Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature analysis
2.2. Distribution map
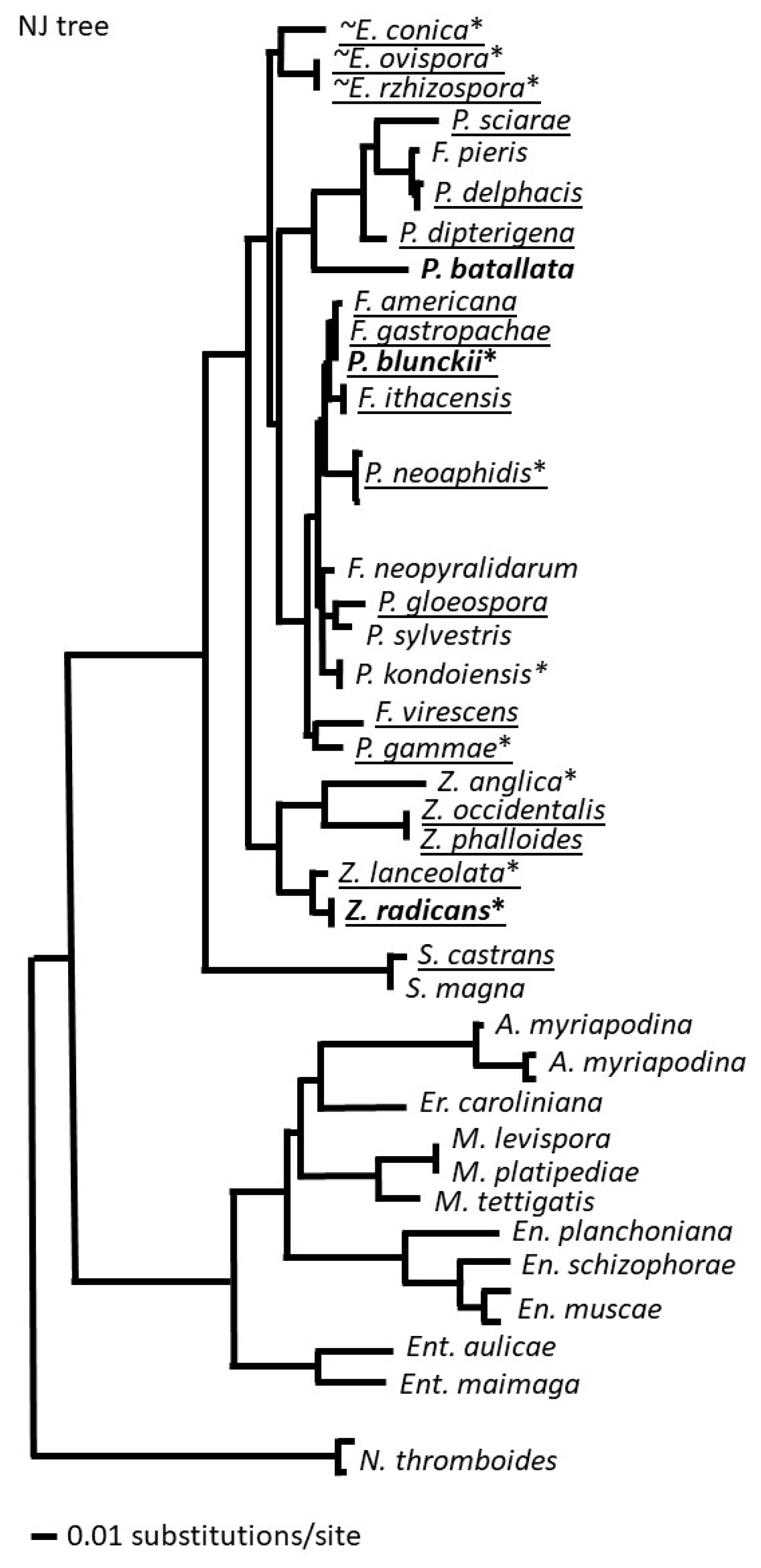
2.3. Phylogenetic tree
3. Results
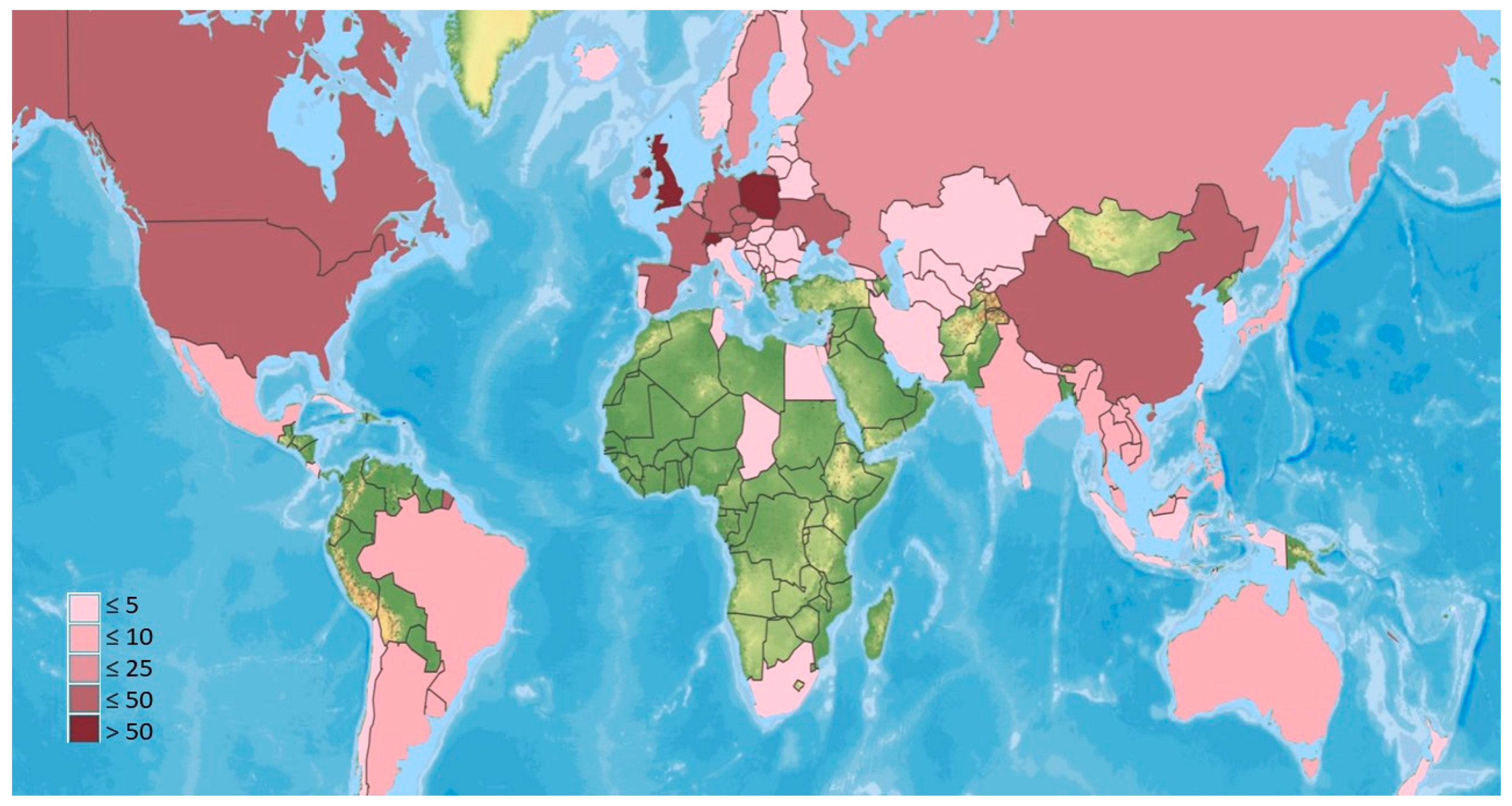
3.1. Geographic distribution
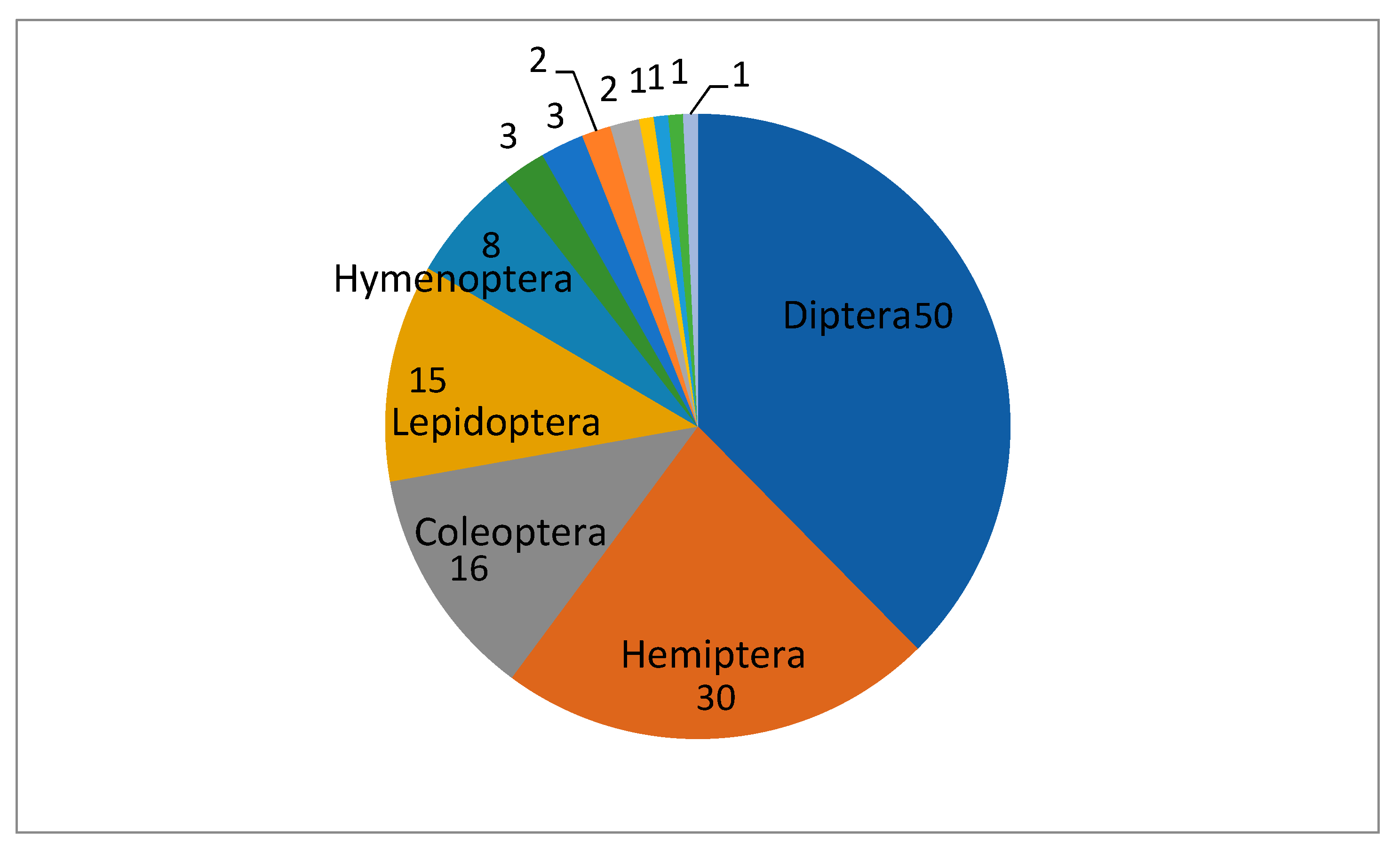
3.2. Host specificity
3.3. Biological and ecological characteristics of EFPSZ fungi as biocenose components
3.4. Cultivability
3.5. Genomics and Biotechnology
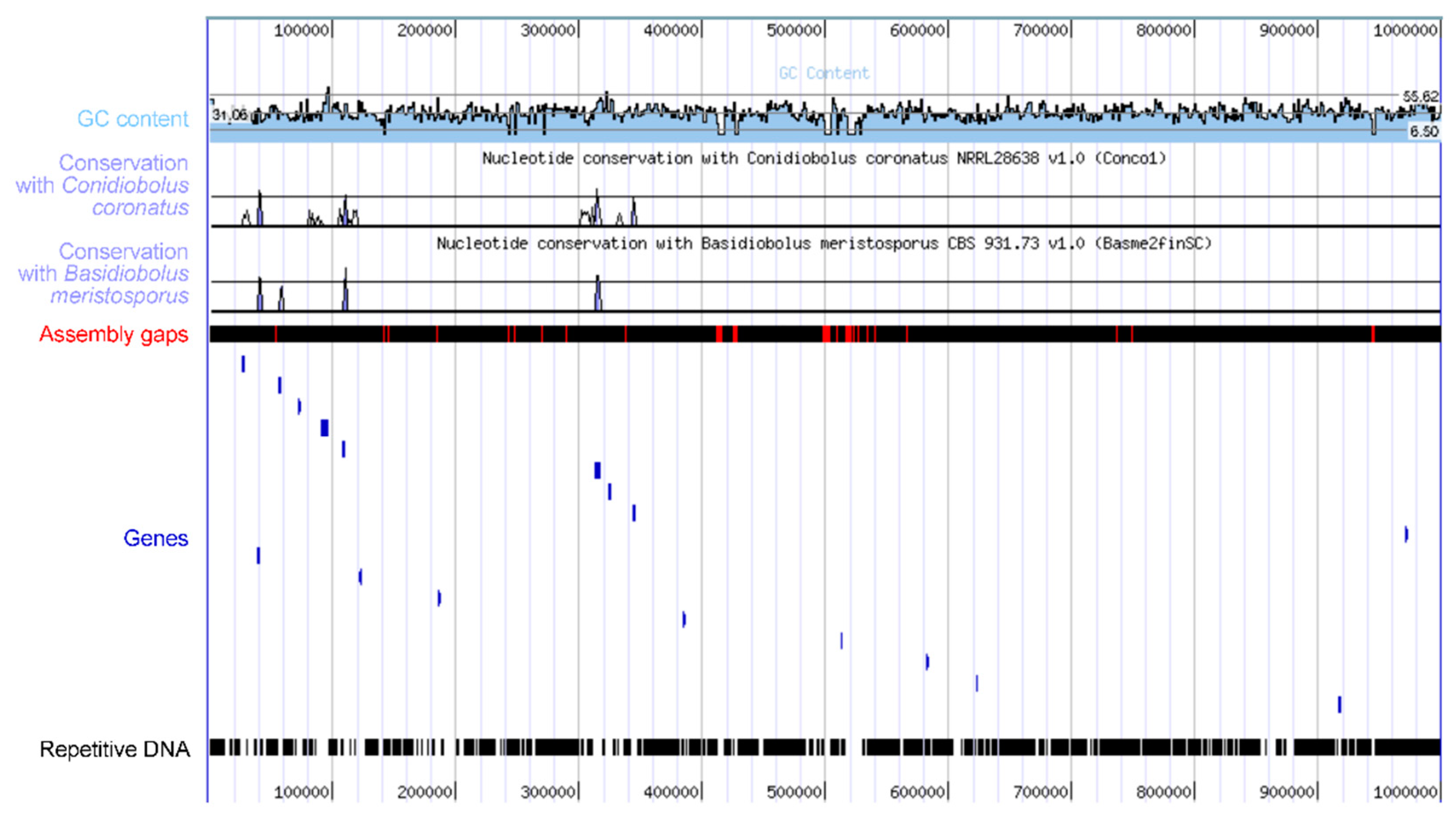
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- N. E. Sacco and A. E. Hajek, “Diversity and Breadth of Host Specificity among Arthropod Pathogens in the Entomophthoromycotina,” Microorganisms, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 1658, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Hajek and J. Eilenberg, Natural enemies : an introduction to biological control, Second edition. Cambridge, UK; New York: Cambridge University Press, 2018., 2018. [Online]. Available: http://find.library.duke.edu/catalog/DUKE010116949.
- S. Keller and O. Petrini, “Keys to the identification of the arthropod pathogenic genera of the families Entomophthoraceae and Neozygitaceae (Zygomycetes), with descriptions of three new subfamilies and a new genus,” Sydowia, vol. 57, pp. 23–53, 2005.
- P. A. Shah and J. K. Pell, “Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents,” Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 413–423, 2003. [CrossRef]
- J. P. M. Araújo and D. P. Hughes, “Chapter One - Diversity of Entomopathogenic Fungi: Which Groups Conquered the Insect Body?,” in Advances in Genetics, vol. 94, B. Lovett and R. J. St. Leger, Eds., in Genetics and Molecular Biology of Entomopathogenic Fungi, vol. 94. , Academic Press, 2016, pp. 1–39. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Evans, S. L. Elliot, and R. W. Barreto, “Entomopathogenic fungi and their potential for the management of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Americas,” Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, vol. 113, no. 3, pp. 206–214, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- B. S. Bamisile, J. A. Siddiqui, K. S. Akutse, L. C. Ramos Aguila, and Y. Xu, “General Limitations to Endophytic Entomopathogenic Fungi Use as Plant Growth Promoters, Pests and Pathogens Biocontrol Agents,” Plants, vol. 10, no. 10, Art. no. 10, 2021. [CrossRef]
- B. I. P. Barratt, “Assessing safety of biological control introductions.,” CABI Reviews, vol. 2011, pp. 1–12, 2012. [CrossRef]
- W. P. Madisson and D. R. Madisson, “Mesquite: a modular system for evolutionary analysis. Version 3.04,” Mesquite project. Accessed: Jun. 23, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.mesquiteproject.org/.
- D. L. Swofford, “PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and other methods) Version 4.0 beta.” 2001.
- B. Lovett and R. J. St. Leger, “The Insect Pathogens,” Microbiology Spectrum, vol. 5, no. 2, p. 10.1128/microbiolspec.funk-0001–2016, 2017. [CrossRef]
- ARSEF, “ARSEF Catalogues: USDA ARS.” Accessed: Oct. 31, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeast-area/ithaca-ny/robert-w-holley-center-for-agriculture-health/emerging-pests-and-pathogens-research/docs/mycology/page-2-arsef-catalogues/.
- M. W. Miller and C. B. Keil, “Redescription of Pandora gloeospora (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) from Lycoriella mali (Diptera: Sciaridae),” Mycotyaxon, vol. 38, pp. 227–231, 1990.
- J. F. Anderson and S. Z. Rongo, “Entomophthora aquatica sp. n. infecting larvae and pupae of floodwater mosquitoes,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 386–393, 1969. [CrossRef]
- S. Bałazy, Flora of Poland. Fungi (Mycota), Entomophthorales, vol. 24. Kraków, Poland: Polish Academy of Sciences, W. Szafer Institute of Botany, 1993.
- M. Gustafsson, “On the species of the genus Entomophthora Fr. in Sweden. 1. Classification and distribution,” Kungliga Landbruks-Högskolans Annaler, vol. 31, pp. 103–121, 1965.
- M. Gustafsson, “On species of the genus Entomophthora Fres. in Sweden. III. Possibility of usage in biological control,” Lantbrukshögsk. Ann., vol. 35, pp. 235–274, 1969.
- S. Keller, “Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales from Switzerland. III. First additions,” Sydowia, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 75–113, 1991.
- S. Keller, “Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales of Switzerland. II. Erynia, Eryniopsis, Neozygites, Zoophthora and Tarichium,” Sydowia, vol. 43, pp. 39–122, 1991.
- S. Keller and Y. G. C. Dhoi, “Insect pathogenic Entomophthorales from Nepal and India,” Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, vol. 80, pp. 211–215, 2007.
- E. Z. Koval, Flora Fungorum Ucrainical. Zygomycotina. Entomophthorales. Kyiv, Ukraine: National Academy of Sciences, 2007.
- D. M. MacLeod and E. Müller-Kögler, “Entomogenous fungi: Entomophthora species with pear-shaped to almost spherical conidia (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae),” Mycologia, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 823–893, 1973. [CrossRef]
- M. Niell and S. Santamaria, “Additions to the knowledge of Entomopathogenic Entomophthorales (Fungi, Zygomycota) from Spain,” Nova Hedwigia, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 167–197, 2001. [CrossRef]
- M. Z. Fan and Z. Z. Li, “Two new pathogens of dipteran insects,” Mycotaxon, vol. 50, pp. 307–314, 1994.
- M. Z. Fan and Z. Z. Li, “Erynia chironomis, comb. nov. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales),” Mycotaxon, vol. 53, p. 369, 1995.
- Z. Z. Li, Flora fungorum sinicorum. Entomophthorales, vol. 13. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
- S. Keller, “Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales from Switzerland. III. First additions,” Sydowia, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 75–113, 2007.
- S. Bałazy, “On some little known epizootics in noxious and beneficial arthropod populations caused by entomophthoralean fungi,” IOBC WPRS Bull., vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 63–68, 2003.
- S. Ben-Ze’ev, Y. Zelig, S. Bitton, and R. G. Kenneth, “The entomophthorales of Israel and their arthropod hosts: Additions 1980–1988,” Phytoparasitica, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 247–257, 1988. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Evlakhova, Entomopathogenic Fungi. Moscow: Nauka, 1974.
- J. A. Hutchison, “The Genus Entomophthora in the Western Hemisphere,” Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science (1903-), vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 237–254, 1963. [CrossRef]
- E. Z. Koval, Identification of Entomophilic Fungi of the USSR. Kyiv, Ukraine: Naukova Dumka, 1974.
- D. Leatherdale, “The arthropod hosts of entomogenous fungi in Britain,” Entomophaga, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 419–435, 1970. [CrossRef]
- M. P. Nadeau, G. B. Dunphy, and J. L. Boisvert, “Entomopathogenic fungi of the order Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina) in adult black fly populations (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Quebec,” Can J Microbiol, vol. 40, no. 8, pp. 682–686, 1994. [CrossRef]
- Z. Z. Li, Z. A. Chen, and Y. W. Xu, “Erynia gigantea, a new pathogen of spittlebug, Aphrophora sp.,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 263-265, 1990.
- L.-S. Zha, T.-C. Wen, K. D. Hyde, and J.-C. Kang, “中国虫霉目真菌及其寄主昆虫名录更新,” Mycosystema, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 666–683, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Keller, “New records of Entomophthoraceae (Fungi, Zygomycetes) from aquatic insects,” Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Gesell., vol. 78, pp. 333–336, 2005.
- R. A. Humber and I. Ben-Ze‘ev, “Erynia (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales): Emendation, Synonymy, and Transfers,” Mycotaxon, vol. XIII, no. 3, pp. 506–516, 1981.
- S. Keller and T. Hülsewig, “Amended description and new combination for Entomophthora nebriae Raunkiaer, (1893), a little known entomopathogenic fungus attacking the ground beetle Nebria brevicollis (Fabricius, 1792),” Alpine Entomology, vol. 2, pp. 1–5, 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. Tkaczyk, S. Bałazy, T. Krzyczkowski, and R. Wegensteiner, “Extended studies on the diversity of arthropod-pathogenic fungi in Austria and Poland,” Acta Mycologica, vol. 46, no. 2, Art. no. 2, 2011. [CrossRef]
- C. S. Jia, “Morphology of Pandora dipterigena collected from Lucilia sericata,” Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, vol. 21, no. 6, p. 546-548, 2010.
- R. Thaxter, “The Entomophthoreae of the United States,” Harvard botanical memoirs, vol. 2, pp. 133–201, 1888.
- S. Keller, “Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales from Switzerland. IV. Second addition,” Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, vol. 85, pp. 115–130, 2012.
- Y. J. Huang and Z. Z. Li, “Furia fujiana, a new pathogen of pale-lined tiger moth, Spilarctia obliqua,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–4, 1993.
- M. J. Filotas, A. E. Hajek, and R. A. Humber, “Prevalence and biology of Furia gastropachae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) in populations of forest tent caterpillar (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae),” The Canadian Entomologist, vol. 135, no. 3, pp. 359–378, 2003. [CrossRef]
- D. M. MacLeod and D. Tyrrell, “Entomophthora crustosa n. sp. as a pathogen of the forest tent caterpillar, Malacosoma disstria (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae),” The Canadian Entomologist, vol. 111, pp. 1137–1144, 1979.
- R. R. de Moraes, A. E. Loeck, and L. C. Berlamino, “Inimigos Naturais de Rachiplusia Nu (Guenne, 1852) e de Pseudoplusia Includens (Walker, 1857) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) em Soja no Rio Grande so Sul. - Portal Embrapa,” Pesq. Agropec. Bras., vol. 26, pp. 57–64, 1991.
- Y. J. Huang, B. N. Zheng, and Z. Z. Li, “Natural and induced epizootics of Erynia ithacensis in mushroom hothouse populations of yellow-legged fungus gnats,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 60, no. 3, p. 254-258, 1992. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ze‘ev, “Erynia neopyralidarum sp. nov. and Conidiobolus apiculatus, pathogens of pyralid moths components of the misdescribed species, Entomophthora pyralidarum (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales),” Mycotaxon, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 273–292, 1982.
- R. M. C. Pena, Y. Kunimi, T. Motobayashi, Y. Endoh, K. Numazawa, and J. Aoki, “Erynia neopyralidarum Ben-Ze’ev (Zygomycetes : Entomophthorales) Isolated from the Mulberry Tiger Moth, Spilosoma imparilis Butler (Lepidoptera : Arctiidae) in Japan,” Applied Entomology and Zoology, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 503–508, 1990. [CrossRef]
- W. Li, X. F. Wang, Z. H. Li, W. A. Xu, and C. F. Sheng, “Survey of entomophthoralean fungi in Shandong,” Entomological Knowledges, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 350–353, 2004.
- Z. Z. Li, M. Z. Fan, and B. Huang, “New combinations of entomophthoralean fungi originally in the genus Erynia,” Mycosystema, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 91–94, 1998.
- L. Villacarlos and N. Wilding, “Four new species of Entomophthorales infecting the leucaena psyllid Heteropsylla cubana in the Philippines,” Mycological Research, vol. 98, no. 2, pp. 153–164, 1994. [CrossRef]
- G. R. Lednev, Pathogens of the insect mycoses. Diagnostics manual. Saint Petersburg: Innovation Center of All-Russian Institute of Plant Protection Ltd., 2003.
- D. C. Steinkraus, A. J. Mueller, and R. A. Humber, “Furia virescens (Thaxter) Humber (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) Infections in the Armyworm, Pseudaletia unipuncta (Haworth) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Arkansas with Notes on Other Natural Enemies,” Journal of Entomological Science, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 376–386, 1993. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Sanchez-Peña, “Entomopathogens from two Chihuahuan desert localities in Mexico,” BioControl, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 63–78, 2000. [CrossRef]
- S. Keller, T. Hülsewig, and A. B. Jensen, “Fungi attacking springtails (Sminthuridae, Collembola) with a description of Pandora batallata, sp. nov. (Entomophthoraceae),” Sydowia, vol. 75, pp. 37–45, 2022.
- I. Ben-Ze’ev, R. G. Kenneth, and S. Bitton, “The Entomophthorales of Israel and their arthropod hosts,” Phytoparasitica, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 43–50, 1981. [CrossRef]
- M. Z. Fan, C. Guo, R. G. Liu, D. J. Li, and C. J. Wang, “New record genus Strongwellsea and Pandora blunckii in China,” Journal of Northwest Forestry College, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 26–30, 1992.
- A. Guzman-Franco, S. Clark, P. Alderson, and J. Pell, “Effect of temperature on the in vitro radial growth of Zoophthora radicans and Pandora blunckii, two co-occurring fungal pathogens of the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella,” BioControl, vol. 53, pp. 501–516, 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Sun, J. N. Liu, Q. Q. Wu, S. B. Wang, R. S. Cai, and B. Huang, “Investigation of Entomophthoralean resourse in Hefei,” Jorunal of Anhui Agricultural University, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 240–242, 2000.
- H. Tomiyama and J. Aoki, “Infection of Erynia blunkii (Lak. ex. Zimm.) Rem. et Henn. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) in the diamondback moth h, Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae),” Applied Entomology and Zoology, vol. 17, pp. 373–384, 1982. [CrossRef]
- L. Villacarlos, “Updated records of Philippine Entomophthorales,” Philippine Entomologist, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 22–52, 2008.
- M. Z. Fan, C. Guo, and Z. Z. Li, “New species and a new record of the genus Erynia in China.,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 95–100, 1991.
- D. M. MacLeod, D. Tyrrell, R. S. Soper, and A. J. De Lyzer, “Entomophthora bullata as a pathogen of Sarcophaga aldrichi,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 75–79, 1973. [CrossRef]
- T. R. Glare and R. J. Milner, “New Records of Entomophthoran Fungi from Insects in Australia,” Aust. J. Bot., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 69–77, 1987. [CrossRef]
- S. Keller, “Taxonomic considerations on some species of Erynia (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) attacking flies (Diptera),” Sydowia, vol. 45, pp. 252–263, 1993.
- S. Zangeneh and M. Ghazavi, “New Records of Entomophthoralean Fungi from Iran,” Rostaniha, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 190–203, 2008.
- C. Montalva, K. Collier, C. Luz, and R. A. Humber, “Pandora bullata (Entomophthoromycota: Entomophthorales) affecting calliphorid flies in central Brazil,” Acta Tropica, vol. 158, pp. 177–180, 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. Eilenberg et al., “Pandora cacopsyllae Eilenberg, Keller & Humber (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), a new species infecting pear psyllid Cacopsylla pyri L. (Hemiptera: Psyllidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 200, p. 107954, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Humber, “Synopsis of a revised classification for the Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina),” Mycotaxon, vol. 34, pp. 441–460, 1989.
- M. K. Miller and J. D. Harper, “Occurrence of Erynia delphacis in the threecornered alfalfa hopper, Spissistilus festinus (Homoptera: Membracidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 81–83, 1987. [CrossRef]
- Z. Z. Li, M. Z. Fan, and C. F. Qin, “New species and new records of Entomophthorales in China,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 182–187, 1992.
- G. M. I. Lorenz, “Pandora delphacis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) an entomopathogenic fungus of the threecornered alfalfa hopper, Spissistilus festinus (Homoptera: Membracidae),” University of Arkansas ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, Ann Arbor, MI, 1995. Accessed: Aug. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.proquest.com/openview/74cf7739893ac6f070c578200c04fcfc/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y.
- M. Takehiko, S. Hiroki, and S. Mitsuaki, “Isolation of an entomogenous fungus, Erynia delphacis (Entomophthorales : Entomophthoraceae), from migratory planthoppers collected over the Pacific Ocean,” Applied Entomology and Zoology, vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 545–549, 1998. [CrossRef]
- A. Foieri, N. Pedrini, and A. Toledo, “Natural occurrence of the entomopathogenic genus Pandora on spittlebug pests of crops and pastures in Argentina,” Journal of Applied Entomology, vol. 142, no. 3, pp. 363–370, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Barta and L. Cagáň, “Aphid-pathogenic Entomophthorales (their taxonomy, biology and ecology),” Biologia, vol. 61, no. 21, pp. S543–S616, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Barta and L. Cagáň, “Observations on the Occurrence of Entomophthorales Infecting Aphids (Aphidoidea) in Slovakia,” BioControl, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 795–808, 2006. [CrossRef]
- I. S. Ben-Ze’ev, “Check-list of fungi pathogenic to insects and mites in Israel, updated through 1992,” Phytoparasitica, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 213–237, 1993. [CrossRef]
- Y. J. Huang and B. N. Zheng, “A new record species of Erynia from China,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 327-328, 1990.
- S. E. Méndez-Sánchez, A. L. Freitas, C. S. de Almeida, G. B. Silva, and L. S. Lima, “Levantamiento preliminar de hongos entomophthorales (Zygomycotina: Zygomycetes), agentes de control natural de insectos al sur de Bahia, Brasil,” Agrotropica, vol. 14, no. 2, Art. no. 2, 2002.
- G. Remaudière and J. P. Latge, “Importancia de los hongos patógenos de insectos (especialmente Aphididae y Cercopidae) en Méjico y perspectivas de uso,” Boletín de sanidad vegetal. Plagas, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 217–225, 1985.
- A. M. Young, D. Tyrrell, and D. M. MacLeod, “Entomophthora echinospora (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), a fungus pathogenic on the neotropical cicada, Procollina biolleyi (Homoptera: Cicadidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 87–90, 1973. [CrossRef]
- P. Baiswar and D. M. Firake, “First record of Pandora formicae on ant, Camponotus angusticollis and Batkoa amrascae on white leaf hopper, Cofana spectra in rice agroecosystem of India,” Journal of Eco-friendly Agriculture, vol. 17, no. 1, Art. no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Małagocka, A. B. Jensen, and J. Eilenberg, “Pandora formicae, a specialist ant pathogenic fungus: New insights into biology and taxonomy,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 143, pp. 108–114, 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. G. Newman and G. R. Carner, “Factors affecting the spore form of Entomophthora gammae,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 29–34, 1975. [CrossRef]
- F. Moscardi, B. S. Correra Ferreira, C. B. Hoffmann-Campo, E. B. de Oliveira, and D. G. Boucias, “Ocorrência de entomopatogenos em lepidópteros que atacam a cultura da soja no Paraná,” presented at the Congresso Brasiliero de Entomologia, Londrina, PR: Resumos, 1984, p. 143.
- S. L. DIez and J. C. Gamundi, “Empleo de enfermedades como método de biocontrol de insectos plagas,” Tecnología para el campo. INTA, vol. 10, pp. 19–20, 1985.
- R. A. Samson, H. C. Evans, and J.-P. Latgé, Atlas of Entomopathogenic Fungi. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1988. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Edelstein and R. E. Lecuona, “Presencia del hongo entomopatógeno Pandora gammae (Weiser) Humber (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales), en el complejo de ‘orugas medidoras de la soja’ (Lepidoptera: Plusiinae) en Argentina,” RIA. Revista de Investigaciones Agropecuarias, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 31–38, 2003.
- C. C. López Lastra and A. C. Scorsetti, “Hongos patógenos de insectos en Argentina (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales,” Revista de Biología Tropical, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 311–315, 2006. [CrossRef]
- C. C. López Lastra and A. C. Scorsetti, “Revisión de los hongos Entomophthorales (Zygomycota: Zygomycetes) patógenos de insectos de la República Argentina,” Boletín de la Sociedad Argentina de Botánica, vol. 41, no. 1–2, pp. 33–37, 2007.
- Z. Z. Li, B. Huang, and M. Z. Fan, “New species, new record, new combinations and emendation of entomophthoralean fungi pathogenic on dipteran insects,” Mycosystema, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 91–96, 1997.
- C. S. Jia and B. Hong, “Zoophthora radicans infecting larvae of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and its epizootic,” Mycosystema, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 322–330, 2012.
- J. J. Hannam and D. C. Steinkraus, “The natural occurrence of Pandora heteropterae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) infecting Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 103, no. 2, pp. 96–102, 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Milner and J. Bourne, “Influence of temperature and duration of leaf wetness on infection of Acyrthosiphon kondoi with Erynia neoaphidis,” Annals of Applied Biology, vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 19–27, 1983. [CrossRef]
- I. M. Hall, A. D. Lowe, and B. B. Given, “New record of aphid hosts of Entomophthora aphidis and Entomophthora planchoniana in New Zealand,” N. Z. J. Zool., vol. 3, pp. 111–112, 1976.
- R. J. Milner, R. E. Teakle, G. G. Lutton, and F. M. Dare, “Pathogens (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) of the blue-green aphid Acyrthosiphon kondoi Shinji and other aphids in Australia,” Aust. J. Bot., vol. 28, no. 6, pp. 601–619, 1980. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kobayashi, K. Mogami, and J. Aoki, “Ultrastructural studies on the hyphal growth of Erynia neoaphidis in the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae,” Trans. Mycol. Soc. Jpn., vol. 25, pp. 425–434, 1984.
- W. H. Lu and W. M. Wang, “Investigation and identification of several aphid entomophthoralean fungi in Shandong Province,” Microbiology, vol. 15, p. 155-159, 1988.
- B. Papierok, “On the occurrence of Entomophthorales (Zygomycetes) in Finland. I. Species attacking aphids (Homoptera, Aphididae),” Ann. Entomol. Fenn., vol. 55, pp. 63–69, 1989.
- M.-G. Feng, J. B. Johnson, and L. P. Kish, “Survey of Entomopathogenic Fungi Naturally Infecting Cereal Aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) of Irrigated Grain Crops in Southwestern Idaho,” Environmental Entomology, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 1534–1542, 1990. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Feng, R. M. Nowierski, A. L. Scharen, and D. C. Sands, “Entomopathogenic fungi (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales) infecting cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Montana.,” Pan-Pacific Entomologist, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 55–64, 1991.
- Z. Yu, G. L. Nordin, G. C. Brown, and D. M. Jackson, “Studies on Pandora neoaphidis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) Infectious to the Red Morph of Tobacco Aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae),” Environmental Entomology, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 962–966, 1995. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Tzean, L. S. Hsieh, and W. J. Wu, Atlas of Entomopathogenic Fungi from Taiwan. Taiwan, Republic of China: Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, 1997.
- C.-S. Yoon, G.-H. Sung, B.-R. Choi, J.-K. Yoo, and J.-O. Lee, “The Aphid-attacking Fungus Pandora neoaphidis; the First Observation and its Host Range in Korea,” The Korean Journal of Mycology, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 407–410, 1998.
- J. L. Hatting, R. A. Humber, T. J. Poprawski, and R. M. Miller, “A Survey of Fungal Pathogens of Aphids from South Africa, with Special Reference to Cereal Aphids,” Biological Control, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–12, Sep. 1999. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Hatting, T. J. Poprawski, and R. M. Miller, “Prevalences of fungal pathogens and other natural enemies of cereal aphids (Homoptera:Aphididae) in wheat under dryland and irrigatedconditions in South Africa,” BioControl, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 179–199, 2000. [CrossRef]
- C. Nielsen, J. Eilenberg, S. Harding, E. Oddsdottir, and G. Halldórsson, “Geographical distribution and host range of entomophthorales infecting the green spruce aphid Elatobium abietinum Walker in Iceland,” J Invertebr Pathol, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 72–80, 2001. [CrossRef]
- C. Nielsen, C. Sommer, J. Eilenberg, K. S. Hansen, and R. A. Humber, “Characterization of aphid pathogenic species in the genus Pandora by PCR techniques and digital image analysis,” Mycologia, vol. 93, no. 5, pp. 864–874, 2001. [CrossRef]
- E. G. Voronina, G. R. Lednev, and T. J. Mukamolova, “Entomophthoralean fungi,” in Pathogens of Insects: structural and functional aspects, V. V. Glupov., Moscow: Kruglyi god, 2001, pp. 271–351.
- W. Li and C.-F. Sheng, “Occurrence and distribution of entomophthoralean fungi infecting aphids in mainland China,” Biocontrol Science and Technology, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 433–439, 2007. [CrossRef]
- A. C. Scorsetti, R. A. Humber, J. J. García, and C. C. L. Lastra, “Natural occurrence of entomopathogenic fungi (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) of aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) pests of horticultural crops in Argentina,” BioControl, vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 641–655, 2007. [CrossRef]
- A. C. Scorsetti, A. Maciá, D. C. Steinkraus, and C. C. López Lastra, “Prevalence of Pandora neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) infecting Nasonovia ribisnigri (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on lettuce crops in Argentina,” Biological Control, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 46–50, 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. Alzugaray et al., “Prospección de agentes de mortalidad natural de áfidos en leguminosas forrajeras en Uruguay,” Agrociencia (Uruguay), vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 27–35, 2010.
- A. Moubasher, M. Abdel-Rahman, A. Abdel-Mallek, and G. Hammam, “Biodiversity of entomopathogenic fungi infecting wheat and cabbage aphids in Assiut, Egypt,” 2010. Accessed: Oct. 29, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Biodiversity-of-entomopathogenic-fungi-infecting-in-Moubasher-Abdel-Rahman/eacd7e417f99819407ecd4adb9c988585db3c1ad.
- I. Ben Fekih, S. Boukhris-Bouhachem, M. Bechir Allagui, A. Bruun Jensen, and J. Eilenberg, “First survey on ecological host range of aphid pathogenic fungi (Phylum Entomophthoromycota) in Tunisia,” Annales de la Société entomologique de France (N.S.), vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 140–144, 2015. [CrossRef]
- I. Ben Fekih et al., “Virulence of Two Entomophthoralean Fungi, Pandora neoaphidis and Entomophthora planchoniana, to Their Conspecific (Sitobion avenae) and Heterospecific (Rhopalosiphum padi) Aphid Hosts,” Insects, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 54, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Keller, “Entomophthorales attacking aphids with a description of two new species,” Sydowia, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 38–74, 2006.
- A. V. Toledo, R. A. Humber, and C. C. L. Lastra, “First and southernmost records of Hirsutella (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) and Pandora (Zygomycota: Entomophthorales) species infecting Dermaptera and Psocodea,” J Invertebr Pathol, vol. 97, no. 2, pp. 193–196, 2008. [CrossRef]
- T. Steenberg, V. Langer, and P. Esbjerg, “Entomopathogenic fungi in predatory beetles (Col.: Carabidae and Staphylinidae) from agricultural fields,” Entomophaga, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 77–85, 1995. [CrossRef]
- Yu. A. Gres and E. Z. Koval, “A new species Entomorphthora terrestris sp. nova. Affecting the sugar-beet root aphid,” Mikrobiologicheskij Zhurnal, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 64–69, 1982.
- A. Barta and L. Cagáň, “Pandora uroleuconii sp. nov. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), a new pathogen of aphids.,” Mycotaxon, vol. 88, pp. 79–86, 2003.
- J. Eilenberg, V. Michelsen, and R. Humber, “Strongwellsea tigrinae and Strongwellsea acerosa (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), two new species infecting dipteran hosts from the genus Coenosia (Muscidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 175, p. 107444, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Batko and J. Weiser, “On the taxonomic position of the fungus discovered by Strong, Wells, and Apple: Strongwellsea castrans gen. et sp. nov. (Phycomycetes; Entomophthoraceae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 455–463, 1965.
- S. Keller, “Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales of Switzerland. I. Conidiobolus, Entomophaga and Entomophthora,” Sydowia, vol. 40, pp. 122–167, 1987.
- J. Eilenberg, V. Michelsen, A. B. Jensen, and R. A. Humber, “Strongwellsea crypta (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), a new species infecting Botanophila fugax (Diptera: Anthomyiidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 186, p. 107673, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Eilenberg, V. Michelsen, A. B. Jensen, and R. A. Humber, “Strongwellsea selandia and Strongwellsea gefion (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), two new species infecting adult flies from genus Helina (Diptera: Muscidae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 193, p. 107797, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Humber, “The systematics of the genus Strongwellsea (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales),” Mycologia, vol. 68, no. 5, pp. 1042–1060, 1976.
- J. Eilenberg and V. Michelsen, “Natural host range and prevalence of the genus Strongwellsea (Zygomycota: Entomophthorales) in Denmark,” J Invertebr Pathol, vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 189–198, 1990. [CrossRef]
- J. Eilenberg and A. B. Jensen, “Strong host specialization in fungus genus Strongwellsea (Entomophthorales),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 157, pp. 112–116, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Turian, “Entomo-mycoses dans la région de Genéve,” Entomol. Ges., vol. 30, pp. 93–98, 1957.
- Z. Z. Li, “Erynia anhuensis, a new pathogen of aphids,” Acta Mycologica Sinica, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1–6, 1986.
- R. X. Gao, G. X. Lin, and X. Guan, “A list of Fujian pathogenic microbes on pest,” Journal of Fujian Agricultural College, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 300–310, 1986.
- L. T. Villacarlos and B. S. Mejia, “Philippine entomopathogenic fungi I. Occurrence and diversity,” Philippine Agricultural Scientist, vol. 87, no. 3, pp. 249–265, 2004.
- E. G. Voronina and T. J. Mukamolova, Diagnostics of Entomophthoroses of harmful insects. Saint Petersburg: OOO Innovation Center VIZR, 2002.
- Z. Z. Li, Z. A. Chen, C. R. Lu, and H. Z. Hong, “Some entomophthoralean species in Shennongjia,” in Fungi and lichens of Shengnongjia, in Mycological and lichenological expedition to Shengnongjia, Academia Sinica (ed.). , Beijing: World Publishing Corporation, 1989, pp. 79–83.
- D. M. MacLeod, D. Tyrrell, and R. S. Soper, “Entomophthora canadensis n.sp., a fungus pathogenic on the woolly pine needle aphid, Schizolachnus piniradiatae,” Canadian Journal of Botany, vol. 57, no. 23, pp. 2663–2672, 1979. [CrossRef]
- C. Aruta and R. Carvillo, “Identificación de hongos del orden Entomophthorales en Chile. III,” Agro Sur., vol. 17, pp. 10–14, 1989.
- A. E. Hajek et al., “Phylogenetic placement of two species known only from resting spores: Zoophthora independentia sp. nov. and Z. porteri comb nov. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae),” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 140, pp. 68–74, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Keller, “Two new species of the genus Zoophthora Batko (Zygomycetes, Entomophthoraceae): Z. lanceolata and Z. crassitunicata,” Sydowia, no. 33, pp. 167–173, 1980.
- C. Nielsen and A. E. Hajek, “Control of Invasive Soybean Aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae), Populations by Existing Natural Enemies in New York State, with Emphasis on Entomopathogenic Fungi,” Environmental Entomology, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 1036–1047, 2005. [CrossRef]
- K. L. Wu, Z. H. Huang, and C. H. Chen, “A new Zoophthora occidentalis pathogenof Myzus persicae in China,” Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, vol. 29, no. 7, p. 673-677, 2014.
- T. R. Glare, R. J. Milner, and G. A. Chilvers, “The effect of environmental factors on the production, discharge, and germination of primary conidia of Zoophthora phalloides Batko,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 48, no. 3, p. 275, 1986. [CrossRef]
- Uziel and R. G. Kenneth, “Survival of primary conidia and capilliconidia at different humidities in Erynia (subgen. Zoophthora) spp. and in Neozygites fresenii (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales), with special emphasis on Erynia radicans,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 118–126, 1991. [CrossRef]
- R. G. Manfrino, L. A. Castrillo, C. C. L. Lastra, A. V. Toledo, W. Ferrari, and A. B. Jensen, “Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Entomophthorales (Entomophthoromycota: Entomophthoromycotina) from Argentina,” Acta Myc, vol. 55, no. 2, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. E. Hajek, K. T. Hodge, J. K. Liebherr, W. H. Day, and J. D. Vandenberg, “Use of RAPD analysis to trace the origin of the weevil pathogen Zoophthora phytonomi in North America,” Mycological Research, vol. 100, no. 3, pp. 349–355, 1996. [CrossRef]
- M. Shimazu, “Resting Spore Formation of Entmophthora sphaerosperma FRESENIUS (Entomophthorales : Entmophthoraceae) in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (STAL)(Hemiptera : Delphacidae),” Appl. entomol. Zool, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 383–388, 1979. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Milner and R. J. Mahon, “Strain Variation in Zoophthora Radicans, a Pathogen on a Variety of Insect Hosts in Australia,” Australian Journal of Entomology, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 195–198, 1985. [CrossRef]
- B. Huang, B. N. Zheng, and H. Q. Zhu, “Isolation, identification and biological determination of Erynia radicans,” Practical Forestry Technology, vol. 1998, no. 6, pp. 16–18, 1988.
- S. Galaini-Wraight, S. P. Wraight, R. I. Carruthers, B. P. Magalhães, and D. W. Roberts, “Description of a Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) epizootic in a population of Empoasca kraemeri (Homoptera: Cicadellidae) on beans in central Brazil,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 311–326, 1991. [CrossRef]
- R. Alzugaray, S. Stewart, and M. S. Zebrino, “Epizootia por hongos sobre Epinotia aporema (Wals) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) en Uruguay,” Boletín de la Sociedad Zoológica de Uruguay, vol. 7, p. 79, 1992.
- R. Alzugaray, M. S. Zerbino, S. Stewart, A. Ribeiro, and J. Eilenberg, “Epizootiologia de hongos Entomophthorales. Uso de Zoophthora radicans (Brefeld) Batko (Zygomicotina: Entomophthorales) para el control de Epinotia aporema (Wals.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) en Uruguay,” Revista de la Sociedad Entomologica Argentina, vol. 58, pp. 307–311, 1999.
- T. Nagahama, H. Sato, M. Shimazu, and J. Sugiyama, “Phylogenetic Divergence of the Entomophthoralean Fungi: Evidence from Nuclear 18S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequences,” Mycologia, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 203–209, 1995. [CrossRef]
- L. G. Leite, S. B. Alves, S. P. Wraight, S. Galaini-Wraight, and D. W. Roberts, “Habilidade de infecção de isolados de Zoophthora radicans sobre Empoasca kraemeri,” Sci Agríc., vol. 53, pp. 152–158, 1996.
- C. Lastra and A. Scorsetti, “Revisión de los hongos Entomophthorales (Zygomycota: Zygomycetes) patógenos de insectos de la República Argentina,” Boletín de la Sociedad Argentina de Botánica, vol. 42, no. 1–2, pp. 33–37, 2007.
- A. W. Guzmán-Franco, S. D. Atkins, P. G. Alderson, and J. K. Pell, “Development of species-specific diagnostic primers for Zoophthora radicans and Pandora blunckii; two co-occurring fungal pathogens of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella,” Mycol Res, vol. 112, no. Pt 10, pp. 1227–1240, 2008. [CrossRef]
- A. W. Guzmán-Franco, S. J. Clark, P. G. Alderson, and J. K. Pell, “Competition and co-existence of Zoophthora radicans and Pandora blunckii, two co-occurring fungal pathogens of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella,” Mycol Res, vol. 113, no. Pt 11, pp. 1312–1321, 2009. [CrossRef]
- L. F. A. Alves, L. G. Leite, and D. G. P. de Oliveira, “Primeiro Registro de Zoophthora radicans (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) em Adultos da Ampola-da-Erva-Mate, Gyropsylla spegazziniana Lizer & Trelles (Hemiptera: Psyllidae), no Brasil,” Neotrop. entomol., vol. 38, pp. 697–698, 2009. [CrossRef]
- G. M. Mascarin, V. da S. Duarte, M. M. Brandão, and Í. Delalibera, “Natural occurrence of Zoophthora radicans (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) on Thaumastocoris peregrinus (Heteroptera: Thaumastocoridae), an invasive pest recently found in Brazil,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 110, no. 3, pp. 401–404, 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. G. Manfrino, L. Zumoffen, C. E. Salto, and C. C. López Lastra, “Potential plant–aphid–fungal associations aiding conservation biological control of cereal aphids in Argentina,” International Journal of Pest Management, vol. 59, no. 4, pp. 314–318, 2013. [CrossRef]
- R. G. Manfrino, A. C. Gutiérrez, D. C. Steinkraus, C. E. Salto, and C. C. López Lastra, “Prevalence of entomophthoralean fungi (Entomophthoromycota) of aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on solanaceous crops in Argentina,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 121, pp. 21–23, 2014. [CrossRef]
- R. Manfrino, J. Hatting, R. Humber, C. Salto, and C. Lastra, “Natural occurrence of entomophthoroid fungi (Entomophthoromycota) of aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on cereal crops in Argentina,” Annals of Applied Biology, vol. 164, pp. 1–8, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Ribeiro, H. Silva, E. Castiglioni, S. Bartaburu, and J. J. Martínez, “Control natural de Crocidosema (Epinotia) aporema (Walsingham) (Lepidoptera:Tortricidae) por parasitoides y hongos entomopatógenos en Lotus corniculatus y Glycine max,” Agrociencia (Uruguay), vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 36–41, 2015.
- S. Choi et al., “Occurrence of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Zoophthora radicans (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) in Jeollabuk-do, Korea,” Korean Journal of Applied Entomology, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 195–201, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Gryganskyi, B. A. Mullens, M. T. Gajdeczka, S. A. Rehner, R. Vilgalys, and A. E. Hajek, “Hijacked: Co-option of host behavior by entomophthoralean fungi,” PLOS Pathogens, vol. 13, no. 5, p. e1006274, May 2017. [CrossRef]
- M.-G. Feng, C. Chen, S.-W. Shang, S.-H. Ying, Z.-C. Shen, and X.-X. Chen, “Aphid dispersal flight disseminates fungal pathogens and parasitoids as natural control agents of aphids,” Ecological Entomology, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 97–104, 2007. [CrossRef]
- A. E. Hajek, B. Papierok, and J. Eilenberg, “Methods for study of the Entomophthorales,” in Manual of Techniques in Invertebrate Pathology (Second Edition), L. A. Lacey, Ed., San Diego: Academic Press, 2012, pp. 285–316. [CrossRef]
- E. Müller-Kögler, “Zur Isolierung und Kultur Insektenpathogener Entomophthoraceen,” Entomophaga, vol. 3, pp. 261–275, 1959.
- L. C. Muskat, Y. Kerkhoff, P. Humbert, T. W. Nattkemper, J. Eilenberg, and A. V. Patel, “Image analysis-based quantification of fungal sporulation by automatic conidia counting and gray value correlation,” MethodsX, vol. 8, p. 101218, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. C. Muskat, L. M. Görg, P. Humbert, J. Gross, J. Eilenberg, and A. V. Patel, “Encapsulation of the psyllid-pathogenic fungus Pandora sp. nov. inedit. and experimental infection of target insects,” Pest Manag Sci, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 991–999, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. E. Hajek, R. A. Humber, and M. H. Griggs, “Decline in virulence of Entomophaga maimaiga (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) with repeated in vitro subculture,” Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 91–97, 1990. [CrossRef]
- J. F. Tabima et al., “Phylogenomic analyses of non-Dikarya fungi supports horizontal gene transfer driving diversification of secondary metabolism in the amphibian gastrointestinal symbiont, Basidiobolus,” G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, vol. 10, no. 9, pp. 3417–3433, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. R. Amses et al., “Diploid-dominant life cycles characterize the early evolution of Fungi,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 119, no. 36, p. e2116841119, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. E. Bushley et al., “The Genome of Tolypocladium inflatum: Evolution, Organization, and Expression of the Cyclosporin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster,” PLoS Genet, vol. 9, no. 6, p. e1003496, 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. de Bekker, R. A. Ohm, H. C. Evans, A. Brachmann, and D. P. Hughes, “Ant-infecting Ophiocordyceps genomes reveal a high diversity of potential behavioral manipulation genes and a possible major role for enterotoxins,” Sci Rep, vol. 7, p. 12508, 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. Seto et al., “A combined microscopy and single-cell sequencing approach reveals the ecology, morphology, and phylogeny of uncultured lineages of zoosporic fungi,” mBio, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. e01313-23, 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Grigoriev et al., “The Genome Portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute,” Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 40, no. D1, pp. D26–D32, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Gryganskyi et al., “Sequencing the Genomes of the First Terrestrial Fungal Lineages: What Have We Learned?,” Microorganisms, vol. 11, no. 7, Art. no. 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- I. V. Grigoriev et al., “MycoCosm portal: gearing up for 1000 fungal genomes,” Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 42, no. D1, pp. D699–D704, 2014. [CrossRef]
- E. Quesada-Moraga, N. González-Mas, M. Yousef-Yousef, I. Garrido-Jurado, and M. Fernández-Bravo, “Key role of environmental competence in successful use of entomopathogenic fungi in microbial pest control,” J Pest Sci, 2023. [CrossRef]
| Species | Host Order (all Insecta, except as noted) | Host family | Location in details | Reference (based on literature search and ARSEF collection records) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~Erynia aquatica* (2) | &Diptera | Culicidae | Europe: Poland, RF, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine; Nepal; USA | [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23] |
| ~E. chironomi | Diptera | Chironomidae | China; Sweden, all of Europe | [15,17,24,25,26] |
| E. cicadellis | Hemiptera | Cicadellidae | Switzerland | [27] |
| ~E. conica* (6) | Diptera, Trichoptera | Chaoboridae, Chironomidae, Culicidae,Psychodidae, Simuliidae, Tipulidae | Asia incl. Israel; Australia; Europe: Poland, RF, Spain, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine; USA | [15,18,19,21,23,28,29,30,31] |
| ~E. curvispora* (3) | &Diptera | Chironomidae, Culicidae, Psychodidae, Simuliidae | China; Europe: Belarus, Estonia, Poland, RF, Switzerland, Ukraine; Israel; NA | [15,18,19,21,26,29,32,33,34] |
| E. delpiniana | Diptera | Muscidae | Italy | [15] |
| E. fluvialis | Diptera | Nematocera | Switzerland | [27] |
| E. gigantea | Hemiptera | Aphrophoridae | China | [35,36] |
| ~E. gracilis | Diptera | Minute gnats | Switzerland; eastern USA | [15,37] |
| ~E. henrici | Diptera | Culicidae | France; Israel | [38] |
| E. jaczewskii | Coleoptera | Carabidae | Ukraine | [21] |
| E. nebriae | Coleoptera | Carabidae | Denmark, Germany | [39] |
| ~E. ovispora* (2) | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Lonchaeidae, Muscidae, Psychodidae, Sarcophagidae, Syrphidae, Tipulidae | Asia: Israel, China, RF; Europe: Austria, Poland, RF, Sakartvelo, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine; NA | [15,16,17,18,19,21,29,30,36,40] |
| ~E. plecopteri | Plecoptera | Nemouridae | Europe: Spain, Switzerland, UK; NZ | [15,23,27] |
| ~E. rhizospora (8) | Diptera, Trichoptera | Hydropsychidae, Phryganeidae | China; Europe: Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK; USA | [15,18,19,31,41,42] |
| ~E. sepulchralis (1) | Diptera, Trichoptera | Anthomyzidae, Rhagionidae, Syrphidae, Tipulidae | Europe: Poland, Ukraine; USA | [15,21,42] |
| ~E. thurgoviensis | Diptera | Psychodidae | Switzerland | [43] |
| E. tumefacta | Diptera | Muscidae | Switzerland | [27] |
| ~E. variabilis | Diptera | Psychodidae | Europe: Poland, Ukraine, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland; NA | [15,18,19,21,23,31,42] |
| Furia americana (5) | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Muscidae, Sarcophagidae | Brazil; Europe: Italy, Switzerland, UK; USA | [15,18,19,26,27,31,33,42] |
| F. creatonoti | Lepidoptera | Arctiidae, Erebidae | China, Sri Lanka, Taiwan | [15,22,26] |
| F. ellisiana | Dermaptera | Forficulidae | Europe: Poland, Switzerland, UK | [15] |
| F. fujiana | Lepidoptera | Erebidae | China | [26,44] |
| F. fumimontana | Diptera | suborder Brachycera | NA; Poland | [3,15] |
| F. gastropachae (13) | Lepidoptera | Lasiocampidae, Noctuidae | Brazil; China; Europe: Ukraine Spain; NA: Canada, USA | [15,21,23,26,45,46,47] |
| F. ithacensis (4) | Diptera | Empididae, Rhagionidae, Sciaridae | China; Europe: Poland, Spain; USA | [15,23,26,48] |
| ~F. montana | Diptera | Chironomidae | UK; USA | [15,18,19,31,33,42] |
| F. neopyralidarum (1) | Lepidoptera | Erebidae, Piralidae, Tortricidae | Israel, Japan | [15,49,50] |
| F. pieris (1) | Lepidoptera | Pieridae, Zygaeindae | China; NA incl. USA | [15,49,50] |
| F. shandongensis | Dermaptera | Forficulidae | China | [26,51] |
| F. triangularis | Hemiptera | Psyllidae | China, Philippines | [26,52,53] |
| F. virescens (4) | Lepidoptera | Noctuidae | Asia: China, Turkmenistan; Europe: Czech, Finland, Germany, Poland, RF, Spain, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine; NA | [15,18,19,23,30,31,32,33,42,54,55] |
| F. vomitoriae | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Stratiomyiidae, Syrphidae | Europe: Austria, Czech, Poland, RF; Mexico | [15,40,56] |
| F. zabri | Coleoptera | Carabidae | Europe: Czech, Ukraine; Uzbekistan | [15,21] |
| Pandora aleurodis | Hemiptera | Aleyrodidae | Romania | [15] |
| P. batallata | Entognatha, Symphypleona | Sminthuridae | Germany | [57] |
| ~P. bibionis | Diptera | Bibionidae, Sciaridae | China; Switzerland | [26,43,51] |
| P. blunckii (34) | Hymenoptera, Lepidoptera | Plutellidae, Tenthredinidae, Tortricidae | Asia: Israel, China, Japan, Philippines; Australia; Europe (not reported in Poland); Mexico | [15,18,19,26,41,58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| P. borea | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Muscidae, Sarcophagidae | China | [26,64] |
| P. brahminae | Coleoptera | Scarabaeidae | Bharat, China | [15,26] |
| P. bullata | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Sarcophagidae | Brazil; Australia; Europe: Spain, Switzerland, UK; Iran; NA: USA, Canada; SА | [15,18,19,23,27,65,66,67,68,69] |
| P. cacopsyllae* | Hemiptera | Psyllidae | Denmark | [70] |
| P. calliphorae | Diptera | Anthomyiidae | China; France | [26,71] |
| ~P. chironomid | Diptera | Chironomidae | China | [24] |
| P. cicadellis | Homoptera | Cicadellidae | China | [26,52] |
| P. dacnusae | Hymenoptera | Braconidae | Poland | [15] |
| P. delphacis (64) | Hemiptera | Delphacidae | Asia: Bharat, China, East Asia, Indonesia, Japan, Philippines; SA: Brazil, Argentina; Switzerland; USA | [15,26,43,62,63,72,73,74,75,76] |
| ~P. dipterigena (8) | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Muscidae, Mycetophilidae,Psychodidae,Rhagionidae, Sciaridae, Syrphidae, Tachinidae, Tipulidae | Asia: Bharat, China, Indonesia, Iran, Israel; Brazil; Europe: Austria, Poland, RF, Sakartvelo, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine; NA: Mexico, USA | [15,16,17,21,23,26,30,31,33,40,41,42,68,77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| P. echinospora | Diptera, Hemiptera | Aphididae, Formicidae, Lauxaniidae | Asia: China, Israel; Europe: Austria, Poland, Sakartvelo, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine; NA: Costa Rica, USA | [15,16,21,23,26,27,29,33,40,42,58,67,83] |
| P. formicae | Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Bharat; Europe incl. Denmark | [15,84,85] |
| P. gammaeI* | &Lepidoptera | Erebidae, Noctuidae | Asia: China, Israel, Turkmenistan; Australia; Europe: Poland, RF, Slovakia, Switzerland, Ukraine; NA incl. Mexico; SA: Argentina, Brazil | [15,18,19,26,30,32,56,66,79,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] |
| ~P. gloeospora | Diptera | Mycetophilidae, Psychodidae, Sciaridae | China; Europe: France, Ukraine; USA | [13,15,21,22,26,93] |
| P. guangdongensis | Hemiptera | Miridae | China | [94] |
| P. heteropterae (1) | Hemiptera | Miridae | NA incl. USA; Poland | [15,95] |
| P. kondoiensis* (5) | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Australia; China | [15,26,64,96] |
| P. lipae | Coleoptera | Cantharidae | Denmark, France, Poland, Switzerland | [15,19] |
| ~P. longissimi | Diptera | Limoniidae | Switzerland | [27] |
| P. minutispora | Hemiptera | Miridae | Czechia, Switzerland | [15,18] |
| P. muscivora | Diptera | Calliphoridae, Drosophilidae, Muscidae, Tachinidae | Canada; Europe: Poland, UK, Ukraine | [15,21,33] |
| P. myrmecophaga | Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Brazil; Europe: Czechia, Germany, Poland, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine, former Yugoslavia; Philippines | [15,18,19,21,63] |
| P. neoaphidis* (TYPE, 173) | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Worldwide, less frequent in tropics: Africa: Egypt, Tunisia, South Africa; Asia: Bharat, China, Iran, Israel, Japan, Korea, Nepal, Philippines, Taiwan; Australia; Europe: Austria, Bosnia & Hercegovina, Denmark, Finland, France, Iceland, Latvia, Poland, Portugal, RF, Serbia, Slovakia, Spain, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine; NA: Canada, Mexico, USA; NZ; SA: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Uruguay | [15,18,19,20,21,26,29,30,40,51,54,56,58,61,63,68,77,78,82,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118] |
| P. nouryi* (5) | Hemiptera & Psocodea | Aphididae, Pseudocaeciliidae | Argentina; Asia: China, Israel; Australia; Europe: Central, Northern & Western, incl. Slovakia; NA | [15,26,51,58,78,100,109,110,112,119,120] |
| P. phalangicida | Mesostigmata & Opiliones (Arachnida) | Parasitidae | Poland, Sweden, UK | [15,33] |
| P. philonthi | Coleoptera | Staphylinidae | Denmark, Poland, Switzerland | [15,27,121] |
| P. phyllobii | Coleoptera | Curculionidae | Poland | [15] |
| P. polonae-majoris | Hemiptera | Cicadellidae, Jassidae | Poland, Ukraine | [15,21] |
| P. psocopterae | Psocodea | Prionoglarididae | France | [15,18,19] |
| ~P. sciarae | Diptera | Sciaridae | Europe: Austria, Denmark, Switzerland, Ukraine; NZ; USA | [15,21,27,31,40] |
| P. shaanxiensis | Diptera | Calliphoridae | China | [24,26] |
| P. sylvestris sp. nova | Lepidoptera | Erebidae | USA | Hajek & Gryganskyi, in press |
| P. terrestris | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Ukraine | [119,122] |
| P. uroleuconii | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Slovakia | [123] |
| Strongwellsea acerosa | Diptera | Muscidae | Europe | [124] |
| S. castrans (2) | Diptera | Anthomyiidae | China; Europe: Czechia, Denmark, Switzerland, UK; USA | [26,59,125,126] |
| S. crypta | Diptera | Anthomyiidae | Denmark | [127] |
| S. gefion | Diptera | Muscidae | Europe | [128] |
| S. magna | Diptera | Muscidae | China; USA | [36,129] |
| S. pratensis | Diptera | Muscidae | Switzerland | [27] |
| S. selandia | Diptera | Muscidae | Europe | [128] |
| S. tigrinae | Diptera | Muscidae | Europe | [124] |
| Strongwellsea sp. nov. | Diptera | Calliphoridae | Europe | [130] |
| Strongwellsea sp. nov. | Diptera | Sarcophagidae | Europe | JE, unpublished |
| Strongwellsea sp. nov. | Diptera | Scatophagidae | Europe | [131] |
| Strongwellsea sp. nov. | Diptera | Anthomyiidae | Europe | JE et al., unpublished |
| Zoophthora anglica* (5) | Coleoptera | Elateridae | Denmark, France, Poland, Romania, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine | [15,21,132] |
| Z. anhuiensis | Hemiptera | Aphididae | China | [15,26,61,133] |
| Z. aphidis* (1) | Hemiptera, Lepidoptera | Aphididae, Cicadellidae, Delphacidae, Erebidae | Asia: China, Philippines, Taiwan; Europe: Armenia, Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Moldova, RF, Sweden, UK, Ukraine; NA: Canada, Puerto Rico, USA | [17,21,30,31,33,105,111,134,135,136] |
| Z. aphrophorae | Hemiptera | Aphrophoridae, Cicadellidae, Miridae, Psyllidae | UK | [33] |
| Z. arginis | Hymenoptera | Argidae | Germany, Poland | [15,28] |
| Z. athaliae | Hymenoptera | Tenthredinidae | China; Switzerland | [15,26,27,64] |
| Z. autumnalis | Diptera | Dryomyzidae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. bialovienzensis* | &Lepidoptera | Geometridae, Pyralidae | Poland, Ukraine | [15,21] |
| Z. brevispora | Lepidoptera | Geometridae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. canadensis | Hemiptera, Lepidoptera | Aphididae, Geometridae | China; NA | [137,138] |
| Z. crassispora | Lepidoptera | Tortricidae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. crassitunicata | Coleoptera | Cantharidae | Austria, Switzerland | [15,27,40] |
| Z. elateridiphaga | Coleoptera | Elateridae | Switzerland | [19] |
| Z. erinacea | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Israel; Slovakia | [15,58,78,119] |
| Z. falcata | Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. forficulae | Dermaptera | Forficulidae | Europe: Poland, Switzerland, UK; NA | [15,31,33,43] |
| Z. geometralis | &Lepidoptera | Geometridae, Yponomeutidae | Europe: Austria, Sweden, Ukraine; NA | [15,16,21,40,42] |
| Z. giardia | Orthoptera | Tettigoniidae | France, Germany, Poland | [15] |
| Z. humberi | Diptera | Tipulidae | Chile | [15,139] |
| Z. ichneumonis* | &Hymenoptera | Ichneumonidae | Poland, Switzerland, Ukraine | [15,21,27] |
| Z. independentia | Diptera | Tipulidae | USA | [140] |
| Z. lanceolata* (3) | Diptera | Drosophilidae, Empididae | Europe: France, Poland, Spain, Switzerland, Ukraine; Israel | [15,21,23,29,141] |
| Z. larvivore | Coleoptera | Cantharidae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. miridis | Hemiptera | Miridae | Poland, Spain, Switzerland | [15,23,141] |
| ~Z. nematoceris | Diptera | Bibionidae, Sciaridae | Poland, Spain, Switzerland | [15,23,141] |
| Z. obtuse | Diptera | Brachycerous or Calyptrate | Poland, Switzerland | [15,43] |
| Z. occidentalis (7) | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Asia incl. China; Europe: Poland, Slovakia, Spain, Switzerland, UK; NA; SA incl. Chile | [15,23,27,31,33,77,78,102,103,139,142,143] |
| Z. opomyzae | Diptera | Opomyzidae | Austria, Germany, Poland | [15,28,40] |
| Z. orientalis | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Israel | [29] |
| Z. pentatomis | Hemiptera | Pentatomidae | China | [26,51,52,137] |
| Z. petchii | Hemiptera | Aphrophoridae, Cercopidae, Cicadellidae, Delphacidae | Asia: China, Israel; Europe: Austria, Switzerland | [15,27,28,29,73] |
| Z. phalloides (2) | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Argentina; Asia: Israel Korea; Europe: Germany, Poland, Slovakia, Switzerland, UK; Australia NZ; NA incl. Mexico | [15,18,19,28,29,77,78,82,98,106,144,145,146] |
| Z. phytonomi* | &Coleoptera | Curculionidae | Asia: Israel, Uzbekistan; Australia; Europe: Poland, Romania, Ukraine; USA | [15,21,29,147] |
| Z. porteri | Diptera | Tipulidae | Ukraine; USA | [21,140] |
| Z. psyllae | Hemiptera | Psyllidae, Triozidae | Poland, Spain, Switzerland | [15,23,27] |
| Z. radicans* (305) | Diptera, Coleoptera, Hemiptera, Homoptera, Hymenoptera, &Lepidoptera, Plecoptera | Agromyzidae, Aphididae, Aphrophoridae, Aleurodidae, Argidae, Chironomidae, Chrysomelidae, Cicadellidae, Crambidae, Delphacidae, Geometridae, Miridae, Muscidae, Nemouridae, Pentatomidae, Pieridae, Plutellidae, Psyllidae, Triozidae, Thaumastocoridae, Tortricidae | Africa: South Africa, Tchad; Asia: China, Indonesia, Israel, Japan, Korea, Kyrgyzstan, Malaysia, Philippines; Australia, NZ; Europe: Belarus, Denmark, Estonia, France, Moldova, Poland, RF, Sakartvelo, Serbia, Slovakia, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, Ukraine, former Yugoslavia; NA: Canada, Cuba, Mexico, Puerto Rico, USA; SA: Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay | [15,16,18,19,21,26,29,30,31,33,51,56,60,61,63,77,78,82,91,92,94,112,113,115,121,137,146,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165] |
| Z. rhagonycharum | Coleoptera | Cantharidae | Europe: Denmark, Poland, Switzerland; NA | AEH, person. observations, [15,27] |
| Z. suturalis | Coleoptera | Chrysomelidae | France, UK | [15] |
| Z. tachypori | Coleoptera | Staphylinidae | Poland | [15] |
| Z. viridis | Hemiptera | Miridae | Western Europe incl. Germany, Switzerland | [15,19] |
| Total 123 species; in ARSEF – 683 specimens of 28 species | Total 14 orders | Total 76 families | Total 57 countries, in ARSEF specimens from 29 countries. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





