1. Introduction
Digital Twins (DT) are virtual representations of real-world objects [
1]. Digital twins can enhance the performance of thematic systems such as City Information Modeling (CIM) [
2], Building Information Modeling (BIM) [
3], Land Information Modeling (LIM) [
4], and Tree Information Modeling (TIM) [
5]. These systems support real-time monitoring and management of spatial objects to achieve sustainable development in a rapidly changing world [
4,
6,
7]. Such systems are developed with the use of new technologies [
1,
2,
8,
9] that exchange data with digital twins [
10]. Data collection systems and automated systems for generating digital models in real-time are needed to develop and update the digital twins [
11]. Over recent years, the growing demand for geospatial monitoring systems and data collection and processing tools that take advantage of machine learning and deep learning algorithms has contributed to significant technological progress [
12,
13,
14,
15].
CIM is a digital tool for visualizing the urban environment. BIM is already used in new construction projects. Existing buildings that were developed without BIM models are implemented in CIM by generating point cloud models based on lidar data [
14,
16,
17] combined with Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) [
18] and indoor scanning [
19] data. Since rather recently, 3D models of buildings at LOD2 have been widely generated [
20,
21,
22] with the use of lidar data, satellite images, and deep learning algorithms [
20,
23,
24]. TLS and lidar data are used to develop LOD3 models of buildings that play an important role in urban space [
25,
26,
27,
28]. Novel solutions for automating the generation of LOD3 building models have been reported in the literature [
29,
30].
Digital twin models recognize the importance of vegetation and trees not only in urban spaces. Real-world trees and forests are represented with the use of TIM [
5,
13,
31] and Forest Digital Twin (FDT) models [
8,
13]. Based on the CityGML standard, trees can be modeled at LOD0 through LOD4 level of detail [
32,
33,
34,
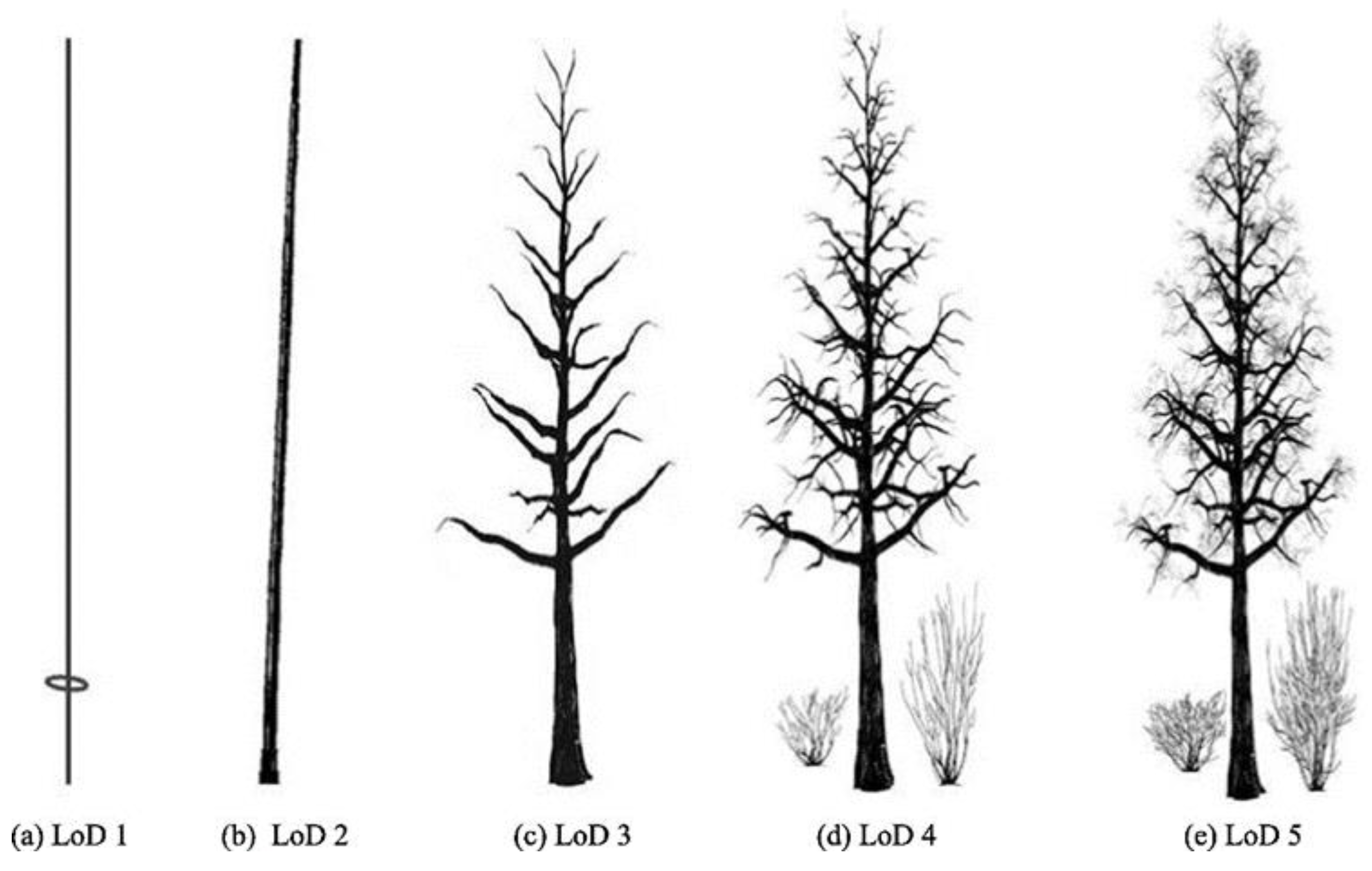
35]. An LOD0 model is a 2D horizontal boundary presenting the position and size of a tree, while an LOD1 model is a 2.5D extruded solid presenting the tree height or root depth. As shown in
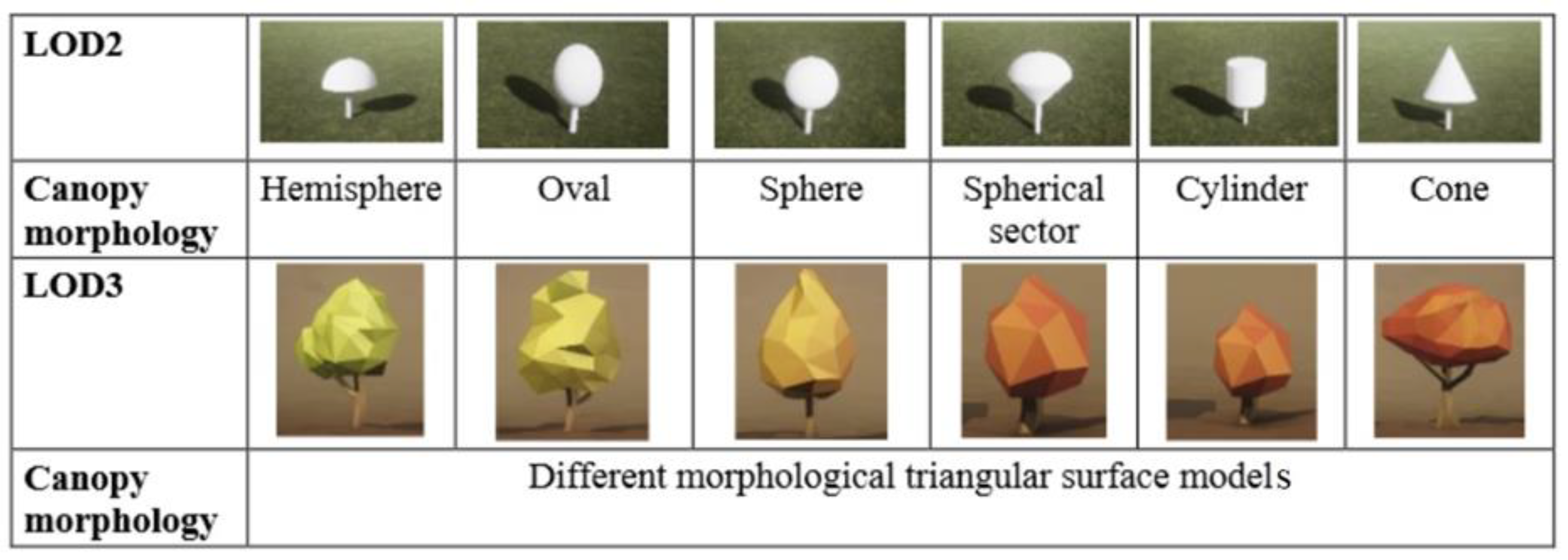
Figure 1, an LOD2 model is a simple 2D solid with coarse morphology, whereas an LOD3 model represents the morphological structure of a complex 3D solid. A LOD4 model is a detailed representation of the structured and semantic components of a 3D solid [
32,
34]. In contrast to the above surface-based modeling, Liang et al. [
35] use trunk and branches to capture different details in a tree model (
Figure 2). They proposed models from LOD1 to LOD5. The most detailed 3D tree model is at LOD5, where the leaves are included in the modeling.
The proposed approach in this paper aims to model tree trunks from lidar point cloud. In this context, the novelty and the contribution of this paper can be summarized as follows:
Highly accurate trunk modeling approach, which can be easily visualized and integrated within 3D scenes regarding its light memory volume.
Automatic discrimination between the point clouds of tree crown and trunk, which helps to model and analyze them independently.
Analysis of the tree trunk geometric shapes, which can provide a deep comprehension supporting the modeling stage.
2. Literature review
TIM systems support the planning and management of vegetation in a city and beyond. These solutions can be deployed to manage tree stands by monitoring individual trees. Individual trees are identified and modeled with the use of remote sensing methods that rely on point clouds of airborne lidar and TLS data [
35,
36], as well as multispectral photogrammetric data [
6,
37,
38,
39]. Different subsets of the dataset describing individual trees are created through splitting to generate 3D models of dendrological objects [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45] or even to identify tree species [
46]. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to classify and segment these subsets [
11,
47]. Very high-resolution images with deep learning-based object detection can enhance the accuracy of automatic tree detection and tree counting [
48,
49]. Models of individual trees are required to describe the basic attributes of trees [
35,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55] as well as entire forests [
48]. These models are essential in forestry [
56] because they can facilitate decision-making in sustainable forestry practice, as well as estimating forest biomass yields [
57,
58,
59].
Efficient and simple solutions for fully automated tree modeling are being sought. There are two groups of methods for generating LOD2 and LOD3 tree models. In the first group, trees are modeled mainly based on canopy, and the trunk is represented by a vertical line extending from the center of the canopy projection or a selected vertex of the canopy [
35]. In these methods, the process of modeling the space between neighboring trees with overlapping canopies may be problematic [
38,
40,
49,
50,
51]. The canopy is modeled by layering the subsets describing the identified sets of lidar points within the adopted range of height values [
49,
60,
61]. In these subsets, the external contours of tree canopies are created at different heights, and these contours are merged to generate simplified [
33,
34] or detailed 3D solids to represent tree canopies. These structures are developed with the use of slices, 3D convex hull, 3D alpha shape, and voxel-based algorithms [
62]. These techniques have been already automated. Dai and Li [
63] and Tockner et al. [
64] proposed various approaches for automating the generation of LOD3 tree models based on the measured parameters and attributes. The developed 3D models rely on the boundary points of the space surrounding physical trees.
The Polish Tree Crown Map [
65] was created in Poland. The map was developed based on Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) data and machine learning methods. Simplified, circle-shaped canopies were used to generate LOD0 models, and 3D solids were used to develop LOD2 models. Other tree parameters, such as heights, trees, surface and crown volume, were described based on lidar data.
Tarsha Kurdi et al. [
66] proposed a unique solution for automating the generation of tree models based on layers of lidar point cloud data. The point cloud of a tree is represented by multiple horizontal layers, each of which is divided into angular sectors. Trees are represented by sectoral layer structures, rather than solid contours. This way, canopies can be visualized with the use of transparent structures that are determined by the distribution of lidar points in the canopy. The resulting 3D models are represented in matrix format.
In the trunk-based modeling approach, the skeletons of trunks and branches are extracted from the point cloud [
60]. Skeletons can be also modeled at different levels of detail. Liang et al. [
35] proposed a classification of tree models at five levels of detail, from LOD1 to LOD 5 (Figure. 2). LOD1 is the simplest tree model represented by two basic parameters: Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) and tree height. LOD2 is a 3D model of the tree trunk. LOD3 is a detailed representation of second-order branches that are directly connected to the trunk. LOD4 contains additional details, including third-order branches that are connected to second-order branches. LOD5 is the most detailed 3D model of a tree that can incorporate leaves. Trunks and branches are modeled based on TLS data as well as ALS data acquired by drones and planes. These models are difficult to generate based on a single source of data. The modeling of tree trunks is done in fragments based on horizontal subsets of the point cloud. [
63,
64]. The modeling process begins with the lower part of the trunk. Second- and third-order branches are modeled in successive steps, and leaves can also be incorporated into the model. The extracted subsets of points are used to model the cross-section of the trunk or trunks for multi-stem trees. Based on these data, a graph structure is generated by topologically arranging the central points of the layered segments of trunks and branches [
67,
68,
69]. Huang et al. [
70] built a connection chain of tree skeletons with the use of a machine learning clustering algorithm. The proposed concept relied on foliage clumps composed of trunks and first-order branches.
In concluding, trunk and branch models play an important role in analyses of tree structure [
71,
72] and monitoring changes in tree stands. A tree's age and growth stage can be determined based on the increment in trunk and branch size. The results can be used to identify mature trees that are ready for harvest and processing. 3D models describing the structure of a tree should be automated.
3. Datasets
Two datasets are used in this paper. The first one was obtained by terrestrial laser scanning and the second by drone lidar. Concerning the terrestrial data, a static Z+F IMAGER 5016 3D laser scanner is utilized to realize the scan on 25 October 2023 (in the spring season of Queensland, Australia). The main characteristics of this scanner are shown in
Table 1. Concerning the point density, it varies regarding the overlap or non-overlap areas, the distance from the scanning station, and the geometric shape of the scanned object. However, the mean distance between neighboring points by considering the laser spot radius is equal to 4 mm.
The airborne dataset was collected by an Unmanned Aircraft Vehicle (UAV) platform on 28 February 2023 (in the summer season of Queensland, Australia). For this object, a DJI M300 RTK (UAV) carrying the TrueView 515 lidar flew the payload. The average flying height is 50 m above the ground, and the average point density is 250 point/m2. The tested tree point clouds are extracted from the terrestrial and drone datasets.
4. Trunk geometry analysis
This paper uses the above two datasets to demonstrate our methodologic development on trunk point cloud extraction and modelling. Before illustrating the suggested trunk modeling algorithm, it is necessary to analyze and describe the expected trunk geometry. Furthermore, the differences between the trunk and the crown point clouds should be underlined. Therefore, the question of the distinguishability of the trunk point cloud must be discussed first.
4.1. Distinguishability of trunk point-cloud
The lidar tree point cloud represents typically the up-ground parts of the tree, which are the tree crown and the tree trunk. These two parts together represent the tree's upper biomass. In laser scanning, the tree crown is the main part of the trees because it holds the tree brunch, leaves, and maybe the flowers and fruits. In general case, the tree crown footprint diameters are much bigger than those of the trunks [
66]. The proportion of the crown/trunk diameter can be reduced in very few species such as the palms and the bamboos. In fact, in either terrestrial or airborne laser scanning, the tree crown will be visible and distinguishable in all cases of tree point clouds. Whereas the tree trunks can be missed because the laser rays cannot arrive at the tree trunk, or the tree trunk or part of it is occluded by obstacles such as grasses, tree branches, and leaves. As such, trunk points cannot be distinguished from the other surrounding points, e.g., in airborne laser scanning a high percentage of cases exist where the tree trunks are indistinguishable. In
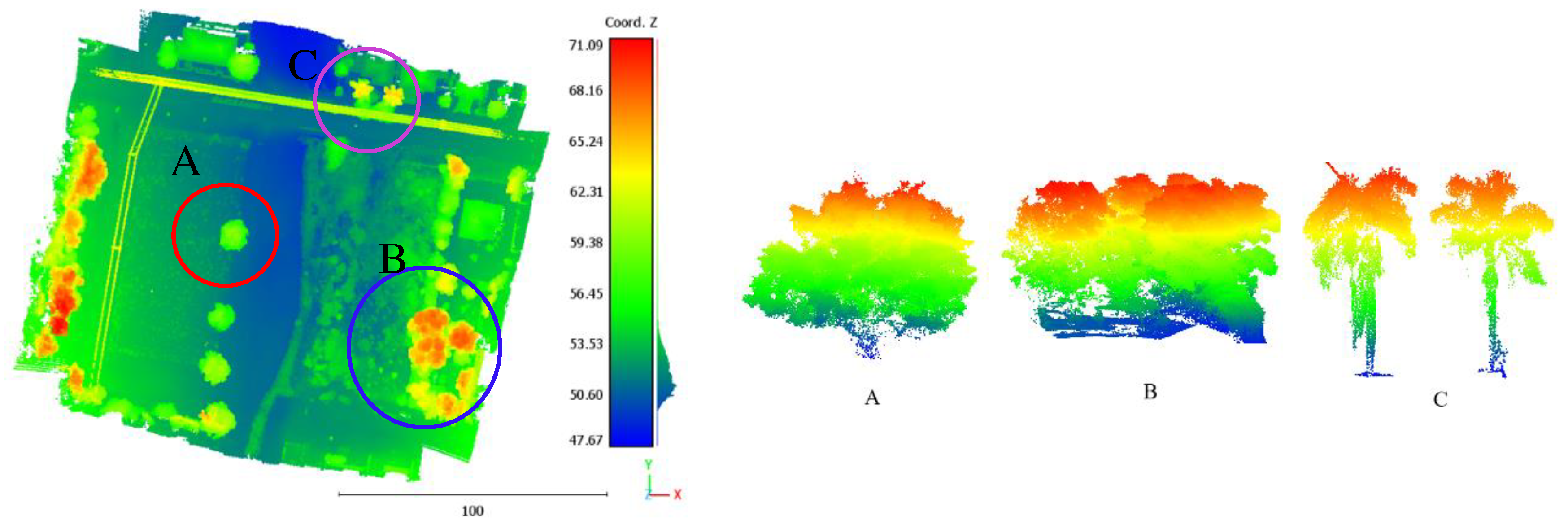
Figure 3, it can be noted that there are individual trees as well as groups of connected trees. Though the point density is very high (250 point/m2), because the scanning was realized by using a drone from a fly height of about 50 m, most of the scanned tree trunks are not distinguishable except for palm trees and a few other ones.
In this context, several factors can play an important role in trunk distinguishability. Clearly, the scanning point density plays an important role in this matter. When the point density increases, the number of laser pulses that penetrate the canopy towards the tree trunk is greater and vice-versa. Besides density, the intrinsic properties of the trees and their geometry to the scanner will also affect the visibility of trunks. First, when the tree is located near the footprints of the flying trajectory, the probability of the trunk appearing decreases since the direction of the laser beams is almost parallel to the trunk. Alternatively, on the edges of the swath far from the flying trajectory, the chance of the trunk appearing increases. Second, the volume of the tree crown and the density of its leaves also affect the visibility of trunks. When the leaf density is high, the penetration of the laser pulse through the canopy to reach to the tree trunk will have a minimal chance. Thirdly, there is interference between the tree structure and the season of the year. Indeed, for deciduous forests in winter and autumn seasons, the laser penetration through the canopy toward the trunk will be easier. Fourth, the ratio of crown height to trunk height represents a major factor. When this ratio is high, the substantial part of the tree trunk may become invisible. As an example, a long and uncovered trunk such as palm trees can provide a good visibility for laser scanning. Finally, when one tree belongs to a group of connected trees, the neighboring trees may present obstacles between the laser scanner and the tree trunk.
In contrast, the distinguishability of tree trunks in terrestrial laser scanning is much higher than in airborne laser scanning, because terrestrial scanning is realized on the land where the laser beams can travel, for most of the time, under the crown levels. Whatever the laser scanning kind, the requested tree modeling algorithm must be able to automatically check if the trunk is distinguishable or not. At this stage, it is important to analyze the trunk geometric forms.
4.2. Trunk geometry
In the context of single tree trunk modeling from lidar data, it is necessary to understand what the tree trunk definition is and what the expected geometric forms of tree trunks are. According to the Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English online [
73], a tree trunk is the thick central woody stem of a tree. It has been seen in
Section 4.1 that the trunk point cloud can be distinguishable or not from the point cloud of the tree. If the trunk point cloud is distinguishable, the envisaged tree modeling function must automatically recognize the trunk points and separate them from the crown points so that they can be modeled separately regarding their different geometries. Afterwards, the two models can be grouped together to obtain the total up-ground tree model. Indeed, the trunk surface geometry is completely different from the crown component geometry. The trunk surface is continuing and approximately straight or twisted cylindrical, whereas a tree crown has irregular, noncontinuous surfaces that are produced by its components such as leaves, branches, flowers, and fruits. Considering a specific trunk, though the trunk may be oblique or twisted, its cross-section can be an approximate circle or circular arc (see
Figure 4b). On the other hand, the crown cross-section is an approximate circular disc containing gaps. Moreover, the lidar point may cover the trunk completely or partially according to the scanning technology and strategy.
However, trees can be classified according to the number of trunks into three categories, tree of single trunk, tree of multiple trunks, and tree of forked trunk (
Figure 5). Opposite to the single-trunk tree, the multiple-trunk tree has several stems where a forked-trunks may be present among them. From another viewpoint, the trunk verticality can be considered to classify the tree trunks where three kinds of trunks can be distinguished: vertical, oblique, and twisted trunks (
Figure 5). In fact, the last two classifications can be used together to describe a tree, e.g., it can be said a vertical single-trunk tree and an oblique single-trunk tree. At this point, it is important to note that the boarders between two kinds of tree trunks may not be always clear, e.g., the tree illustrated in
Figure 5a and
Figure 3f can be classified as a forked trunk tree and as a multiple trunk tree. This confusion can happen regarding the huge diversity of tree geometric forms. Nevertheless, it is necessary to create this categorical classification to facilitate the task and discussion of trunk modeling. Once the tree trunk geometry is analyzed and discussed, the trunk modeling algorithm will be detailed in the next section.
5. Suggested trunk modeling approach
As it was mentioned in
Section 4.1, the above-ground tree biomass could be classified into two classes: the tree crown and the tree trunk. In the context of tree modeling, though the tree trunk may be sometimes indistinguishable. The developed trunk modeling approach should consider its particular geometry, which is different from the tree crown geometry. This paper proposes a new algorithm that focuses on trunk modeling. As illustrated in
Figure 6, the input of the suggested approach is the 3D lidar tree point cloud and the output is the 3D tree trunk model. The suggested trunk modeling algorithm starts by extracting the trunk point cloud from the tree point cloud. Thereafter, the trunk point cloud is further segmented into multiple single stem point clouds. Finally, the last step constructs a 3D model of each individual tree stem.
5.1. Extraction of trunk point cloud
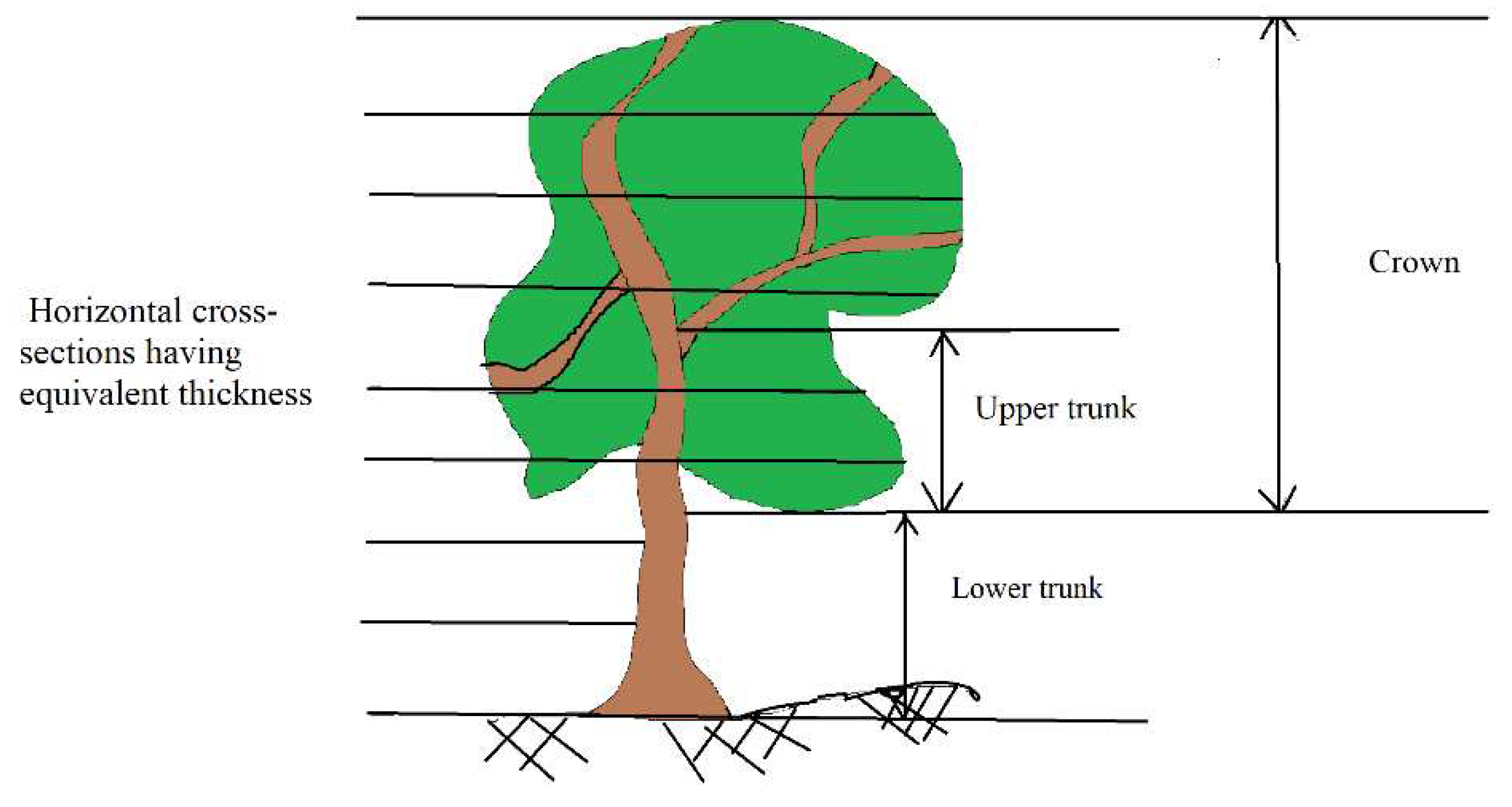
To extract the trunk, point cloud, one tree trunk may be divided into two parts: the upper trunk part that is surrounded by branches and leaves, and the lower trunk part, which is not surrounded by branches and leaves, and is normally located in the lower part of the tree (
Figure 7). In this section, trunk point cloud extraction means the extraction of the lower trunk point cloud.
The proposed trunk modeling approach as shown in
Figure 6 consists of three main steps. After extracting the trunk point cloud, the tree trunk stems are segmented into single stems, which are then modeled separately.
In the context of the calculation of the trunk model, the trunk point-cloud should be first extracted from the complete tree point cloud. For this purpose, two features will be used. The first feature is the trunk radius which must be significantly smaller than the tree footprint radius. To calculate the footprint radius, the middle of the bounding box of the projected point cloud on the horizontal plane (OXY) is determined. The basic assumption is that the Z axis of the coordinate system is vertical and the XY plane is horizontal. Thereafter, the maximum distance between the middle point and the footprint points is calculated. This value will be used later to calculate two thresholds. The first threshold is named Trunk Radius THreshold (TR
TH) and the second one is named Tolerated Trunk radius Threshold (TTr
TH) (Equations 1 and 2).
where MFR is the Maximum Footprint Radius value. The coefficient (0.3) in Equation 1 is considered according to Tarsha Kurdi et al. [
66]. In Equation 2, which represents a tolerant threshold, the coefficient value is increased (becomes more tolerated) because the applied clause in this case will consider the footprint radius value and the number of cross-section points simultaneously.
The second feature is the number of points located within a trunk horizontal cross-section. From
Figure 4, it can be noticed that the number of points located within a crown point cloud cross-section is much greater than a similar cross-section of the trunk point cloud. At this stage, a threshold is determined to compare the number of trunk cross-section points, named maximum Trunk Cross-section Number of Points (TCNP), where its value depends on the number of points of maximum crown cross-section points. To calculate the TCNP value, the tree point cloud is divided into a list of horizontal cross-sections having equivalent thickness (
Figure 7), e.g., the cross-section thickness equals 20 cm. The horizontal cross-section containing the greatest number of points is considered for assigning the TCNP threshold value (Equation 3).
where PD is the point density, the coefficient (0.63) is calculated by considering the trunk cross-section geometric form is cylindrical, then the expected number of lidar points distributed on this surface equals 0.2×2×π× 0.5 ×PD=0.63×DP, where 0.5 m is the expected value of the tree trunk radius.
After descending sorting of the tree point cloud according to the Z coordinate values, the last four points of the tree point cloud are assigned to the trunk section. Then, the mean location of the selected points is calculated. Afterwards, the distance between the selected points and the mean is calculated. If the maximum of these distances is greater than TRTH, then another test is carried out. If the maximum distance is greater than TTrTH or the number of the trunk considered points is greater than TCNP, this operation stops, otherwise the next upper point is added to the selected trunk points, and the same procedure repeats.
The number of trunk points is used to control the loop. It will not exceed the expected number located within the given slid cylinder having a given height according to the point density, e.g., h = 30 cm. If a new point is added to the upper part of the trunk, one point from the lower part of the detected trunk will be removed from the calculation. In fact, this operation makes this algorithm work as a slid cylinder along the trunk, and it allows the detection of not only the vertical trunk but also the oblique and the twist trunks. As the considered trunk modeling algorithm does not request the skeleton located inside the crown, the result of trunk detection algorithm is satisfactory.
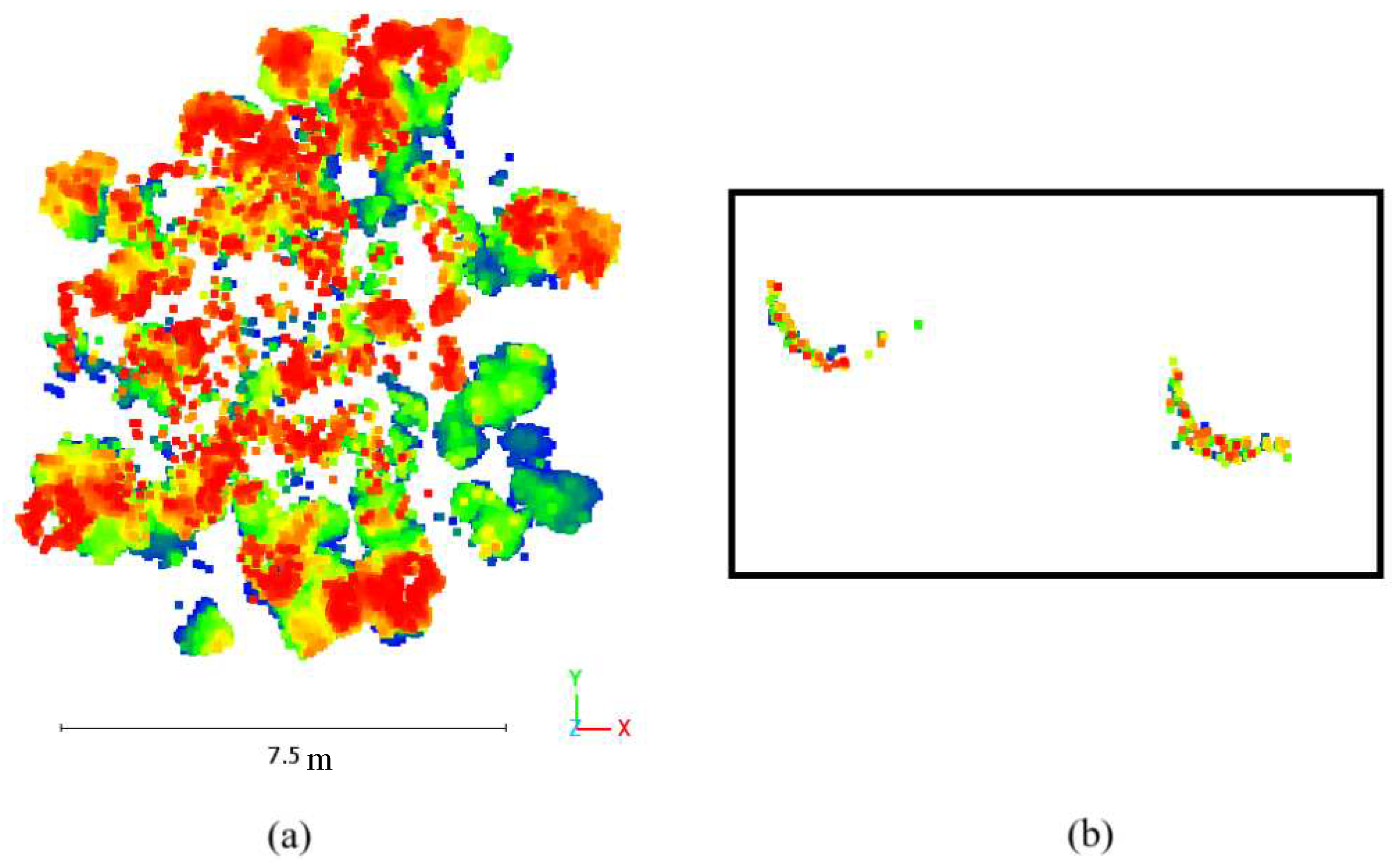
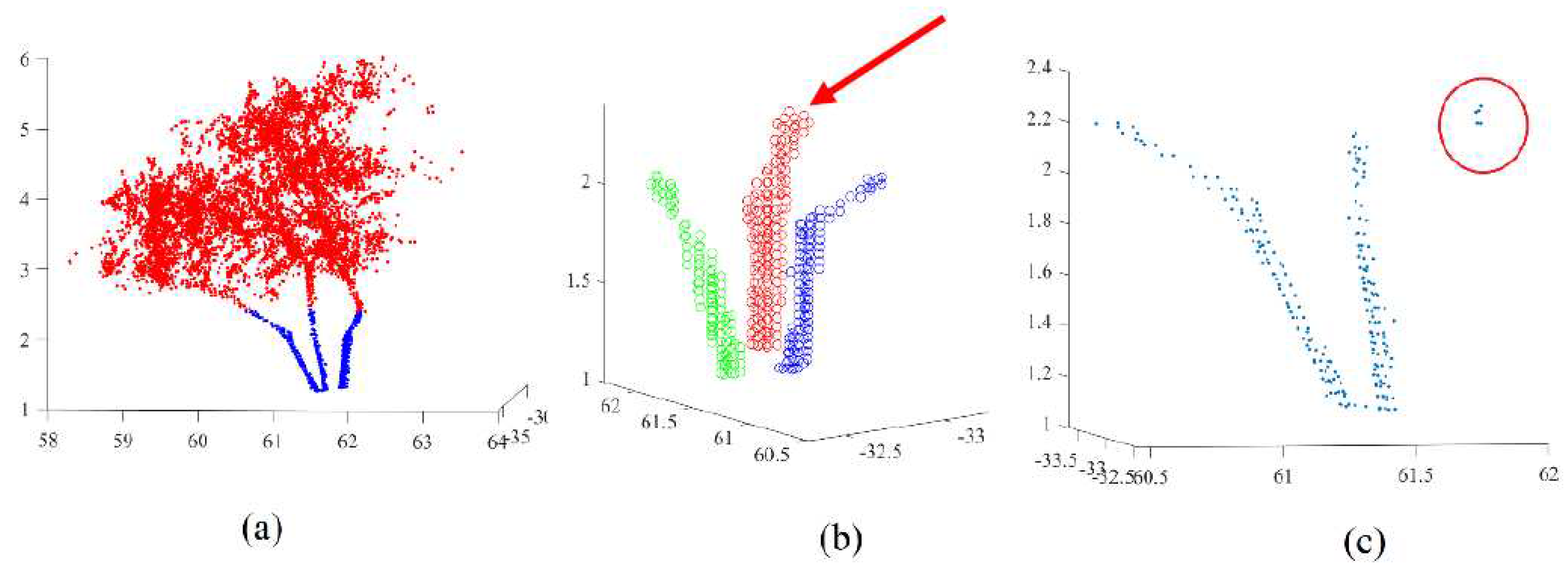
Figure 8a shows the extracted trunks where the trunk point cloud is in blue and the tree crown point in red.
At this point, it is important to underline that the three used thresholds represent smart or dynamic thresholds because the used threshold values will be automatically adapted from one tree point cloud to another by using Equations 1, 2, and 3. This advantage increases the efficiency of the suggested algorithm in this paper.
5.2. Segmentation of tree trunk into single stems
After extraction of the trunk point cloud, it should be segmented into single stems. As shown in
Section 4.1, one tree trunk may consist of only one stem (vertical or oblique) or multiple stems (
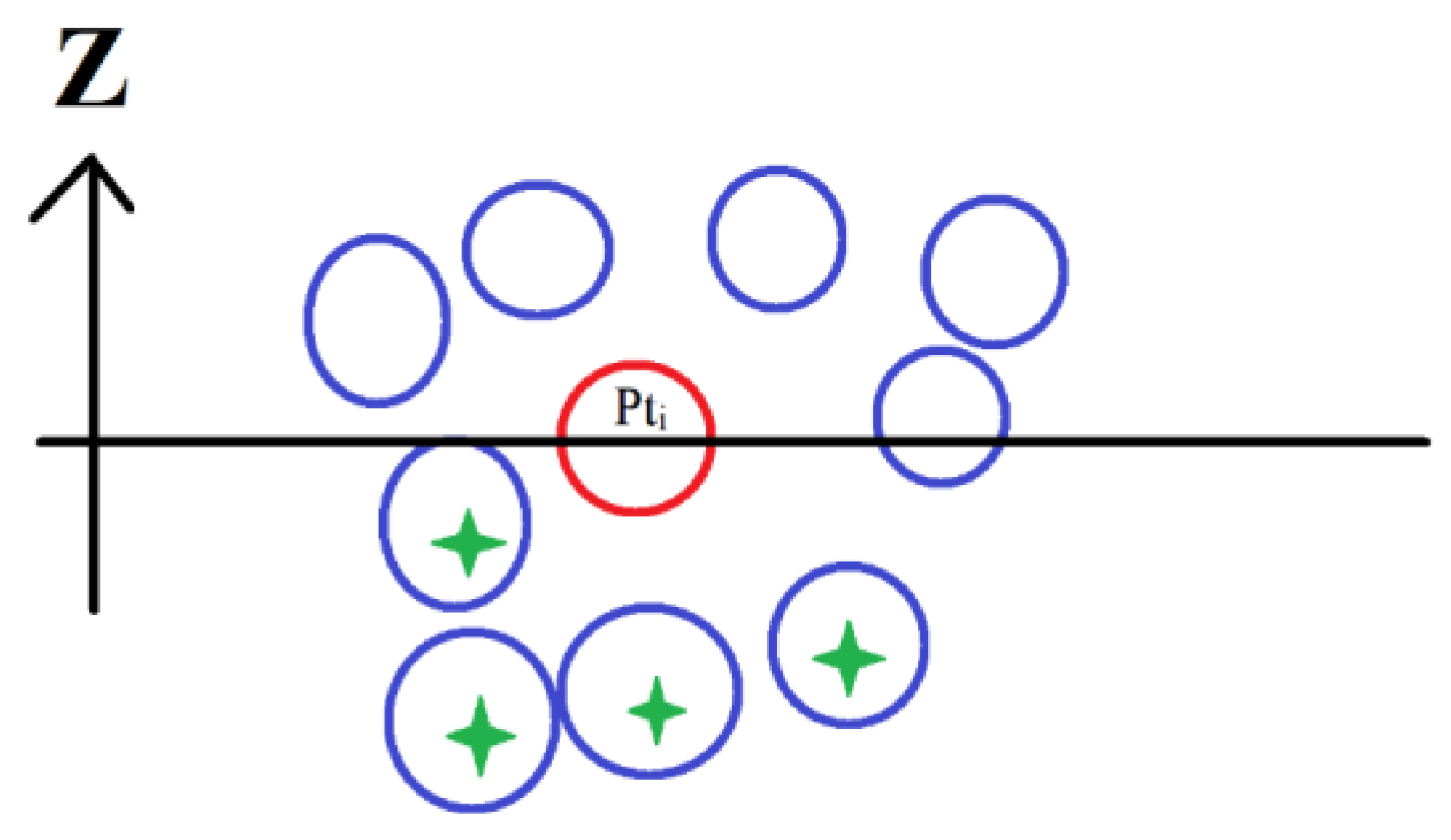
Figure 5). This section suggests an algorithm that segments the tree trunk into its basic stems. The proposed algorithm starts by descending sorting of trunk point cloud according to the Z coordinate values. The basic hypothesis is that the highest point of the trunk point cloud belongs only to one stem of the trunk. That is why this point is considered the first point of the trunk point cloud. Next, the n neighboring points are selected, these points belong also to the target stem because the distances between the neighboring points of one stem are smaller than the distance between two neighboring stems. If the distance between two neighboring stems is very small (negligible), the two stems will be considered as only one stem.
At this point, the number of selected neighboring points n may be related to the point density. However, the algorithm is not sensitive to the variation of the n value. In the tested tree clouds in this paper, the n value is considered to equal nine. Thereafter, for each detected point Pt
i, the n neighboring points are chosen. Only the points having a Z coordinated value smaller than ZPt
i are considered (
Figure 9). This choice has been adopted to avoid detecting the multiple stems of the forked trunk.
This algorithm will stop when no additional points can be found. The output will be two point-clouds. The first one is the detected stem point cloud and the second is the remained points. To detect the other stems of the same tree, the remaining point cloud is considered as the input point cloud to the same algorithm described above. When the number of remaining points is negligible, the stem detection loop stops. Moreover, if the number of points of a detected stem is negligible, the detected stem may represent noisy points and then can be ignored.
Figure 8b illustrates the result of the segmentation of the tree trunk into three single stems. Each stem is independently recognized. At this stage, it is important to note that if there are noise points presenting in the trunk point cloud, these points can generate erroneous results of the depicted algorithm, e.g., in
Figure 8c, noise points appear inside the red circle. To eliminate this kind of noise points, the detected neighboring points must be checked. If the maximum distance between the neighboring points and the considered point is greater than a given threshold, the considered point should be assigned to the noise class. This threshold represents the maximum expected distance between two neighboring points belonging to the tree trunk.
Figure 10 shows the results of the segmentation of different tree trunk point clouds. In this figure, each tree trunk is shown two times. In the first one, the colors are calculated as a function of Z coordinate values, whereas in the second time the colors are calculated as a function of the segmentation results of the trunk into individual stems. It is noticed in
Figure 10 that the tested trunks have different levels of complexity, demonstrating the efficiency and flexibility of the suggested algorithm.
5.3. Modeling of single stems
Once the tree trunk point cloud is segmented into single stems, the individual stem modeling stage can be carried out. In
Section 4.2, it was mentioned that the stem cross-section has variant shapes, and its geometric form may vary along the same stem. Furthermore, the stem geometric form is irregular, which is why the suggested approach in this paper divides the tree's single stem using horizontal planes into tiny slices, and then model each slice independently. Each slice can be presented by a cylinder. The division step should consider the point density where one slice must contain at least the minimal number of points which is sufficient to model a cylinder. In this paper, the slice height is considered equal to 15 cm where the number of points is between 20 and 40 points per slice. To model one slice, all slice points are projected on a horizontal plane, and then the least squares theory is applied to fit the best circle. This operation allows calculating the cylinder base center as well as the cylinder radius. The cylinder height is equal to the slice height.
At this stage, it is unavoidable to mention that the fitting operation does not always succeed in finding the correct circle parameters that describe the stem geometrical form. Indeed, the cross-section may not be complete because the cloud points do not completely cover the trunk surfaces, as well the cross-section does not represent geometrically a perfect circle. Also, it is supposed that the slice represents a cylinder having a vertical axis, whereas this hypothesis does not always faithfully reflect the reality. Nevertheless, this hypothesis is adopted to realize the best simulation of the trunk's complicated geometrical form. To solve the problem of gap-fitting of the slice cylinder, three solutions are suggested. The first one is applying the improved RANdom SAmple Consensuses (RANSAC) paradigm [
74,
75] using clauses that help to detect the best cylinder. These clauses consider the minimum and maximum expected radius regarding the last detected cylinders. The other solution is to check the list of fitted cylinders by comparing each one to its neighboring ones. This operation allows adjusting the cylinder radius values to harmonize with the trunk geometric form. The last choice is applying the last two methods together which is adopted in this paper.
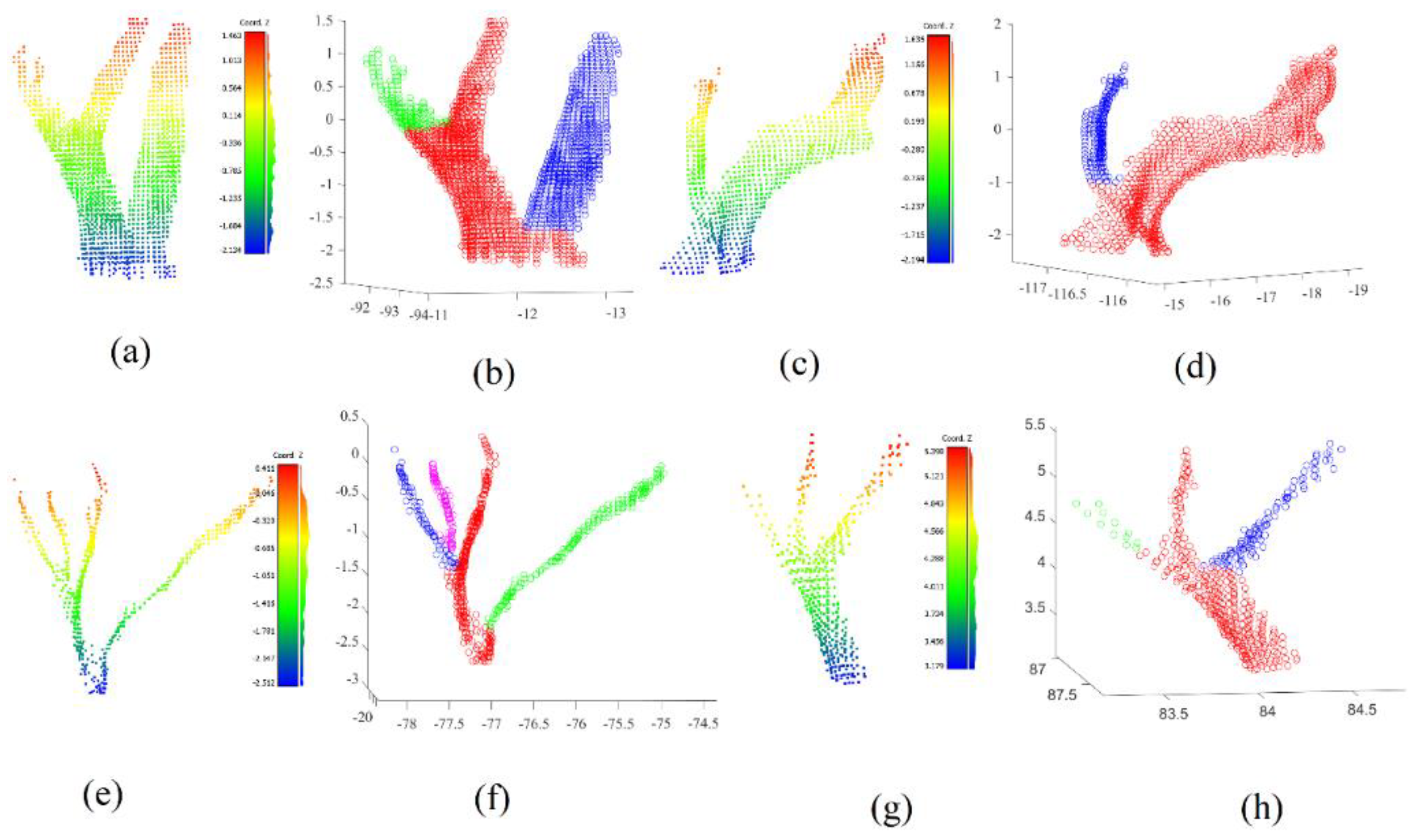
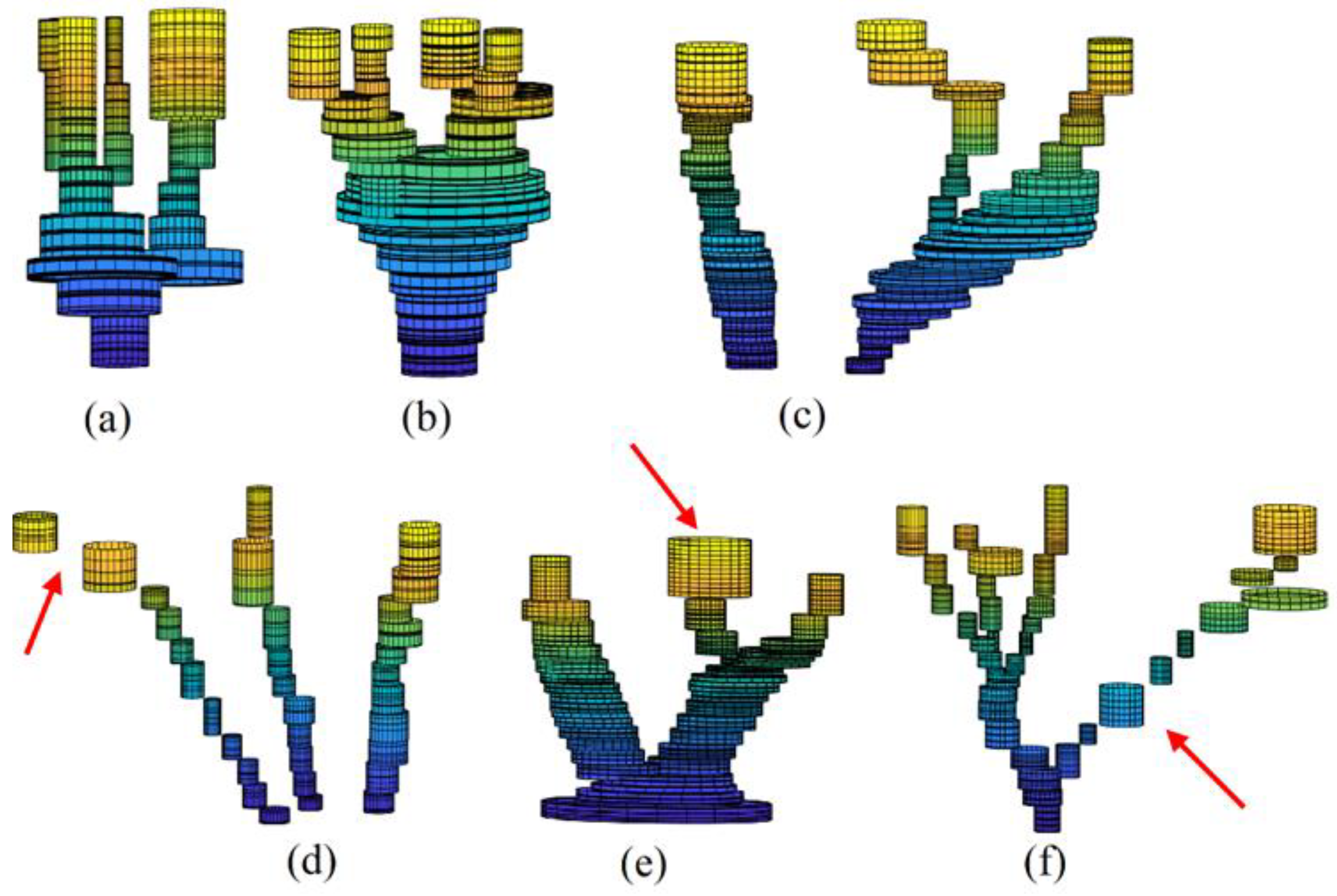
Figure 11 shows the visualization of constructed 3D trunk models, where
Figure 11d represents the trunk related to the tree shown in
Figure 8, whereas
Figure 11e and
Figure 11f correspond to the trees in
Figure 10a and
Figure 10e respectively.
6. Accuracy
The accuracy of the constructed trunk models is estimated by calculating the standard deviation of each tree trunk model.
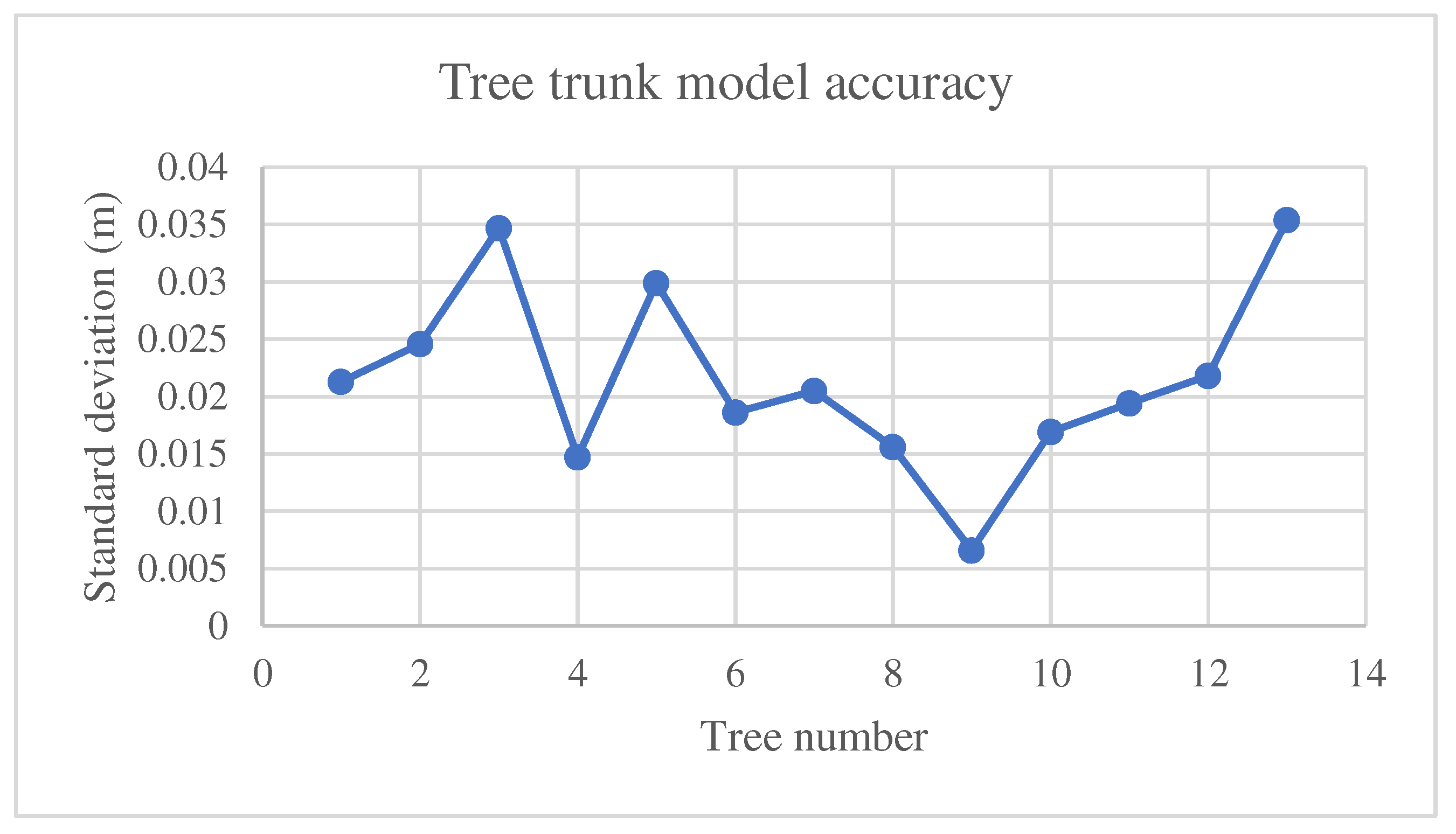
Figure 12 exposes the standard deviation graph of 3D tree trunk models presented in
Figure 11 in addition to 6 other tree point clouds. It shows that the reason for this slight accuracy difference comes from the complexity level of the tree trunk, e.g., when the trunk is twisted or forked, the accuracy drops down by a small amount. However, the modeling accuracy of the selected trees is better than 4 cm, 63 % of the mean distance between two neighboring lidar points, and thus can be considered high-quality results regarding the employed point cloud.
The trunk models shown in
Figure 11 represent promising results for high complexity and variation of trunk geometric forms, which confirms the efficacity of the suggested approach. However, there are limitation for the constructed models. First, the slice cylinders should not be always vertical (see red arrow in
Figure 11f). Indeed, the slice cylinder axis must be parallel to the stem slop. Second, the cylinder radiuses are not always fitted accurately (see
Section 5.3 and the red arrow in
Figure 11e), where the harmonization level between the neighboring cylinder radiuses must be improved. Finally, gaps between neighboring cylinders must be analyzed and filed (see red arrow in
Figure 11d). All these can help in future work to improve the proposed modeling algorithm.
7. Conclusion
The construction of digital twins requires automated tools for creating 3D models of objects, including 3D tree models. In a previous study [
66], the authors modeled tree crowns using lidar measurement data, and trunks were represented by vertical lines. In the present study, tree trunks are modeled based on their real shapes, including indentations and bends. Point cloud segmentation is conducted by selecting points located on tree trunks. Trunk models are generated by dividing subsets into slices and fitting cylinders to the obtained data. The accuracy with which cylinders are fitted to the points in the point cloud is calculated. The satisfactory modeling results suggest a maximum standard deviation of 3.6 cm for a data sample containing 13 trees. The initial trunk models are presented graphically, and the results are used to formulate recommendations for further improvement of the algorithm. Algorithms should be refined because tree models should accurately represent real-world objects to support sustainable forest management. Future work should focus on improving the proposed algorithm, e.g., enhancing the determination of stem diameters, filling the gaps located among the trunk model, and making the cylinder axis parallel to the main trunk axis. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm should be tested using point clouds of more diverse point densities and other tree species. Finally, the tree trunk model can be merged with the crown model to form a complete tree model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.T.K.; E.L. and Z.G.; methodology, F.T.K. and E.L.; software, F.T.K.; validation, F.T.K.; E.L. and J.S.; formal analysis, F.T.K. and J.S.; resources, F.T.K; E.L., data curation, F.T.K. and E.L.; writing—original draft preparation, F.T.K. writing—review and editing, Z.G. and J.S.; visualization, F.T.K., E.L. and J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Mr. Paul Reed Managing Director of East Coast Surveys (Aust) Pty Ltd, and ScanXPlus Pty Ltd. companies for supporting this work,
http://www.eastcoastsurveys.com.au (accessed on 05 December 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tao, F.; Xiao, B.; Qi, Q.; Cheng, J.; Ji, P. Digital twin modeling. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 64, 372-389. [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, O.; Liu, H.; Abudayyeh, O.; Houshyar, A.; Almatared, M.; Alhawiti, A. Data Fusion for Smart Civil Infrastructure Management: A Conceptual Digital Twin Framework. Buildings 2023, 13, 2725. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.M.; Aliyu, A.A. The need for landscape information modelling (LIM) in landscape architecture. In Proceedings of the 13th Digital Landscape Architecture Conference, Weimar, Germany, 31 May–2 June 2012. 40.
- Song, J.; Park, S.; Lee, K.; Bae, J.; Kwon, S.; Cho, C.-S.; Chung, S. Augmented Reality-Based BIM Data Compatibility Verification Method for FAB Digital Twin implementation. Buildings 2023, 13, 2683. [CrossRef]
- Mylo, M.D.; Ludwig, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Shu, Q.; Fleckenstein, C.; Speck, T.; Speck, O. Conjoining. Trees for the Provision of Living Architecture in Future Cities: A Long-Term Inosculation Study. Plants 2023, 12, 1385. [CrossRef]
- Austin, M.; Delgoshaei, P.; Coelho, M.; Heidarinejad, M. Architecting smart city digital twins: Combined semantic model and machine learning approach. Journal of Management in Engineering. 36(4), 2020, 04020026.\ . [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.; Bueno, C. City Information Modelling as a support decision tool for planning and management of cities: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108403. [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, L.; Yates, J.; Valentini, R. A Proposal for a Forest Digital Twin Framework and Its Perspectives. Forests 2022, 13, 498. [CrossRef]
- Veglianti, E.; Magnaghi, E.; De Marco, M.; Li, Y. Smart city in China: The state of art of Xiong a new area. In Organizing Smart Buildings and Cities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 81–97. 39. [CrossRef]
- Jeddoub, I.; Nys, G.; […] Billen, R. Digital Twins for cities: Analyzing the gap between concepts and current implementations with a specific focus on data integration International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation (2023) 122 103440 . [CrossRef]
- Richa, J.P.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Goulette, F.; Dalmasso, N. AdaSplats: Adaptive Splatting of Point Clouds for Accurate 3D Modeling and Real-Time High-Fidelity LiDAR Simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6262. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y. Intelligent Generation Method of Innovative Structures Based on Topology Optimization and Deep Learning. Materials. 2021, 14, 7680. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Amakhchan, W.; Gharineiat, Z.; Boulaassal, H.; El Kharki, O. Contribution of geometric feature analysis for deep learning classification algorithms of urban LiDAR data. Sensors 2023, 23, 7360. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Gharineiat, Z.; Campbell, G.; Awrangjeb, M.; Dey, E.K. Automatic Filtering of Lidar Building Point Cloud in Case of Trees Associated to Building Roof. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 430. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Reed, P.; Gharineiat, Z.; Awrangjeb, M. 2023. Efficiency of terrestrial laser scanning in survey works: assessment, modelling, and monitoring. International Journal of Environment Sciences and Natural Resources. 2023; 28(2): 556234. [CrossRef]
- McTegg, S.J.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Simmons, S.; Gharineiat, Z. Comparative approach of unmanned aerial vehicle restrictions in controlled airspaces. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 822. [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, P.; Ramiya, A. M. 3D CITYGML building modelling from LIDAR point cloud data, Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., 2018, XLII-5, 175–180, . [CrossRef]
- Schwab, B.; Beil, C.; Kolbe, T.H. Spatio-Semantic Road Space Modeling for Vehicle–Pedestrian Simulation to Test Automated Driving Systems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3799. [CrossRef]
- Nikoohemat, S.; Peter, M.; Oude Elberink, S.; Vosselman, G. Semantic Interpretation of Mobile Laser Scanner Point Clouds in Indoor Scenes Using Trajectories. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1754. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; et al. Vectorized rooftop area data for 90 cities in China. Scientific Data 2022 9:1, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–12, Mar. 2022, . [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Dukai, B.; Vitalis, S.; van Liempt, J.; Stoter, J. Automated 3D Reconstruction of LoD2 and LoD1 Models for All 10 million Buildings of the Netherlands. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 165–170, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Milojevic-Dupont, N.; Wagner, F.; Nachtigall, F. et al. EUBUCCO v0.1: European building stock characteristics in a common and open database for 200+ million individual buildings. Sci Data 10, 147 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, S.; Bittner, K.; Fraundorfer, F. Machine-learned regularization and polygonization of building segmentation masks, in 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 3098–3105, 10–15 January 2021, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., Tang, H., Feng, L., Lyu, S. CBRA: The first multi-annual (2016-2021) and high-resolution (2.5 m) building rooftop area dataset in China derived with Super-resolution Segmentation from Sentinel-2 imagery. Earth System Science. August 2023, 15(8):3547-3572. [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, O.; Xia, Y.; Wysocki, M.; Grilli, E.; Hoegner, L.; Cremers, D.; Stilla, U. Scan2LoD3: Reconstructing semantic 3D building models at LoD3 using ray casting and Bayesian networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, L. Accurate Reconstruction of the LoD3 Building Model by Integrating Multi-Source Point Clouds and Oblique Remote Sensing Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 135. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Awrangjeb, M. Comparison of LiDAR Building Point Cloud with Reference Model for Deep Comprehension of Cloud Structure, Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 603–621, 2020, . [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Rosero, B G.; Achanta, R.; et al. Generating LOD3 building models from structure-from-motion and semantic segmentation Automation in Construction, 141, 9 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lewandowicz, E.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Gharineiat, Z. 3D LoD2 and LoD3 Modeling of Buildings with Ornamental Towers and Turrets Based on LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4687. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Lewandowicz, E.; Gharineiat, Z.; Shan, J. Modeling Multi-Rotunda Buildings at LoD3 Level from LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3324. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Rötzer, T.; Detter, A.; Ludwig, F. Tree Information Modeling: A Data Exchange Platform for Tree Design and Management. Forests 2022, 13, 1955. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, X.; He, Z. Semantic Urban Vegetation Modelling Based on an Extended CityGML Description. Conference: 2022, Digital Landscape Architecture Conference, Journal of Digital Landscape Architecture · 7-2022, pp. 200-212 © Wichmann Verlag, VDE VERLAG GMBH · Berlin · Offenbach. ISBN 978-3-87907-724-3, ISSN 2367-4253. [CrossRef]
- CHEN, Y. M. Garden Trees. China Forestry Publishing House (Ortega-Códrowa M. Urban Vegetation Modeling 3D Levels of Detail. Master of Science in Geomaptics for the Build Environment. 2018, https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid%3A8b8967a8-0a0f-498f-9d37-71c6c3e532af (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Chen, Z., Xu, B., Devereux, B., Urban landscape pattern analysis base on 3D landscape models. Apield Geogrphy, 2014, 55, 82-91. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Kankare, V.; Hyyppa, J.; Wang, Y.; Kuuo, A.; Vastaranta, M. Terresial laser scanning in forest inventories. ISPRS Journal of Photoigrmetry and Remonte Sensing, 2016, 115, 63-67. [CrossRef]
- Lombard, L.; Ismail, R.; Poona, N. K. Modelling forest species using Lidar-derived metrics of forest canopy gaps. South African Journal of Geomatics, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 31–43, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H.; Leckie, D.; Gougeon, F.; Yu, X.; Maltamo, M. Review of methods of small-footprint airborne laser scanning for extracting forest inventory data in boreal forests. Int J Remote Sens, 2008, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 1339–1366, Mar. [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Zhang, L. Trends in Automatic Individual Tree Crown Detection and Delineation—Evolution of LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 333. [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhao, A.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Comparison of Modeling Algorithms for Forest Canopy Structures Based on UAV-LiDAR: A Case Study in Tropical China. Forests 2020, 11, 1324. [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dai, W.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y. Automatic Forest Mapping at Individual Tree Levels from Terrestrial Laser Scanning Point Clouds with a Hierarchical Minimum Cut Method. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 372. [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, J.; Huber, M.O. Detecting Tree Stems from Volumetric TLS Data in Forest Environments with Rich Understory. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 9. [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Weinmann, M.; Mallet, C.; Brédif, M. A Classification-Segmentation Framework for the Detection of Individual Trees in Dense MMS Point Cloud Data Acquired in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 277. [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, J.; Huber, M.O. Constrained Spectral Clustering of Individual Trees in Dense Forest Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1056. [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ye, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, F. A supervoxel approach to the segmentation of individual trees from LiDAR point clouds. Remote Sensing Letters. 2018, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 515–523, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zou, P.; Shu, Y.; Yu, R. Individual tree delineation in deciduous forest areas with LiDAR point clouds. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 152–163 . [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, M.; Rapiński, J. A Review of Tree Species Classification Based on Airborne LiDAR Data and Applied Classifiers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 353. [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; W. Amakhchan, W.; Gharineiat, Z. Random Forest Machine Learning Technique for Automatic Vegetation Detection and Modelling in LiDAR Data. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 1–3, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Montes, C.R.; Peduzzi, A. A Comparison of Modeling Methods for Predicting Forest Attributes Using Lidar Metrics. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1284. [CrossRef]
- Putra, J. C.; Arie Wahyu Wijayanto, A. W. Automatic detection and counting of oil palm trees using remote sensing and object-based deep learning. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment. Vol. 2, January 2023, 100914 . [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, G. Automatic Identification of Street Trees with Improved RandLA-Net and Accurate Calculation of Shading Area with Density-Based Iterative α-Shape. IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 132384–132395, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.; Hudak, A.T.; Vierling, L.A.; Loudermilk, E.L.; O’Brien, J.J.; Hiers, J.K.; Jack, S.B.; Gonzalez-Benecke, C.; Lee, H.; Falkowski, M.J. Imputation of individual longleaf pine (Pinus palustris Mill.) tree attributes from field and LiDAR data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 554–5730 . [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Litkey, P.; Kaartinen, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M. Single-Sensor Solution to Tree Species Classification Using Multispectral Airborne Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 108. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Estimating Individual Tree Height and Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) from Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) Data at Plot Level. Forests 2018, 9, 398. [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.; Heyder, U.; Weinacker, H. Detection of individual tree crowns in airborne lidar data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 357–363 . [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-A.; Lee, W.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Biging, G.S.; Gong, P. Detection of individual trees and estimation of tree height using LiDAR data. J. For. Res. 2007, 12, 425–434. DOI 10.1007/s10310-007-0041-9.
- Deng, D.; Ye, C.; Tong, K.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of the Sustainable Forest Management Performance in Forestry Enterprises Based on a Hybrid Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model: A Case Study in China. Forests 2023, 14, 2267. [CrossRef]
- Konstantinavičienė, J. Assessment of Potential of Forest Wood Biomass in Terms of Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13871. [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ma, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, B.; Su, X. 3PG-MT-LSTM: A Hybrid Model under Biomass Compatibility Constraints for the Prediction of Long-Term Forest Growth to Support Sustainable Management. Forests 2023, 14, 1482. [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.M.; Tonini, H.; Behling, M.; Hoshide, A.K. Eucalyptus Carbon Stock Research in an Integrated Livestock-Forestry System in Brazil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7750. [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Furuya, N.; Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, H. Airborne laser scanning in forest management: Individual tree identification and laser pulse penetration in a stand with different levels of thinning. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 752–760. [CrossRef]
- Béland, M.; Widlowski, J. L.; Fournier, R. A.; Côté J.F.; Verstraete, M. M. Estimating leaf area distribution in savanna trees from terrestrial LiDAR measurements. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology Volume 151, Issue 9, 15 September 2011, Pages 1252-1266 . [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, R.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Ruan, X.; Xiao, Y. A Concave Hull Methodology for Calculating the Crown Volume of Individual Trees Based on Vehicle-Borne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 623. [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Li G. Soft Segmentation and Reconstruction of Tree Crown from Laser Scanning Data. Electronics. 2023; 12(10):2300. [CrossRef]
- Tockner, A.; Gollob, C.; Kraßnitze, R.; Ritte, T.; Nothdurft, A. Automatic tree crown segmentation using dense forest point clouds from Personal Laser Scanning (PLS) International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation (2022) 114, . [CrossRef]
- Treemap. Available online: https://www.mapadrzew.com/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Lewandowicz, E.; Shan, J.; Gharineiat, Z. 3D modeling and visualization of single tree Lidar point cloud using matrixial form. (Submitted in June 2023).
- Godin, Ch. Representing and encoding plant architecture: A review. Annals of Forest Science 57(5) (2000) 413–438 https://www.afs-journal.org/articles/forest/pdf/2000/05/f0502.pdf.
- Bucksch A.; Lindenbergh R.; Menenti M. SkelTre: Robust skeleton extraction from imperfect point clouds. The Visual Computer: International Journal of Computer. Graphics Volume 26 Issue 10 October 2010, 283–1300, . [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shan, J.; Wang, G. Hierarchical Modeling of Street Trees Using Mobile Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2321. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Fan, J.; Eichhorn, M.P.; An, F.; Chen, B.; Cao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yun, T. Retrieval of Aerodynamic Parameters in Rubber Tree Forests Based on the Computer Simulation Technique and Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1318. [CrossRef]
- Azaïs, R.; Habibeche, S.; Ben-Naoum, Ben.; Godin, Ch. Exploring symmetries in plant architectures. Conference: 10th International Conference on Functional-Structural Plant Models: FSPM 2023 At: Berlin Germany; https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373013986_Exploring_symmetries_in_plant_architectures.
- Godin, C.; Ferraro, P. Quantifying the Degree of Self-Nestedness of Trees: Application to the Structural Analysis of Plants. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 688-703, October 2010. [CrossRef]
- Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English Online (https://www.ldoceonline.com/).
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer. P. Hough-transform and extended RANSAC algorithms for automatic detection of 3D building roof planes from Lidar data. ISPRS Workshop on Laser Scanning 2007 and SilviLaser 2007, Espoo, Finland, Sept. 12-14th. ISPRS, Int. Arch. of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Systems. Vol. XXXVI, Part 3 / W52, 2007, pp. 407-412.
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. Extended RANSAC algorithm for automatic detection of building roof planes from Lidar data.” The Photogrammetric Journal of Finland, vol. 21, n°1, 2008, pp. 97-109.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).