Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Conclusions
References
- Andreadis, A. (2012). Tau splicing and the intricacies of dementia. J. Cell. Physiol. 227, 1220–1225.
- Buchholz, S., Bell-Simons, M., Aghyad, M., Kabbani, A., Kluge, L., Klimek, J., and Zempel, H. (2022). The TAU isoform 1N4R restores vulnerability of MAPT knockout human iPSC-derived neurons to Amyloid beta-induced neuronal dysfunction. Prepr. (Version 1) Available Res. Sq.
- Buee, L., and Delacourte, A. (1999). Comparative biochemistry of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, FTDP-17 and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathol 9, 681–693.
- Bullmann, T., Holzer, M., Mori, H., and Arendt, T. (2009). Pattern of tau isoforms expression during development in vivo. Int J Dev Neurosci 27, 591–597.
- Dawson, H.N.N., Ferreira, A., Eyster, M.V. V, Ghoshal, N., Binder, L.I.I., and Vitek, M.P.P. (2001). Inhibition of neuronal maturation in primary hippocampal neurons from tau deficient mice. J Cell Sci 114, 1179–1187.
- Fischer, I., and Baas, P.W. (2020). Resurrecting the Mysteries of Big Tau. Trends Neurosci. 43.
- Georgieff, I.S., Liem, R.K.H., Mellado, W., Nunez, J., and Shelanski, M.L. (1991). High molecular weight tau: Preferential localization in the peripheral nervous system. J. Cell Sci. 100.
- Goedert, M., Spillantini, M.G., Potier, M.C., Ulrich, J., and Crowther, R.A. (1989). Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J 8, 393–399.
- Goedert, M., Jakes, R., Spillantini, M.G., Crowther, R.A., Cohen, P., Vanmechelen, E., Probst, A., Gotz, J., and Burki, K. (1995). Tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 23, 80–85.
- Goedert, M., Spillantini, M.G., and Crowther, R.A. (2006). Cloning of a big tau microtubule-associated protein characteristic of the peripheral nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89, 1983–1987.
- Hefti, M.M., Farrell, K., Kim, S.H., Bowles, K.R., Fowkes, M.E., Raj, T., and Crary, J.F. (2018). High-resolution temporal and regional mapping of MAPT expression and splicing in human brain development. PLoS One 13.
- Karczewski, K.J., Francioli, L.C., Tiao, G., Cummings, B.B., Alföldi, J., Wang, Q., Collins, R.L., Laricchia, K.M., Ganna, A., Birnbaum, D.P., et al. (2020). The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 581.
- Ke, Y.D., Suchowerska, A.K., van der Hoven, J., De Silva, D.M., Wu, C.W., van Eersel, J., Ittner, A., and Ittner, L.M. (2012). Lessons from tau-deficient mice. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012, 873270.
- Koolen, D.A., Vissers, L.E.L.M., Pfundt, R., De Leeuw, N., Knight, S.J.L., Regan, R., Kooy, R.F., Reyniers, E., Romano, C., Fichera, M., et al. (2006). A new chromosome 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome associated with a common inversion polymorphism. Nat. Genet. 38.
- Koolen, D.A., Pfundt, R., Linda, K., Beunders, G., Veenstra-Knol, H.E., Conta, E.H., Fortuna, A.M., Gillessen-Kaesbach, G., Dugan, S., Halbach, S., et al. (2016). The Koolen-de Vries syndrome: A phenotypic comparison of patients with a 17q21.31 microdeletion versus a KANSL1 sequence variant. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 24.
- Liu, Y., Lee, J.W., and Ackerman, S.L. (2015). Mutations in the microtubule-associated protein 1A (Map1a) gene cause Purkinje cell degeneration. J. Neurosci. 35.
- Morales, J., Pujar, S., Loveland, J.E., Astashyn, A., Bennett, R., Berry, A., Cox, E., Davidson, C., Ermolaeva, O., Farrell, C.M., et al. (2022). A joint NCBI and EMBL-EBI transcript set for clinical genomics and research. Nature.
- Nunez, J., and Fischer, I. (1997). Microtubule-Associated Proteins (MAPs) in the Peripheral Nervous System during Development and Regeneration. J. Mol. Neurosci. 8.
- Pangratz-Fuehrer, S., Bubna-Littitz, H., Propst, F., and Reitsamer, H. (2005). Mice deficient in microtubule-associated protein MAP1B show a distinct behavioral phenotype and altered retina function. Behav. Brain Res. 164.
- Sahara, N., and Yanai, R. (2023). Limitations of human tau-expressing mouse models and novel approaches of mouse modeling for tauopathy. Front. Neurosci. 17.
- Shaw-Smith, C., Pittman, A.M., Willatt, L., Martin, H., Rickman, L., Gribble, S., Curley, R., Cumming, S., Dunn, C., Kalaitzopoulos, D., et al. (2006). Microdeletion encompassing MAPT at chromosome 17q21.3 is associated with developmental delay and learning disability. Nat. Genet. 38.
- Takuma, H., Arawaka, S., and Mori, H. (2003). Isoforms changes of tau protein during development in various species. Dev. Brain Res. 142.
- Teng, J., Takei, Y., Harada, A., Nakata, T., Chen, J., and Hirokawa, N. (2001). Synergistic effects of MAP2 and MAP1B knockout in neuronal migration, dendritic outgrowth, and microtubule organization. J Cell Biol 155, 65–76.
- Trabzuni, D., Wray, S., Vandrovcova, J., Ramasamy, A., Walker, R., Smith, C., Luk, C., Gibbs, J.R., Dillman, A., Hernandez, D.G., et al. (2012). MAPT expression and splicing is differentially regulated by brain region: relation to genotype and implication for tauopathies. Hum Mol Genet 21, 4094–4103.
- Zimmer-Bensch, G., and Zempel, H. (2021). Dna methylation in genetic and sporadic forms of neurodegeneration: Lessons from alzheimer’s, related tauopathies and genetic tauopathies. Cells 10.
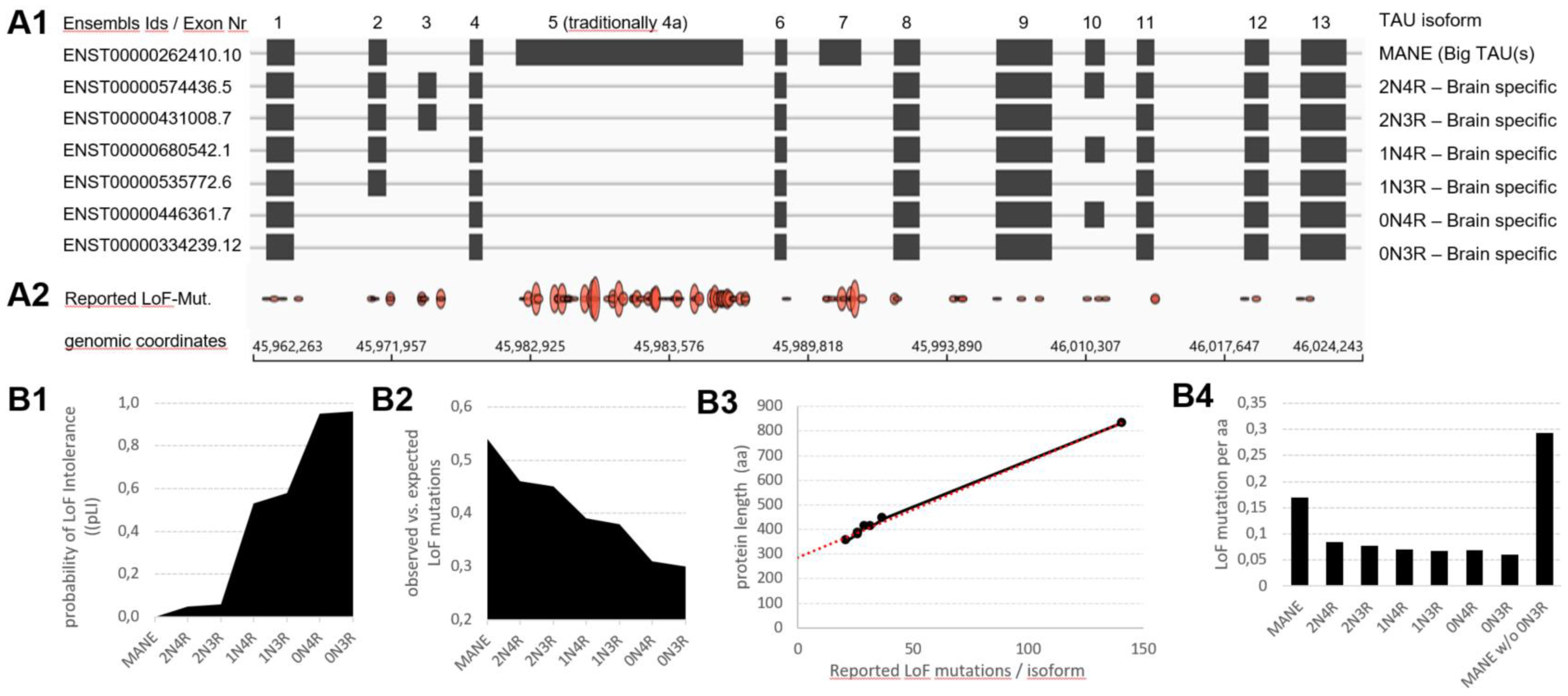
| TAU isoform | aa | pLI | LoF o/e | LoF-Mut load | LoF-Mut/aa |
| MANE | 833 | 0.00 | 0.54 (0.41 - 0.72) | 141 | 0.169268 |
| 2N4R | 441 | 0.05 | 0.46 (0.31 - 0.68) | 37 | 0.0839 |
| 2N3R | 412 | 0.06 | 0.45 (0.31 - 0.68) | 32 | 0.07767 |
| 1N4R | 410 | 0.53 | 0.39 (0.26 - 0.61) | 29 | 0.070732 |
| 1N3R | 383 | 0.58 | 0.38 (0.25 - 0.61) | 26 | 0.067885 |
| 0N4R | 381 | 0.95 | 0.31 (0.19 - 0.53) | 26 | 0.068241 |
| 0N3R | 352 | 0.96 | 0.3 (0.18 - 0.53) | 21 | 0.059659 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





