1. Introduction
Severe bleeding in soft tissues is an extremely challenging issue in both trauma emergency care and surgery, especially in cases of visceral injuries. Serious bleeding can be life-threatening within minutes. Rapid and effective hemostasis in trauma care can significantly reduce blood loss and prevent fatal outcomes due to blood loss [1-3]. Traditional hemostatic methods include the use of gauze compression, tourniquets, hemostatic sponges, hemostatic powders, and surgical suturing. However, the effectiveness of these methods is significantly influenced by the location of the bleeding. For instance, while tourniquets are effective in the short term for controlling limb hemorrhage, their effectiveness is not long-lasting. Gauze compression can be somewhat effective for deep soft tissue bleeding, but its hemostatic effectiveness depends on the degree of compression and the shape of the bleeding site [
4]. Hemostatic sponges and powders can evenly cover deep tissue surfaces, but their effectiveness is often diluted due to tissue movement and wet conditions, leading to recurrent bleeding [5-7]. Therefore, developing innovative hemostatic materials that can provide rapid, effective, and biocompatible hemostasis in wet visceral tissues is crucial for effectively managing such bleeding.
Among the various materials being explored, injectable hydrogels have emerged as promising candidates due to their unique physical properties, adaptability, and compatibility with biological tissues [
8]. There are numerous types of absorbable polymer-based hemostatic materials, including Polyethylene Glycol (PEG), Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA), Polylactic Acid (PLA), and Polycaprolactone (PCL). These materials can rapidly form gels, assisting in blood clotting and promoting wound healing, and are widely used in the research of hemostatic hydrogels [
9]. As a classic synthetic polymer, PEG is highly esteemed for its outstanding biocompatibility and unique physicochemical properties. The hydrogels made from PEG exhibit high hydratability, enabling them to absorb a significant amount of water, thereby forming a dense gel structure at the wound site. Notably, the mechanical properties of PEG hydrogels can be flexibly altered by adjusting the cross-linking density of the polymer network, allowing their hardness and elasticity to be tailored to different application needs [
10]. Consequently, PEG hydrogels hold a broad spectrum of prospects in the field of biomedical applications. However, PEG-based hydrogels primarily control bleeding through physical adhesion and water absorption, lacking other bioactive properties. This has motivated researchers to innovatively modify these hydrogels to achieve a more comprehensive integration of biocompatibility, pro-coagulation, hemostasis, and customizability, thus better meeting clinical demands.
PEG succinimidyl succinate (PEG-SS) is a unique derivative of PEG, characterized by its active succinimidyl succinate ester groups. These active ester groups are particularly prone to reacting with compounds containing active hydrogen, such as amines. When encountering PEG amine (PEG-NH
2), the active ester group in PEG-SS is attacked by the amine, leading to the cleavage of the ester bond and the formation of a new covalent amide bond [
11]. This process is highly specific, occurring rapidly at room temperature without the need for a catalyst, demonstrating its efficiency. Notably, the amine group in PEG-NH
2 can also chelate with metal substrates, a feature that can further strengthen the cross-linked network within the gel, enhancing its structural integrity and endowing the hydrogel with additional functions [12-14].
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is renowned for its excellent biocompatibility and multifunctionality, has a long and extensive history of applications in the field of pharmaceutical development. Zn2+, being vital trace elements in human blood, play a crucial role in the blood coagulation process. They activate key coagulation enzymes, such as thrombin, and promote platelet aggregation, thereby effectively facilitating the clotting process [15, 16]. As a metal ion, Zn2+ can chelate with the amino groups present in PEG-NH2 [12-14]. This chelation not only speeds up the gelling process of hydrogels but also acts as a secondary cross-linking network, enhancing the internal structure and stability of the hydrogel.
In this study, we combined PEG-based hydrogel with ZnO to develop a dual-network structure formed by amide bonds and metal ion chelation, resulting in a denser PEG hemostatic hydrogel. This hydrogel, through its adhesive properties, can slowly release zinc ions at the site of bleeding, effectively promoting coagulation and accelerating hemostasis. Experimental results indicate that the enhanced PEG/ZnO hydrogel exhibits superior mechanical properties and adhesion strength, especially in terms of coagulation effects, showing significant improvement compared to traditional PEG hydrogels. It meets both in vitro and in vivo coagulation requirements, offering a promising hemostatic solution for surgeries and emergency trauma care.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and characterization of hydrogels
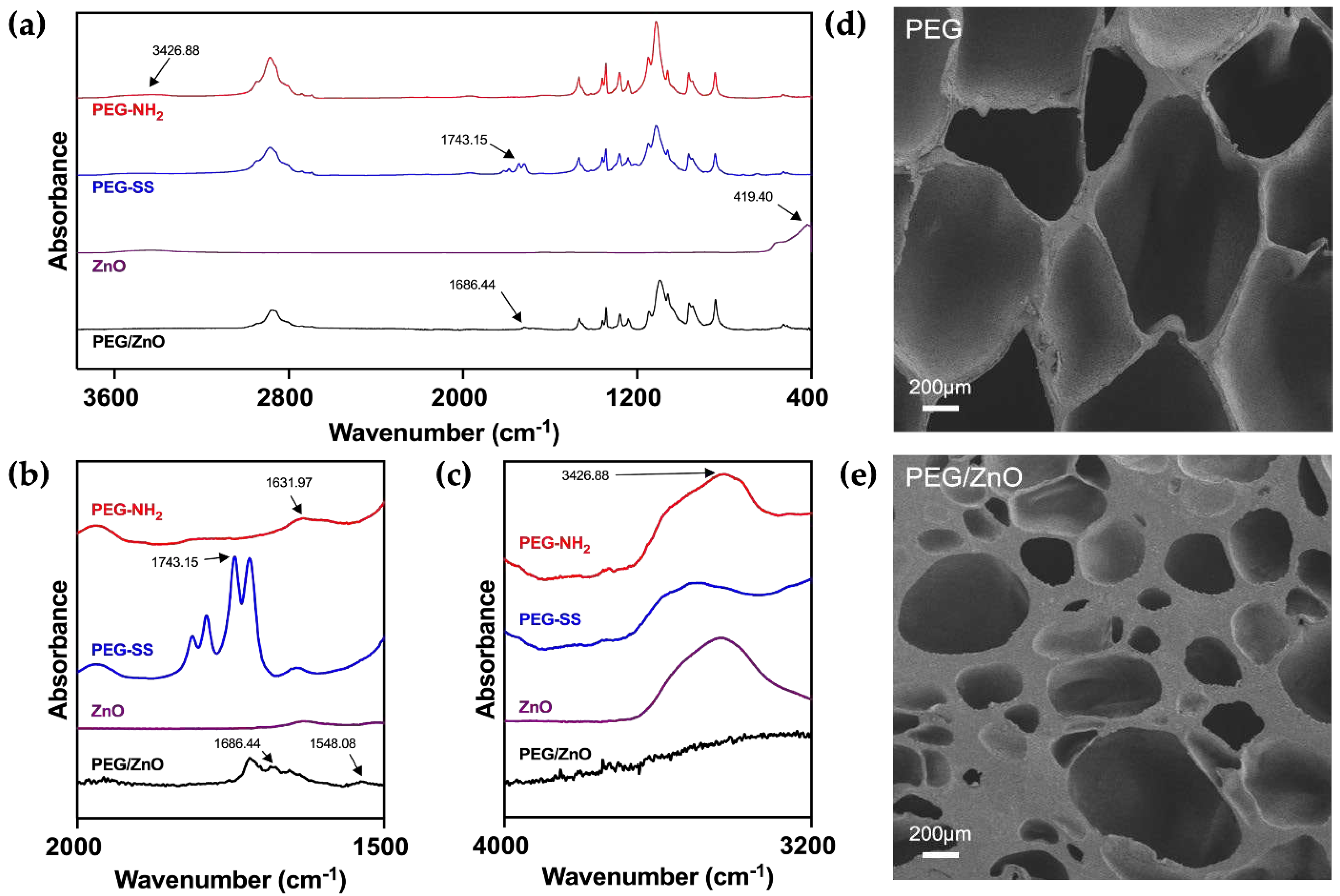
Different concentration PEG-NH
2 and PEG-SS solution were made by dissolving different proportions (wt%) of 4-arm PEG-NH
2 and 4-arm PEG-SS in PBS (7.4). Then PEG/ZnO and PEG hydrogels were mad by mixing equal volume of PEG solution with or without ZnO particles [
11]. The chemical structures were analyzed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), including PEG-NH
2, PEG-SS, ZnO, and PEG/ZnO hydrogel (
Figure 1a). As illustrated in
Figure 1b and 1c, for PEG-NH
2, the N-H stretching vibration of amino group typically appears between 3300-3500 cm⁻¹, with a peak at 3426.88 cm⁻¹, while the N-H bending vibration of the amino group generally occurs in the range of 1550-1650 cm⁻¹, as shown at 1631.97 cm⁻¹. For PEG-SS, the absorption peak at 1743.15 cm⁻¹ corresponds to the stretching vibration of C=O in the active ester group (1730-1750 cm⁻¹). During the formation of PEG hydrogel, FT-IR analysis revealed the disappearance of characteristic absorption peaks at 3426.88 cm⁻¹ and 1631.97 cm⁻¹, indicating the involvement of amino groups (-NH
2) in the formation of amide bonds [
17]. Simultaneously, the C=O absorption peak at 1743.15 cm⁻¹ in PEG-SS disappears, replaced by a new absorption peak at 1686.44 cm⁻¹ corresponding to the newly formed amide bond (C=O), which called the amide I band [
18]. These results suggest a condensation reaction between amino groups (-NH
2) and active esters, forming amide bonds (-CONH-), which connect the PEG-NH
2 and PEG-SS, resulting in a new covalently linked product. With the addition of ZnO into the PEG hydrogel system, Zn
2+ undergo chelation reactions with the amino groups (-NH
2), forming a secondary network that strengthens the hydrogel structure and accelerates gelation time. The characteristic absorption peak at 419.4 cm⁻¹ for hydrogen bonding vibrations in metal oxides between zinc and oxygen ions disappears after chelation reactions with corresponding functional groups, with the N-H absorption peak at 3426.88 cm⁻¹ correspondingly weakened or disappearing due to the chelation reaction of the amino groups [19, 20].
We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the impact of ZnO on the microstructure of PEG hydrogels using scanning electron microscopy. The porous structure of hydrogels is crucial for cellular migration and proliferation within a biological system [
21]. As illustrated in the
Figure 1d and 1e, the chemical interactions among PEG molecules result in a uniformly porous structure in the PEG hydrogel. These interconnecting pores contribute to excellent biological properties. Upon the addition of ZnO, there is a slight reduction in pore size within the hydrogel structure [
22]. The increase in cross-linking density leads to a significant improvement in mechanical properties. This is correlated with the chelation reaction observed in FT-IR, where zinc ions interact with PEG functional groups, forming a second cross-linked network [
14]. These findings suggest that the addition of ZnO can significantly influence the microstructure of PEG hydrogels, with the potential to alter the mechanical properties of the PEG hydrogel.
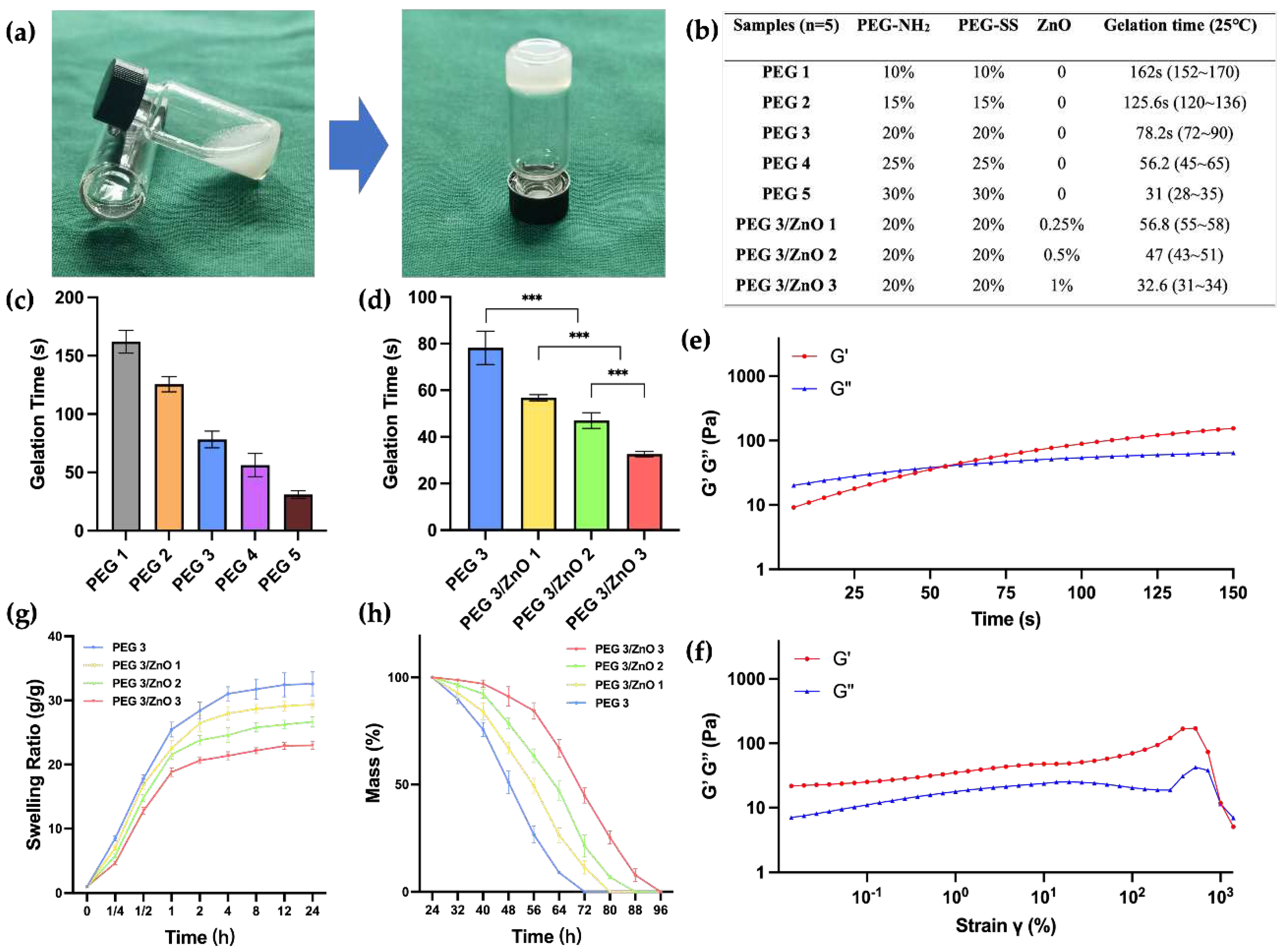
Achieving an appropriate gelation time is crucial for the effectiveness of hemostatic hydrogels. Prolonged gelatinization can result in delayed hemostasis, leading to extensive tissue adhesion when the liquid hydrogel precursor diffuses into neighboring healthy tissues. Conversely, a gelation time that is too short may not be conducive to practical clinical applications. To address this, we determined the gelation time of various hydrogels at 25°C by adjusting the concentration of PEG-NH
2, PEG-SS, and ZnO. The gelation time was assessed using the tube inversion test, as illustrated in
Figure 2A. The amino groups of PEG-NH
2 can rapidly react with the succinimidyl-active ester of PEG-SS under ammonolysis conditions. Increasing the concentrations of both PEG-SS and PEG-NH
2 from 10wt% to 30wt% led to a gradual decrease in gelation time from 162s to 31s (
Figure 2B and 2C). The gelation time of the PEG hydrogel can be easily controlled by adjusting the concentration of PEG content. Through practical validation, we have determined that a gelation time of around 50-60s is most suitable for clinical applications, allowing for suction, injection, and in situ gelation. We found that the gelation times of PEG3 and PEG4 both meet this optimal duration. Considering the chelation effect of zinc ions, which may accelerate the gelation process, there is a possibility that the PEG4 group exceeds the optimal gelation time. Therefore, we chose PEG3, which has a relatively lower concentration of PEG to investigate the impact of adding ZnO on the gelation time. As depicted in
Figure 2D, the gelation time of PEG/ZnO hydrogels significantly decreased after the addition of ZnO. With 0.25wt% to 1wt% ZnO addition, the gelation time of the PEG/ZnO hydrogels reduced from 56.8s to 32.6s. Through chelation reactions, zinc ions can markedly enhance the gelation speed of PEG-based hydrogels, allowing for achieving the desired gelation time at lower PEG concentrations [
23].
Next, we conducted the investigation of the rheological properties of the hydrogel. Sweep at fixed frequency and strain revealed the transition of the hydrogel from a liquid to a solid state. Here, G' represents the storage modulus, reflecting the solid-like characteristics of the material, while G'' represents the loss modulus, reflecting the liquid-like characteristics. As illustrated in
Figure 2e, upon mixing PEG-NH
2, PEG-SS, and ZnO, the hydrogel precursor exhibited G'' > G' for the initial 55 seconds, indicating its liquid state. However, after 55 seconds, both G' and G'' curves reversed, indicating the transition of the hydrogel from a liquid to a solid state. This observation aligns with the gelation time determined in our previous analysis. After gelation, we conducted strain sweep on the hydrogel under an angular frequency of 10 rad/s. As illustrated in
Figure 2f, at shear strains approaching 1x10
3, the molecular structure of the hydrogel experienced forces exceeding its capacity to maintain the gel state. This resulted in a transition from its original state to a liquid state, accompanied by the rupture of the hydrogel's structure.
PEG-based hydrogels exhibit excellent swelling performance [
24]. However, for biological hemostatic hydrogels, swelling properties have both advantages and disadvantages. The high swelling rate of hydrogels can simulate the softness and elasticity of human tissues, aiding better adaptation within the biological environment. Moreover, a high swelling rate implies superior water absorption, enabling the maintenance of a moist microenvironment in bleeding wounds and absorption of wound exudate. However, excessively high swelling rates may lead to the disruption of the hydrogel network, causing it to lose its original shape and structure. As the mechanical strength of the hydrogel decreases, both compressive strength and adhesive strength are compromised. This can be a significant issue for its use in internal hemostasis, where the decrease in hydrogel adhesion may result in recurrent bleeding.
Figure 2g demonstrates that with the addition of ZnO, zinc ions chelate with amino and carboxylic anhydride groups, resulting in a more compact gel network formation in the hydrogel. This phenomenon becomes more pronounced with increasing ZnO concentration. Compared to PEG hydrogel, PEG/ZnO hydrogel exhibits lower swelling rates, allowing it to maintain mechanical stability during the absorption process [
25]. All hydrogel groups reach a stable swelling rate after 24 hours, and we measured their degradation time in vitro. The coordination structure of zinc ions provides a second network structure for PEG-based hydrogels, contributing to an extended degradation time for PEG/ZnO hydrogel. As shown in
Figure 2h, the 20wt% PEG hydrogel completely degrades after 3 days, and as the ZnO concentration increases, the degradation time gradually lengthens [
11]. This indicates that a more compact network promotes greater stability in the hydrogel.
2.2. Mechanical property of the hydrogels
Hemostatic hydrogels need to possess robust mechanical strength to withstand pressure and prevent rupture in the body. Simultaneously, excellent adhesive strength helps maintain their position at the wound site in the moist and smooth environment inside the body, which is crucial for the reliability of hemostasis [
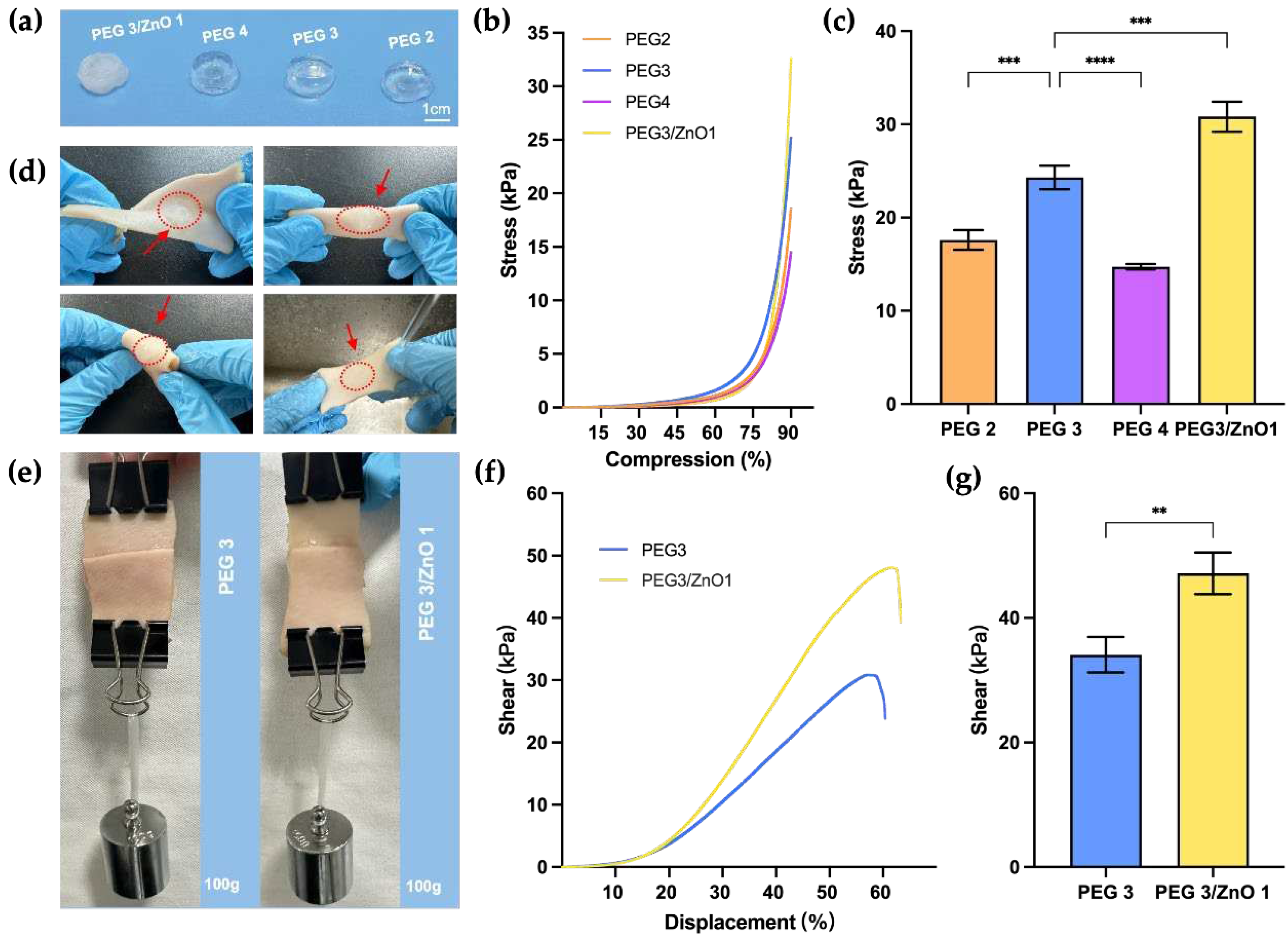
26]. We initially selected PEG2, PEG3, PEG4, and PEG3/ZnO1 based on gelation time for compression strength testing.
Figure 3a illustrates the overall appearance of the prepared hydrogel blocks, and the samples underwent compression testing on a mechanical testing machine at a rate of 2 mm/min until to a deformation extent of 90%. As shown in
Figure 3b and 3c, comparing the PEG2, PEG3, and PEG4 groups, before reaching a PEG content concentration of 20wt%, the compressive strength of the hydrogel increases with an elevation in concentration, reaching a maximum value of 24.30±1.03kPa (PEG3). Beyond this concentration, the compressive strength of hydrogels decreased with increasing PEG concentration. Since the compressive strength of PEG3 hydrogel was superior to the other two groups, we selected PEG3 with the addition of ZnO to explore the changes in mechanical properties. After adding ZnO, the compressive strength of PEG3/ZnO1 reached 30.81±1.31 kPa, indicating an improvement in compressive strength. This suggests that the addition of ZnO significantly increases the cross-linking density of the hydrogel, thereby reinforcing its polymeric network structure.
Next, we selected the two hydrogel groups with the highest compression strength for further experiments. We applied PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO1 onto the surface of fresh porcine skin to assess their anti-torsion performance and waterproof properties on moist skin surfaces. As shown in
Figure 3d, the hydrogel adhered tightly to the porcine skin surface under torsion and bending conditions, demonstrating resistance to the flushing action of water. Subsequently, we trimmed the fresh porcine skin into strips, applied 400μl of PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogels on the respective cut ends, and then overlapped them with an overlap area of approximately 15mm x 10mm (
Figure 3e). After allowing them to stand for 5 minutes, a weight of 100g was suspended below the porcine skin. We observed that both hydrogel groups securely adhered to the fractured porcine skin and withstood the 100g weight, preventing the porcine skin from breaking again.
To clarify the influence of ZnO on the adhesive strength of PEG-based hydrogels, we conducted further mechanical tests at a stretching speed of 10mm/min. The test aimed to determine the maximum adhesive strength of the two hydrogels when porcine skin was stretched until rupture. As shown in
Figure 3f and 3g, the PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogel exhibited a maximum adhesive strength of 47.16±2.73kPa, significantly higher than the maximum adhesive strength of the PEG3, which was 34.10±2.34kPa. The increase in adhesive strength may be attributed to the chelation between zinc ions and amino groups on the tissue surface. These results indicate that the addition of ZnO not only enhances the mechanical performance of PEG-based hydrogels but also increases the adhesive strength to tissues, which is highly beneficial for adhesion in the dynamic and moist environment of internal tissues. The robust mechanical resilience of these hydrogels enables them to remain stable under dynamic tissue movements and external forces, which is a crucial auxiliary step in achieving hemostasis [
27].
2.3. In vitro biocompatibility
Good biocompatibility is a prerequisite for the in vivo application of biomaterials [
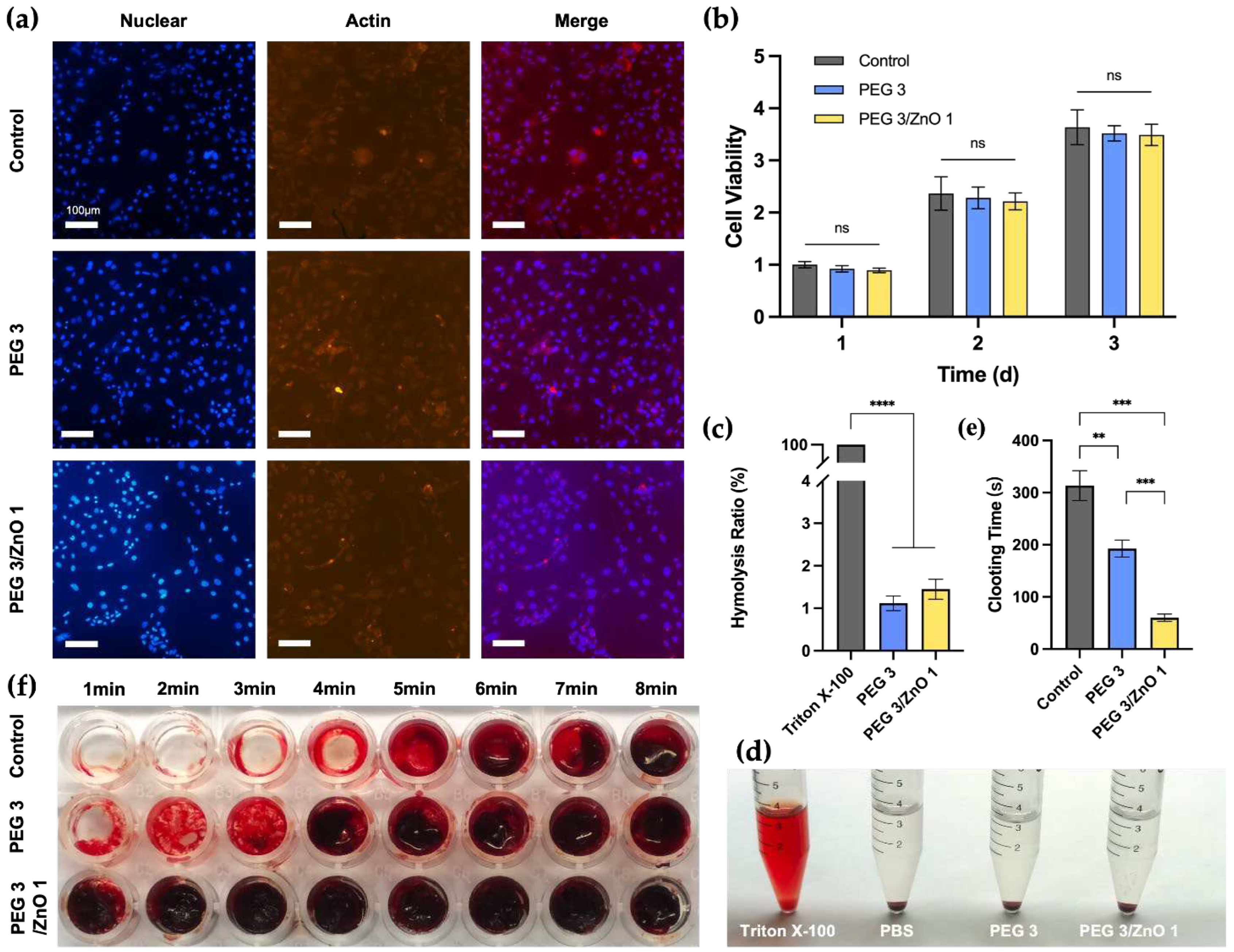
28]. We selected NIH-3T3 cells for the fluorescence staining and the CCK-8 assay to assess the biocompatibility of the hydrogels. Based on measurements of gelation time, compressive strength, and adhesive strength, we chose PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO1 as experimental candidate groups to evaluate the impact of ZnO concentration on biocompatibility. After co-culturing cells with the hydrogel extract for 24 hours, we performed fluorescence staining on NIH-3T3 cells (
Figure 4a). All cells displayed a spindle-shaped morphology in all groups, with clear nuclear staining, indicating that the hydrogel exhibits excellent biocompatibility. At the same time, the quantitative analysis results (
Figure 4b) showed that cells in the PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO1 groups exhibited a significant proliferation trend within three days, with no statistically significant differences between each group. On the first day, the cell survival rates for both the PEG and PEG/ZnO groups were above 90%. Moreover, by the third day of culture, the cell proliferation rates for the PEG and PEG/ZnO groups reached 3.52±0.12 and 3.49±0.17, respectively. The hydrogel's excellent adhesive properties and appropriate porosity contribute to its outstanding biocompatibility.
2.4. In vitro hemocompatibility and procoagulant ability
Due to the hydrogel's need to remain in the tissue after hemostasis, the blood compatibility of this material is crucial [
29]. We co-cultured rat red blood cells with 0.1% Triton X-100, PBS, PEG3 hydrogel extract, and PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogel extract for 12 hours (
Figure 4c and 4d). The appearance of the samples after centrifugation is shown in the
Figure 4d. Similar to the negative control group (PBS group), the supernatant of the PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO hydrogel groups was clear, while the supernatant of the positive control group (Triton X-100) was bright red. The hemolysis rate of each group was measured by a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 545nm, showing that the hemolysis rate of the PEG hydrogel groups was less than 1%. The hydrogel can interact with blood without negatively affecting blood cells or triggering undesirable responses, demonstrating its excellent blood compatibility.
Simultaneously, we conducted in vitro determination of the hydrogel's blood clotting time using whole blood from rats. As shown in the
Figure 4e and 4f, the control group served as the untreated whole blood of rats, and we observed the blood clotting time to be approximately 313.4±25.62s by inclining the culture dish. In the experimental group, where PEG3 hydrogel covered the bottom of the culture dish, the time for blood clot formation was slightly shortened to 192.8±14.55s. Previous studies have reported zinc ions as crucial cofactors in thrombosis, capable of altering the structure of fibrin and reducing fibrinolysis. It is noteworthy that with the addition of 0.25% ZnO to the PEG3 hydrogel, the coagulation time was significantly reduced, forming a solid blood clot in approximately 1 minute (60.2±6.34s). Therefore, the incorporation of ZnO into the PEG hydrogel significantly enhances its procoagulant ability, providing a robust foundation for our subsequent in vivo hemostasis experiments [30, 31].
2.5. In vivo Hemostatic Performance
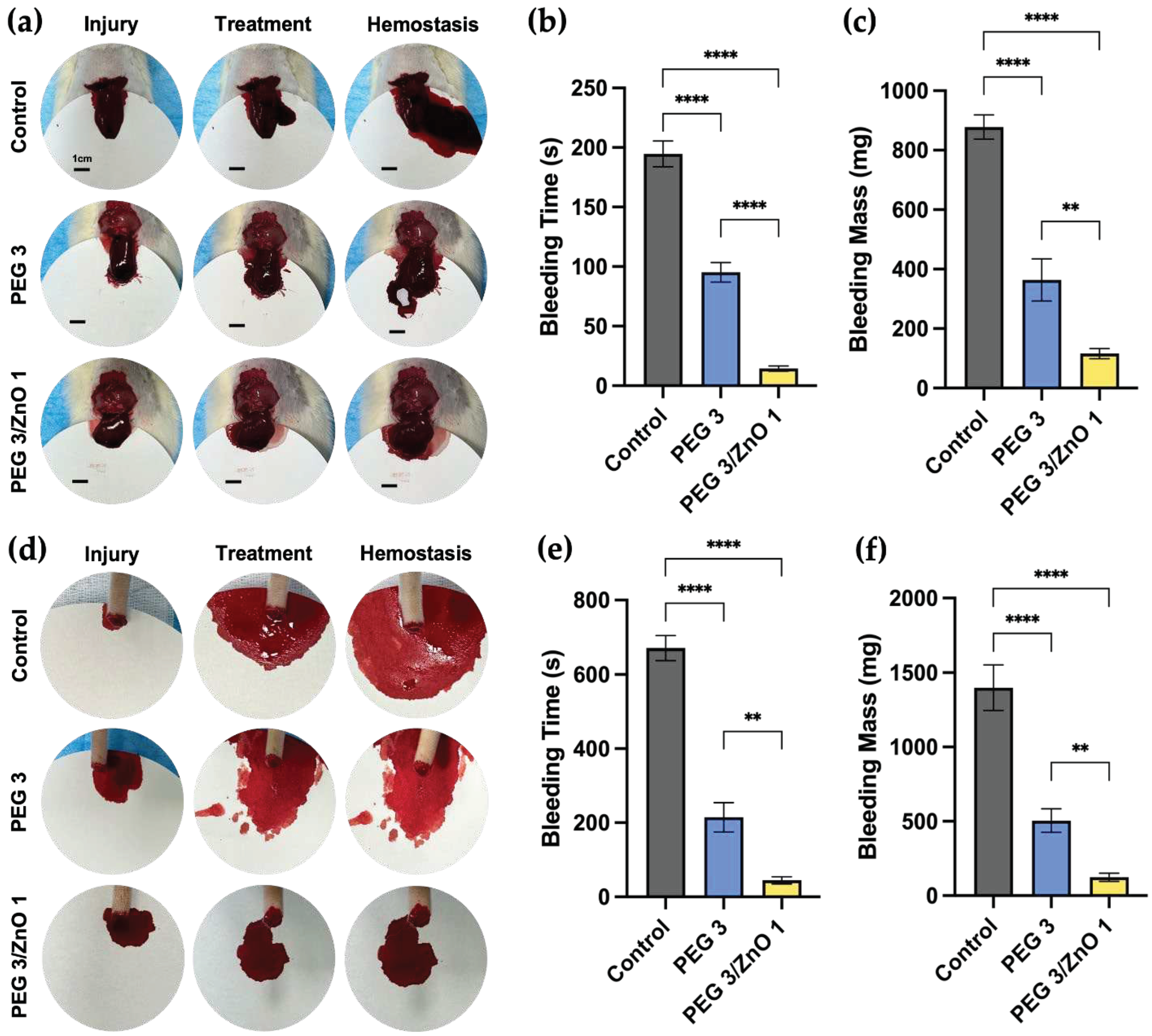
Based on the superior gelation speed, mechanical strength, biocompatibility, and in vitro pro-coagulant performance of PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels, we further investigated the in vivo adhesion and hemostatic capabilities of them. We utilized rat liver bleeding and tail amputation bleeding models to simulate visceral and peripheral vascular bleeding, respectively. In the rat liver injury model (depicted in
Figure 5a), a 1cm incision was made on the rat's liver lobe, resulting in substantial bleeding. Subsequently, 400μl of PEG3 hydrogel and PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogel were separately injected into the bleeding sites of the experimental group. As shown in
Figure 5b and 5c, after injecting PEG3 hydrogel, a small amount of blood continued to flow out from the liver surface and mixed with the gel, turning the transparent hydrogel mixture red and gradually coagulating at the bleeding site. Compared to the control group, the bleeding time of PEG3 hydrogel decreased from 194.67±8.81 s to 95.23±6.72 s, and the bleeding mass decreased from 877.78±33.24 mg to 363.88±57.65 mg. In contrast, after injecting PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogel, the hydrogel rapidly diffused and solidified at the bleeding site, immediately stopping the bleeding. The coagulated hydrogel remained milky white, indicating that the hydrogel had already played a role in promoting coagulation before blood mixed into the liquid hydrogel. Quantitative data also supported this view, as the bleeding time for PEG3/ZnO1 shortened to 14.43±1.82 s, and the bleeding volume reduced to 115.84±13.91 mg compared to the PEG3 group.
Similar results were obtained in the hemostasis experiment using the rat tail amputation bleeding model to simulate peripheral tissue bleeding (
Figure 5d). As shown in
Figure 5e and 5f, the untreated control group of rats had an average bleeding time of 671±27.36 s and an average bleeding volume of 1399±125.32 mg. After treatment with PEG3 and PEG3/ZnO1 hydrogels, the bleeding time for the experimental group of rats shortened to 214.67±32.36 s and 44.67±7.85 s, and the bleeding mass decreased to 504.33±64.51 mg and 123.33±21.79 mg, respectively. These results indicate that PEG-based hydrogels exhibit excellent hemostatic performance and highlight the effective procoagulant effect of adding ZnO, representing a promising approach for acute bleeding treatment.
3. Conclusions
This study significantly advances the development of hemostatic materials, focusing on PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels, crucial for rapid and effective bleeding control in trauma and surgery. The combination of polyethylene glycol (PEG) with zinc oxide (ZnO) enhances the hydrogel's mechanical strength, adhesion, and coagulation, as revealed by chemical analyses including FT-IR and electron microscopy. These modifications not only improve structural integrity but also speed up gelation, making them highly practical for clinical use.
The PEG/ZnO hydrogels show remarkable advancements in compression and adhesion, vital for stability and effectiveness in internal tissues, as confirmed by in vitro tests demonstrating their biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. Moreover, in vivo experiments with rat liver and tail bleeding models reveal these hydrogels' superior hemostatic capabilities, significantly reducing bleeding time and volume, and demonstrating enhanced coagulation, compared to traditional PEG hydrogels.
In conclusion, the study presents a promising approach to managing severe bleeding, especially in complex cases like visceral injuries. The enhanced PEG/ZnO hydrogels, with their improved mechanical properties, rapid gelation, and excellent biocompatibility, offer a significant improvement over traditional hemostatic method. These findings open the door to further research and development, potentially leading to widespread clinical adoption and ultimately saving lives in trauma and surgical settings.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4-arm PEG-NH2 (Mw≈10K) and 4-arm PEG-SS (Mw≈10K) was purchased from SINOPEG. ZnO was purchased from Anhui Senrise Technology Co, Ltd. All experimental materials are within their shelf life.
4.2. Characterization
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was recorded on a Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS20 (Thermofisher, United States of America) in the range 400-4000 cm-1. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained at an acceleration voltage of 0.02-30kV on a ZEISS Gemini 300 (ZEISS, Germany). The samples were directly sputter-coated with a thin layer and adhere them to conductive adhesive. Use the Quorum SC7620 Sputter Coater to gold coat for 45 seconds, with the sputtering set at 10 mA. Subsequently, employ the SEM for imaging the sample morphology with an accelerating voltage of 3 kV. The rheological behavior tests of the hydrogels were performed at room temperature. The prepared precursor solutions were placed in the Anton Paar MCR 302 rheometer (Anton Paar, Austria). During the time sweep, the hydrogels were tested under an angular frequency of 6.28 rad/s and a strain of 0.5%. In the strain sweep, the hydrogels were tested under an angular frequency of 10 rad/s.
4.3. Preparation of the hydrogels
The solutions of PEG-NH2 and PEG-SS were separately prepared by dissolving predetermined proportions of each in PBS (pH 7.4). These solutions were then combined in equal volumes, followed by thorough mixing and vibration to form the PEG hydrogel. For the PEG/ZnO hydrogel, a specific amount of ZnO was dissolved in the PEG-SS solution to create the PEG-SS/ZnO solution. This was subsequently mixed in equal parts with the PEG-NH2 solution, undergoing a similar process of mixing and vibration, resulting in the formation of the PEG/ZnO hydrogel.
4.4. Gelation time and injectability
The determination of gelation times for both PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels was conducted using the tube inversion method. This involved mixing 200μl of each PEG solution, after which the test tube was tilted to assess the fluid's mobility. The point at which the hydrogel ceased flowing and remained adhered to the tube's bottom upon inversion marked the gelation time. Each hydrogel formulation underwent this test five times for consistency. Subsequently, 10 seconds after mixing the PEG-NH2 and PEG-SS (ZnO) solutions, the resulting liquid hydrogel precursor was carefully applied onto fresh porcine skin using a syringe for further evaluation.
4.5. Swelling ratio and degradation of the hydrogels
Upon achieving the gelation state, each group of hydrogels was subjected to a freeze-drying process for 24 hours and subsequently immersed in PBS. At predetermined time intervals, the hydrogels were extracted from the PBS solution, and surface moisture was meticulously blotted off with filter paper to ensure consistent weight measurements. The swelling ratio (SR) was calculated using the formula:
where W
t represents the weight of the hydrogels at various time points post-removal, and W
d denotes the weight of the hydrogels following freeze-drying. After a complete swelling period of 24 hours, the hydrogels were extracted and weighed. This initial weight was recorded as W
0. Subsequently, the hydrogels were immersed back into PBS, and at regular intervals, they were removed to be weighed again, with these subsequent weights marked as W
t. The mass percentage was then calculated using the formula:
where W
t represents the weight of the hydrogels at each extraction point, and W
0 is the initial weight post-swelling.
4.6. Compression strength test
10 minutes post-gelation, the cylindrical hydrogel samples were carefully removed. Their compression strength was then accurately assessed using a universal testing machine (Japan), operating at a steady compression speed of 2 mm/min until a compression level of 90% was achieved. This procedure was meticulously repeated three times for each hydrogel sample to ensure reliability and consistency in the measurements.
4.7. Adhesion strength test
Fresh porcine skin was meticulously cut into strips, each measuring 30mm by 15mm. A precise amount of 400μl of hydrogel was then uniformly injected over a specific area of 15mm by 10mm on the edge of one strip of porcine skin. Subsequently, a second strip of porcine skin of identical size was carefully placed over the gel-coated area, ensuring proper alignment, and left undisturbed for 2 hours to ensure adequate bonding. To measure the adhesion strength of the hydrogel, a universal testing machine (Japan) was employed, applying a tensile force at a consistent rate of 10 mm/min until the bonded skin samples separated, indicating sample fracture. This process was rigorously repeated thrice for each hydrogel variant to guarantee accuracy and repeatability in the results.
4.8. Adhesion strength test
To evaluate the impact of hydrogels on cellular proliferation, both CCK-8 assays and fluorescence staining were conducted. NIH-3T3 cells were initially grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin, sourced from Biological Industries, Israel. After a 24-hour culture period, the cells were evenly distributed into 96-well plates at a concentration of 2x10⁴ cells per well. Following a further 24-hour incubation in a humidified 5% CO
2 environment, the medium was replaced with a hydrogel-conditioned medium, which had been previously incubated with the hydrogel for 24 hours. Cell proliferation was then measured at intervals of 1, 2, and 3 days at 37℃ using the CCK-8 assay. This process was rigorously repeated five times for each hydrogel to ensure reliable results. The absorbance of the sample solutions was recorded at 450 nm, and cell viability was calculated as follows:
where OD
sample represents the absorbance of hydrogel group, OD
control is the absorbance of control group in complete medium, and OD
blank refers to the blank well's absorbance. Concurrently, after 1 day of incubation, cells were stained with DAPI and phalloidin (both from Solarbio, China) to visualize the nuclei and actin proteins, respectively.
4.9. Hemocompatibility
For hemolysis assessment, 0.4 g of both PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels were immersed in 4 ml of PBS for 12 hours to create hydrogel extracts. Fresh rat whole blood was diluted with 5 ml PBS to form a diluted solution. Subsequently, 500μl of this diluted blood was added to 3 ml of each hydrogel extract, as well as to PBS and 0.1% Triton X-100, serving as negative and positive controls, respectively. These mixtures were then incubated at 37 °C for 12 hours. Post-incubation, the supernatants were separated by centrifuging at 4,000 rpm for 3 minutes. The absorbance of these supernatants was measured at 540 nm to determine hemolysis levels. The hemolysis ratio was calculated with the formula:
where OD
sample is the absorbance of the hydrogel extract, OD
positive is the absorbance of the purified water group, and OD
negative is that of the PBS group. Each hydrogel was tested 5 times for consistency.
4.10. In vitro clotting time
100μl of the prepared hydrogel precursor solution was injected to cover the bottom of the 96-well plate. Then, 100μl of citrated rat blood mixed with 5μl of calcium chloride (CaCl2) was added into both the blank and hydrogel-covered wells. The plate was periodically tilted, and the wells were washed every minute with PBS to remove uncoagulated blood. The clotting time was recorded, defined as the duration when there was no significant flow of blood upon tilting the culture plate and the blood clot could not be washed away by PBS. Each hydrogel was tested 5 times for consistency.
4.11. In vivo hemostatic performance
The assessment of hemostatic efficacy was conducted on rat liver and tail hemorrhage models using eighteen 8-week-old female Sprague-Dawley rats, each weighing approximately 200±15g. These subjects were randomly categorized into three distinct groups: control, PEG, and PEG/ZnO. Administered intraperitoneally with 2% w/v Pentobarbital sodium, the rats were anesthetized and securely positioned on the surgical table. Following the preparation of the operative area, which involved shaving the fur, a 1.5 cm horizontal incision was precisely made beneath the xiphoid process. This incision penetrated the epidermal layer, subcutaneous tissue, and fascia. To arrest the bleeding, the area was adequately compressed with gauze, revealing the left hepatic lobe. Excess intra-abdominal fluid was then meticulously aspirated using gauze. A pre-measured piece of filter paper was strategically placed under the liver for accurate blood collection. A subsequent transverse cut, measuring 10 mm in length and 5 mm in depth, was executed on the liver. The cranial aspect of the rat was slightly elevated, and 400μl of hydrogel was precisely administered to the hemorrhagic site for the treatment groups, whereas the control group received no intervention. Once the cessation of active bleeding was confirmed, the filter paper was weighed to accurately record both the volume and duration of the bleeding episode. In the tail hemorrhage model, the distal third of the rat's tail was amputated. Here, 200μl of hydrogel was applied to the bleeding site, and blood loss was collected on a pre-weighed piece of filter paper. Post cessation of active bleeding, the paper was weighed, facilitating the quantification of both the total bleeding volume and time. To ensure the consistency and reproducibility of results, each hydrogel formulation was subjected to three independent tests.
4.12. Statistical analysis
All gathered experimental data were meticulously computed and presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis of the data was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post-hoc test to determine the significance of differences among groups. In this statistical framework, a p-value of less than 0.05 (*p < 0.05) was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z., B.W. and JY.C.; methodology, CY.Z., YF.W, ZH.W. and TX.Y.; investigation, CY.Z. and Y.X.; resources, PF.C and B.L.; writing—original draft preparation, CY.Z. and YF.W.; writing—review and editing, CY.Z. YF.W. and JY.C.; project administration, JY.C.; funding acquisition, Z.W. and B.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172392 and 8237091648), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (L212049), Military Logistics Key Projects (145-BHQ090003000X13).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal studies were carried out in accordance with Committee of Chinese PLA General Hospital, IACUC of PLAGH on the use of Institutional Animal Care and Use. (Ethics Approval No. SQ2022438).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors will thank all the colleagues of Department of Orthopedics of Chinese PLA General Hospital for their great help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- J.S. Davis, S.S. Satahoo, F.K. Butler, H. Dermer, D. Naranjo, K. Julien, R.M. Van Haren, N. Namias, L.H. Blackbourne, C.I. Schulman, An analysis of prehospital deaths: Who can we save?, J Trauma Acute Care Surg 77(2) (2014) 213-8. [CrossRef]
- P. Rhee, B. Joseph, V. Pandit, H. Aziz, G. Vercruysse, N. Kulvatunyou, R.S. Friese, Increasing trauma deaths in the United States, Ann Surg 260(1) (2014) 13-21. [CrossRef]
- J.L. Pellegrino, N.P. Charlton, J.N. Carlson, G.E. Flores, C.A. Goolsby, A.V. Hoover, A. Kule, D.J. Magid, A.M. Orkin, E.M. Singletary, T.M. Slater, J.M. Swain, 2020 American Heart Association and American Red Cross Focused Update for First Aid, Circulation 142(17) (2020) e287-e303. [CrossRef]
- M. Mandrioli, K. Inaba, A. Piccinini, A. Biscardi, M. Sartelli, F. Agresta, F. Catena, R. Cirocchi, E. Jovine, G. Tugnoli, S. Di Saverio, Advances in laparoscopy for acute care surgery and trauma, World J Gastroenterol 22(2) (2016) 668-80. [CrossRef]
- X. Fan, M. Li, Q. Yang, G. Wan, Y. Li, N. Li, K. Tang, Morphology-controllable cellulose/chitosan sponge for deep wound hemostasis with surfactant and pore-foaming agent, Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 118 (2021) 111408. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, M.A. Carlson, Y.S. Zhang, Y. Hu, J. Xie, Fabrication of injectable and superelastic nanofiber rectangle matrices ("peanuts") and their potential applications in hemostasis, Biomaterials 179 (2018) 46-59. [CrossRef]
- M. Kilbourne, K. Keledjian, J.R. Hess, T. Scalea, G.V. Bochicchio, Hemostatic efficacy of modified amylopectin powder in a lethal porcine model of extremity arterial injury, Ann Emerg Med 53(6) (2009) 804-10. [CrossRef]
- X. Du, Y. Liu, X. Wang, H. Yan, L. Wang, L. Qu, D. Kong, M. Qiao, L. Wang, Injectable hydrogel composed of hydrophobically modified chitosan/oxidized-dextran for wound healing, Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 104 (2019) 109930. [CrossRef]
- Y.D. Taghipour, V.R. Hokmabad, A.R. Del Bakhshayesh, N. Asadi, R. Salehi, H.T. Nasrabadi, The Application of Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers for Tissue Engineering, Curr Med Chem 27(16) (2020) 2658-2680. [CrossRef]
- S.L. Chen, R.H. Fu, S.F. Liao, S.P. Liu, S.Z. Lin, Y.C. Wang, A PEG-Based Hydrogel for Effective Wound Care Management, Cell Transplant 27(2) (2018) 275-284. [CrossRef]
- Y. Bu, L. Zhang, G. Sun, F. Sun, J. Liu, F. Yang, P. Tang, D. Wu, Tetra-PEG Based Hydrogel Sealants for In Vivo Visceral Hemostasis, Adv Mater 31(28) (2019) e1901580. [CrossRef]
- D. Wang, N. Zhang, T. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Jing, Y. Zhou, J. Long, L. Meng, Amino acids and doxorubicin as building blocks for metal ion-driven self-assembly of biodegradable polyprodrugs for tumor theranostics, Acta Biomater 147 (2022) 245-257. [CrossRef]
- C.N. Glover, C. Hogstrand, Amino acid modulation of in vivo intestinal zinc absorption in freshwater rainbow trout, J Exp Biol 205(Pt 1) (2002) 151-8. [CrossRef]
- H. Xie, H. Xia, L. Huang, Z. Zhong, Q. Ye, L. Zhang, A. Lu, Biocompatible, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory zinc ion cross-linked quaternized cellulose-sodium alginate composite sponges for accelerated wound healing, Int J Biol Macromol 191 (2021) 27-39. [CrossRef]
- G. Marx, A. Eldor, The procoagulant effect of zinc on fibrin clot formation, Am J Hematol 19(2) (1985) 151-9. [CrossRef]
- K.A. Taylor, N. Pugh, The contribution of zinc to platelet behaviour during haemostasis and thrombosis, Metallomics 8(2) (2016) 144-55. [CrossRef]
- E.P. van Dam, H. Yuan, P.H.J. Kouwer, H.J. Bakker, Structure and Dynamics of a Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel, J Phys Chem B 125(29) (2021) 8219-8224. [CrossRef]
- T.J. Measey, B.N. Markiewicz, F. Gai, Amide I Band and Photoinduced Disassembly of a Peptide Hydrogel, Chem Phys Lett 580 (2013) 135-140. [CrossRef]
- R. Chen, Z. Jalili, R. Tayebee, UV-visible light-induced photochemical synthesis of benzimidazoles by coomassie brilliant blue coated on W-ZnO@NH(2) nanoparticles, RSC Adv 11(27) (2021) 16359-16375.
- I. Erol, Ö. Hazman, M. Aksu, E. Bulut, Synergistic effect of ZnO nanoparticles and hesperidin on the antibacterial properties of chitosan, J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 33(15) (2022) 1973-1997. [CrossRef]
- J.S. Varghese, N. Chellappa, N.N. Fathima, Gelatin-carrageenan hydrogels: role of pore size distribution on drug delivery process, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 113 (2014) 346-51. [CrossRef]
- N. Masood, R. Ahmed, M. Tariq, Z. Ahmed, M.S. Masoud, I. Ali, R. Asghar, A. Andleeb, A. Hasan, Silver nanoparticle impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel enhances wound healing in diabetes induced rabbits, Int J Pharm 559 (2019) 23-36. [CrossRef]
- P. Huang, W. Su, R. Han, H. Lin, J. Yang, L. Xu, L. Ma, Physicochemical, Antibacterial Properties, and Compatibility of ZnO-NP/Chitosan/β-Glycerophosphate Composite Hydrogels, J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(4) (2022) 522-530. [CrossRef]
- K.I. Hoshino, T. Nakajima, T. Matsuda, T. Sakai, J.P. Gong, Network elasticity of a model hydrogel as a function of swelling ratio: from shrinking to extreme swelling states, Soft Matter 14(47) (2018) 9693-9701. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, Y. Qi, Z. Zhang, Swelling Behaviour of Polystyrene Microsphere Enhanced PEG-Based Hydrogels in Seawater and Evolution Mechanism of Their Three-Dimensional Network Microstructure, Materials (Basel) 15(14) (2022). [CrossRef]
- F.D. Victorelli, C.F. Rodero, V. Lutz-Bueno, M. Chorilli, R. Mezzenga, Amyloid Fibrils Enhance the Topical Bio-Adhesivity of Liquid Crystalline Mesophase-Based Drug Formulations, Adv Healthc Mater 12(12) (2023) e2202720. [CrossRef]
- Y. Bu, L. Zhang, J. Liu, L. Zhang, T. Li, H. Shen, X. Wang, F. Yang, P. Tang, D. Wu, Synthesis and Properties of Hemostatic and Bacteria-Responsive in Situ Hydrogels for Emergency Treatment in Critical Situations, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(20) (2016) 12674-83. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, R. Huang, B. Zheng, W. Guo, C. Li, W. He, Y. Wei, Y. Du, H. Wang, D. Wu, H. Wang, Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing, Adv Sci (Weinh) 8(8) (2021) 2003627. [CrossRef]
- K. Alula, T. Adali, O. Han Ebedal, Preparation characterization and blood compatibility studies of silk fibroin/gelatin/curcumin injectable hydrogels, Biomed Mater Eng 34(1) (2023) 77-93. [CrossRef]
- H. Steuer, R. Krastev, N. Lembert, Metallic oxide nanoparticles stimulate blood coagulation independent of their surface charge, J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 102(5) (2014) 897-902. [CrossRef]
- S.A. Chaudhry, M. Serrata, L. Tomczak, S. Higgins, J. Ryu, D. Laprise, K. Enjyoji, R. Bekendam, V. Kaushik, R. Flaumenhaft, P.K. Bendapudi, Cationic zinc is required for factor XII recruitment and activation by stimulated platelets and for thrombus formation in vivo, J Thromb Haemost 18(9) (2020) 2318-2328. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
(a) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS, ZnO and PEG/ZnO hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 400-3600cm-1. (b) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS and PEG hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 1500-2000cm-1. (c) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS and PEG/ZnO hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 3200-4000cm-1. (d, e) SEM images of the PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels, Scale bar: 200 μm.
Figure 1.
(a) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS, ZnO and PEG/ZnO hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 400-3600cm-1. (b) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS and PEG hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 1500-2000cm-1. (c) FT-IR spectra of PEG-NH2, PEG-SS and PEG/ZnO hydrogel in the wavenumber range of 3200-4000cm-1. (d, e) SEM images of the PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels, Scale bar: 200 μm.
Figure 2.
(a) Gelation process and the method of gelation time testing. (b) Composition Concentration and Gelation Time of PEG and PEG/ZnO Hydrogels in Different Groups. (c, d) Gelation time of PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels at different concentrations (n=5). (e) Time sweep of PEG/ZnO under an angular frequency of 6.28 rad/s and strain of 0.5%. (f) Strain sweep of PEG/ZnO under an angular frequency of 10 rad/s. (g) Swelling curves of the hydrogels (n=3). (h) Degradation curves of the hydrogels (n=3). (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 2.
(a) Gelation process and the method of gelation time testing. (b) Composition Concentration and Gelation Time of PEG and PEG/ZnO Hydrogels in Different Groups. (c, d) Gelation time of PEG and PEG/ZnO hydrogels at different concentrations (n=5). (e) Time sweep of PEG/ZnO under an angular frequency of 6.28 rad/s and strain of 0.5%. (f) Strain sweep of PEG/ZnO under an angular frequency of 10 rad/s. (g) Swelling curves of the hydrogels (n=3). (h) Degradation curves of the hydrogels (n=3). (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 3.
(a) Hydrogel samples used for compressive strength test. (b) Stress−compression curves of hydrogels (n=3). (c) Compressive stress of hydrogels at 90% compression level (n=3). (d) The porcine skin injected with hydrogels for torsion, folding, and waterproof testing. (e) Adhesion of PEG and PEG/ZnO on the porcine skin. (f) Shear-displacement curves of different hydrogels (n=3). (g) Shear stress of different hydrogels. (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 3.
(a) Hydrogel samples used for compressive strength test. (b) Stress−compression curves of hydrogels (n=3). (c) Compressive stress of hydrogels at 90% compression level (n=3). (d) The porcine skin injected with hydrogels for torsion, folding, and waterproof testing. (e) Adhesion of PEG and PEG/ZnO on the porcine skin. (f) Shear-displacement curves of different hydrogels (n=3). (g) Shear stress of different hydrogels. (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 4.
(a) Fluorescence staining of NIH-3T3 cells after incubation with the hydrogels for 24h, the cell nucleus is stained blue with DAPI, and actin protein is stained red with phalloidin. Scale bar: 100 μm. (b) Cell viability analysis of the hydrogels for 1, 2 and 3 days. (c) Hemolysis ratio of the hydrogels (n=5). (d) Hemolysis test of the hydrogels. (e) Clotting time of the hydrogels (n=5). (f) Procoagulant effects of the hydrogels. (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 4.
(a) Fluorescence staining of NIH-3T3 cells after incubation with the hydrogels for 24h, the cell nucleus is stained blue with DAPI, and actin protein is stained red with phalloidin. Scale bar: 100 μm. (b) Cell viability analysis of the hydrogels for 1, 2 and 3 days. (c) Hemolysis ratio of the hydrogels (n=5). (d) Hemolysis test of the hydrogels. (e) Clotting time of the hydrogels (n=5). (f) Procoagulant effects of the hydrogels. (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 5.
(a) Photograph of rat liver bleeding and hemostasis process (Scale bar = 1 cm). (b) Bleeding time in the liver hemorrhage (n=3). (c) Bleeding mass in the liver hemorrhage (n=3). (d) Photograph of rat tail bleeding and hemostasis process. (e) Bleeding time in the tail hemorrhage (n=3). (f) Bleeding mass in the tail hemorrhage (n=3). (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
Figure 5.
(a) Photograph of rat liver bleeding and hemostasis process (Scale bar = 1 cm). (b) Bleeding time in the liver hemorrhage (n=3). (c) Bleeding mass in the liver hemorrhage (n=3). (d) Photograph of rat tail bleeding and hemostasis process. (e) Bleeding time in the tail hemorrhage (n=3). (f) Bleeding mass in the tail hemorrhage (n=3). (Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significant difference).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).