Submitted:
15 December 2023
Posted:
15 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
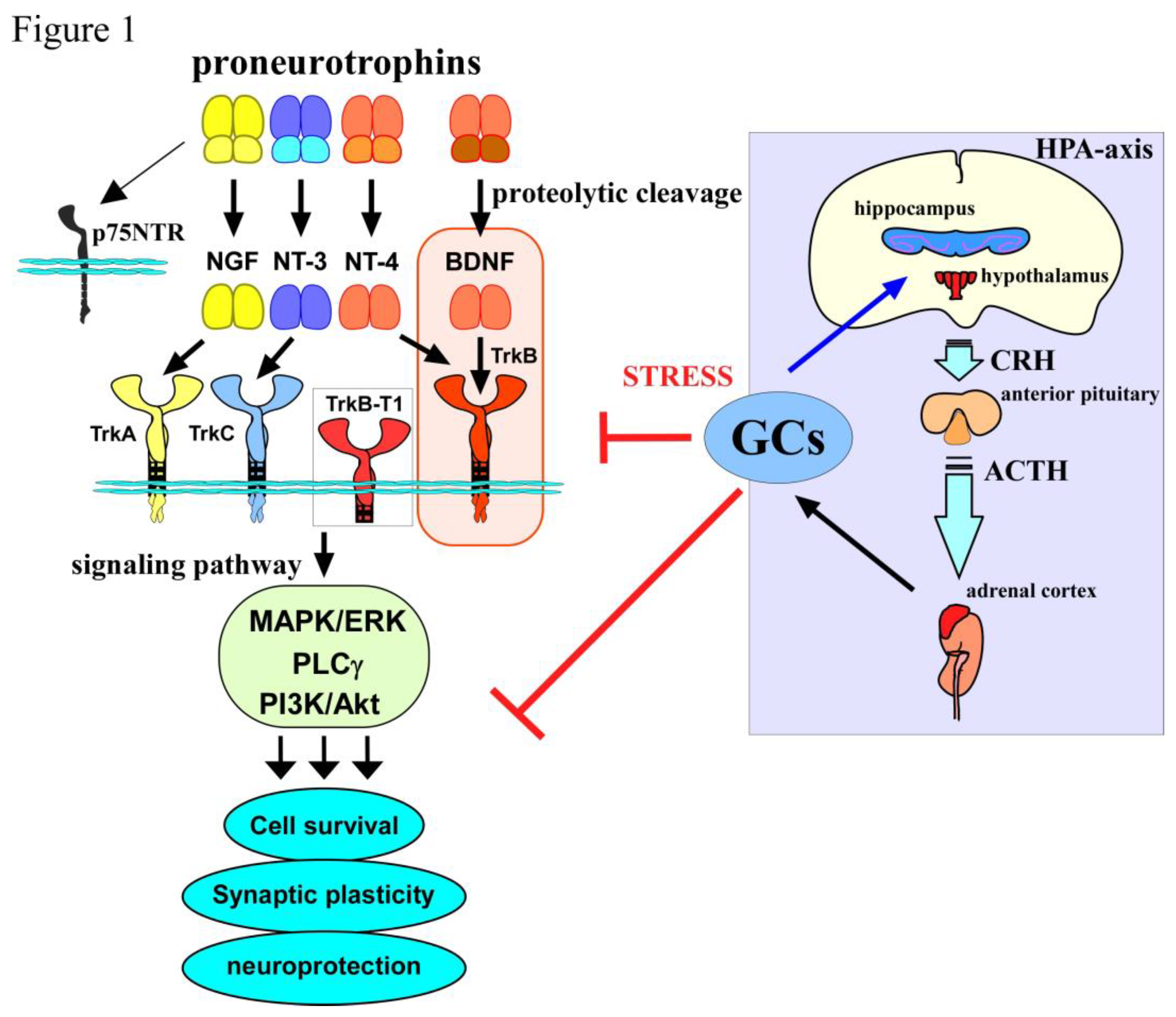
1. Introduction
2. BDNF/TrkB system in neuronal function
3. Glucocorticoids and neuronal functions
4. Glucocorticoid stress, BDNF, and neuronal functions
5. The Interplay of BDNF and Glucocorticoids in AD
5.1. The Role of BDNF in AD
5.2. The Role of Glucocorticoids in AD
5.3. Crosstalk Between BDNF and GCs
5.4. BDNF and GCs as Therapeutic Targets in AD
| Targets | Types | AD models | Treatments | Therapeutic Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | BDNF Mimetics | 5XFAD mouse | Oral administration of R13 (a TrkB receptor agonist) at doses of 7.25, 21.8, and 43.6 mg/kg for a duration of 3 months | Prevention of Aβ deposition, alleviation of the loss of hippocampal synapses, and improvement in memory deficits | [115] |
| 3XTg mouse | Daily oral administration of 3 mg/kg of CF3CN, a TrkB receptor agonist | Reduction of brain Aβ levels and recovery of cognitive functions | [116] | ||
| Rat subjected to elevated intraocular pressure through microbead injections | Intraperitoneal administration of 5 mg/kg of 7,8-DHF for a duration of 8 weeks | Downregulation of Aβ levels | [118] | ||
| C57BL/6J mouse injected with scopolamine (1 mg/kg) | Oral administration of Yuk-Gunja-Tang at a dosage of 150 mg/kg per day for a duration of 14 weeks | Improvement of memory function as assessed by the Y-maze, novel object recognition, and passive avoidance tests | [117] | ||
| Primary rat hippocampus neurons and HT-22 cell treated with Aβ 1-42 | 7.8-DHF were introduced with lipofectamine 3000 | Enhanced GAP-43 protein expression, reduced amyloidogenesis, ROS levels and caspase-3 activity | [119] | ||
| Gene Therapy | Transgenic mouse carrying the APP Swedish (K670M) and Indiana (V717F) | Introducing the BDNF gene lentivirally into the entorhinal cortex at the age of 2 months | Recovery of neuronal loss and hippocampal-dependent contextual fear conditioning | [120] | |
| P301L mutant tau mouse | Injections of AAV-BDNF to ventricles at the age of 3 months | Mitigation of behavioral deficits, prevention of neuronal loss, alleviation of synaptic degeneration, and reduction of neuronal abnormality | [121] | ||
| Physical Exercise | APP/PS1 mouse | Voluntary running on a running wheel for a period of 3 weeks | Upregulation of BDNF and the α-secretase processing of APP, leading to a reduction in the production of Aβ peptides | [122] | |
| 3XTg mouse | Training on a rodent motor-driven treadmill with a frequency of 5 days per week for a duration of 12 weeks | Reduced levels of Aβ plaque burden and neuroinflammation, as well as the alleviation of mitochondrial dysfunction | [123] | ||
| Wistar rat | Voluntary running on a treadmill for 40 minutes daily over a period of 6 days | Improved learning and memory abilities, accompanied by the upregulation of both BDNF and TrkB | [124] | ||
| Glucocorticoid | 11β-HSD1 Inhibitor | C57BL/6J mouse (24-month-old) | Intraperitoneal administration of UE1961 at a dose of 10 mg/kg, twice daily, for a duration of 10 days | Improvement of spatial memory performance in the Y-maze | [128] |
| Tg2576 mouse | Continuous infusions of UE2316 at a rate of 10 mg/kg/day for a duration of 29 days | Downregulation of Aβ plaques in the cerebral cortex, upregulation of insulin-degrading enzyme levels, and improvement in memory | [129] | ||
| GRM | 3XTg mouse | Subcutaneous administration of CORT108297 at a dose of 1.2 mg per day for a duration of 21 days | Downregulation of the levels of APP C-terminal fragments | [130] | |
| Rat injected intracerebroventricularly with Aβ25–35 | Intraperitoneal injection of CORT108297 at a dose of 20 mg/kg for a duration of 1 week | Recovery of hippocampal amyloid-β peptide generation, attenuation of neuroinflammation and apoptotic processes, restoration of hippocampal levels of synaptic markers, and improvement in cognitive function | [131] | ||
| Physical Exercise | NMRI mouse injected with streptozotocin (0.2 mg/mouse) | 4-week swimming exercise program (days 8 to 35) | Improved cognitive function, decreased anxiety- and depression-like behavior, increased BDNF levels, decreased hippocampal glutamate and TNF-α | [133] | |
| APP/PS1 mouse | Resistance exercise (climbing a ladder with a progressive overload), every other day, for 4 weeks | Reduction of Aβ plaques in the hippocampus, decreased plasma corticosterone levels, recovery of the behavioral dificits | [134] | ||
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meeker, R.B.; Williams, K.S. The p75 neurotrophin receptor: at the crossroad of neural repair and death. Neural Regen Res 2015, 10, 721-725. [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 5455-5463. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Harte-Hargrove, L.C.; Siao, C.J.; Marinic, T.; Clarke, R.; Ma, Q.; Jing, D.; Lafrancois, J.J.; Bath, K.G.; Mark, W.; et al. proBDNF negatively regulates neuronal remodeling, synaptic transmission, and synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. Cell Rep 2014, 7, 796-806. [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Steliga, A.; Moryś, J. BDNF: A Key Factor with Multipotent Impact on Brain Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2018, 38, 579-593. [CrossRef]
- Pisani, A.; Paciello, F.; Del Vecchio, V.; Malesci, R.; De Corso, E.; Cantone, E.; Fetoni, A.R. The Role of BDNF as a Biomarker in Cognitive and Sensory Neurodegeneration. J Pers Med 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dhapola, R.; Reddy, D.H. Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues. Apoptosis 2023, 28, 943-957. [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.E. Function of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamus: Implications for depression pathology. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 1028223. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the pathogenesis of stress-related brain diseases. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1247422. [CrossRef]
- Bassil, K.; Krontira, A.C.; Leroy, T.; Escoto, A.I.H.; Snijders, C.; Pernia, C.D.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; de Nijs, L.; van den Hove, D.; Kenis, G.; et al. In vitro modeling of the neurobiological effects of glucocorticoids: A review. Neurobiol Stress 2023, 23, 100530. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 2010, 25, 237-258. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurogenesis. In Factors Affecting Neurodevelopment, Elsevier: 2021; pp 121-131.
- Cao, T.; Matyas, J.J.; Renn, C.L.; Faden, A.I.; Dorsey, S.G.; Wu, J. Function and Mechanisms of Truncated BDNF Receptor TrkB.T1 in Neuropathic Pain. Cells 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.L.; Liu, P.; Wang, G.; Pu, J.G.; Xue, X.; Zhao, J.H. Transplantation of hypoxic preconditioned neural stem cells benefits functional recovery via enhancing neurotrophic secretion after spinal cord injury in rats. J Cell Biochem 2018, 119, 4339-4351. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Sun, J.; Feng, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q.; Gao, F.; Ni, Q.; Mao, L.; Yang, M.; et al. Administration of intramuscular AAV-BDNF and intranasal AAV-TrkB promotes neurological recovery via enhancing corticospinal synaptic connections in stroke rats. Exp Neurol 2023, 359, 114236. [CrossRef]
- Buch, L.; Lipi, B.; Langhnoja, J.; Jaldeep, L.; Pillai, P.P.; Prakash, P. Role of astrocytic MeCP2 in regulation of CNS myelination by affecting oligodendrocyte and neuronal physiology and axo-glial interactions. Exp Brain Res 2018, 236, 3015-3027. [CrossRef]
- Datta, I.; Ganapathy, K.; Razdan, R.; Bhonde, R. Location and Number of Astrocytes Determine Dopaminergic Neuron Survival and Function Under 6-OHDA Stress Mediated Through Differential BDNF Release. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 5505-5525. [CrossRef]
- Harley, S.B.R.; Willis, E.F.; Shaikh, S.N.; Blackmore, D.G.; Sah, P.; Ruitenberg, M.J.; Bartlett, P.F.; Vukovic, J. Selective Ablation of BDNF from Microglia Reveals Novel Roles in Self-Renewal and Hippocampal Neurogenesis. J Neurosci 2021, 41, 4172-4186. [CrossRef]
- Stanton, L.M.; Price, A.J.; Manning, E.E. Hypothalamic corticotrophin releasing hormone neurons in stress-induced psychopathology: Revaluation of synaptic contributions. J Neuroendocrinol 2023, 35, e13268. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Kumar, V.; Moore, S.; Li, F.; Murphy, G.G.; Watson, S.J.; Akil, H. High emotional reactivity is associated with activation of a molecularly distinct hippocampal-amygdala circuit modulated by the glucocorticoid receptor. Neurobiol Stress 2023, 27, 100581. [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, M.K.R.; Amelinez-Robles, N.; Polsfuss, I.; Herbert, K.; Kim, C.; Varghese, N.; Parry, T.J.; Buller, B.; Verdoorn, T.A.; Billing, C.B., Jr.; et al. NTS-105 decreased cell death and preserved long-term potentiation in an in vitro model of moderate traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 2023, 371, 114608. [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Numakawa, T.; Murata, T.; Kawaminami, M.; Himi, T. Enhanced social reward response and anxiety-like behavior with downregulation of nucleus accumbens glucocorticoid receptor in BALB/c mice. J Vet Med Sci 2023, 85, 30-39. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Yagasaki, Y.; Izumi, A.; Kunugi, H. Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-gamma signaling for glutamate release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 647-652. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N.; Chiba, S.; Ooshima, Y.; Matsuno, H.; Nakajima, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Fumimoto, K.; Hirai, Y.; et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor increased glucocorticoid receptors in cortical neurons through MAP kinase pathway. Neurochem Int 2018, 118, 217-224. [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.E.; Lustberg, D.J.; Shaughnessy, E.K.; Carstens, K.E.; Farris, S.; Alexander, G.M.; Radzicki, D.; Zhao, M.; Dudek, S.M. Novel role for mineralocorticoid receptors in control of a neuronal phenotype. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26, 350-364. [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, K.R.; Bridi, M.S.; Folts, L.M.; Marx-Rattner, R.; Zierden, H.C.; Wulff, A.B.; Kodjo, E.A.; Thompson, S.M.; Bale, T.L. Chemogenetic activation of CRF neurons as a model of chronic stress produces sex-specific physiological and behavioral effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023. [CrossRef]
- You, I.J.; Bae, Y.; Beck, A.R.; Shin, S. Lateral hypothalamic proenkephalin neurons drive threat-induced overeating associated with a negative emotional state. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6875. [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos, R.C.; Sweeten, B.L.W.; Stelly, C.E.; Tasker, J.G. The Neuroendocrine Impact of Acute Stress on Synaptic Plasticity. Endocrinology 2023, 164. [CrossRef]
- Ciubuc-Batcu, M.T.; Stapelberg, N.J.C.; Headrick, J.P.; Renshaw, G.M.C. A mitochondrial nexus in major depressive disorder: Integration with the psycho-immune-neuroendocrine network. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2023, 1870, 166920. [CrossRef]
- Khacho, M.; Harris, R.; Slack, R.S. Mitochondria as central regulators of neural stem cell fate and cognitive function. Nat Rev Neurosci 2019, 20, 34-48. [CrossRef]
- Daviu, N.; Bruchas, M.R.; Moghaddam, B.; Sandi, C.; Beyeler, A. Neurobiological links between stress and anxiety. Neurobiol Stress 2019, 11, 100191. [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, N.V. Glucocorticoids Orchestrate Adult Hippocampal Plasticity: Growth Points and Translational Aspects. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2023, 88, 565-589. [CrossRef]
- Barfield, E.T.; Gourley, S.L. Prefrontal cortical trkB, glucocorticoids, and their interactions in stress and developmental contexts. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2018, 95, 535-558. [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lievano, M.; Borie, A.M.; Dromard, Y.; Murat, M.; Desarmenien, M.G.; Garabedian, M.J.; Jeanneteau, F. Persistence of learning-induced synapses depends on neurotrophic priming of glucocorticoid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 13097-13106. [CrossRef]
- McCarty, K.J.; Pratt, S.L.; Long, N.M. Effects of Exogenous Glucocorticoid Infusion on Appetitic Center Development in Postnatal Dairy Bull Calves. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; An, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Neonatal DEX exposure leads to hyperanxious and depressive-like behaviors as well as a persistent reduction of BDNF expression in developmental stages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 527, 311-316. [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Haghparast, A.; Fayazmilani, R. The downstream effects of forced exercise training and voluntary physical activity in an enriched environment on hippocampal plasticity in preadolescent rats. Brain Res 2021, 1759, 147373. [CrossRef]
- Kumamaru, E.; Numakawa, T.; Adachi, N.; Yagasaki, Y.; Izumi, A.; Niyaz, M.; Kudo, M.; Kunugi, H. Glucocorticoid prevents brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated maturation of synaptic function in developing hippocampal neurons through reduction in the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol 2008, 22, 546-558. [CrossRef]
- Ferrero Restelli, F.; Federicci, F.; Ledda, F.; Paratcha, G. Sprouty4 at the crossroads of Trk neurotrophin receptor signaling suppression by glucocorticoids. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1090824. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Li, R.; Cai, L.; Wu, S.D.; Li, C.M. Ro41-5253, a selective antagonist of retinoic acid receptor α, ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in rats: Involvement of regulating HPA axis and improving hippocampal neuronal deficits. Brain Res Bull 2019, 146, 302-309. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.N.; Meng, Q.Y.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Wang, G.H.; Zhou, J.N. The involvement of retinoic acid receptor-alpha in corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression and affective disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2009, 66, 832-839. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, O.; Li, N.; Sha, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J. Association between the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1143833. [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003, 112, 257-269. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13, 363. [CrossRef]
- Musazzi, L.; Tornese, P.; Sala, N.; Lee, F.S.; Popoli, M.; Ieraci, A. Acute stress induces an aberrant increase of presynaptic release of glutamate and cellular activation in the hippocampus of BDNF(Val/Met) mice. J Cell Physiol 2022, 237, 3834-3844. [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.; Notaras, M.; Grech, A.M.; Schroeder, A.; van den Buuse, M.; Hill, R.A. BDNF Val66Met genotype and adolescent glucocorticoid treatment induce sex-specific disruptions to fear extinction and amygdala GABAergic interneuron expression in mice. Horm Behav 2022, 144, 105231. [CrossRef]
- Thacker, J.S.; Mielke, J.G. The combined effects of corticosterone and brain-derived neurotrophic factor on plasticity-related receptor phosphorylation and expression at the synaptic surface in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Horm Behav 2022, 145, 105233. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Yan, X.J.; Lei, F.; Wang, M.L.; He, L.L.; Luo, Y.Y.; Gao, H.W.; Feng, Y.L.; Yang, S.L.; Li, J.; et al. Proteomic profiling of the neurons in mice with depressive-like behavior induced by corticosterone and the regulation of berberine: pivotal sites of oxidative phosphorylation. Mol Brain 2019, 12, 118. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.H.; Chao, H.W.; Lin, P.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Liu, T.H.; Chen, H.W.; Huang, Y.S. CPEB3-dowregulated Nr3c1 mRNA translation confers resilience to developing posttraumatic stress disorder-like behavior in fear-conditioned mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1669-1679. [CrossRef]
- Wahl, P.; Mathes, S.; Köhler, K.; Achtzehn, S.; Bloch, W.; Mester, J. Acute metabolic, hormonal, and psychological responses to different endurance training protocols. Horm Metab Res 2013, 45, 827-833. [CrossRef]
- Jeanneteau, F.; Chao, M.V. Are BDNF and glucocorticoid activities calibrated? Neuroscience 2013, 239, 173-195. [CrossRef]
- Hermann, R.; Schaller, A.; Lay, D.; Bloch, W.; Albus, C.; Petrowski, K. Effect of acute psychosocial stress on the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in humans - a randomized cross within trial. Stress 2021, 24, 442-449. [CrossRef]
- de Assis, G.G.; Gasanov, E.V. BDNF and Cortisol integrative system - Plasticity vs. degeneration: Implications of the Val66Met polymorphism. Front Neuroendocrinol 2019, 55, 100784. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. Neurotrophins and Other Growth Factors in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Life (Basel) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, H.T.; Qin, X.Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y. Postmortem Brain, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Blood Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Mol Neurosci 2018, 65, 289-300. [CrossRef]
- Garzon, D.; Yu, G.; Fahnestock, M. A new brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcript and decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts 1, 2 and 3 in Alzheimer's disease parietal cortex. J Neurochem 2002, 82, 1058-1064. [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.K.S.; Ho, C.S.H.; Tam, W.W.S.; Kua, E.H.; Ho, R.C. Decreased Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease (AD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Veverova, K.; Katonová, A.; Vyhnalek, M.; Hort, J. Serum PAI-1/BDNF Ratio Is Increased in Alzheimer's Disease and Correlates with Disease Severity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36025-36031. [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Oguchi, T.; Kasuga, K.; Kimura, A.; Futamura, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Kasai, H.; Kuroda, T.; Yano, S.; et al. Serum BDNF as a Potential Biomarker of Alzheimer's Disease: Verification Through Assessment of Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 653267. [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.Y.; Laws, S.M.; Perin, S.; Pietrzak, R.H.; Fowler, C.; Masters, C.L.; Maruff, P. BDNF VAL66MET polymorphism and memory decline across the spectrum of Alzheimer's disease. Genes Brain Behav 2021, 20, e12724. [CrossRef]
- Bessi, V.; Mazzeo, S.; Bagnoli, S.; Padiglioni, S.; Carraro, M.; Piaceri, I.; Bracco, L.; Sorbi, S.; Nacmias, B. The implication of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in progression from subjective cognitive decline to mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a 9-year follow-up study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2020, 270, 471-482. [CrossRef]
- del Toro, D.; Canals, J.M.; Ginés, S.; Kojima, M.; Egea, G.; Alberch, J. Mutant huntingtin impairs the post-Golgi trafficking of brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not its Val66Met polymorphism. J Neurosci 2006, 26, 12748-12757. [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.T.; Vickers, J.C.; Stuart, K.E.; Cechova, K.; Ward, D.D. The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Modulates Resilience of Neurological Functioning to Brain Ageing and Dementia: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Eggert, S.; Kins, S.; Endres, K.; Brigadski, T. Brothers in arms: proBDNF/BDNF and sAPPα/Aβ-signaling and their common interplay with ADAM10, TrkB, p75NTR, sortilin, and sorLA in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Biol Chem 2022, 403, 43-71. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sabirzhanov, B.; Keifer, J. Oligomeric amyloid-{beta} inhibits the proteolytic conversion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), AMPA receptor trafficking, and classical conditioning. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 34708-34717. [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Xue, Z.; Li, D.; Ni, S.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Dysregulated CRTC1-BDNF signaling pathway in the hippocampus contributes to Aβ oligomer-induced long-term synaptic plasticity and memory impairment. Exp Neurol 2021, 345, 113812. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Lian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zong, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates learning deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease induced by aβ1-42. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0122415. [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Čechová, K.; Průša, R.; Hort, J. Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications. CNS Neurosci Ther 2019, 25, 303-313. [CrossRef]
- Gerenu, G.; Martisova, E.; Ferrero, H.; Carracedo, M.; Rantamäki, T.; Ramirez, M.J.; Gil-Bea, F.J. Modulation of BDNF cleavage by plasminogen-activator inhibitor-1 contributes to Alzheimer's neuropathology and cognitive deficits. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2017, 1863, 991-1001. [CrossRef]
- Jerónimo-Santos, A.; Vaz, S.H.; Parreira, S.; Rapaz-Lérias, S.; Caetano, A.P.; Buée-Scherrer, V.; Castrén, E.; Valente, C.A.; Blum, D.; Sebastião, A.M.; et al. Dysregulation of TrkB Receptors and BDNF Function by Amyloid-β Peptide is Mediated by Calpain. Cereb Cortex 2015, 25, 3107-3121. [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nat Rev Neurol 2021, 17, 157-172. [CrossRef]
- Patterson, S.L. Immune dysregulation and cognitive vulnerability in the aging brain: Interactions of microglia, IL-1β, BDNF and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 11-18. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-TrkB Signaling in Inflammation-related Depression and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Curr Neuropharmacol 2016, 14, 721-731. [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Acute and subacute IL-1β administrations differentially modulate neuroimmune and neurotrophic systems: possible implications for neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 59. [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Balazs, R.; Soiampornkul, R.; Thangnipon, W.; Cotman, C.W. Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol Aging 2008, 29, 1380-1393. [CrossRef]
- Barbereau, C.; Yehya, A.; Silhol, M.; Cubedo, N.; Verdier, J.M.; Maurice, T.; Rossel, M. Neuroprotective brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the TAU-P301L tauopathy zebrafish model. Pharmacol Res 2020, 158, 104865. [CrossRef]
- Oreshko, A.S.; Rodnyy, A.Y.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Naumenko, V.S. Effects of central administration of the human Tau protein on the Bdnf, Trkb, p75, Mapt, Bax and Bcl-2 genes expression in the mouse brain. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet Selektsii 2023, 27, 342-348. [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat Rev Neurol 2019, 15, 501-518. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Strickland, M.R.; Soranno, A.; Holtzman, D.M. Apolipoprotein E: Structural Insights and Links to Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. Neuron 2021, 109, 205-221. [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Nelson, T.J.; Alkon, D.L. ApoE4 and Aβ Oligomers Reduce BDNF Expression via HDAC Nuclear Translocation. J Neurosci 2015, 35, 7538-7551. [CrossRef]
- Laczó, J.; Cechova, K.; Parizkova, M.; Lerch, O.; Andel, R.; Matoska, V.; Kaplan, V.; Matuskova, V.; Nedelska, Z.; Vyhnalek, M.; et al. The Combined Effect of APOE and BDNF Val66Met Polymorphisms on Spatial Navigation in Older Adults. J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 78, 1473-1492. [CrossRef]
- Pietzuch, M.; Bindoff, A.; Jamadar, S.; Vickers, J.C. Interactive effects of the APOE and BDNF polymorphisms on functional brain connectivity: the Tasmanian Healthy Brain Project. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14514. [CrossRef]
- Viho, E.M.G.; Buurstede, J.C.; Mahfouz, A.; Koorneef, L.L.; van Weert, L.; Houtman, R.; Hunt, H.J.; Kroon, J.; Meijer, O.C. Corticosteroid Action in the Brain: The Potential of Selective Receptor Modulation. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 109, 266-276. [CrossRef]
- Koning, A.; Buurstede, J.C.; van Weert, L.; Meijer, O.C. Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptors in the Brain: A Transcriptional Perspective. J Endocr Soc 2019, 3, 1917-1930. [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzoli, M.; Losurdo, M.; Paolone, G.; Medelin, M.; Jaupaj, L.; Cisterna, B.; Slanzi, A.; Malatesta, M.; Coco, S.; Buffelli, M. Glucocorticoid receptors modulate dendritic spine plasticity and microglia activity in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 132, 104568. [CrossRef]
- Popoli, M.; Yan, Z.; McEwen, B.S.; Sanacora, G. The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011, 13, 22-37. [CrossRef]
- Dioli, C.; Papadimitriou, G.; Megalokonomou, A.; Marques, C.; Sousa, N.; Sotiropoulos, I. Chronic Stress, Depression, and Alzheimer's Disease: The Triangle of Oblivion. Adv Exp Med Biol 2023, 1423, 303-315. [CrossRef]
- Klyubin, I.; Ondrejcak, T.; Hu, N.-W.; Rowan, M.J. Glucocorticoids, synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer's disease. Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research 2022, 25, 100365.
- Du, F.; Yu, Q.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Waites, C.L. Glucocorticoid-driven mitochondrial damage stimulates Tau pathology. Brain 2023, 146, 4378-4394. [CrossRef]
- Kulstad, J.J.; McMillan, P.J.; Leverenz, J.B.; Cook, D.G.; Green, P.S.; Peskind, E.R.; Wilkinson, C.W.; Farris, W.; Mehta, P.D.; Craft, S. Effects of chronic glucocorticoid administration on insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in the aged macaque. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2005, 64, 139-146. [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, M.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Chronic glucocorticoid exposure accelerates Aβ generation and neurotoxicity by activating calcium-mediated CN-NFAT1 signaling in hippocampal neurons in APP/PS1 mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 168, 113407. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, G.; Gerber, H.; Koch, P.; Bruestle, O.; Fraering, P.C.; Rajendran, L. The Alzheimer's Disease γ-Secretase Generates Higher 42:40 Ratios for β-Amyloid Than for p3 Peptides. Cell Rep 2017, 19, 1967-1976. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Tang, J.; Song, M.; Xu, X.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Bai, Y. Glucocorticoids facilitate astrocytic amyloid-β peptide deposition by increasing the expression of APP and BACE1 and decreasing the expression of amyloid-β-degrading proteases. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2704-2715. [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, I.; Catania, C.; Riedemann, T.; Fry, J.P.; Breen, K.C.; Michaelidis, T.M.; Almeida, O.F. Glucocorticoids trigger Alzheimer disease-like pathobiochemistry in rat neuronal cells expressing human tau. J Neurochem 2008, 107, 385-397. [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, I.; Catania, C.; Pinto, L.G.; Silva, R.; Pollerberg, G.E.; Takashima, A.; Sousa, N.; Almeida, O.F. Stress acts cumulatively to precipitate Alzheimer's disease-like tau pathology and cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 7840-7847. [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Hao, S.; Wosiski-Kuhn, M.; Stranahan, A.M. Glucocorticoid-mediated activation of GSK3β promotes tau phosphorylation and impairs memory in type 2 diabetes. Neurobiol Aging 2017, 57, 75-83. [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Brown, C.; Whitehead, G.; Piers, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Perez, C.M.; Regan, P.; Whitcomb, D.J.; Cho, K. Glucocorticoids activate a synapse weakening pathway culminating in tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus. Pharmacol Res 2017, 121, 42-51. [CrossRef]
- Milligan Armstrong, A.; Porter, T.; Quek, H.; White, A.; Haynes, J.; Jackaman, C.; Villemagne, V.; Munyard, K.; Laws, S.M.; Verdile, G.; et al. Chronic stress and Alzheimer's disease: the interplay between the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, genetics and microglia. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2021, 96, 2209-2228. [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Nigro, M.; Travagli, A.; Gessi, S. Microglia and Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y. Microglia Polarization From M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 815347. [CrossRef]
- Harris-White, M.E.; Chu, T.; Miller, S.A.; Simmons, M.; Teter, B.; Nash, D.; Cole, G.M.; Frautschy, S.A. Estrogen (E2) and glucocorticoid (Gc) effects on microglia and A beta clearance in vitro and in vivo. Neurochem Int 2001, 39, 435-448. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G. Navigating Alzheimer's Disease via Chronic Stress: The Role of Glucocorticoids. Curr Drug Targets 2020, 21, 433-444. [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takahashi, T.; Sumitani, K.; Takatsu, H.; Urano, S. Glucocorticoid Generates ROS to Induce Oxidative Injury in the Hippocampus, Leading to Impairment of Cognitive Function of Rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2010, 47, 224-232. [CrossRef]
- Abramov, A.Y.; Potapova, E.V.; Dremin, V.V.; Dunaev, A.V. Interaction of Oxidative Stress and Misfolded Proteins in the Mechanism of Neurodegeneration. Life (Basel) 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, W.; Li, J. The Potential Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation as a Link Between Mitochondria ROS Generation and Neuroinflammation in Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13, 73. [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.G.; Mandal, P.K.; Maroon, J.C. Oxidative Stress Occurs Prior to Amyloid Aβ Plaque Formation and Tau Phosphorylation in Alzheimer's Disease: Role of Glutathione and Metal Ions. ACS Chem Neurosci 2023, 14, 2944-2954. [CrossRef]
- Jeanneteau, F.; Borie, A.; Chao, M.V.; Garabedian, M.J. Bridging the Gap between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Glucocorticoid Effects on Brain Networks. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 109, 277-284. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lombès, M.; Le Menuet, D. Glucocorticoid receptor represses brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in neuron-like cells. Mol Brain 2017, 10, 12. [CrossRef]
- Suri, D.; Vaidya, V.A. Glucocorticoid regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: relevance to hippocampal structural and functional plasticity. Neuroscience 2013, 239, 196-213. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, W.M.; Xu, C.F.; Neubert, T.A.; Chao, M.V.; Garabedian, M.J.; Jeanneteau, F.D. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling rewrites the glucocorticoid transcriptome via glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 2013, 33, 3700-3714. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N. Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Glucocorticoid Stress in Neurogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Chiba, S.; Kunugi, H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glucocorticoids: reciprocal influence on the central nervous system. Neuroscience 2013, 239, 157-172. [CrossRef]
- Radecki, D.T.; Brown, L.M.; Martinez, J.; Teyler, T.J. BDNF protects against stress-induced impairments in spatial learning and memory and LTP. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 246-253. [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, J. BDNF-TrkB signaling-mediated upregulation of Narp is involved in the antidepressant-like effects of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine in a chronic restraint stress mouse model. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 182. [CrossRef]
- Wurzelmann, M.; Romeika, J.; Sun, D. Therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and a small molecular mimics of BDNF for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 2017, 12, 7-12. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Kang, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K. The prodrug of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone development and therapeutic efficacy for treating Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, 578-583. [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chen, C.; Ahn, E.H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Edgington-Mitchell, L.E.; Lu, Z.; Ming, S.; Ye, K. Targeting both BDNF/TrkB pathway and delta-secretase for treating Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108737. [CrossRef]
- Pak, M.E.; Yang, H.J.; Li, W.; Kim, J.K.; Go, Y. Yuk-Gunja-Tang attenuates neuronal death and memory impairment via ERK/CREB/BDNF signaling in the hippocampi of experimental Alzheimer's disease model. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 1014840. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Chitranshi, N.; Gupta, V.; You, Y.; Rajput, R.; Paulo, J.A.; Mirzaei, M.; van den Buuse, M.; Graham, S.L. TrkB Receptor Agonist 7,8 Dihydroxyflavone is Protective Against the Inner Retinal Deficits Induced by Experimental Glaucoma. Neuroscience 2022, 490, 36-48. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, E.J.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, S.S.; Suh, S.W.; Ahn, E.H. GAP-43 closely interacts with BDNF in hippocampal neurons and is associated with Alzheimer's disease progression. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1150399. [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Mateling, M.; Kovacs, I.; Wang, L.; Eggert, S.; Rockenstein, E.; Koo, E.H.; Masliah, E.; Tuszynski, M.H. Early BDNF treatment ameliorates cell loss in the entorhinal cortex of APP transgenic mice. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 15596-15602. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.S.; Shen, L.L.; Zhu, C.; Bu, X.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Yao, X.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, H.D.; Walker, D.G.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against tau-related neurodegeneration of Alzheimer's disease. Transl Psychiatry 2016, 6, e907. [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.M.; Xu, S.; Kritikou, J.S.; Marosi, K.; Brodin, L.; Mattson, M.P. Exercise and BDNF reduce Aβ production by enhancing α-secretase processing of APP. J Neurochem 2017, 142, 286-296. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cho, J.; Kang, H. Protective effect of exercise training against the progression of Alzheimer's disease in 3xTg-AD mice. Behav Brain Res 2019, 374, 112105. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, D.; Cai, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, A. Moderate Exercise Combined with Enriched Environment Enhances Learning and Memory through BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway in Rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.X.; Liang, J.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.Q. Effects of physical activity and exercise on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr 2019, 19, 181. [CrossRef]
- Canet, G.; Hernandez, C.; Zussy, C.; Chevallier, N.; Desrumaux, C.; Givalois, L. Is AD a Stress-Related Disorder? Focus on the HPA Axis and Its Promising Therapeutic Targets. Front Aging Neurosci 2019, 11, 269. [CrossRef]
- Watermeyer, T.; Robb, C.; Gregory, S.; Udeh-Momoh, C. Therapeutic implications of hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal-axis modulation in Alzheimer's disease: A narrative review of pharmacological and lifestyle interventions. Front Neuroendocrinol 2021, 60, 100877. [CrossRef]
- Sooy, K.; Webster, S.P.; Noble, J.; Binnie, M.; Walker, B.R.; Seckl, J.R.; Yau, J.L. Partial deficiency or short-term inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 improves cognitive function in aging mice. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 13867-13872. [CrossRef]
- Sooy, K.; Noble, J.; McBride, A.; Binnie, M.; Yau, J.L.; Seckl, J.R.; Walker, B.R.; Webster, S.P. Cognitive and Disease-Modifying Effects of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Inhibition in Male Tg2576 Mice, a Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4592-4603. [CrossRef]
- Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Medeiros, R.; Martinez-Coria, H.; LaFerla, F.M.; Green, K.N. Mifepristone alters amyloid precursor protein processing to preclude amyloid beta and also reduces tau pathology. Biol Psychiatry 2013, 74, 357-366. [CrossRef]
- Pineau, F.; Canet, G.; Desrumaux, C.; Hunt, H.; Chevallier, N.; Ollivier, M.; Belanoff, J.K.; Givalois, L. New selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators reverse amyloid-β peptide-induced hippocampus toxicity. Neurobiol Aging 2016, 45, 109-122. [CrossRef]
- da Costa Daniele, T.M.; de Bruin, P.F.C.; de Matos, R.S.; de Bruin, G.S.; Maia Chaves, C.J.; de Bruin, V.M.S. Exercise effects on brain and behavior in healthy mice, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease model-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Brain Res 2020, 383, 112488. [CrossRef]
- Bashiri, H.; Enayati, M.; Bashiri, A.; Salari, A.A. Swimming exercise improves cognitive and behavioral disorders in male NMRI mice with sporadic Alzheimer-like disease. Physiol Behav 2020, 223, 113003. [CrossRef]
- Campos, H.C.; Ribeiro, D.E.; Hashiguchi, D.; Glaser, T.; Milanis, M.D.S.; Gimenes, C.; Suchecki, D.; Arida, R.M.; Ulrich, H.; Monteiro Longo, B. Neuroprotective effects of resistance physical exercise on the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci 2023, 17, 1132825. [CrossRef]
- Irazoki, E.; Contreras-Somoza, L.M.; Toribio-Guzmán, J.M.; Jenaro-Río, C.; van der Roest, H.; Franco-Martín, M.A. Technologies for Cognitive Training and Cognitive Rehabilitation for People With Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. A Systematic Review. Front Psychol 2020, 11, 648. [CrossRef]
- Cutuli, D.; Decandia, D.; Giacovazzo, G.; Coccurello, R. Physical Exercise as Disease-Modifying Alternative against Alzheimer's Disease: A Gut-Muscle-Brain Partnership. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





