1. Introduction
Vascularity diseases, characterized by either blocked or excessive blood supply to organs and tissues, are among the most serious health problems [
1]. They may lead to life-threatening conditions, like stroke or heart attack, and are accompanied by the presence of abnormalities in blood-vessels lumen geometry, such as stenoses caused by pathological deposition of atherosterotic plaque inside the vessel. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases require accurate lumen geometry quantification, in a non-invasive way where possible. Three-dimensional imaging is the main technique used to acquire quantitative information about the vasculature. Example modalities include magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) which can be blood-flow-dependent [time-of-flight (TOF) or phase contrast angiography (PCA)] or flow-independent. An invasive alternative is computed tomography angiography (CTA). The vasculature images can be contrast-enhanced (CE) or nonenhanced, which is obtained by injecting a contrastive substance into the blood circulatory system.
Parametric evaluation of the shape of blood vessels lumen requires identification and quantification of 3D image regions that represent the relevant part of the circulatory system. This certainly is not a trivial task, for many reasons. The vasculature exhibits a complex tree-like structure of highly curved, different-diameter branches. Their diameter may change from 50 mm for the aorta to 50 m for venules and arterioles. At the same time, imaging systems spatial resolution is limited, say to cuboids (voxels) having the shortest sidelength of 0.2 mm for clinical scanners. Thus the thin vessels’ regions are heavily blurred in the image and thinnest of them are not visible. In search of the resolution increase, the voxel volume is reduced using various technical solutions, but this causes the decrease of the signal collected from this volume, so random noise becomes a significant component of the image intensity. Its presence increases the uncertainty of the intensity evaluation inside the lumen, vessel wall and in the background and adversely affects the lumen geometry measurements. Image artefacts make the situation even worse.
Typically, the vessels of interest are closely surrounded by other arteries, veins and tissues. Thus the background region features uneven image intensity, and the spatially blurred signals from different regions overlap. Moreover, the intensity inside the vessel walls is not constant − the plaque depositions, especially those calcified, exhibit different properties to the blood or to the contrastive medium, e.g. [
2]. Classical, numerically efficient segmentation-through-thresholding becomes highly inaccurate in these conditions. The pointed out factors make the task of vessel quantification in 3D images especially challenging for radiologists. Manual vessel delineation in 3D images is tedious, time-consuming and error-prone [
3]. Its adequacy depends much on the readers experience and their level of fatigue. There is a strong need to develop automated techniques for accurate, fast and objective vascularity evaluation from volumetric image data [
4].
There have been numerous methods of lumen segmentation and quantification proposed for the last few decades [
3,
4,
5]. The research in this area has been further intensified with the advent of deep learning as an approach to image segmentation [
6,
7]. One can identify two main approaches to vascular structures segmentation and quantification in 3D images [
8,
9]:
The result of direct 3D image segmentation is another image. In its basic form it is a grid having the same spatial resolution as the original volume whose nodes (e.g. centers of the voxels) are attributed binary intensity values. Some of these voxels are marked by a label indicating they represent the lumen, all the others are assigned the label of the background. The boundary of the lumen region, which otherwise is smooth and continuous in the physical space, thus becomes discretized. For random boundary location in space, the variance of the discretization error could only be reduced by decreasing the voxel sidelength, always at the price of increased noise. Thus the lumen surface, when visualized, would exhibit a stair-like, or voxelized form. It would need additional spatial smoothing for visualization or for building a geometric model for blood flow simulation. However, part of the information about the actual course of this continuous surface, needed for faithfull reconstruction, had been lost in the binary segmentation step, in which the continuous intensities got replaced by two-level values. From this point of view, image segmentation, although intuitive, is an unnecessary processing step. Yet another disadvantage of some of the segmentation algorithms are the time-consuming iterative calculations [
10,
11].
We focus on the second approach to estimate the lumen geometry parameters from 3D image cross-sections. These cross-sections are computed as 2D images on planes perpendicular to the vessel centerline, approximated by a smooth curve in 3D space beforehand [
12]. This is less troublesome than volumetric segmentation of the lumen; various algorithms are available [
13,
14]. Normal vectors to the centerline define the cross-section planes. The cross-section images are obtained through the 3D discrete image interpolation and resampling. The center of the cross-section image grid is usually set to lie on the vessels centerline. Then, lumen contours are delineated in these images, either semi-manually [
15] or automatically [
12]. For automated contour delineation, a 2D image formation model is defined. It accounts for image smoothing by an equivalent scanner impulse response, either one-dimensional along radial lines [
12,
16] or two-dimensional over the image plane [
17], as well as for the random noise. The model is fitted with the use of the least-squares (LS) algorithm. This involves long-lasting iterative minimization of a nonlinear error function and is likely to get stuck in its local minima, depending on the initial parameter values. We will use the LS fitting as a reference method, and apply the convolutional neural network driven by 2D cross-section images for fast estimation of the model parameters [
17,
18]. The contours found at predefined increments along the centerline arc are lofted to build the geometric models. Lofting is a technique used in computer-assisted-design programs to create 3D surfaces or solid objects [
15]. They are formed from sequences of cross-section curves − contours of the lumen in our case.
The past works that followed the modeling approach incorporate circular or elliptical cylinders as the abstract geometric objects that represent the vessels’ lumen in the image space. In fact, the actual shape of the lumen contours significantly deviate from this idealized figures. This happens in particular in the vessels narrowed by atherosclerotic plaque [
19]. The novelty of our method is in using B-splines as part of the image formation model − the parameterised curves that accurately represent the natural lumen shapes in normal and pathological vasculature. Although B-splines were used for blood-vessel contouring [
20], they were fitted to the approximate surface extracted from the 3D image. In our approach, the fitting process takes place in the image intensity instead of the spatial domain. No cross-section image preprocessing is performed. Innovatively, lumen contour parameters are estimated by a neural network with increased speed and robustness compared to LS fitting. Moreover, the usage of B-splines makes our method compatible with the isogeometric approach [
21] to image analysis, test objects (physical phantoms) design and computational blood flow simulation.
2. Materials and Methods
To illustrate the properties and capabilities of the proposed lumen modeling method, real-life and synthetic images were used. They include:
These datasets will be characterized in the following subsections.
2.1. PAVES MR dataset
Steady-state MR contrast-enhanced volumes, available as part of the PAVES dataset, are high spatial resolution images which, in principle, allow evaluation of the shape of arteries’ lumen, e.g. in search for stenosis. However, these images take several minutes to acquire. During this rather long time both arteries and veins become filled with the gadolinium-based contrast medium. In effect, the intensity of these regions shows similar values, making the arterial regions difficult to identify and to distinguish from the neighbouring veins. The arteries are of smaller diameter, and their cross-section is close to circular, except for pathological stenosed vessels featuring wall-thickening. On the other hand, veins typically have oval shape and are located in pairs next to an artery. Thus the cross-section of artery-vein complexes do not exhibit circular shape − it is non-circular, although its boundaries are smooth. As highlighted in [
24], veins can be used by surgeons to introduce a „bypass” to a blocked artery, provided they are of correct diameter and length. Therefore, delineating veins and arteries in the high-resolution GdCE (gadolinium contrast-enhanced) MR images is a valid medical image processing task, formulated as a Grand Challenge [
22].
The research problem defined in this example is to evaluate suitability of the proposed method to delineate boundaries of the veins and arteries given their steady-state GdCE MR volume. The PAVES dataset No. 5 was selected for the purpose, as the clinical significance of its properties was characterized in [
24]. To obtain the cross-sections, centerlines of the blood-vessel regions were extracted and smoothly approximated by application of the following 3D image preprocessing steps [
12]:
Multiscale „vesselness” filtering [
13,
25] to enhance the blood-vessels regions [
26];
Vesselness map thresholding to obtain binary lumen representation;
Binary regions thinning to produce their skeleton;
Skeleton parsing [
27] to identify the blood-vessel tree branches between bifurcations;
Approximating the skeleton branches by a differentiable function in 3D (to initialize their centerline).
Tangent vectors to the smooth vessel centerline curve were computed at a number of consecutive points, separated by about 0.5 mm from each other. Together with the binormal vectors, they define the Frenet-Serret frame at each point. This frame often gets rotated around the tangent vector, causing undesirable twist of the elongated objects surface. A rotation minimizing frame algorithm [
28] was then used to compute the vessel local coordinate systems 0
xy, in which 2D lumen cross-sections were calculated by resampling the MR volume. The above image preprocessing and analysis algorithms were implemented both in
(version R2022B) and
(version 3.10.13). The codes will be made available to the interested readers on request.
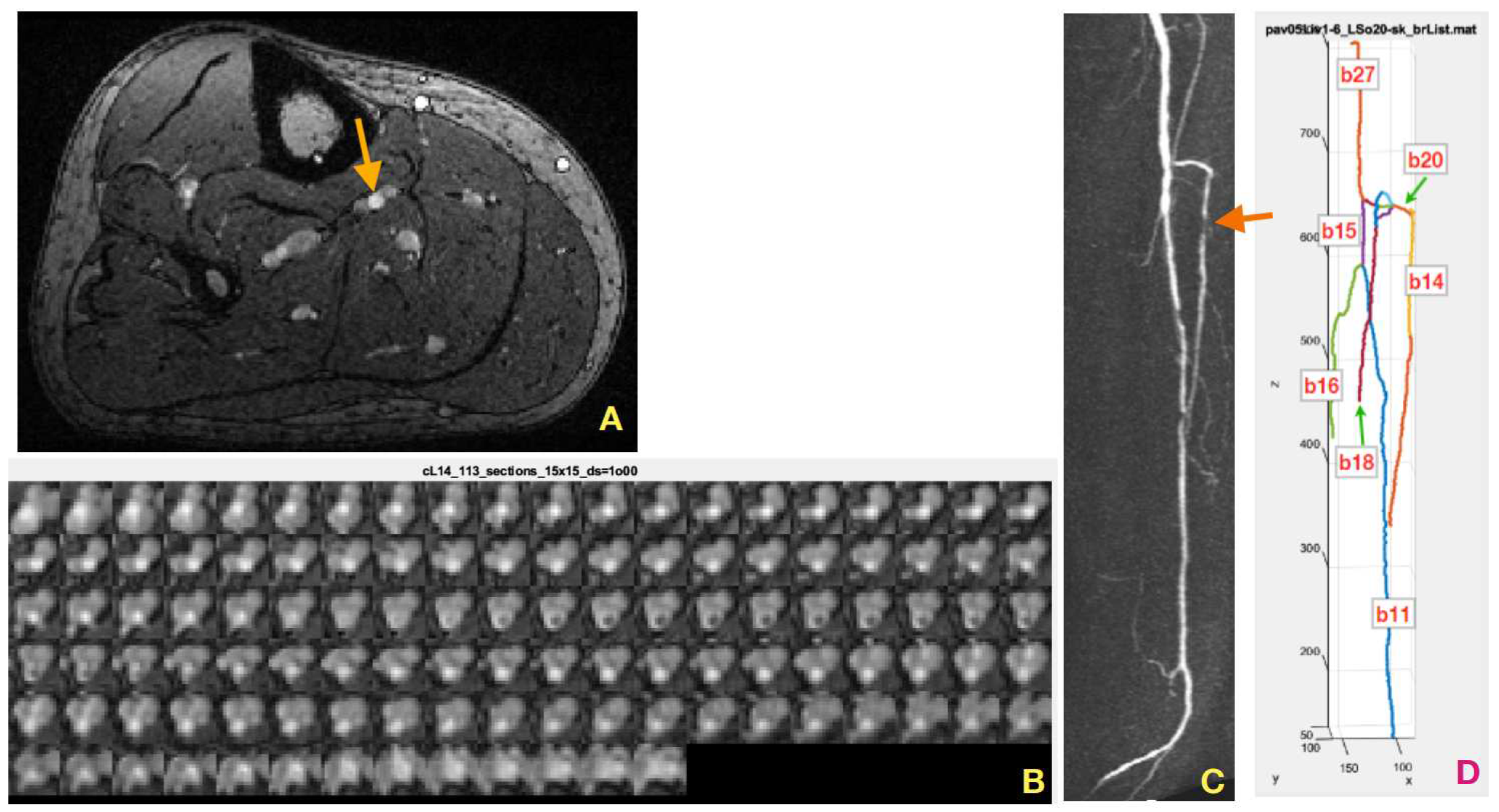
Examples of such cross-sections are presented in
Figure 1B, in a form of the mosaic of 15×15 pixel images, where the pixel size is 1.0 mm×1.0 mm. The consequtive lumen cross-sections show a minimal twist. These images were obtained in result of applying the above-outlined algorithm to segment b14 of the tibial artery whose binary skeleton is pictured in
Figure 1D, among other vessel-tree branches, enumerated by the skeleton parsing algorithm. Basically, a cross-section contains a dark background where there is no tissue filled with blood, a medium-intensity vein region and a bright artery blob of highest concentration of the contrastive medium. As shown in upper two rows of
Figure 1B, the healthy arteries feature circle-like cross-sections. However, the atherosclerotic occlusions cause narrowing of the vessel lumen (row 3, left part) and reduce the intensity of the artery region. In effect of collateral blood circulation, the width of the artery lumen may be restored down the vessel, as can be seen in rows 4, 5, and 6,
Figure 1B.
2.2. CAT08 coronary CTA dataset
We applied the proposed lumen modeling method to 3D images of the training set available from Rotterdam Coronary Algorithm Evaluation Framework [
23,
29,
30]. It was designed for development of algorithms of lumen segmentation, detection and quantification of coronary arteries stenoses, and provided in the MICCAI 2008 Coronary Artery Tracking Challenge (CAT08). There are 48 datasets available in the Rotterdam Challenge data repository. Anatomical segments of the arteries (specified in [
29], visualized in the images, are manually annotated by three experts for 18 of them. These 18 sets constitute the CAT08 training set. For 78 of the training-set segments, expert-annotated contours of the arteries cross-sections are available. We used this information, together with the corresponding 3D images, for the CNN estimator training and as a reference for its testing. It is worth noting the three observers needed approximately 300 hours to complete annotation of this data [
23].
The CT images of the Rotterdam dataset were acquired with different scanners over one year, for a number of patients who underwent a cardiac examination. The average voxel size for the whole dataset is 0.32 mm×0.32 mm×0.4 mm. We clipped the CT volumes intensity to HU and normalized it to . The volumes were resampled on the planes of marked contours to obtain lumen cross-sections centered at the centerline points.
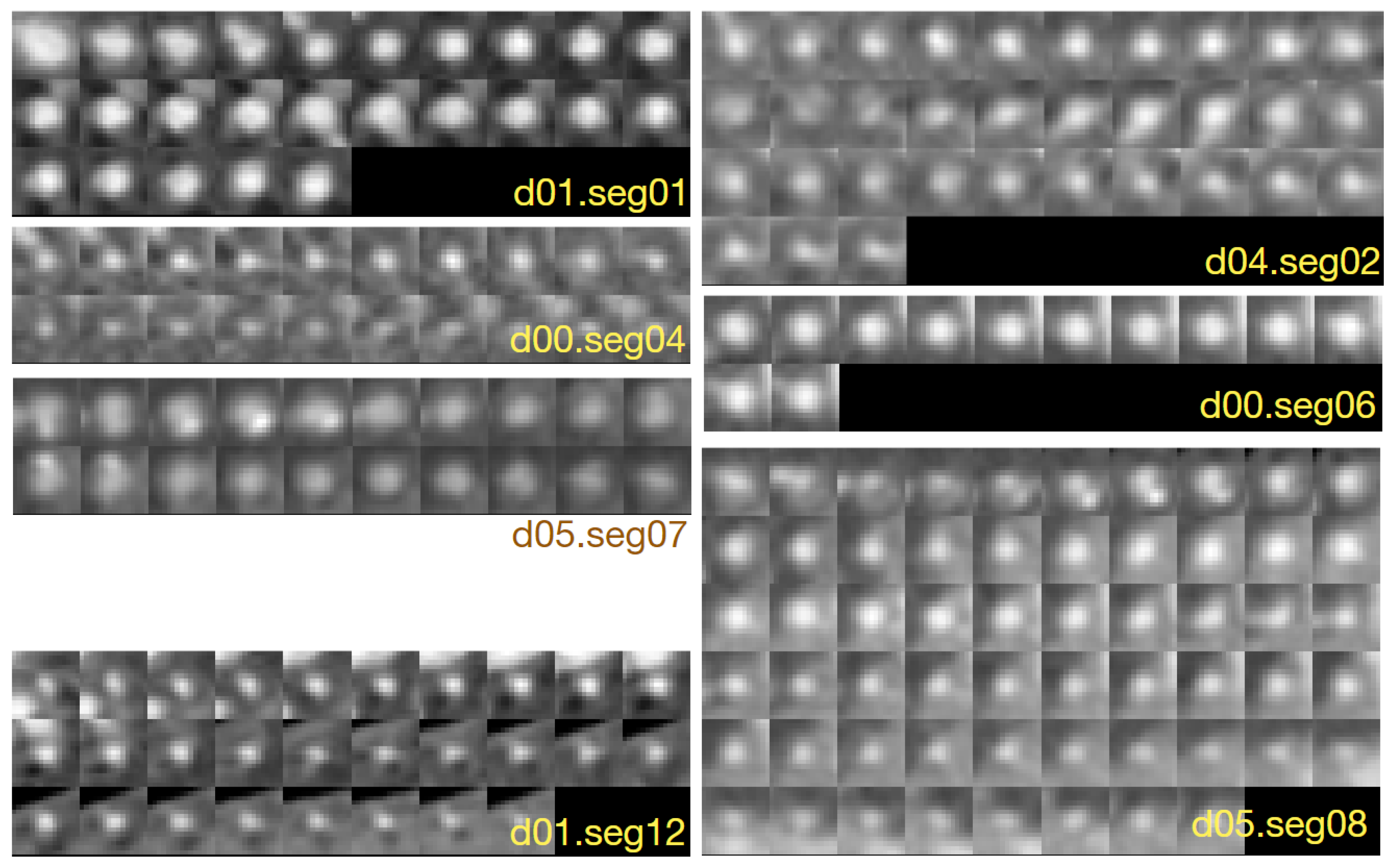
Figure 2 shows examples of cross-sections of a few segments in the CAT08 dataset, computed for the sampling interval of 0.45 mm. Segments
and
are consecutive anatomical parts of the right coronary artery (RCA). The sections of these segments presented in
Figure 2 belong to different datasets, though. Their appearance is quite different. The contrast of the 25 images of
is much higher and the area of its lumen region does not change as much as that of the 33 sections of
. Thresholding would not be useful for the lumen region segmentation in
. Lumen diameter apparently decreases along the 20 sections of
(from left to right, row by row) and approaches subpixel values in the bottom row. At the same time, bright regions are present in the background, actually dominating the image content. The contrast of images in
is good, the lumen region is well defined, its shape is close to circular. However, it shows a significant blur, similarly to all other images. This property, originating in limited spatial resolution of the CT scanners, leads to high uncertainty of lumen boundaries localization, especially in noisy images. Segments
and
form consecutive parts of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). First section (the leftmost in the upper row) of
is closet to the heart, last section (rightmost in the lower row) is the immediate neighbour of the first section in
. The sections in the upmost row of
exhibit a reduced lumen area and bright image spots in the sixth and seventh section, apparently caused by an atherosclerotic plaque. If they become part of the lumen model in result of image analysis, postprocessing is needed to detect and quantify them.
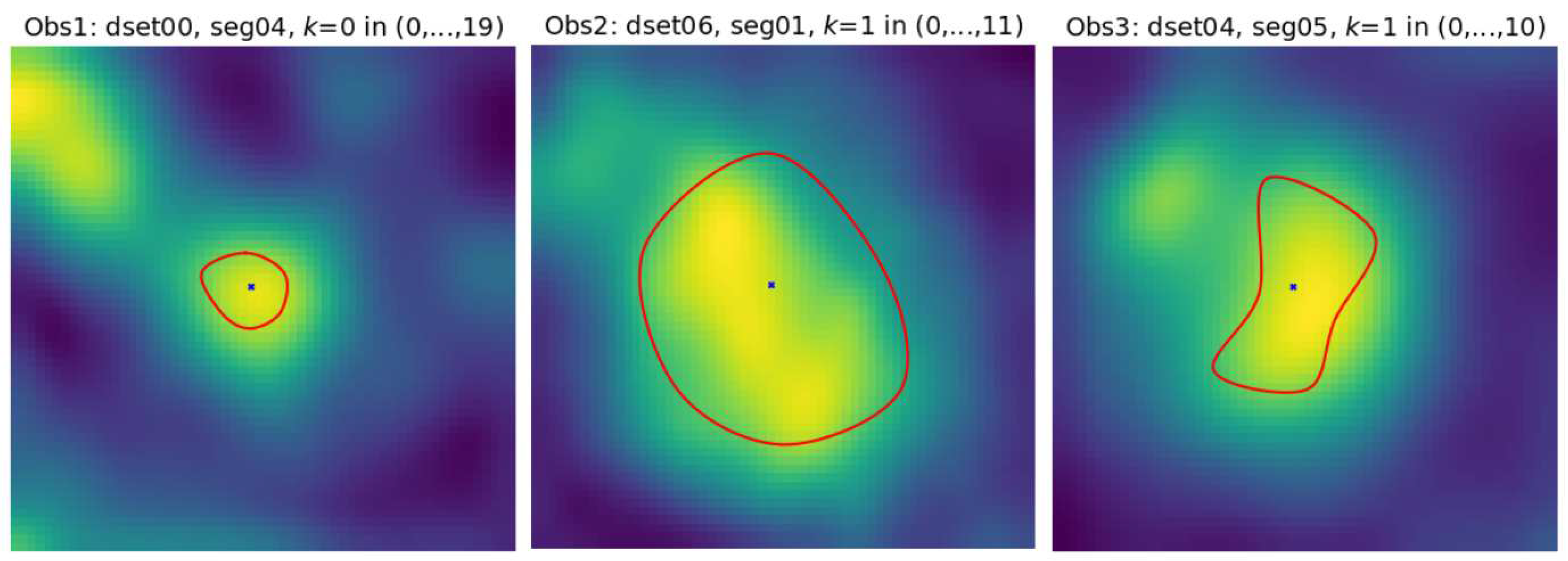
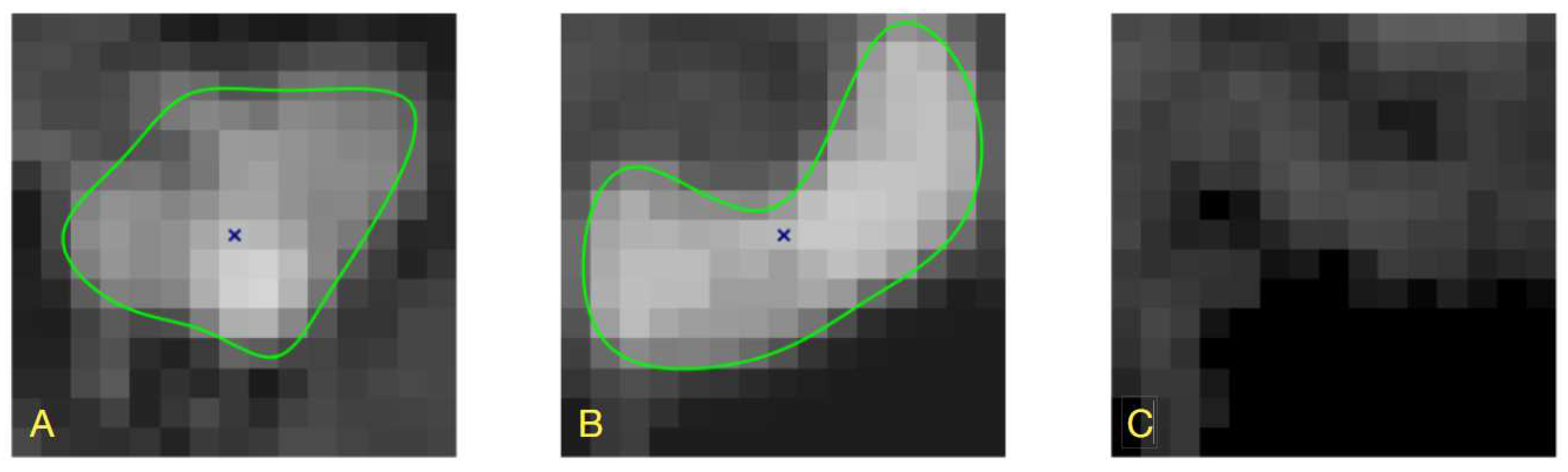
is the first obtuse marginal artery (OM1). Its lumen is well distinguished from immediate background, however, significant part of its sections is occupied by black (triangular shape) regions where the normalized intensity is close to zero (-300 HU or less in the scanner-acquired CT volumes). Typical cross-section shape of the vessels lumen marked by observers is neither circular nor elliptical,
Figure 3.
All the image nonidealities pointed out in the previous paragraph make the lumen modeling task difficult. In our numerous experiments, the LS model fitting method failed in too many cases of the CAT08 arterial branches, being attracted by background regions of locally higher intensity than the lumen. On the other hand, the proposed parameterized B-spline lumen contour model can be robustly identified by a feedforward CNN, which will be demonstrated in the section.
2.3. Image formation model
We assumed the blood-vessel cross-section image centered at any point
in the 3D space is a convolution of the function
, which represents the lumen and its background, with
− the imaging system effective impulse response (point spread function PSF)
where
are image coordinates on the cross-section plane. The function
in (
1) combines the effects of the 3D image scanner impulse response and interpolation necessary for computing the cross-section intensity from the 3D image via resampling. This assumption, though idealized, is relevant to most practical situations [
31].
Further, we assume the function is constant within the lumen region, surrounded by the background of different, but also constant intensity. These expectations are, in turn, often not met, as it was mentioned before with regard to the coronary artery CE CTA images. We will demonstrate in the section that CNN-based lumen geometry restoration features robustness to image intensity variations in the regions of interest.
We considered equidistant sampling on a Cartesian grid of points (although other sampling strategies are possible to tune the estimator properties)
where
denotes the sampling interval. The cross-section image size is
. The image intensity at
is the sampled convolution (
1) multiplied by lumen intensity step
b and added to the background intensity
a:
The lumen section boundary at each centerline point
,
is described in this paper by a closed (periodic) B-spline curve which encloses the higher-intensity lumen region
in
The in-plane blur in our model is assumed isotropic Gaussian [
31,
32,
33] where
w is a parameter
The lumen contour is approximated by a parameterized curve lying on a plane of the vessel cross-section. The concept of B-spline curve [
34,
35] was chosen here. B-spline is a smooth, piecewise polynomial allowing stable, locally controlled approximation of real-world data. To define a curve of this kind, one has to specify a sequence of
,
, real numbers, the knots
which define the curve segments boundaries,
, and
n is the B-spline degree. At the boundaries (internal knots), the segments are joined together to satisfy continuity constraints. The third-degree polynomials are used in our work, meaning first and second derivatives are continuous along the curve arclength.
The closed B-spline of degree
n is controlled by
points
, such that the first control point
overlaps with the last one in their sequence. For any
t within the B-spline segments, the curve points can be computed as [
36]
The B-spline (
7) is a linear combination of degree
n basis B-splines
. Those can be defined recursively with the de Boor algorithm [
34]
To compute a cross-section model intensity (
3), one needs to specify the boundary of the lumen region
in (
4). It is described by a B-spline curve controlled by a sequence of points which have to be defined. In our approach, the control points, for a cross-section centered at the vessel centerline, are located on the radial lines extruding from the image center at
D angles
The distance in the physical space from the image center to the
ith control point
is
,
.
R is a scale factor (fixed for the image of given size) and
a vector of adjustable B-spline parameters. The coordinates of the control points are computed as
It follows from our experience with blood-vessel images of various modalities that the
w parameter of the PSF in (
5) does not change significantly within an image. Then a constant value of
w is assumed, measured separately e.g. via analysis of appropriate edge blur. Then, there are altogether
adjustable parameters
. Combining expressions from (
1) to (
11), one obtains
where
given by (
1) is multiplied by the parameter
b (the intensity pulse corresponding to the lumen region) and added to the background intensity
a. The lumen is represented in (
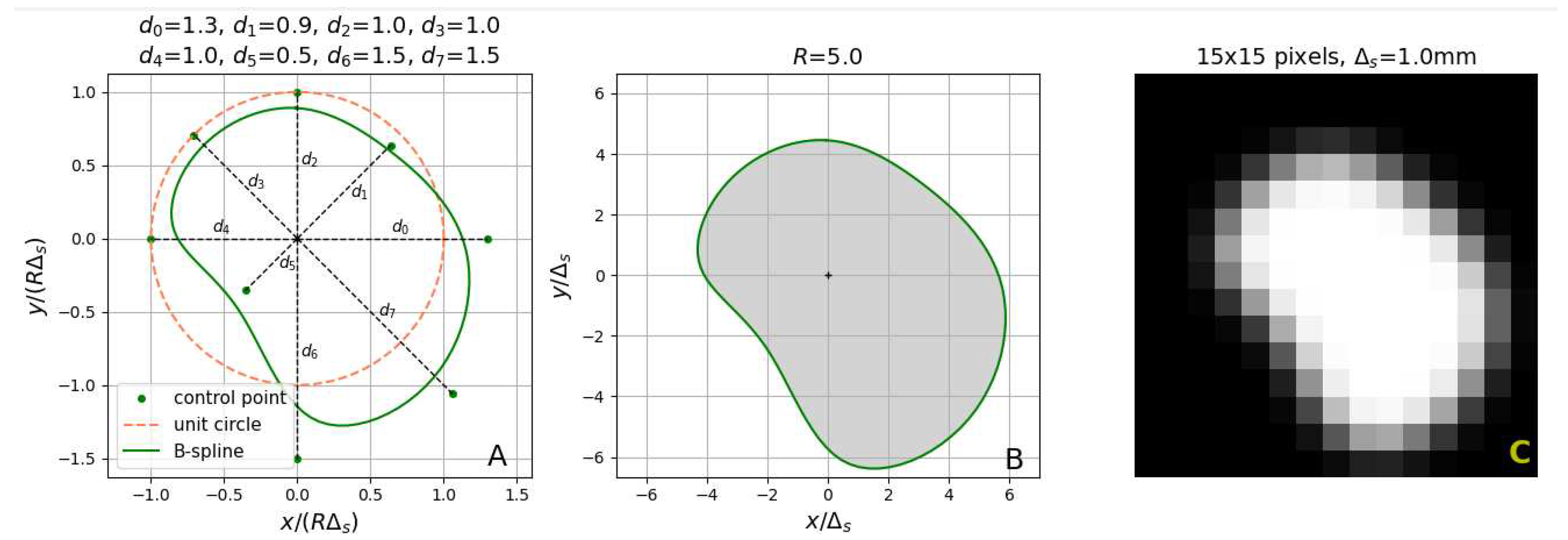
4) by a set of points of unit intensity (the shaded area in
Figure 4B), surrounded by the background points having the intensity equal to zero (the white area in
Figure 4B).
Considering the complex shape of the region
, no closed-form expression for the integral (
1) is apparently available. To compute 2D images for the training and testing datasets, we evaluated the right-hand side in (
1) numerically, with a
implementation of the
(version 4.6.0) library.
2.4. Least-squares model fitting for the PAVES dataset
The aim is to find the estimate of the parameter vector
, given an acquired 2D digital image
of the lumen cross-section of known
R,
w and
. This image is the input to the CNN which approximates the mapping from the image space to the parameter space. We will compare the performance of two approaches to the parameter vector estimation – a least-squares (LS) model fitting and the prediction by convolutional neural network [
17]. Using the former method, the lumen contour parameters can be estimated by minimizing the sum of squared differences between the acquired and modeled image samples
The
(version 1.11.4)
module was used to perform the minimization of the sum-of-squares in (
13).
2.5. Quantitative evaluation of contours (dis)similarity
The lumen contour is defined by a closed continuous curve on the cross-section plane in the physical space. For numerical analysis, it is represented by a finite set of discrete points − vertices of a polygon chosen to approximate this curve. We will use the term contour to refer to its discrete version. We applied two measures to evaluate the discrepancy between contours. Consider the contours
A and
B comprised of respectively
and
points, resampled respectively to
and
. The mean distance of them is defined as
where
is a set of Euclidean distances between a given point
x and each of the points in set
Y. In our experiments, we interpolated the contours being compared such that the cardinality of them was
=
= 100 and
=
= 500.
The second measure was the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), computed for the sets
and
, which denote all the points of a common contours’ plane, that lie inside the contour
A and
B, respectively. It is defined as
In our numerical experiments, the sets
and
were approximated by all the points of a high-resolution image (e.g. 800×800 points, coplanar with the contours), which were lying inside a polygon defined, respectively, by the points of
A and
B.
2.6. CNN-based model parameter estimation
A neural network was trained to predict the B-spline parameter vector
d. The architecture is shown in
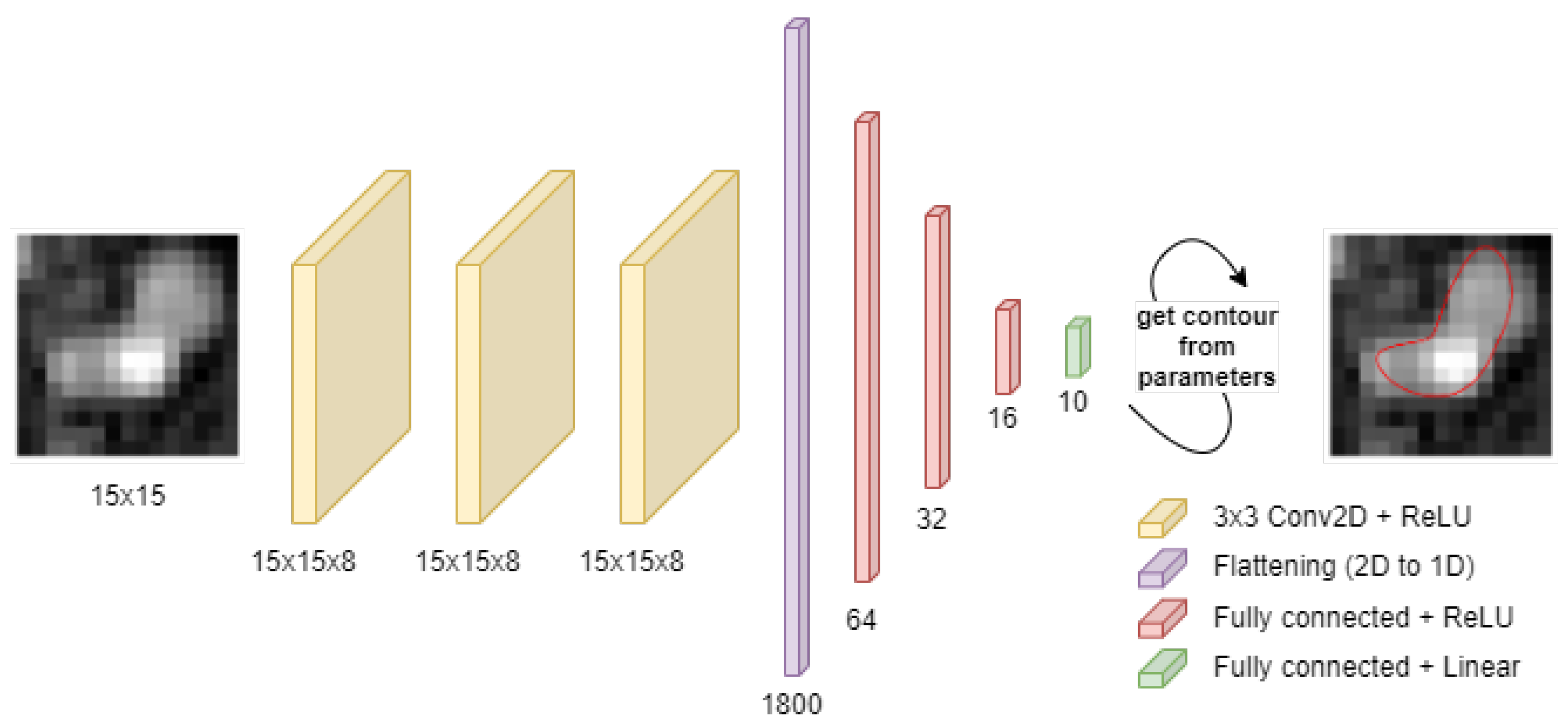
Figure 5. Three 2D convolution layers are followed by a flattening layer and by four fully-connected layers. The three convolutional layers feature 3x3 kernels, with kernel number equal to 8 for each layer, ‘same’ input padding type and ReLU nonlinear activation function. The flattening layer transforms the multichannel 2D feature maps into vectors. The latter are then processed by three fully-connected layers with 64, 32 and 16 neurons, respectively, and ReLU activation. The output layer estimates the 10 elements of vector
d and features a linear activation function. In total, the network has 119 290 trainable parameters and was implemented in
keras (version 2.13.1).
Network training was performed with the mean squared error as the cost function, optimized using the Adam algorithm. Mini-batches of 64 examples were used during training. The maximum number of training epochs was set to 500, but an early stopping algorithm was employed to stop training before overfitting occurred. The early stopping patience parameter was set to 15 epochs.
The synthetic dataset of 10000 examples was used to train the network for prediction on the PAVES dataset. 10% of data was excluded for the test set, which yielded 9 000 examples in the training set. The validation set used in the early stopping algorithm was extracted from the training set as its 20% fraction. The synthetic dataset was considered in two versions: noiseless and noisy. The noise addition procedure is described in further sections.
The CAT08 dataset used for neural network training, validation and testing has 652 examples. 66 of them (10%) were excluded for the test set, and the rest was split into training and validation sets in the same proportion, 90:10. Targets in the form of B-spline-approximated expert contour annotations constitute three separate sets, each for one expert. The training procedure was repeated for each expert’s target set, yielding three trained models.
In summary, five models were trained: two for the PAVES (noiseless and noisy) and three for the CAT08 datasets. Evaluation of these models is described in the Results.
4. Discussion
Using the examples of two publicly available datasets, PAVES and CAT08, it is demonstrated that incorporation of B-spline-approximated lumen contours in the image formation model can be used to quantify non-circular shape of blood vessels with a subvoxel accuracy. Such an accuracy is not available with the use of existing circular or elliptical approximations.
The experimental results obtained for PAVES dataset demonstrate a good agreement between the B-spline parameters estimated by the CNN and those computed with the use of LS model fitting. It was shown that the differences can be reduced by proper augmentation of the synthesized images used for the CNN transfer training. Further study is planned on the design of training datasets, involving realistic texture synthesis to simulate spurious image intensity variations and noise in real-life images.
There is a significant difference between the CNN and LS algorithms in terms of the computation time needed. When implemented on a moderate-performance PC (Intel Core i5 plus NVIDIA GeForce 1050), the CNN predicts the contour parameters in microseconds per image, compared to ca
s for the iterative nonlinear LS program. Moreover, the estimation task can be successfully executed with the use of rather simple CNN architecture having a modest number of adjustable weights,
Figure 5. Time needed for its training is short, in order of 2 minutes.
Due to the complexity of CT images content in the case of coronary artery cross-sections, the LS model fitting does not offer the expected stability. Even with the use of troublesome constrained optimization it finds local minima too often and the fitting results depend much on the initialization points. On the contrary, the CNN can be trained to ignore the image noidealities (e.g. bright objects in the background) and produce lumen contours which are consistent with the observers’ delineations. It is, of course, much faster than human experts. Its application to image annotation would relieve the radiologist of this task.
Our experiments show the CNN can be trained to mimick the individual observers’ style of contour marking. Indeed, there is a good agreement between the shapes of CNN- and observer-produced contours. The CNN reproduces the interobserver variability very well. This raises the question of the ground truth. Future work is planned to design and implement realistic digital and physical phantoms of known tubular geometry and blood distribution, simulate and acquire their images respectively, present them to radiologists and CNNs, and quantitatively compare respective contour delineations with the phantom properties.
Figure 1.
() Coronal slice of a gadolinium contrast-enhanced (GdCE) MR 3D image (PAVES, dataset no. 2) of the lower part of a volunteer right leg. The arrow marks a pair of veins (gray ovals) on the left and right side of an artery (brighter circular blob). () Maximum intensity projection of the PAVES dataset no. 5 TWIST (subtracted time-resolved acquisition) volume on the axial plane, left volunteer extremity. The arrow indicates a stenosis in the anterior tibial artery. () A mosaic of 113 coronal cross-sections of the tibial artery, taken at 0.5-mm intervals along its centerline. () Binary skeleton of the blood vessels, after parsing. The tibial artery branch was assigned a code of b14.
Figure 1.
() Coronal slice of a gadolinium contrast-enhanced (GdCE) MR 3D image (PAVES, dataset no. 2) of the lower part of a volunteer right leg. The arrow marks a pair of veins (gray ovals) on the left and right side of an artery (brighter circular blob). () Maximum intensity projection of the PAVES dataset no. 5 TWIST (subtracted time-resolved acquisition) volume on the axial plane, left volunteer extremity. The arrow indicates a stenosis in the anterior tibial artery. () A mosaic of 113 coronal cross-sections of the tibial artery, taken at 0.5-mm intervals along its centerline. () Binary skeleton of the blood vessels, after parsing. The tibial artery branch was assigned a code of b14.
Figure 2.
Example 15×15-pixel cross-sections of coronary artery segments in CAT08, pixel size: 0.45×0.45 mm.
Figure 2.
Example 15×15-pixel cross-sections of coronary artery segments in CAT08, pixel size: 0.45×0.45 mm.
Figure 3.
Example contours marked by the three observers on coronary artery sections in CAT08 dataset. Cross-sections were interpolated to
pixel resolution to make their appearance similar to the example shown in Fig. 4 of [
23]. Pseudocolor palette was used to enhance visibility of the intensity variations.
Figure 3.
Example contours marked by the three observers on coronary artery sections in CAT08 dataset. Cross-sections were interpolated to
pixel resolution to make their appearance similar to the example shown in Fig. 4 of [
23]. Pseudocolor palette was used to enhance visibility of the intensity variations.
Figure 4.
() Geometry of an eight-parameter B-spline curve normalized to the scale factor R. () Ideal lumen region in the cross-section image space. The shaded area represents the constant-intensity lumen region . () Low-resolution noiseless image of the lumen on its background.
Figure 4.
() Geometry of an eight-parameter B-spline curve normalized to the scale factor R. () Ideal lumen region in the cross-section image space. The shaded area represents the constant-intensity lumen region . () Low-resolution noiseless image of the lumen on its background.
Figure 5.
The neural network architecture used in the described experiments.
Figure 5.
The neural network architecture used in the described experiments.
Figure 6.
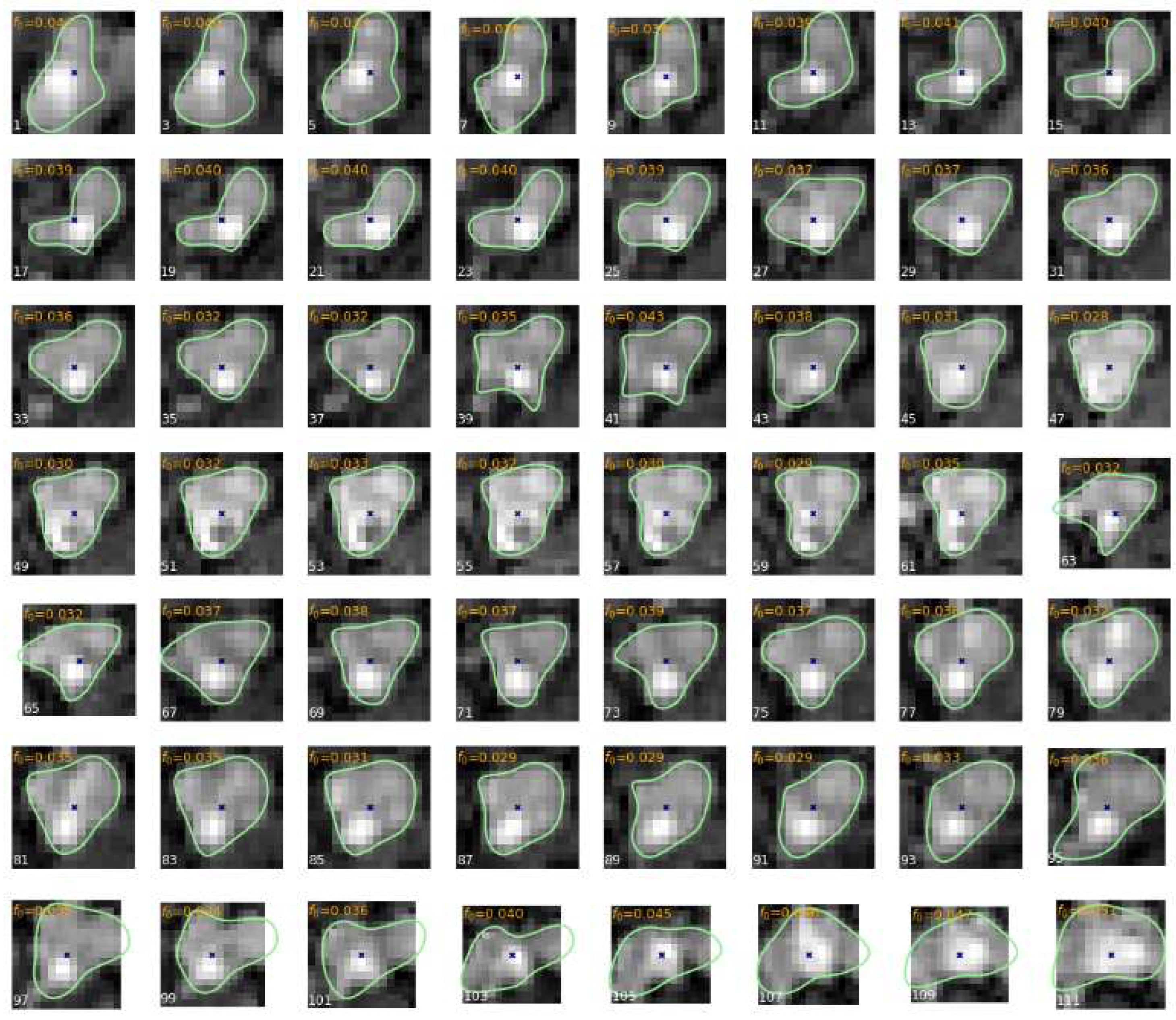
Example contours (lightgreen lines) of the veins-artery lumen obtained in result of LS model fitting to -pixel odd-numbered (1,3,...) sections of branch b14 in the PAVES 05 dataset. Twelve-parameter (a, b, ) B-spline lumen model, =1.0mm, R=11, =0.65. The points marked by a blue „x” symbol indicate the approximate centerline location.
Figure 6.
Example contours (lightgreen lines) of the veins-artery lumen obtained in result of LS model fitting to -pixel odd-numbered (1,3,...) sections of branch b14 in the PAVES 05 dataset. Twelve-parameter (a, b, ) B-spline lumen model, =1.0mm, R=11, =0.65. The points marked by a blue „x” symbol indicate the approximate centerline location.
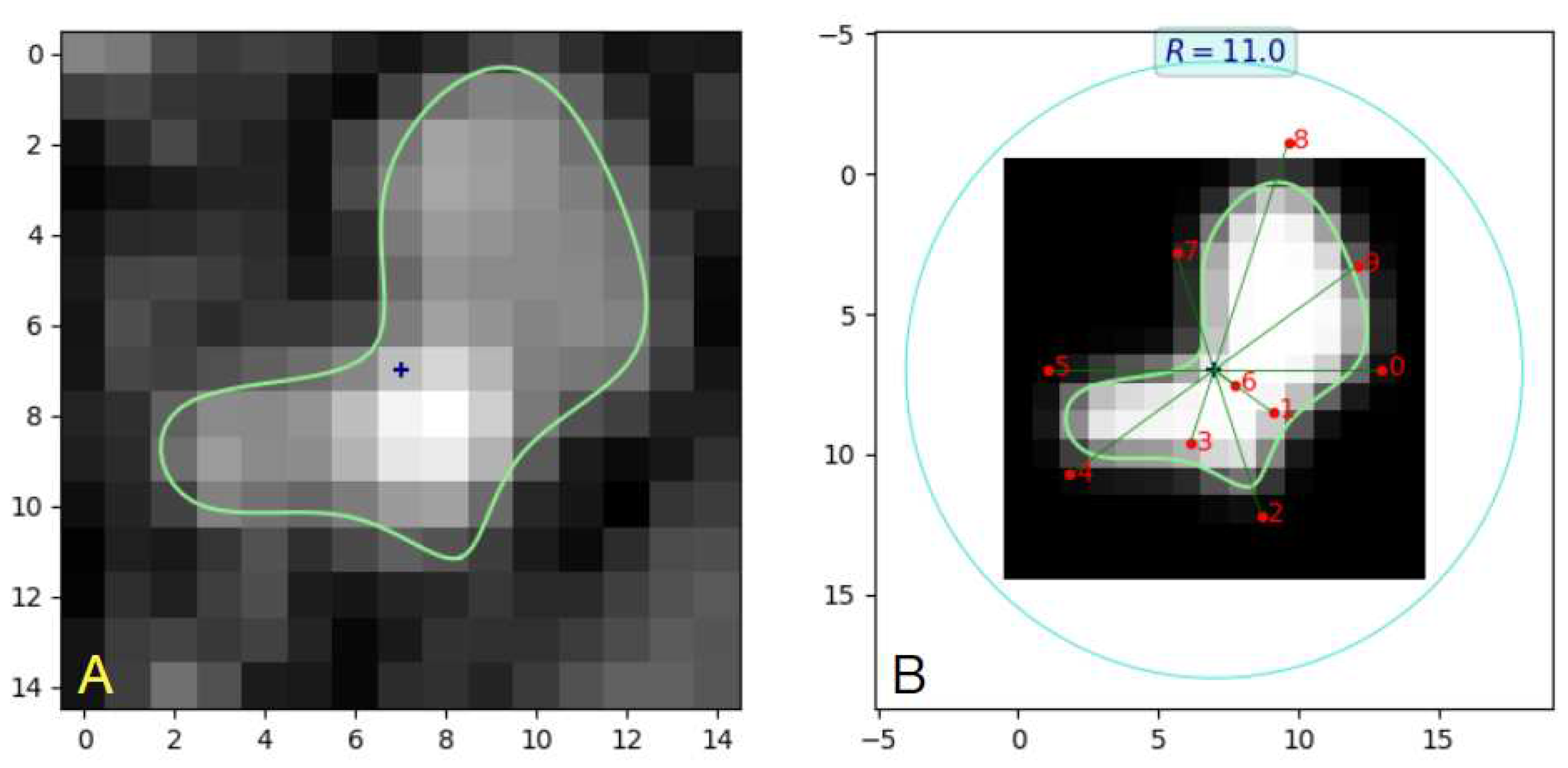
Figure 7.
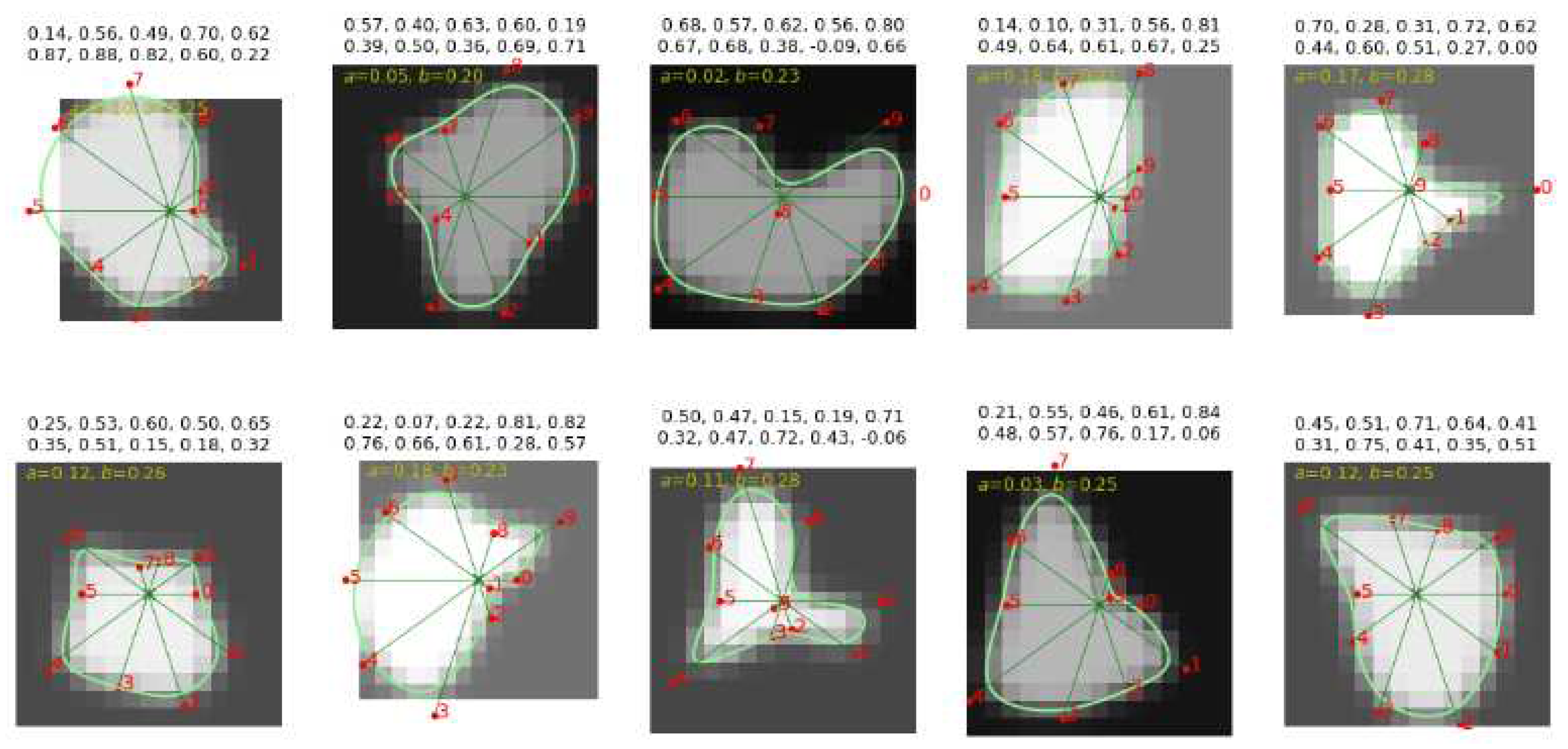
() B-spline contour example for section no. 14 of branch b14 in PAVES 05. () B-spline geometry and synthesized image. The control points are marked by numbered red dots. Control point is located on the radial line at angle -36° (instead of 216°) which indicates negative value of . Indeed, the LS-identified vector for this image is (0.5,0.23,0.50,0.25,0.58, 0.54,-0.08,0.40,0.77,0.57).
Figure 7.
() B-spline contour example for section no. 14 of branch b14 in PAVES 05. () B-spline geometry and synthesized image. The control points are marked by numbered red dots. Control point is located on the radial line at angle -36° (instead of 216°) which indicates negative value of . Indeed, the LS-identified vector for this image is (0.5,0.23,0.50,0.25,0.58, 0.54,-0.08,0.40,0.77,0.57).
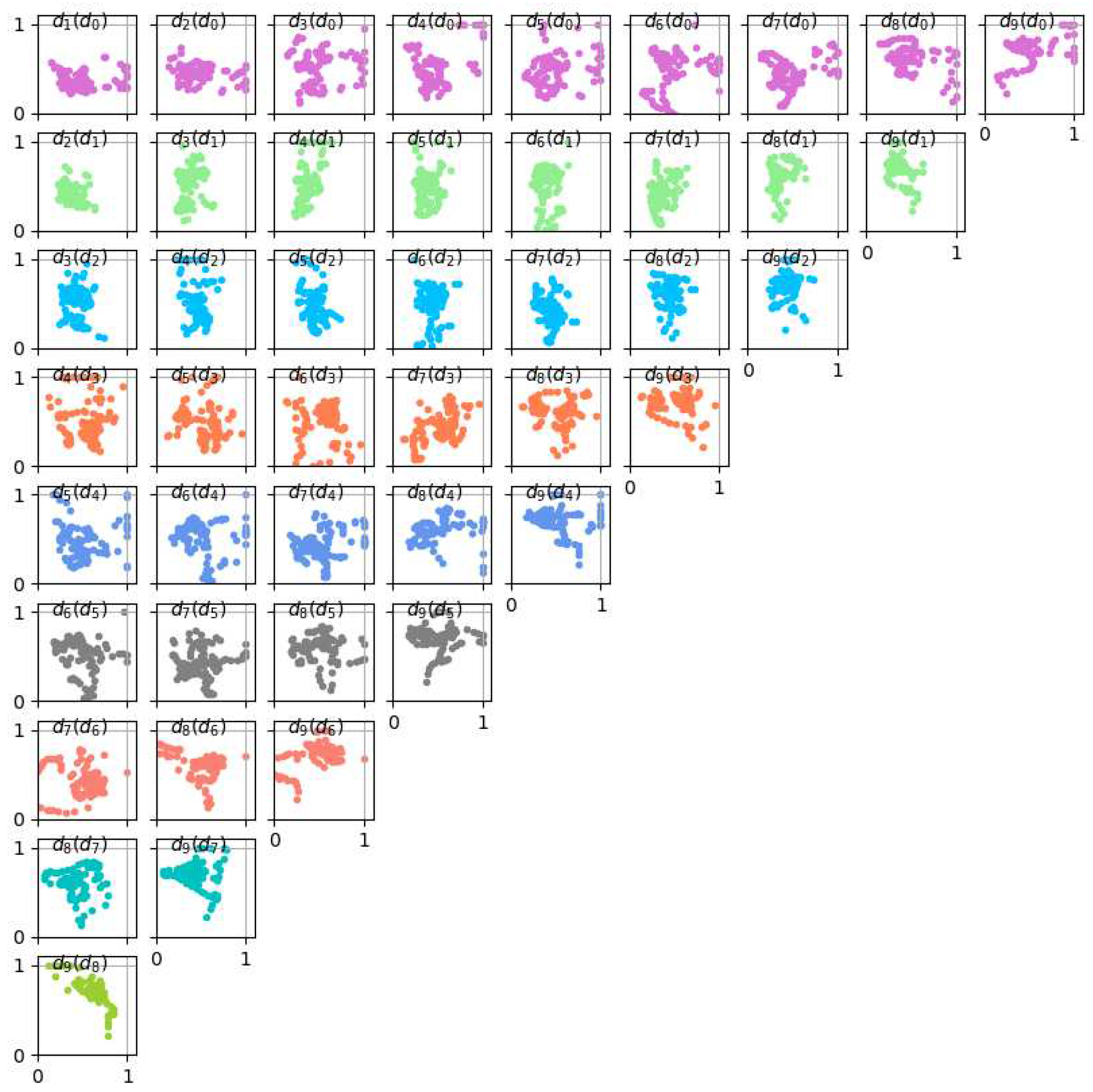
Figure 8.
Scatter plots for LS-estimated B-spline contour parameters for all branch b14 cross-sections in PAVES 05. Each subplot is annotated with a "" text meaning and are its horizontal and vertical coordinates, respectively.
Figure 8.
Scatter plots for LS-estimated B-spline contour parameters for all branch b14 cross-sections in PAVES 05. Each subplot is annotated with a "" text meaning and are its horizontal and vertical coordinates, respectively.
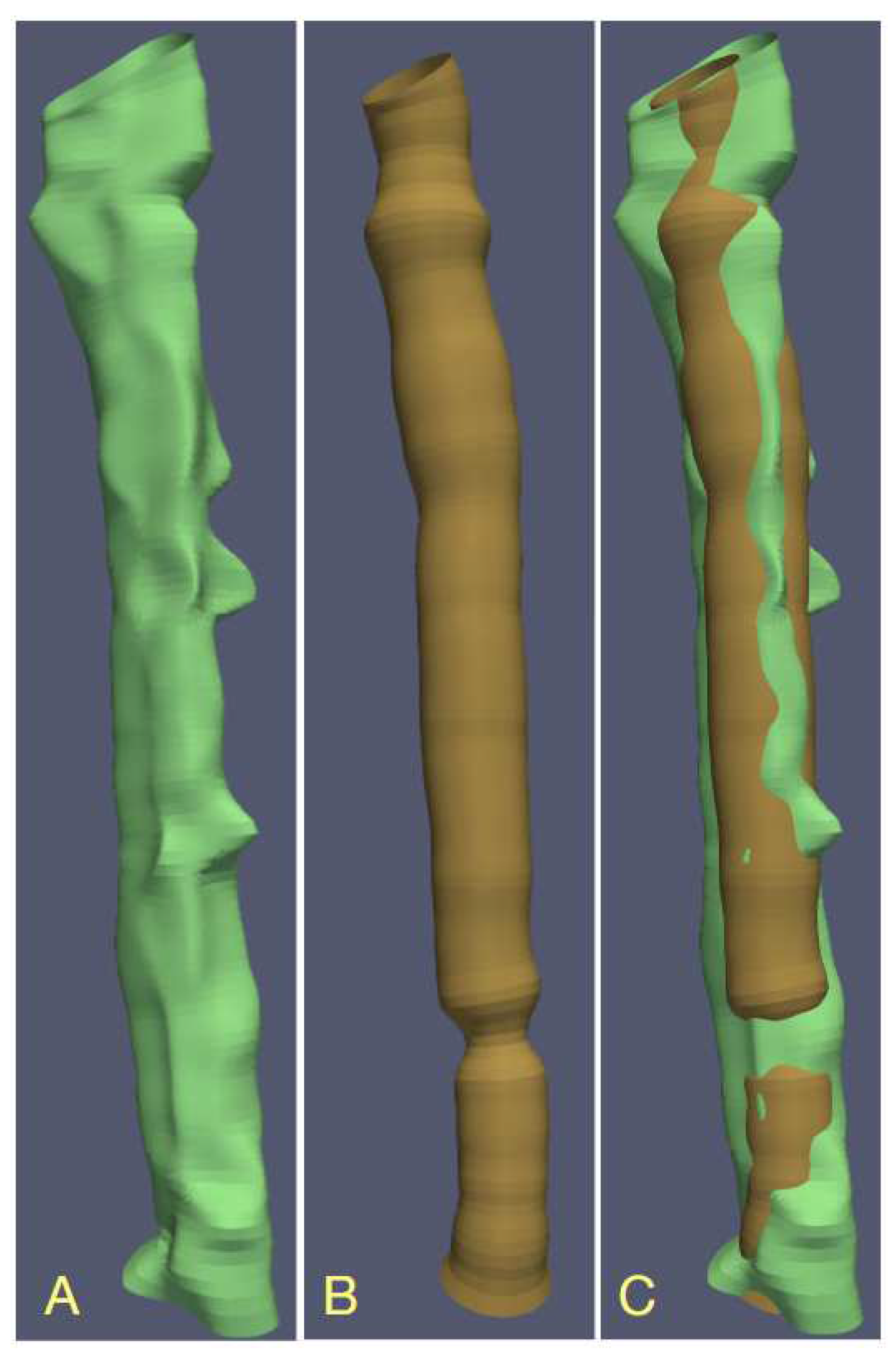
Figure 9.
Visualization of the PAVES b14 branch of vein-artery lumen based on contours obtained with different LS-identified image formation models, () B-spline contours, () circular lumen boundaries, () union of the surfaces in () and ().
Figure 9.
Visualization of the PAVES b14 branch of vein-artery lumen based on contours obtained with different LS-identified image formation models, () B-spline contours, () circular lumen boundaries, () union of the surfaces in () and ().
Figure 10.
Examples of computer-simulated noiseless images for CNN transfer training.
Figure 10.
Examples of computer-simulated noiseless images for CNN transfer training.
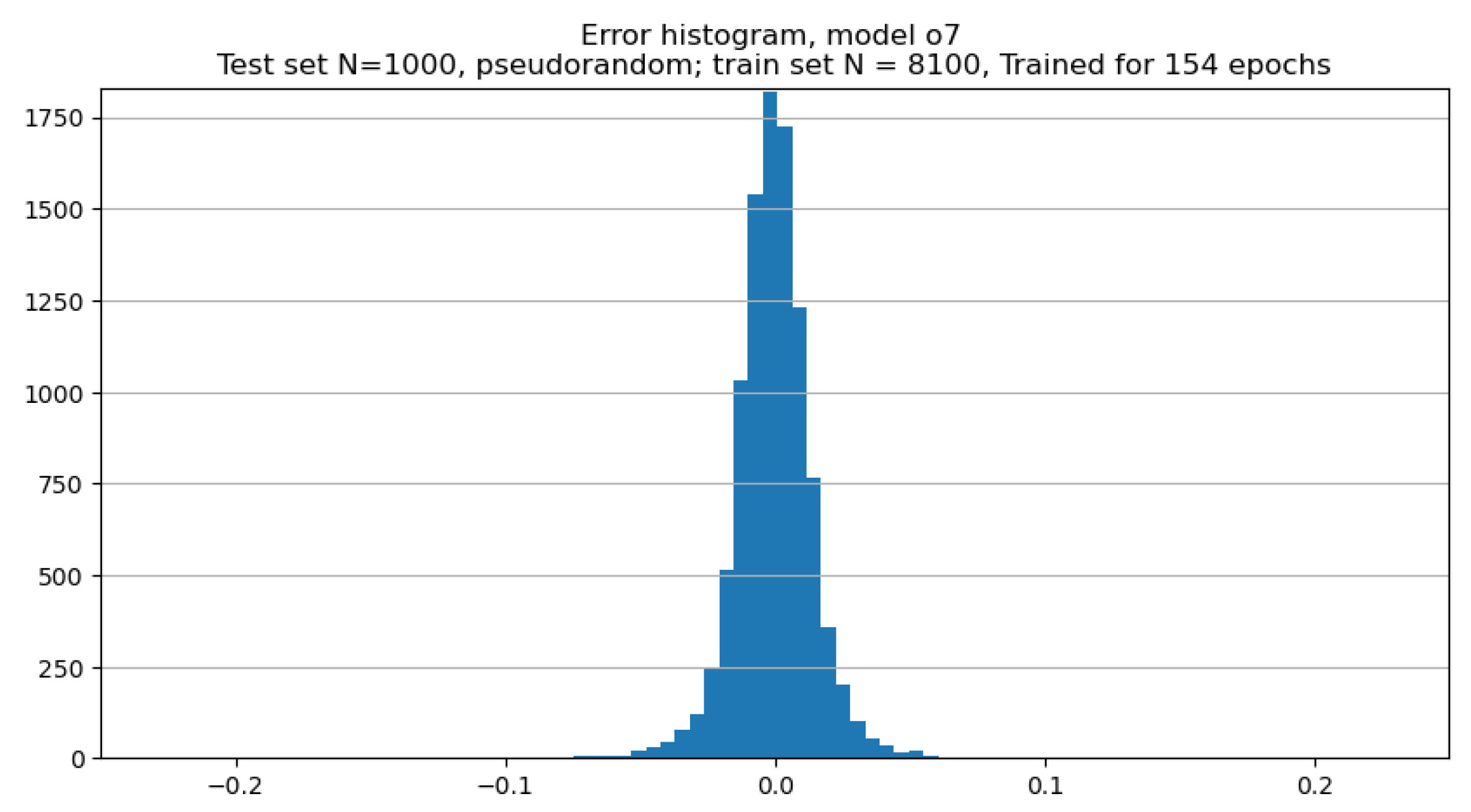
Figure 11.
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and true values of B-spline parameters for the noiseless test set.
Figure 11.
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and true values of B-spline parameters for the noiseless test set.
Figure 12.
Examples of noiseless images of the test set, synthesized with the use of randomly generated B-spline parameters (turquoise lines). Red lines mark contours computed with the use of CNN-predicted B-spline parameters.
Figure 12.
Examples of noiseless images of the test set, synthesized with the use of randomly generated B-spline parameters (turquoise lines). Red lines mark contours computed with the use of CNN-predicted B-spline parameters.
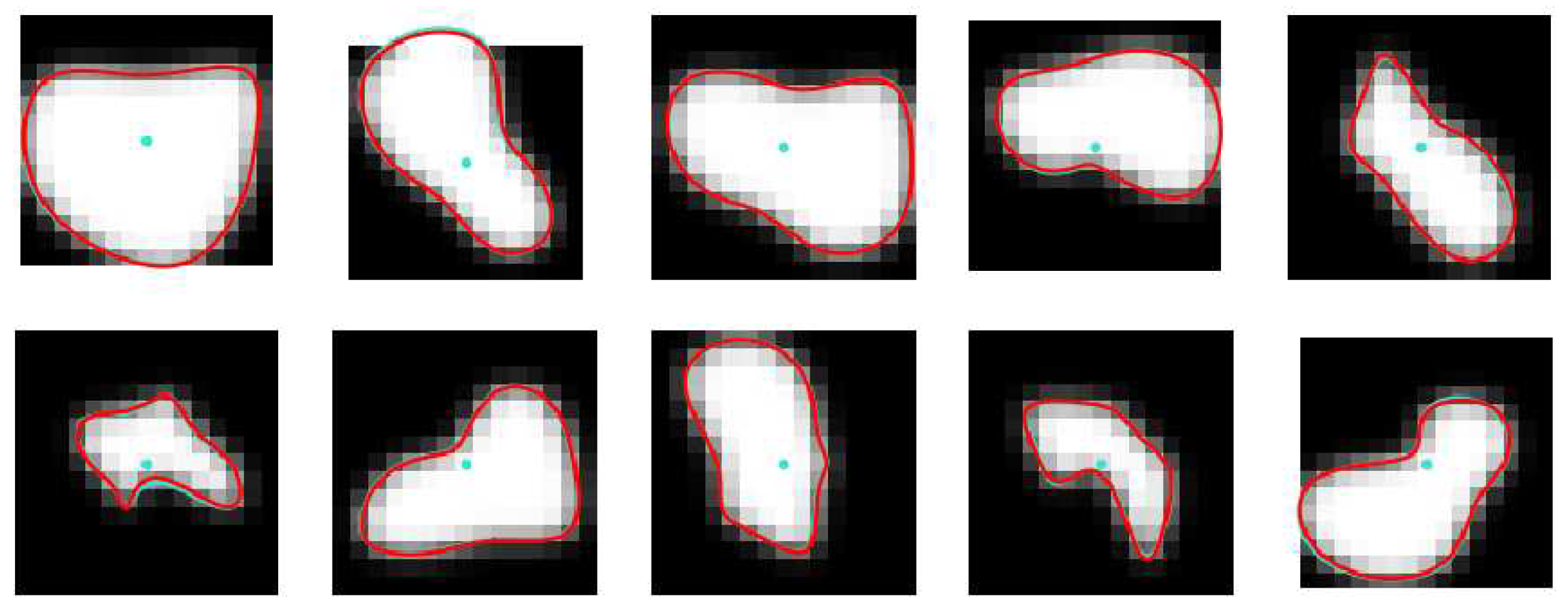
Figure 13.
Example sections of PAVES b14 branch, taken at random. Turquoise lines: lumen contours obtained via LS modeling. Red lines: contours computed with the use of B-spline parameters predicted by the CNN trained on synthesized noiseless images (A) and noisy images (B).
Figure 13.
Example sections of PAVES b14 branch, taken at random. Turquoise lines: lumen contours obtained via LS modeling. Red lines: contours computed with the use of B-spline parameters predicted by the CNN trained on synthesized noiseless images (A) and noisy images (B).
Figure 14.
(A) Example section no. 27 of PAVES b14 branch with LS-predicted lumen contour. One can note random intensity variations. (C) Sample of GIMP-generated fractal-like texture, visually similar to patterns observed in the PAVES data. (B) The image in (C) added to a noiseless image synthesized with the use of contour marked by the lightgreen line.
Figure 14.
(A) Example section no. 27 of PAVES b14 branch with LS-predicted lumen contour. One can note random intensity variations. (C) Sample of GIMP-generated fractal-like texture, visually similar to patterns observed in the PAVES data. (B) The image in (C) added to a noiseless image synthesized with the use of contour marked by the lightgreen line.
Figure 15.
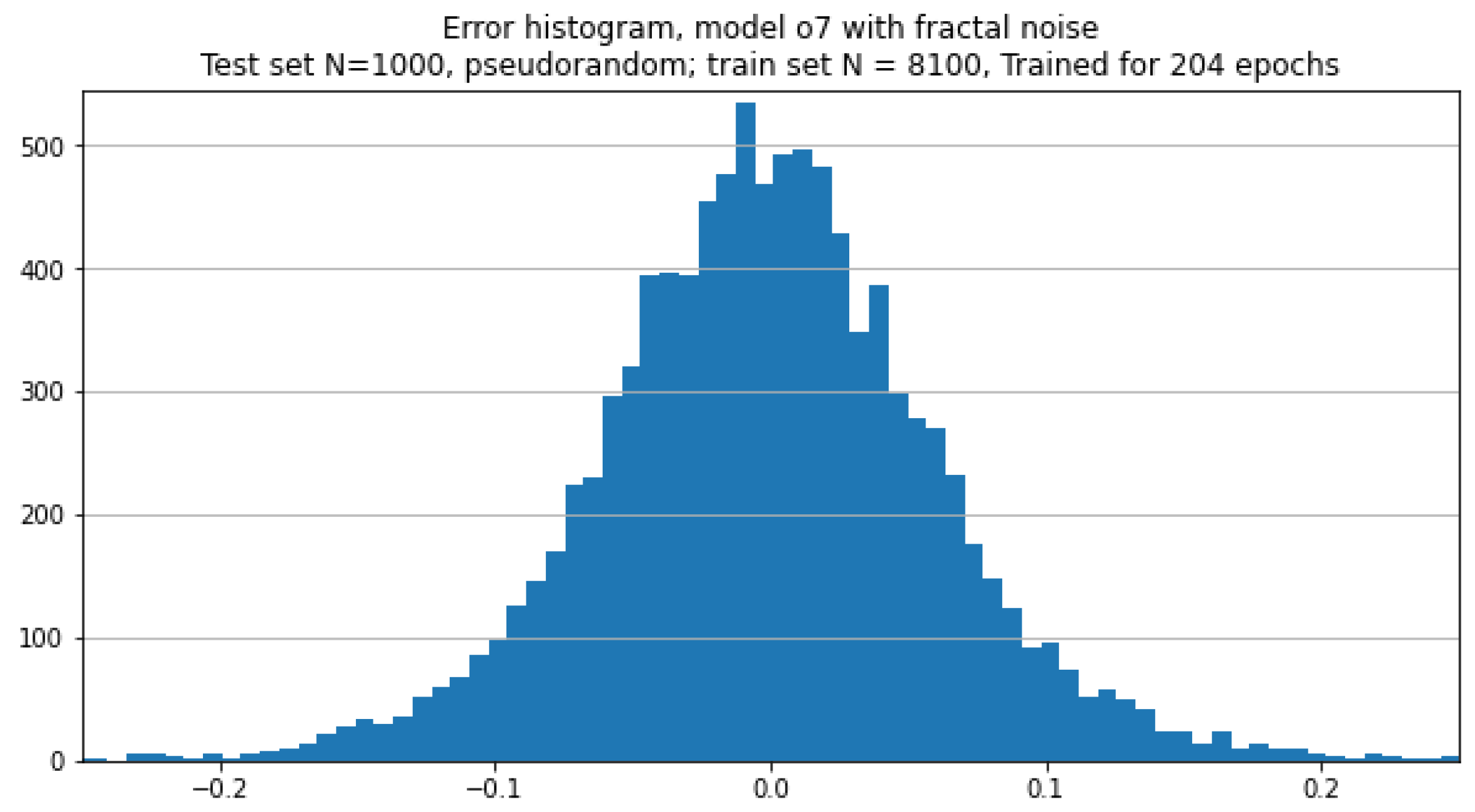
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and true values of B-spline parameters for the noisy test set.
Figure 15.
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and true values of B-spline parameters for the noisy test set.
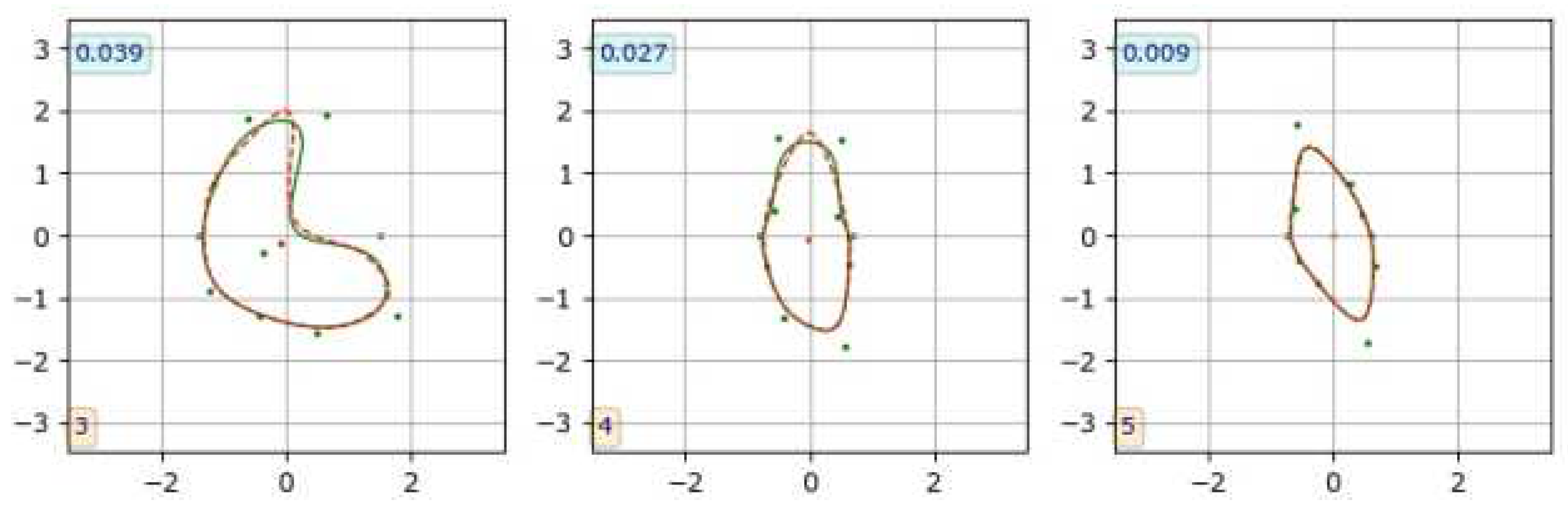
Figure 16.
Three examples of fitting B-spline curves to observer-marked contours (CAT08 data), to find B-spline parameters for CNN training. Dashed red line: contour marked by an observer, green line: B-spline curve. The numbers in boxes indicate the corresponding value.
Figure 16.
Three examples of fitting B-spline curves to observer-marked contours (CAT08 data), to find B-spline parameters for CNN training. Dashed red line: contour marked by an observer, green line: B-spline curve. The numbers in boxes indicate the corresponding value.
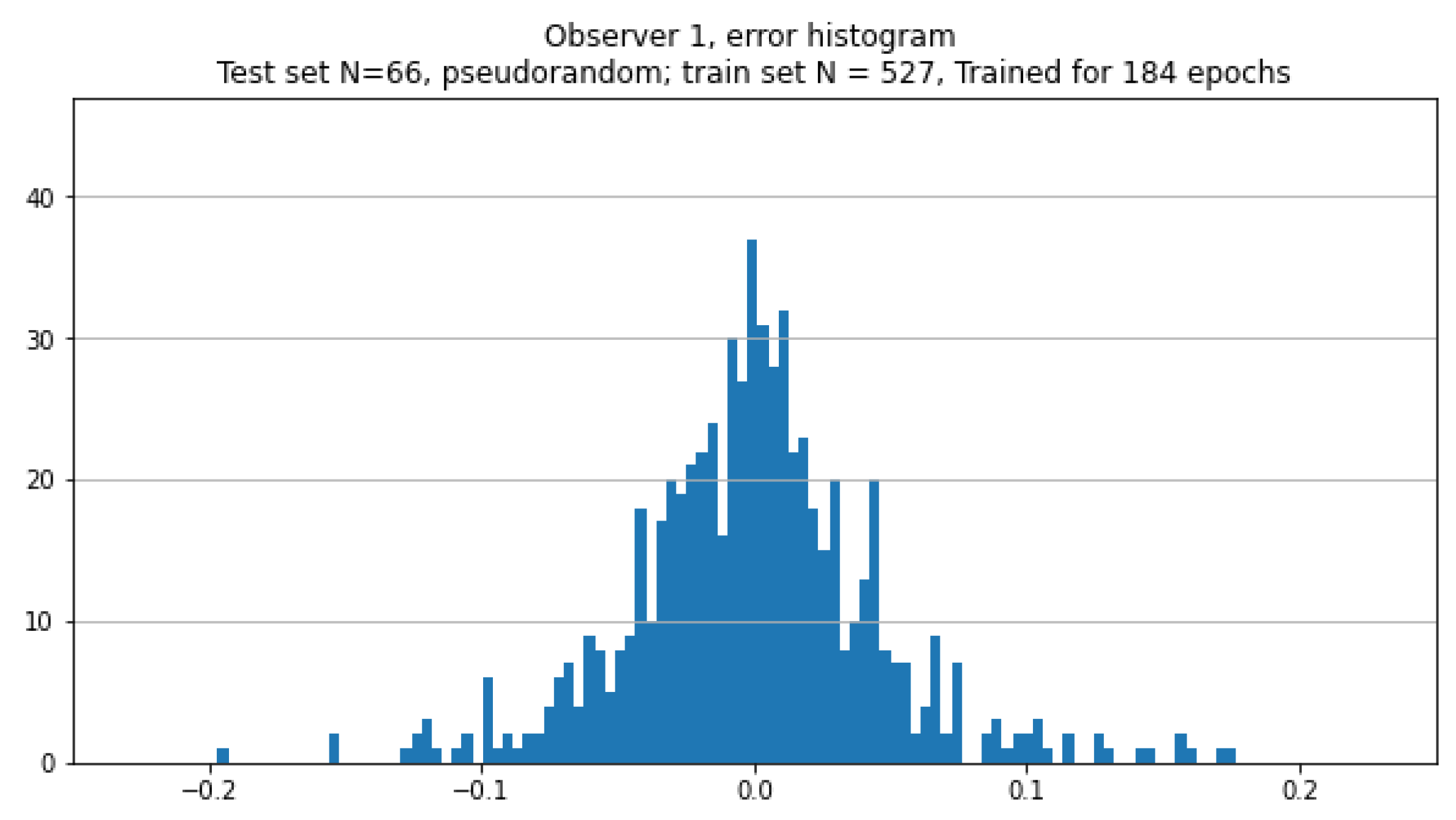
Figure 17.
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and observer-contour-related values of B-spline parameters for the training set (CAT08 data).
Figure 17.
Histogram of the differences between CNN-estimated and observer-contour-related values of B-spline parameters for the training set (CAT08 data).
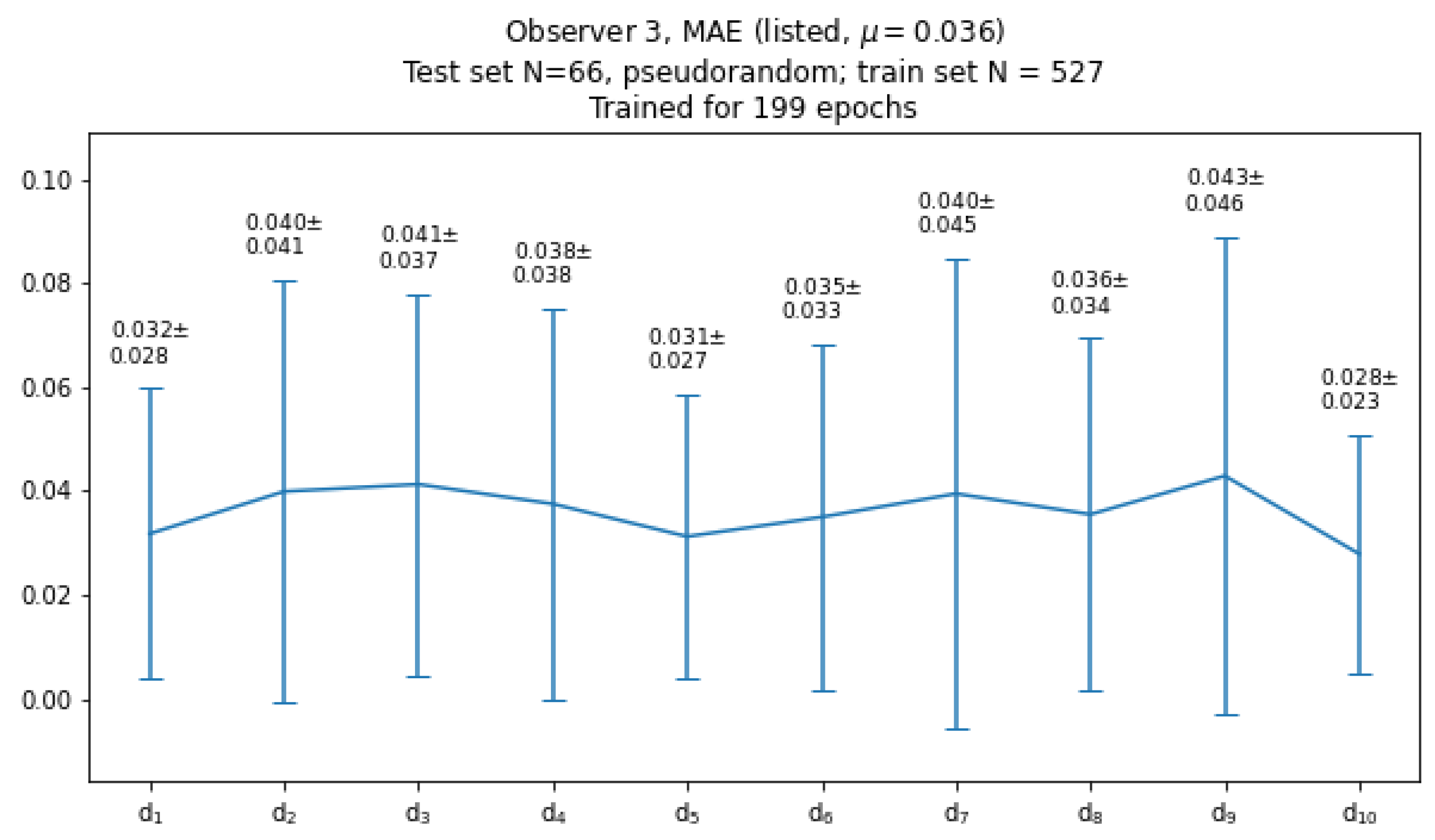
Figure 18.
Plot of the mean values and standard deviations of mean absolute differences between CNN-estimated and observer-contour-related B-spline parameters over the test set (CAT08 data).
Figure 18.
Plot of the mean values and standard deviations of mean absolute differences between CNN-estimated and observer-contour-related B-spline parameters over the test set (CAT08 data).
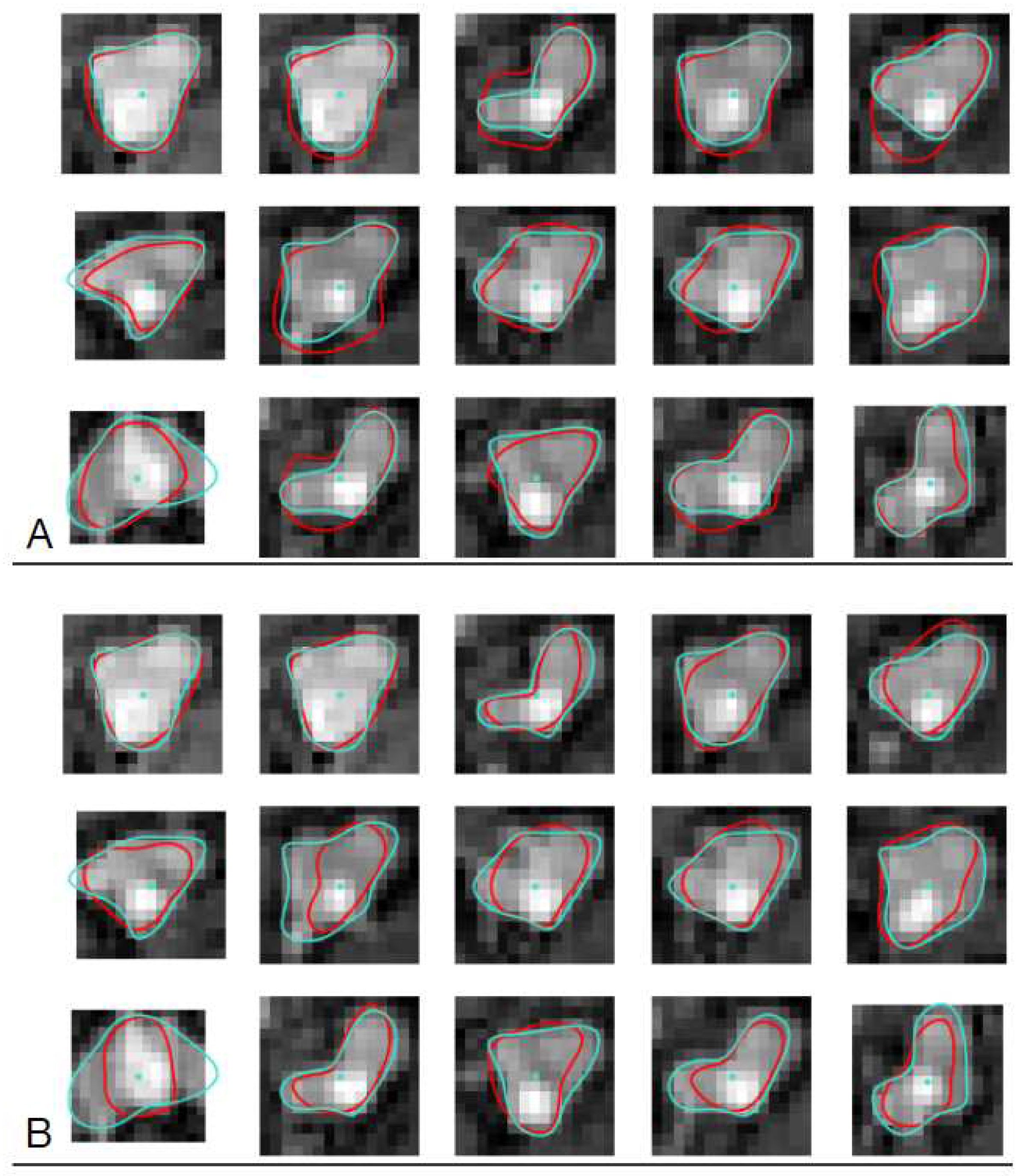
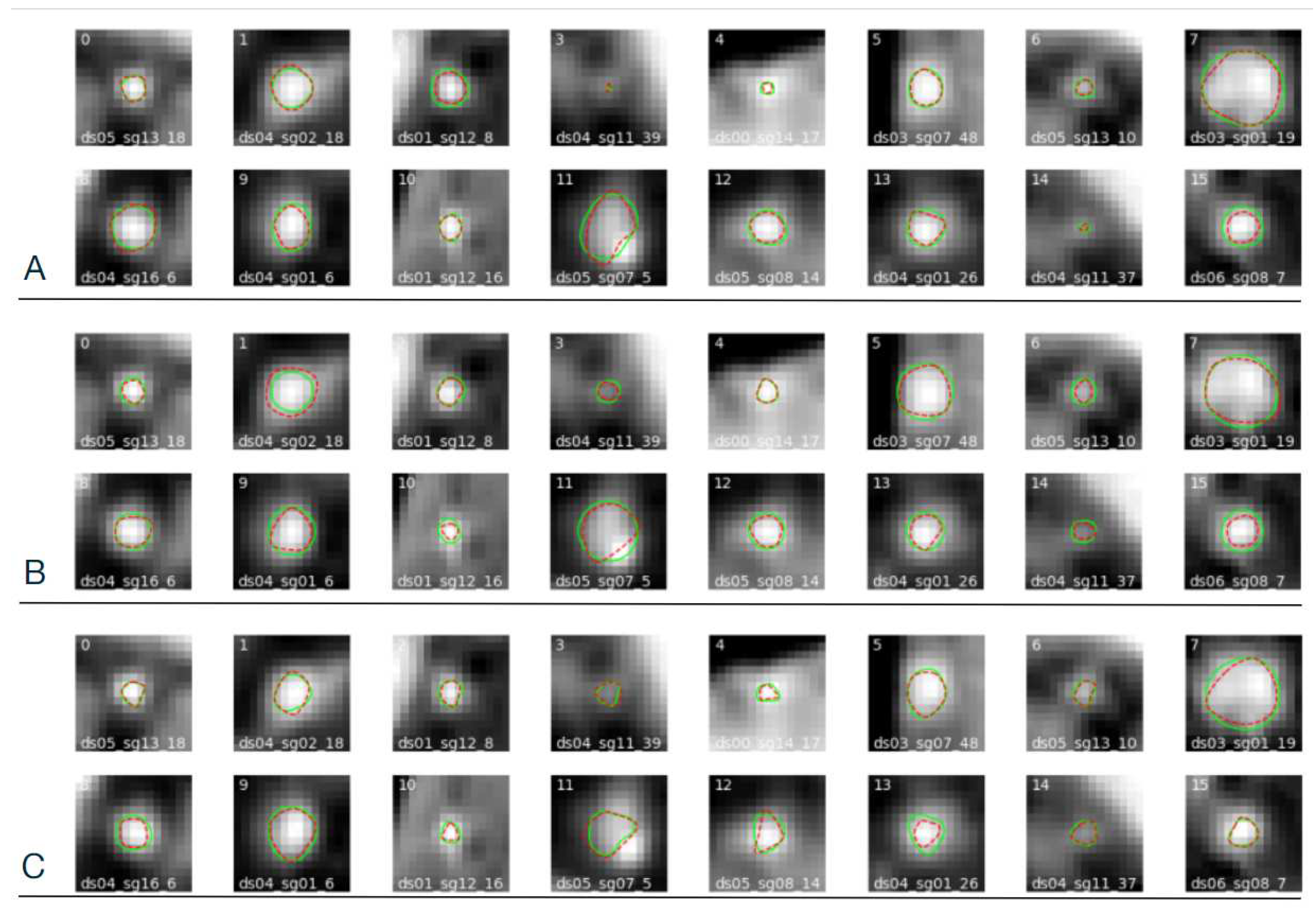
Figure 19.
Example forty eight images of the test set from CAT08 data. Red line: contours marked by observer, green line: CNN-predicted contours. (A) observer no. 1, (B) observer no. 2, (C) observer no. 3.
Figure 19.
Example forty eight images of the test set from CAT08 data. Red line: contours marked by observer, green line: CNN-predicted contours. (A) observer no. 1, (B) observer no. 2, (C) observer no. 3.
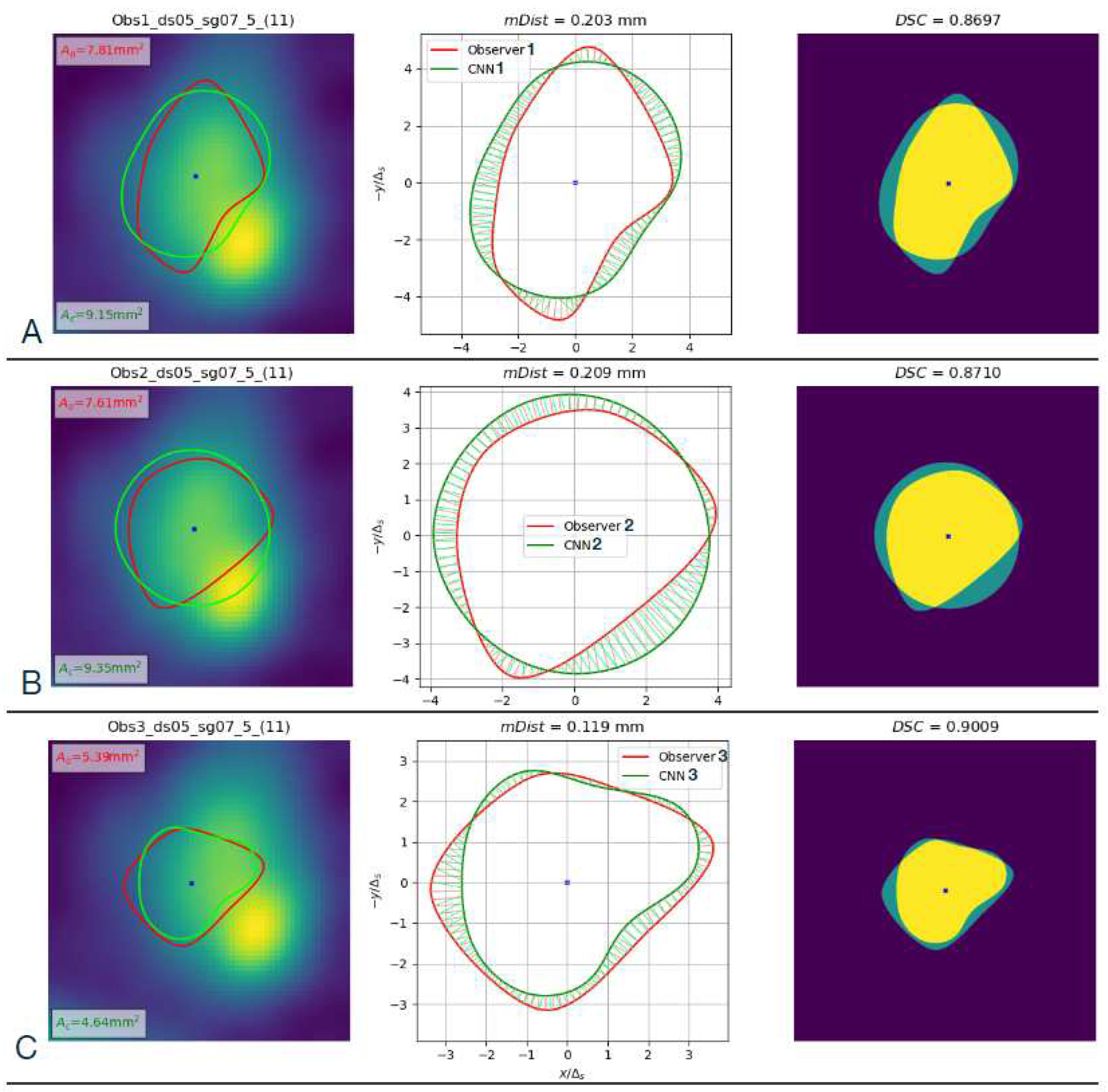
Figure 20.
Left column: Comparison of contours marked by the three observers and computed with the corresponding CNN-predicted B-spline parameters for cross-section No. 11 in the test set (CAT08 dataset 05, segment 07, section No. 5). () observer No. 1, () observer No. 2, () observer No. 3. Middle column: Geometric illustration of calculation. Right column: Image regions used to compute the .
Figure 20.
Left column: Comparison of contours marked by the three observers and computed with the corresponding CNN-predicted B-spline parameters for cross-section No. 11 in the test set (CAT08 dataset 05, segment 07, section No. 5). () observer No. 1, () observer No. 2, () observer No. 3. Middle column: Geometric illustration of calculation. Right column: Image regions used to compute the .
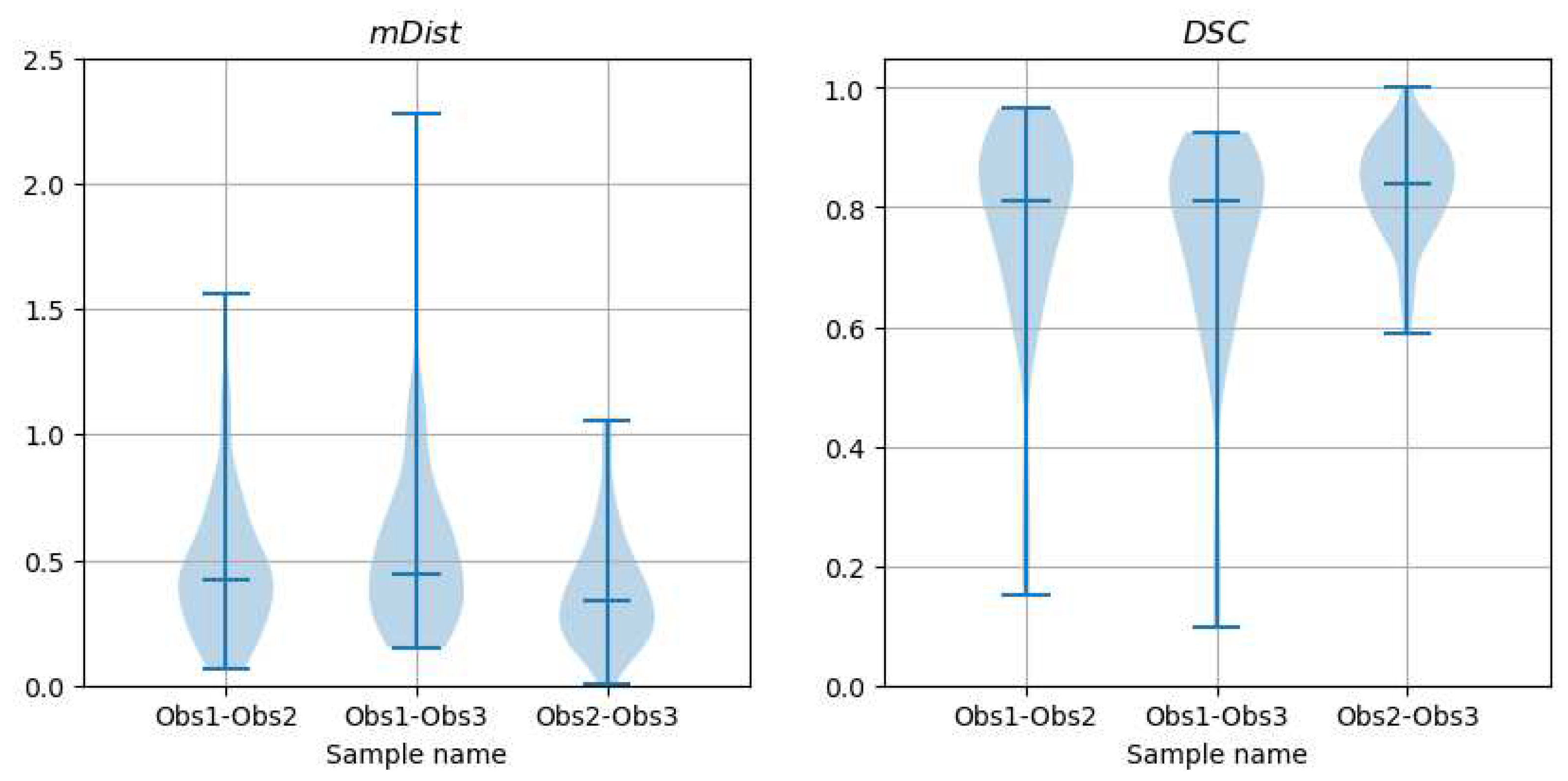
Figure 21.
Violin plots of and descriptors of differences between contours marked by different observers on CAT08 images (interobserver differences).
Figure 21.
Violin plots of and descriptors of differences between contours marked by different observers on CAT08 images (interobserver differences).
Figure 22.
Violin plots of and descriptors of differences between contours marked by observers on CAT08 images and those computed from CNN predictions (trained on the corresponding observer data), over the test set.
Figure 22.
Violin plots of and descriptors of differences between contours marked by observers on CAT08 images and those computed from CNN predictions (trained on the corresponding observer data), over the test set.
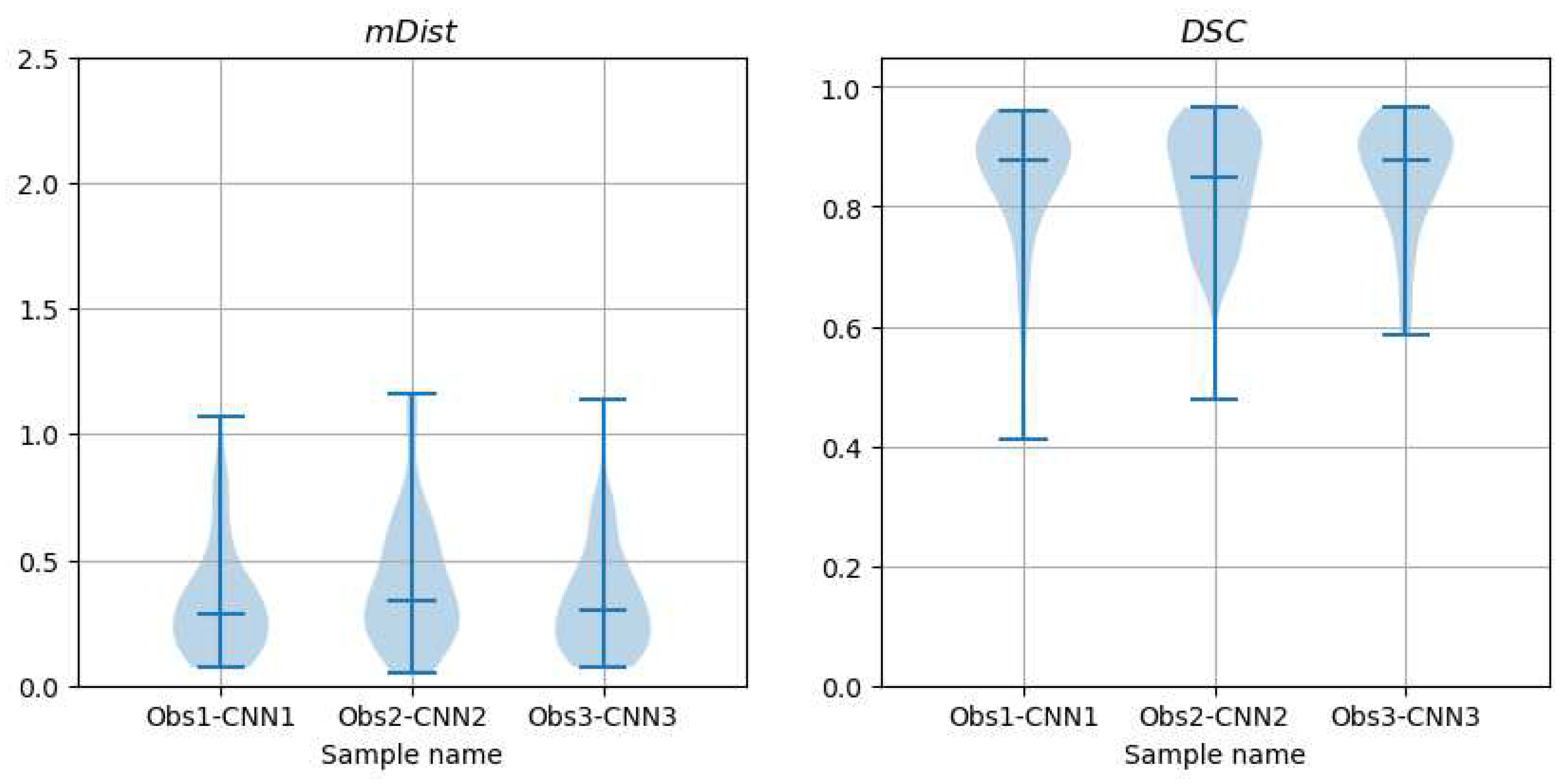
Figure 23.
Violin plots of and for the test set.
Figure 23.
Violin plots of and for the test set.
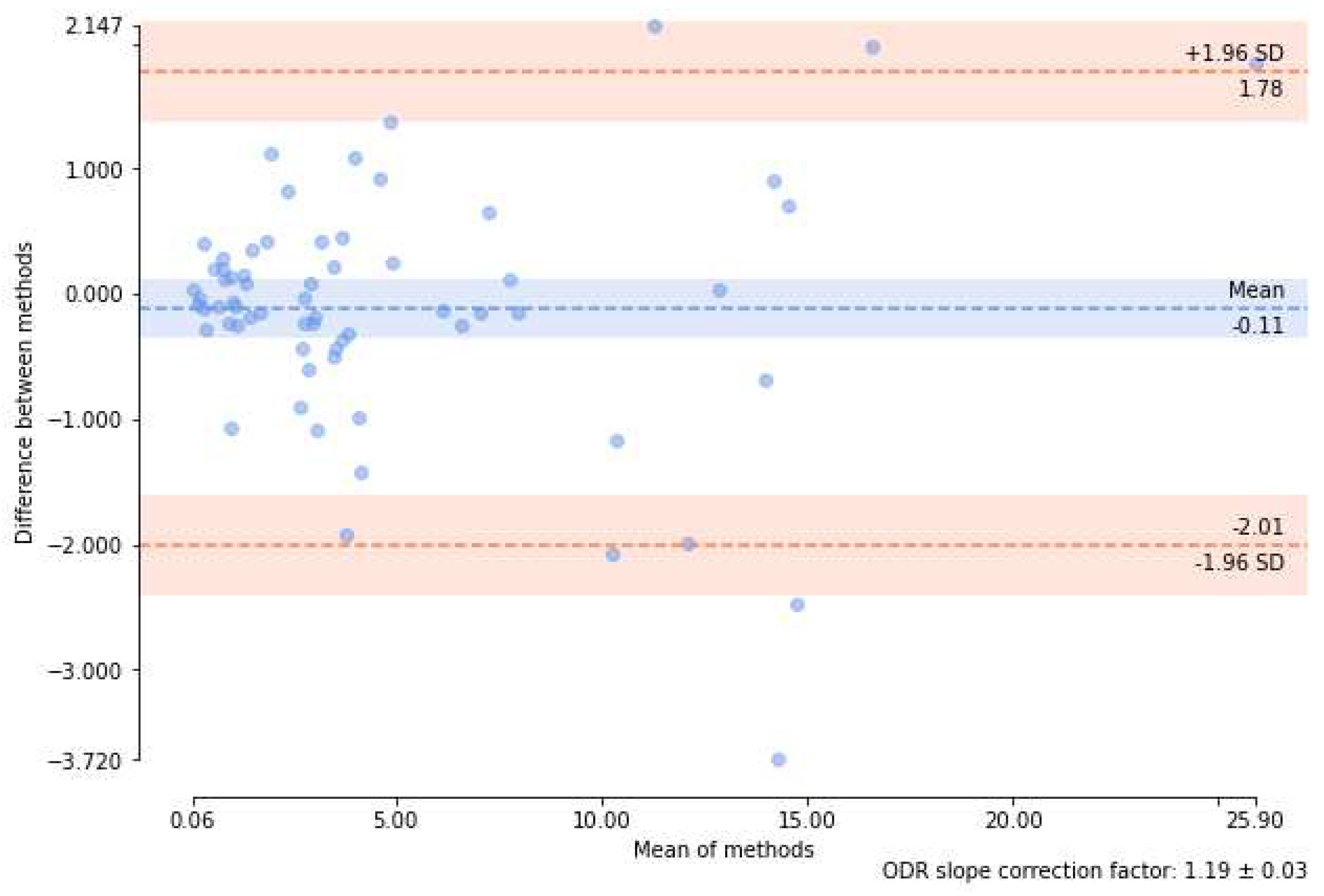
Figure 24.
Bland-Altman plot for
and
over the test set. Computed with ’ODR’ option of
[
37] to "model and remove a multiplicative offset between each assay by orthogonal distance regression".
Figure 24.
Bland-Altman plot for
and
over the test set. Computed with ’ODR’ option of
[
37] to "model and remove a multiplicative offset between each assay by orthogonal distance regression".
Table 1.
Descriptors of observers-marked and CNNs-predicted contours in
Figure 20.
†: Obs1 vs CNN1,
‡: Obs2 vs CNN2, *: Obs3 vs CNN3.
Table 1.
Descriptors of observers-marked and CNNs-predicted contours in
Figure 20.
†: Obs1 vs CNN1,
‡: Obs2 vs CNN2, *: Obs3 vs CNN3.
| |
Obs 1 |
Obs 2 |
Obs3 |
|
, mm |
|
|
|
|
, − |
|
|
|
|
, mm2
|
7.81 |
7.61 |
5.39 |
|
, mm2
|
9.15 |
9.35 |
4.64 |
Table 2.
Median/mean values of and descriptors of shape differences between contours marked by different observers on the same images in CAT08, over the test set.
Table 2.
Median/mean values of and descriptors of shape differences between contours marked by different observers on the same images in CAT08, over the test set.
| |
Obs1 vs Obs2 |
Obs1 vs Obs3 |
Obs2 vs Obs3 |
|
, mm |
0.422/0.462 |
0.440/0.527 |
0.334/0.380 |
|
, − |
0.813/0.771 |
0.809/0.743 |
0.841/0.832 |
Table 3.
Median/mean values of and descriptors of shape differences between observers-marked and CNNs-predicted contours for CAT08 images, over the test set.
Table 3.
Median/mean values of and descriptors of shape differences between observers-marked and CNNs-predicted contours for CAT08 images, over the test set.
| |
Obs1 vs CNN1 |
Obs2 vs CNN2 |
Obs3 vs CNN3 |
|
, mm |
0.284/0.333 |
0.336/0.405 |
0.298/0.335 |
|
, − |
0.876/0.844 |
0.849/0.837 |
0.878/0.851 |
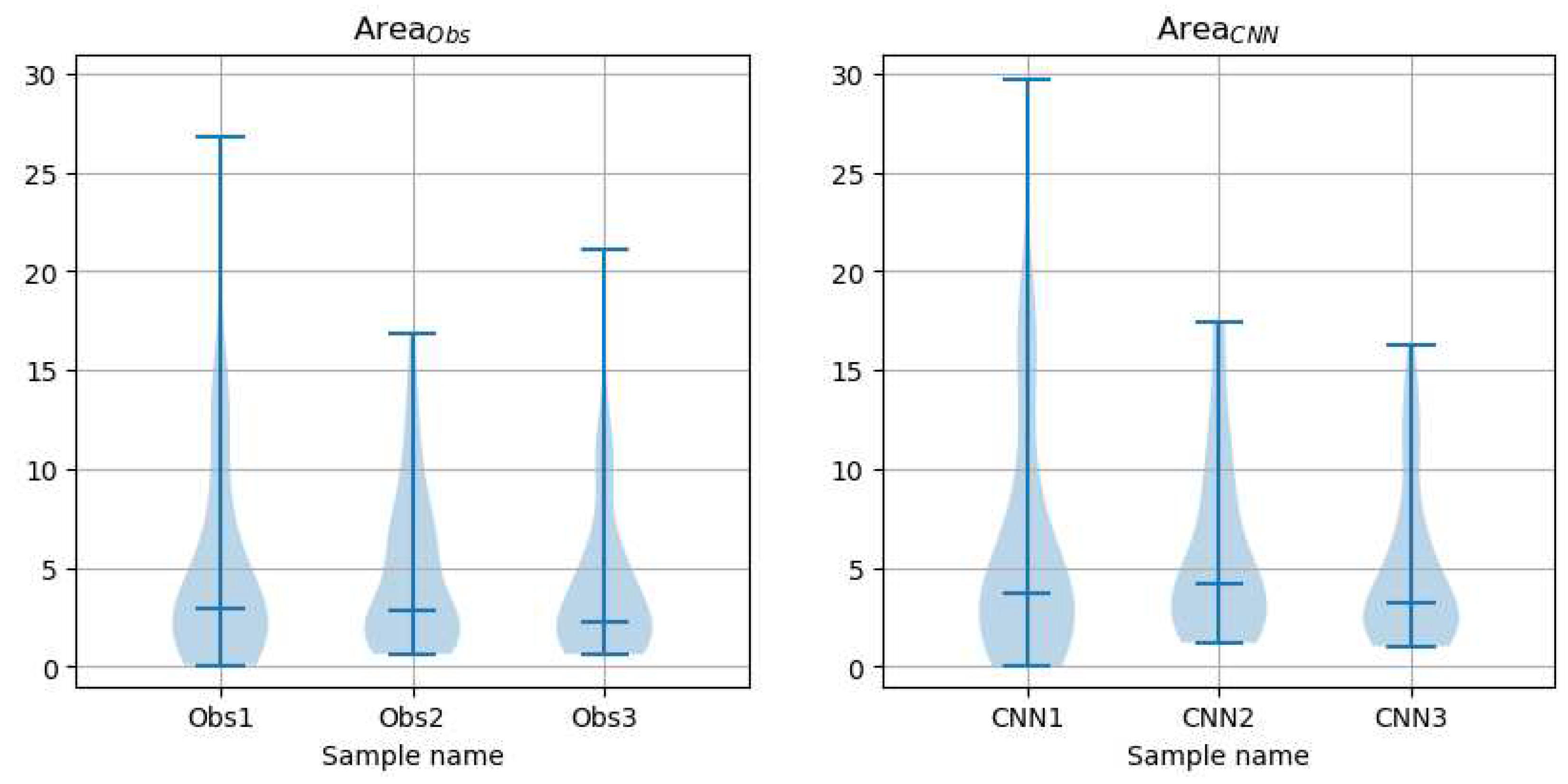
Table 4.
Median/mean values of the area of contours marked by observers and predicted by CNNs , over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository.
Table 4.
Median/mean values of the area of contours marked by observers and predicted by CNNs , over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository.
| |
Obs 1 |
Obs 2 |
Obs 3 |
|
, mm2
|
2.90/4.79 |
2.83/4.71 |
2.23/4.12 |
|
, mm2
|
3.73/5.83 |
4.18/5.68 |
3.26/4.82 |
Table 5.
p-values of the paired Wilcoxon test for and coefficients, over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository.
Table 5.
p-values of the paired Wilcoxon test for and coefficients, over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository.
| |
Observer |
CNN |
Observer vs CNN |
| Obs1 vs Obs2 |
0.775 |
0.751 |
− |
| Obs1 vs Obs3 |
0.085 |
0.034 |
− |
| Obs2 vs Obs3 |
3.5e-5 |
1.9e-5 |
− |
| Obs1 vs CNN1 |
− |
− |
1.4e-8 |
| Obs2 vs CNN2 |
− |
− |
1.2e-7 |
| Obs3 vs CNN3 |
− |
− |
9.7e-9 |
Table 6.
Mean values (in mm
2) of the differences between paired
and
coefficients, over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository. Columns ’None’, ’Linear’, and ’ODR’ correspond to detrending options available in
function used to compare the distributions [
37].
Table 6.
Mean values (in mm
2) of the differences between paired
and
coefficients, over the test set drawn from CAT08 repository. Columns ’None’, ’Linear’, and ’ODR’ correspond to detrending options available in
function used to compare the distributions [
37].
| |
’None’ |
’Linear’ |
’ODR’ |
| Obs1 vs CNN1 |
-1.04 |
-0.20 |
-0.11 |
| Obs2 vs CNN2 |
-0.98 |
-0.76 |
-0.33 |
| Obs3 vs CNN3 |
-0.70 |
-0.93 |
-0.65 |