atoms distributed over the surface of the sphere in 12 pentagons and 20 hexagons [
2]. Pentagons are energetically closed structures (diamagnetic), while hexagons are open-closed structures that "breathe" (paramagnetic) [
9].
Due to its physical properties, based on symmetry, C
60 is not soluble in water. It can become toxic when it comes under the influence of external factors which lead to the opening of one of the two (C=C) bonds in the hexagons.. The first fullerene derivative FD-C
60 (commercially named Fullerenol C
60(OH)
x)) was synthesized by adding OH groups in order to achieve solubility in water as well as to reduce possible toxicity [
10]. Solubility in water depends on the number of OH groups, which can be different, but the stability of fullerenol has proven to be the best if it has 12, 24, 36 or 48 OH groups. Since the diameter of the C
60 molecule, at the position of the carbon atom, is 0.71 nm, and the outer diameter is about 1 nm (due to
π- electrons), the diameter of fullerenol is roughly 1.3 nm with addition of OH groups. It has been shown that the toxicity of C
60 is reduced by 50% if OH groups are added [
11]. Fullerene hydroxylation increases water solubility and affects how these nano particles interact with biological systems. It was demonstrated that increasing fullerene water solubility through surface modification is related to significantly decreased toxicity. Specifically, this study observed decreased toxicity of hydroxylated fullerene compared to cytotoxic effect of fullerene aggregates to human skin (HDP) and liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells [
11]. Similarly, it was observed that hydroxylation decreases toxic potential of fullerene on mouse L929 fibrosarcoma, rat C6 glioma, and U251 human glioma cell lines [
12]. Additionally, hydroxylated fullerene induced apoptotic changes on investigated cells lines, while fullerene C
60 induced necrotic cell death. Distinct effects of pristine and modified fullerene originate from the different nanoparticles’ interaction with the intracellular metabolic pathways [
11,
12].
Beneficial effects of fullerenol are well documented. In human breast cancer cell lines, C
60(OH)
22 inhibited cancer cells growth and suppressed the doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity [
13]. In the study of Jiao et.al. [
14] fullerenol C
60(OH)
20 has shown antitumor and antimetastatic activity in
in vivo EMT-6 breast cancer metastasis model. Antitumor effect of fullerenol C
60(OH)
20 may be exerted through effects on oxidative stress status, inhibition of formation of angiogenesis factors as well as through modulation of immune profile [
15].
However, fullerene hydroxylation did not provide the absolute absence of the toxicity on living systems [
16,
17]. Additionally, the degree of fullerene hydroxylation affects toxicity [
18,
19]. Therefore, the physicochemical properties of fullerene derivatives are of prime importance for achieving optimal effects in living systems.
In order to further reduce toxicity and even completely eliminate it, as well as to improve the transfer of vibrational modes of C
60 molecules to biological water and biomolecules, the second derivative of C
60, SD-C
60 (C
60(OH)
36@(H
2O)
144-2528), commercial name 3HFWC – Hyper-Harmonized Hydroxylated Fullerene Water Complex
, was designed, syntheses and tested [
20,
21,
22]. In reference [
22] an explanation of the creation of stable water layers around FD-C
60 (fullerenol) and the obtaining of SD-C
60 (3HFWC) as three-dimensional Penrose tilings (3DPT), is given. This is a consequence of the sequential change of the angle between the hydrogen bonds in the water molecules according to the Fibonacci sequence of the Φ number, i.e. by its eigenvalues of T
1u, T
2u, T
1g, T
2g of icosahedral symmetry.
Experimental results with SD-C
60 (3HFWC) in the field of biomedicine, agriculture and cosmetics have shown desirable effects. Specifically, effects on melanoma [
22,
23,
24], influence on Alzheimer's disease [
25], reduction of pain and improved memory in mice [
26], formation of hydrogen peroxide in tomatoes, as well as increase of licopen and regulation on flow of water from the extracellular space into the cell [
27]. Also, good effects on skin hydration, synthesis of collagen and elastin and biphysical properties of the human skin was demonstarted [
28,
29].
Bearing in mind the increasing interest for application of both FD-C
60 (fullerenol) [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38] and SD-C
60 (3HFWC) [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29] in biomedicine and cosmetics, it is necessary to present a comparative physicochemical characterization of them. There are several studies that presented the physicochemical characteristics of fullerenols [
39,
40,
41,
42], but since funerenol can have a different number of OH groups (usually from 12 to 48), there can be significant differences in the properties of fullerones. For this reason, this paper will characterize fullerenol (FD-C
60), which is a precursor to the second derivative of C
60 molecules, SD-C
60 (3HFWC), i.e. with the same number of OH groups. In order to determine size, stability, exothermic and endothermic properties, spectral characteristics and the existence of water shells (layers), research of FD-C
60 and SD-C
60 in a solution and in a dry state was carried out in several laboratories in the Europe, using devices such as AFM/MFM, TEM/STEM,
13C-NMR,
1H-NMR, GPC, ZetaPro, XRD, TGA/DTA, UV-Vis-NIR and FTIR spectrometars.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples preparation
The fullerenol (C60(OH)36) or FD-C60, molecular weight 1332 Da, dust (yellow color), purity 99.99% (as precursor of SD-C60), was ordered, in dark bottle, from Solaris Chem, Canada. It was storaged in a dark room, humidity 35 ±2%, and temperature 20±2°C.
The SD-C
60 (C
60(OH)
36)@(H
2O)
144-2528 ) or 3HFWC, molecular weight 3.826 – 47.126 Da was synthesized at TFT NanoCenter, Belgrade, Serbia (3g fullerol was mixed with 20 L of ultra-pure water for commercial use), according to the patented procedure [
20,
21]. Formation of SD-C
60 start from 0.150 g/L hydroxylated fullerene C
60(OH)
36 in high-purity water (0.05 µS/cm) under the influence of an external oscillatory magnetic field +250/-92 mT, according to icosahedral eigenvalues T
1g, T
2g, T
1u and T
2u (Fibonacci numbers Φ,-Φ,-φ,φ ). At the same time under the internal action of the vibrations of the C
60 molecules (same vibration law as an external magnetic field), the principle: “between a rock and a hard place” in the reactor at 37°C, the formation of 3HFWC, was realized [
22]. Composition of SD-C
60 (3HFWC) was as follows: (1) solid state 2.5-3%, (2) ordered water in chains (crystalline, linear chains between solid state 3HFWC units) 58-60%, (3) fullerenol (around which water layers failed to form) about 0.05%, and (4) free water about 38% [
22]. The SD-C
60 solid state of 2.5-3% is the value of the dry residue that was obtained when the solution is dried immediately before the experiment for its characterization. The SD-C
60 was stored in a dark bottle, at a dark place, at room humidity 35 ±2% and temperature 20±2°C. In relation to when SD-C
60 solutions were produced, there were three solution samples: 3 years old, 2 years old and 8 months old. Investigations of SD-C
60 in the solution state were carried out using UV-VIS-NIR, FTIR, ZetaPro and GPC techniques, while dried SD-C
60 (solid state) was investigated using TEM/STEM, AFM/MFM, XRD, TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR and NMR techniques. Dry samples of SD-C
60 were made immediately before the experiment, which was also the data for how long the solid form of SD-C
60 could survive in the solution (
S2: Supplementary Table 2).
2.2. UV-VIS-NIR and FTIR
UV-VIS-NIR characterization of both FD-C60 (fullerol) and SD-C60 (3HFWC ) were done by Lambda 500 spectrometer, Perkin-Elmer, USA in the range of 250 – 3000 nm, as well as FTIR characterisation of both FD-C60 (fullerol) and SD-C60 (3HFWC) were done by the Spectrum Spotlight 400 FTIR Imaging System, Perkin-Elmer, USA in the range of 2500 - 14000 nm. Also, following instumentations were used for characterization: Near Infrared Spectrometer, PerkinElmer Lambda 1050+ up to 2600 nm, Infrared Spectrometer, Spectrum Two FT-IR Perkin Elmer, Laser HeNe Class 1, Scanned Range 370–7800 cm-1, UV/Vis Spectrometer, Specord 205, Analytik Jena, Resolution ± 0.5 nm, Scanned Range 190 – 1100 nm.
2.3. TEM and HAADF-STEM
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM ) analysis of dry particles of both FD-C60 (fullerenol) and SD-C60 (3HFWC) ware performed in order to determine their solid state size. The samples in liquid state ware applied to the TEM copper mash coated with carbon and dried at air. After drying the samples, they were analyzed and recorded in three TEM laboratorises: (1) the CM12 Philips/FEI Transmission Electron Microscopy, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, magnification x45,000 and x60,000 (solution was 6 months old), (2) TEM, JEM 1400, JEOL, Japan, magnification x 120,000 up to x 200,000 (solutions were 8 months old and 3 years old). and (3) HAADF-STEM: High Angle Annular Dark Field - Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy, Thermo-Fisher Talos / Osiris 200kV, Zeis Libra 120kV, 200kV electron energy, STEM mode with bright field, Evaluation software Thermo-Fisher Velox 3.7 and EDXS: energy dispersive X-ray analysis EDXS mapping = ChemiSTEM, with Z > 8 instaled (solution sample was 8 months old).
2.4. AFM/MFM
AFM/MFM characterization of FD-C60 and SD-C60 was done after drying on copper coated with carbon, the samples (solution was 8 months old) were stored in dark closed containers and kept at room temperature until use. Characterization of dry samples was done by JSPM-5200, Scanning Probe Microscopy, JEOL, Japan. Two methods were used: AFM (Atomic Force Microscopy), and MFM (Magnetic Force Microscopy). Both techniques are non-invasive: AFM method is based on van der Waals forces and London-type dispersive forces between tip and sample, while MFM, in the non-contact imaging mode, is based on magnetic dipole-dipole interaction between tip and sample (measuring ± deflection of tip “φ” in deg.). For the purpose of magnetic gradient investigation, specialized cantilevers, type HQ NSC18/Co-Cr Al BS (Micro Mash, Estonia) with force constant in the range between 1.2 and 5.5 N/m and with the resonant frequency range between 60 to 90 kHz were used. Scan sizes at 30 nm, 100 nm and 300 nm were performed.
2.5. XRD
Powder x-ray diffractogramms (XED) were recorded on a Rigaku SmartLab 3kW from 5 – 85° 2Theta at room temperature. For preparation, an aqueous 3HFWC solution was lyophilized for 7 days to a brownish powder. Fullerenol was used as powder as delivered from Solaris Chem, Canada.
2.6. TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR
TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR measurements were performed on a STA 449C Jupiter (TGA/DTA), Aeolos QMS 403 C (MS) from the company Netzsch, Germany and a Bruker Tensor 27 with gas chamber (FTIR). Lyophilized 3HFWC and fullerenol that was dried under vacuum (10 mbar / 30 °C) were weighed in Al2O3 crucibles. During measurement, the samples were heated from 30 to 900 °C with a constant heating rate of 10 K/min under synthetic air atmosphere.
2.713. C- NMR and 1H-NMR
Avance DRX 400, Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Cryo Frequency 400 MHz (1H) and 100 MHz (13C),temperature 300 K, solution saturated solution. The sample was dissolved in D2O and 1H and 13C spectra were recorded. 1H-NMR spectrums are done with water suppression while 13C-NMR spectrums are made with water suppression without TMS.
2.8. Zeta potential
Zeta Potential by electrophoretic light scattering, Analytical instrument, BeNano 180 ZetaPro. Sample preparation: Roller mixer measuring temperature 25°C, measuring cell -Folded Capillary Cell, repetitions 5 fold measurements, evaluation mean value from 5 measurements.
2.9. GPC
Precolumn PSS Suprema, 5 µm, Guard, ID 8.0 mm x 50 mm PSS Suprema, 5 µm, 30 Å, ID 8.0 mm x 300 mm PSS Suprema, 5 µm, 1000 Å, ID 8.0 mm x 300 mm PSS Suprema, 5 µm, 1000 Å, ID 8.0 mm x 300 mm Pump PSS SECcurity 1260 HPLC-pump Flow rate 1.0 mL/min Injection volume 100 µL, temperature 35 °C, detectors PSS SECcurity refractive detector (RI) PSS SECcurity ultraviolet light detector (UV) Calculation PSS-WinGPC Unity Version 8.4. Sample preparation for gel permeation chromatography (GPC) is based on procedure that the received sample solutions have been transferred into injections vials and injected by an autosampler without any further pre-treatment. Several pullulan standards with different molecular weight were measured to get a calibration curve. The calculation of the average molecular weights and the molecular weight distribution of the samples was done by the so-called “slice by slice” method based on the pullulan calibration.
3. Results
Since two spectroscopic domains 2,500-3,300 nm and 6,000-7,000 nm are important for fullerenol and 3HFWC application in biomedicine, we will begin the presentation of similarities and differences between them with these results. The first spectra domain is important for the organization of water molecules into water layers (shells), while the second domain is important for the biophysical influence of the first and second C60 derivatives on biomolecules. Beside water (…H-O-H…O-H…O-H…) and DNA (A=T, C≡G) the amide-I (…H-N-C=O…H-N-C=O…) hydrogen bonds have very important rule for secondary structure of biomolecules (proteins), their stability, conformation states and functionality.
3.1. NIR and FTIR spectroscopies
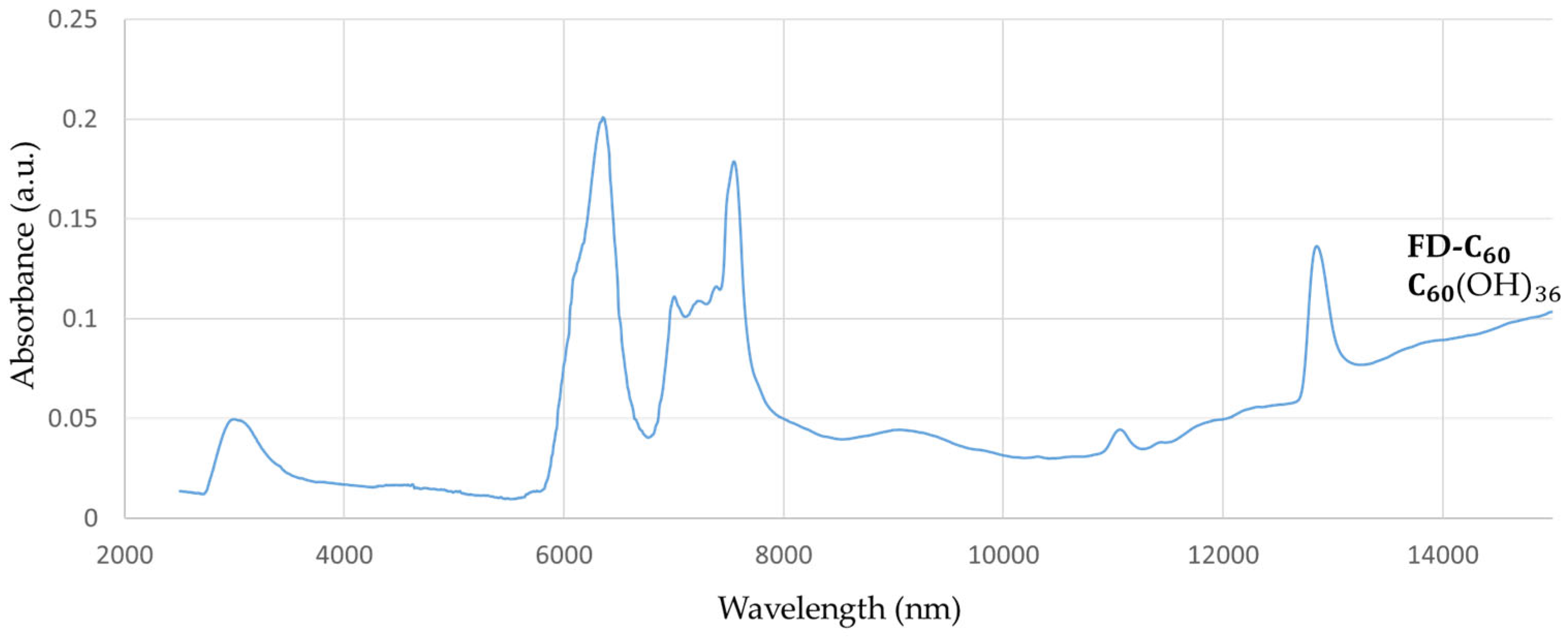
FD-C
60 (fullerenol with 36 OH groups, in average,
Supplementary Materials S3: Supplementary Figure S1) has one peak at 3,088 nm, with low intensity (0.05 a.u.), which means that it contains OH groups and has hydrogen bonds that are connected to water molecules as humidity (
Figure 1). There are also three more peaks at 6,377 nm, 7,562 nm and 12,865 nm with peaks intensity 0.20, 0.17 and 0.13 a.u. respectability, that can affect biomolecules via vibrational modes.
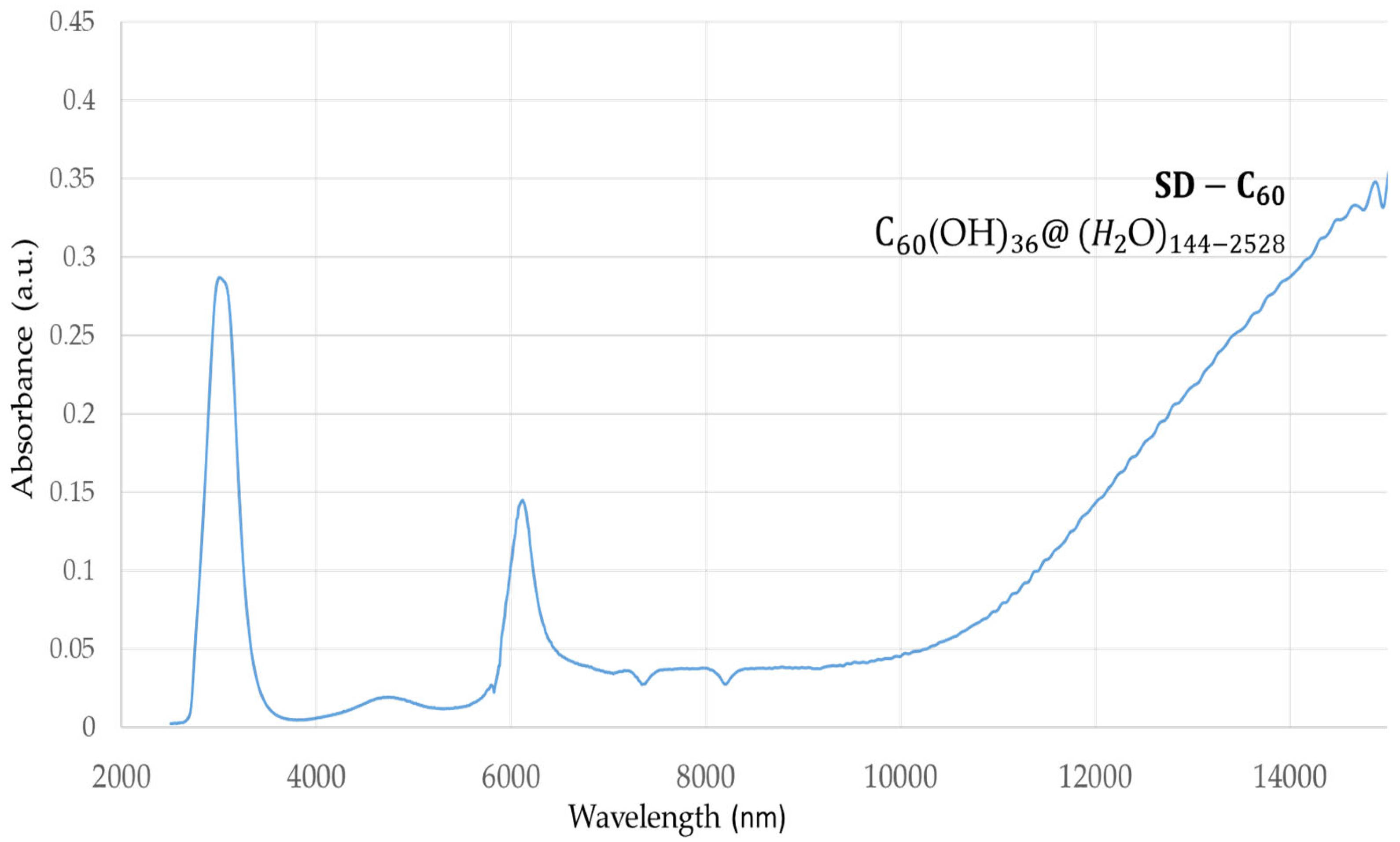
SD-C
60 (3HFWC, whose precursor is fullerenol with 36 OH groups) has a peak at 3,064 nm with an intensity of 0.28 a.u., which shows that due to the OH group, water from humidity also has water layers (
Figure 2). In addition, there is one peak at 6,132 nm, intensity 0.14 a.u. and one area from 10,000 nm to 15,000 nm, with an intensity of 0.05 a.u. up to 0.35 a.u..
If peaks from
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 are compared at around 3,000 nm, it can be seen that the peak is 5, 6 times more intense with 3HFWC than with fullerenol. This result shows that there are many more hydrogen bonds in 3HFWC than in fullerenols. Nature of that intramolecular water hydrogen bonds, which first formed rings on surface of sphere (“chelate”) and then order them in closed water shell as a three-dimensional Penrose tiles [
22]. The C
60(OH)
n replaced the ion role (in classical sense) in the center of the coordinate bonds that is the reason why “chelate” is written in quotation marks. As fullerenol (C
60(OH)
n) was a precursor for 3HFWC, when we subtract the intensity of the peak of fullerenol from 3HFWC, we get the intensity of the peak of only hydrogen bonding water shells (layers) of 3HFWC, which is 0.23 a.u.. Also a big difference in peak intensity of about 0.22 a.u. is in the range of 10,000-15,000 nm, which gives a 2,7 times higher value of the intensity of the effect to biomolecules.
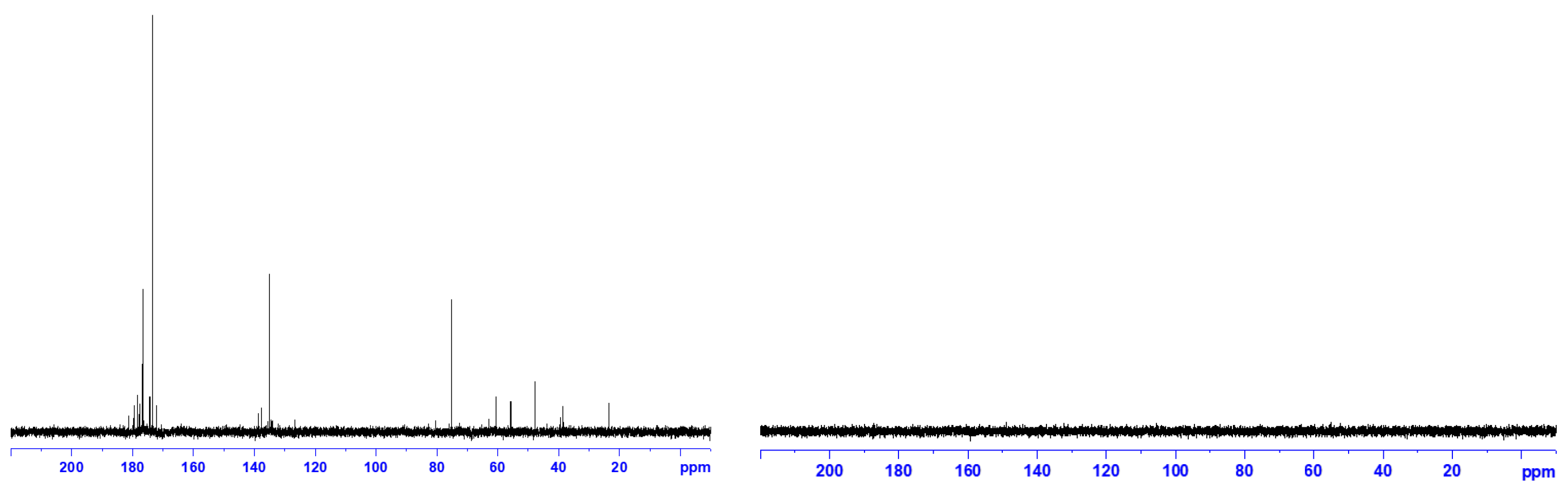
3.2. 13C-NMR and 1H-NMR
The results of the characterization of fullerenol and 3HFWC using
13C-NMR and
1H-NMR showed similarities and differences between these two substances (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). The
13C-NMR spectra of fullerenol has peaks from 172 to 181 ppm (the number of OH groups: 32, 36, 44, 48 with dominant peak 176.49 ppm, 36 OH groups), while signals (126-138 ppm) showing C=C bond in the C
60 molecule, as well as C-O-H bond (75,25 ppm), were observed. Having in mind that the intensity for 36 – OH groups is much higher it can be concluded that the most abundant number of –OH groups is 36 (
Supplementary Materials S3, Supplementary Figure S1).
As can be seen, not a single peak was observed in the 13C-NMR spectrum of 3HFWC. This indicates two possibilities; either the 13C signal was so weak (in nature only 1.1% of carbon atoms is 13C) that the device could not detect it or the 3HFWC water layers absorbed the 13C magnetic signal. Bearing in mind that the same fullerenol material was used in both cases, with the same concentration (0.150 g/L), we are more inclined to think that the 13C signal was absorbed by water layers than that it was not detected due to weakness. However, in order to give a valid conclusion, it is necessary to do additional research.
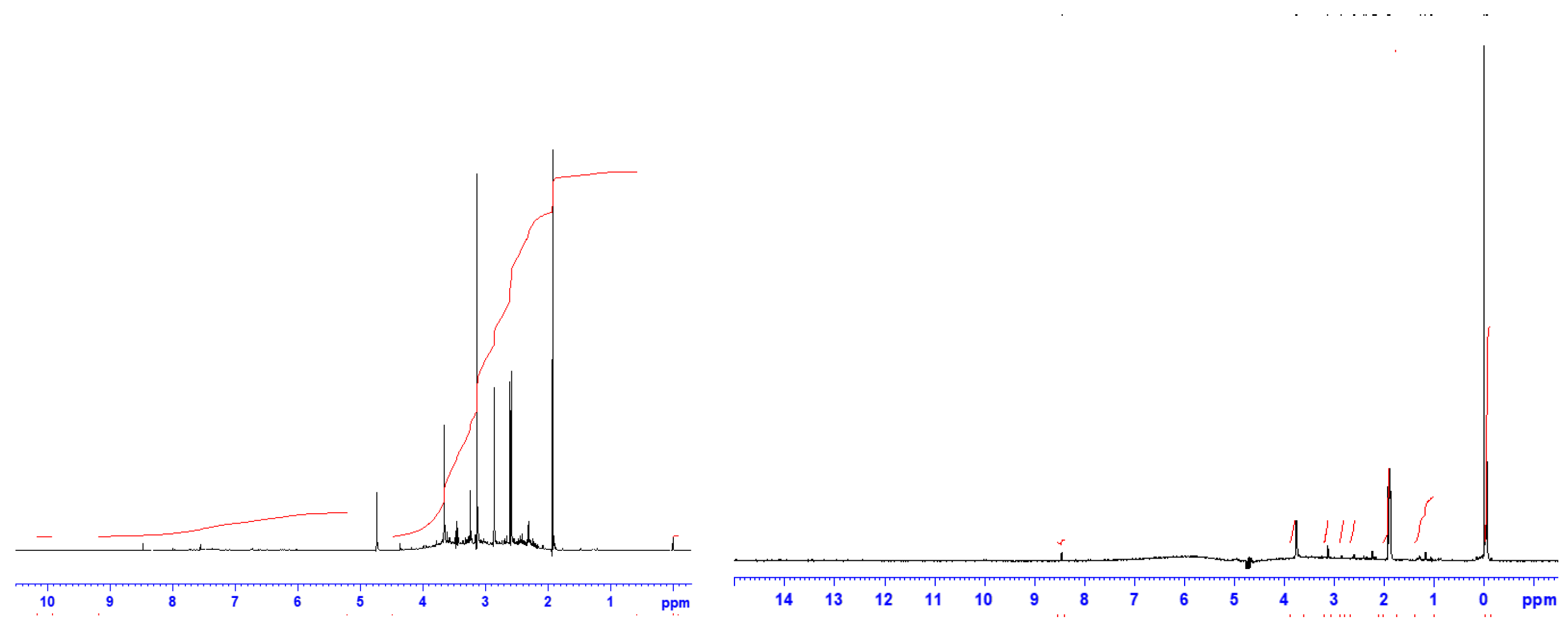
1H-NMR spectra, both ppm and integral, of fullerenol and 3HFWC without TMS is present on
Figure 4 and
Table 1.
Significant chemical shift of 3HFWC in
1H-NMR spectra (without TMS), is on 8.45 ppm, while fullerenol has many peaks between 8.76 and 4.81 ppm. Integral spectra of 3HFWC has value 3.57, while fullerenol has 15.31. This values structures and values tell us that protons of 3HFWC has a higher symmetry order then fullerenol (
Supplementary S4: Supplementary Figure S2).
3.3. TEM images
TEM images of dry fullerenol and dry 3HFWC were done in three independent laboratories. Samples of 3HFWC solutions, before drying, were old from eight months to three years. The information on the age of the solution speaks about the stability of 3HFWC (soft solid state, which will become a dry residue during drying) in the given solution. Fullerenol was prepared as solution and drying just before experiments.
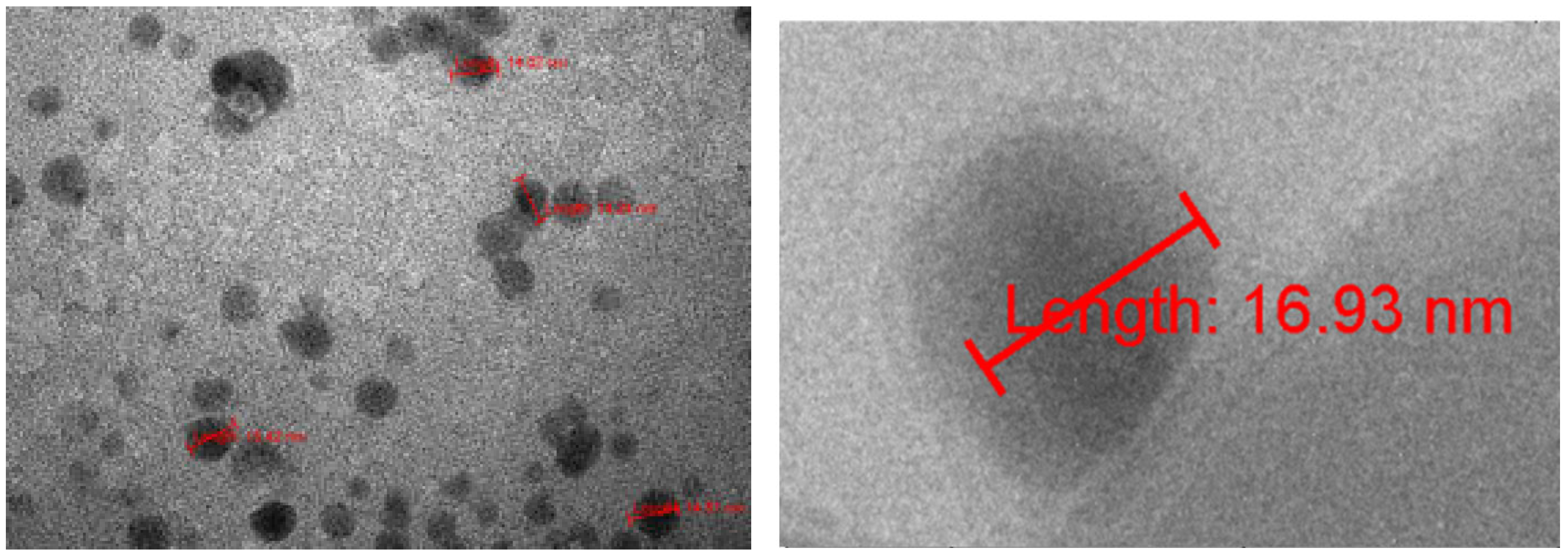
TEM characterization showed that fullerenol has diameter 2.0±0.6 nm (
Figure 5, left) and under humidity can be clustered, forming large agglomerates (a few hundred nano meters), molecular weight is between 1,230 – 1,536 Da, (average 1,332 Da). In theory fullerenol is about 1.3 nm which indicates that at room temperature and normal room humidity 35-45%) fullerenol is organized as a monomer (1.3 nm) and dimer (2.6 nm).
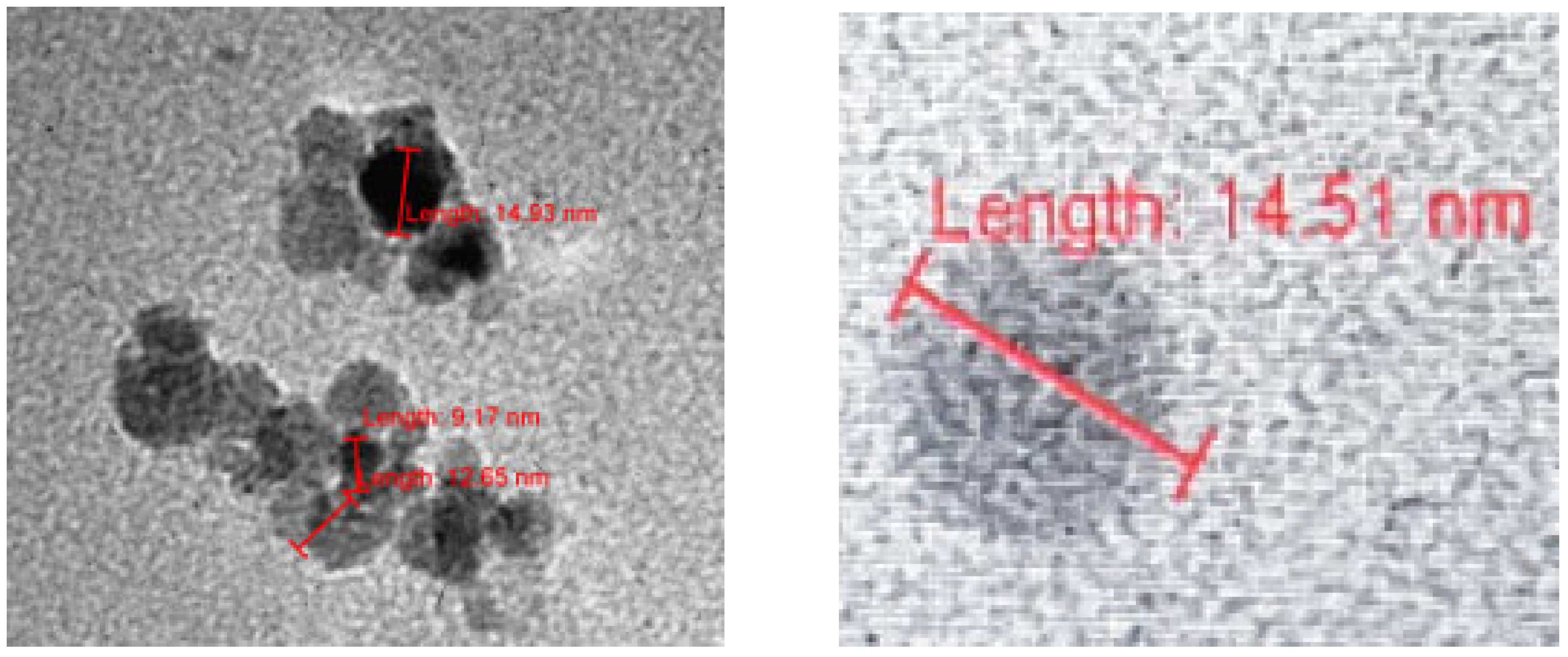
All three TEM laboratories (two at the University of Belgrade and one at LAUS, Germany) obtained similar results for the dry 3HFWC (SD-C
60). Dry state of 3HFWC showed a spherical nano particle in size from 10 nm to 30 nm (
Figure 5(right),
Figure 6 and
Figure 7).
3.4. AFM/MFM images
Results of AFM/MFM characterization of both dry substances, fullerenol and 3HFWC, are presented in
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12. In
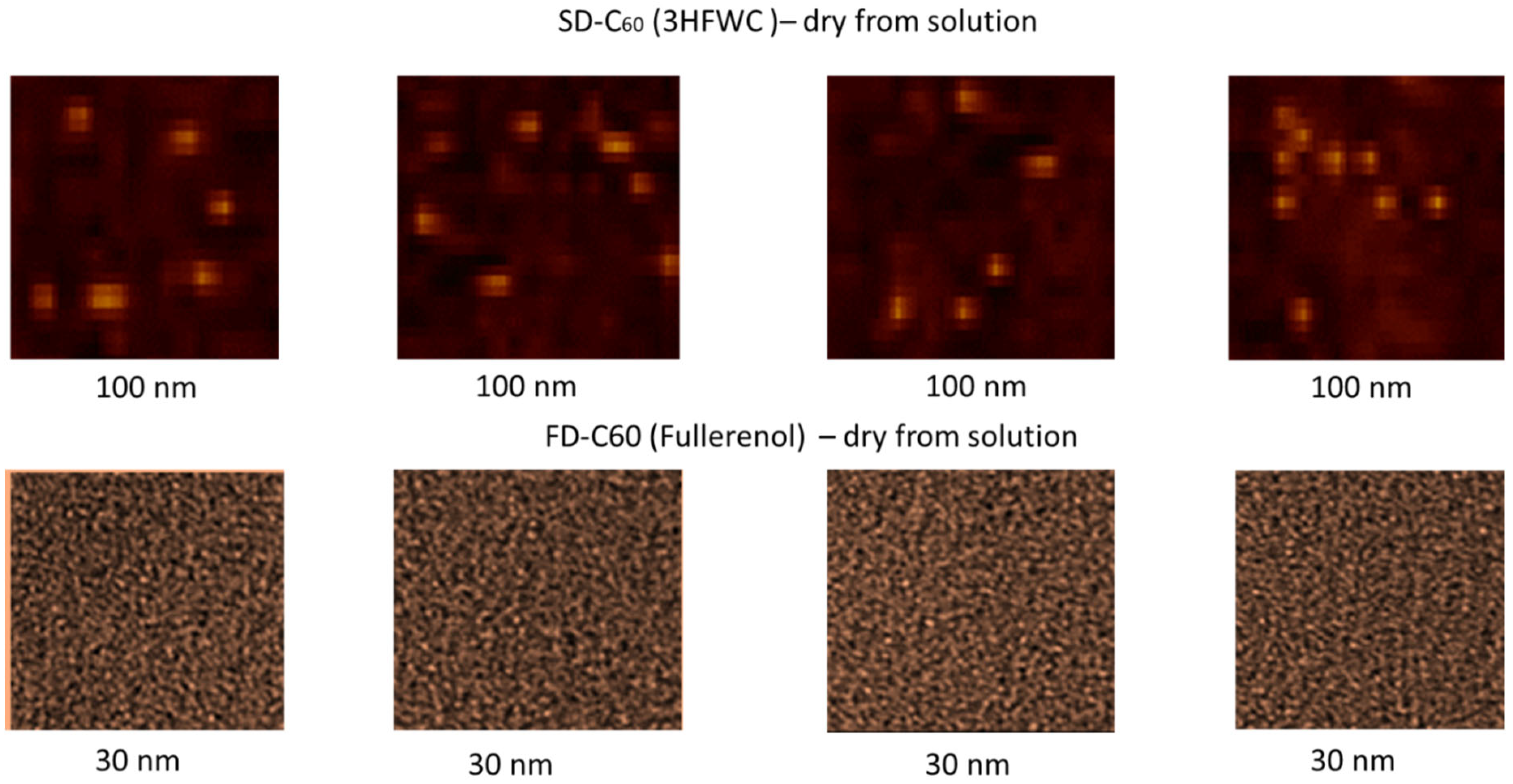
Figure 8 shows four images of fullerenol and 3HFWC each. The pictures clearly show the dimensions, shape and number of particles. Fullerenol is most often organized as a dimer (size 2.6 nm, two molecules are liked with water molecules from humidity), while 3HFWC is seen as an individual particle with a size of about 15-30 nm.
A higher resolution of fullerenol and 3HFWC is shown in
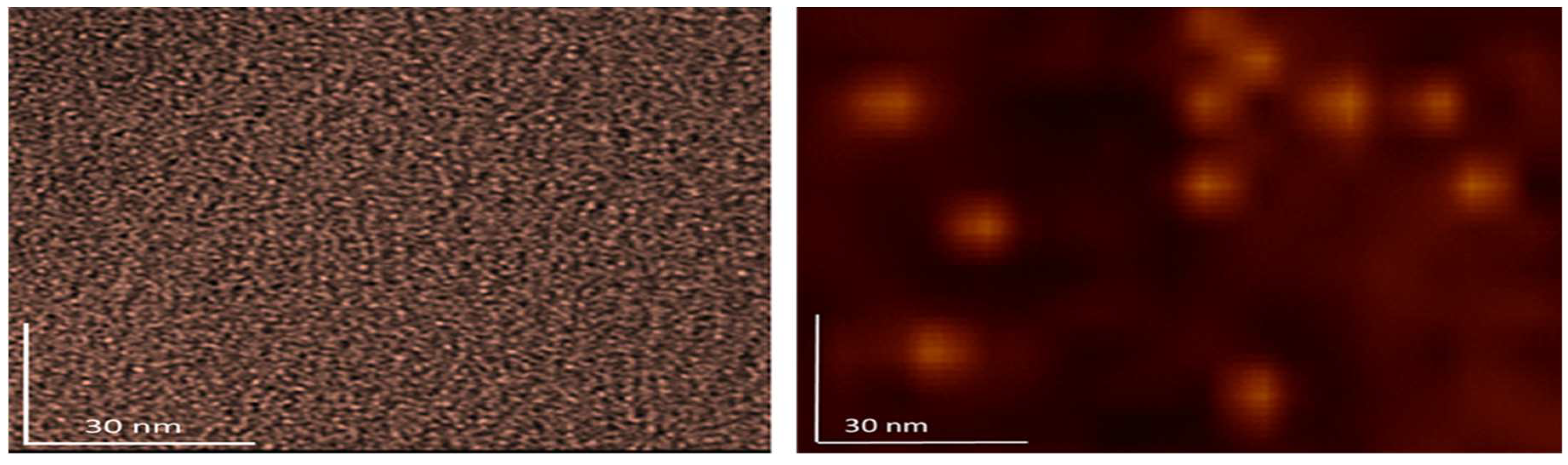
Figure 9. With fullerenol, in addition to dimers, organization into trimers can be seen, but in most cases it is a granular molecular structure of monomers. In the case of 3HFWC, spherical monomeric structures with a size of about 10-15 nm are clearly visible.
The exact value of 14.7 nm, one of several SD-C
60 (3HFWC) is shown in
Figure 10. A similar or the same value of the size of 3HFWC was obtained on several TEM images, which indicates that the most frequently recorded size of SD-C
60 (3HFWC) is around 15 nm.
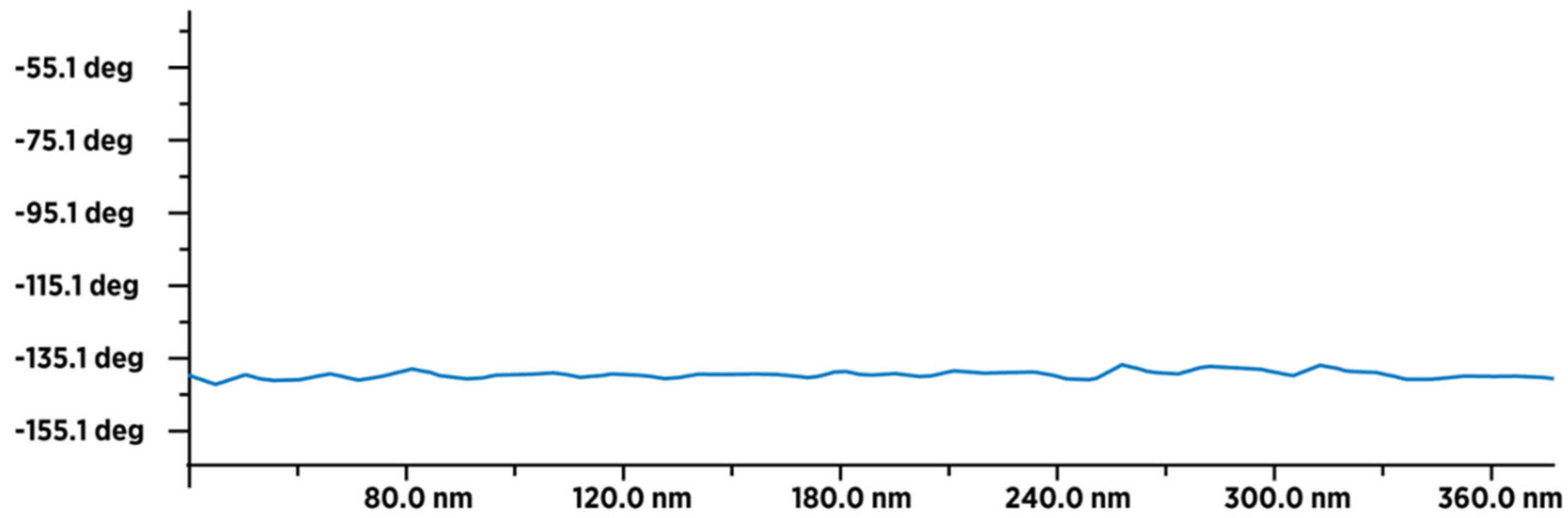
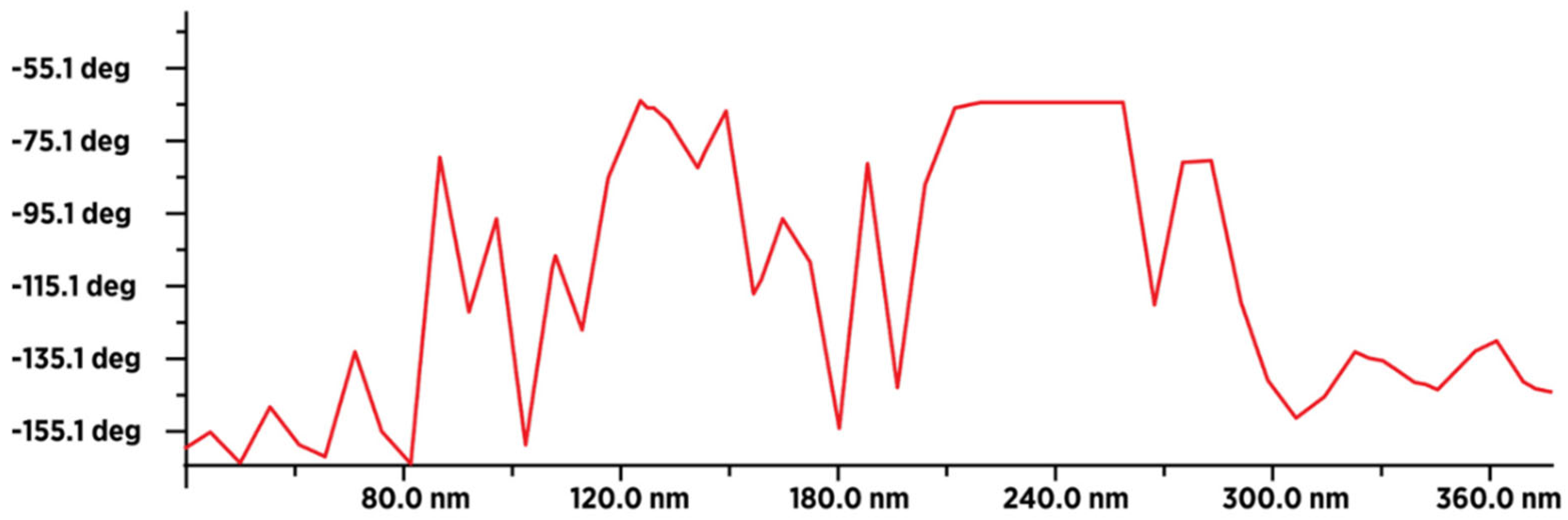
The result of a comparative examination of the presence of water in dried fullerenol (FD-C
60) and dried 3HFWC (SD-C
60) using MFM (Magnetic Force Microscopy) shows that fullerenol contains a minimal number of water molecules that originate from humidity during measurement (
Figure 11), while 3HFWC has significantly more pronounced peak values and contains a significantly larger number of water molecules (
Figure 12). The comparative presentation of the MFM values of fullerenol and 3HFWC on one diagram is shown in
Supplementary Materials S5: Supplementary Figure S3) and is in agreement with the previously presented results [
22].
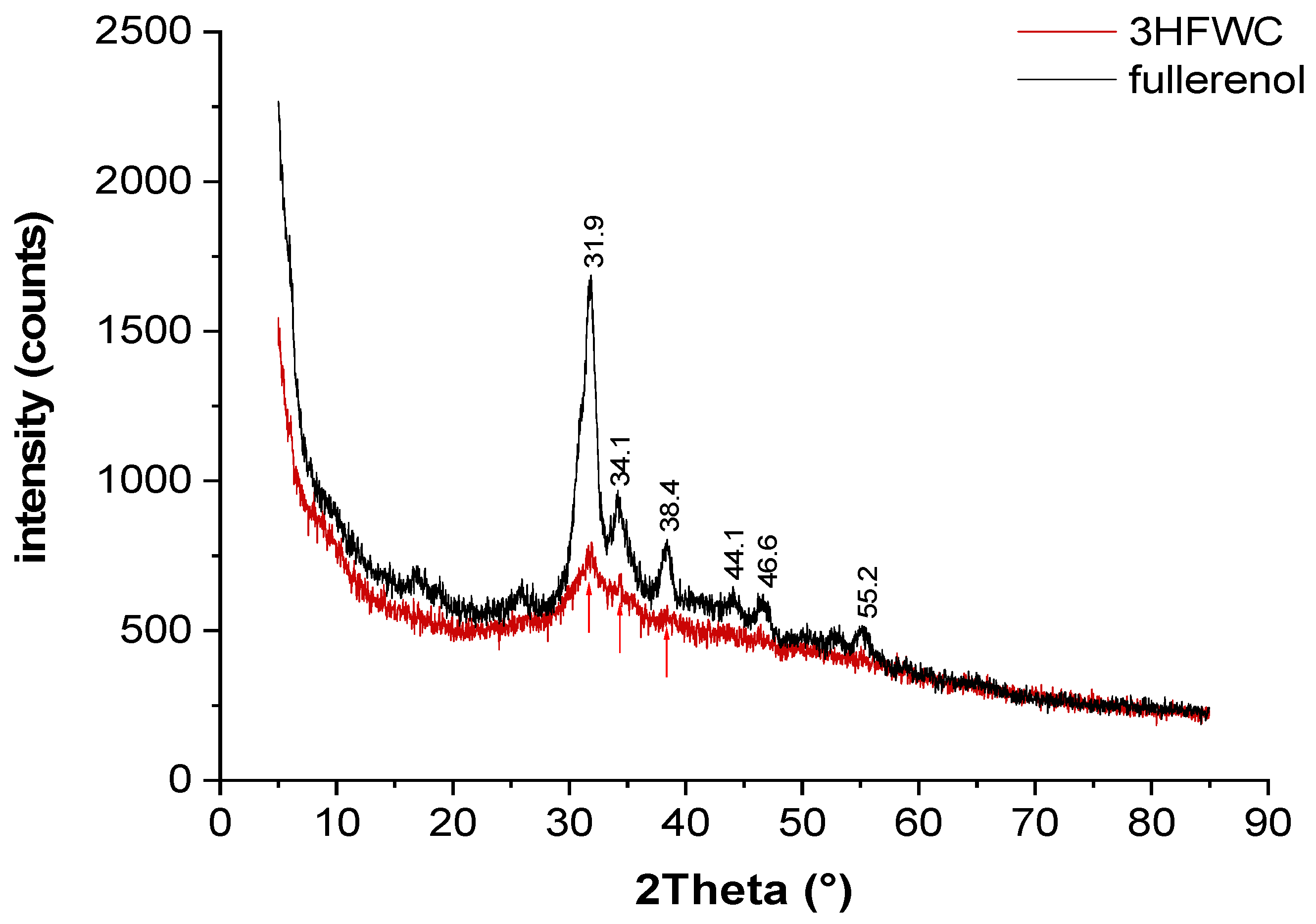
3.5. X-ray diffraction (XRD)
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed to see if there is difference in fullerenol and 3HFWC samples structural order (
Figure 13).
Fullerenol was used as-delivered (yellow dust material) and was additionally dried under vacuum (10 mbar / 30°C); 3HFWC was lyophilized to a powder prior to the measurement.
Both fullerenol and 3HFWC are hydrophilic. Lyophilized fullerenol is a molecular powder with interstitial water clusters formed from humidity. The XRD patterns of fullerenol show broad Bragg peaks at 27 – 57° 2Theta due to partial crystallization of interstitial water. Higher water content (humidity + extra water) in 3HFWC induces a decrease in reflex intensity and further broadening of the reflexes. This indicates that the structure of 3HFWC is less ordered, caused by extra water, which molecules are organized in aperiodic three-dimensional Penrose tilings with different “lattice” size (there is sixteen different tiling types [
22]). The Penrose three-diminsional tiling pattern (3DPT) is a type of quasicrystal, which means that it has an ordered yet never-repeating structure.
However, it is precisely this organization that enables SD-C
60 (3HFWC) to have exothermic properties at a temperature of 133
°C, while fullerenol has endothermic properties at 100
°C (
Figure 14 and 15).
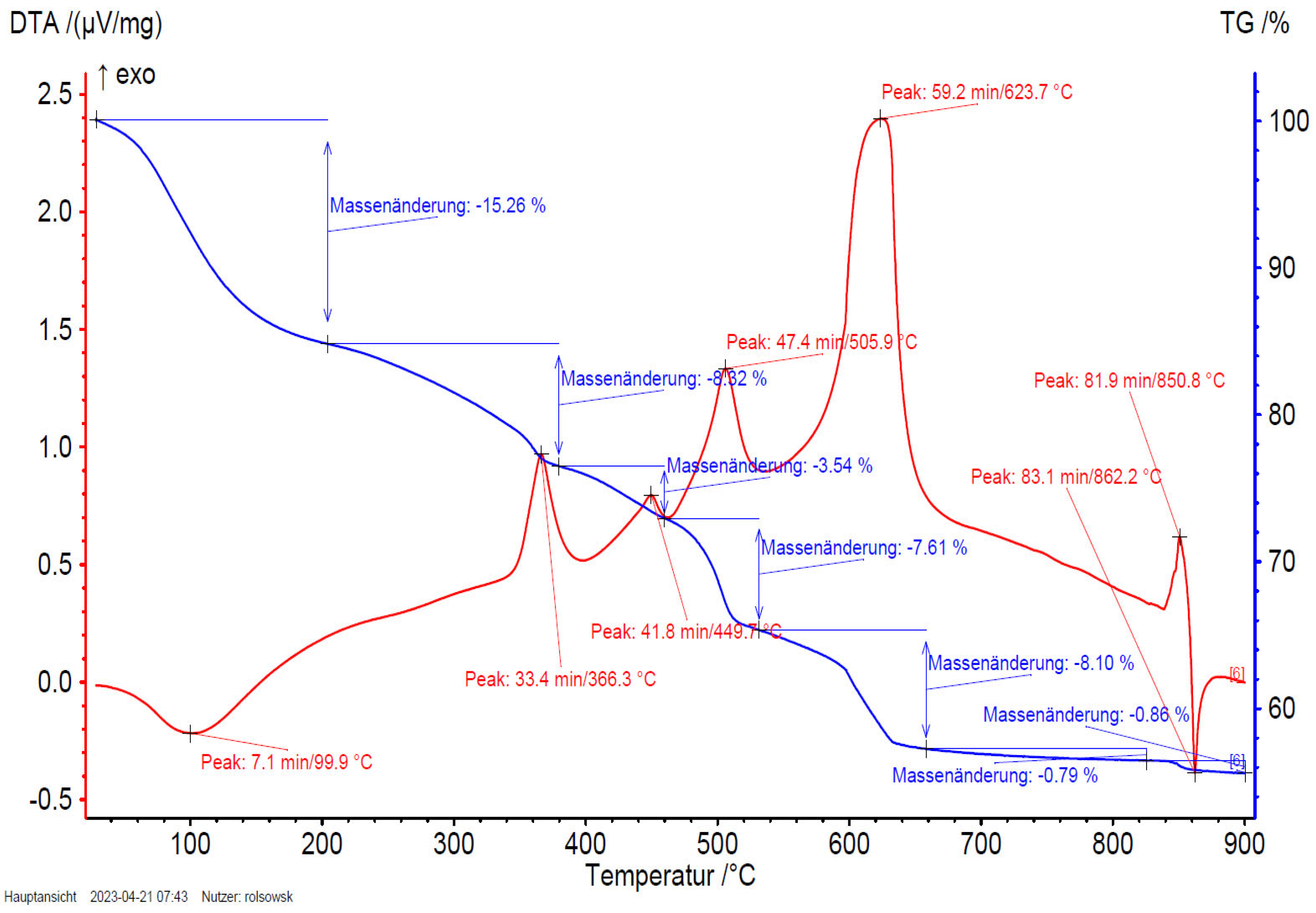
3.6. TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR
Figure 14 and
Figure 15 show the results of TGA/DTA measurements of fullerenol (
Figure 14) and 3HFWC (
Figure 15). As 3HFWC is supposed to be used as a cosmetic product, the focus in the interpretation of the results will be on temperature processes < 200 °C. In this temperature range, adsorbed solvents and water layers will be removed.
The mass loss of the sample fullerenol in the first mass loss step is 15.3 wt%. Taking into account that 3HFWC was freeze-dried at 0.37 mbar and 20°C before measurement, it is noticeable that the mass loss up to approx. 200°C is still high at 10.5 wt%. Interestingly, the corresponding DTA results of these processes show different enthalpies. While the first mass loss is an endothermic reaction in the sample fullerenol, 3HFWC shows an exothermic reaction. Additionally, the maximum of the DTA process is shifted to a higher temperature in 3HFWC. While the DTA peak in the endothermic process of fullerenol is at 100 °C, the peak maximum of 3HFWC is located at 133°C.
TGA is showing the mass loss of a sample during heating and sample decomposition, while DTA is showing if the single decomposition processes are of an endo- or exothermic nature. Exothermic reactions are releasing energy. In contrast, endothermic processes, like the evaporation of solvents, need additional energy to be initiated. Thus, a DTA measurements can indicate differences in the binding ratios of different substances during their decomposition.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermo analysis (DTA) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) and infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) are performed of 3HFWC to identify differences in the bonding of water layers.
Both, MS and FTIR have demonstrated the release of water at temperatures below 200 °C under synthetic air conditions. 3HFWC releases water in an exothermic reaction; fullerenol in an endothermic reaction. Even under the same sample treatment in vacuum, the difference in the reaction enthalpies, while releasing water, were obtained.
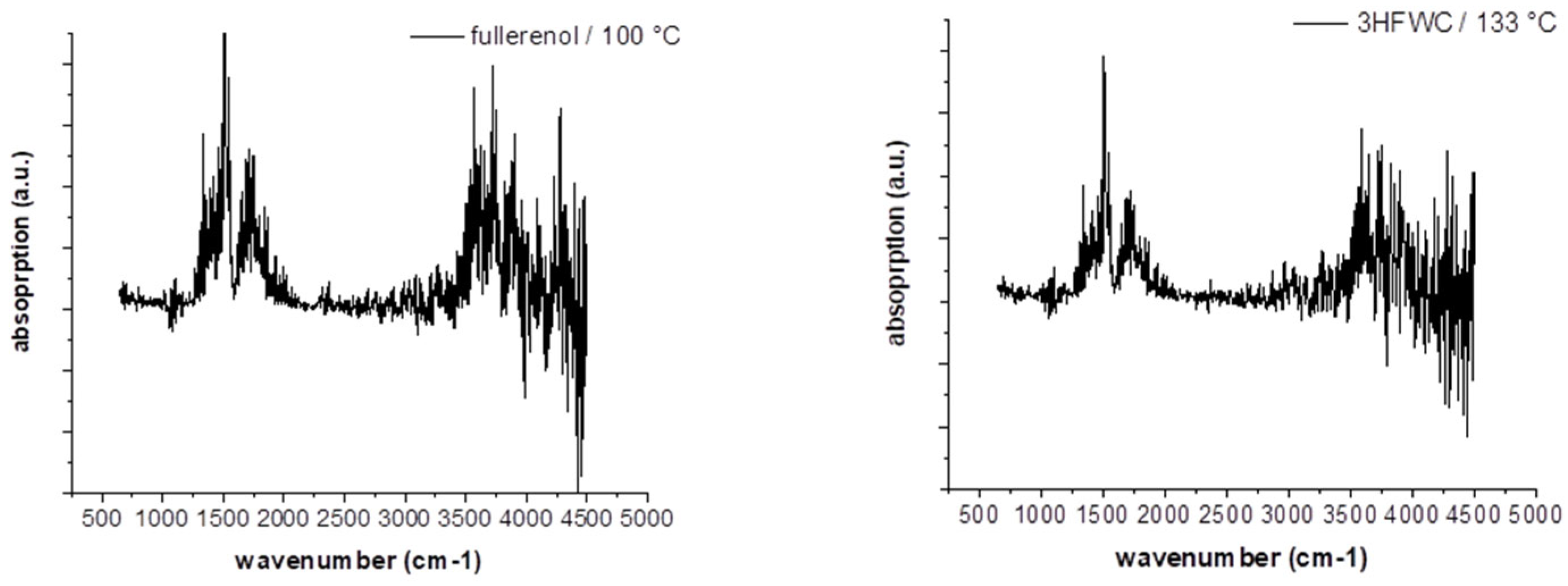
Figure 16 shows the FTIR-spectrum of fullerenol at 100°C and 3HFWC at 133°C at the temperature of the DTA signal’s maximum. In case of MS (
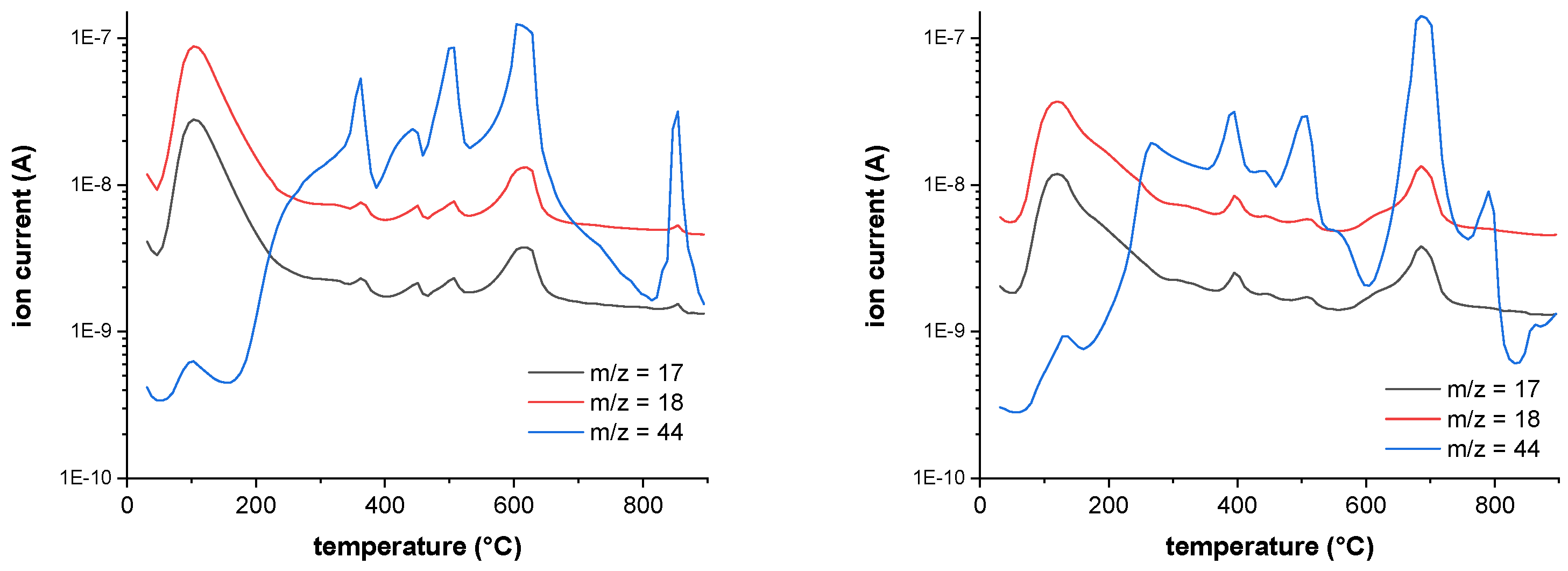
Figure 17), the m/z fragments, which can be detected below 200 °C – 17 (OH
+), 18 (H
2O
+) and 44 (CO
2+) – are plotted.
FTIR indicates a release of only water, which is underlinded in MS due to high ion currents of m/z = 17 (OH+) and 18 (H2O+). CO2 (m/z = 44) is also released in a small amount with an ion current of 2 potencies less (10-9 → 10-7).
The decomposition of 3HFWC and fullerenol at higher temperatures (< 800°C) takes place in a similar way with a tendency that the DTA signals at 3HFWC are usually slightly shifted to higher temperatures. This indicates differences in the structure of the two samples and highlights the differences in the water layers of 3HFWC, as even with the same pretreatment, the differences in reaction enthalpies can be seen.
As no additional bands and m/z fragments can be detected in fullerenol, water is also released from 3HFWC and no further decomposition processes take place below 200 °C. Bearing in mind, 3HFWC releases water in an exothermic reaction, water molecules are bond to 3HFWC in a different way than in fullerenol.
Interestingly, the last decomposition process at 850 – 860°C shows an endothermic process in the decomposition of 3HFWC, but an exothermic followed by an endothermic process in fullerenol. This different decomposition behavior also indicates a difference in the structure of the samples.
3.7. GPC
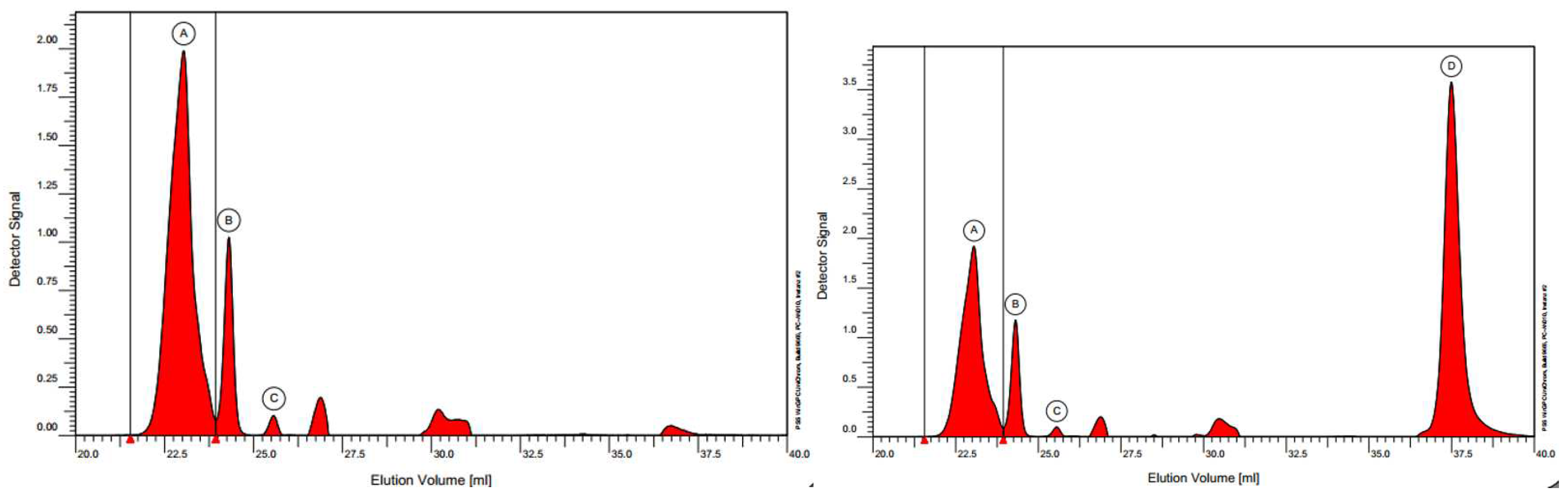
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) results of fullerenol (FD-C
60) and 3HFWC (SD-C
60) analysis of the UV signal at 250 nm are presented in
Figure 18. As fullerenols are expected to exhibit UV activity, calculations of molar mass distributions have only been carried out for the UV active species. Peak areas of refractive index (RI) signal of side components have been analyzed as well. Peaks at elution volumes of appr. 27 and 31 mL are presumably system peaks.
Summary of GPC results for 3HFWC: The peak-area of fullerenol shows 3 different separated peaks while for 3HFWC shows 4 different separated peaks. The relative content of each “species” and the molar mass at the peak maximum, Mp, is different. Three peaks and their oberserved masses are within the calibration curve and one (peak D) is out of the calibration curve. We assume it was a 3HFWC with water layers. The mass of the 4th peak (D) cannot be determined, but it should be more hydrophilic than the fullerenol.
3.8. Zeta potential
At the same concentration of C
60(OH)
36 (0.150 g/L) in water (pH= 6.24, conductivity 2.2 μS/cm) for fullerenol (FD-C
60) solution the pH = 9.349, while for 3HFWC (SD-C
60) solution the pH=7.107 (
Table 2).
Zeta potential (ZP) value is very important criteria for stability of substance (
Supplementary Materials S7: Supplementary Figure S5). ZP of fullerenol is -25.85 mV, while for 3HFWC is -43.29 mV, what indicate that 3HFWC is more stable than fullerenol. These findings clearly underline the difference between 3HFWC and its precursor (fullerenol) (
Table 2).
The zeta potential (electrostatic charge) of 3HFWC is higher than that of fullerenol of equivalent concentration. This is due to the hydration shells of water surrounding the fullerenol molecules having more ordered bonding and, thus, greater polarity. This explains the stability of 3HFWC, as greater electrostatic charge, greater electrostatic repulsion between 3HFWC molecules and less agglomeration/sinking.
4. Discussion with summary
Characterization of fullerenol (FD-C
60) and 3HFWC (SD-C
60) in solution form, at a temperature of 20°C±1°C using NIR and FTIR spectroscopy showed differences in the spectrum between these two substances in the range of 2,500 – 3,300 nm (NIR) and 2,500 -14,000 nm (FTIR). Using NIR spectroscopy, in addition to an atmospheric pressure and the temperature of 20
°C for 3HFWC (SD-C
60), spectra at temperatures of 80
°C, 90
°C, 120
°C and 140
°C were performed (
S8: Supplementary Figure 6). The obtained results indicated that at some of the temperatures between 120
°C and 140
°C, water layers evaporate, i.e. non-covalent hydrogen bonds are broken. At what exact temperature does the breaking of hydrogen bonds occur was given by testing TGA/DTA. This happens at a temperature of 132.9°C (133°C), while with fullerenol evaporation (moisture) happens at 100°C.
13C-NMR and
1H-NMR show clear difference in structure of fullerenol and 3HFWC. The absence of a peak on
13C-NMR spectrum of 3HFWC can be interpreted in two ways: a weak signal (because only 1.1% of carbon atoms in nature is
13C), but bearing in mind that we obtained clean signals with the same material in the form of fullerenol, we suspect that it is possible that the water layers of 3HFWC may absorbed the
13C signal. Also, the comparison of the FTIR signal intensity for C
60, fullerenol, and 3HFWC (
Table 3) indicates that the vibrational peaks of C
60 (with the corresponding shift) are present both in fullerol and in 3HFWC, but there is a big difference, up to 7 times when it comes to 3HFWC. The difference in peak intensity between C
60 and fullerenol is almost non-existent. To confirm the absence of the
13C-NMR signal of 3HFWC and explain differences in FTIR spectra of C
60, fullerenol, and 3HFWC, additional extensive research is needed, which we intend to carry out in the near future.
Characterization of the dry 3HFWC substance using TEM was performed three times: 2018, 2019 and 2023 in three independent laboratories (
Supplementary material S2). The age of the substance was from several months to 4 years. In all cases, it was shown that the size of 3HFWC in the dry state is in average 15 nm, depending on the number of water layers it contained. The characterization of fullerenol was performed only once in 2023 and it was shown that the size is 1.3 to 2.6 nm, and in some cases around 1 μm, which indicates that as soon as it comes into contact with moisture from the air it forms aggregates. Similar results are obtained with AFM/MFM characterization. 3HFWC is observed in size 10−30 nm as one body object. Fullerenol is in size 1.2 −1.4 nm as one body object and from 2.5 to 6.0 nm as aggregates. Magnetic Force Microscopy spectra of 3HFWC and fullerenol is different. Since intensity of magnetic spectra is proportional to number of dipole-dipole interaction it means that 3HFWC is more rich with molecules which possess dipoles (water in layers) then fullerenol (only water from humidity).
Stability and pH values are important for substances which are used for biomedicine and cosmetics. The value of the Zeta potential of the 3HFWC substance is - 43.29 mV, which indicates that it is very stable while fullerenol has a value of -25.85 mV, which indicates that it is at the limit of stability. Also there is difference in pH values, 9.35 for fullerenol and 7.11 for 3HFWC.
In the paper, the contradiction regarding the results of the degree of order of the structures of fullerenol and 3HFWC obtained with 1H-NMR and XRD is explained. When the order of protons in the structure is observed, then 3HFWC is more ordered than fullerenol. The reason for this lies in the possibility of O-H rotation in the C-O-H structure, so that the hydrogen atom can occupy various positions. Bearing in mind that it is about 36 OH groups, the position of the hydrogen atom is a very complex system. However, with 3HFWC this is not the case because all hydrogen atoms in the precursor (fullerenol) and in three-dimensional Penrose tiling (3DPT) are fixed. But if these two structures are considered from the aspect of classical crystallography (XRD), then fullerenol has a more ordered structure than 3HFWC because fullerenol is a molecular crystal structure while 3HFWC is a quasi-crystalline molecular structure, because 3DPT (in water layers) are aperiodically ordered.
TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR measurements showed the release of water at temperatures below 200°C under synthetic air conditions. There are differences in the bonding and release of the water layer. 3HFWC releases water (humidity water + extra water) in an exothermic reaction; fullerenol (humidity water) in an endothermic reaction. Even under the same sample treatment in vacuum, the difference in the reaction enthalpies while releasing water were obtained.
SD-C60 (3HFWC: C60(OH)36@(H2O)144-2252+humidity), shows a different decomposition behavior under synthetic air atmosphere than FD-C60 (fullerenol: C60(OH)36 +humidity). The main differences are: (1) 3HFWC shows and exothermic reaction at 133°C under release of water, while (2) fullerenol shows and endothermic release of water at 100°C. Except for one exception all decomposition steps are slightly shifted to higher temperatures. The exception is the last exothermic process, which is shifted to lower temperatures at 3HFWC.
In summary, the core result is that water is bound in a different way in SD-C60 (3HFWC), than in FD-C60 (fullerenol), and fullerenol and 3HFWC are two different substances in terms of structure, size and physicochemical properties.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. S1: Icosahedral symmetry group S2: Characterization of dry 3HFWC in five independent institutions, S3: Fullerenol OH groups determination, S4: Structure order of fullerenol and 3HFWC, S5: Water presence in fullerenol and 3HFWC, S6: Zeta potential of fullerenol and 3HFWC, and S7: NIR Spectra of 3HFWC for different temperatures.
Author Contributions
Investigation, visualization, formal analysis, and writing—original draft preparation and editing, Dj.K. and L.M.; investigation, formal analysis, S.I., D.K., C.B., A.K., and V.P.; conceptualization, supervision, formal analysis, data curation, and writing—review and editing, Dj.K,.; conceptualization, methodology, resources, and writing—review and editing, L.M.; supervision, formal analysis, data curation, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, D.K., B.W and S.D, substance manufacturing and project administration, J.J. and N.J.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Grant number No.: 451-03-47/2023-01/200007, Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia and Faculty of Mechanical Engineering University of Belgrade, Contract research project No.: MF/TFT-01/23, January 15,2023 Zepter International, Belgrade, Serbia and Faculty of Mechanical Engineering University of Belgrade; Contract research project No.: 22032914G860, July 8, 2022 BIOPTRON, AG, Switzerland and LAUS GmbH, Germany, and Contract research project No.: 2023-3760-140-45-00533-11, April 24,2023 BIOPTRON, AG, Switzerland and Fraunhofer-Institut für silicatforschung ISC, Germany.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgment
The first author (Dj.K.) would like to thank Aleksandra Korać and her co-workers, Faculty of Biology, University of Belgrade for collaboration and the first electron microscopy images of 3HFWC, Zoran Mitrović, ProTech, d.o.o, Belgrade for his cooperation within Nano World, Belgrade in building the first reactor for the production of SD-C60, as well as for building together with Dušan Ječmenica, Metalelektrik, Belgrade, and financial support of Zepter International, Belgrade the second reactor for commercial production of 3HFWC within the TFT Nano Center Belgrade. Also, many thanks to the operators for the production of SD-C60 (3HFWC) within the TFT Nano Centre; Marija Slavković, Nenad Jeftić, Nataša Knežević, Zorana Jović, Milica Paunović and Jelena Janać as well as their assistance in biomedical studies and the administration of the TFT NanoCentre in the period 2018-2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Eiji Osawa, Cornannulene, Kagaku, 25:854, 1970.
- Kroto, H.W. , Heath, J.R., O’Brien, S.C., Curl, R.F., Smalley, R.E., C₆₀: Buckministerfullerene, Nature, 318:162, 1985.
- W. Krätschmer, Lowell D. Lamb, K. Fostiropoulos & Donald R. Huffman, Solid C₆₀: a new form of carbon, Nature, 347:354–358, 1990.
- Koruga, Dj. Simi-Krstic, J., Trifunovic, M., Jankovic, S., Hameroff, S., Withers, J., Loutfy, R., Imaging Fullerene C₆₀ with atomic resolution using a scanning tunneling microscope, Fullerene Science and Technology, 1(1):93-100, 1993, ISSN: 1064-122X. [CrossRef]
- Harter, W.G. , and Weeks, D.E. Rotation-vibration spectra of icosahedral Molecule I: Icosahedral symmetry analysis and fine structure. J. Chem Phys 90(9): 4724-4743,1989. [CrossRef]
- Markus Arndt, Olaf Nairz, Julian Vos-Andreae, Claudia Keller, Gerbrand van der Zouw & Anton Zeilinger, Wave–particle duality of C60 molecules, Nature, 401: 680–682,1999.
- Kamaseki, T., and Kadota, K., The “vesicle in a basket”, J. Cell Biol 42:202-220, 1969. [CrossRef]
- Ericson, R.O. , Tubular pacing of spheres in biological fine structures, Science, 181:705-708,1973. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Haddon, Magnetism of the carbon allotropes, Nature, 378, 249–255, 1995. [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L. Y.; Upasani, R. B.; Swirczewski, J. W., Process of forming polysubstituted fullerenes U. S. Patent 5,177,248, 1993. and Chiang, L. Y.; Upasani, R. B.; Swirczewski, J. W. U.S. Patent 5,294,732, 1994.
- Sayes, C. M. , Fortner, J. D., Guo, W., Lyon, D. Y., Boyd, A. M., Ausman, K., Tao, Y. J., Sitharaman, B., Wilson, L. J., Hughes, J. B., et al. (2004). The differential cytotoxicity of water-soluble fullerenes. Nano Lett. 4, 1881–1887. [CrossRef]
- Isakovic A, Markovic Z, Todorovic-Markovic B, Nikolic N, Vranjes-Djuric S, Mirkovic M, Dramicanin M, Harhaji L, Raicevic N, Nikolic Z, Trajkovic V. Distinct cytotoxic mechanisms of pristine versus hydroxylated fullerene. Toxicol Sci. 2006 May;91(1):173-83. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanović, G., Kojić, V., Dordević, A., Canadanović-Brunet, J., Vojinović-Miloradov, M., & Baltić, V. V. (2004). Modulating activity of fullerol C60(OH)22 on doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicology in vitro: an international journal published in association with BIBRA, 18(5), 629–637. [CrossRef]
- Jiao F, Liu Y, Qu Y, Li W, Zhou G, Ge C, Li Y, Sun B, Chen C. Studies on anti-tumor and antimetastatic activities of fullerenol in a mouse breast cancer model. Carbon. 2010: 48: 2231-2243. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Jiao, F., Qiu, Y., Li, W., Qu, Y., Tian, C., Li, Y., Bai, R., Lao, F., Zhao, Y., Chai, Z., & Chen, C. (2009). Immunostimulatory properties and enhanced TNF- alpha mediated cellular immunity for tumor therapy by C60(OH)20 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology, 20(41), 415102. [CrossRef]
- Yamawaki H, Iwai N. Cytotoxicity of water-soluble fullerene in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290(6):C1495-C1502. [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Lyles DN, Peifley K, Lockett S, et al. Fullerenol cytotoxicity in kidney cells is associated with cytoskeleton disruption, autophagic vacuole accumulation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;248(3):249-258. [CrossRef]
- Saathoff JG, Inman AO, Xia XR, Riviere JE, Monteiro-Riviere NA. In vitro toxicity assessment of three hydroxylated fullerenes in human skin cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011;25(8):2105-2112. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu K, Kubota R, Kobayashi N, et al. Cytotoxic Effects of Hydroxylated Fullerenes in Three Types of Liver Cells. Materials (Basel). 2013;6(7):2713-2722. Published 2013 Jul 9. [CrossRef]
- Koruga, Dj. Composition of Matter Containing Harmonized Hydroxyl Modified Fullerene Substance. U.S. Patent 8,058,483 B2, 15 November 2011.
- Koruga, Dj. Compositions Comprising Hyper Harmonised Hydroxyl Modified Fullerene Substances. International Patent WO 2021/110234 A1, 10 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lidija Matija, Ivana Stanković, Milica Purić, Milica Miličić, Danijela Maksimović-Ivanić, Sanja Mijatovic, Tamara Krajnović,Vuk Gordić, Djuro Koruga, The Second Derivative of Fullerene C60 (SD-C60) and Biomolecular Machinery of Hydrogen Bonds: Water-Based Nanomedicine, Micromachines 2023, 14, 2152. [CrossRef]
- Markelić M, Mojić M, Bovan D, Jelača S, Jović Z, Purić M, Koruga D, Mijatović S, Maksimović-Ivanić D. Melanoma Cell Reprogramming and Awakening of Antitumor Immunity as a Fingerprint of HyperHarmonized Hydroxylated Fullerene Water Complex (3HFWC) and Hyperpolarized Light Application In Vivo. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;13(3):372. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markelić M, Drača D, Krajnović T, Jović Z, Vuksanović M, Koruga Dj, Mijatović S, Maksimović-Ivanić D. Combined Action of Hyper-Harmonized Hydroxylated Fullerene Water Complex and Hyperpolarized Light Leads to Melanoma Cell Reprogramming In Vitro. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;12(8):1331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perovic M, Ciric J, Matovic V, Srbovan M, Koruga Dj, Kanazir S, Ivkovic S. The presymptomatic treatment with 3HFWC nanosubstance decreased plaque load in 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Lazovic J, Zopf LM, Hren J, Gajdoš M, Slavkovic M, Jovic Z, Stankovic I, Matovic V, Koruga Dj. FullereneFiltered Light Spectrum and Fullerenes Modulate Emotional and Pain Processing in Mice. Symmetry. 2021; 13:2004. [CrossRef]
- Subotić A, Jevremović S, Milošević S, Trifunović-Momčilov M, Đurić M, Koruga Đ. Physiological Response, Oxidative Stress Assessment and Aquaporin Genes Expression of Cherry Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Exposed to Hyper-Harmonized Fullerene Water Complex. Plants. 2022;11:2810. [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic S, Jeftic B, Stankovic I, Stojiljkovic N, Koruga Dj. Mechanisms of skin moisturization with hyperharmonized hydroxyl modified fullerene substance. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3018-3025. [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic S, Jeftic B, Sarac D, Matovic V, Slavkovic M, Koruga Dj. Influence of hyper-harmonized fullerene water complex on collagen quality and skin function. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:494–501. [CrossRef]
- Serda, M.; Szewczyk, G.; Krzysztyńska-Kuleta, O.; Korzuch, J.; Dulski, M.; Musioł, R.; Sarna, T. Developing [60]Fullerene Nanomaterials for Better Photodynamic Treatment of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. ACS Biomater. Sci Eng. 2020, 6, 5930–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, E.; Hernandez Garcia, A.; Zavala, G.; Echegoyen, L. Fullerenes in Biology and Medicine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6523–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, J.P.; Devasagayam, T.P.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Mohan, H. Reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage induced by fullerene derivatives and its possible biological implications. Toxicology 2000, 155, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, P.; Pawlak, A.; Satti, M.; Lee, H.; Wharton, T.; Gali, H.; Sarna, T.; Hamblin, M.R. Functionalized fullerenes mediate photodynamic killing of cancer cells: Type I versus Type II photochemical mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franskevych, D.; Palyvoda, K.; Petukhov, D.; Prylutska, S.; Grynyuk, I.; Schuetze, C.; Drobot, L.; Matyshevska, O.; Ritter, U. Fullerene C60 Penetration into Leukemic Cells and Its Photoinduced Cytotoxic Effects. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakry, R.; Vallant, R.M.; Najam-Ul-Haq, M.; Rainer, M.; Szabo, Z.; Huck, C.W.; Bonn, G.K. Medicinal applications of fullerenes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 639–649. [Google Scholar]
- Anilkumar, P.; Lu, F.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Liu, J.-H.; Sahu, S.; Ii, K.N.T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Fullerenes for applications in biology and medicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrievsky, G.V.; Bruskov, V.I.; Tykhomyrov, A.A.; Gudkov, S.V. Peculiarities of the antioxidant and radioprotective effects of hydrated C-60 fullerene nanostuctures in vitro and in vivo. Free Radical. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chiang, L.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy with fullerenes in vivo: Reality or a dream? Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K.N. Semenov, N.A. Charykov, V.N. Postnov, V.V. Sharoyko, I.V. Vorotyntsev, M.M. Galagudza, I.V. Murin, Fullerenols: Physicochemical properties and applications, Progress in Solid State Chemistry, Vol. 44, 59-74, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Konstantin, N. Semenov, Elena V. Andrusenkoa, Nikolai A. Charykovb, Elena V. Litasovac, Gayane G. Panovad, Anastasia V. Penkovaa, Igor V. Murina, Levon B. Piotrovskiy, Carboxylated fullerenes: Physico-chemical properties and potential applications, Progress in Solid State Chemistry, Vol. 47-48,19-36, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Vileno, B.; Marcoux, P.R.; Lekka, M.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Feher, T.; Forro, L. Spectroscopic and photophysical properties of a highly derivatized C-60 fullerol. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldi, D.M.; Prato, M. Excited-state properties of C(60) fullerene derivatives. Accounts Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S. , Dresselhaus, M.S.,Eklund, P.C., Science of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes, Academic Press, San Diego,1996.
- Kettle, S.F.A., Symmetry and structure, John Willey and Sons, Chichester, 1995.
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) in domain 2,500-15,000 nm. There are four dominant peaks at 3,088 nm (spontaneously water shell around FD-C60 ) with intensity 0.05 a.u., 6,377 nm with intensity 0.20 a.u., 7,562 nm with intensity 0.17 a.u. and 12,865 nm with 0.13 a.u.,.
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) in domain 2,500-15,000 nm. There are four dominant peaks at 3,088 nm (spontaneously water shell around FD-C60 ) with intensity 0.05 a.u., 6,377 nm with intensity 0.20 a.u., 7,562 nm with intensity 0.17 a.u. and 12,865 nm with 0.13 a.u.,.
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of 3HFWC (SD-C60) in domain 2,500 -16,000 nm. There are two dominant peaks at 3,064 nm (intramolecular “chelate” hydrogen bonds) with intensity 0.28 a.u., and 6,132 nm with intensity 0.14 a.u. and one increasing value of 0.05-0.35 a.u. in the domain of 10,000-15,000 nm, the peak of which is in the area above 15,000 nm (which could not be detected because it is outside of instrument′s wavelength domain). .
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of 3HFWC (SD-C60) in domain 2,500 -16,000 nm. There are two dominant peaks at 3,064 nm (intramolecular “chelate” hydrogen bonds) with intensity 0.28 a.u., and 6,132 nm with intensity 0.14 a.u. and one increasing value of 0.05-0.35 a.u. in the domain of 10,000-15,000 nm, the peak of which is in the area above 15,000 nm (which could not be detected because it is outside of instrument′s wavelength domain). .
Figure 3.
(Left) 13C-NMR spectra with water suspension of fullerenol (FD-C60), concentration 0.15 μg/μl. Thirteen peaks from 172 to 181 ppm shows different forms of fullerenol (from 30 to 50 OH groups) with dominant peak at 176.49 ppm (36 OH group). Second peak from 126-138 ppm showed C=C in C60, while peak 75.25 ppm represent C−OH group in hydroxylated fullerene. (Right) 13C-NMR spectra with water suspension of 3HFWC (SD-C60) with same concentration of fullerenol (0.15 μg/μl, as precursor). 13C-NMR could not detect peaks of 13C atoms in spite that was a same concentration as in fullerenol. We assume that there are two possible reasons for this: (1) to much lower number of 13C atoms in the sample too detect signal, or (2) that the water layers of 3HFWC absorbed the magnetic signal of 13C atoms. .
Figure 3.
(Left) 13C-NMR spectra with water suspension of fullerenol (FD-C60), concentration 0.15 μg/μl. Thirteen peaks from 172 to 181 ppm shows different forms of fullerenol (from 30 to 50 OH groups) with dominant peak at 176.49 ppm (36 OH group). Second peak from 126-138 ppm showed C=C in C60, while peak 75.25 ppm represent C−OH group in hydroxylated fullerene. (Right) 13C-NMR spectra with water suspension of 3HFWC (SD-C60) with same concentration of fullerenol (0.15 μg/μl, as precursor). 13C-NMR could not detect peaks of 13C atoms in spite that was a same concentration as in fullerenol. We assume that there are two possible reasons for this: (1) to much lower number of 13C atoms in the sample too detect signal, or (2) that the water layers of 3HFWC absorbed the magnetic signal of 13C atoms. .
Figure 4.
1H-NMR spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) with six dominant peaks from 4.8 ppm to 1.9 ppm (left), and 3HFWC (SD-C60) with three dominant peaks from 0 ppm to 3.8 ppm (right). Black lines represent a chemical shift (ppm) while red lines represent integral spectra..
Figure 4.
1H-NMR spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) with six dominant peaks from 4.8 ppm to 1.9 ppm (left), and 3HFWC (SD-C60) with three dominant peaks from 0 ppm to 3.8 ppm (right). Black lines represent a chemical shift (ppm) while red lines represent integral spectra..
Figure 5.
TEM images of dry state of fullerenol (FD-C60) (left) and 3HFWC (SD-C60) (right). Fullerenol molecule is about 1.3 nm in diameter but under humidity may forming conglomerates with different size (until hundreds nm) and different shapes (linear, random foling and balls). 3HFWC is spherical molecule, about 15 nm in diameter (from 10 nm to 30 nm). .
Figure 5.
TEM images of dry state of fullerenol (FD-C60) (left) and 3HFWC (SD-C60) (right). Fullerenol molecule is about 1.3 nm in diameter but under humidity may forming conglomerates with different size (until hundreds nm) and different shapes (linear, random foling and balls). 3HFWC is spherical molecule, about 15 nm in diameter (from 10 nm to 30 nm). .
Figure 6.
TEM images of dry 3HFWC spherical molecule with size about 15 nm. In the center of the 3HFWC is fullerenol (diameter 1.3 nm), surrounded by water shells (layers, average diameter 14.51-1.30 = 13.21 nm). Water molecules are ordering according to icosahedral tree-dimensional Penrose tilling (3DPT) [
22]
.
Figure 6.
TEM images of dry 3HFWC spherical molecule with size about 15 nm. In the center of the 3HFWC is fullerenol (diameter 1.3 nm), surrounded by water shells (layers, average diameter 14.51-1.30 = 13.21 nm). Water molecules are ordering according to icosahedral tree-dimensional Penrose tilling (3DPT) [
22]
.
Figure 7.
TEM images of dry 3HFWC spherical molecules with size about 17 nm. In case, image left, water shell has dimeter 15.63 nm (16.93 – 1.30 = 15.63 nm) with water molecules order according tree-dimensional Penrose tilling (3DPT) [
22]
.
Figure 7.
TEM images of dry 3HFWC spherical molecules with size about 17 nm. In case, image left, water shell has dimeter 15.63 nm (16.93 – 1.30 = 15.63 nm) with water molecules order according tree-dimensional Penrose tilling (3DPT) [
22]
.
Figure 8.
AFM/MFM images of dry 3HFWC (SD-C60) and dry fullerenol (FD-C60), with four different scanning spots. Scanning surface of 3HFWC was 100 x 100 nm while for fullerenol was 30 x 30 nm. Different scanning surfaces were chosen due to the different sizes of these two substances (fullerenol is about 1.3 nm, 3HFWC is between 10-30 nm). 3HFWC molecules are observed as separate structures (individual), while in the images of fullerenol, individual molecules as well as their smaller conglomerates are observed.
Figure 8.
AFM/MFM images of dry 3HFWC (SD-C60) and dry fullerenol (FD-C60), with four different scanning spots. Scanning surface of 3HFWC was 100 x 100 nm while for fullerenol was 30 x 30 nm. Different scanning surfaces were chosen due to the different sizes of these two substances (fullerenol is about 1.3 nm, 3HFWC is between 10-30 nm). 3HFWC molecules are observed as separate structures (individual), while in the images of fullerenol, individual molecules as well as their smaller conglomerates are observed.
Figure 9.
In order to clearly compare the size and organization of dry fullerenol (left) and dry 3HFWC (right) the AFM/MFM images with same scanning spots 100 x 100 nm are made. As you can see from the pictures, the difference in size and way of organization are different. As fullerenol is a precursor for 3HFWC, they differ in that water layers with a thickness of 7 nm to 14 nm have formed around fullerenol.
Figure 9.
In order to clearly compare the size and organization of dry fullerenol (left) and dry 3HFWC (right) the AFM/MFM images with same scanning spots 100 x 100 nm are made. As you can see from the pictures, the difference in size and way of organization are different. As fullerenol is a precursor for 3HFWC, they differ in that water layers with a thickness of 7 nm to 14 nm have formed around fullerenol.
Figure 10.
AFM/MFM image of dry 3HFWC with a scan area of 269.8 nm
2 with 14 molecules of 3HFWC which can be seen in the image. The molecular size of 3FFWC, which was chosen for accurate measurement, is 14.7 nm. As can be seen from the image, the surface of the molecules is not smooth (there are two gentle passes at 5.9 nm and 7.4 nm) which is in agreement with the previously obtained results [
22].
Figure 10.
AFM/MFM image of dry 3HFWC with a scan area of 269.8 nm
2 with 14 molecules of 3HFWC which can be seen in the image. The molecular size of 3FFWC, which was chosen for accurate measurement, is 14.7 nm. As can be seen from the image, the surface of the molecules is not smooth (there are two gentle passes at 5.9 nm and 7.4 nm) which is in agreement with the previously obtained results [
22].
Figure 11.
MFM image of 50-60 dry fullerenol molecules (in line) with an average value of the type-sample interaction intensity of -140 deg, which indicates that the sample is paramagnetic. The intensity and form of the graph indicate that a thin layer of humidity (water molecules) covered (evenly) the surface layer of fullerenol.
Figure 11.
MFM image of 50-60 dry fullerenol molecules (in line) with an average value of the type-sample interaction intensity of -140 deg, which indicates that the sample is paramagnetic. The intensity and form of the graph indicate that a thin layer of humidity (water molecules) covered (evenly) the surface layer of fullerenol.
Figure 12.
MFM image of about 18-20 dry 3HFWC molecules (in line) with an average value of the type-sample interaction intensity of -100 deg (minimum -165 deg., and maximum -65 deg.), which indicates that the sample is less paramagnetic than fullerenol. This means that fullerenol, even if it has a smaller number of atoms (1.332 Da), has more unpaired electrons than 3HFWC, which has a significantly higher number of atoms (~3.200 Da).The intensity and form of the graph show that in addition to a thin layer of moisture, there are also water layers in 3HFWC (around fullerenol as precursor of 3HFWC).
Figure 12.
MFM image of about 18-20 dry 3HFWC molecules (in line) with an average value of the type-sample interaction intensity of -100 deg (minimum -165 deg., and maximum -65 deg.), which indicates that the sample is less paramagnetic than fullerenol. This means that fullerenol, even if it has a smaller number of atoms (1.332 Da), has more unpaired electrons than 3HFWC, which has a significantly higher number of atoms (~3.200 Da).The intensity and form of the graph show that in addition to a thin layer of moisture, there are also water layers in 3HFWC (around fullerenol as precursor of 3HFWC).
Figure 13.
Powder XRD is performed to show differences in samples structural order. The XRD patterns of fullerenol show broad Bragg peaks at 27° – 57° 2Theta due to partial crystallization of interstitial water. Higher water content (humidity + extra water) in 3HFWC induces a decrease in reflex intensity and further broadening of the reflexes.
Figure 13.
Powder XRD is performed to show differences in samples structural order. The XRD patterns of fullerenol show broad Bragg peaks at 27° – 57° 2Theta due to partial crystallization of interstitial water. Higher water content (humidity + extra water) in 3HFWC induces a decrease in reflex intensity and further broadening of the reflexes.
Figure 14.
Fullerenol (FD-C60) TGA/DTA diagram with peak at 99.9°C (100°C) with endothermic reaction (water evaporation).
Figure 14.
Fullerenol (FD-C60) TGA/DTA diagram with peak at 99.9°C (100°C) with endothermic reaction (water evaporation).
Figure 15.
3HFWC (SD-C60) TGA/DTA diagram with peak at 132.9°C (133°C) with exothermic reaction (shifted to higher temperature for evaporation).
Figure 15.
3HFWC (SD-C60) TGA/DTA diagram with peak at 132.9°C (133°C) with exothermic reaction (shifted to higher temperature for evaporation).
Figure 16.
FTIR spectras of fullerenol (FD-C60) with the first endothermic DTA process at 100°C (left) and 3HFWC (SD-C60) with the first exothermic DTA process at 133°C (right) in TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR investigation.
Figure 16.
FTIR spectras of fullerenol (FD-C60) with the first endothermic DTA process at 100°C (left) and 3HFWC (SD-C60) with the first exothermic DTA process at 133°C (right) in TGA/DTA-MS-FTIR investigation.
Figure 17.
MS spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) at 100°C (first endothermic DTA process) shows m/z fragments of 18 (H2O+) and 17 (OH+), signals of fragment 44 (CO2+) are very low at 100 °C (left), and MS scan of 3HFWC (SD-C60) at 133 °C (first exothermic DTA process) shows m/z fragments of 18 (H2O+) and 17 (OH+), signals of fragment 44 (CO2 +) are very low at 133 °C (right).
Figure 17.
MS spectra of fullerenol (FD-C60) at 100°C (first endothermic DTA process) shows m/z fragments of 18 (H2O+) and 17 (OH+), signals of fragment 44 (CO2+) are very low at 100 °C (left), and MS scan of 3HFWC (SD-C60) at 133 °C (first exothermic DTA process) shows m/z fragments of 18 (H2O+) and 17 (OH+), signals of fragment 44 (CO2 +) are very low at 133 °C (right).
Figure 18.
GPC fullerenol diagram (left) with three peaks (A~2.00 a.u.,B ~1.00 a.u. and C~0.10 a.u.) and GPC diagram of 3HFWC (right) with four peaks (A, B, C with same intensity as fullerenol and a new peak D ~3.5 a.u.). As can be seen D peak intesity of 3HFWC on diagram (right) is dominant and much higher than peaks A, B and C (since fullerenol is precursor for 3HFWC synthesis peaks A.B and C are same intensity on diagrams left and right. Peak D in this case may only represent water layers of 3HFWC).
Figure 18.
GPC fullerenol diagram (left) with three peaks (A~2.00 a.u.,B ~1.00 a.u. and C~0.10 a.u.) and GPC diagram of 3HFWC (right) with four peaks (A, B, C with same intensity as fullerenol and a new peak D ~3.5 a.u.). As can be seen D peak intesity of 3HFWC on diagram (right) is dominant and much higher than peaks A, B and C (since fullerenol is precursor for 3HFWC synthesis peaks A.B and C are same intensity on diagrams left and right. Peak D in this case may only represent water layers of 3HFWC).
Table 1.
Difference between fullerenol and 3HFWC based on 1H-NMR spectra (chemical shift/ppm and integral difference without TMS). Difference in chemical shift is small, about 0.3 ppm, while integral value is significantly different, about 4.3 times.
Table 1.
Difference between fullerenol and 3HFWC based on 1H-NMR spectra (chemical shift/ppm and integral difference without TMS). Difference in chemical shift is small, about 0.3 ppm, while integral value is significantly different, about 4.3 times.
Table 2.
Zeta potential, pH, electrophoretic mobility and conductivity of fullerenol and 3HFWC (same concentration 0.150 g/L of C60(OH)36 in fullerenol solution and 3HFWC solution).
Table 2.
Zeta potential, pH, electrophoretic mobility and conductivity of fullerenol and 3HFWC (same concentration 0.150 g/L of C60(OH)36 in fullerenol solution and 3HFWC solution).
| Test item |
Temperature
(°C) |
pH |
Zeta potential
(mV) |
Electrophoretic
mobility
(μm/s)/(Vcm) |
Conductivity
(μS/cm) |
|
Fullerenol (FD-C60) |
25 |
9.35 |
-25.85 ±1.71 |
-2.01±0.13 |
0.18 |
3HFWC
(SD-C60) |
25 |
7.11 |
-43.29±1.23 |
-3.37±0.10 |
0.17 |
| Difference |
0 |
2.24 |
-17.44 |
-1.36 |
0.01 |
Table 3.
Wavelength shift and difference in the intensity of C
60 [
43], fullerenol (
Figure 1) and 3HFWC (
Figure 2) peaks in the 7,000-9,000 nm FTIR range.
Table 3.
Wavelength shift and difference in the intensity of C
60 [
43], fullerenol (
Figure 1) and 3HFWC (
Figure 2) peaks in the 7,000-9,000 nm FTIR range.
| Peak |
C60
|
Fullerenol |
C60/Fulerenol (shift/ difference)
|
3HFWC |
C60/Fulerenol
(shift/ difference)
|
1. |
Wavelength (nm) |
7.003 |
6.370 |
633 |
7.340 |
337 |
| Intensity (a.u.) |
0.192 |
0.190 |
0.002 |
0.027 |
0.165 |
2. |
Wavelength (nm) |
8.453 |
7.555 |
898 |
8.220 |
665 |
| Intensity (a.u.) |
0.210 |
0.178 |
0.032 |
0.028 |
0.150 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).