1. Introduction
Ficus carica L., belonging to the Moraceae family, is a fruit-bearing tree that has been cultivated since ancient times and is native to Central Asia and the Mediterranean coastline of Europe. This Asian flowering plant species holds significant historical importance as one of the earliest cultivated fruit trees in these regions[
1,
2]. The commonly recognized name for
Ficus carica L. is fig fruit which has been widely consumed and utilized for both food and medicinal purposes for centuries. [
3,
4]. Fresh fig fruit can be eaten both with and without peel. However, a large number of fresh figs are spoilage every year owing to the physicochemical damage during harvest and storage processes. In order to decrease the spoilage on processing, fig fruit could be processed into spirit beverage, fruit juice, dried fruit or jam, etc[
5]. Figs are abundant in minerals, vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, phenols, flavonoids and polysaccharides, which exhibit various biological activities[
5,
6].
Natural polysaccharides as an essential biological macromolecule which consist of more than ten monosaccharide molecules connected together by glycosidic bonds, these polysaccharides can be derived from diverse sources, including animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi[
7,
8,
9,
10]. Recently, natural polysaccharides have received significant attention due to their multitude of biological properties, including antioxidant, antiviral, regulation of intestinal, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and immunomodulatory effects, etc[
11,
12,
13,
14]. Likewise, polysaccharides from figs (FCPs) are one sort of the main bioactive compounds with beneficial potency and low toxicity. It has been reported that polysaccharides from figs have a good immunomodulatory activity on RAW 264.7 macrophages, and it has also been discovered that the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) activates macrophages in response to FCPs via the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-B) p65 signaling pathway[
15]. The biological functions of polysaccharides are known to vary based on factors such as molecular weight, degree of branching, glycosidic bonds, and other chemical structures. [
16,
17]. Consequently, the structural characteristics of polysaccharides forms needed to be investigated for understanding their biological activities. Nevertheless, available information on the precise structure and mechanisms underlying the biological activity of the purified polysaccharides of
Ficus carica L. is still limited. In particular, the mechanisms underlying their immunomodulatory activities remain largely unexplored, like Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and its role as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) participate in immunomodulatory activities or not which still need to be further investigated. Based on the existing knowledge gap, we have formulated a hypothesis that a novel polysaccharide derived from fig fruit may possess a distinct structure and exhibit significant immunomodulatory activity which Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) may be implicated in this biological processes.
Previous studies have reported that cyclophosphamide (CTX, Cy), as a potent immunosuppressive agent, can result in immunosuppression of mice[
18,
19]. At present, there are few studies on the effects of FCP on the immunoregulation of CTX-induced immunosuppressed mice. Therefore, in this study, hot water extraction was employed to extract crude fig polysaccharides, deproteinized using sevag method, and purified through ultrafiltration to obtain a pure polysaccharide fraction. The pure fig polysaccharide was then used to structural characterization, and its immunomodulatory activity
in vitro based on RAW 264.7 macrophages and
in vivo based on CTX injection a classic modelling method were assessed. The findings of our research offer valuable information about the intricate composition of fig polysaccharides. Additionally, these results lay the foundation for food and functional products using polysaccharides extracted from
Ficus carica L. Therefore, the new polysaccharides from figs are worthy for further development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and reagents
Dried ‘Brunswick’ figs were bought from Sichuan JINSIFANG Fruit Co., Ltd (Neijiang, China). Standard monosaccharides (galactose, Gal; fucose, Fuc; rhamnose, Rha; arabinose, Ara; glucose, Glu; fructose, Fru; xylose, Xyl; ribose, Rib; mannose, Man; galacturonic acid, GalA; glucuronic acid, GluA; galactosamine hydrochloride, GalH; glucosamine hydrochloride, GluH; N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine, GluNAc; guluronic acid, GulA; mannuronic acid, ManA) and methylation reagent kit (BRT-JJH, AR) were acquired from Bo Rui Saccharide Biotech Co., Ltd (Yangzhou, China). RPMI-1640 medium, penicillin, streptomycin were purchased from Biosharp (Hefei, China). Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was acquired from ExCell Bio (Nanjing, China). Murine RAW 264.7 (ATCC TIB-71) macrophages were bought from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was acquired from SHANGHAI TAOSHU BIOLOGY SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Mouse TNF-α and IL-6 ELISA kit were acquired from Shanghai WellBio Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Griess reagent kit and neutral red were obtained from Beyotime (Shanghai, China). Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit was acquired from SolarBio (Beijing, China). Resatorvid (TAK-242) and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were obtained from MedChemExpress (Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA). Cyclophosphamide (CTX, Cy) was bought from Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd (Lianyungang, China). Remaining chemicals were all of analytical grade.
2.2. Polysaccharide extraction and purification
Polysaccharide was extracted according to our previously reported method[
20] with minor modifications. Briefly, dried ‘Brunswick’ figs were ground with a pulverizer and passed through a 60-mesh sieve, and incubated in 100% (v/v) ethanol (1:10, w/v) at 60 ℃ for 1 h to remove most of the small molecule impurities three times. Then, the extract residues were used to extract water soluble polysaccharides and deproteinization by Sevag reagent (CHCl
3:CH
3OH = 4:1, v/v) according to the Sevag method[
21]. The crude water soluble polysaccharides solution was dialyzed against distilled water for 48 h and ultrapure water for 24 h (cut-off Mw 8000-14000 Da). After ultrafiltration (cut-off Mw 100000 Da), the filtrate solution was lyophilized as pure polysaccharide, named FCP, for subsequent investigation.
2.3. Characterization of FCP
2.3.1. Determination of basic components in FCP
The total carbohydrate, uronic acid, protein, starch, and total polyphenols were determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid colorimetric method[
22], meta-hydroxydiphenyl method[
23], bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay, I-KI assay[
24] and folin-ciocalteu method[
25].
2.3.2. Molecular weight of FCP
The molecular weight (Mw) of FCP was measured by high performance size exclusion chromatography coupled with multi angle laser light scattering and refractive index detector (HPSEC-MALLS-RID) according to our previously reported method[
26] with minor modifications. In brief, HPSEC-MALLS-RID measurements were performed using a multi-angle laser light scattering detector (MALLS, DAWN HELEOS, Wyatt Technology Co., Santa Barbara, CA, USA) coupled with an Agilent 1260 series LC system (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). Two columns, TSK-Gel G5000PWXL (300 mm × 7.8 mm, i.d.) and TSK-Gel G3000PWXL (300 mm × 7.8 mm, i.d.), were connected in series and maintained at a temperature of 30 °C. The mobile phase consisted of a 0.9% NaCl aqueous solution, and the sample was eluted using this mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The concentration of the sample was approximately 1.0 mg/mL, and an injection volume of 100 μL was used for the analysis[
26].
2.3.3. Monosaccharide composition analysis
A 5 mg sample of FCP was subjected to hydrolysis in a sealed ampoule using 2 mL of 3 mol/L trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) at a temperature of 121 °C for a duration of 3 h. The excess TFA was removed three times using nitrogen gas and methanol. Subsequently, the final hydrolyzate sample and standards were dissolved in ultrapure water and prepared for injection into the ion-exchange chromatography ICS-5000 system (Thermo Fisher, CA, USA). The system was equipped with a Dionex™ CarboPac™ PA20 column (150 mm × 3 mm, 10 μm) and an electrochemical detector[
27].
2.3.4. UV analysis
The UV absorbance spectrum of the FCP (1 mg⋅mL-1) was analyzed based on an UV-1800PC spectrophotometer (MAPADA Instruments, Shanghai, China) with a spectrum range of 200 to 800 nm.
2.3.5. FT-IR spectroscopy analysis
The Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis of FCP (1 mg) mixed with potassium bromide powderat a range of 4000–400 cm
−1 was performed on an FT-IR spectrophotometer Nicolet iS 10 FT-IR instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)[
28].
2.3.6. SEM analysis
The SEM of FCP was analyzed using a SU8100 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan). Briefly, FCP powder sample was placed on a carbon-coated electrical film and coated with a sputtered of gold powder using a MC1000 sputter coater (Hitachi, Japan), then the FCP sample was imaged using magnifications of 500 and 5000 at an accelerating potential of 2 kV.
2.3.7. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis
The morphology and molecular characteristics of FCP was analyzed using SPM-9700 atomic force microscopy (AFM) (SHIMADZU, Japan) in a tapping mode. Specifically, 10 μL of the FCP solution (5 μg⋅mL
-1) was dropped onto a mica sheet and allowed to air dry at room temperature for 2 h, the prepared sample was then placed under the microscope for observation and analysis[
29].
2.3.8. Methylation analysis
For the analysis of monosaccharide linkage, methylation was performed following the methods described by Ma et al[
30].
2.3.9. Triple-helix construction analysis
The triple-helix structures of FCP was acquired based on the Congo red method in the previously reported literature[
27].
2.4. Immunomodulatory activity of FCP in vitro
2.4.1. Cell culture, grouping and administration
RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 1% penicillin and 1% streptomycin, all cells were incubated in a humidified 5% CO
2 incubator at 37 °C[
27].
The cells were seeded into a 96-well flat bottom plate at a density of 3000 cells per well and incubated overnight. Then FCP at different concentrations (100 μg⋅mL-1, FCP-L; 300 μg⋅mL-1, FCP-M; 500 μg⋅mL-1, FCP-H;) were added to the wells. Apple polysaccharide (500 μg⋅mL-1, AP) and LPS (10 μg⋅mL-1) were used as positive control. RPMI-1640 medium was used as negative control (CK). To investigate whether Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) serves as the recognition site for FCP on macrophage activation, TLR4 inhibitor resatorvid (10 nM, TAK-242) and TLR4 inhibitor resatorvid (10 nM, TAK-242) with FCP (500 μg⋅mL-1, FCP-H) were performed. A blank (wells without cell) was included. Three plates of each group were run simultaneously.
2.4.2. Cell viability assessment
RAW 264.7 cells were grown in 96-well plates and processed as described in “2.4.1”. The cells were then incubated in a humidified 5% CO
2 incubator at 37 °C for 48 h. Then cells were incubated with 10 μL per well CCK-8 regent for 1 h at 37 °C, cell viability was estimated using the CCK-8 assay[
29] following the manufacturer’s instructions and the absorbance was measured using a DR-200Bc microplate reader (WUXI HIWELL-DIATEK INSTRUMENTS Co., Ltd, Wuxi, China) at 450 nm.
2.4.3. Pinocytic test
RAW 264.7 cells were cultured under “2.4.1” treated, then 20 μL neutral red solution was added and thoroughly wash out with PBS after 2 h of incubation, then 200 μL of cell lysate solution was added and the plates were kept on a shaker for 10 min at room temperature. Finally, the absorbance was measured using a DR-200Bc microplate reader (WUXI HIWELL-DIATEK INSTRUMENTS Co., Ltd, Wuxi, China) at 540 nm.
2.4.4. Determination of NO and IL-6, TNF-a cytokine production level
RAW 264.7 cells in 96-well plate were cultured under “2.4.1” treated and the culture supernatant was collected from each well for NO, TNF-α and IL-6 analysis by commercial Griess reaction kit, IL-6 and TNF-α ELISA kit.
2.5. Immunomodulatory activity of FCP in vivo
2.5.1. Animal experiments
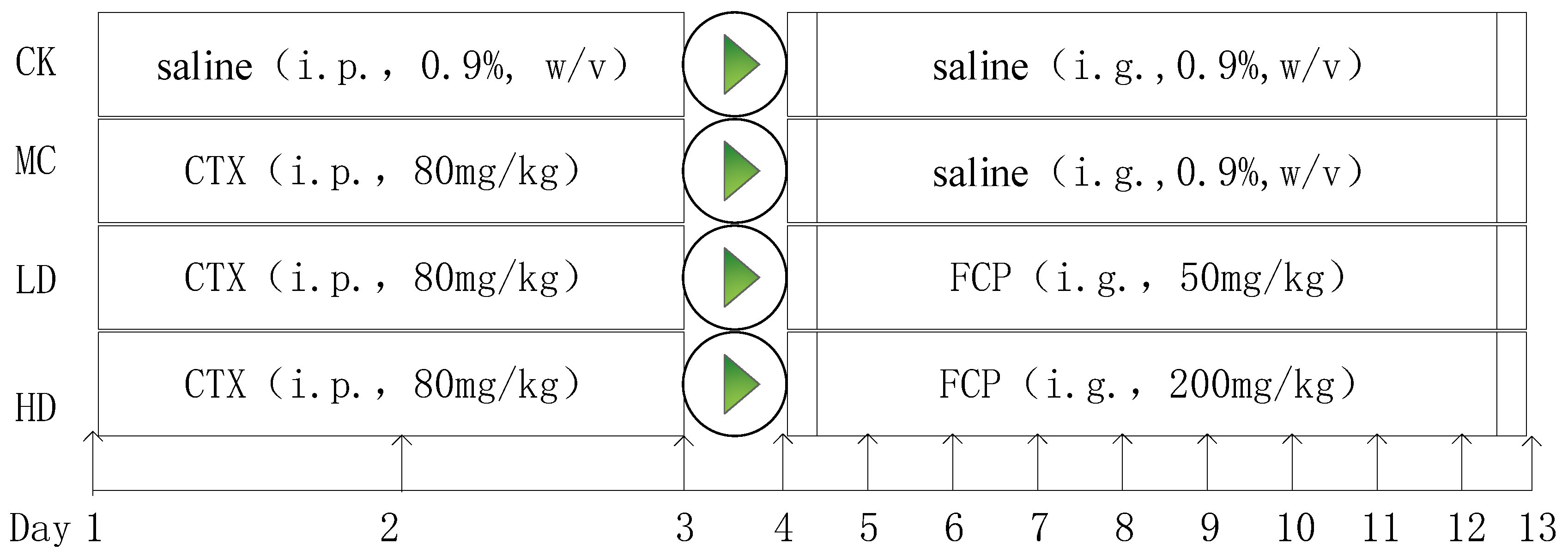
28 male mice from the Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) were bought from Chengdu Dashuo Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. in Chengdu, China. These mice were specific pathogen-free (SPF) and weighed approximately 30 g±2 g. They were housed in plastic cages with shavings, under controlled condition (a 12-h light/dark cycle, humidity: 70 ± 5%, temperature: 23 ± 2 °C) with ad libitum access to food.
After 1 week adaptation, 7 mice were separated into a normal control group (CK). The remaining 21 mice were injected intraperitoneally with 80 mg/kg⋅bw/day of CTX for 3 days to induce immunosuppression[
18]. These CTX-treated mice were then randomly divided into 3 groups (n= 7 per group): a model control group (MC), a low-dose group (FCP 50 mg/kg, LD), and a high-dose group (FCP 200 mg/kg, HD). In the LD and HD groups, mice were given different doses of FCP through intragastric gavage for 9 days. The NC and MC groups received a saline solution instead. Animal care and use were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University. The experimental design was shown in
Figure 1.
2.5.2. Determination of serum cytokines
After feeding for 9 days, all mice were anesthetized by diethyl ether and blood samples were subsequently collected. The serum was then collected and stored at 4℃. The levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the serum were analyzed using ELISA kits in accordance with the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
2.6. Statistical analysis
All experiments were conducted in triplicate unless otherwise stated. Data obtained were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). SPSS 26.0 software was used to test the normality of the data, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s test were used to analyze the differences between groups. p-value < 0.05 considered the difference to be statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical compositions and and molecular weight of FCP
In this study, the crude fig polysaccharide was purified by sevag and ultrafiltration. The content of total carbohydrate was 93.46%, uronic acid was 60.40%, protein was 1.59%, starch and total phenolics were not detected (
Table 1). These results showed the fig polysaccharide with very low level of impurities after purified. In addition, FCP had a molecular weight of 127.5 kDa and a polydispersity index (M
w/M
n) of 1.85, indicating a narrow molecular weight distribution of the purified FCP.
3.2. Monosaccharide composition analysis
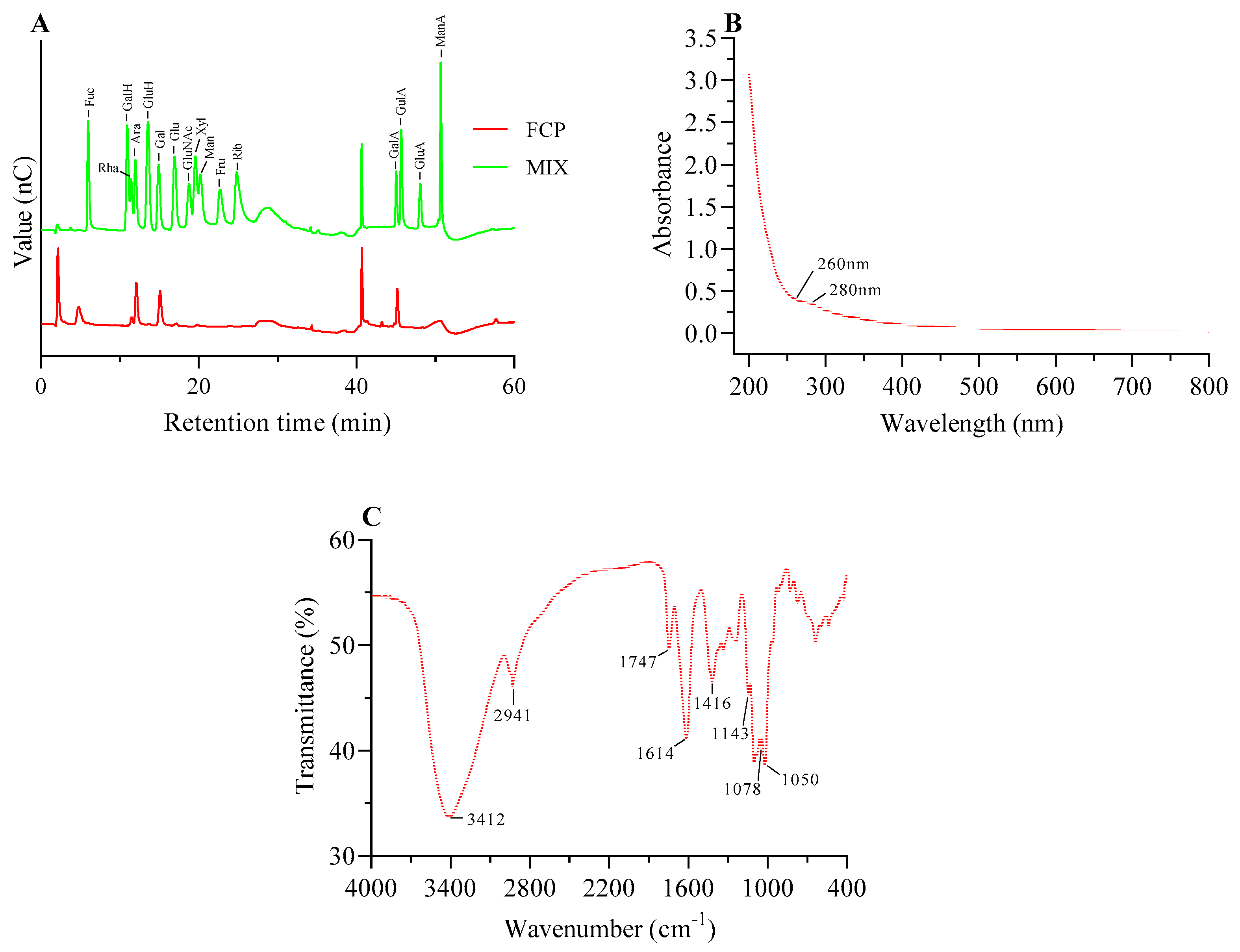
The IC system analysis revealed the presence of the following constituent monosaccharides in FCP: galacturonic acid (GalA), arabinose (Ara), galactose (Gal), rhamnose (Rha), glucose (Glc), and xylose (Xyl). The molar ratios of these monosaccharides were found to be 0.321:0.287:0.269:0.091:0.013:0.011, respectively.(
Figure 2A).
3.3. Ultraviolet spectrum analysis
The protein content in fig polysaccharide was found to be very low, which was consistent with the UV-Vis analysis indicating the absence of protein (<3%), this was confirmed by the absence of absorption peaks at 280 nm in the spectrum (
Figure 2B) [
31]. Furthermore, there was no absorption peak at 260nm, which indicated that there was no nucleic acid in fig polysaccharide (
Figure 2B).
3.4. FT-IR analysis
As shown in
Figure 2C, two characteristic absorptions of the polysaccharide were observed at 3412 cm
-1 and 2941cm
-1, these two strong absorption peak were O-H telescopic vibration and C-H asymmetric tensile vibration[
32,
33]; The absorption peaks of 1747 cm
-1 and 1614 cm
-1 were attributed to the C=O and carboxylate (-COO-) telescopic vibrations of carboxylic ester (-COOR), respectively, which also indicated the presence of uronic acid[
34]. The absorption peaks of 1416 cm
-1 and 1143 cm
-1 were attributed to the bending vibrations of C-H or O-H and C-O-C, respectively, which indicated the presence of -OCH
3[
35]; the C-O absorption of 1078 cm
-1 and 1050 cm
-1 indicated that fig polysaccharide was of pyran configuration[
29].
3.5. SEM characterization of FCP
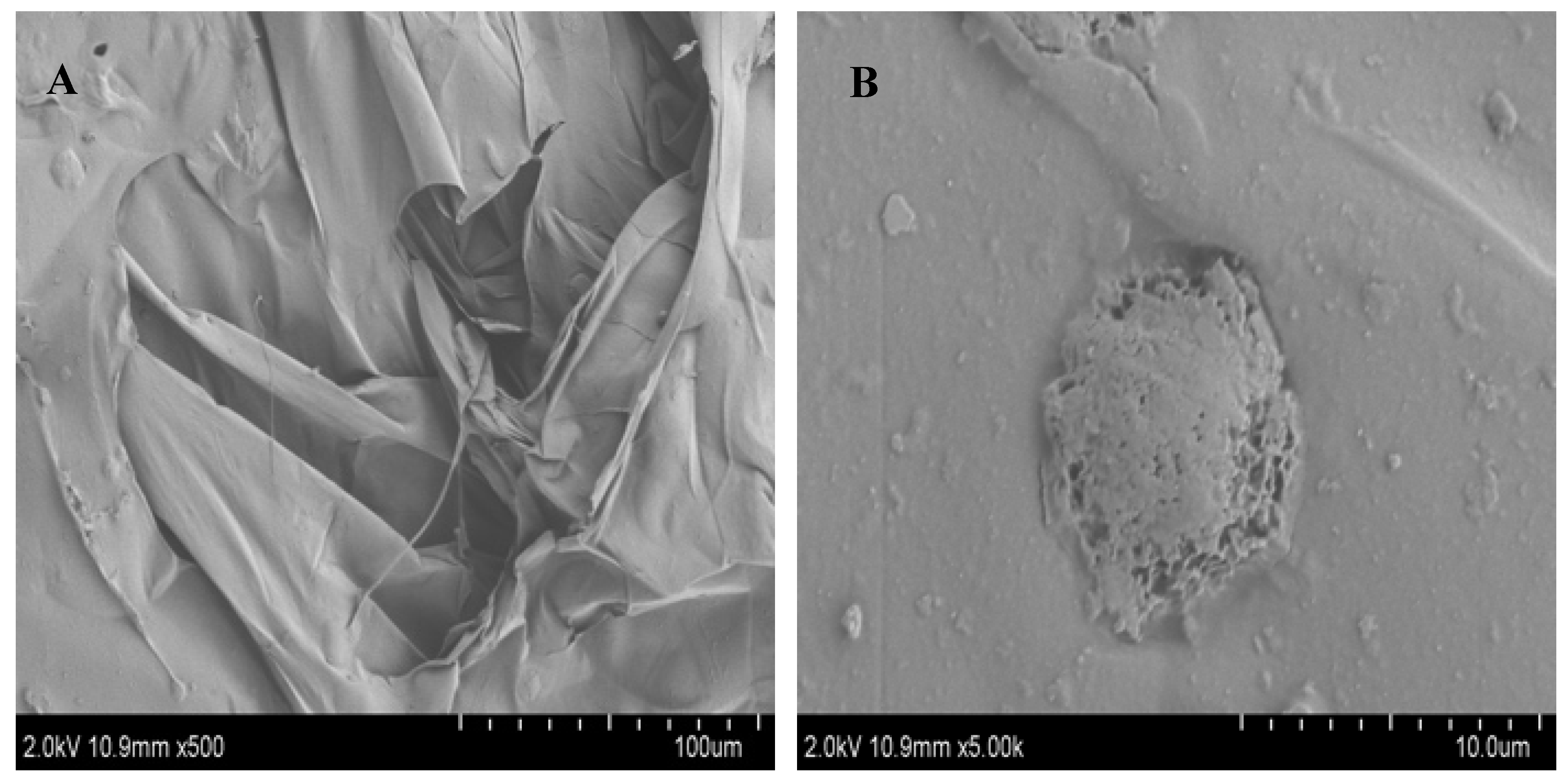
It is known that SEM can be used to detect the surface morphology of polysaccharides and that the images of SEM can indicate the molecular morphological features of the polysaccharide[
27]. The morphological characteristic of FCP was carried out by SEM with magnifications of 500x and 5000x magnification (
Figure 3). At low magnification (500 ×) (
Figure 3A), the polysaccharide was observed to have a smooth surface and lamellar structure, whereas at high magnification it had a distinct raised structure (5000 ×) (
Figure 3B), these structures were relatively complete, indicating that the polysaccharides of each components were tightly polymerized and the interaction between molecules were strong, which may be related to the arrangement of polysaccharides of different molecules[
32].
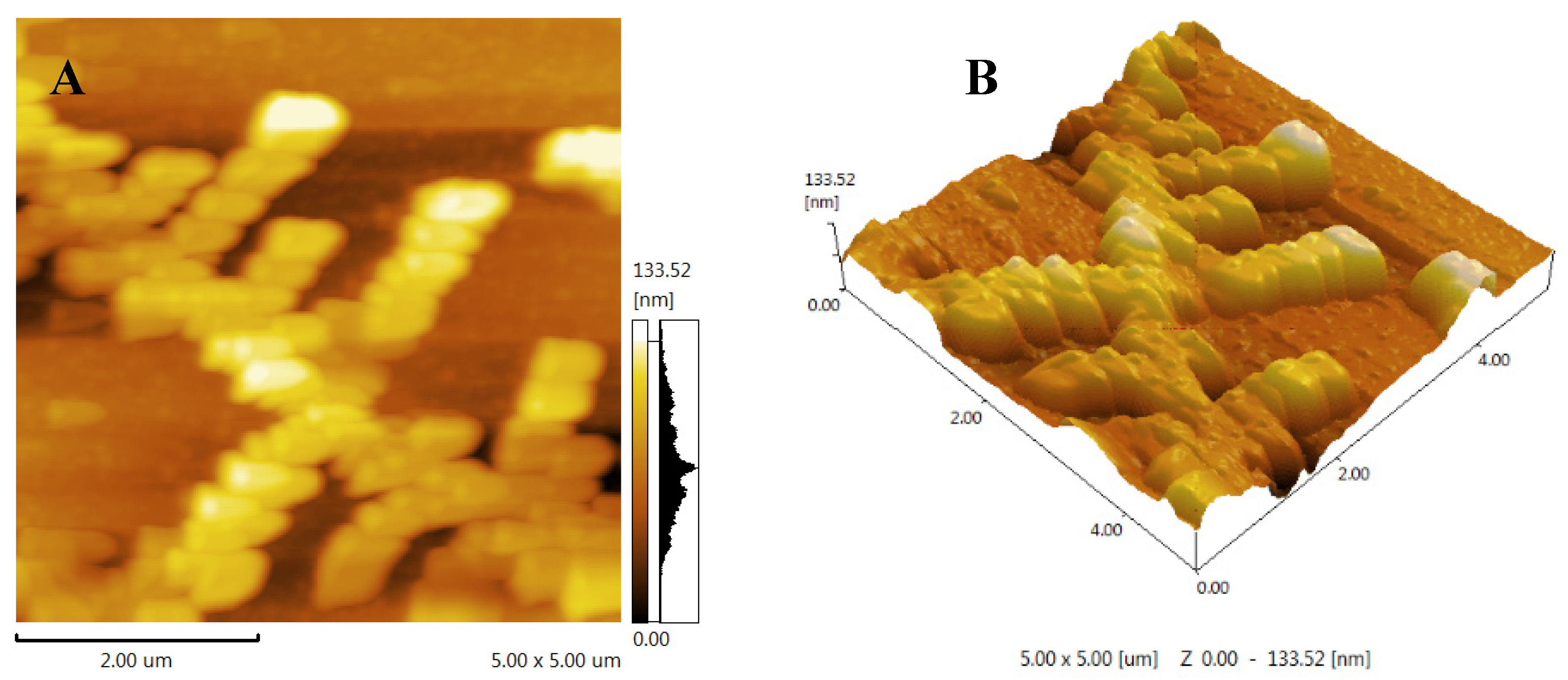
3.6. AFM analysis of FCP
AFM is a typical method to directly show the macromolecular samples and provide two-dimensional images but also observe three dimensional surface images of polysaccharides directly with natural conditions[
29]. Generally speaking, sugar chains with various compositions always have a propensity to form into the conformation that has the lowest free energy[
31]. Fig polysaccharide showed a chain with multiple branches structure (
Figure 4), these results suggest that FCP may first aggregate and then self-assemble into a long chain, with branching likely related to α-1,4-glycosidic linkages, which may be galacturonic acid, consistent with the methylation analysis[
29].
3.7. Methylation analysis
Methylation is a reliable method for determining the glycosidic bonds present in polysaccharides. In this study, the methylation reaction products of FCP were hydrolyzed and converted to the corresponding alditol acetates[
36]. A total of 19 products were obtained and analysed by GC-MS as shown in
Table 2. By comparing the obtained data with the standard data in the Complex Carbohydrate Research Centre (CCRC) spectral database for partially methylated alditol acetates (PMAAs)[
37], the bonds of the monosaccharides in FCP were identified. These results agreed with the previously described analysis of the monosaccharide composition of FCP, showing a strong correlation between the two analyses.
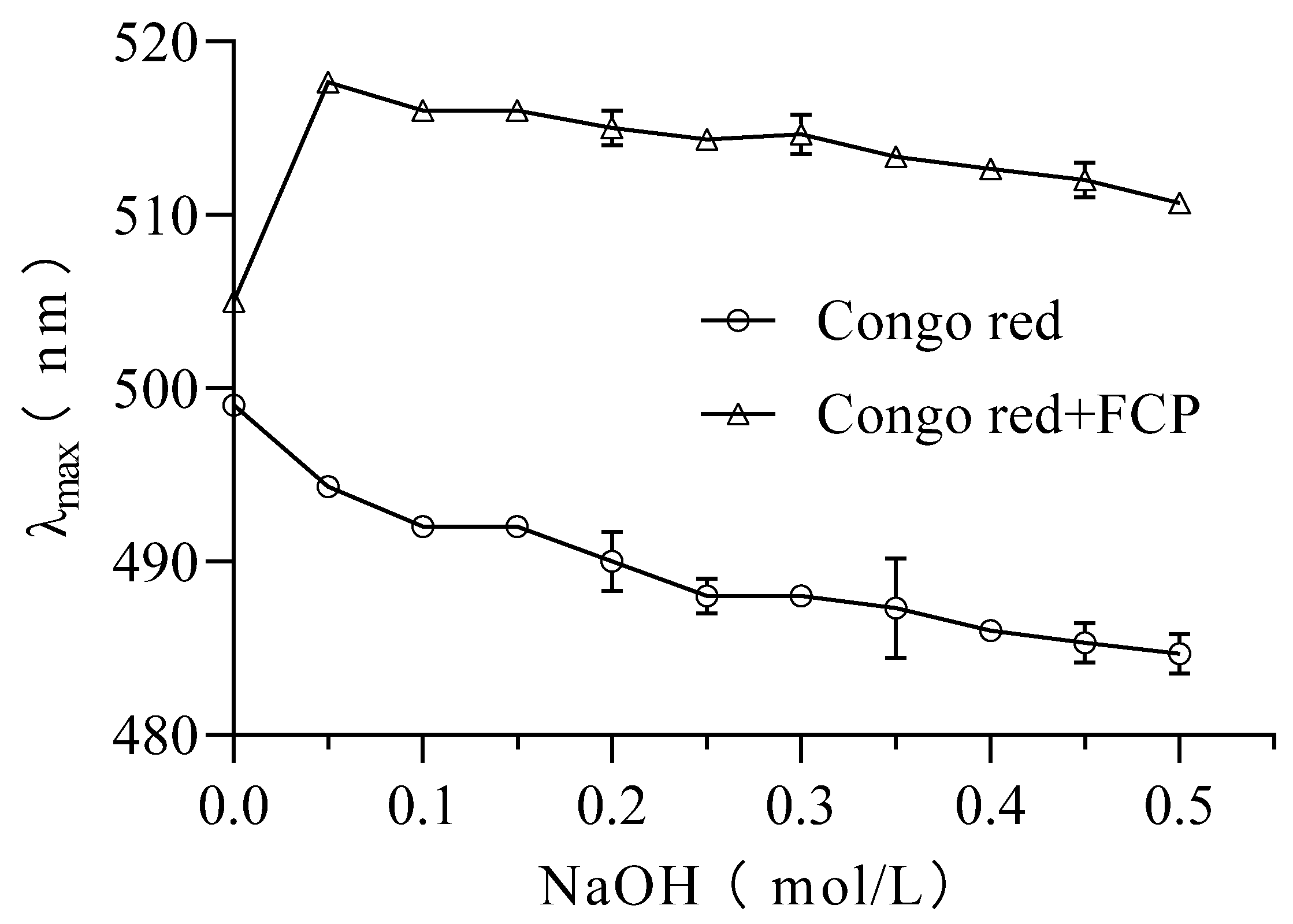
3.8. Congo red analysis
In this study, the Congo red assay was used to investigate the presence of triple helix structures in FCP[
27]. It is known that polysaccharides forming triple helixes can cause a red shift in the maximum absorption wavelength (λ max) of the Congo red polysaccharide complex. The results showed that the maximum wavelength of UV-Vis absorption of FCP +Congo red complex increased from 505 nm to 517 nm in the absence of NaOH (0.0 M)(
Figure 5). This shift of λ max indicates the presence of a triple helix structure in FCP[
38].
3.9. Immunomodulatory activity in vitro
3.9.1. Assessment of cell proliferation
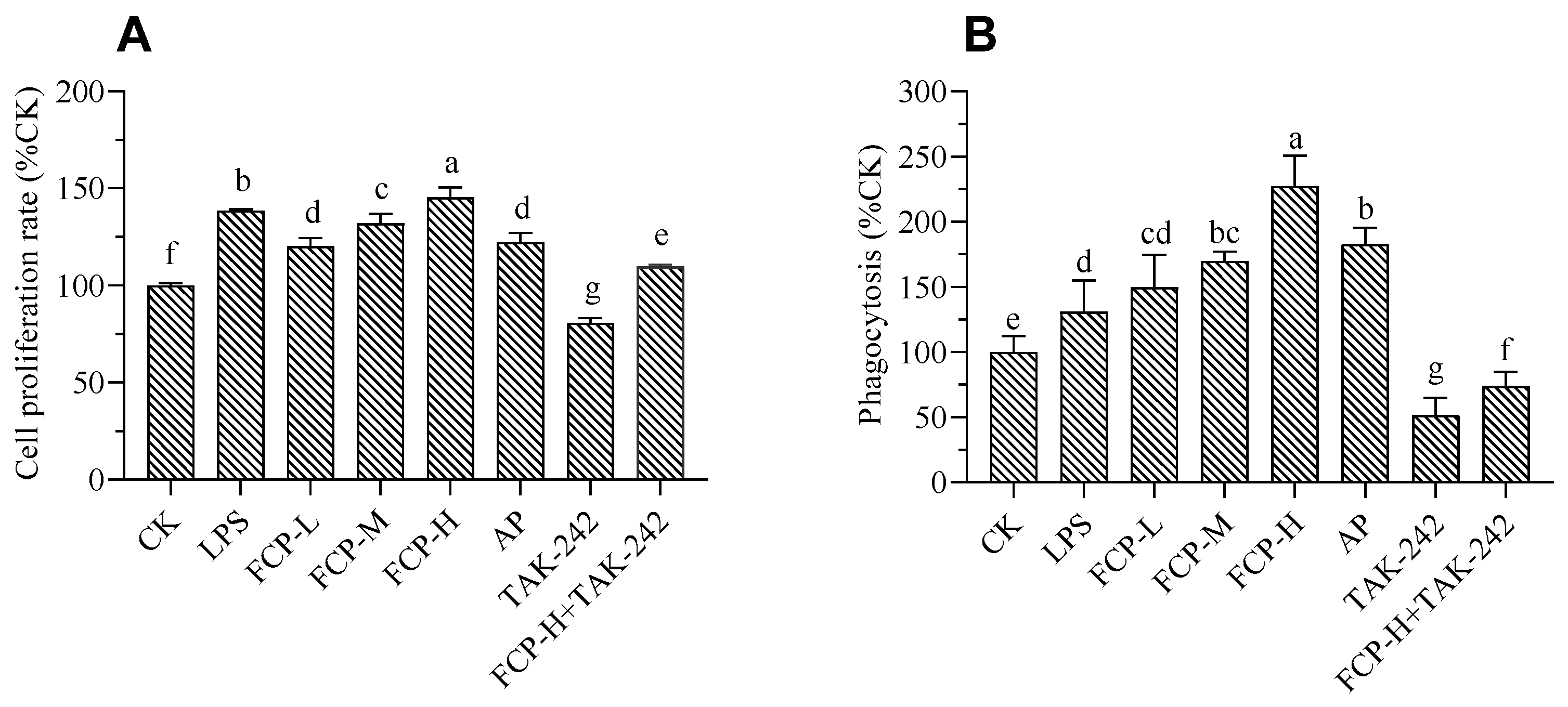
The results shown in
Figure 6A indicate that the tested concentrations of FCP did not have any impact on the viability of the cells. Moreover, the cells that were treated with FCP demonstrated a noteworthy enhancement in their viability when compared to the cells that were not treated. These results suggest that FCP does not induce cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 macrophages and may even promote cell viability. At the same time, treatment with TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 can markedly restrain cell viability, while FCP+TAK-242 can markedly promoted cell viability.
3.9.2. Assay of phagocytosis.
As shown in
Figure 6B, FCP could enhance the phagocytosis of macrophages, this suggests that FCP has a stimulatory effect on the phagocytic ability of macrophages during the immune response. At the same time, treated with TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 could markedly restrain phagocytic on macrophages, while FCP+TAK-242 could markedly stimulate phagocytic on macrophages.
3.9.3. Determination of NO
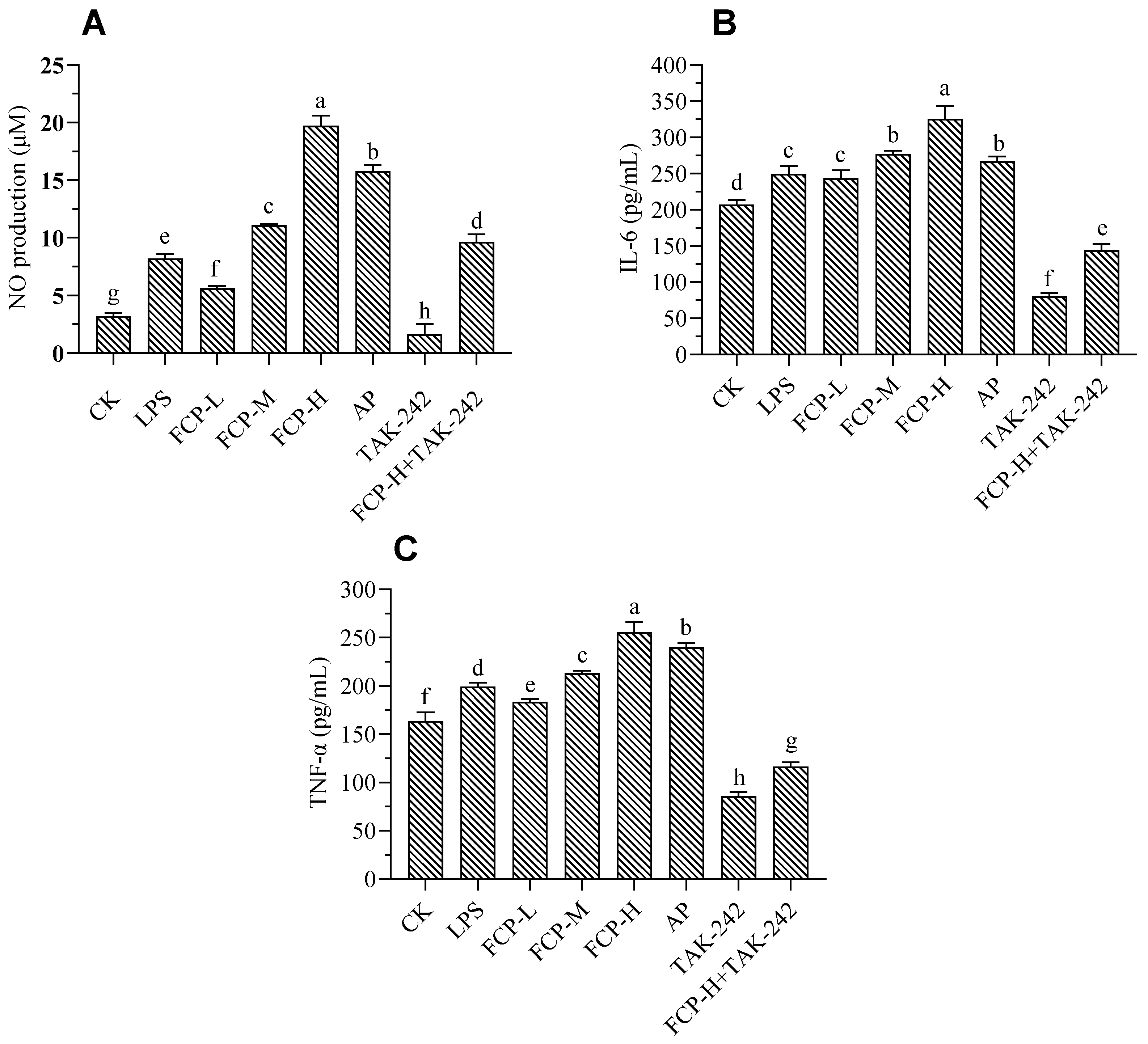
The production of NO by macrophages is an essential defense mechanism that helps eliminate pathogens and control tumor growth. It underscores the critical role of macrophages in the immune system's ability to fight infection and control tumor development.[
32].After treatment of the cells with FCP, the culture supernatants were collected and the nitrite content was determined (
Figure 7A). From
Figure 7A, it was evident that treatment with different concentrations of FCP significantly increases nitric oxide production with dose-dependent. Moreover, treated by TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 could significantly decrease the release of nitric oxide on macrophages, whereas FCP +TAK-242 can significantly increase the release of nitric oxide on macrophages.
3.10. Immunomodulatory activity in vivo
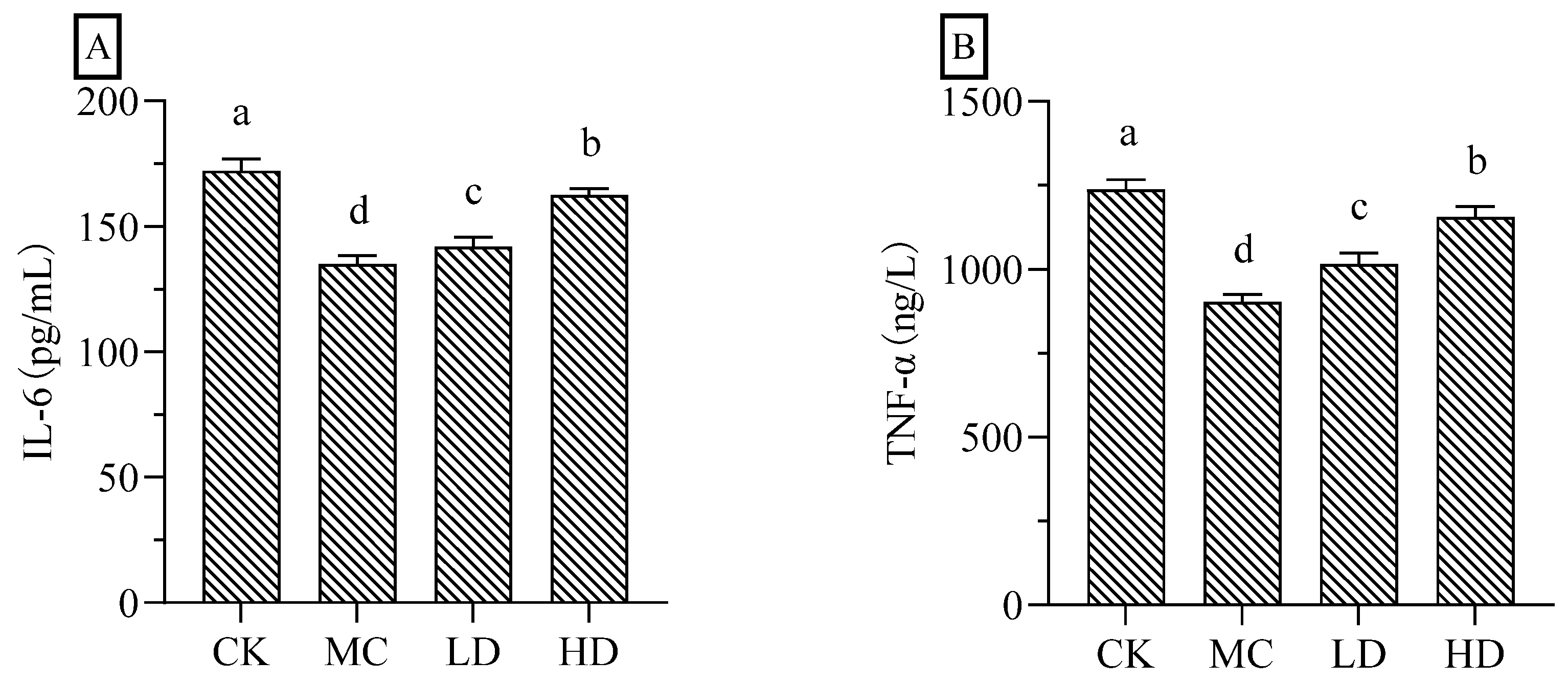
As shown in
Figure 8, the serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the model group of mice were significantly reduced compared with those in the normal group; and the high dose group of fig polysaccharides significantly increased the serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the CTX-induced immunosuppressed mice compared with the model group. These two results indicate that fig polysaccharide can improve the cellular immune function of CTX-induced immunosuppressed mice, and has strong immunomodulatory function.
4. Discussion
Ficus carica L., has recently attracted more attention as a component of Chinese medicine and as a food for health purposes. Reports about 'Brunswick' Ficus carica L on the chemical composition and pharmacological mechanisms are currently limited. This study aimed to address this knowledge gap by employing sevag and ultrafiltration purification techniques to identify and characterize a polysaccharide from the plant, which was subsequently designated as FCP. FCP is a heteropolysaccharide consisting of galacturonic acid (GalA), arabinose (Ara), galactose (Gal), rhamnose (Rha), glucose (Glu), and xylose (Xyl) with the molar ratios of 0.321:0.287:0.269:0.091:0.013:0.011, and its molecular weights of 127.5 kDa. In vitro experiments revealed that FCP directly stimulated the activation of RAW 264.7 macrophages. In vivo data indicated FCP possessed immune-enhancing effect in vivo to alleviate immunosuppression which could be considered as a functional component and an immunological modulator in the food nutrition industry.
In a previous study, Du et al reported the composition of polysaccharides from common
Ficus carica L., which primarily consisted of five monosaccharides: rhamnose, arabinose, galactose, glucose, and mannose with ratios of these monosaccharides were found to be 2.69:23.85:49.68:3.74:1.00, respectively[
15].Besides, Chen et al reported the presence of two polysaccharide fractions derived from
Ficus carica L. The first fraction, FPs-1-1, primarily consisted of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose, and galactose, with molar percentages of 6.57:8.25:4.79:18.93:54.82:6.64, respectively[
39]. The second fraction, FPs-2-1, primarily consisted of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose, and galactose, with molar percentages of 22.21:33.24:7.26:3.21:10.19:23.89, respectively[
39]. The observed differences in polysaccharide composition of
Ficus carica L. in these results could be due to differences in extraction methods and the specific species used as starting material. In our present study, a specific species of ‘Brunswick’
Ficus carica L. was used, however, the above two previous studies just purchased common figs from the local market without designated a specific species. At the time, the above two previous studies indicate that galactose was relatively high content of fig polysaccharides which in line with our present results, we also find a triple-helical structure in FCP, these features could potentially be valuable for chemical characterization and quality assurance of
Ficus carica L.
Although the chemical properties of polysaccharides from species of
Ficus carica L. were different, most of them possess immune modulatory capacities. As is known to all, macrophages are monocyte-derived phagocytes that play crucial parts in the innate immune system's defense and adaptive immune reactions, because phagocytic cells function in the host immune system as regulatory and immune effector cells[
40,
41,
42]. Polysaccharide from
Ficus carica L. was reported to increase proliferation, promote the phagocytic function, release of NO production and secretion of cytokines such as TNF-α and IL -6 by macrophages in vitro[
15], which is agree with our results. After FCP treatment, the proliferation, phagocytic function, NO production, TNF-α and IL-6 level were all dose-dependently increase. The Toll-like receptor (TLR) family plays a central role in the mammalian immune response as it constitutes a significant part of the primary response mechanism to infections. Previous studies have reported that polysaccharides can activate macrophages through Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)[
43]. In the present study, it was observed that FCP exhibited a symbolic impact on promote proliferation, phagocytic function, NO production, TNF-α and IL-6 level. Furthermore, it was found that FCP-induced macrophage activation was significantly inhibited in the presence of TLR4 inhibitors. which revealed FCP activate RAW 264.7 cells by binding the TLR4.
Cytokines are a class of small protein or glycoprotein molecules secreted by activated immune cells or certain non-immune cells that have a variety of biological functions[
44]. IL-6 is a humoral immunomodulatory factor secreted by Th2 cells and is one of the most essential immunoinflammatory mediators that regulate various cellular functions such as B and T cell proliferation and differentiation[
45].TNF-α is secreted predominantly by macrophages, although a number of other types of cells are also capable of producing it, inhibits viral replication, and enhances IL-2-mediated immunoglobulin production, NK cell activity and monocyte proliferation[
45]. The results of this experiment showed that compared with the model group, fig polysaccharide gavage intervention could alleviate the immunosuppressive state of mice by promoting the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α, thus exerting the function of regulating immunity. These results are consistent with previous findings[
18,
46].
As mentioned above, FCP showed a signification activation on macrophage, it could be applied as a new drug or nutrient food about enhance host immune system in future. However, to further investigate and develop FCP in immunomodulatory activity, FCP activate macrophage in immunomodulatory activity by which signaling pathway, like MAPKs, NF-kB or others signaling pathway. Although animal experiment was carried out in this study, but how fig polysaccharides are digested and absorbed in the body, and which genes are affected thus affecting the body's immune function, these issues need further study..
5. Conclusions
In summary, the current study showed that FCP was a heteropolysaccharide from ‘Brunswick’ Ficus carica L. with a molecular weights of 127.5 kDa, the composition of FCP was found to consist of galacturonic acid (GalA), arabinose (Ara), galactose (Gal), rhamnose (Rha), glucose (Glu), and xylose (Xyl) with molar ratios of 0.321:0.287:0.269:0.091:0.013:0.011. In the in vitro study, FCP showed a remarkable ability to increase phagocytosis and proliferation of RAW 264.7 macrophages, also promote the secretion of nitric oxide (NO), TNF-α and IL-6. In addition, significant involvement of TLR4 in macrophage activation was detected. Moreover, the in vivo based on CTX injection a classic modelling method were assessed and the results indicate that FCP showed significant increase serum pro-inflammatory factors in immunosuppressed mice. These results suggest that FCP has the potential to address immune deficiency and exert immunomodulatory effects as a functional dietary supplement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.-T.W. and W.Q.; methodology, L.Y.; software, L.Y.; validation, L.Y., Q.-Q.Z., S.L., Q.Z., J.Y., S.-X.L., D.-T.W. and W.Q.; formal analysis, L.Y.; investigation, L.Y., Q.-Q.Z., S.L., Q.Z., J.Y., S.-X.L., D.-T.W. and W.Q.; resources, W.Q.; data curation, L.Y. and W.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.-X.L. and W.Q.; visualization, L.Y. and W.Q.; supervision, W.Q.; project administration, W.Q.; funding acquisition, W.Q.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key R & D Project of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, grant number 20ZDYF0006 and 23ZDYF3041.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Giordano, C., L. Maleci, G. Agati, and R. Petruccelli. Ficus Carica L. Leaf Anatomy: Trichomes and Solid Inclusions. Annals of Applied Biology. 2020, 176, 47–54. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Q. Cao, J. Fan, and Y. Han. Optimization of Conditions for Extraction of Polysaccharide from Ficus Carica by Using Response Surface Methodology. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi. 2017, 29, 93–97.
- Uddin, M.S. A Review on Nutritional Values and Pharmacological Importance of Ficus Carica. Journal of Current Research in Food Science. 2021, 2, 07–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ayuso, M., M. Carpena, O. Taofiq, T.G. Albuquerque, J. Simal-Gandara, M.B.P. Oliveira, M.A. Prieto, I.C. Ferreira, and L. Barros. Fig “Ficus Carica L.” and Its by-Products: A Decade Evidence of Their Health-Promoting Benefits Towards the Development of Novel Food Formulations. Trends in Food Science Technology. 2022, 127, 1–13.
- Rahmani, A.H., and Y.H. Aldebasi. Ficus Carica and Its Constituents Role in Management of Diseases. Asian Journal Pharmaceutical Clinical Research. 2017, 10, 49–53. [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A. Nutritional and Pharmacological Importance of Ficus Carica-a Review. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy. 2017, 7, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakka, V.P., and T. Zhou. Carboxymethylation of Polysaccharides: Synthesis and Bioactivities. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 165, 2425–2431. [CrossRef]
- Huang, G., F. Chen, W. Yang, and H. Huang. Preparation, Deproteinization and Comparison of Bioactive Polysaccharides. Trends in Food Science. 2021, 109, 564–568. [CrossRef]
- Mzoughi, Z., A. Abdelhamid, C. Rihouey, D. Le Cerf, A. Bouraoui, and H. Majdoub. Optimized Extraction of Pectin-Like Polysaccharide from Suaeda Fruticosa Leaves: Characterization, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities. Carbohyd Polym. 2018, 185, 127–137. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Y. Sun, and G. Huang. Preparation and Antioxidant Activities of Important Traditional Plant Polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018, 111, 780–786. [CrossRef]
- Ai, J., B. Bao, M. Battino, F. Giampieri, C. Chen, L. You, C.L. Cespedes-Acuña, M. Ognyanov, L. Tian, and W. Bai. Recent Advances on Bioactive Polysaccharides from Mulberry. Food&Function. 2021, 12, 5219–5235. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, S., W. Yang, and G. Huang. Antioxidant Activities and Mechanisms of Polysaccharides. Chemical Biology Drug Design. 2021, 97, 628–632. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S., J. Hu, M. Li, S. Zhu, S. Guo, H. Guo, T. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, and J. Wang. The Role of Se Content in Improving Anti-Tumor Activities and Its Potential Mechanism for Selenized Artemisia Sphaerocephala Polysaccharides. Food & function. 2021, 12, 2058–2074. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLi, X.J., C. Chen, A.J. Leng, and J.L. Qu. Advances in the Extraction, Purification, Structural Characteristics and Biological Activities of Eleutherococcus Senticosus Polysaccharides: A Promising Medicinal and Edible Resource with Development Value. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Du, J., J. Li, J. Zhu, C. Huang, S. Bi, L. Song, X. Hu, and R. Yu. Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of a Novel Polysaccharide from Ficus Carica. Food & function. 2018, 9, 3930–3943. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X., Z. Xue, Y. Fang, X. Liu, Y. Yang, G. Shi, S. Feng, and L.J.F. Zhao. Structure–Immunomodulatory Activity Relationships of Hedysarum Polysaccharides Extracted by a Method Involving a Complex Enzyme Combined with Ultrasonication. Food & function. 2019, 10, 1146–1158. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-G., K.-W. Wang, Z.-R. Zhao, P. Zhang, H. Liu, G.-J. Zhou, Y. Cheng, W.-J. Wu, Y.-H. Cai, and B.-L. Wu. A Novel Polysaccharide from Dendrobium Devonianum Serves as a Tlr4 Agonist for Activating Macrophages. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019, 133, 564–574. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., B. Cai, J. Wang, Z. Sheng, H. Yang, D. Wang, J. Chen, and Q. Ning. Mulberry Leaf-Derived Polysaccharide Modulates the Immune Response and Gut Microbiota Composition in Immunosuppressed Mice. J Funct Foods. 2021, 83, 104545. [CrossRef]
- Tian, B., R. Liu, T. Xu, M. Cai, R. Mao, L. Huang, K. Yang, X. Zeng, and S. Peilong. Modulating Effects of Hericium Erinaceus Polysaccharides on the Immune Response by Regulating Gut Microbiota in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. J Sci Food Agr. 2023, 103, 3050–3064. [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.-R., H.-Y. Li, G. Du, S. Lin, R. Hu, H.-Y. Li, L. Zhao, Q. Zhang, H. Chen, and D.-T. Wu. Structural Characteristics, Rheological Properties, and Biological Activities of Polysaccharides from Different Cultivars of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus) Collected in China. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019, 139, 459–467. [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.U., I.U. Kakar, M.Z. Mehboob, S. Zada, H. Soomro, M. Umair, I. Iqbal, M. Umer, S. Shaheen, and S.F. Syed. A Review on Polysaccharides from Artemisia Sphaerocephala Krasch Seeds, Their Extraction, Modification, Structure, and Applications. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 252, 117113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M., K. Gilles, J. Hamilton, P. Rebers, and F. Smith. A Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Sugars. Nature. 1951, 168, 167–167. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenkrantz, N., and G. Asboe-Hansen. New Method for Quantitative Determination of Uronic Acids. Analytical biochemistry. 1973, 54, 484–489. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S., K. Ming, N. Ma, J. Sun, D. Wang, M. Ding, and Y.J.J.o.F.F. Ding. Portulaca Oleracea L. Polysaccharide Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Barrier Dysfunction in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Monolayers. J Funct Foods. 2022, 91, 104997. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, S., R.E. Kenari, Z.R. Amiri, F. Sohbatzadeh, and M.H.H.J.I.J.o.B.M. Khodaparast. Effect of Ultrasound-Assisted Cold Plasma Pretreatment on Cell Wall Polysaccharides Distribution and Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Hyssop (Hyssopus Officinalis L.). Int J Biol Macromol. 2023, 233, 123557. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y., F. Li, Y. Ding, H.-Y. Li, X.-R. Xiang, Q. Ye, J. Zhang, L. Zhao, W. Qin, R.-Y. Gan, and D.-T. Wu. Polysaccharides from Loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica) Leaves: Impacts of Extraction Methods on Their Physicochemical Characteristics and Biological Activities. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 146, 508–517. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L., J. Liu, X. Xia, I.N. Wong, S.K. Chung, B. Xu, H.R. El-Seedi, B. Wang, and R. Huang. Sulfated Heteropolysaccharides from Undaria Pinnatifida: Structural Characterization and Transcript-Metabolite Profiling of Immunostimulatory Effects on Raw264. 7 Cells. Food Chemistry: X. 2022, 13, 100251.
- Fu, Y., K.-L. Feng, S.-Y. Wei, X.-R. Xiang, Y. Ding, H.-Y. Li, L. Zhao, W. Qin, R.-Y. Gan, and D.-T. Wu. Comparison of Structural Characteristics and Bioactivities of Polysaccharides from Loquat Leaves Prepared by Different Drying Techniques. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 145, 611–619. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zongo, A.W.-S., D. Zogona, Z. Zhang, M. Youssef, P. Zhou, Y. Chen, F. Geng, Y. Chen, J. Li, B.J.F. Li, and Function. Immunomodulatory Activity of Senegalia Macrostachya (Reichenb. Ex Dc.) Kyal. & Boatwr Seed Polysaccharide Fraction through the Activation of the Mapk Signaling Pathway in Raw264. 7 Macrophages. Food & Function. 2022, 13, 4664–4677. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z., Q. Sun, L. Chang, J. Peng, M. Zhang, X. Ding, Q. Zhang, G. Liu, X. Liu, and Y.J.F.C. Lan. A Natural Anti-Obesity Reagent Derived from Sea Buckthorn Polysaccharides: Structure Characterization and Anti-Obesity Evaluation in Vivo. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131884. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X., K. Liu, S. Yin, Y. Qin, P. Shen, and Q.J.A. Peng. A Novel Pectic Polysaccharide of Jujube Pomace: Structural Analysis and Intracellular Antioxidant Activities. Antioxidants. 2020, 9, 127. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., J. Mo, W. Xiang, X. Shi, L. Guo, Y. Li, Y. Bao, and L. Zheng. Immunoregulatory Effects of Tetrastigma Hemsleyanum Polysaccharide Via Tlr4-Mediated Nf-Κb and Mapk Signaling Pathways in Raw264. 7 Macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114471.
- Tabarsa, M., S. You, K. Yelithao, S. Palanisamy, N.M. Prabhu, and M. Nan. Isolation, Structural Elucidation and Immuno-Stimulatory Properties of Polysaccharides from Cuminum Cyminum. Carbohyd Polym. 2020, 230, 115636. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F., Y. Wei, L. Liang, L. Huang, G. Yu, and Q. Li. A Novel Low-Molecular-Mass Pumpkin Polysaccharide: Structural Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and Hypoglycemic Potential. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 251, 117090. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X., J. Qi, C.-T. Ho, B. Li, J. Mu, Y. Zhang, H. Hu, W. Mo, Z. Chen, and Y. Xie. Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of a Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Ganoderma Leucocontextum Fruiting Bodies. Carbohyd Polym. 2020, 249, 116874. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S., G. Huang, and G. Chen. Extraction, Structural Analysis, Derivatization and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from Chinese Yam. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130089. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Nokab, M.E.H., and P.C. Van Der Wel. Use of Solid-State Nmr Spectroscopy for Investigating Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels: A Review. Carbohyd Polym. 2020, 240, 116276. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., B. Huang, B. Yang, L. Ye, J. Zeng, Z. Xiong, Y. Chen, S. Guo, Y. Yang, and W. Ma. Structural Elucidation of a Novel Polysaccharide from Ophiopogonis Radix and Its Self-Assembly Mechanism in Aqueous Solution. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134165. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R., H. Li, S. Li, C. Jin, and J. Lu. Extraction Optimization, Preliminary Characterization and Immunological Activity of Polysaccharides from Figs. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015, 72, 185–194. [CrossRef]
- Yin, X., X. Zhuang, W. Luo, M. Liao, L. Huang, Q. Cui, J. Huang, C. Yan, Z. Jiang, and Y.J.F.i.I. Liu. Andrographolide Promote the Growth and Immunity of Litopenaeus Vannamei, and Protects Shrimps against Vibrio Alginolyticus by Regulating Inflammation and Apoptosis Via a Ros-Jnk Dependent Pathway. Frontiers in Immunology. 2022, 13.
- Park, W.S., J. Lee, G. Na, S. Park, S.-K. Seo, J.S. Choi, W.-K. Jung, and I.-W.J.I.J.o.M.S. Choi. Benzyl Isothiocyanate Attenuates Inflammasome Activation in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lps-Stimulated Thp-1 Cells and Exerts Regulation through the Mapks/Nf-Κb Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23, 1228.
- Huang, Z., Y.-J. Zeng, X. Chen, S.-Y. Luo, L. Pu, F.-Z. Li, M.-H. Zong, and W.-Y. Lou. A Novel Polysaccharide from the Roots of Millettia Speciosa Champ: Preparation, Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 145, 547–557. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X., R. Zeng, J. Qi, C.-T. Ho, B. Li, Z. Chen, S. Chen, C. Xiao, H. Hu, and M.J.F.C.X. Cai. Immunoregulatory Activity of a Low-Molecular-Weight Heteropolysaccharide from Ganoderma Leucocontextum Fruiting Bodies in Vitro and in Vivo. Food Chemistry: X. 2022, 14, 100321. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M., Y. Song, M.C. Martínez-Cuesta, C. Peláez, E. Li, T. Requena, H. Wang, and Y. Sun. Immunological Activity and Gut Microbiota Modulation of Pectin from Kiwano (Cucumis Metuliferus) Peels. Foods. 2022, 11, 1632. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M., Y. Sun, Y. Bai, J. Xu, J. Sun, L. Han, H. Sun, and R. Han. A Polysaccharide from Pleurotus Citrinopileatus Mycelia Enhances the Immune Response in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Mice Via P62/Keap1/Nrf2 Signal Transduction Pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023, 228, 165–177. [CrossRef]
- Xie, H., J. Fang, M.A. Farag, Z. Li, P. Sun, and P. Shao. Dendrobium Officinale Leaf Polysaccharides Regulation of Immune Response and Gut Microbiota Composition in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. Food Chemistry: X. 2022, 13, 100235. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).