Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sugarcane MicroRNAs and SCMV Genome Data Retrieval and Processing
2.2. Potential Targets of Sugarcane MicroRNAs in SCMV Genome
2.4. RNA22
2.5. TAPIR
2.6. psRNATarget
2.7. RNAhybrid
2.8. RNAfold
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
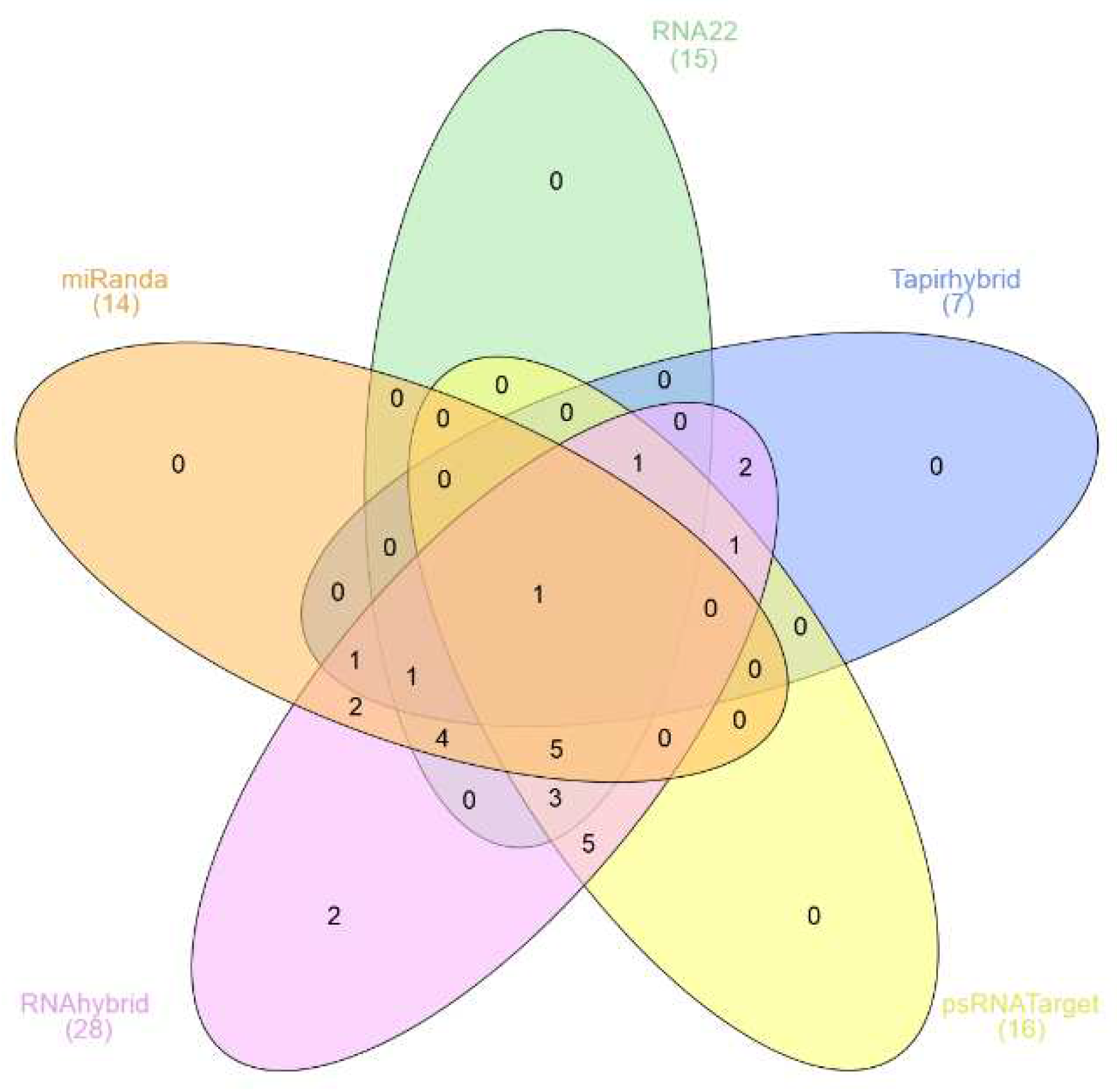
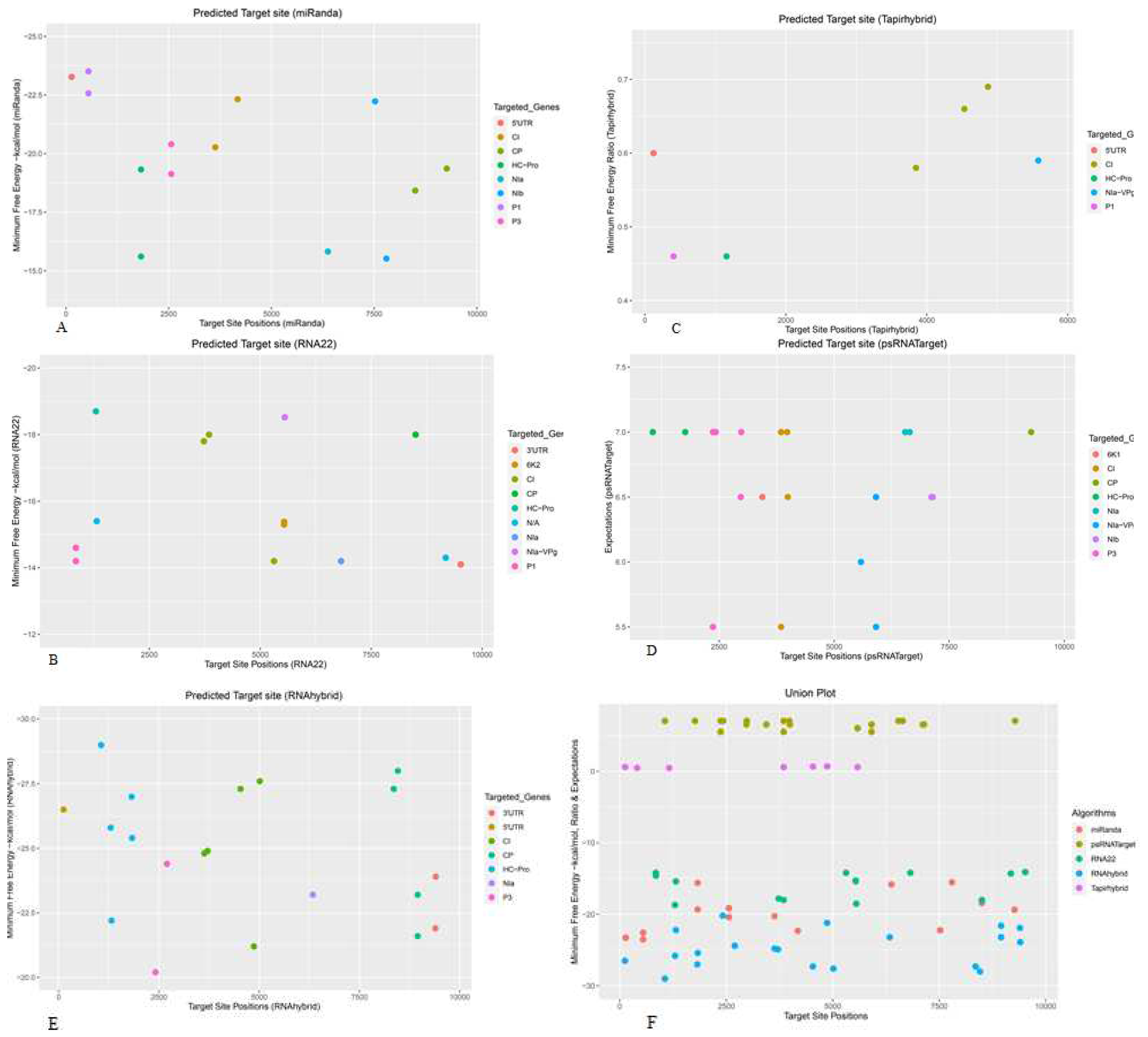
3.1. Prediction and Analyysis of Sugarcane MicroRNAs Targeting SCMV Genome
3.2. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting P1
3.3. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting HC-Pro
3.4. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting P3
3.5. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting 6K1
3.6. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting CI
3.7. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting 6K2
3.8. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting NIa-VPg
3.9. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting NIa
3.10. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting NIb
3.10.1. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting CP
3.10.2. Sugarcane miRNAs Targeting UTR
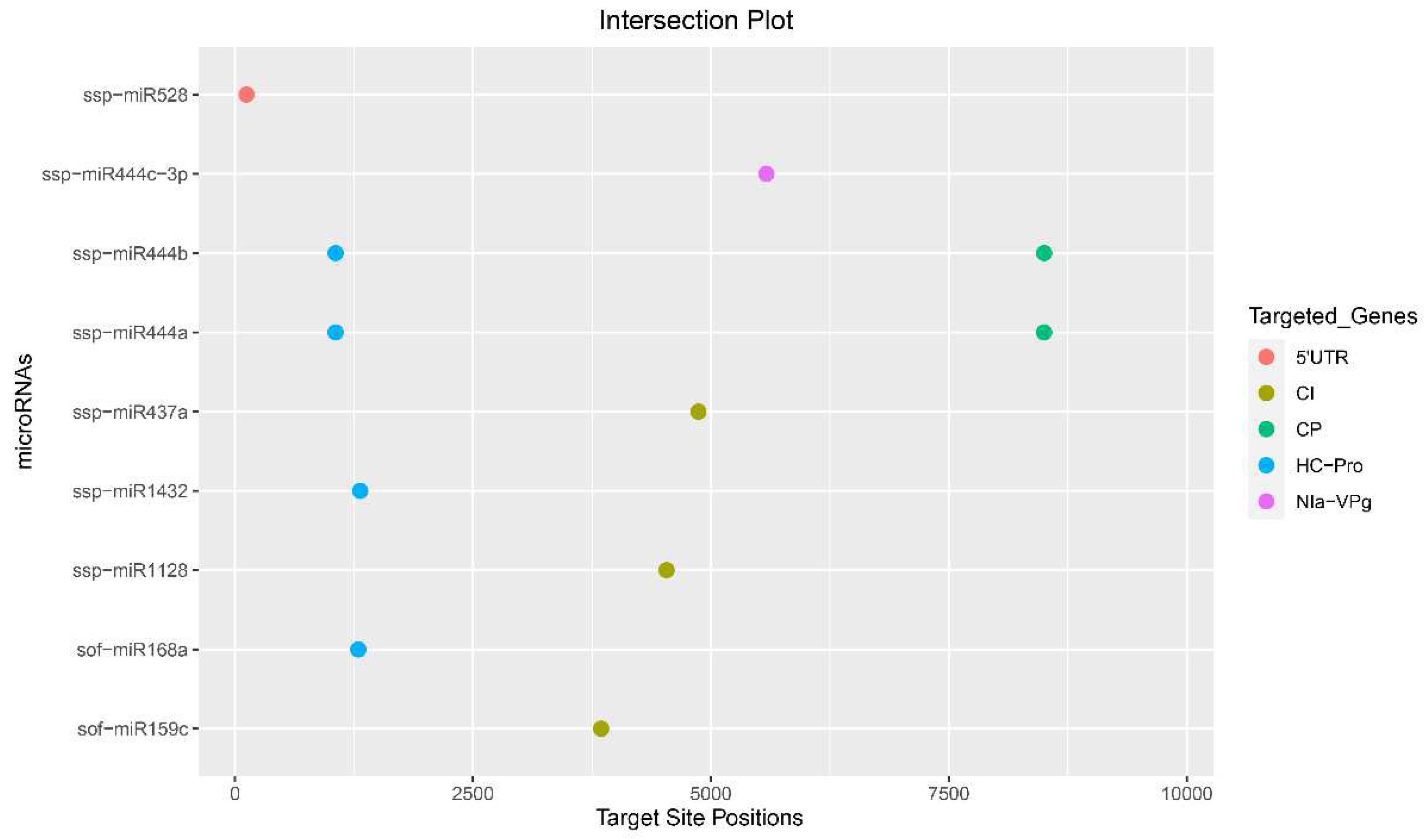
3.5. Identification of Consensual Sugarcane MicroRNAs
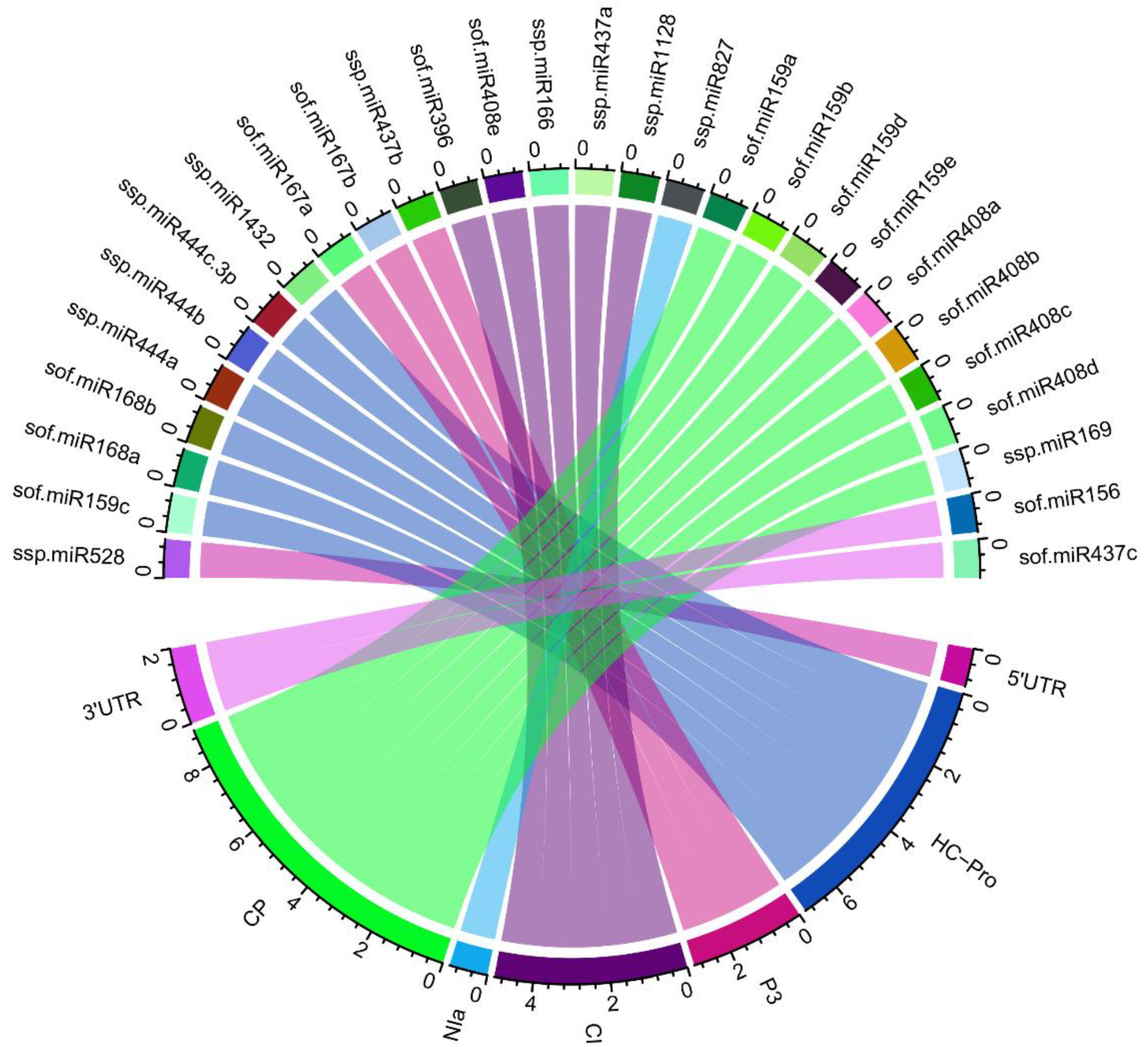
3.7. Identification of miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network
3.8. RNA Secondary Structures
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho-Netto, O.V.; Bressiani, J.A.; Soriano, H.L.; Fiori, C.S.; Santos, J.M.; Barbosa, G.V.; Xavier, M.A.; Landell, M.G.; Pereira, G.A. The potential of the energy cane as the main biomass crop for the cellulosic industry. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Dompreh, E.; Gasparatos, A. Human wellbeing outcomes of involvement in industrial crop production: Evidence from sugarcane, oil palm and jatropha sites in Ghana. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0215433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F. Measuring convergence in the sugarcane industry in China’s Guangxi province. Plos one 2021, 16, e0244617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperidis, G.; Piperidis, N.; D’Hont, A. Molecular cytogenetic investigation of chromosome composition and transmission in sugarcane. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 2010, 284, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Jing, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, Z.; Wu, J. Characterization of chromosome composition of sugarcane in nobilization by using genomic in situ hybridization. Molecular cytogenetics 2018, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Acevedo, R.; Moreno Díaz de la Espina, S.; Jouve, N.; De La Torre, C. Genome remodelling in three modern S. officinarum× S. spontaneum sugarcane cultivars. Journal of experimental botany 2004, 55, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, X.; Ma, X.; Zhu, F.; Jones, T.; Zhu, X.; Bowers, J. Allele-defined genome of the autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum L. Nature genetics 2018, 50, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, J.R.; Pootakham, W.; Sonthirod, C.; Naktang, C.; Yoocha, T.; Sangsrakru, D.; Jomchai, N.; Tongsima, S.; Piriyapongsa, J.; Ngamphiw, C. A draft chromosome-scale genome assembly of a commercial sugarcane. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 20474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhou, H.; Luo, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, R.; Luo, T.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Characterization of full-length transcriptome in Saccharum officinarum and molecular insights into tiller development. BMC Plant Biology 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, R.; Han, S.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Transcriptome analysis of sugarcane young leaves and protoplasts after enzymatic digestion. Life 2022, 12, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Que, Y.; Mo, P.; Liu, X. Characterization and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Sugarcane (Saccharum spp. Hybrids) Line A1. Diversity 2022, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Pan, Y.-B.; Grisham, M.P.; Xu, L. Sugarcane mosaic disease: Characteristics, identification and control. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, E.-Q.; Bao, W.-Q.; Sun, S.-R.; Hu, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Bi, Z.-W.; Xie, Y.; Lu, J.-J.; Gao, S.-J. Incidence and Distribution of Four Viruses Causing Diverse Mosaic Diseases of Sugarcane in China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhave, K.R.; Gautam, S.; Rasmussen, D.A.; Srinivasan, R. Aphid transmission of Potyvirus: the largest plant-infecting RNA virus genus. Viruses 2020, 12, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, A.L.; Ferreira, S.S.; Ten-Caten, F.; Margarido, G.R.; Dos Santos, J.M.; Barbosa, G.V.d.S.; Carneiro, M.S.; Souza, G.M. Genomic resources for energy cane breeding in the post genomics era. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2019, 17, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, T.; Xu, X.; Li, X.-D.; Tian, Y. The complete genomic sequence of Sugarcane mosaic virus from Canna spp. in China. Virology journal 2018, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Herath, V.; Ahmed, K.; Tahir, M.; Verchot, J. Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of sugarcane mosaic virus, comparing whole genome and coat protein sequence phylogenies. Archives of Virology 2022, 167, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Dong, Z.; Gan, H. Genetic changes and host adaptability in sugarcane mosaic virus based on complete genome sequences. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution 2020, 149, 106848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, W.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, P.; An, T.; Cui, A.; An, D. Molecular variability and distribution of Sugarcane mosaic virus in Shanxi, China. PLoS one 2016, 11, e0151549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, E.J.; Matzke, M.A. The small RNA world. Journal of cell science 2003, 116, 4689–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.A. The function of miRNAs in plants. Plants 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Waheed, A.; Idrees, A.; Rashid, J.; Zeng, F. Role of plant microRNAs and their corresponding pathways in fluctuating light conditions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 2022, 119304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Chen, M.; Xiang, M.; Guo, Z. RNAi-based antiviral innate immunity in plants. Viruses 2022, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.W.; Falk, B.W. Artificial microRNA guide strand selection from duplexes with no mismatches shows a purine-rich preference for virus-and non-virus-based expression vectors in plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2022, 20, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Roshdi, M.R.; Ammara, U.; Khan, J.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Shahid, M.S. Artificial microRNA-mediated resistance against Oman strain of tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Prasad, M. Silencing AC1 of Tomato leaf curl virus using artificial microRNA confers resistance to leaf curl disease in transgenic tomato. Plant Cell Reports 2020, 39, 1565–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; Baker, B.; Luo, L. Polycistronic artificial microRNA-mediated resistance to cucumber green mottle mosaic virus in cucumber. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, Q.; Ai, X.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yan, F. Transgenic Rice Plants Expressing Artificial miRNA Targeting the Rice Stripe Virus MP Gene Are Highly Resistant to the Virus. Biology 2022, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Amin, I.; Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S. Artificial microRNA-mediated resistance against the monopartite begomovirus Cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. Virology journal 2013, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Zou, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Que, Y. miRNA alteration is an important mechanism in sugarcane response to low-temperature environment. BMC genomics 2017, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Khraiwesh, B.; Pugalenthi, G.; Gupta, R.S.; Singh, J.; Duttamajumder, S.K.; Kapur, R. Subtractive hybridization-mediated analysis of genes and in silico prediction of associated microRNAs under waterlogged conditions in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.H.; Gentile, A.; Vilela, R.D.; Costa, G.G.L.; Dias, L.I.; Endres, L.; Menossi, M. microRNAs associated with drought response in the bioenergy crop sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapna, M.; Kumar, S. MicroRNAs and their regulatory role in sugarcane. Frontiers in Plant Science 2017, 8, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, M.R.; Kumar, R.; Chinnaswamy, A.; Karuppaiyan, R.; Kulshreshtha, N.; Ram, B. Current breeding and genomic approaches to enhance the cane and sugar productivity under abiotic stress conditions. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.d.O.L.; Silva, R.G.d.; Nogueira, L.d.F.; Zingaretti, S.M. MicroRNAs regulate tolerance mechanisms in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) under aluminum stress. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, A.M.; Liao, F.; Qin, C.X.; Chen, Z.L.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.R.; Li, X.F.; Lakshmanan, P.; Huang, D.L. Control of sucrose accumulation in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrids) involves miRNA-mediated regulation of genes and transcription factors associated with sugar metabolism. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 14, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.; Ashraf, M.A.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S. A novel computational approach to the silencing of Sugarcane Bacilliform Guadeloupe A Virus determines potential host-derived MicroRNAs in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). PeerJ 2020, 8, e8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ashraf, F.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Shen, L.; Khan, J.; Zhang, S. Potential targets for evaluation of sugarcane yellow leaf virus resistance in sugarcane cultivars: in silico sugarcane miRNA and target network prediction. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2021, 35, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Ashraf, F.; Shen, L.; Iqbal, M.S.; Zhang, S. In silico identification of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) genome encoded microRNAs targeting sugarcane bacilliform virus. PloS one 2022, 17, e0261807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, H.; Wu, Z.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Qi, Y. Integrated analysis of miRNAs associated with sugarcane responses to low-potassium stress. Frontiers in Plant Science 2022, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Bourexis, D.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Comeau, D.C.; Funk, K.; Kim, S.; Klimke, W. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, A.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome biology 2003, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human microRNA targets. PLoS biology 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.C.; Huynh, T.; Tay, Y.; Ang, Y.-S.; Tam, W.-L.; Thomson, A.M.; Lim, B.; Rigoutsos, I. A pattern-based method for the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell 2006, 126, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loher, P.; Rigoutsos, I. Interactive exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3322–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, E.; He, Y.; Billiau, K.; Van de Peer, Y. TAPIR, a web server for the prediction of plant microRNA targets, including target mimics. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic acids research 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic acids research 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic acids research 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.; Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.; Hofacker, I. ViennaRNA package 2.0. algorithms for molecular biology. vol 2013, 6, 26–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gandrud, C. Reproducible research with R and RStudio; Chapman and Hall/CRC: 2018.
- Bajczyk, M.; Jarmolowski, A.; Jozwiak, M.; Pacak, A.; Pietrykowska, H.; Sierocka, I.; Swida-Barteczka, A.; Szewc, L.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. Recent Insights into Plant miRNA Biogenesis: Multiple Layers of miRNA Level Regulation. Plants 2023, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jia, T.; Chen, X. The ‘how’and ‘where’of plant micro RNA s. New Phytologist 2017, 216, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Hu, B.; Zhang, C. microRNAs and their roles in plant development. Frontiers in Plant Science 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramzow, L.; Lobbes, D.; Innard, N.; Theißen, G. Independent origin of MIRNA genes controlling homologous target genes by partial inverted duplication of antisense-transcribed sequences. The Plant Journal 2020, 101, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, A.; Lopez-Moya, J.J.; Garcia, J.A. Recombination and gene duplication in the evolutionary diversification of P1 proteins in the family Potyviridae. Journal of General Virology 2007, 88, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, F.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A. The hypervariable amino-terminus of P1 protease modulates potyviral replication and host defense responses. PLoS Pathogens 2014, 10, e1003985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaTourrette, K.; Garcia-Ruiz, H. Determinants of Virus Variation, Evolution, and Host Adaptation. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, S.F. Local adaptation of plant viruses: lessons from experimental evolution. Molecular Ecology 2017, 26, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatineni, S.; Qu, F.; Li, R.; Morris, T.J.; French, R. Triticum mosaic poacevirus enlists P1 rather than HC-Pro to suppress RNA silencing-mediated host defense. Virology 2012, 433, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasschau, K.D.; Carrington, J.C. Long-distance movement and replication maintenance functions correlate with silencing suppression activity of potyviral HC-Pro. Virology 2001, 285, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, C.; Atreya, P.; Thornbury, D.; Pirone, T. Site-directed mutations in the potyvirus HC-Pro gene affect helper component activity, virus accumulation, and symptom expression in infected tobacco plants. Virology 1992, 191, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Del Toro, F.; Makki, M.; Tenllado, F.; Canto, T. Adaptation of a Potyvirus Chimera Increases Its Virulence in a Compatible Host through Changes in HCPro. Plants 2022, 11, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, A.A.; Gallo, A.; Rodamilans, B.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. The HCPro from the Potyviridae family: an enviable multitasking Helper Component that every virus would like to have. Molecular plant pathology 2018, 19, 744–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanobar, N.; Lin, P.-C.; Pan, Z.-J.; Fang, R.-Y.; Tjita, V.; Chen, F.-F.; Wang, H.-C.; Tsai, H.-L.; Wu, S.-H.; Shen, T.-L. Investigating the viral suppressor HC-pro inhibiting small rna methylation through functional comparison of HEN1 in angiosperm and bryophyte. Viruses 2021, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Pollari, M.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Association of host protein VARICOSE with HCPro within a multiprotein complex is crucial for RNA silencing suppression, translation, encapsidation and systemic spread of potato virus A infection. PLoS Pathogens 2020, 16, e1008956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, H.; Shine, M.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, N.; Kachroo, P.; Zhi, H.; Kachroo, A. The potyviral P3 protein targets eukaryotic elongation factor 1A to promote the unfolded protein response and viral pathogenesis. Plant Physiology 2016, 172, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, C.E.; Wang, X.; Tomimura, K.; Ohshima, K.; Ponz, F.; Walsh, J.A. The dual role of the potyvirus P3 protein of Turnip mosaic virus as a symptom and avirulence determinant in brassicas. Molecular plant-microbe interactions 2003, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Liao, W.; Niu, H.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Zhi, H. Comprehensive analysis of soybean mosaic virus P3 protein interactors and hypersensitive response-like lesion-inducing protein function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, S.; Arena, G.D.; Ray, S.; Flannigan, S.; Casteel, C.L. The Potyviral Protein 6K1 Reduces Plant Proteases Activity during Turnip mosaic virus Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, A. Plum pox virus 6K1 protein is required for viral replication and targets the viral replication complex at the early stage of infection. Journal of virology 2016, 90, 5119–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, A. The multifunctional protein CI of potyviruses plays interlinked and distinct roles in viral genome replication and intercellular movement. Virology journal 2015, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorel, M.; García, J.A.; German-Retana, S. The Potyviridae cylindrical inclusion helicase: a key multipartner and multifunctional protein. Molecular plant-microbe interactions 2014, 27, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, C.; Hong, J.; Xiong, R.; Kasschau, K.D.; Zhou, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Wang, A. Formation of complexes at plasmodesmata for potyvirus intercellular movement is mediated by the viral protein P3N-PIPO. PLoS pathogens 2010, 6, e1000962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lõhmus, A.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Protein composition of 6K2-induced membrane structures formed during Potato virus A infection. Molecular plant pathology 2016, 17, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Nihranz, C.T.; Casteel, C.L. The potyviral protein 6K2 from Turnip mosaic virus increases plant resilience to drought. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2023, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dong, M.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Shang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F. Selective interaction of sugarcane EIF4E with VPGS from sugarcane mosaic pathogens. Viruses 2021, 13, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I. The genome-linked protein VPg of vertebrate viruses—a multifaceted protein. Current opinion in virology 2011, 1, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, S.; Chatel, H.; Fortin, M.G.; Laliberté, J.-F. Interaction of the viral protein genome linked of turnip mosaic potyvirus with the translational Eukaryotic Initiation Factor (iso) 4E ofArabidopsis thalianaUsing the Yeast two-hybrid system. Virology 1997, 234, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho de Oliveira, L.; Volpon, L.; Rahardjo, A.K.; Osborne, M.J.; Culjkovic-Kraljacic, B.; Trahan, C.; Oeffinger, M.; Kwok, B.H.; Borden, K.L. Structural studies of the eIF4E–VPg complex reveal a direct competition for capped RNA: Implications for translation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 24056–24065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płochocka, D.; Wełnicki, M.; Zielenkiewicz, P.; Ostoja-Zagorski, W. Three-dimensional model of the potyviral genome-linked protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1996, 93, 12150–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puustinen, P.; Makinen, K. Uridylylation of the potyvirus VPg by viral replicase NIb correlates with the nucleotide binding capacity of VPg. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 38103–38110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelin, K.; Hafrén, A.; Rantalainen, K.I.; Mäkinen, K. Potyviral VPg enhances viral RNA translation and inhibits reporter mRNA translation in planta. Journal of virology 2011, 85, 9210–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaad, M.C.; Lellis, A.D.; Carrington, J.C. VPg of tobacco etch potyvirus is a host genotype-specific determinant for long-distance movement. Journal of virology 1997, 71, 8624–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daròs, J.-A.; Carrington, J.C. RNA binding activity of NIa proteinase of tobacco etch potyvirus. Virology 1997, 237, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Rodrigo, G.; Aragonés, V.; Ruiz, M.; Lodewijk, I.; Fernández, U.; Elena, S.F.; Daròs, J.-A. Interaction network of tobacco etch potyvirus NIa protein with the host proteome during infection. BMC genomics 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Valdez, P.; Olvera, R.E.; Carrington, J.C. Functions of the tobacco etch virus RNA polymerase (NIb): subcellular transport and protein-protein interaction with VPg/proteinase (NIa). Journal of virology 1997, 71, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.; Eskelin, K.; Lohmus, A.; Mäkinen, K. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying potyvirus infection. Journal of General Virology 2014, 95, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Lõhmus, A.; Dutta, P.; Pollari, M.; Mäkinen, K. Interplay of HCPro and CP in the Regulation of Potato Virus A RNA Expression and Encapsidation. Viruses 2022, 14, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenau, S.; Winter, S.; Margaria, P. The amino-proximal region of the coat protein of cucumber vein yellowing virus (family Potyviridae) affects the infection process and whitefly transmission. Plants 2021, 10, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Turiño, S.; García, J.A. Potyviral coat protein and genomic RNA: A striking partnership leading virion assembly and more. Advances in Virus research 2020, 108, 165–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Roberts, R.; Rakotondrafara, A.M. The role of the 5′ untranslated regions of Potyviridae in translation. Virus research 2015, 206, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Zhang, J.; Mayberry, L.K.; Tatineni, S.; Browning, K.S.; Rakotondrafara, A.M. A unique 5′ translation element discovered in triticum mosaic virus. Journal of virology 2015, 89, 12427–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome research 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of Sugarcane mosaic virus. Virus research 2013, 171, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Tariq, H.K.; Hu, X.-W.; Khan, J.; Zou, Z. Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches Identify Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) Genome Encoded MicroRNAs Targeting Rubber Tree Virus 1. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ali, B.; Brown, J.K.; Shahid, I.; Yu, N. In Silico Identification of Cassava Genome-Encoded MicroRNAs with Predicted Potential for Targeting the ICMV-Kerala Begomoviral Pathogen of Cassava. Viruses 2023, 15, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.N.; Rashid, S.; Iqbal, M.S.; Jamal, A.; Khalid, S. In Silico prediction of potential mirnas to target zymv in cucumis melo. Pak. J. Bot 2022, 54, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, B.; Iqbal, M.S.; Batcho, A.A.; Nasir, I.A.; Rashid, B.; Husnain, T.; Henry, R.J. Target prediction of candidate miRNAs from Oryza sativa for silencing the RYMV genome. Computational biology and chemistry 2019, 83, 107127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, Y.; Khan, J.A. Genome wide identification of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)-encoded microRNA targets against Cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. Gene 2018, 638, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Jabbar, B.; Sharif, M.N.; Ali, Q.; Husnain, T.; Nasir, I.A. In silico MCMV silencing concludes potential host-derived miRNAs in maize. Frontiers in plant science 2017, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, Y.Z.A.; Ziebell, H. Novel targets for engineering Physostegia chlorotic mottle and tomato brown rugose fruit virus-resistant tomatoes: in silico prediction of tomato microRNA targets. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Schmid, M.; Wang, Y. miRNA mediated regulation and interaction between plants and pathogens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.A.; Tenkegna, T.A. The role of miRNA in plant–virus interaction: a review. Molecular Biology Reports 2021, 48, 2853–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchthai, U.; Yee, C.S.L.; Wong, S.-M. Resistance to CymMV and ORSV in artificial microRNA transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana plants. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhao, J.-H.; Fang, Y.-Y.; He, X.-F.; Guo, H.-S.; Duan, C.-G. A Brassica miRNA regulates plant growth and immunity through distinct modes of action. Molecular plant 2020, 13, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Motawaa, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Khalid, A.; Cai, X.; Li, F. Simple webserver-facilitated method to design and synthesize artificial miRNA gene and its application in engineering viral resistance. Plants 2022, 11, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, S.S.; Bahmanpour, Z.; Daneshmandpour, Y.; Roudbari, F.; Sheervalilou, R.; Kazeminasab, S.; Emamalizadeh, B. An updated overview and classification of bioinformatics tools for MicroRNA analysis, which one to choose? Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 134, 104544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahed, N.; Patarroyo, C.; Sun, J.; Vali, H.; Laliberté, J.-F.; Zheng, H. Cylindrical inclusion protein of Turnip mosaic virus serves as a docking point for the intercellular movement of viral replication vesicles. Plant Physiology 2017, 175, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ding, G.; Jin, Y. Evolution of MIR159/319 microRNA genes and their post-transcriptional regulatory link to siRNA pathways. BMC evolutionary biology 2011, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Algorithms | Features | Organism | Parameters | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRanda | Seed-based interaction, multiple target sites, free energy of miRNA-mRNA duplex, conservation | Human, rat, fly, worms | Score threshold = 140, Free energy = −20 Kcal/mol, Gap open penalty = −9.00, Gap extend penalty = −4.00 |
http://www.microrna.org/ (retrieved 14 August 2019) |
| RNA22 | Pattern recognition, folding energy, heteroduplex, | Human, mouse, fly and worms | Number of paired-up bases = 12, Sensitivity (63%), Specificity (61%), Folding energy = −15 Kcal/mol |
https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22/Interactive/ (retrieved on 22 June 2019) |
| TAPIR | Sees pairing, target site accessibility, multiple sites | Plants | Free energy ratio = 0.2 Score= 9 |
http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/tapir (retrieved on 25 June 2021) |
| psRNATarget | Complementarity scoring, multiple target sites, translation inhibition | Plants | Expectation Score = 6.5, Penalty for G:U pair = 0.5 HSP size = 19 Penalty for opening gap= 2 |
https://www.zhaolab.org/psRNATarget/analysis?function=2 (accessed on 26 May 2022) |
| RNAhybrid | Seed pairing and free energy | Any | Free energy = −20 Kcal/mol, Hit per target = 1 |
http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid (accessed on 26 May 2022) |
| Sugarcane miRNA |
Position miRanda |
Position RNA22 | Position TAPIR |
Position psRNATarget |
Position RNAhybrid |
MFE * miRanda |
MFE ** RNA22 |
MFE Ratio TAPIR |
Expectation psRNATarget |
MFE* RNAhybrid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sof-miR159c | 3847 | 3847 | 3847 | −18.00 | 0.58 | 5.50 | ||||
| sof -miR168a | 1296 | 1296 | −18.70 | −25.80 | ||||||
| ssp –miR437a | 4869 | 4868 | 0.69 | −21.20 | ||||||
| ssp-miR528 | 122 | 121 | 0.60 | −26.50 | ||||||
| ssp-miR444a | 8501 | 8502 | 1058 | 1057 | −18.42 | −18.00 | 7.00 | −29.00 | ||
| ssp-miR444b | 8501 | 8502 | 1058 | 1057 | −18.42 | −18.00 | 7.00 | |||
| ssp-miR444c-3p | 5583 | 5583 | 0.59 | 6.00 | ||||||
| ssp-miR1128 | 4534 | 4533 | 0.66 | −27.30 | ||||||
| ssp-miR1432 | 1315 | 1316 | −15.40 | −22.20 |
| miRNA ID | Accession ID | Mature Sequence (5′–3′) |
Target Genes ORF(s) |
Target Binding Locus Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sof-miR159c | MIMAT0001662 | CUUGGAUUGAAGGGAGCUCCU | CI | 3847–3868 |
| sof-miR168a | MIMAT0001665 | UCGCUUGGUGCAGAUCGGGAC | HC-Pro | 1296–1317 |
| ssp-miR437a | MIMAT0020280 | AAAGUUAGAGAAGUUUGACUU | CI | 4869-4890 |
| ssp-miR528 | MIMAT0020288 | UGGAAGGGGCAUGCAGAGGAG | 5′UTR | 122–143 |
| ssp-miR444a | MIMAT0020284 | UGCAGUUGUUGCCUCAAGCUU | CP | 8501–8521 |
| ssp-miR444a (1) | MIMAT0020284 | UGCAGUUGUUGCCUCAAGCUU | HC-Pro | 1058–1078 |
| ssp-miR444b | MIMAT0020285 | UGCAGUUGUUGCCUCAGGCUU | CP | 8501–8521 |
| ssp-miR444b (1) | MIMAT0020285 | UGCAGUUGUUGCCUCAGGCUU | HC-Pro | 1058–1079 |
| ssp-miR444c-3p | MIMAT0020286 | UGCAGUUGUUGUCUCAAGCUU | NIa-VPg | 5583–5604 |
| ssp-miR1128 | MIMAT0020289 | UACUACUCCCUCCGUCCCAAA | CI | 4534–4555 |
| miRNA ID | Accession ID | MFE */Kcal/mol | AMFE ** | MFEI *** | (G+C)% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sof-MIR159c | MI0001760 | −110.60 | −46.47 | −0.87 | 53.36 |
| sof-MIR168a | MI0001763 | −66.20 | −63.65 | −0.83 | 75.96 |
| ssp-MIR437a | MI0001763 | −57.10 | −32.62 | −1.29 | 25.14 |
| ssp-MIR528 | MI0001763 | −48.50 | −52.71 | −0.86 | 60.84 |
| ssp-MIR444a | MI0001763 | −57.70 | −54.94 | −1.28 | 42.86 |
| ssp-MIR444b | MI0001763 | −63.70 | −60.09 | −1.38 | 43.39 |
| ssp-MIR444c | MI0001763 | −61.80 | −57.22 | −1.31 | 43.52 |
| ssp-MIR1128 | MI0001763 | −101.70 | −36.98 | −1.18 | 31.27 |
| ssp-MIR1432 | MI0001763 | −57.10 | −64.88 | −1.14 | 56.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





