Submitted:
07 December 2023
Posted:
08 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
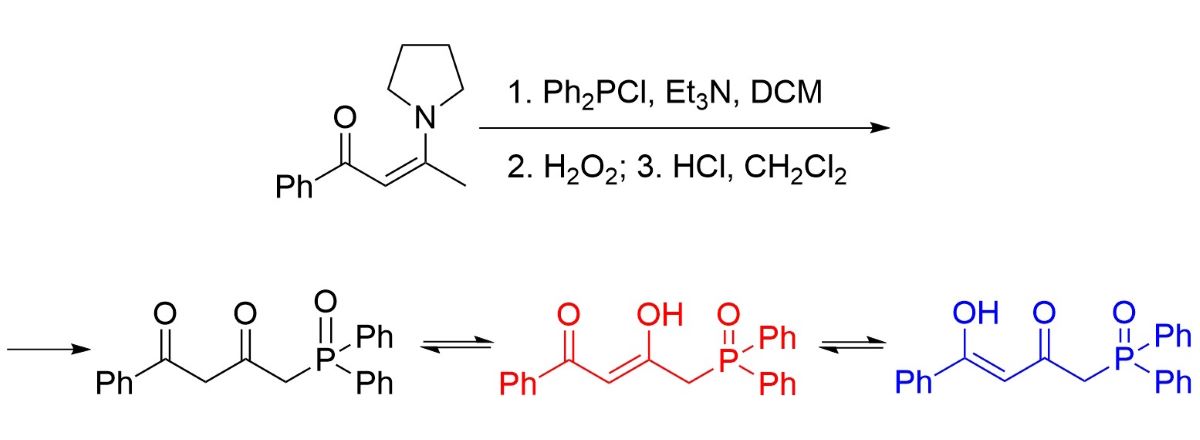
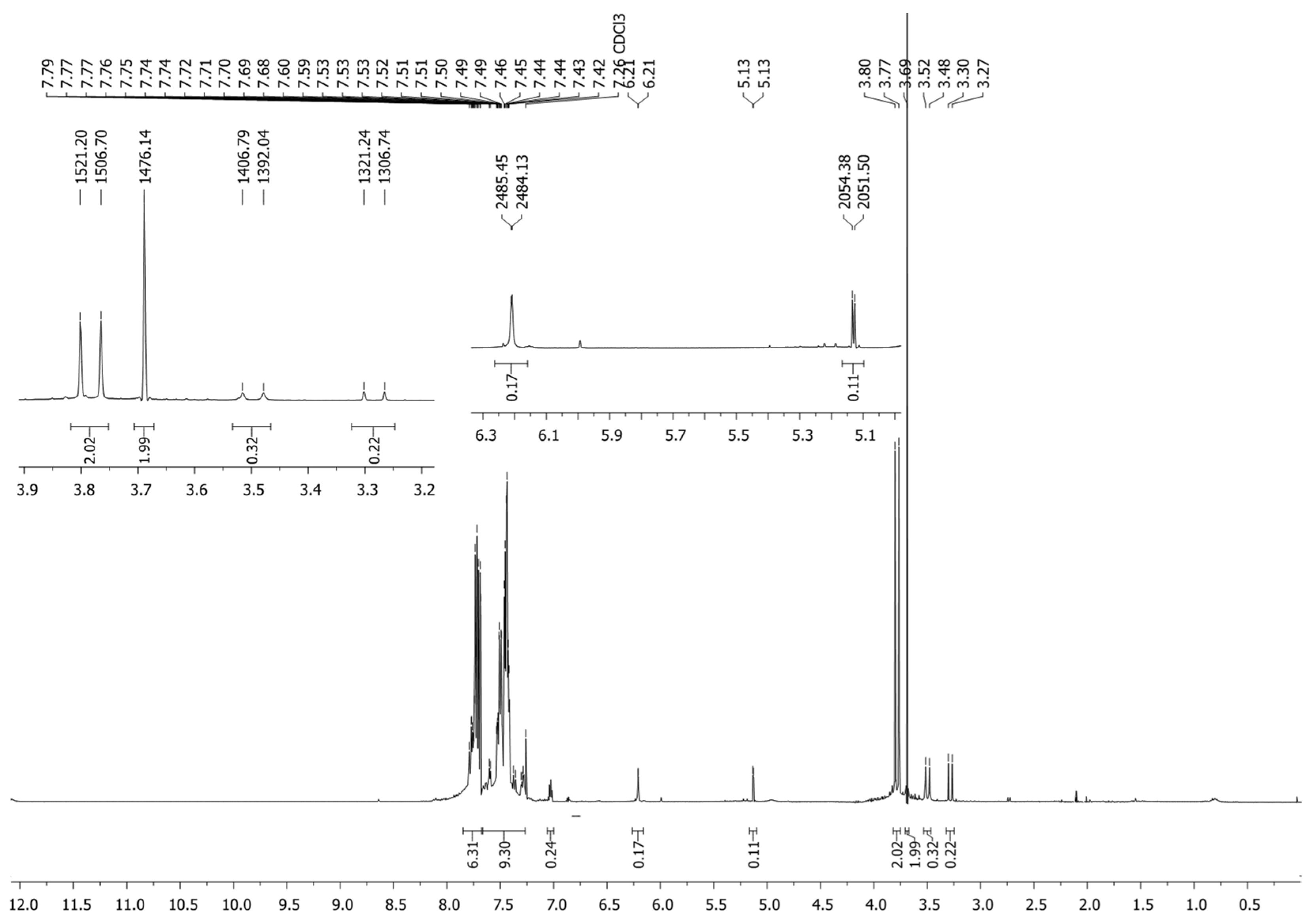
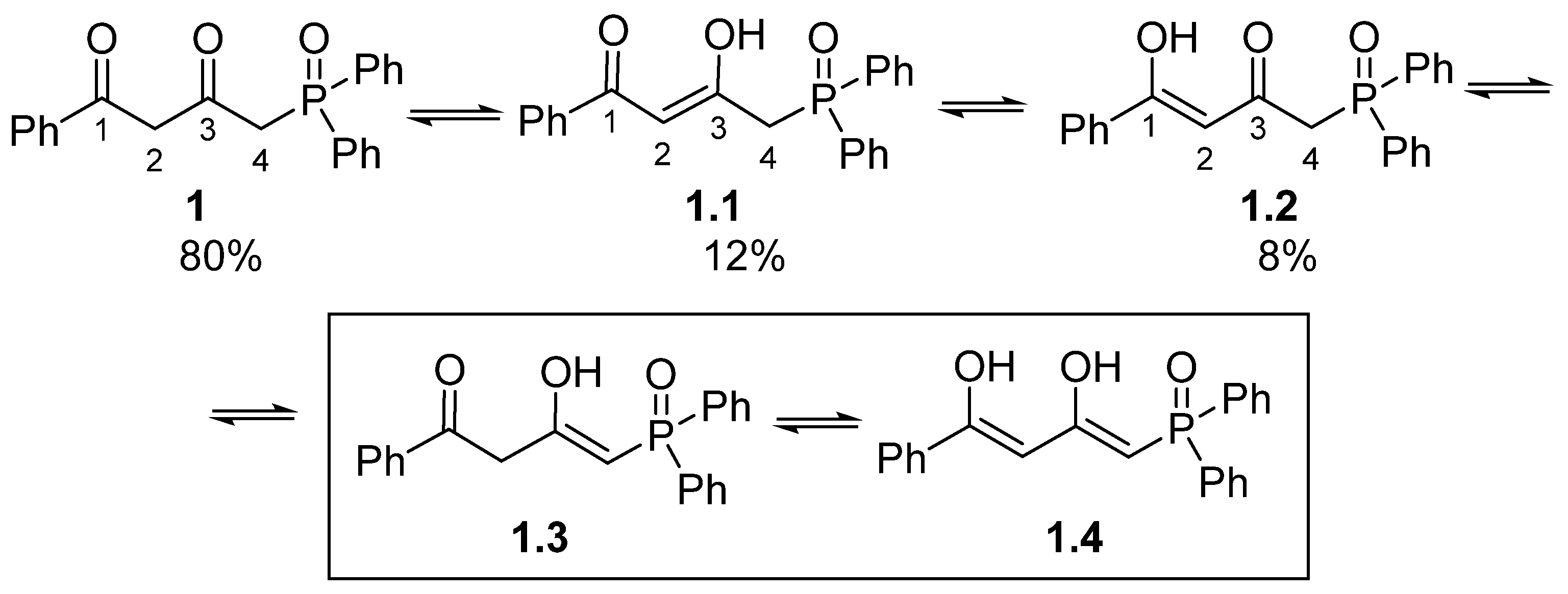
2. Results and Discussion
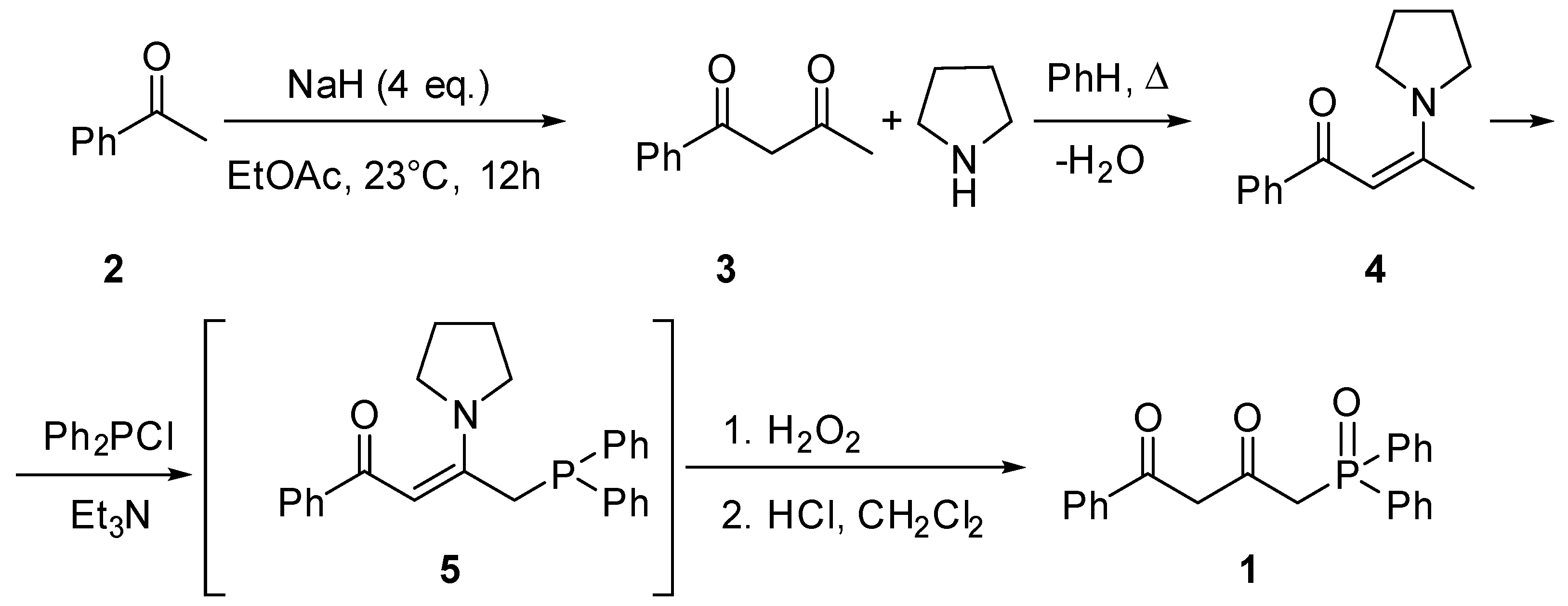
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Platt, A.W.G. Lanthanide Phosphine Oxide Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 340, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslandukov, A.N.; Utochnikova, V. V.; Goriachiy, D.O.; Vashchenko, A.A.; Tsymbarenko, D.M.; Hoffmann, M.; Pietraszkiewicz, M.; Kuzmina, N.P. The Development of a New Approach toward Lanthanide-Based OLED Fabrication: New Host Materials for Tb-Based Emitters. Dalt. Trans. 2018, 47, 16350–16357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.-H.; Cheng, C.-H. A Highly Efficient Universal Bipolar Host for Blue, Green, and Red Phosphorescent OLEDs. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2468–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liang, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. A Phosphanthrene Oxide Host with Close Sphere Packing for Ultralow-Voltage-Driven Efficient Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. Zairov, A. Dovzhenko, N. Terekhova, T. Kornev, Y. Zhou, Z. Huang, D. Tatarinov, G. Nizameeva, R.R. Fayzullin, A.T. Gubaidullin, T. Salikhova, F. Enrichi, V.F. Mironov, A. Mustafina, Phosphineoxide-Chelated Europium(III) Nanoparticles for Ceftriaxone Detection, Nanomaterials. 13 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Aromí, G.; Gamez, P.; Reedijk, J. Poly Beta-Diketones: Prime Ligands to Generate Supramolecular Metalloclusters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 964–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigato, P.A.; Peruzzo, V.; Tamburini, S. The Evolution of β-Diketone or β-Diketophenol Ligands and Related Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1099–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.K.; Li, F.; Lindoy, L.F. Oligo-β-Diketones as Versatile Ligands for Use in Metallo-Supramolecular Chemistry: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 455, 214355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, P.; Xie, L.-H.; Huang, W. Photophysical and Electroluminescent Properties of a Series of Monochromatic Red-Emitting Europium-Complexed Nonconjugated Copolymers Based on Diphenylphosphine Oxide Modified Polyvinylcarbazole. Polymer (Guildf). 2011, 52, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.B.A.; Francis, B.; Reddy, M.L.P.; Butorac, R.R.; Lynch, V.M.; Cowley, A.H. Highly Luminescent Poly(methyl Methacrylate)-Incorporated Europium Complex Supported by a Carbazole-Based Fluorinated β-Diketonate Ligand and a 4,5-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-Dimethylxanthene Oxide Co-Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9055–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zairov, R.R.; Dovzhenko, A.P.; Sapunova, A.S.; Voloshina, A.D.; Tatarinov, D.A.; Nizameev, I.R.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Petrov, K.A.; Enrichi, F.; Vomiero, A.; et al. Dual Red-NIR Luminescent Eu Yb Heterolanthanide Nanoparticles as Promising Basis for Cellular Imaging and Sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyuk, A.N.; Svyaschenko, Y. V; Volochnyuk, D.M.; Lysenko, N. V; Tolmachev, A.A.; Pinchuk, A.M. Structural Sensitivity in Phosphorylation of Enamines—Derivatives of β-Aminocrotonic Acid with Diphenylchlorophosphine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 6487–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Saito, K.; Suto, S.; Aihara, H.; Sugawara, A.; Tamura, S.; Kawano, T. Synthesis of 5-Aryl-3(2 H )-Furanones Using Intramolecular Cyclization of Sulfonium Salts. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13834–13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A General Synthesis Of 4-Isoxazolecarboxylic Esters: Ethyl 3-Ethyl-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolecarboxylate. Org. Synth. 1973, 53, 59. [CrossRef]
- Maass, J.S.; Wilharm, R.K.; Luck, R.L.; Zeller, M. Photoluminescent Properties of Three Lanthanide Compounds of Formulae LnCl3(diphenyl((5-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Yl)methyl)phosphine oxide)2, Ln = Sm, Eu and Tb: X-Ray Structural, Emission and Vibrational Spectroscopies, DFT and Thermogravimetric Studies. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; Dwek, R.A. An N.m.r. Study of Keto–enol Tautomerism in β-Diketones. J. Chem. Soc. B 1966, 161–163. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.-W.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Li, S.-H. KIO 3 -Mediated γ-C(sp 3 )–H Sulfenylation of Enaminones. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7533–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




