Submitted:
19 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Historical Background
- i)
- Modifications of the chemical or physical properties of the drug;
- ii)
- Mixing with co-ingredients or co-solvents;
- iii)
- Development of drug carrier systems that improve the interactions between the drug and surrounding biological molecules, tissues and cells.
Drug Modification
Co-Ingredients and Co-Solvents
Drug Carrier Systems
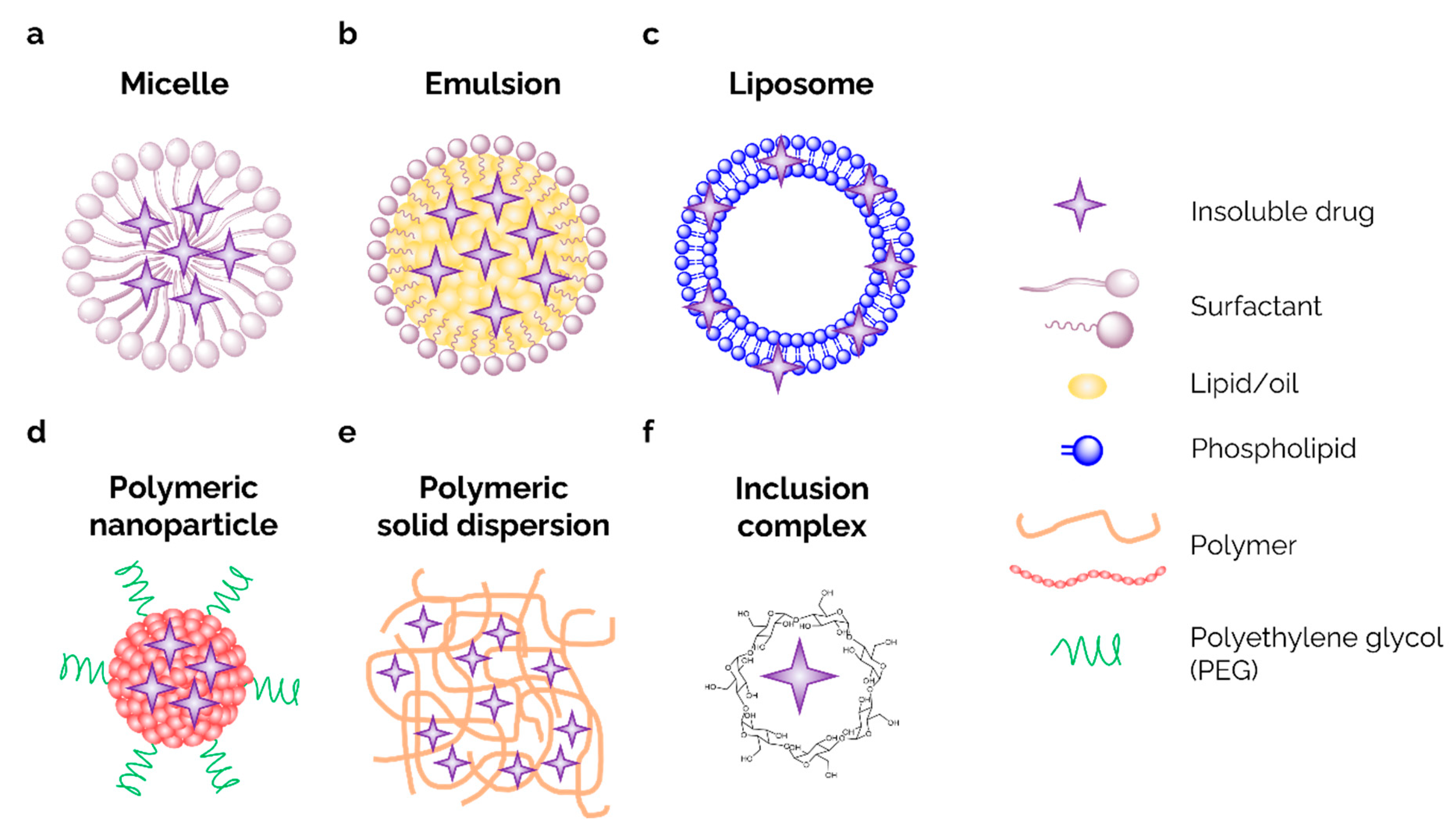
Dendrimer
Nano-Gel
Alternative and Non-Canonical Delivery Technology
Stealth Effect
| Type of modification | NameTM/R | Parent Company | Main Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical moiety | Norvir | Abbvie | Antiviral | [11] |
| Chemical moiety | Losentic | Novartis | Antihypertensive | [12] |
| Chemical moiety | Vasotec | Merck | Antihypertensive | [12] |
| Chemical moiety | Ceftin | GSK | Antibiotic | [13] |
| Chemical moiety | Cipro IV | Merck | Antibiotic | [16] |
| Supramolecular | BioPerine | Sabina Corp | Blood Sugar Lower | [17] |
| Supramolecular | Taxol | BMS | Antineoplastic | [20] |
| Supramolecular | Taxotere | Sanofi | Antineoplastic | [21] |
| Micelle/Emulsion | MyCell | Glow Life Tech | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [22] |
| Micelle/Emulsion | Curepods | Cure Pharma | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [23] |
| Micelle/Emulsion | uGOO | EmbarkoNano | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [26] |
| Liposome | Cyclosome | Hi-Tech Pharma | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [27] |
| Liposome | Phytosome | Indesa | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [34] |
| Polymeric Nanoparticle | Genexol | Samyang | Antineoplastic | [35] |
| Nano Solid Dispersion | Sporanox | Janseen Pharma | Antifungal | [37] |
| Nano Solid dispersion | Nimotop | Bayer | Antihypertensive | [38] |
| Inclusion Complex | Fenumat | Akay Ingredients | Lipophilic Drug Carrier | [44] |
| Inclusion Complex | CyLoc | Tesseract Medical Research | Cyclodextrin Cages as a Carrier | [45] |
| Inclusion Complex | SSRM | Folium Labs Corp | HA Dispersion as a Carrier | [52] |
Conclusion
Conflict of interest
References
- DeFelice, S.L. The nutraceutical revolution: Its impact on food industry R&D. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D. Hypothesis for changing models: Current pharmaceutical paradygms, trends and approaches in drug discovery. PeerJ PrePrint.
- Feynman, R. (2018). There’s plenty of room at the bottom. In Feynman and computation (pp. 63-76). CRC Press.
- Bangham, A.D. Liposomes: The Babraham connection. Chemistry and physics of lipids 1993, 64, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, K.J., Senyei, A.E., & Scarpelli, D.G. Magnetic microspheres: A model system for site specific drug delivery in vivo. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1978, 158, 141–146. [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargason, A.M.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. The evolution of commercial drug delivery technologies. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkus, F.W.H.M., Verhoef, J.C., Marttin, E., Romeijn, S.G., Van der Kuy, P.H.M., Hermens, W.A.J.J., & Schipper, N.G.M. Cyclodextrins in nasal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 36, 41–57.
- Kim, J.H. , Shin, J.U., Kim, S.H., Noh, J.Y., Kim, H.R., Lee, J.,... & Lee, K.H. Successful transdermal allergen delivery and allergen-specific immunotherapy using biodegradable microneedle patches. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Thornber, C.W. Isosterism and molecular modification in drug design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1979, 8, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, D.J.; Sham, H.L.; Marsh, K.C.; Flentge, C.A.; Betebenner, D.; Green, B.E.; McDonald, E.; Vasavanonda, S.; Saldivar, A.; Wideburg, N.E.; et al. Discovery of Ritonavir, a Potent Inhibitor of HIV Protease with High Oral Bioavailability and Clinical Efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, K.; Webster, R.; Gardner, I.; Dack, K. , Design of Ester Prodrugs to Enhance Oral Absorption of Poorly Permeable Compounds: Challenges to the Discovery Scientist. Curr. Drug Metab. 2003, 4, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. , Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T. (2007). Case Study: Cefuroxime Axetil: An Oral Prodrug of Cefuroxime. In: Stella, V.J., Borchardt, R.T., Hageman, M.J., Oliyai, R., Maag, H., Tilley, J.W. (eds) Prodrugs. Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects, vol V. Springer, New York, NY. [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.; Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. , Microenvironmental pH-modification to improve dissolution behavior and oral absorption for drugs with pH-dependent solubility. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda, S.A.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F.; Manzo, R.H.; Olivera, M.E. , Solubility behavior and biopharmaceutical classification of novel high-solubility ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin pharmaceutical derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myungjoo, K.; JaeYoul, C.; ByungHo, S.; DukKi, K.; JaehWi, L. , Bioavailability enhancing activities of natural compounds from medicinal plants. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Lázaro D, Mielgo-Ayuso J, Córdova Martínez, A., Seco-Calvo, J. Iron and Physical Activity: Bioavailability Enhancers, Properties of Black Pepper (Bioperine®) and Potential Applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1886. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-g.; Pratap Singh, A. Emerging strategies for enhancing buccal and sublingual administration of nutraceuticals and pharamaceuticals. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani MC, Horwitz SB. Nature as a remarkable chemist: A personal story of the discovery and development of Taxol. Anticancer Drugs 2014, 25, 482–487. [CrossRef]
- Sohail MF, Rehman, M., Sarwar HS; et al. Advancements in the oral delivery of Docetaxel: Challenges, current state-of-the-art and future trends. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018, 13, 3145–3161. [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D.; Cohen, J.; Rosanelli, L.; McKibbon, K.; Nanostructure Lipid Carrier Delivery System, Composition and Metods. US Patent US 20230094753A1. 2020.
- Fuoco, D. Classification framework and chemical biology of tetracycline-structure-based drugs. Aantibiotics 2012, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Zheng-Xian, and Carl Artmann. Relative bioavailability comparison of different coenzyme Q10 formulations with a novel delivery system. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2009, 15, 42–46.
- Shah, A.V.; Desai, H.H.; Thool, P.; Dalrymple, D.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble nutraceuticals. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Guo, Y.; Song, D.; Bruno, R.S.; Lu, X. Quercetin-Containing Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Improving Oral Bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D.; di Tomasso, J.; Boulos, C.; Morais, J.A. Identifying nutritional, funtional, and qualityof life correlates with male hypogonadism in advanced cancer patients. eCancerMedicalScience 2015, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D. A new method for characterization of natural zeolites and organic nanostructure using atomic force microscopy. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D. Cytotoxicity Induced by Tetracycline via Protein Photooxidation. Adv. Toxicol. 2015, 2015, 787129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani M, Sangiovanni E, Angarano, M.; et al. Phytosomes as Innovative Delivery Systems for Phytochemicals: A Comprehensive Review of Literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6983–7022. [CrossRef]
- Park JW, Lagniton PNP, Liu, Y., Xu RH. mRNA vaccines for COVID-19: What, why and how. Int J Biol Sci. 2021, 17, 1446–1460. [CrossRef]
- Alberts, D.S.; Garcia, D.J. Safety Aspects of Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin in Patients with Cancer. Drugs 1997, 54 (Suppl. S4), 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner ME, Cummings ND, Sethi, M.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of Genexol-PM, a nanoparticle formulation of paclitaxel, as a novel radiosensitizer for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013, 86, 463–468. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H. , Anti-PEG IgM elicited by injection of liposomes is involved in the enhanced blood clearance of a subsequent dose of PEGylated liposomes. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povsic, T.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Lincoff, A.M.; Mehran, R.; Rusconi, C.P.; Zelenkofske, S.L.; Huang, Z.; Sailstad, J.; Armstrong, P.W.; Steg, P.G.; et al. Pre-existing anti-PEG antibodies are associated with severe immediate allergic reactions to pegnivacogin, a PEGylated aptamer. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1712–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.; Temtem, M.; Gil, M.; Gaspar, F. , Overcoming poor bioavailability through amorphous solid dispersions. Ind Pharm 2011, 30, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barone JA, Moskovitz BL, Guarnieri, J.; et al. Enhanced bioavailability of itraconazole in hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin solution versus capsules in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1862–1865. [CrossRef]
- Saixu Huang, Zhiyong Huang, Zhiqin Fu, Yamin Shi, Qi Dai, Shuyan Tang, Yongwei Gu, Youfa Xu, Jianming Chen, Xin Wu & Fuzheng Ren. A Novel Drug Delivery Carrier Comprised of Nimodipine Drug Solution and a Nanoemulsion: Preparation, Characterization, in vitro, and in vivo Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1161–1172. [CrossRef]
- Uchino, T.; Yasuno, N.; Yanagihara, Y.; Suzuki, H. Solid dispersion of spironolactone with porous silica prepared by the solvent method. Die Pharm. -Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 62, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Beg, S.; Swain, S.; Rizwan, M.; Irfanuddin, M.; Shobha Malini, D. Bioavailability enhancement strategies: Basics, formulation approaches and regulatory considerations. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, K.; Ravi, A.; Kumar, D.; Kuttan, R.; Maliakel, B. An enhanced bioavailable formulation of curcumin using fenugreek-derived soluble dietary fibre. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhou, J.; Guo, J.; Gladden, I.; Kong, L. Starch inclusion complex for the encapsulation and controlled release of bioactive guest compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.-W. Controlled drug delivery systems based on calixarenes. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D.; Cohen, J. Process for the purification of whey protein isolate and formulation thereof. Patent. CA3086093A1. 2020.
- Souto, E.B. Patenting nanomedicines: Legal aspects, intellectual property and grant opportunities. Springer Science & Business Media: 2012.
- Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Elwy, H.M.; Shehadi, I.; Adem, A. Physicochemical properties of antifungal drug–cyclodextrin complexes prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide and by conventional techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, R.L.; Miller, L.A.; Ahmed, I. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2007, 123, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouton, C.W. Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: Non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, S93–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conniot, J.; Silva, M.J.; Fernandes, J.; Liana, C.S.; Gaspar, R.; Brocchini, S.; Florino, H.F.; and Barata, T.S. Cancer immunotherapy: Nanodelivery approaches for immune cell targeting and tracking. Front. Chem. 2014, 105, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, S.K.; Deseale, S.S.; Bronich, K.T. Nanogels: An overview of propreties, biomedical applications and obstacles to clinical transaltion. J Control Release 2016, 240, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. ; Nanoparticle-Hydrogel: A Hybrid Biomaterial System for Localized Drug Delivery. Ann Biomed Eng 2016, 44, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, F.; Boudovith, D. Complexes comprising a carbohydrate and an active ingredient and processes for their preparation. Patent. W02021113986A1. 2022.Huang, G.; Huang, H., Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 766–772. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, P.; Lee, B.-J.; Oh, D.H.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, Y.-I.; Kim, D.-D.; Jee, J.-P.; Lee, Y.-B.; Woo, J.S.; Yong, C.S.; et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10 by self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 374, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J. , Recent progresses in the development of hyaluronic acid-based nanosystems for tumor-targeted drug delivery and cancer imaging. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Pang, L.; Feng, H.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y.; Bing, Y. Recent advantage of hyaluronic acid for anti-cancer application: A review of “3S” transition approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad R, Gulshad L, Haq IU; et al. Nanotechnology: A novel tool to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients. Food Sci Nutr. 2021, 9, 3354–3361. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S., Su, R., Nie, S.; et al. Application of nanotechnology in improving bioavailability and bioactivity of diet-derived phytochemicals. J Nutr Biochem. 2014, 25, 363–376. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakov, N.E.; Kispert, L.D. Water soluble biocompatible vesicles based on polysaccharides and oligosaccharides inclusion complexes for carotenoid delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 128, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyue, W.; Wendong, K.; Dirisala, A.; Toh, K.; Tanaka, M.; Li, J. Stealth and pseudo-stealth nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 198, 114895. [Google Scholar]
- Salmaso, S.; Calicetti, P. Stealth Properties to Improve Therapeutics Efficacy of Drug Nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 374252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottler, S.; Becker, G.; Winzen, S.; Steinbach, T.; Mohr, K. Protein adsorption is required for stealth effect of poly(ethylen glycol)- and poly(phosphoester)-coated nanocarriers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 2015–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, S.; Simon, J.; Pablick, D.; Frey, M.-L. ; Brush Conformation of Polyethylene Glycol Determines the Stealth Effect of Nanocarries in the Low Protein Adsorption Regime. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, D.; Poletti, A.; Forini, N. 3D Surface of Natural Zeolites Investigate using High Resolution Microscopy. ICP-Rivista della Industria Chimica Italiana. 2008. 100-105.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




