1. Introduction
Efficient functioning of membrane proteins relies on their accurate insertion into the membrane. The mechanisms of membrane insertion have been the subject of considerable research. Membrane insertion depends on the size of the protein to be inserted. Large membrane proteins, which are characterized by multiple transmembrane domains, require Sec translocons, which are membrane protein complexes that form pores for proteins to permeate the membrane (Sec-dependent membrane insertion process) [
1,
2]. Since highly homologous Sec translocons are present in all organisms, the mechanism of Sec-dependent insertion is considered to be basically conserved. In contrast, Sec-independent processes have been shown to occur in a subset of small membrane proteins and tail-anchored (TA) membrane proteins that cannot use translocons [
3,
4]. In eukaryotes, chaperones for membrane targeting of TA proteins have been identified [
5,
6]. However, because such chaperones have not been found in
Escherichia coli (
E. coli), the Sec-independent process in
E. coli was previously considered to be a spontaneous process. Then, it became evident that spontaneous insertion into liposomes composed only of commercially available
E. coli phospholipids (EPLs) does not reflect the correct biological phenomena. For example, mannitol permease (MtlA), a Sec-dependent protein, spontaneously inserted into EPL liposomes even without the Sec translocon, whereas such improper insertion did not occur in the inner membrane vesicles [
7]. These results suggested that a blocking factor for spontaneous insertion was present in the inner membrane of
E. coli. Diacylglycerol (DAG) was subsequently identified as a factor that blocks unregulated spontaneous insertion into EPL membranes. DAG is a simple molecule with two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol moiety via ester bonds. Nishiyama et al. reported that spontaneous membrane insertion of proteins was significantly inhibited in EPL liposomes containing a physiological concentration of DAG (2–3 w/w% of EPLs) [
7,
8]. Furthermore, in a later study, they discovered that a minor component of
E. coli membrane, membrane protein integrase (MPIase), restored Sec-independent insertions that were suppressed by DAG [
7,
9,
10]. MPIase is also involved in Sec-dependent integration and translocation [
7,
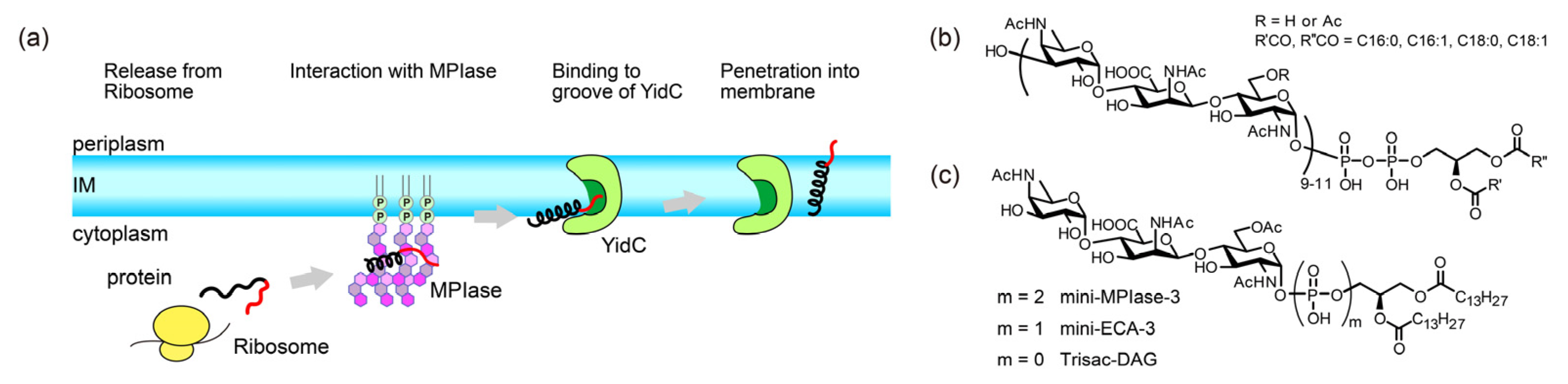
11]. Despite its name, structural analysis revealed that MPIase is a novel glycolipid composed of a DAG anchor moiety, a long sugar chain consisting of approximately ten trisaccharide units, and a pyrophosphate linker (
Figure 1b) [
10]. MPIase dose-dependently enhances Sec-independent insertion into DAG-containing liposomes [
9].
Moreover, in the Sec-independent insertion process, substrate proteins require the help of a proteinaceous factor called YidC, as the hydrophilic proportion of the substrate proteins increases [
12,
13,
14]. YidC transiently captures the hydrophilic regions of a substrate protein in its hydrophilic groove in the membrane (
Figure 1a) [
15]. In addition, the short transmembrane domain of YidC locally thins the lipid bilayer, facilitating the crossing of the hydrophilic region of the protein through the bilayer [
12,
16,
17]. Thus, YidC is recognized as an insertase; however, most previous studies have been conducted in the absence of DAG and MPIase. Nishiyama et al. reported that substrate proteins were not inserted into DAG-containing liposomes without MPIase, even in the presence of YidC, whereas insertion was dependent on MPIase without YidC. In contrast, when YidC coexists with MPIase in DAG-containing liposomes, it accelerates insertion [
18,
19]. Therefore, we consider that MPIase functions at the initial step of protein integration into the membrane, whereas YidC completes insertion later.
To date, several MPIase analogs have been synthesized to elucidate insertion mechanisms [
20,
21]. A minimal structural unit of MPIase, mini-MPIase-3 (
Figure 1c), consisting of only one trisaccharide unit, displayed significant activity, although it was less efficient than natural MPIase [
21]. Trisac-DAG, a mini-MPIase-3 analog lacking pyrophosphate, and mini-ECA-3, which has a monophosphate linker instead of a pyrophosphate linker (
Figure 1c), exhibited lower integration activity than mini-MPIase-3. Structure-activity relationship studies have enabled us to analyze the insertion process at the atomic level using natural MPIase and its synthetic analogs [
20,
21]. We examined the Sec-independent membrane protein insertion mechanisms facilitated by MPIase based on physicochemical analytical techniques such as solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), fluorescence measurements, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [
22,
23,
24].
In this review, we describe the mechanism of the initial step of Sec-independent membrane insertion induced by MPIase. Before discussing the role of MPIase, we outline the physicochemical characteristics of membranes that may affect protein membrane insertion. Subsequently, we introduce our results to verify the effects of membrane properties on insertion using physicochemical analytical methods and describe how MPIases support membrane insertion into DAG-containing membranes. Next, we discuss the interactions between MPIase and membrane proteins, which affect the efficiency prior to insertion. Finally, the proposed insertion mechanism facilitated by MPIase is described in detail.
2. Factors influencing membrane protein insertion
Membrane insertion that does not require Sec translocons is affected by the physicochemical characteristics of the membranes. Historically, the membrane insertion of peptides, especially antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), has been extensively studied in various membranes. In this section, we describe the general effects of membrane lipids on alterations in membrane properties.
2.1. Charges of membrane lipids
Membrane insertion can be affected by the charges of membrane lipids. The polar head of phospholipids commonly has a negatively charged monovalent phosphate diester group. The net charge of lipids depends on the attached functional group; phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), which have positively charged choline and ethanolamine groups, respectively, are neutral, whereas phosphatidylglycerol (PG), which has an uncharged glycerol group, and phosphatidylserine (PS), which has a twitterionic serine residue, are acidic with negative net charges. The lipid composition varies considerably among organisms; eukaryotic cell membranes contain large amounts of PC and cholesterol, whereas bacterial cell membranes are rich in PE and PG. In general, positively charged peptides exhibit a higher insertion ability into negatively charged membranes than into electrically neutral membranes. For example, many positively charged AMPs demonstrate greater binding and insertion into PG-rich membranes than into PC-only membranes [
25,
26]. This difference is thought to be one of the reasons why antimicrobial peptides selectively disrupt bacterial membranes.
2.2. Acyl chain ordering
The acyl chain ordering of membrane lipids also influences membrane insertion. In cholesterol-containing membranes, the acyl chains of the membrane lipids are ordered. Since the polar head of cholesterol is a hydroxyl group, which is much smaller than that of phospholipids, cholesterol tends to fit between lipids with large head groups, such as PC. Under the "umbrella" of the phospholipid head groups, the acyl chains of the phospholipid and sterol ring of cholesterol become tightly packed, making insertion difficult [
27]. Indeed, the presence of cholesterol has been shown to significantly inhibit peptide membrane binding and insertion [
25]. Cholesterol is abundant in mammalian membranes, but absent in bacterial membranes. As mentioned later, in
E. coli membranes, DAG functions in a manner similar to that of cholesterol.
2.3. Spontaneous lipid curvature
Non-cylindrical lipids in the bilayers tend to modify the physicochemical properties of membranes. When non-cylindrical lipids form a bilayer, their curvature differs from the spontaneous curvature of the lipid. To compensate for this difference, lateral pressure was induced in the membrane. For example, a membrane composed of cone-shaped lipids increases the lateral pressure in the acyl chain region, whereas that of inverted cone-shaped lipids results in higher lateral pressure in the head group region. Alterations in the lateral pressure influence the ability to insert a protein into the membrane. The depth of peptide membrane insertion depends on the spontaneous curvature of the lipids constituting the membrane [
28]. In membranes containing lipids with negative spontaneous curvature, peptides bind easily to the membrane surface because of the lower pressure in the region of the head group. However, deeper insertions of peptides become difficult owing to the higher lateral pressure inside the membrane. In contrast, in membranes containing lipids with a positive spontaneous curvature, peptides have difficulty binding to the membrane surface; however, once bound, the peptides can easily penetrate deeper into the bilayer.
In addition, binding and insertion into membranes containing cone-shaped PE depends on the type of peptide. The intervesicular transfer of the hydrophobic transmembrane helix peptide, (AALALAA)
3, decreased as the PE fraction increased [
29]. The tightness of the PE membranes hampered their transfer. For the amphipathic α-helical peptide, Ac-18A-NH
2, however, there was an increased partitioning of the peptide to the membrane correlating with the rise in the PE mole fraction [
30]. In this case, the positively charged side of the amphipathic peptide was in contact with the hydrophilic membrane surface. Although the small head group of PE is advantageous for accepting the peptide, the amphipathic peptide could not be further embedded in the hydrophobic core region and accumulated on the membrane surface.
2.4. Membrane defects
The induction of positive curvature in the membrane causes structural defects. With structural defects, the hydrophobic core of the membrane is more exposed to the membrane surface, making it easier for the hydrophobic side chains of the peptides to interact with the membrane. For example, the amphiphilic helical peptide EpN-18, derived from the N-terminus of epsin-1, induces positive membrane curvature. Coexistence with EpN-18 enhances the plasma membrane permeability of the octa-arginine peptide, possibly because EpN-18 increases structural defects in the membrane, exposing its hydrophobic core to the membrane surface [
31,
32].
2.5. Conformational changes of proteins associated with membranes
Conformational changes are often observed when peptides bind into membranes. When an amphiphilic peptide is inserted into the membrane, favorable interactions between nonpolar residues and the lipid tail and between charged residues and the solvent molecules or charged sites of the lipid head group convert the peptide from a random coil to a helix. In some cases, amphiphilic peptides are further inserted into the hydrophobic core. Hydrophobic peptides are readily inserted into the hydrophobic core of the membrane and are simultaneously converted to the α-helix structure.
3. Factors influencing membrane protein insertion
In this section, the verification of the effect of membrane properties on membrane insertion using a Sec-independent substrate is described. Generally, membrane proteins have one or two hydrophobic transmembrane regions and basic amino acid residues at the cytoplasmic loop, which is known as the “positive-inside rule” [
33,
34]. As a model substrate for Sec-independent integration, we have used the Pf3 coat protein (hereafter referred to as Pf3 coat), a major coat protein of the bacteriophage Pf3, and its derivatives (
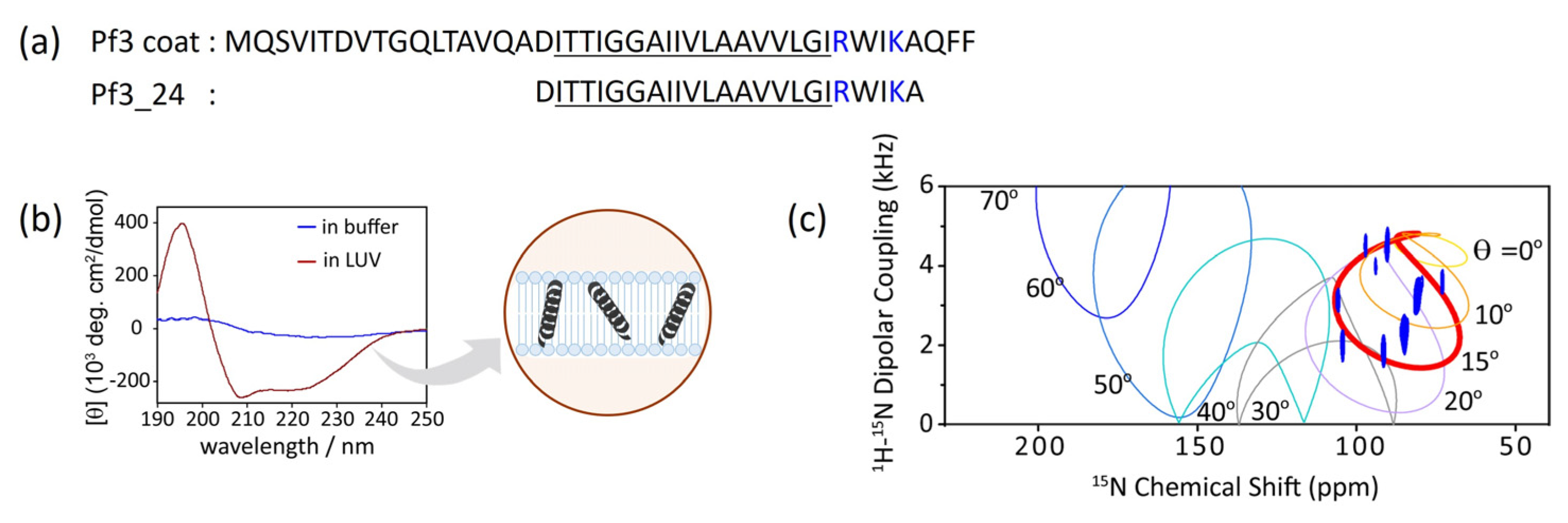
Figure 2a). To fully penetrate the extramembrane region, the insertion of intact Pf3 coat into the lipid bilayer sometimes requires YidC or a membrane potential. Because we focused on the initial insertion process, truncated Pf3 coat (Pf3_24) corresponding to the transmembrane region was used as the simplest model for verification.
3.1. Conformational changes and topology of Pf3_24 in membranes
Typically, the transmembrane regions of membrane proteins are inclined to adopt α-helical or β-strand conformations. Circular dichroism (CD) spectrum showed that Pf3_24 adopts an α-helical conformation when inserted into the lipid bilayer (
Figure 2b, dark red) although it is difficult to determine the secondary structure of Pf3_24 in buffer solution due to its tendency to form aggregates and precipitates (
Figure 2b, blue). Solid-state NMR is a useful technique for obtaining the accurate tilt angles of helical peptides or helical parts of proteins with respect to the membrane. The topology of Pf3_24 in bicelles was determined using
1H–
15N SAMPI4 spectra (
Figure 2c) [
35]. A characteristic PISA wheel pattern of Pf3_24 (
Figure 2c, blue) implies the formation of an α-helical structure in bicelles [
36]. The insertion angle of Pf3_24 into the membrane from the bilayer normal was determined to be approximately 15° by fitting, to account for the wobbling motion of the bicelles. Based on its angle and hydrophobicity, Pf3_24 directly accessed the deeper regions of the membrane. Simultaneously, conversion to the α-helix structure likely occurs.
3.2. Insertion of Pf3_24 into membranes
We estimated insertion efficiency based on the strong correlation between
15N NMR chemical shifts and protein secondary structure [
37,
38]. Wang and Jardetzky reported that the averaged
15N chemical shift values of valine residues were 123.27 ppm for the β-strand, 119.66 ppm for the random coil, and 119.53 ppm for the α-helix [
37]. As aforementioned, Pf3_24 has a complete α-helical structure in large unilamellar vesicles (LUV) of 1,2-dimyristoyl-
sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) (
Figure 3a, top), which was verified by the chemical shift value for valine. Conversely, in the absence of membranes, Pf3_24 formed aggregates, yielding signals at 125 and 120 ppm, which indicate that most of it adopted β-strand-rich structures, whereas some parts formed random coils and α-helical structures (
Figure 3a, middle). To observe membrane insertion, as shown in
Figure 3b, Pf3_24 solubilized in 1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DHPC) solution was mixed with LUVs composed of various lipid types. During incubation, some Pf3_24 was inserted into the LUVs, whereas the remainder formed aggregates outside the LUVs. The third spectrum was obtained from the experiment conducted in the presence of DMPC LUVs (
Figure 3a, bottom). We considered that the third spectrum represents the weighted sum of the first and second spectra, with the coefficient of the first spectrum corresponding to the insertion efficiency. Thus, the relative peak intensities corresponding to the α-helix and the aggregates in the third spectrum provided an insertion efficiency of 46% for the DMPC membrane. Similarly, we calculated the insertion efficiency values for membranes with various lipid compositions (
Figure 3c).
In comparing the efficiencies of the major membrane lipids, we noted significantly lower levels in PE and EPL membranes, which contained cone-shaped lipids. Thus, the membrane insertion efficiency depends more on the molecular shape than on the charge of the lipids.
3.3. Acyl chain mobility and membrane surface packing
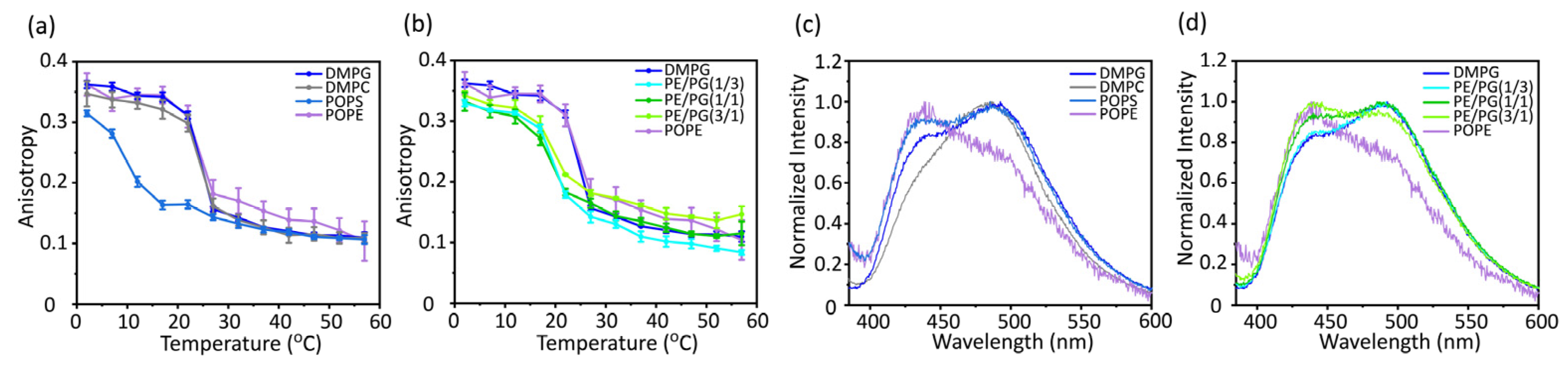
The mobility inside the membrane was analyzed by measuring the anisotropy of the fluorescent probe 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene (DPH), which was incorporated near the bilayer core region (
Figure 4a,b). An increase in the fluorescence anisotropy values of DPH reflects an increase in the molecular order in the membrane core region [
39]. The membrane mobility of PE was significantly lower than that of the other bulk lipids (
Figure 4a). In addition, the membrane mobility decreased as the PE concentration increased (
Figure 4b).
Membrane packing was also analyzed by measuring the emission spectra of Laurdan, which resides around the hydrophilic-hydrophobic interface of the lipid bilayers (
Figure 4c and d). [
40] The emission spectrum of Laurdan is sensitive to the water content of the surrounding environment. The red shift of Laurdan's emission spectrum indicates more hydration by loosening the lipid packing, whereas the blue shift of the spectrum indicates membrane tightening. The generalized polarization (GP) values [
GP = (
I440-
I490)/(
I440+
I490)] express the degree of hydration. The membranes composed of the cone-shaped lipid PE showed the strongest tightening of membrane packing (
Figure 4c). Furthermore, the membrane packing became remarkably tight as the PE concentration increased (
Figure 4d).
3.4. Correlation between membrane physicochemical properties and membrane insertion efficiency of Pf3_24
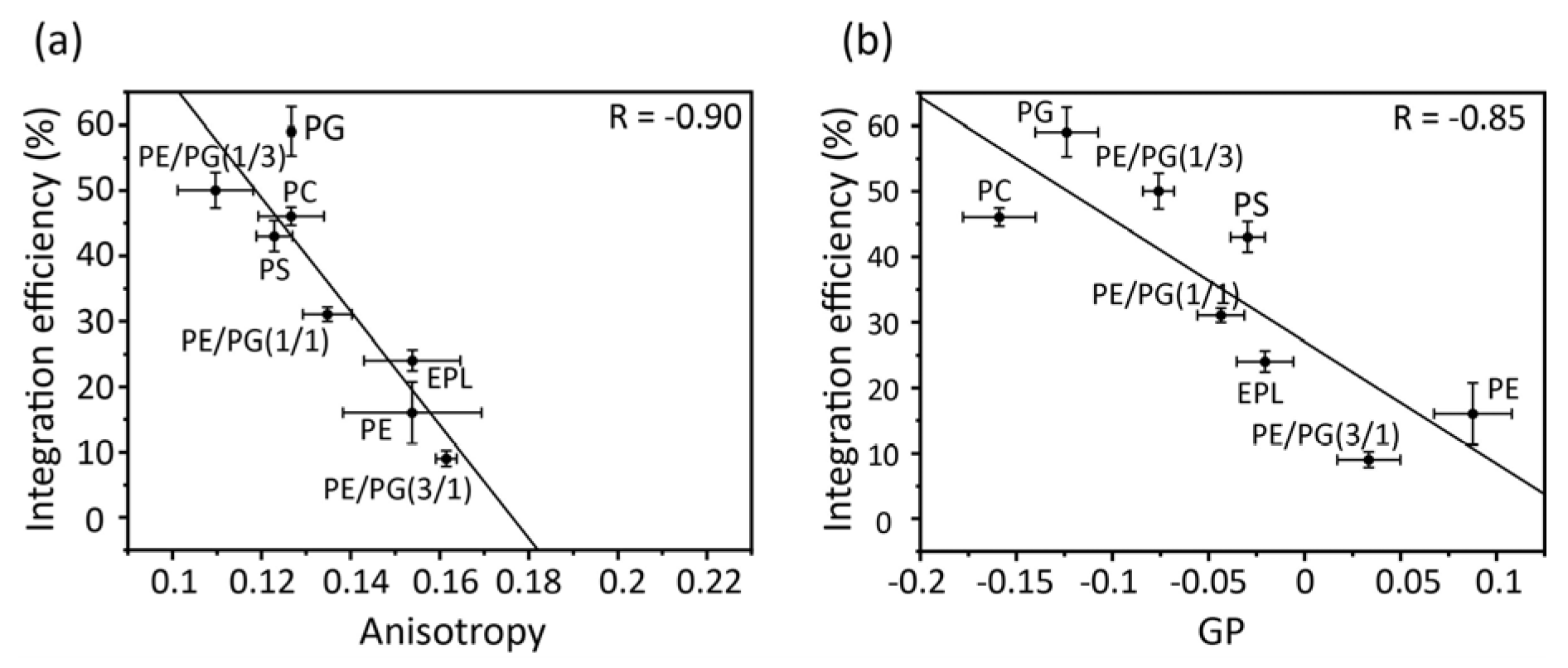
Correlation plots of acyl chain mobility (DPH anisotropy) and membrane surface packing (Laudan GP) in various membranes against insertion efficiency (
Figure 5a,b) indicate the contribution of physicochemical properties to membrane insertion. Both the anisotropy and GP values strongly correlated with the membrane insertion efficiency. Thus, in membranes composed only of bulk phospholipids, acyl chain mobility and membrane packing play direct roles in insertion, with regression lines serving as reliable guidelines. For example, proteins are readily inserted into loosely packed membranes formed by cylindrical lipids, such as PC, PG, and PS. However, as the concentration of PE increased, the acyl chain mobility decreased and the surface packing tightened, leading to the suppression of insertion. PE easily results in negative curvature stress in membranes owing to its small head group, which makes it difficult for the protein to interact with the core of the membranes.
4. Role of MPIase on membrane protein insertion
Thus far, we have evaluated the insertion of Pf3_24 into membranes composed only of bulk lipids. However, in actual
E. coli inner membranes, the presence of minor endogenous components, DAG and MPIase, efficiently regulates membrane protein insertion. Spontaneous membrane insertion is blocked by DAG, whereas suppressed insertion is recovered by MPIase. In our study, at physiological concentrations, neither MPIase nor DAG destabilized the lipid bilayer structure or caused membrane fusion [
24]. Thus, the membrane insertion of proteins supported by MPIase is not accompanied by membrane disruption, as is the case with antimicrobial peptides. DAG is a small cone-shaped lipid, whereas MPIase is an inverted cone-shaped glycolipid containing a DAG substructure and an additional head group consisting of a long sugar chain and pyrophosphate. Owing to their unique molecular structures compared to other membrane lipids, they exert distinct effects on membrane properties. In this section, we describe the mechanism by which MPIase supports membrane protein insertion into the
E. coli membranes in the presence of DAG [
23].
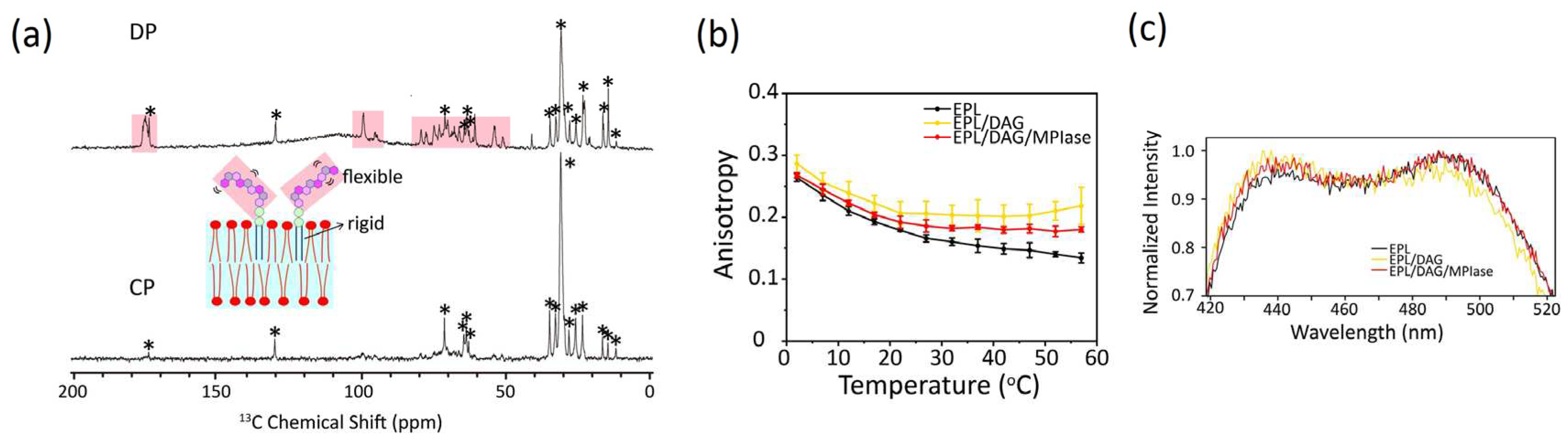
4.1. Mobility of MPIase in membranes
The relative molecular mobility of MPIase and bulk membrane lipids was examined by measuring the
13C cross-polarization (CP) and direct polarization (DP) NMR spectra of EPL liposomes containing uniformly
13C-labeled natural MPIase (5 wt%) using magic angle spinning (MAS) (
Figure 6a). A comparison of the relative signal intensity observed in the DP (
Figure 6a, top) and CP (
Figure 6a, bottom) spectra suggests a higher mobility of the MPIase sugar chain than its lipid part and the other lipids in the liposomes. Higher fluctuation of sugar chain head groups compared to its lipid moiety has also been observed in other glycolipids [
41,
42,
43], and generally, longer sugar chains amplify this effect [
44]. Moreover, in the
31P T1 values of the head group of bulk lipids, fluctuation of the MPIase sugar chain increased their movement. DAG had little influence on the lipid head group mobility because its small head groups were not exposed to the membrane surface [
24].
4.2. Effects on Flip-Flop motion of DAG
DAG has a very rapid flip–flop rate compared to phospholipids owing to their compact shape [
45]. The rapid flip-flop motion of DAG likely disturbs membrane protein insertion. Once a transient defect is formed among phospholipids in the membrane, DAG can flip across the lipid bilayer, filling the space and reducing unfavorable exposure to the hydrophobic acyl chains. This weakens the contact of proteins with the inside of the membrane and blocks the insertion of membrane proteins. In contrast, the flip–flop is diminished in the presence of mini-MPIase-3 [
24]. Locally unfilled hydrophobic spaces are formed more frequently and are retained longer, allowing proteins to insert more easily into the membrane.
4.3. Effects of DAG and MPIase on acyl chain mobility and membrane surface packing
Acyl chain mobility in the EPL membrane core region was analyzed using the anisotropy of DPH (
Figure 6b). The acyl chain mobility was significantly reduced by DAG. However, MPIase partially restored the reduced mobility of the DAG-containing membranes. Lipid acyl chain ordering was also studied by measuring the
2H NMR spectra. Quadrupole splitting increased in the presence of DAG, but returned to the original levels after the addition of natural MPIase (5 wt%) into the DAG-containing liposomes. Thus, DAG promotes the ordering of lipid acyl chains, whereas MPIase compensates for the membrane ordering induced by DAG. The increased packing of the hydrophobic segment by DAG further reduced lateral lipid diffusion. Similar to cholesterol, DAG fits under the polar head groups of lipids, enhancing the order of acyl chains. However, MPIase rebalances the head group and acyl chain volumes of lipids in the membranes and releases the packing pressure inside the membrane.
Membrane surface packing was analyzed by measuring the emission spectra of Laurdan (
Figure 6c). DAG slightly tightened the membrane packing, whereas MPIase partially loosened the packing in DAG-containing membranes. Thus, MPIase counteracted the effects of DAG on membrane properties, both in the membrane core region and on the surface. However, the influence of DAG and MPIase on the membrane surface region was less than that on the membrane core region, suggesting that access to the membrane core region is more critical than initial contact with the surface region for successful protein insertion.
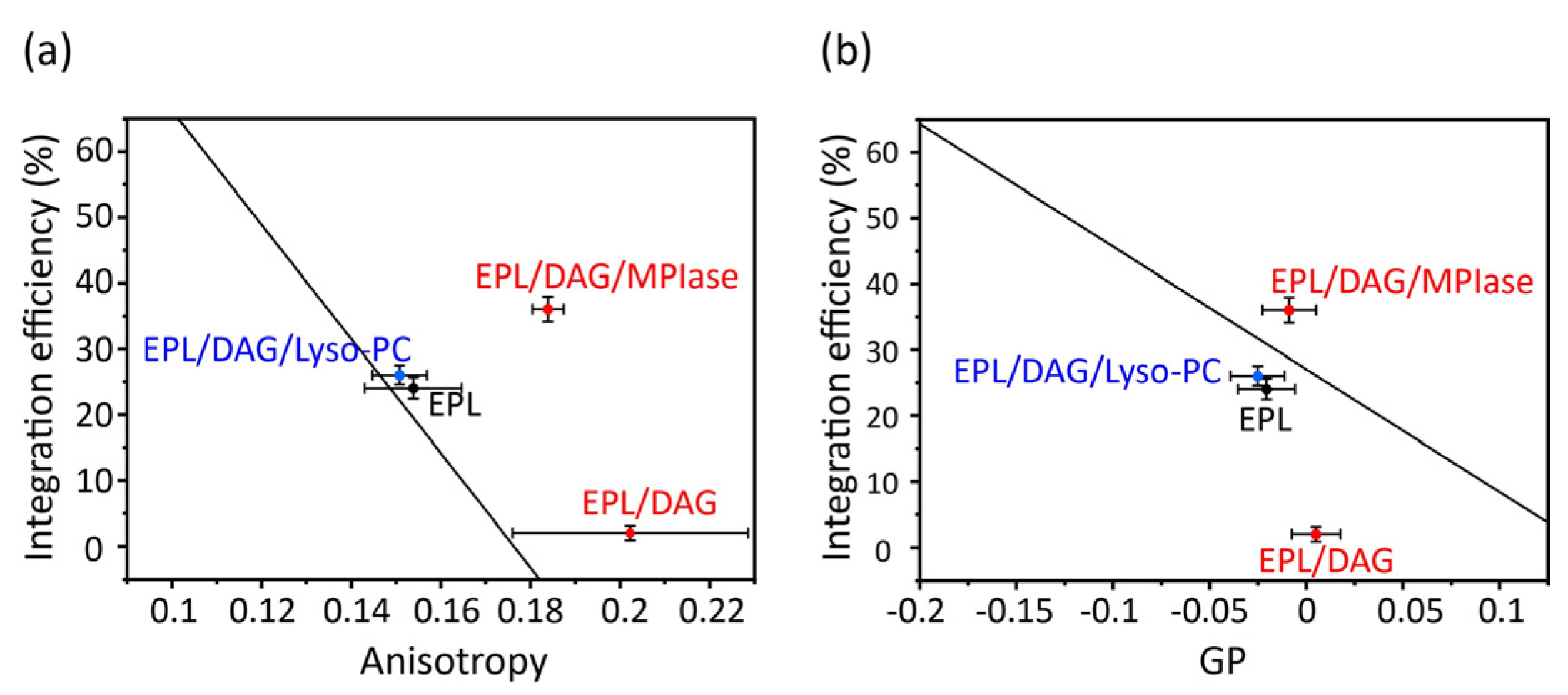
The correlation plots clearly demonstrate how alterations in the physicochemical properties of DAG and MPIase contribute to their insertion into EPL membranes (
Figure 7). In the presence of DAG (5 mol% to EPLs), the mobility of the core region was dramatically reduced (
Figure 7a); however, the mobility of the membrane surface region was not significantly reduced (
Figure 7b). Therefore, we conclude that the drastic inhibition of insertion by DAG is attributable to decreased mobility of the core region. Moreover, we considered that the high insertion efficiency of MPIase was due, at least partly, to compensation for the effects in shape. Thus, we compared MPIase with lyso-PC, which has an inverse-cone shape similar to that of MPIase, because it is known that the presence of lyso-PC enhances the insertion of antimicrobial peptides in PC membranes [
46]. The addition of lyso-PC (5 mol%) to the DAG-containing EPL membrane restored both the membrane mobility and the insertion efficiency of Pf3_24. The correlation is on the regression line, indicating that the effect of lyso-PC on insertion can be explained only by the alteration of membrane physicochemical properties. Conversely, after adding MPIase (1 mol%) to the DAG-containing EPL membrane, the insertion efficiency was much higher than what was expected from the correlation plot against anisotropy values. Therefore, factors other than membrane properties should also support the high insertion efficiency in the presence of MPIase. To identify other causes, we focused on the intermolecular interactions between MPIase and substrate proteins.
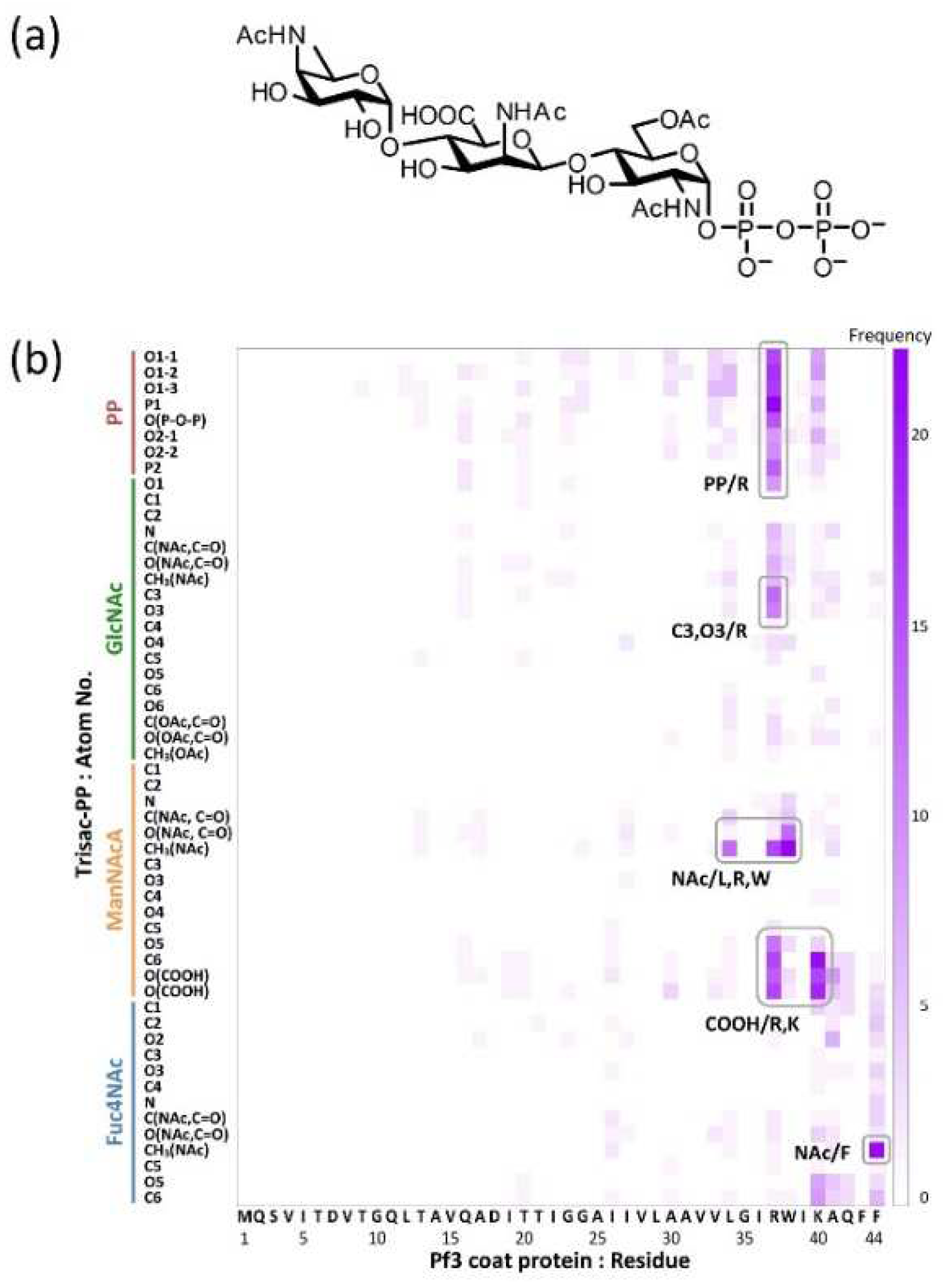
4.4. Identification of the contact sites by using docking simulations
The functional groups required for molecular interactions between MPIase and the protein were estimated by docking simulations using the MOE software [
47]. Docking simulations of pyrophosphorylated trisaccharide moieties, Trisac-PP, with Pf3 coat suggested the hydrophobic interactions between acetyl groups in MPIase and hydrophobic residues of Pf3 coat, and electrostatic interactions between pyrophosphate or carboxylate of MPIase and basic amino acid residues of Pf3 coat (
Figure 8). The reduction in contact in all combinations observed when using MPIase analogs lacking 6-
O-acetyl of GlcNAc or pyrophosphate emphasizes the importance of these functional groups.
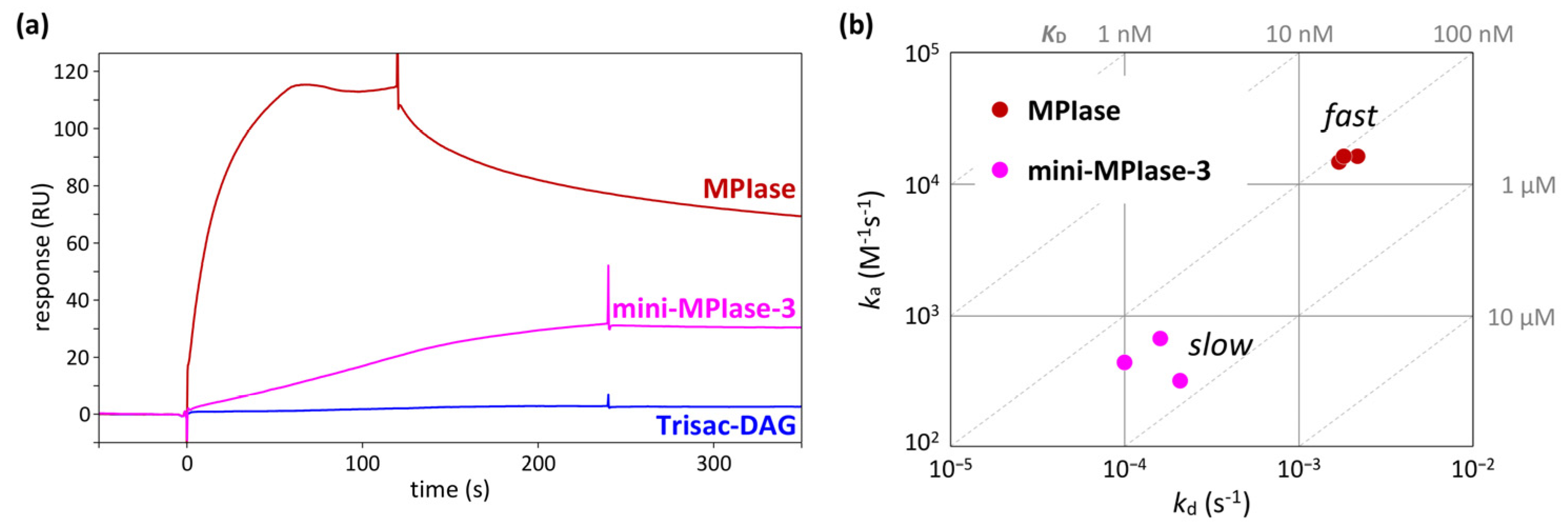
4.5. Binding kinetics and affinity of MPIase−Pf3 coat interactions
In an integration activity assay using in vitro translation [
48], MPIase with a long sugar chain showed much higher activity than mini-MPIase-3 [
21]. In addition, Trisac-DAG, a mini-MPIase-3 analog without a pyrophosphate group, exhibited much lower insertion than mini-MPIase-3 [
20]. These differences in insertion activity can be understood by analyzing binding kinetics and affinity using SPR [
49,
50]. In the SPR measurements, the glycolipid analytes flowed over the flow cells on which Pf3 coat had been immobilized. While direct comparisons of response levels are unsuitable because of notable variations in molecular weight among ligands, the comparison of responses induced by MPIase, mini-MPIase-3, and Trisac-DAG highlights the involvement of pyrophosphate in the interaction of MPIase-Pf3 coat (
Figure 9a) [
22]. The on-off rate map, in which the association (
ka) and dissociation (
kd) rates determined by fitting analyses were plotted, clearly demonstrated a greater contribution of the long sugar chain of MPIase to rapid contact with Pf3 coat (
Figure 9b). This is likely the reason for the higher integration activity of MPIase compared with that of mini-MPIase-3.
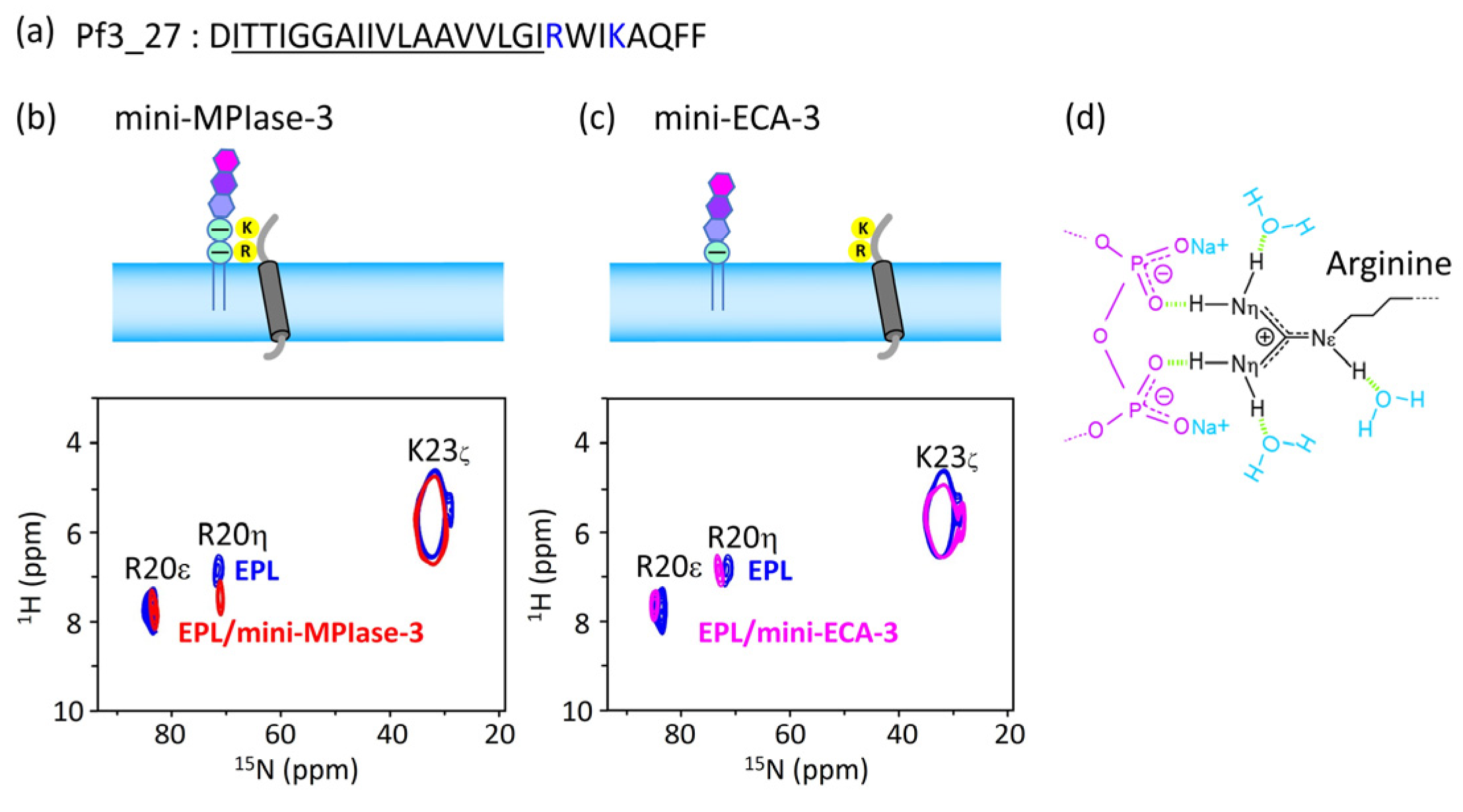
4.6. Interaction of the MPIase pyrophosphate group with basic residues in Pf3_27
As can be seen from the results of the docking simulations and SPR experiments, the MPIase pyrophosphate linker is one of the key structures involved in membrane insertion activity.
1H-
15N FSLG-HETCOR spectrum of Pf3_27, which has a transmembrane region followed by cytoplasmic residues (
Figure 10a), exhibited a selective interaction between the pyrophosphate in MPIase and Arg residues (
Figure 10b-d). The signal of the R20 H
η protons was shifted 0.53 ppm downfield in the presence of mini-MPIase-3 (
Figure 10b), whereas the proton signal did not change with mini-ECA-3 that has a monophosphate linker (
Figure 10c) [
20,
23]. Generally, basic residues in membrane proteins are abundant near the membrane surface on the cytoplasmic side; this is known as the positive-inside rule [
33,
34]. Therefore, the double negatively charged pyrophosphate group of MPIase attracts basic residues to the membrane surface (
Figure 10d). The downfield shift value of 0.53 ppm due to hydrogen bonding of Pf3_27 with MPIase is smaller than that observed for the ligand-receptor complex (about 2–3 ppm) [
23,
51]. Therefore, the binding of the guanidino group of R20 to the pyrophosphate of MPIase is weaker than that in the ligand-receptor complex and more transient. Transient binding allows MPIase to detach the protein after insertion into the membrane.
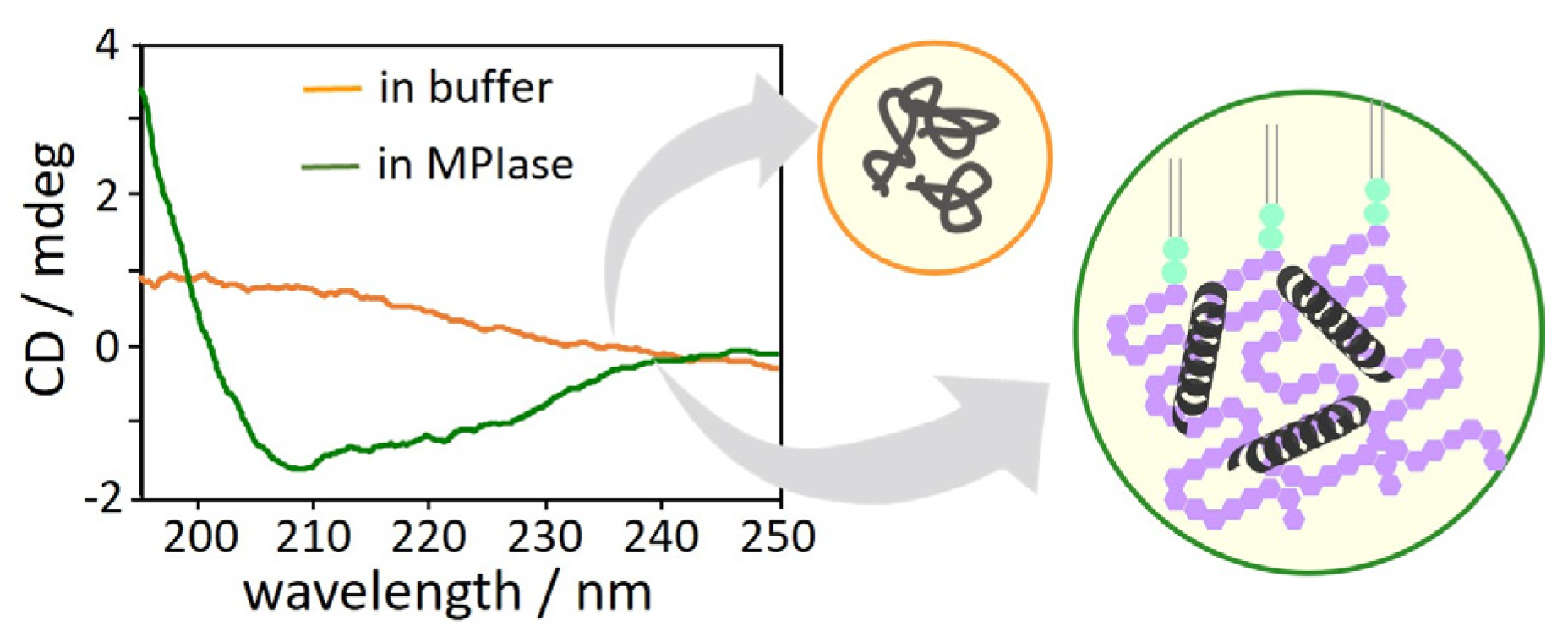
4.7. Inhibition of protein aggregation by MPIase.
The interactions between MPIase and Pf3 coat induce changes in the secondary structure of Pf3 coat [
22]. The CD spectra of Pf3 coat clearly exhibited that without MPIase, Pf3 coat did not form a definite secondary structure (
Figure 11, orange), while it exhibited mostly an α-helical structure with MPIase (
Figure 11, green). The long sugar chain of MPIase is likely to capture nascent proteins through multiple interactions, such as the acetyl groups of MPIase and the hydrophobic region of the proteins or the carboxyl groups of MPIase and the basic amino acid residues of the proteins, which prevent the protein from aggregating. Therefore, MPIase might act as a chaperone during membrane insertion.
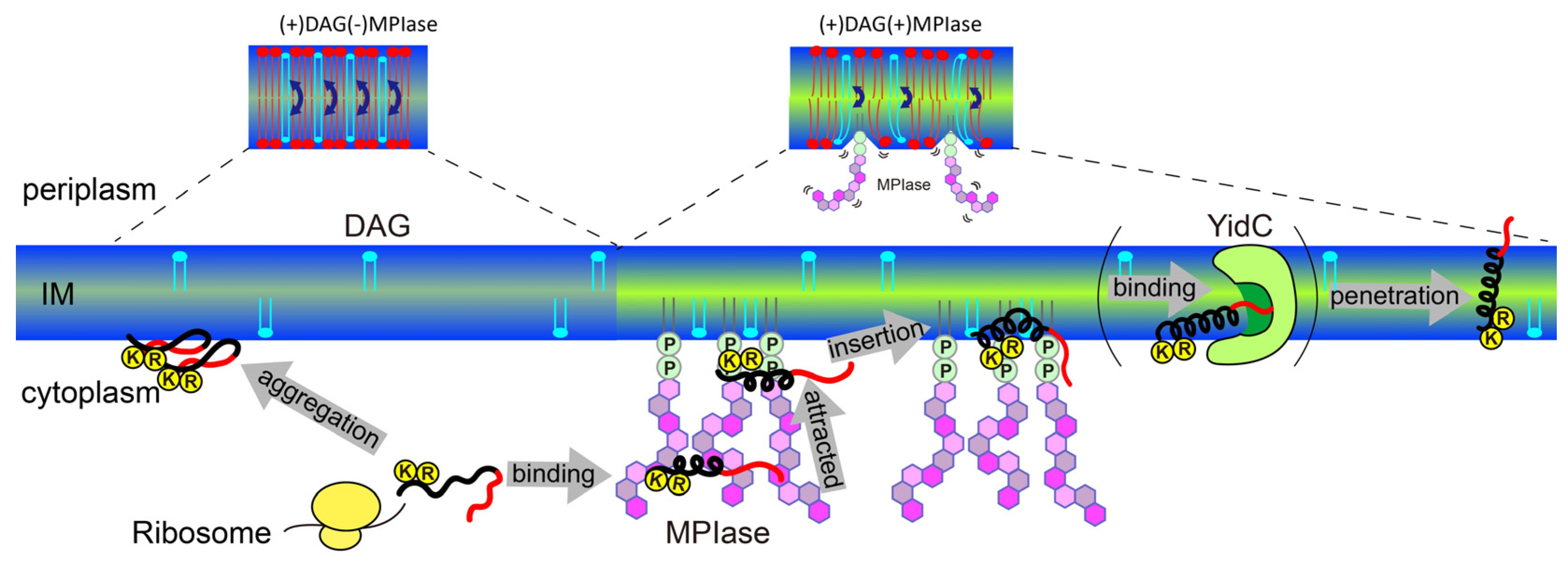
5. Mechanism of Sec-independent membrane protein insertion by MPIase
Finally, the insertion mechanism of small hydrophobic proteins into
E. coli membranes under the regulation of MPIase and DAG is summarized in
Figure 12.
DAG blocks spontaneous insertion by reducing acyl chain mobility in the membrane core. The rapid flip-flop of DAG also reduces lateral diffusion and fills membrane defects, exposing acyl chains and making it difficult for proteins to contact the inside of the membranes. However, the presence of MPIase cancels out the effect of DAG and restores mobility. The flexible bulky sugar chain of MPIase makes the membrane surface flexible, increases the mobility of the membrane core region, and reduces the flip-flop motion of DAG. Small hydrophobic membrane proteins preferentially associate with the membrane core region rather than with the aqueous environment outside the membrane.
After a protein is released from a ribosome, the long sugar chain of MPIase captures the protein and prevents its aggregation. The protein efficiently changes its conformation through rapid association with and dissociation from the flexible long sugar chains of MPIase.
The basic residues that generally exist in the cytoplasmic loops near the hydrophobic transmembrane regions of the protein are attracted towards the membrane surface through electrostatic interactions with the pyrophosphate of MPIase.
The protein easily gains access to the loosened membrane core through hydrophobic interactions, and finally integrates into the membrane.
MPIase interacts with proteins via its pyrophosphate group. However, this binding is weak, and MPIase can easily detach from the protein. It is likely that the protein is then delivered to YidC in the inner membrane. The detached MPIase can assist another substrate that has not yet been inserted into the membrane. Thus, MPIase efficiently supports membrane insertion.
5. Conclusions
This study discusses the various membrane properties that affect Sec-independent membrane insertion and the contributions of MPIase and DAG to membrane properties. Both MPIase and DAG are minor components of
E. coli membranes. However, by acting in opposite directions, they effectively alter membrane properties. Comprehensive analysis of the membrane insertion activity, physicochemical properties, and molecular interactions between MPIase and its substrates provides an understanding of the atomic-level molecular mechanisms by which MPIase prevents substrate protein aggregation, attracts substrates near the membrane surface, and promotes membrane insertion. These findings reveal novel biological roles of glycolipids. Since MPIase is also involved in other protein translocation pathways across membranes [
7,
11], further studies on MPIase clustering on the membrane and its distribution in cells will provide insights into the diverse functions of MPIase, including membrane transport.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K. N. and K. S; methodology, K. N. and K. S.; formal analysis, K. N. and S. M.; investigation, K. N. and S. M.; resources, K. N., S. M. and K. S.; writing—original draft preparation, K. N.; writing—review and editing, K. N., S. M. and K. S.; supervision, K. S.; funding acquisition, K. N. and K. S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by JSPS KAKENHI, grant numbers JP18K06143 and JP22K05323 to K. N.; JP19H02843 and JP22H02213 to K. S.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data is reported in this review article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Ken-ichi Nishiyama (Iwate University), Dr. Kohki Fujikawa, Ms. Tsukiho Osawa, Dr. Toshiyuki Yamaguchi (Suntory Foundation for Life Sciences), Prof. Tsuyoshi Shirai, Prof. Masafumi Shionyu, Prof. Takao Yoda (Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology), Dr. Taku Yoshiya, Dr. Hideki Nishio, Mr. Shun Masuda, Dr. Kumiko Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, Dr. Shugo Tsuda (Peptide Institute, Inc.), Prof. Kenichi Morigaki (Kobe University), and Prof. Toshinori Shimanouchi (Okayama University) for their contribution to the research of MPIase.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Membrane protein integrase |
MPIase |
| Escherichia coli |
E. coli |
| diacylglycerol |
DAG |
|
E. coli phospholipids |
EPLs |
| phosphatidylethanolamine |
PE |
| phosphatidylglycerol |
PG |
| cardiolipin |
CL |
| antimicrobial peptides |
AMPs |
| phosphatidylcholine |
PC |
| phosphatidylserine |
PS |
| 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
DMPC |
| 1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
DHPC |
| large unilamellar vesicles |
LUV |
| cross polarization under magic angle spinning |
CPMAS |
| 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene |
DPH |
| generalized polarization |
GP |
| 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol) |
DMPG |
| 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine |
POPS |
| 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine |
POPE |
| magic angle spinning |
MAS |
| surface plasmon resonance |
SPR |
| association rate |
ka
|
| dissociation rate |
kd
|
| Circular dichroism |
CD |
References
- Luirink, J.; von Heijne, G.; Houben, E.; de Gier, J.W. Biogenesis of inner membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, P.B.; Rice, M.; Wickner, W. Effects of two sec genes on protein assembly into the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, B.L.; Wickner, W. M13 procoat inserts into liposomes in the absence of other membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 13281–13285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, D.; Hu, X.; Dalbey, R.; Kuhn, A. Negatively charged amino acid residues play an active role in orienting the Sec-independent Pf3 coat protein in the Escherichia coli inner membrane. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, M.; Li, X.; Stefanovic, S.; Sharma, A.; Mateja, A.; Keenan, R.J.; Hegde, R.S. A ribosome-associating factor chaperones tail-anchored membrane proteins. Nature 2010, 466, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, M.; Mateja, A.; Dobosz, M.; Bove, E.; Hegde, R.S.; Keenan, R.J. The mechanism of membrane-associated steps in tail-anchored protein insertion. Nature 2011, 477, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.; Ikegami, A.; Moser, M.; Schiltz, E.; Tokuda, H.; Muller, M. A derivative of lipid A is involved in signal recognition particle/SecYEG-dependent and -independent membrane integrations. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35667–35676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, Y.; Miyazaki, E.; Müller, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishiyama, K.-i. Diacylglycerol Specifically Blocks Spontaneous Integration of Membrane Proteins and Allows Detection of a Factor-assisted Integration. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24489–24496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Maeda, M.; Abe, M.; Kanamori, T.; Shimamoto, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Ueda, T.; Tokuda, H. A novel complete reconstitution system for membrane integration of the simplest membrane protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.-i.; Maeda, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Nagase, R.; Komura, H.; Iwashita, T.; Yamagaki, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Tokuda, H.; Shimamoto, K. MPIase is a glycolipozyme essential for membrane protein integration. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.; Nagamori, S.; Huber, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishiyama, K. Glycolipozyme MPIase is essential for topology inversion of SecG during preprotein translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 9734–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Samuelson, J.C.; Jiang, F.; Muller, M.; Kuhn, A.; Dalbey, R.E. Direct Interaction of YidC with the Sec-independent Pf3 Coat Protein during Its Membrane Protein Insertion. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7670–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, J.C.; Chen, M.; Jiang, F.; Möller, I.; Wiedmann, M.; Kuhn, A.; Phillips, G.J.; Dalbey, R.E. YidC mediates membrane protein insertion in bacteria. Nature 2000, 406, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serek, J.; Bauer-Manz, G.; Struhalla, G.; van den Berg, L.; Kiefer, D.; Dalbey, R.; Kuhn, A. Escherichia coli YidC is a membrane insertase for Sec-independent proteins. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazaki, K.; Chiba, S.; Takemoto, M.; Furukawa, A.; Nishiyama, K.; Sugano, Y.; Mori, T.; Dohmae, N.; Hirata, K.; Nakada-Nakura, Y.; et al. Structural basis of Sec-independent membrane protein insertion by YidC. Nature 2014, 509, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, M.A.; Heimes, M.; Sinning, I. Structural and molecular mechanisms for membrane protein biogenesis by the Oxa1 superfamily. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickles, S.; Singharoy, A.; Andreani, J.; Seemayer, S.; Bischoff, L.; Berninghausen, O.; Soeding, J.; Schulten, K.; van der Sluis, E.O.; Beckmann, R. A structural model of the active ribosome-bound membrane protein insertase YidC. Elife 2014, 3, e03035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Sawasato, K.; Nishiyama, K.I. Interplay between MPIase, YidC, and PMF during Sec-independent insertion of membrane proteins. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Nishikawa, H.; Suzuki, S.; Moser, M.; Huber, M.; Sawasato, K.; Matsubayashi, H.T.; Kumazaki, K.; Tsukazaki, T.; Kuruma, Y.; et al. The bacterial protein YidC accelerates MPIase-dependent integration of membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18898–18908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, K.; Han, Y.; Osawa, T.; Mori, S.; Nomura, K.; Muramoto, M.; Nishiyama, K.-i.; Shimamoto, K. Structural Requirements of a Glycolipid MPIase for Membrane Protein Integration. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, K.; Suzuki, S.; Nagase, R.; Ikeda, S.; Mori, S.; Nomura, K.; Nishiyama, K.I.; Shimamoto, K. Syntheses and Activities of the Functional Structures of a Glycolipid Essential for Membrane Protein Integration. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Nomura, K.; Fujikawa, K.; Osawa, T.; Shionyu, M.; Yoda, T.; Shirai, T.; Tsuda, S.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Masuda, S.; et al. Intermolecular Interactions between a Membrane Protein and a Glycolipid Essential for Membrane Protein Integration. ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Mori, S.; Fujikawa, K.; Osawa, T.; Tsuda, S.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Masuda, S.; Nishio, H.; Yoshiya, T.; Yoda, T.; et al. Role of a bacterial glycolipid in Sec-independent membrane protein insertion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Mori, S.; Fujikawa, K.; Nishiyama, K.I.; Shimanouchi, T.; Tanimoto, Y.; Morigaki, K.; Shimamoto, K. Alteration of Membrane Physicochemical Properties by Two Factors for Membrane Protein Integration. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Soblosky, L.; Nguyen, K.; Geng, J.; Yu, X.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Chen, Z. Physiologically-relevant modes of membrane interactions by the human antimicrobial peptide, LL-37, revealed by SFG experiments. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Heng, C.; Separovic, F.; Aguilar, M.I. Comparison of reversible membrane destabilisation induced by antimicrobial peptides derived from Australian frogs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Feigenson, G.W. A microscopic interaction model of maximum solubility of cholesterol in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 2142–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, E.; Ulrich, A.S. AMPs and OMPs: Is the folding and bilayer insertion of beta-stranded outer membrane proteins governed by the same biophysical principles as for alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Ogura, M.; Matsuzaki, K. Thermodynamics of Insertion and Self-Association of a Transmembrane Helix: A Lipophobic Interaction by Phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6806–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintou, K.; Nakano, M.; Kamo, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Handa, T. Interaction of an Amphipathic Peptide with Phosphatidycholine/Phosphatidylethanolamine Mixed Membranes. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 3900–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Masuda, T.; Afonin, S.; Kawano, K.; Takatani-Nakase, T.; Ida, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Fukuma, T.; Ulrich, A.S.; Futaki, S. Loosening of Lipid Packing Promotes Oligoarginine Entry into Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7644–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujals, S.; Miyamae, H.; Afonin, S.; Murayama, T.; Hirose, H.; Nakase, I.; Taniuchi, K.; Umeda, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Ulrich, A.S.; Futaki, S. Curvature engineering: positive membrane curvature induced by epsin N-terminal peptide boosts internalization of octaarginine. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanov, M.; Xie, J.; Dowhan, W. Lipid-protein interactions drive membrane protein topogenesis in accordance with the positive inside rule J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9637–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Heijne, G. Membrane-protein topology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 7, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevzorov, A.A.; Opella, S.J. Selective averaging for high-resolution solid-state NMR spectroscopy of aligned samples. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 185, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorov, A.A.; Opella, S.J. A "magic sandwich" pulse sequence with reduced offset dependence for high-resolution separated local field spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2003, 164, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jardetzky, O. Probability-based protein secondary structure identification using combined NMR chemical-shift data. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Sykes, B.D.; Richards, F.M. Relationship between nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift and protein secondary structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, B.R. Use of fluorescent probes to monitor molecular order and motions within liposome bilayers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1993, 64, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antollini, S.S.; Soto, M.A.; Bonini de Romanelli, I.; Gutiérrez-Merino, C.; Sotomayor, P.; Barrantes, F.J. Physical state of bulk and protein-associated lipid in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-rich membrane studied by laurdan generalized polarization and fluorescence energy transfer. Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, D.; Giziewicz, J.B.; Moir, D.; Smith, I.C.; Jarrell, H.C. Dynamics and orientation of glycolipid headgroups by 2H-NMR: gentiobiose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 983, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, H.C.; Wand, A.J.; Giziewicz, J.B.; Smith, I.C. The dependence of glyceroglycolipid orientation and dynamics on head-group structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 897, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, J.P.; Giziewicz, J.B.; Smith, I.C.; Jarrell, H.C. Glycolipid membrane surface structure: orientation, conformation, and motion of a disaccharide headgroup. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Sakae, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Kato, K. Exploration of conformational spaces of high-mannose-type oligosaccharides by an NMR-validated simulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10941–10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Pagano, R.E. Measurement of spontaneous transfer and transbilayer movement of BODIPY-labeled lipids in lipid vesicles. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 8840–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandberg, E.; Tiltak, D.; Ehni, S.; Wadhwani, P.; Ulrich, A.S. Lipid shape is a key factor for membrane interactions of amphipathic helical peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOE (Molecular Operating Environment), 2022.02 ed., Chemical Computing Group ULC, Montreal (QC, Canada), 2022.
- Nishikawa, H.; Sasaki, M.; Nishiyama, K.I. In vitro Assay for Bacterial Membrane Protein Integration into Proteoliposomes. Bio-Protoc. 2020, 10, e3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jason-Moller, L.; Murphy, M.; Bruno, J. Overview of Biacore systems and their applications. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 2006, Chapter 19, Unit 19.13. 19.
- O'Shannessy, D.J.; Brigham-Burke, M.; Soneson, K.K.; Hensley, P.; Brooks, I. Determination of rate and equilibrium binding constants for macromolecular interactions by surface plasmon resonance. Meth. Enzymol. 1994, 240, 323–349. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, T.; Pascal, S.M.; Singer, A.U.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; Kay, L.E. NMR Pulse Schemes for the Sequence-Specific Assignment of Arginine Guanidino 15N and 1H Chemical Shifts in Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 3556–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic model of the Sec translocon-independent membrane protein integration pathway into the inner membrane (IM) of the E. coli. (black: hydrophobic region, red: hydrophilic region). MPIase is presumed to function prior to an insertase YidC. (b) Molecular structure of MPIase. Approximately one-third of the 6-position on GlcNAc residues is O-acetylated. The number of repeating trisaccharide units ranges from 7 to 14, but most are from 9 to 11. (c) Molecular structures of synthesized MPIase analogs.
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic model of the Sec translocon-independent membrane protein integration pathway into the inner membrane (IM) of the E. coli. (black: hydrophobic region, red: hydrophilic region). MPIase is presumed to function prior to an insertase YidC. (b) Molecular structure of MPIase. Approximately one-third of the 6-position on GlcNAc residues is O-acetylated. The number of repeating trisaccharide units ranges from 7 to 14, but most are from 9 to 11. (c) Molecular structures of synthesized MPIase analogs.
Figure 2.
(a) Amino acid sequence of Pf3_24 and substructure of Pf3 coat, Pf3_24. Hydrophobic region is underlined, and basic residues are colored in blue. (b) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of Pf3_24 in 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) liposomes (dark red) or in buffer (blue). (c) 1H–15N SAMPI4 spectrum of Pf3_24 in DMPC/1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DHPC) bicelles. The simulated PISA wheels with varied tilt angles θ (0–70°) were overlaid onto the spectrum.
Figure 2.
(a) Amino acid sequence of Pf3_24 and substructure of Pf3 coat, Pf3_24. Hydrophobic region is underlined, and basic residues are colored in blue. (b) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of Pf3_24 in 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) liposomes (dark red) or in buffer (blue). (c) 1H–15N SAMPI4 spectrum of Pf3_24 in DMPC/1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DHPC) bicelles. The simulated PISA wheels with varied tilt angles θ (0–70°) were overlaid onto the spectrum.
Figure 3.
(
a)
15N cross polarization under magic angle spinning (CPMAS) NMR spectra of Pf3_24. (top) Pf3_24 was fully reconstituted into DMPC LUVs. (middle) Pf3_24 in aggregates. The sample was prepared without the use of LUVs (
Figure 3b). (bottom) The sample was prepared using the procedure shown in
Figure 3b for DMPC LUVs. The pink dashed line shows the chemical shift for the β-strand conformation, and the light blue dashed line shows that for α-helix and/or random-coil conformations. The signal observed at approximately 110 ppm originated from glycine. (
b) Procedure for inserting Pf3_24 into the membranes. (i) Pf3_24 (dark gray) solubilized in DHPC solution was mixed with LUVs composed of various lipid types. (ii) The mixture was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. (iii) Then, it was diluted with a buffer solution until the DHPC concentration reached below its critical micelle concentration. (iv) The supernatant containing DHPC was removed by centrifugation. Precipitates containing both LUVs and aggregates were subjected to
15N CPMAS NMR. (
c) Membrane insertion efficiency of Pf3_24, determined using the procedure shown in
Figure 3b, into several types of membranes.
Figure 3.
(
a)
15N cross polarization under magic angle spinning (CPMAS) NMR spectra of Pf3_24. (top) Pf3_24 was fully reconstituted into DMPC LUVs. (middle) Pf3_24 in aggregates. The sample was prepared without the use of LUVs (
Figure 3b). (bottom) The sample was prepared using the procedure shown in
Figure 3b for DMPC LUVs. The pink dashed line shows the chemical shift for the β-strand conformation, and the light blue dashed line shows that for α-helix and/or random-coil conformations. The signal observed at approximately 110 ppm originated from glycine. (
b) Procedure for inserting Pf3_24 into the membranes. (i) Pf3_24 (dark gray) solubilized in DHPC solution was mixed with LUVs composed of various lipid types. (ii) The mixture was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. (iii) Then, it was diluted with a buffer solution until the DHPC concentration reached below its critical micelle concentration. (iv) The supernatant containing DHPC was removed by centrifugation. Precipitates containing both LUVs and aggregates were subjected to
15N CPMAS NMR. (
c) Membrane insertion efficiency of Pf3_24, determined using the procedure shown in
Figure 3b, into several types of membranes.
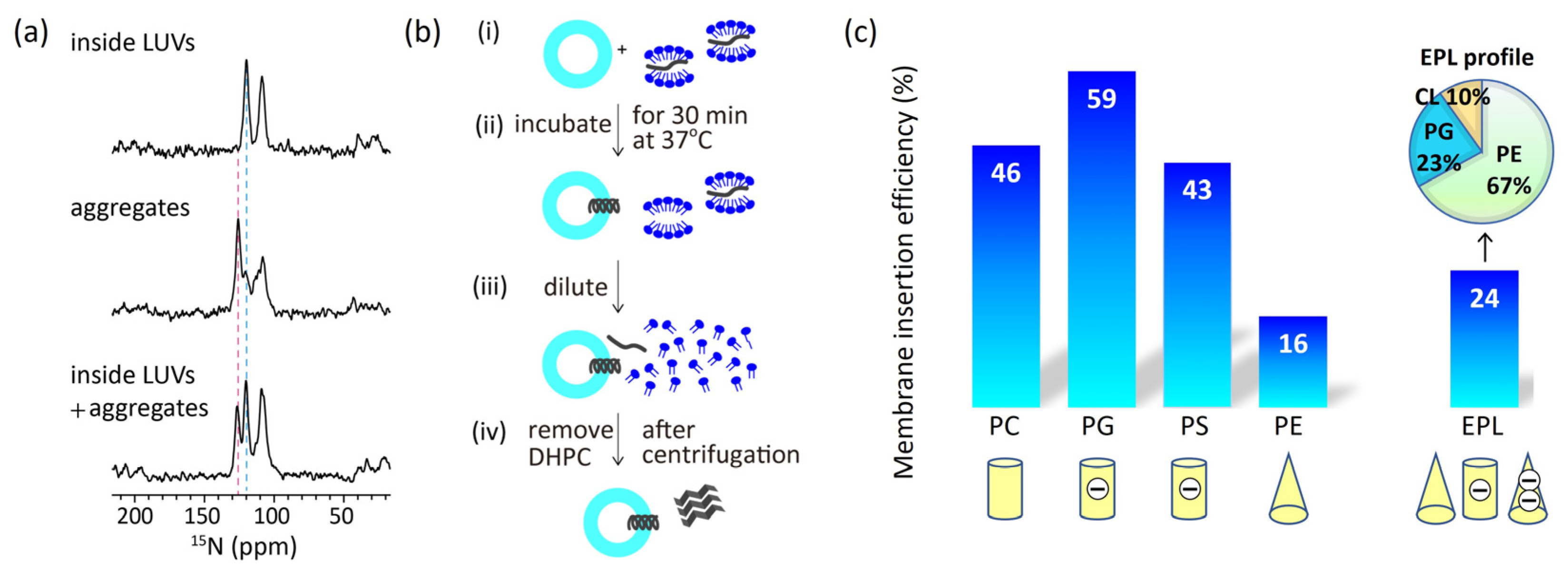
Figure 4.
Fluorescence anisotropy of DPH (a and b) and fluorescence emission spectra of Laurdan at 37 °C (c and d) incorporated into various types of membranes. DMPG, 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol); DMPC, 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; POPS, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine; POPE, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine.
Figure 4.
Fluorescence anisotropy of DPH (a and b) and fluorescence emission spectra of Laurdan at 37 °C (c and d) incorporated into various types of membranes. DMPG, 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol); DMPC, 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; POPS, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine; POPE, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine.
Figure 5.
Correlation between membrane insertion efficiency values and fluorescence anisotropy values of DPH at 37°C (a) and Laurdan GP values, GP=(I440-I490)/(I440+I490), (b) in various types of membranes. Global linear fits were performed for all bulk phospholipids.
Figure 5.
Correlation between membrane insertion efficiency values and fluorescence anisotropy values of DPH at 37°C (a) and Laurdan GP values, GP=(I440-I490)/(I440+I490), (b) in various types of membranes. Global linear fits were performed for all bulk phospholipids.
Figure 6.
(a) Direct polarization (DP) (top) and cross polarization (CP) (bottom) 13C NMR spectra of EPL liposomes in the presence of uniformly 13C-labeled natural MPIase (5 wt%) under MAS with a spinning speed of 5 kHz. The sugar chain signals that appeared only in the DP spectrum are shown in salmon pink. The peaks from EPL are marked with *. (b and c) Fluorescence anisotropy of DPH (b) and fluorescence emission spectra of Laurdan at 37 °C (c) incorporated into EPL-based membranes.
Figure 6.
(a) Direct polarization (DP) (top) and cross polarization (CP) (bottom) 13C NMR spectra of EPL liposomes in the presence of uniformly 13C-labeled natural MPIase (5 wt%) under MAS with a spinning speed of 5 kHz. The sugar chain signals that appeared only in the DP spectrum are shown in salmon pink. The peaks from EPL are marked with *. (b and c) Fluorescence anisotropy of DPH (b) and fluorescence emission spectra of Laurdan at 37 °C (c) incorporated into EPL-based membranes.
Figure 7.
Correlation between membrane insertion efficiency values and fluorescence anisotropy values of DPH at 37 °C (
Figure 6b) (
a), and membrane insertion efficiency values and Laurdan GP values at 37 °C calculated from the emission spectra (
Figure 6c) (
b) in the EPL-based membranes. The black line shows the regression line obtained from the global linear fits performed on the bulk phospholipids in
Figure 5.
Figure 7.
Correlation between membrane insertion efficiency values and fluorescence anisotropy values of DPH at 37 °C (
Figure 6b) (
a), and membrane insertion efficiency values and Laurdan GP values at 37 °C calculated from the emission spectra (
Figure 6c) (
b) in the EPL-based membranes. The black line shows the regression line obtained from the global linear fits performed on the bulk phospholipids in
Figure 5.
Figure 8.
(a) Molecular structure of Trisac-PP. (b) Heat map of frequencies in the docking simulation. It illustrates the frequencies of interaction between each atom of Trisac-PP and each amino acid residue of Pf3 coat.
Figure 8.
(a) Molecular structure of Trisac-PP. (b) Heat map of frequencies in the docking simulation. It illustrates the frequencies of interaction between each atom of Trisac-PP and each amino acid residue of Pf3 coat.
Figure 9.
(a) SPR sensorgrams of the binding of natural MPIase, mini-MPIase-3, and Trisac-DAG to Pf3 coat. (b) The on-off rate map showing the kinetic profiles of the interaction of MPIase and mini-MPIase-3 with Pf3 coat.
Figure 9.
(a) SPR sensorgrams of the binding of natural MPIase, mini-MPIase-3, and Trisac-DAG to Pf3 coat. (b) The on-off rate map showing the kinetic profiles of the interaction of MPIase and mini-MPIase-3 with Pf3 coat.
Figure 10.
(a) Amino acid sequence of substructure of Pf3 coat, Pf3_27. Hydrophobic region is underlined, and basic residues are colored in blue. (b and c) Arg and Lys side chain signal regions of the 2D 1H-15N FSLG-HETCOR spectrum of Pf3_27 in EPL membranes in the presence of mini-MPIase-3 (a, blue) or mini-ECA-3 (b, pink) and absence of them (a and b, blue). (d) Schematic models of Arg side chain (black) interaction with the pyrophosphate linker part of MPIase (purple). Light green dots show hydrogen bonding.
Figure 10.
(a) Amino acid sequence of substructure of Pf3 coat, Pf3_27. Hydrophobic region is underlined, and basic residues are colored in blue. (b and c) Arg and Lys side chain signal regions of the 2D 1H-15N FSLG-HETCOR spectrum of Pf3_27 in EPL membranes in the presence of mini-MPIase-3 (a, blue) or mini-ECA-3 (b, pink) and absence of them (a and b, blue). (d) Schematic models of Arg side chain (black) interaction with the pyrophosphate linker part of MPIase (purple). Light green dots show hydrogen bonding.
Figure 11.
CD spectra of Pf3 coat in buffer in the presence (green) and absence(orange) of MPIase.
Figure 11.
CD spectra of Pf3 coat in buffer in the presence (green) and absence(orange) of MPIase.
Figure 12.
Schematic model of the membrane insertion of a small hydrophobic substrate protein (black: hydrophobic region, red: hydrophilic region) supported by MPIase in E. coli membranes.
Figure 12.
Schematic model of the membrane insertion of a small hydrophobic substrate protein (black: hydrophobic region, red: hydrophilic region) supported by MPIase in E. coli membranes.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).