Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
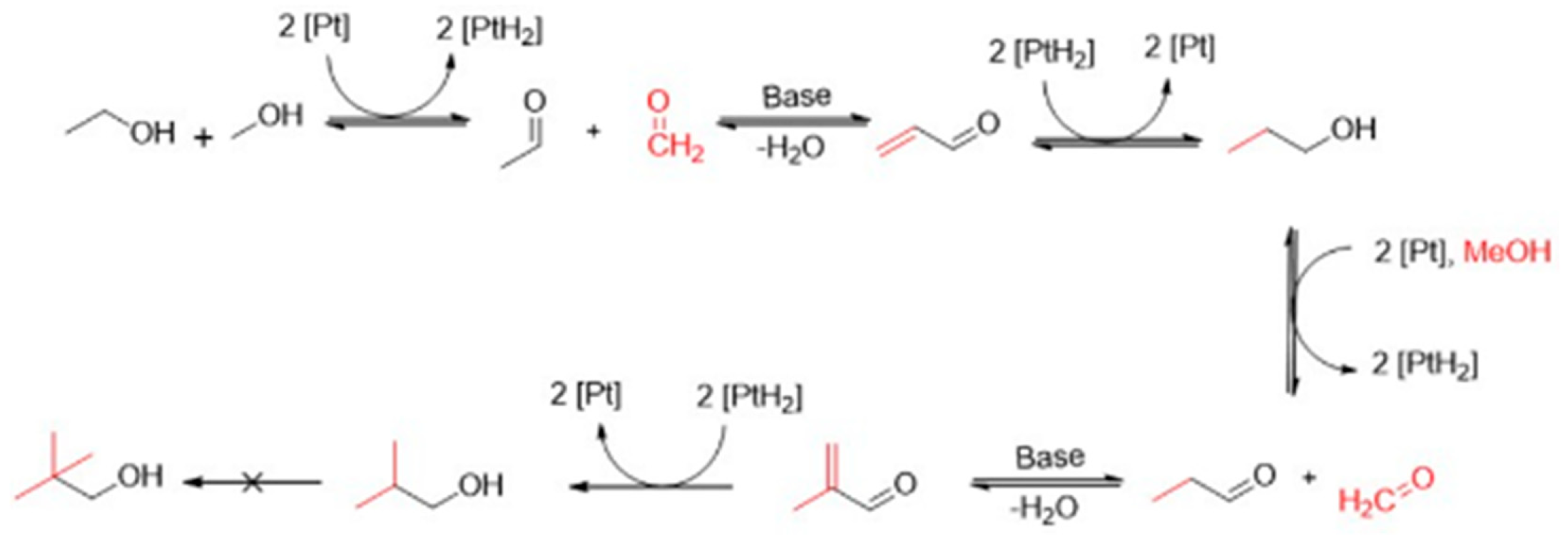
2. Results and discussion
2.1. NiPt catalysts prepared by conventional wet impregnation
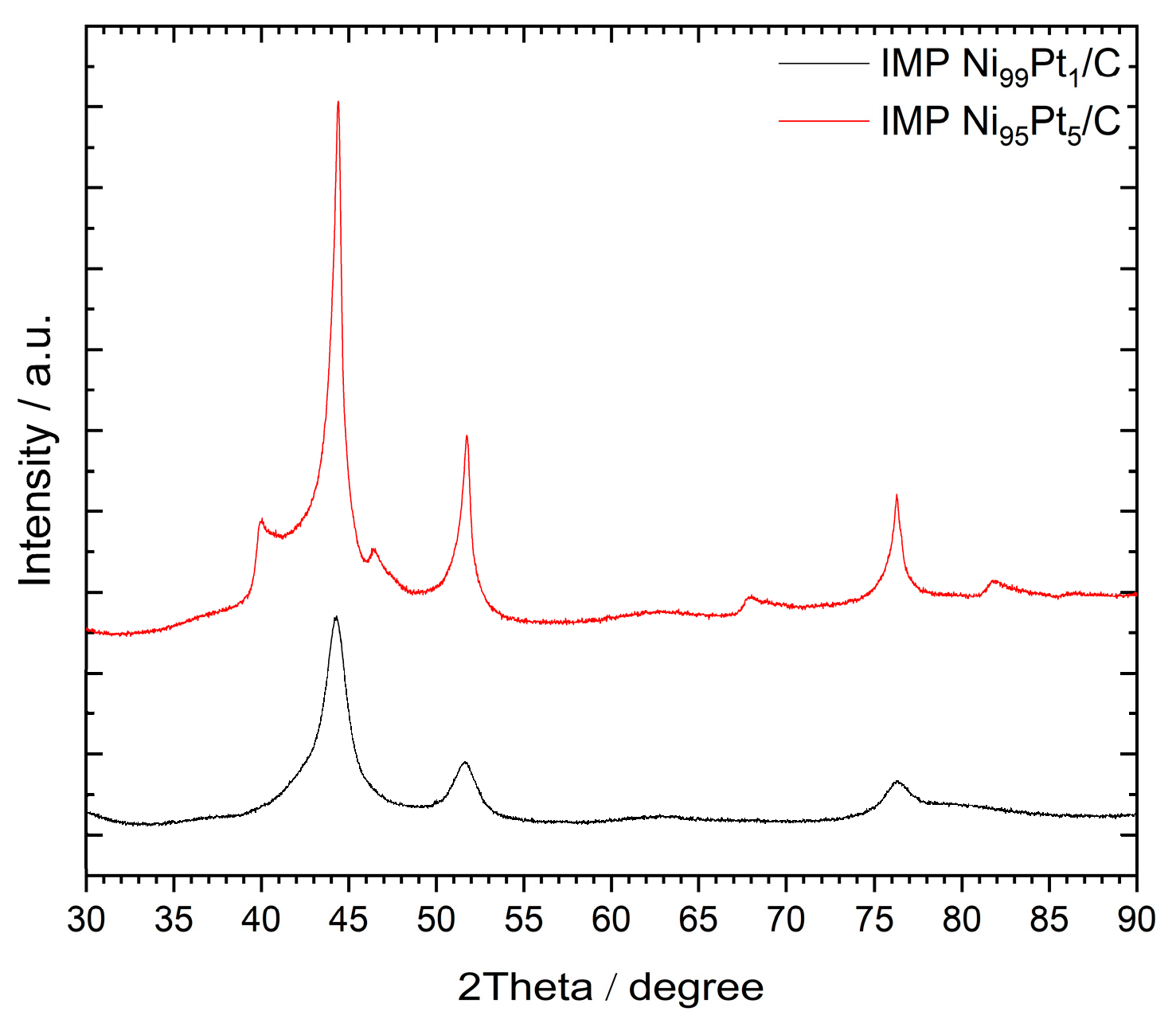
2.1.1. XRD analysis
2.1.2. ICP–OES
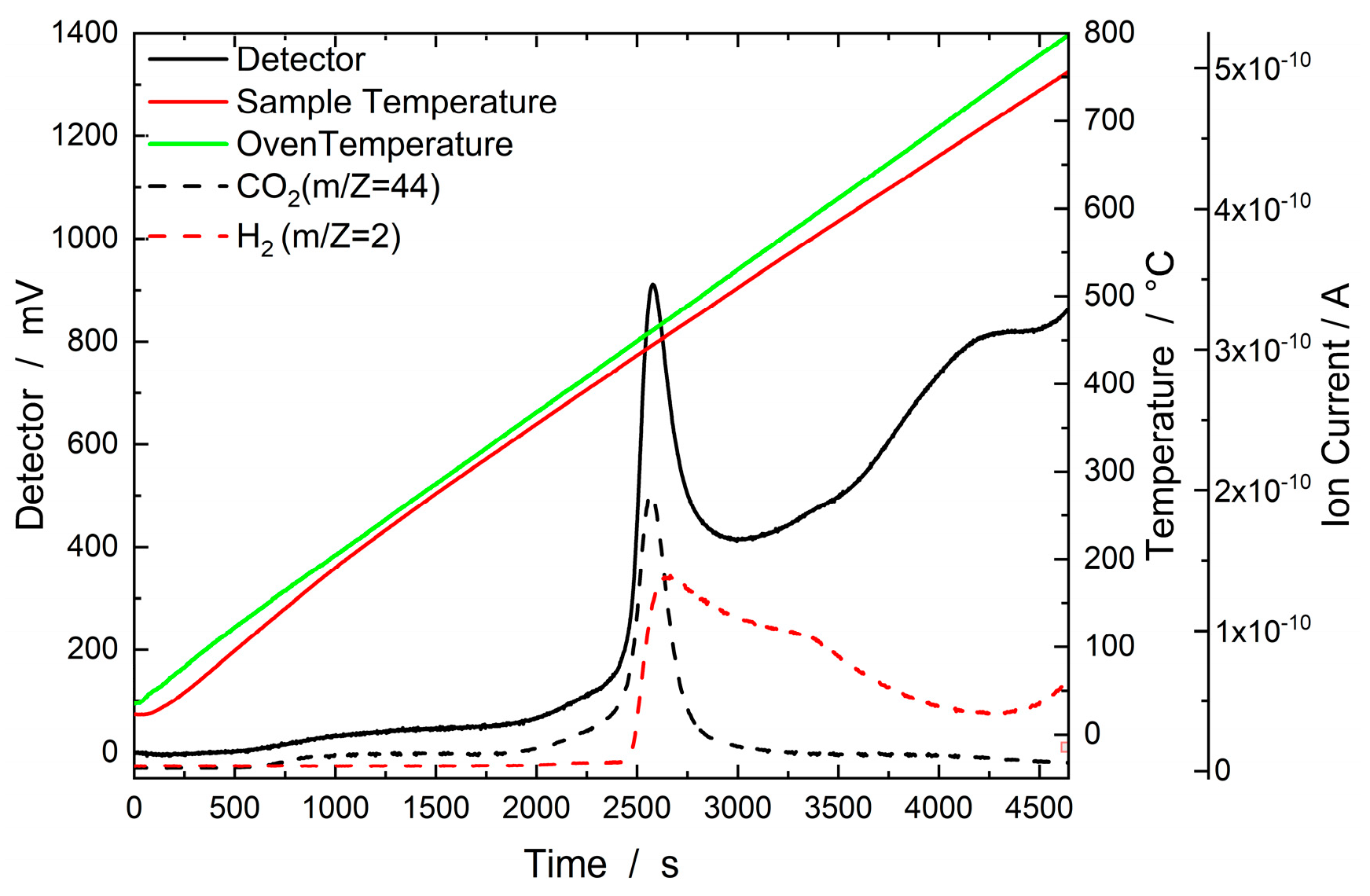
2.1.3. H2–TPD
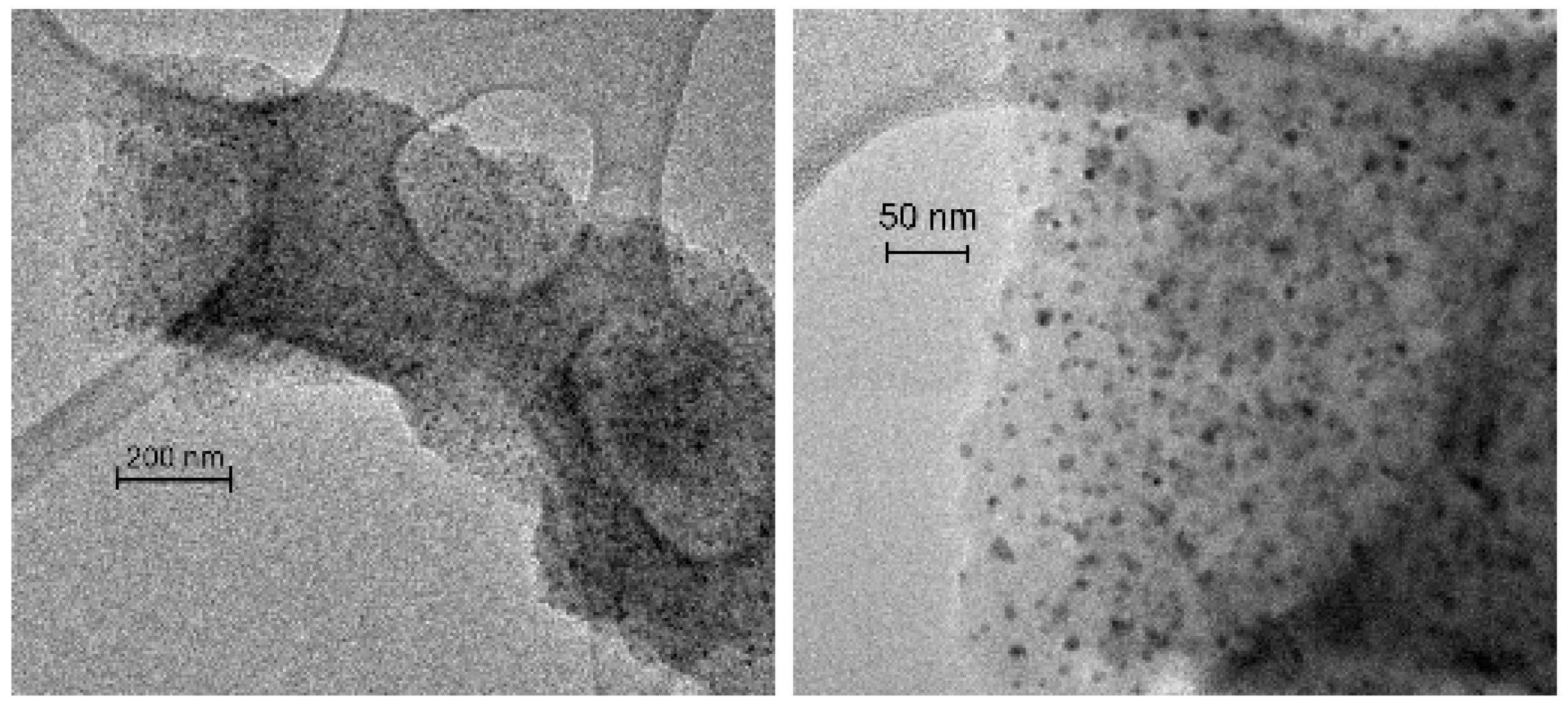
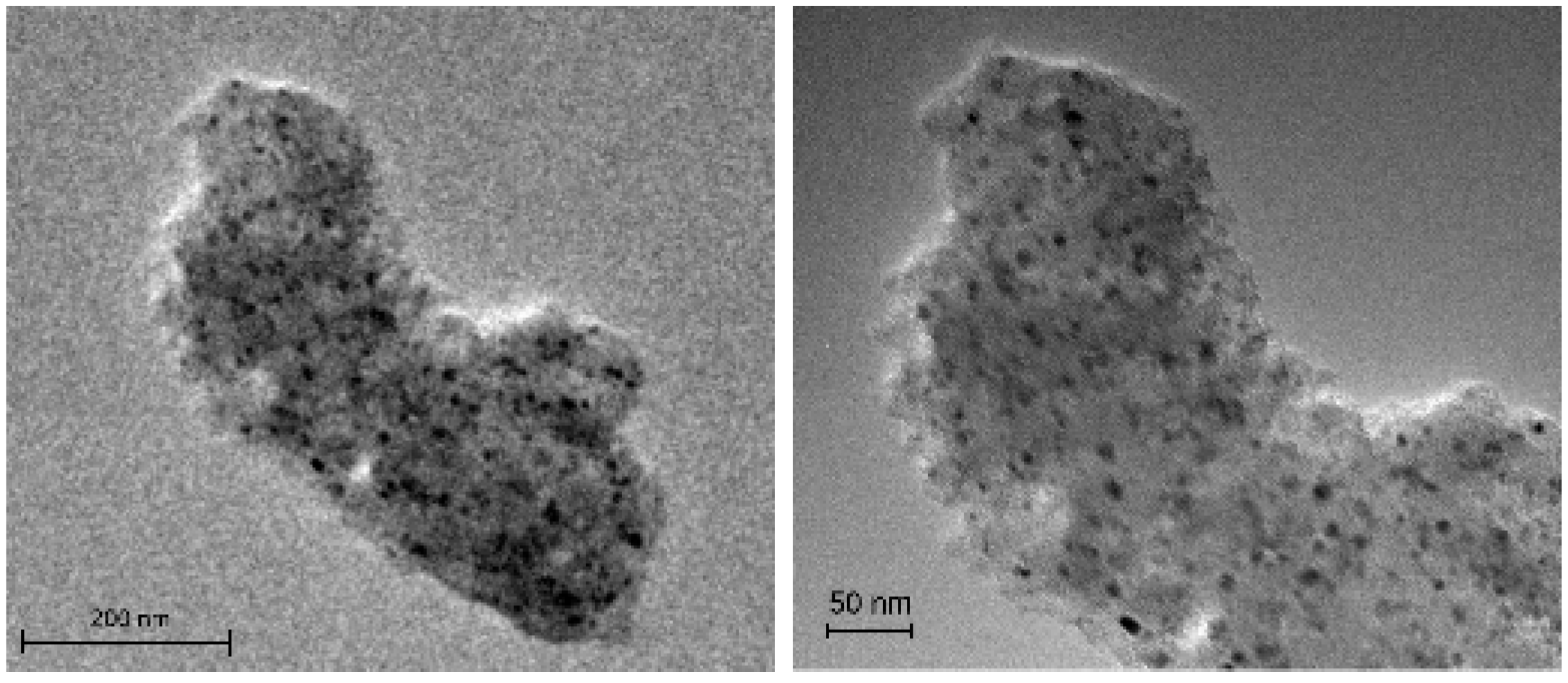
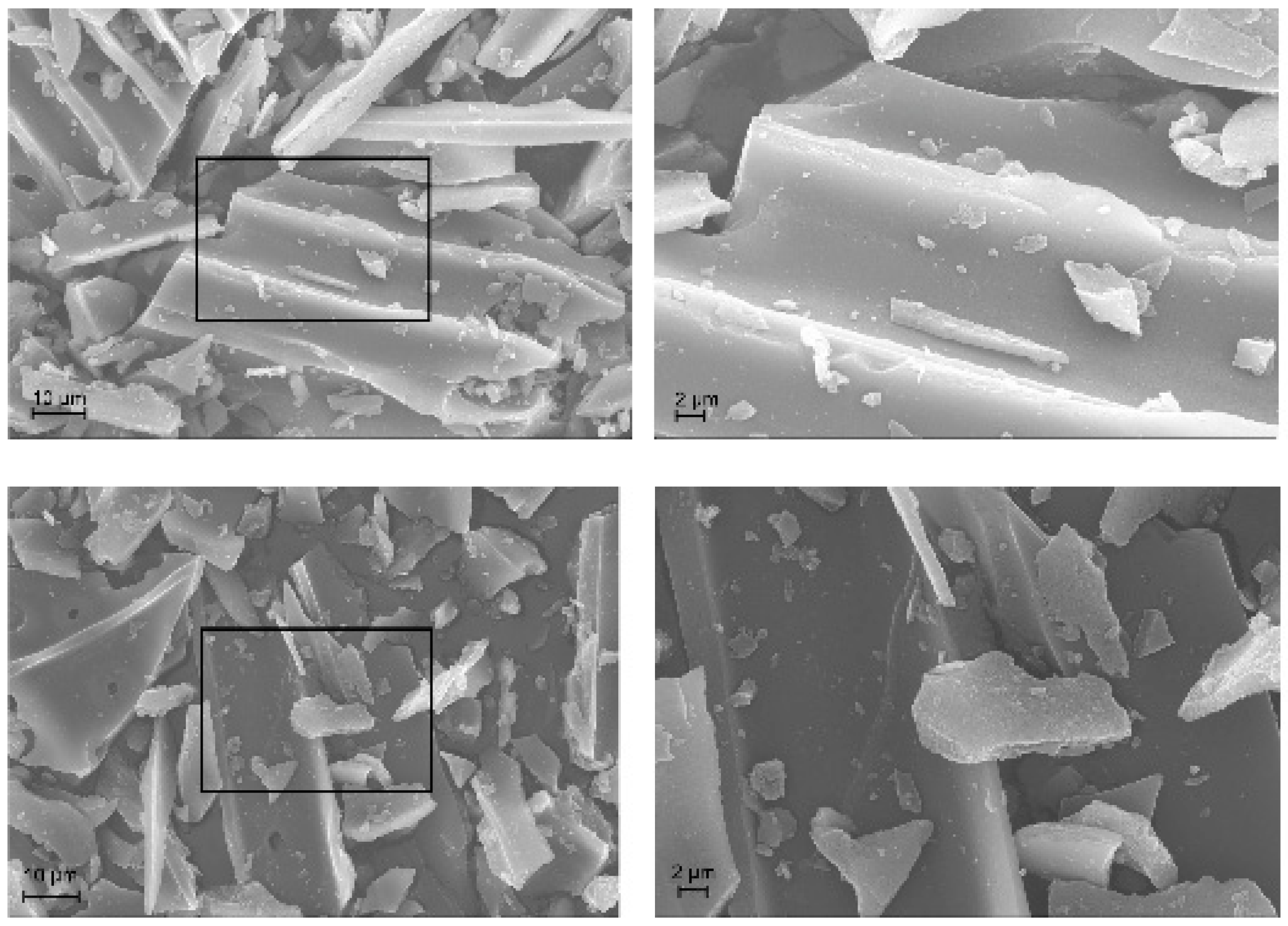
2.1.4. TEM / SEM combined with EDX
2.1.5. Catalytic activity
2.2. NiPt catalysts prepared by surface redox reactions
2.2.1. VIS spectroscopy/ICP–OES
| Catalyst | βVIS [mg l-1] | βICP-OES [mg l-1] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRR 15 buffer | 942 | 930 | |
| SRR 30 buffer | 931 | 930 | |
| SRR 60 buffer | 919 | 910 |
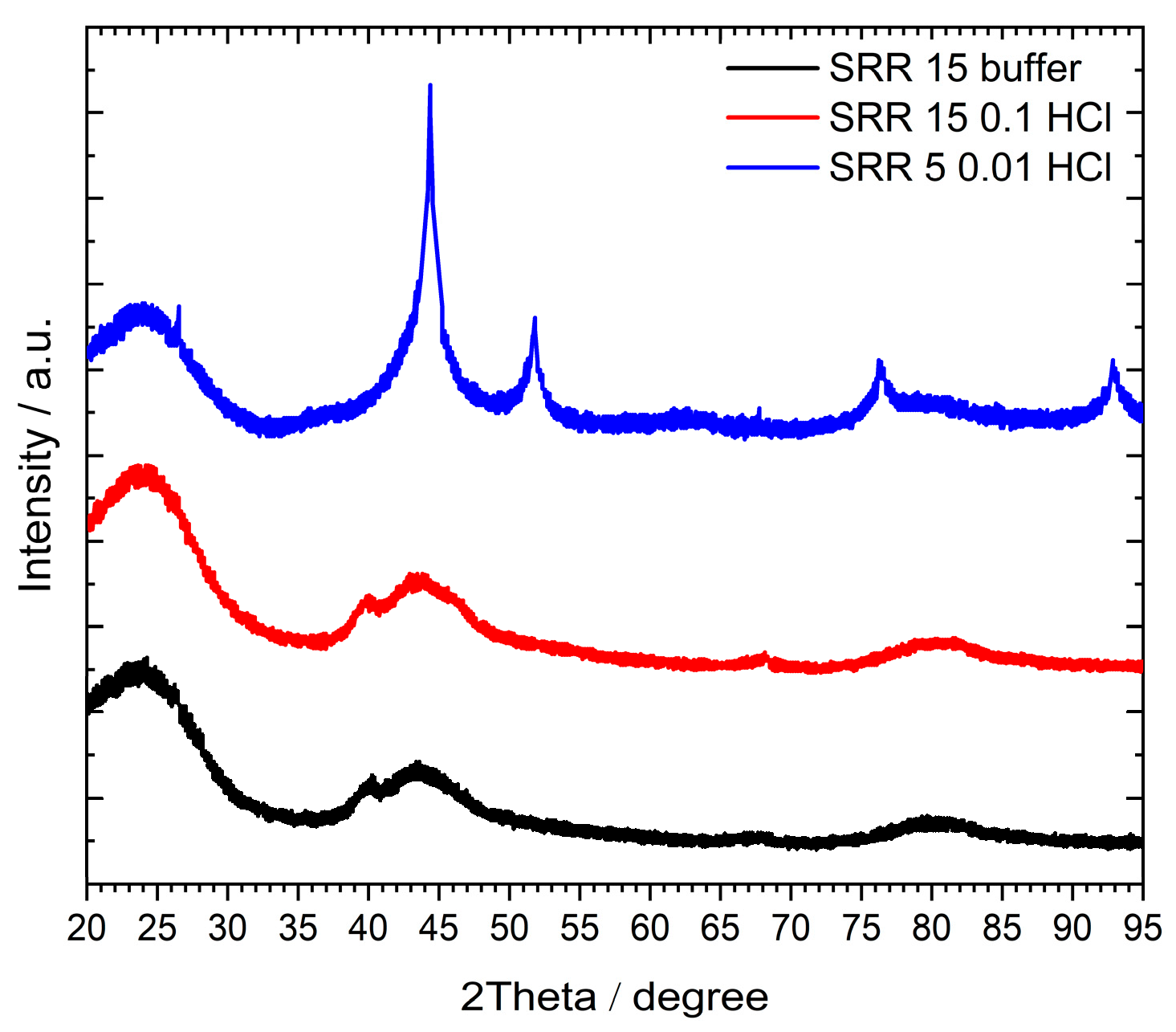
2.2.2. XRD analysis
2.2.3. TGA
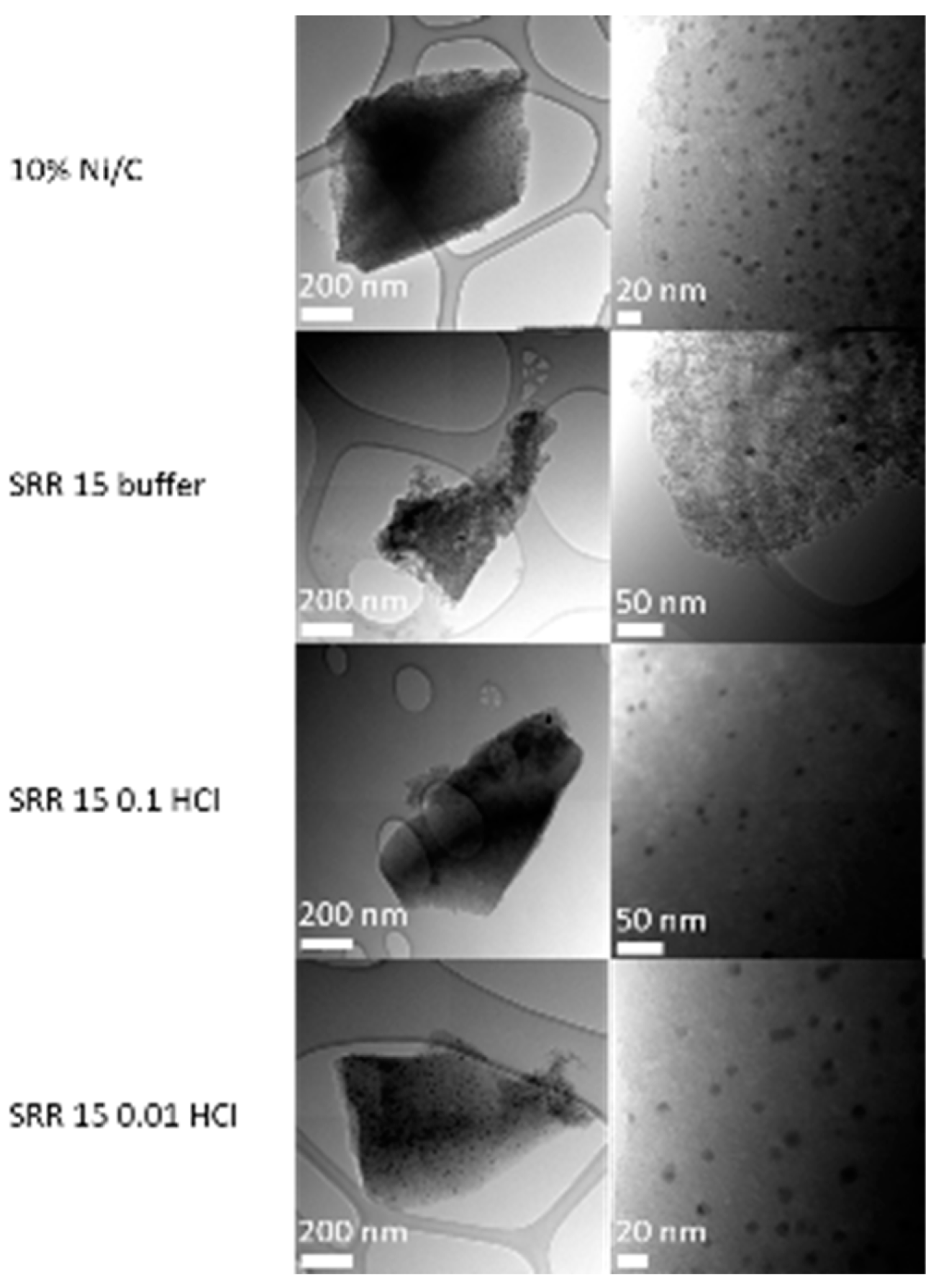
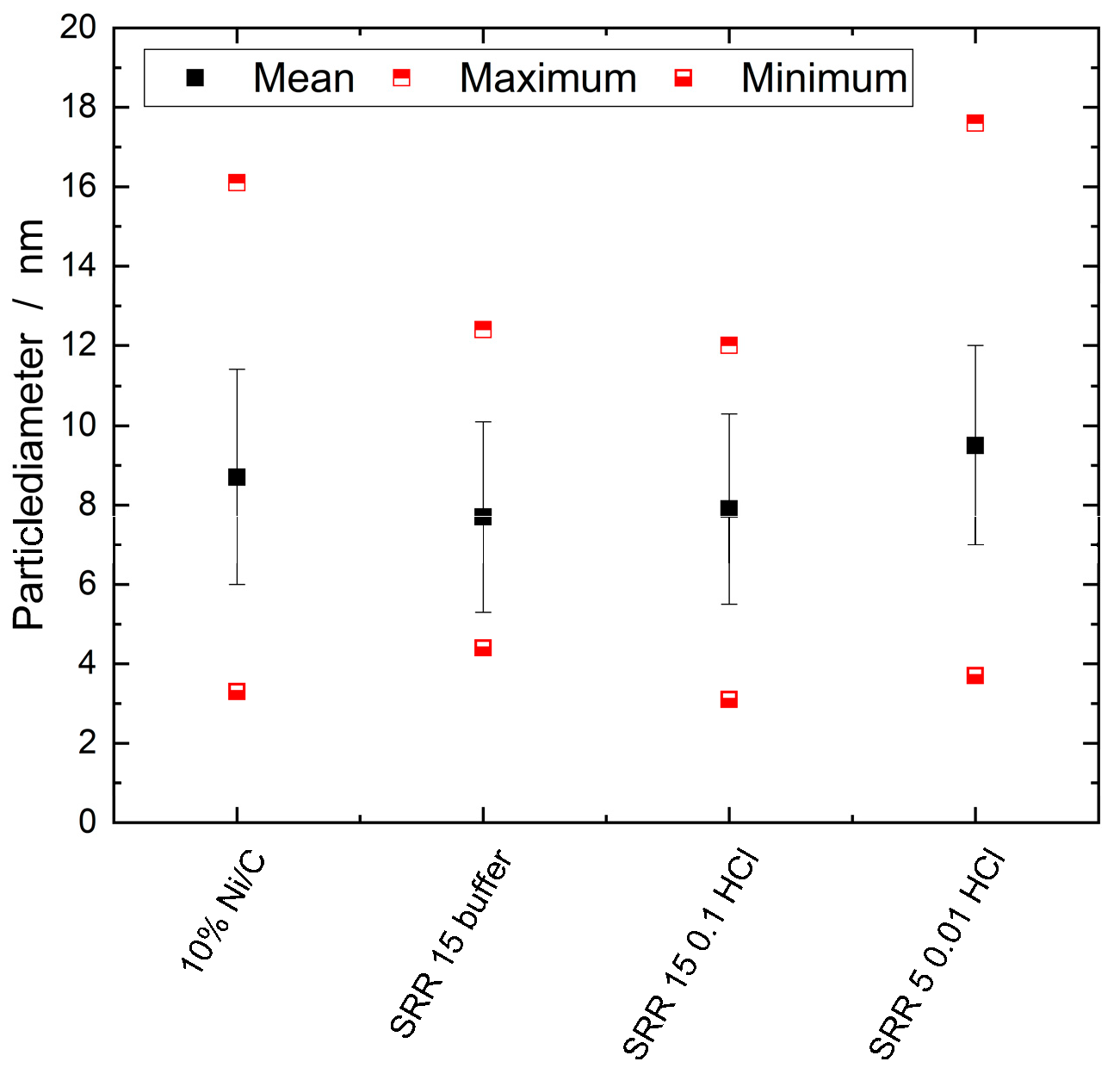
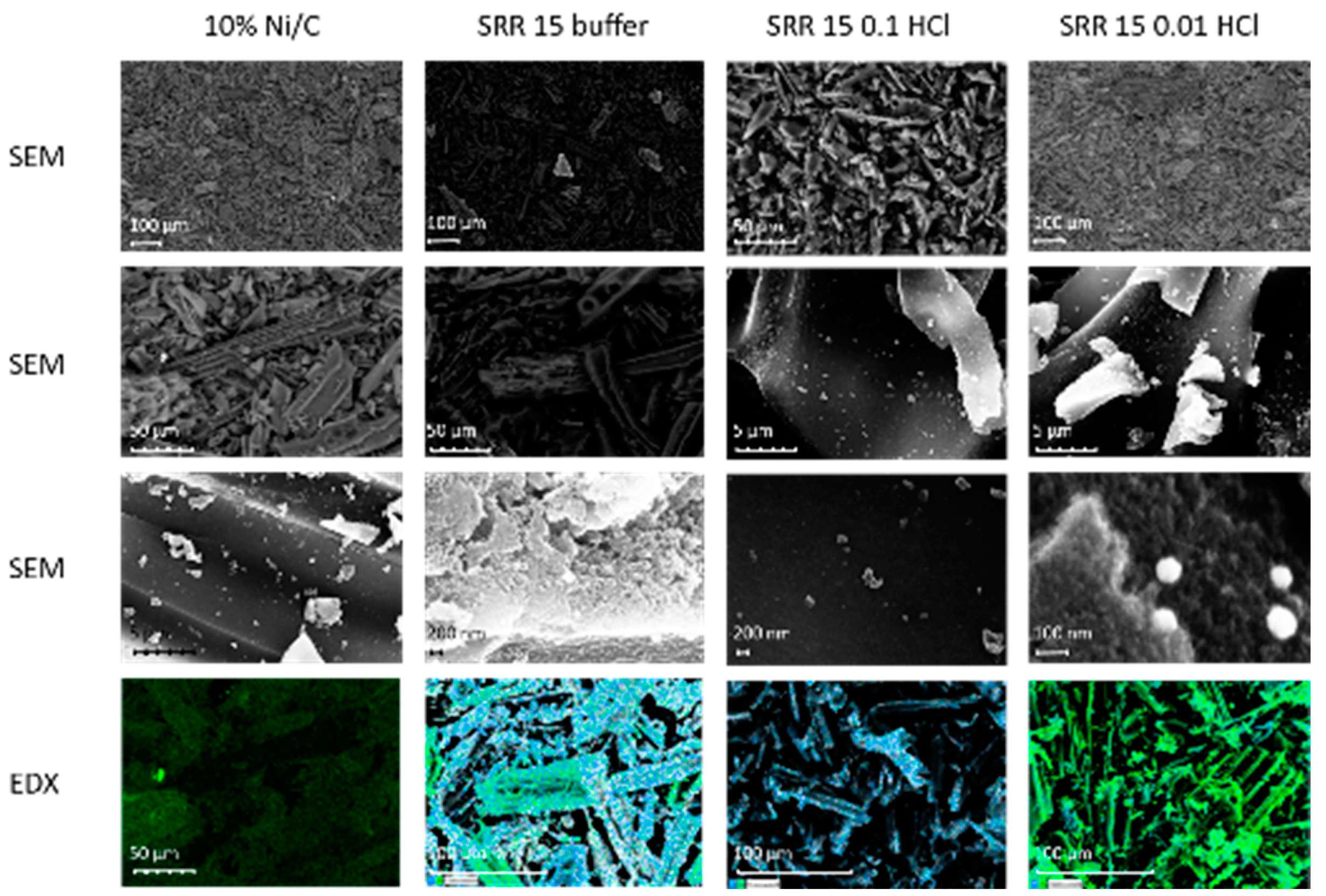
2.2.4. TEM / SEM combined with EDX
2.2.5. H2–TPD
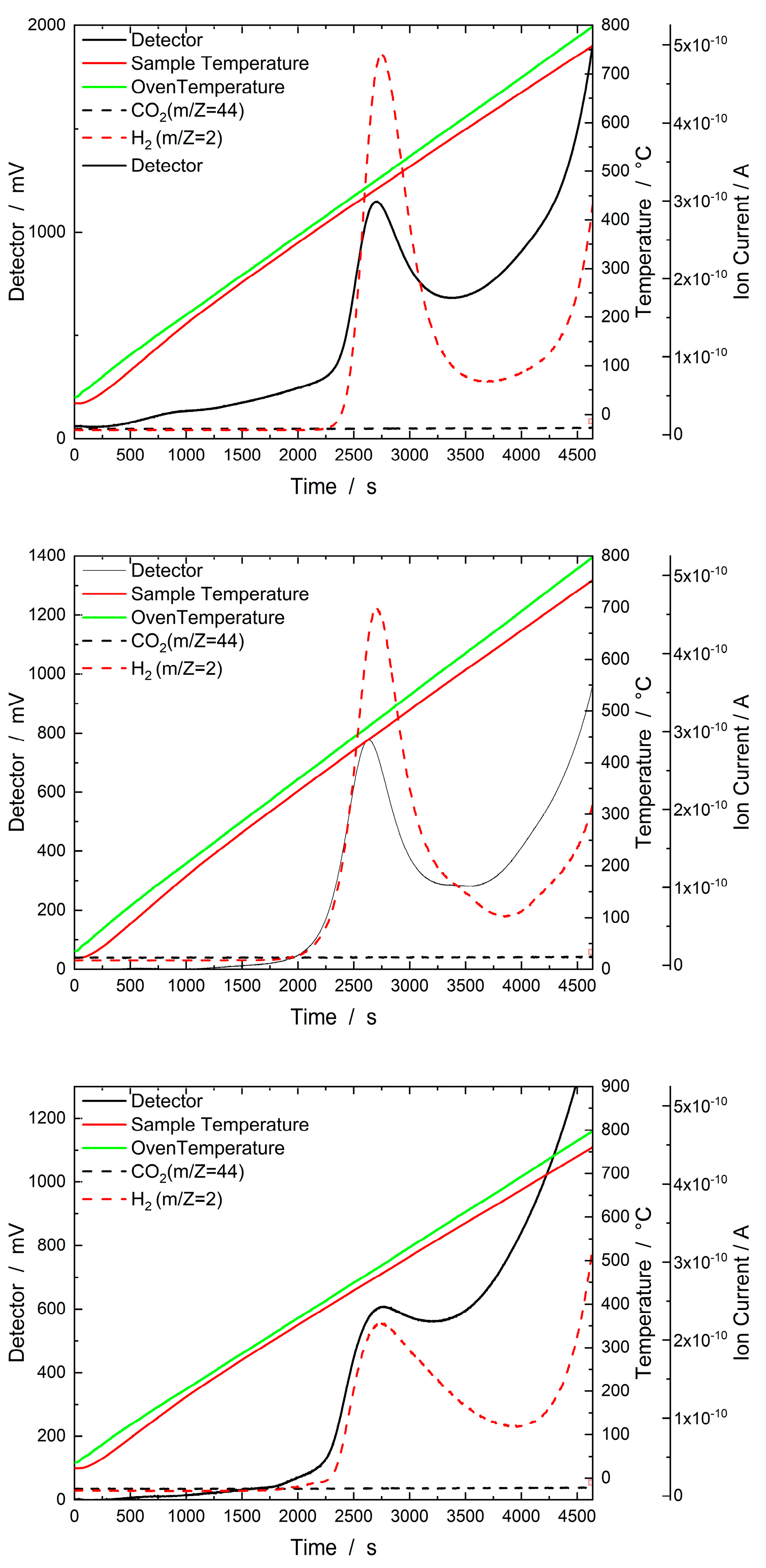
2.2.6. Catalytic activity
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Synthesis of the impregnated cataylsts
3.2. Synthesis of the catalysts via the surface redox reaction
3.2.1. KCl/HCl buffer as a polar solution
3.2.2. 0.1 M HCl as a polar solution
3.2.3. 0.01 M HCl as a polar solution
3.3. Catalytic experiments
3.4. Vis spectroscopy
3.5. TGA
3.6. H2–TPD
3.7. ICP–OES
3.8. XRD
3.9. N2 sorption
3.10. TEM
3.11. SEM/EDX
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M.R. Allen, O.P. Dube, W. Solecki, IPCC Special Report Global Warming of 1.5°C, Chapter 1 - Framing and Context, FAQ 1.2, Figure 1.
- R. Rohde, Global temperature report for 2020, http://berkeleyearth.org/global-temperature-report-for-2020/.
- Y.-l. Li, Y.-c. Yu, Z.-w. Wang, J.-f. Wang, Physical and chemical properties of isobutanol-gasoline blends, 34 (2015) 908-914. [CrossRef]
- J. Häusler, Synthese von höheren Alkoholen als zukünftige Kraftstoffe für den Verkehrssektor, PhD thesis, Fakultät für Maschinenwesen, RWTH Aachen, in preparation.
- J. Pasel, J. Häusler, D. Schmitt, H. Valencia, M. Meledina, J. Mayer, R. Peters, Ethanol Dehydrogenation: A Reaction Path Study by Means of Temporal Analysis of Products, 10 (2020) 1151. [CrossRef]
- S.R. Brankovic, J.X. Wang, R.R. Adžić, Metal monolayer deposition by replacement of metal adlayers on electrode surfaces, Surface Science 474 (2001) L173-L179. [CrossRef]
- S.R. Brankovic, J.X. Wang, Y. Zhu, R. Sabatini, J. McBreen, R.R. Adžić, Electrosorption and catalytic properties of bare and Pt modified single crystal and nanostructured Ru surfaces, Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 524-525 (2002) 231-241. [CrossRef]
- K. Sasaki, Y. Mo, J.X. Wang, M. Balasubramanian, F. Uribe, J. McBreen, R.R. Adzic, Pt submonolayers on metal nanoparticles—novel electrocatalysts for H2 oxidation and O2 reduction, Electrochimica Acta 48 (2003) 3841-3849. [CrossRef]
- M. Van Brussel, G. Kokkinidis, A. Hubin, C. Buess-Herman, Oxygen reduction at platinum modified gold electrodes, Electrochimica Acta 48 (2003) 3909-3919. [CrossRef]
- M. Van Brussel, G. Kokkinidis, I. Vandendael, C. Buess-Herman, High performance gold-supported platinum electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction, Electrochemistry Communications 4 (2002) 808-813. [CrossRef]
- Mintsouli, J. Georgieva, E. Valova, S. Armyanov, A. Kakaroglou, A. Hubin, O. Steenhaut, J. Dille, A. Papaderakis, G. Kokkinidis, S. Sotiropoulos, Pt–Ni carbon-supported catalysts for methanol oxidation prepared by Ni electroless deposition and its galvanic replacement by Pt, Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry 17 (2013) 435-443. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hu, Q. Shao, P. Wu, H. Zhang, C. Cai, Synthesis of hollow mesoporous Pt–Ni nanosphere for highly active electrocatalysis toward the methanol oxidation reaction, Electrochemistry Communications 18 (2012) 96-99. [CrossRef]
- L. Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, A. Balčiūnaitė, A. Vaiciukevičienė, A. Selskis, V. Pakštas, Investigation of nanostructured platinum–nickel supported on the titanium surface as electrocatalysts for alkaline fuel cells, Journal of Power Sources 208 (2012) 242-247. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, H. Wang, R. Wang, Q. Wang, Z. Lei, Carbon-supported platinum-decorated nickel nanoparticles for enhanced methanol oxidation in acid media, Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry 16 (2012) 1049-1054. [CrossRef]
- T. Burger, H.M.S. Augenstein, F. Hnyk, M. Döblinger, K. Köhler, O. Hinrichsen, Targeted Fe-Doping of Ni−Al Catalysts via the Surface Redox Reaction Technique for Unravelling its Promoter Effect in the CO2 Methanation Reaction, 12 (2020) 649-662. [CrossRef]
- P. Badenes, L. Daza, I. Rodriguez-Ramos, A. Guerrero-Ruiz, Mechanism of hydrogen spillover over carbon supported metal catalysts, in: C. Li, Q. Xin, (Eds.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier, 1997, pp. 241-250.
- J.T. Miller, B.L. Meyers, M.K. Barr, F.S. Modica, D.C. Koningsberger, Hydrogen Temperature-Programmed Desorptions in PlatinumCatalysts: Decomposition and Isotopic Exchange by SpilloverHydrogen of Chemisorbed Ammonia, Journal of Catalysis 159 (1996) 41-49. [CrossRef]
- S. Brunauer, P.H. Emmett, E. Teller, Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers, Journal of the American Chemical Society 60 (1938) 309-319.

| Percentage values | IMP Ni99Pt1/C | IMP Ni95Pt5/C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-OES | calculated | ICP-OES | calculated | ||
| wt% Ni | 8.4 | 11.2 | 7.7 | 10.0 | |
| wt% Pt | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 1.5 | |
| at% Ni | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
| at% Pt | 99 | 99 | 98 | 95 | |
| Reaction products | IMP Ni99Pt1/C Y [%] | IMP Ni99Pt1/C S [%] | IMP Ni95Pt5/C Y [%] | IMP Ni95Pt5/C S [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iso-butanol | 2.45 | 61.03 | 3.01 | 69.49 | |
| 2-methylpropanal | 0.34 | 8.55 | 0.39 | 8.94 | |
| 1-propanol | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.36 | |
| 2-methylbutane-1-ol | 0.03 | 1.28 | 0.05 | 2.19 | |
| 2-ethylbutane-1-ol | 0.02 | 1.20 | 0.03 | 2.20 | |
| 1-hexanol | 0.21 | 15.32 | 0.22 | 15.47 | |
| 2-ethylhexane-1-ol | 0.12 | 15.32 | 0 | 0 |
| Percentage Values | SRR 15 buffer ICP-OES |
SRR 15 buffer calculated |
SRR 30 buffer ICP-OES |
SRR 30 buffer calculated |
SRR 60 buffer ICP-OES |
SRR 60 buffer calculated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% Ni | 0.32 | 8.59 | 0.40 | 8.59 | 0.40 | 8.59 |
| wt% Pt | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.33 |
| Percentage Values | SRR 15 buffer ICP–OES |
SRR 15 buffer calculated |
SRR 15 0.1 HCl ICP–OES |
SRR 15 0.1 HCl calculated |
SRR 5 0.01 HCl ICP–OES |
SRR 5 0.01 HCl calculated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% Ni | 0.32 | 8.59 | 0.10 | 8.59 | 7.33 | 8.56 |
| wt% Pt | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.38 |
| Catalyst | Specific STY [mole g-1 h-1] | Y(iso-butanol) [%] | S to iso-butanol [%] | Specific surface areas [m2 g-1] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP Ni99Pt1/C | 1.02 | 2.45 | 61.03 | 706 | |
| IMP Ni95Pt5/C | 1.35 | 3.01 | 69.49 | 703 | |
| SRR 15 buffer | 21.26 | 2.40 | 68.68 | 780 | |
| SRR 30 buffer | 15.16 | 3.01 | 67.11 | - | |
| SRR 60 buffer | 17.52 | 2.04 | 70.48 | - | |
| SRR 15 0.1 HCl | 79.87 | 3.49 | 74.49 | 758 | |
| SRR 30 0.1 HCl | 42.07 | 6.02 | 80.09 | - | |
| SRR 5 0.01 HCl | 3.30 | 6.92 | 76.19 | 671 |
| Reaction products | SRR 15 buffer Y [%] | SRR 15 buffer S [%] | SRR 15 0.1 HCl Y [%] | SRR 15 0.1 HClS [%] | SRR 5 0.01 HCl Y [%] | SRR 5 0.01 HCl S [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iso-butanol | 2.40 | 68.67 | 3.49 | 74.49 | 6.92 | 76.19 |
| 2-methylpropanal | 0.49 | 14.01 | 0.60 | 12.75 | 1.23 | 13.56 |
| 1-propanol | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.23 |
| 2-methylbutane-1-ol | 0.01 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 1.35 |
| 2-ethylbutane-1-ol | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.01 |
| 1-hexanol | 0.19 | 16.36 | 0.19 | 8.68 | 0.23 | 7.65 |
| 2-ethylhexane-1-ol | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





