Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
06 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
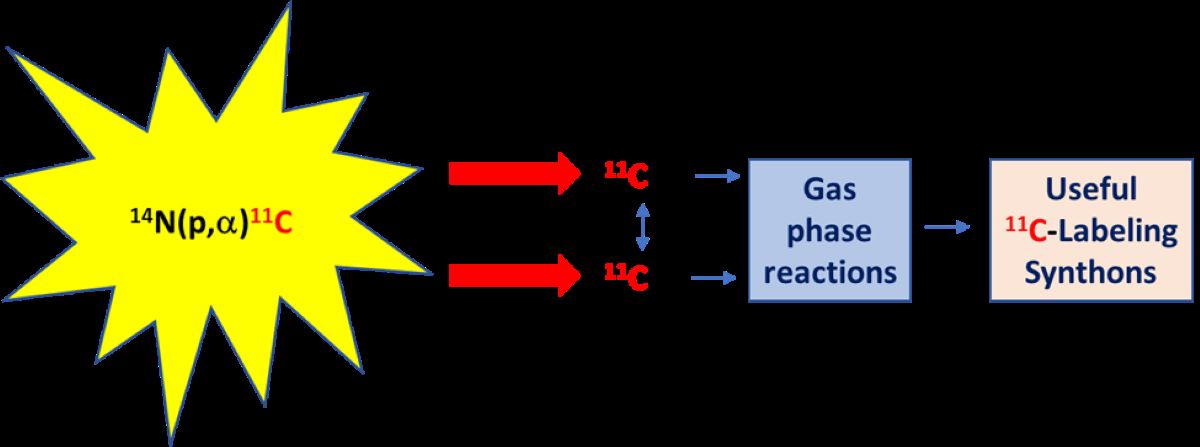
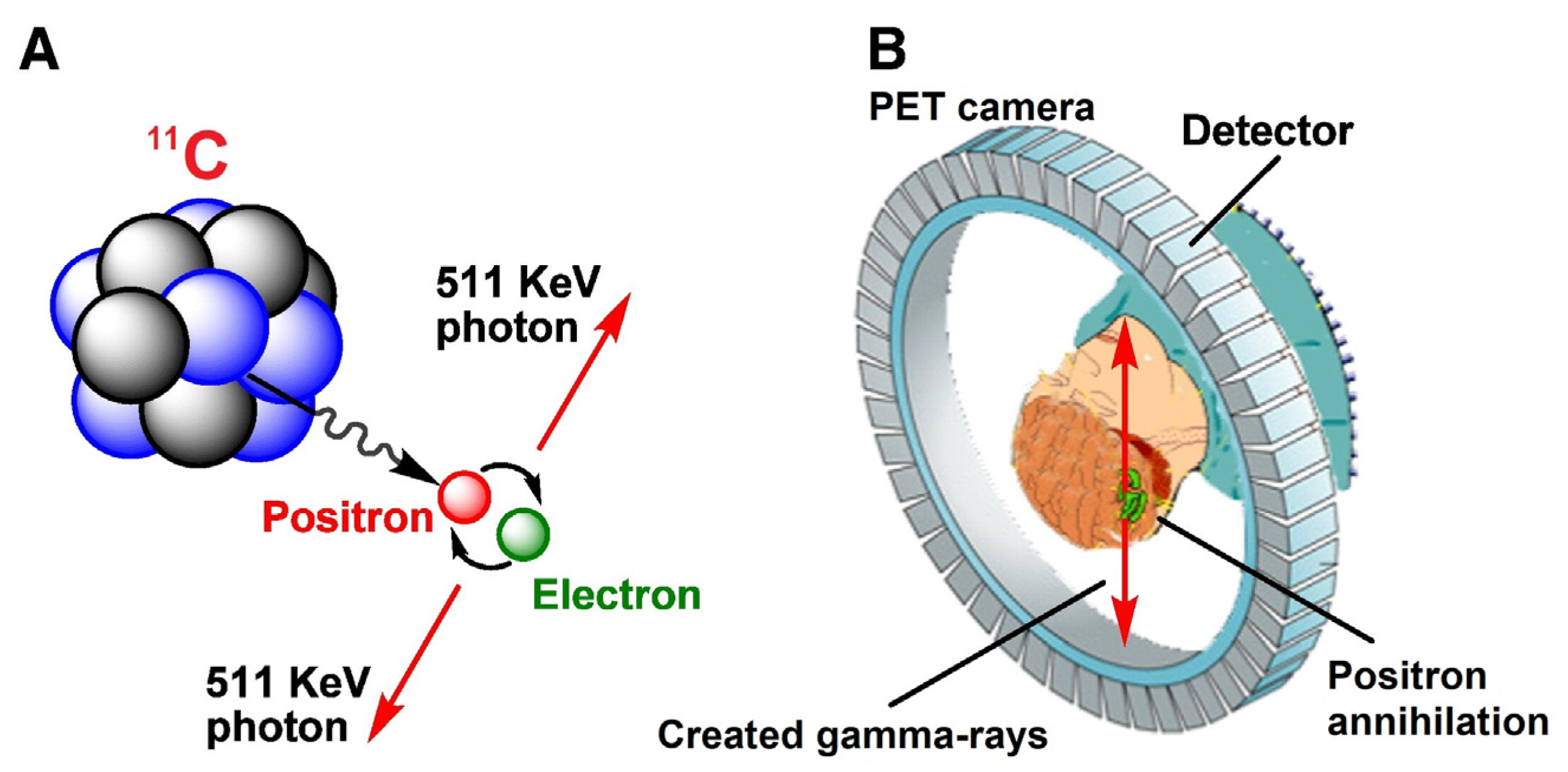
2. Carbon-11 Production
3. Conversions of Cyclotron-produced 11C-Labeled Materials
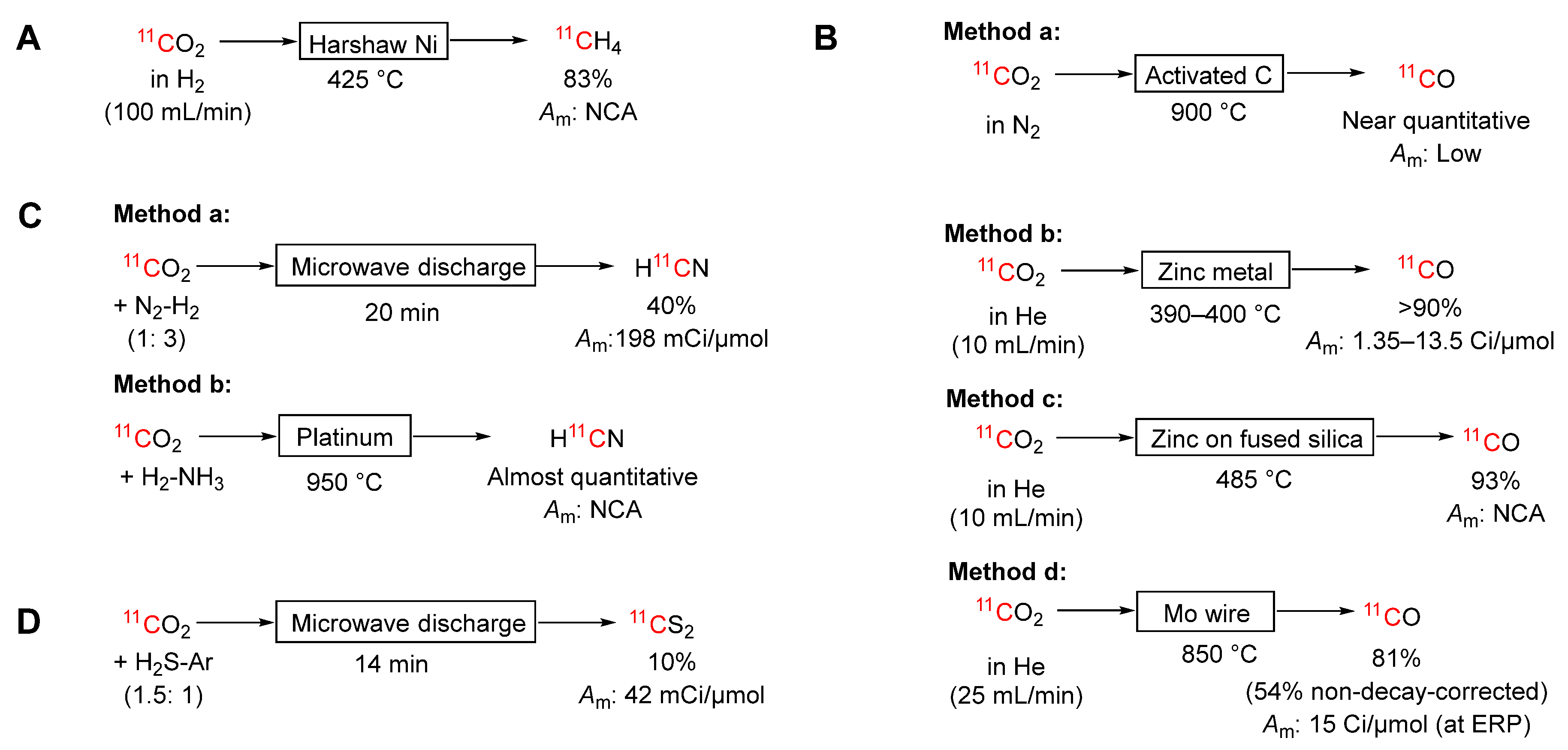
3.1. Conversions of [11C]Carbon Dioxide
3.1.1. Into [11C]Methane
3.1.2. Into [11C]Carbon Monoxide
3.1.3. Into [11C]Hydrogen Cyanide
3.1.4. Into [11C]Carbon Disulfide
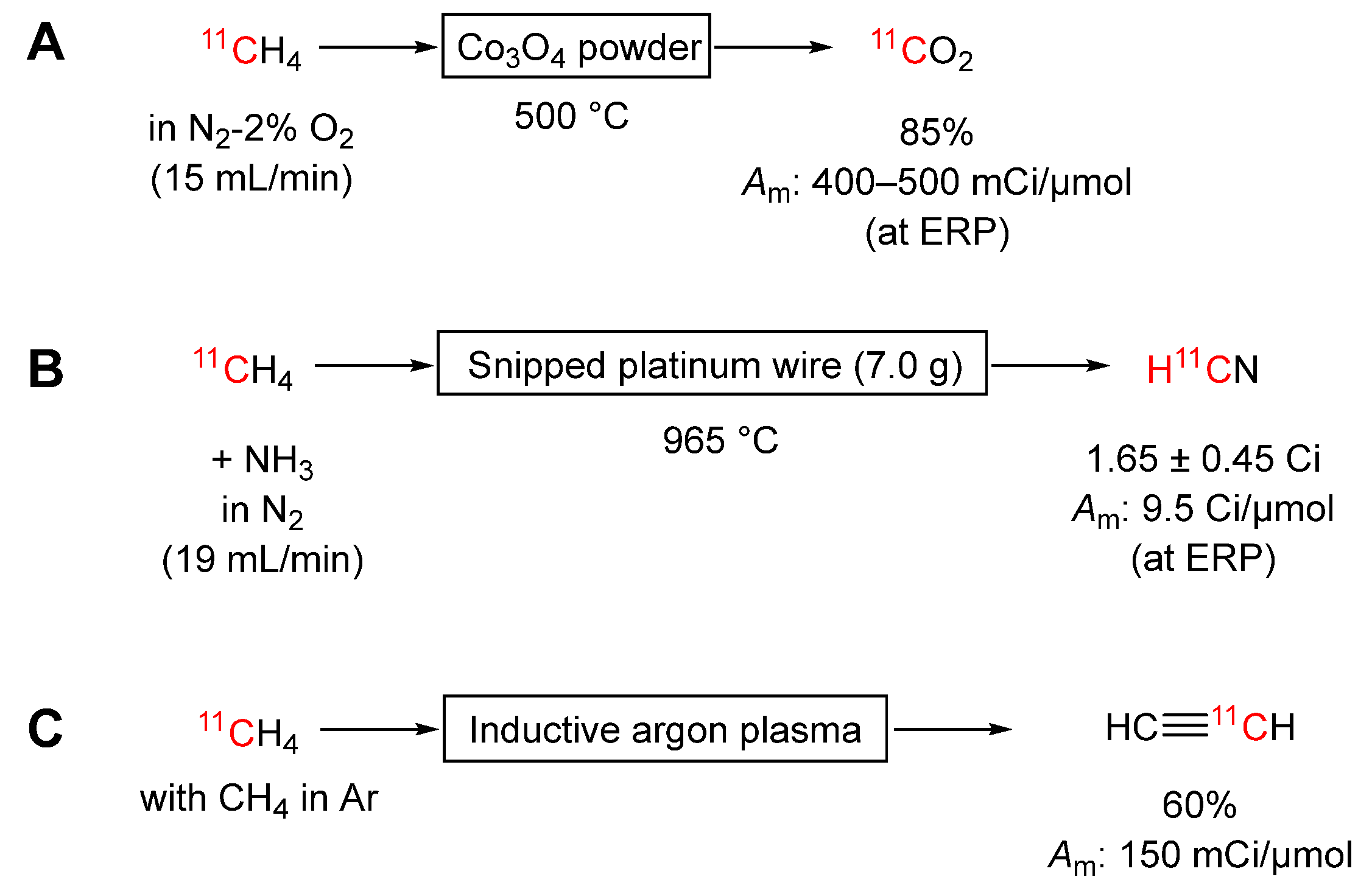
3.2. Conversions of [11C]Methane
3.2.1. Into [11C]Carbon Dioxide
3.2.2. Into [11C]Hydrogen Cyanide
3.2.3. Into CA [1-11C]Acetylene
3.2.4. Into [11C]Fluoroform
3.2.5. Into [11C]Chloromethanes
3.2.6. Into [11C]Bromomethane
3.2.7. Into [11C]Iodomethane
3.3. Gas phase Transformations of Other 11C-Labeled Compounds
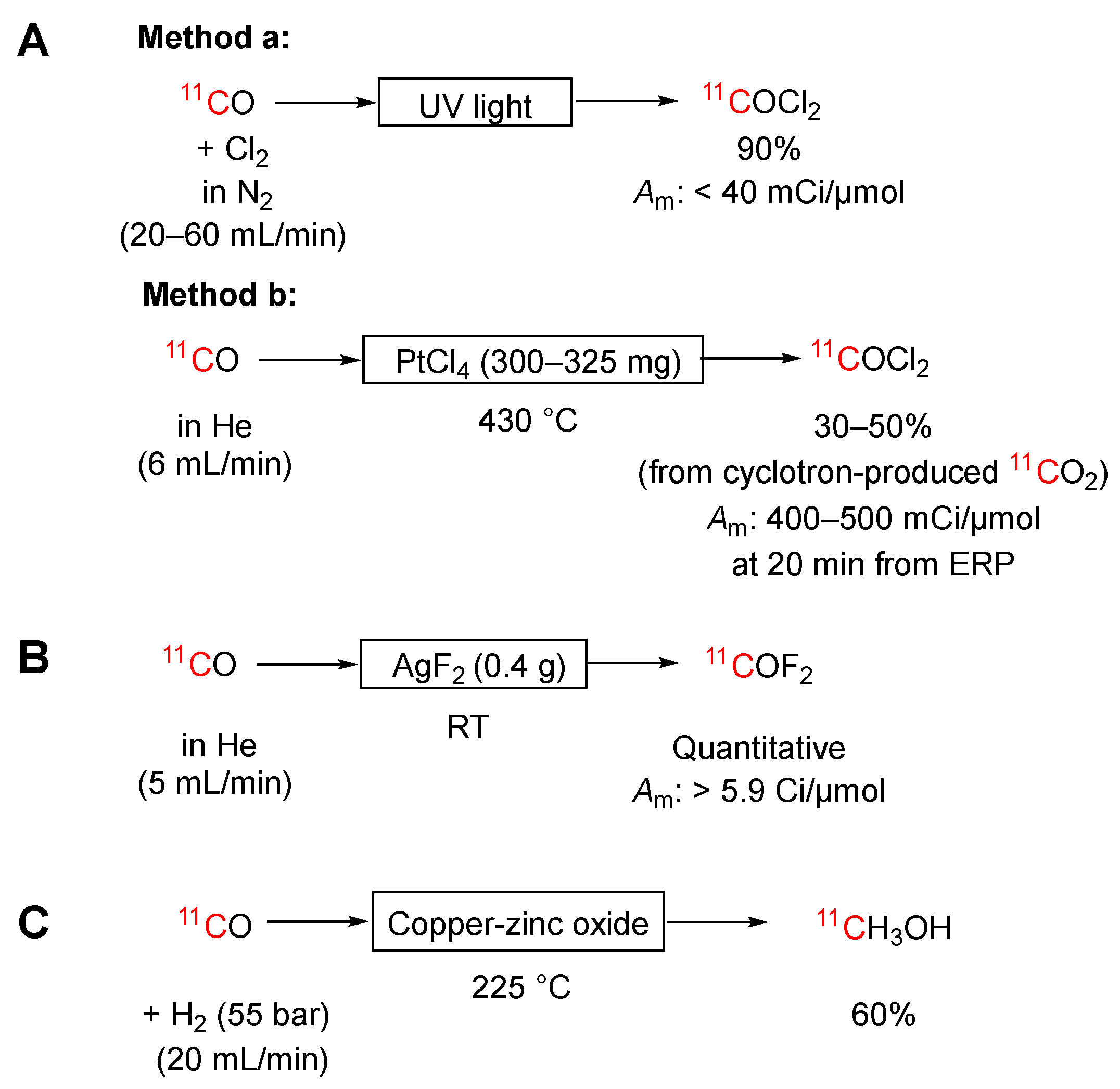
3.3.1. [11C]Carbon Monoxide into [11C]Phosgene
3.3.2. [11C]Carbon Monoxide into [11C]Carbonyl Difluoride
3.3.3. [11C]Carbon Monoxide into [11C]Methanol
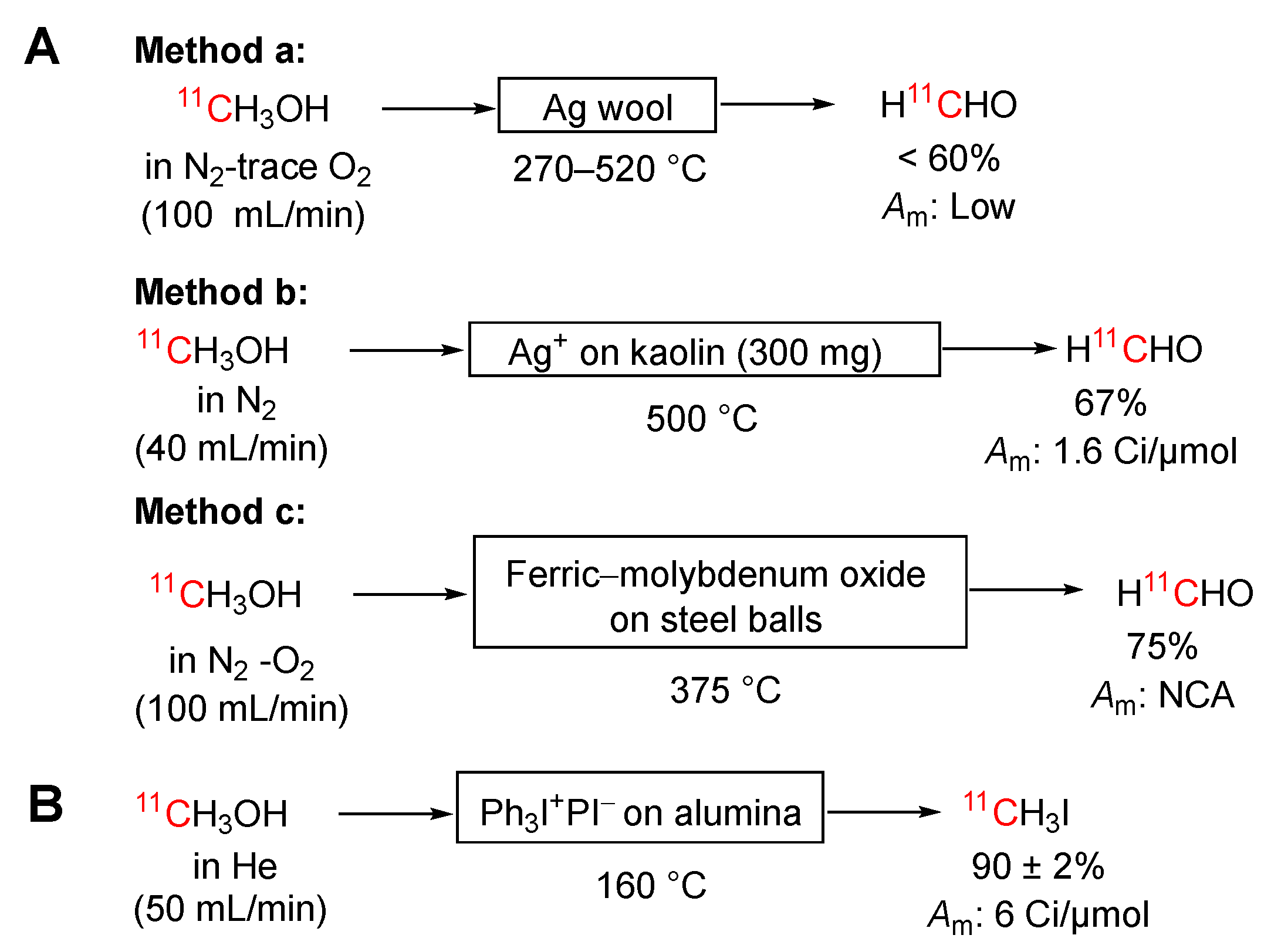
3.3.4. [11C]Methanol into [11C]Formaldehyde
3.3.5. [11C]Methanol into [11C]Iodomethane
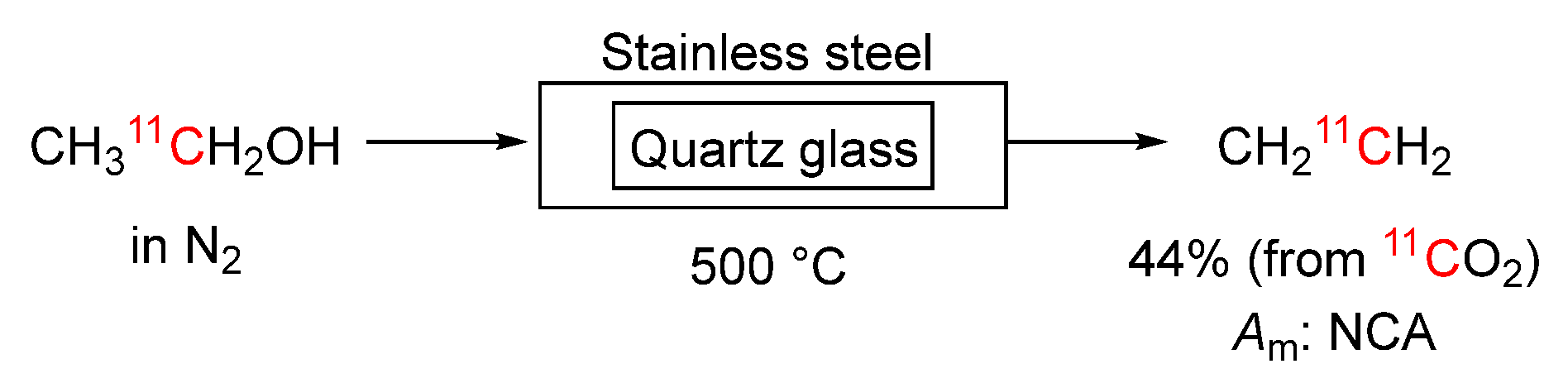
3.3.6. [1-11C]Ethanol into [1-11C]Ethylene
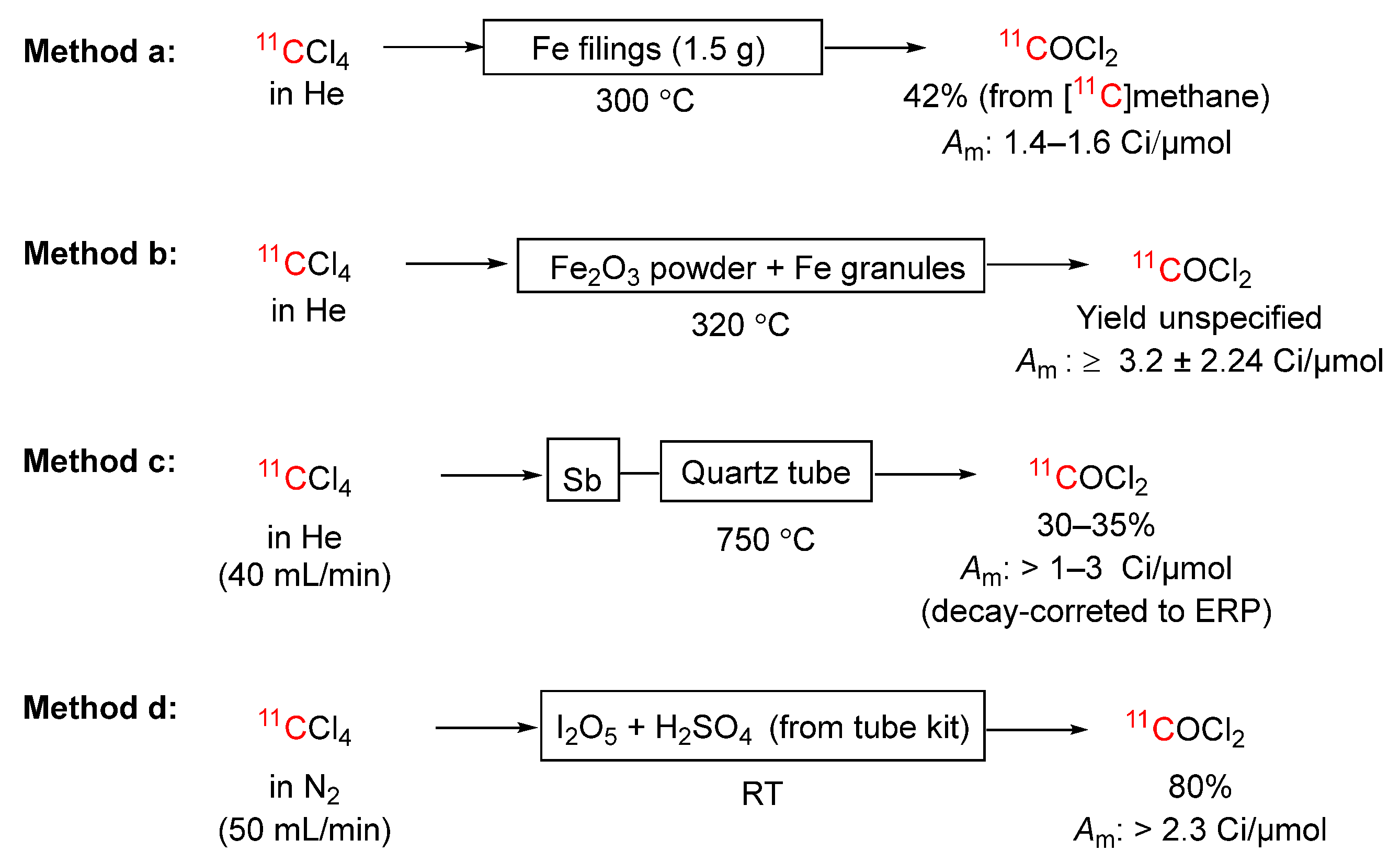
3.3.7. [11C]Carbon Tetrachloride into [11C]Phosgene
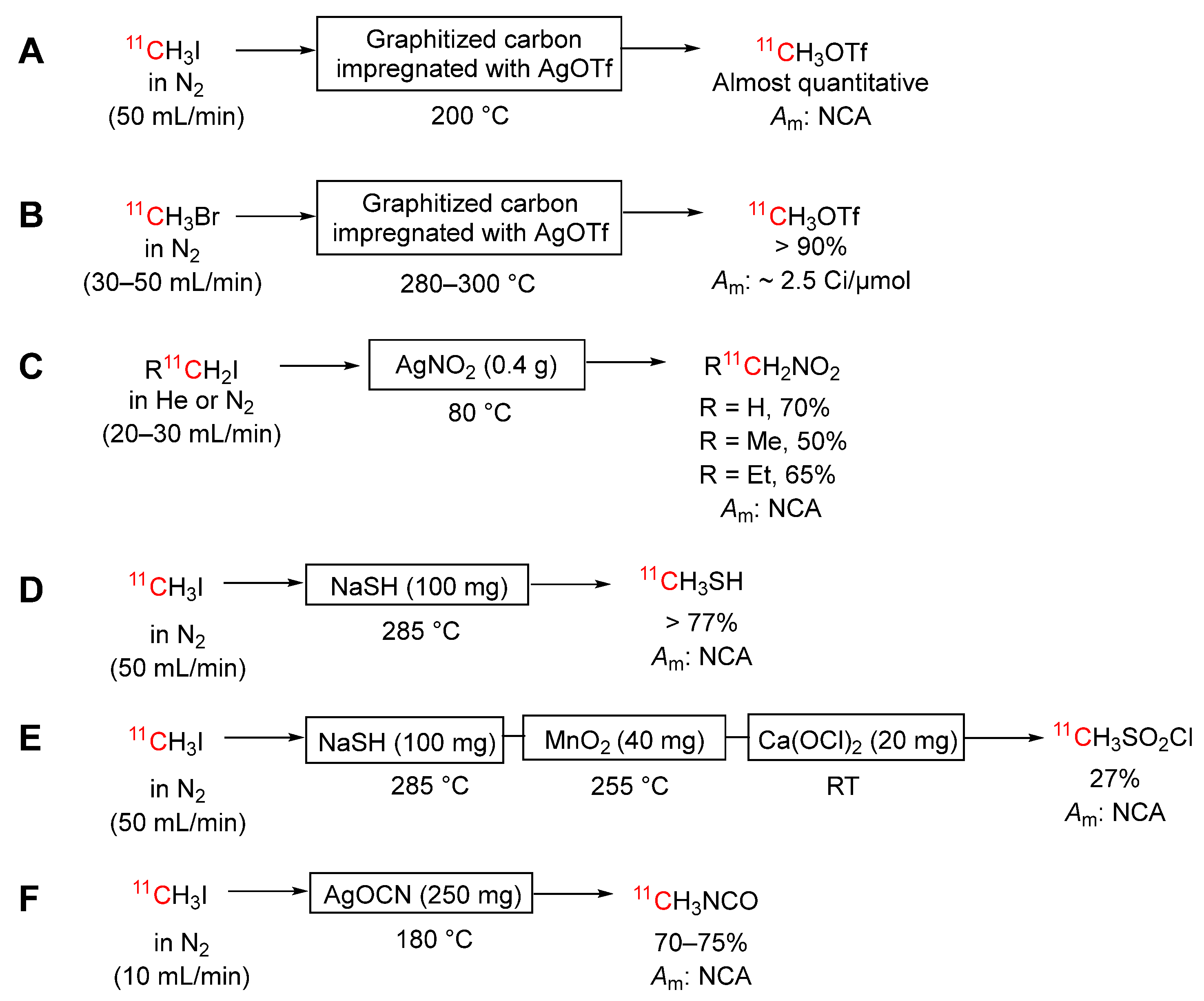
3.3.8. [11C]Iodomethane into [11C]Methyl Triflate
3.3.9. [11C]Bromomethane into [11C]Methyl triflate
3.3.10. Lower [1-11C]Iodoalkanes into Lower [1-11C]Nitroalkanes
3.3.11. [11C]Iodomethane into [11C]Methanethiol and then [11C]Mesyl Chloride
3.3.12. [11C]Iodomethane to [methyl-11C]Methyl Isocyanate
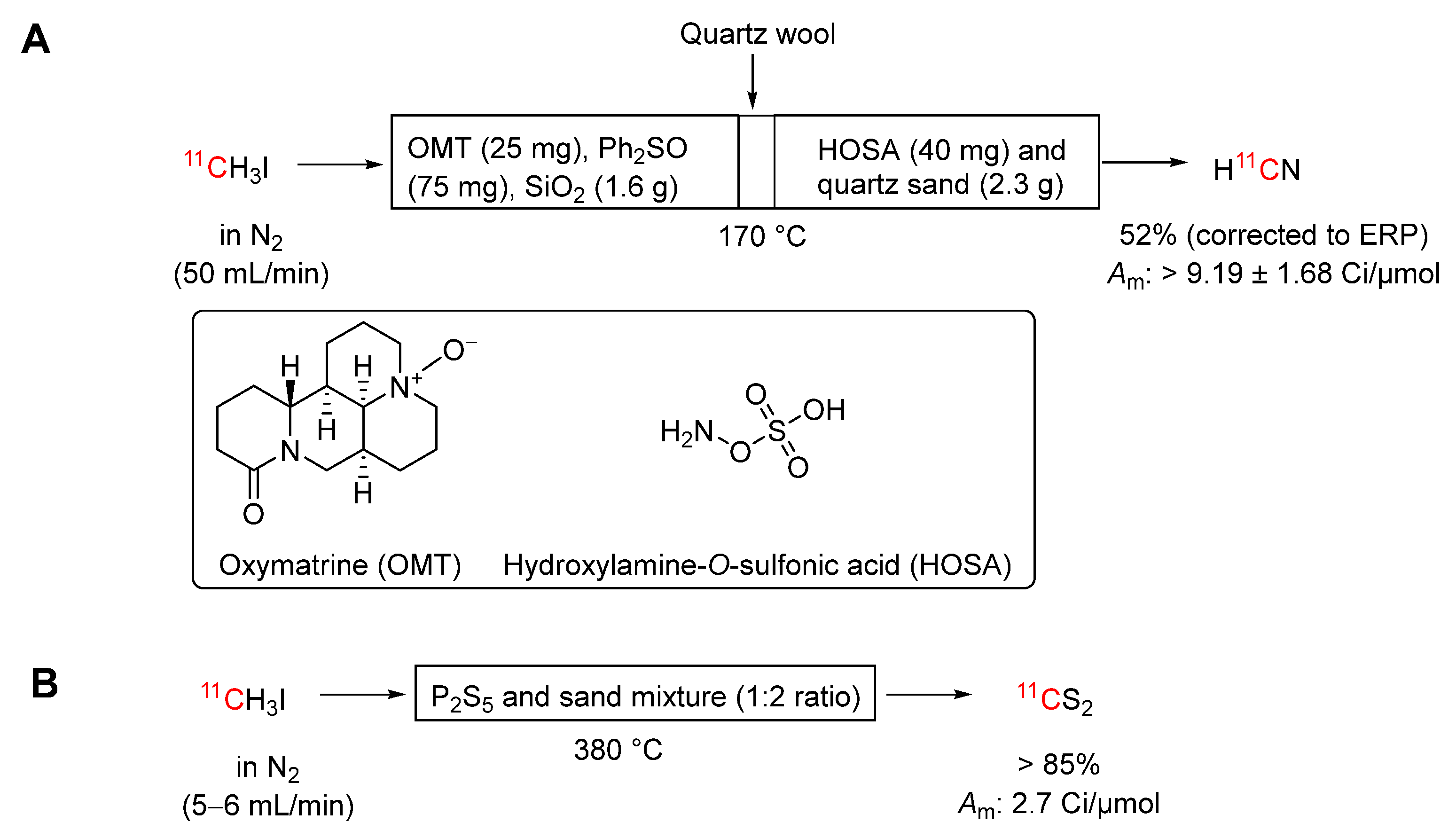
3.3.13. [11C]Iodomethane into [11C]Hydrogen Cyanide via [11C]Formaldehyde.
3.3.14. [11C]Iodomethane into [11C]Carbon Disulfide
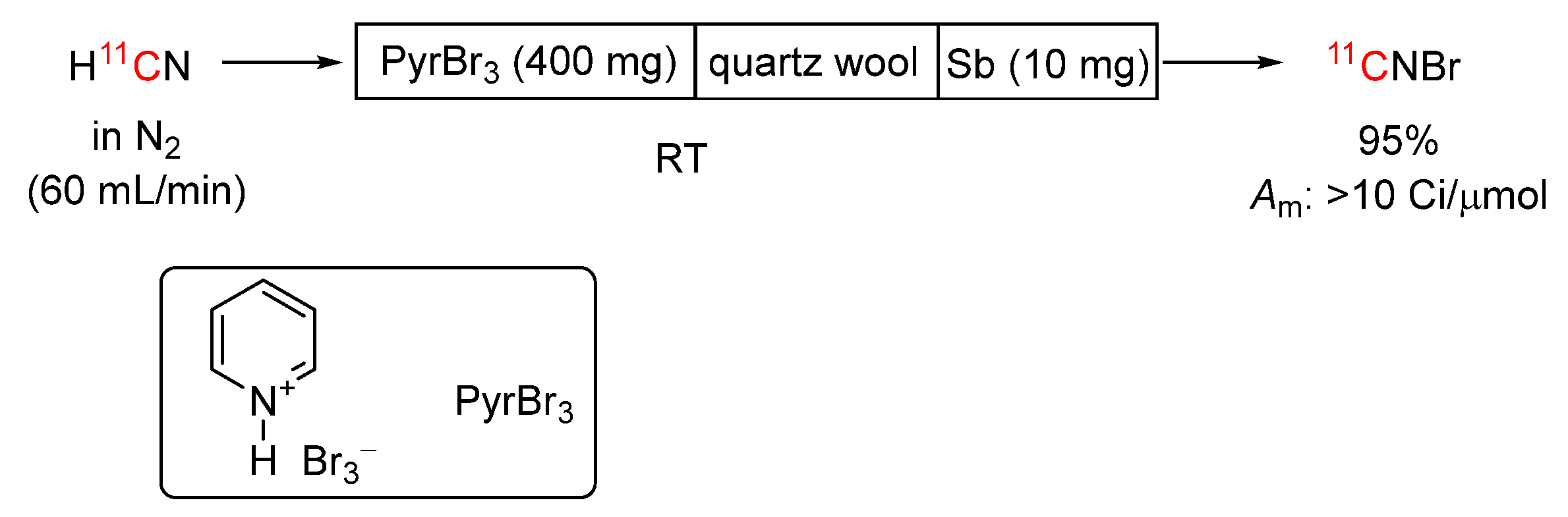
3.3.15. [11C]Hydrogen Cyanide into [11C]Cyanogen Bromide
3.3.16. [1-11C]Butyric Acid into [1-11C]Propylketene
4. Conclusion and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phelps, M.E. Positron emission tomography provides molecular imaging of biological processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 9226–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, S.R.; Badawi, R.D.; Karp, J.S.; Moses, W.W.; Price, P.; Jones, T. Total-body imaging: Transforming the role of positron emission tomography. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, Article ID eaaf6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Conti, P.S. Radiopharmaceutical chemistry for positron emission tomography. Adv. Drug Delivery. Rev. 2010, 62, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrieri, R.A.; Wolf, A.P. The chemistry of positron emitting nucleogenic (hot) atoms with regard to preparation of labelled compounds of practical utility. Radiochim. Acta 1983, 34, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrieri, R.A. Production and Application of Synthetic Precursors Labeled with Carbon-11 and Fluorine-18. In Handbook of Radiopharmaceuticals - Radiochemistry and Applications; 2002; pp. 229-282. [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.C.; Buckingham, P.D. Short-lived Radioactive Gases for Clinical Use; Butterworths: London, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Casella, V.R.; Christman, D.R.; Ido, T.; Wolf, A.P. Excitation-function for 14N(p,α)11C reaction up to 15-MeV. Radiochim. Acta 1978, 25, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bida, G.T.; Ruth, T.J.; Wolf, A.P. Experimentally determined thick target yields for the 14N (p,α)11C reaction. Radiochim. Acta 1980, 27, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, D.R.; Finn, R.D.; Karlstrom, K.I.; Wolf, A.P. Production of ultra high activity 11C-labeled hydrogen cyanide, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and methane via 14N(p,α)11C reaction (XV). Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1975, 26, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Appendix 1: PET Cyclotron Comparison. In Cyclotron Produced Radionuclides: Principles and Practice, Technical Reports Series No. 465, IAEA: Vienna, 2008. https://www.iaea.org/publications/7849/cyclotron-produced-radionuclides-principles-and-practice.
- Ruth, T.J. Accelerators available for isotope production. In Handbook of Radiopharmaceuticals - Radiochemistry and Applications; 2002; pp. 71-85. [CrossRef]
- Ache, H.J.; Wolf, A.P. Effect of radiation on the reactions of recoil carbon-11 in the nitrogen-oxygen system. J. Phys. Chem. 1968, 72, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewson, T.J.; Banks, W.; Franceschini, M.; Hoffpauir, J. A trap for the removal of nitrogen oxides from carbon-11 carbon dioxide. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1989, 40, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, B.H.; Vavrek, M.T.; Mulholland, G.K. Solid-phase reversible trap for [11C]carbon dioxide using carbon molecular sieves. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landais, P.; Crouzel, C. A new synthesis of carbon-11 labelled phosgene. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.R.; Huser, J.M.; Jivan, S.; Chun, K.S.; Ruth, T.J. 11C-methane production in small volume, high pressure gas targets. Radiochim. Acta 2000, 88, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Truong, P.; Halldin, C. In-target produced [11C]methane: Increased specific radioactivity. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, J.F.; James, R.W.; Winchell, H.S. Recoil synthesis of high specific activity 11C-cyanide. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1971, 22, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.J.; Osterholz, A.; Harms, T. A systematic investigation of [11C]HCN production. Radiochim. Acta 1990, 50, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Sasaki, M.; Kubodera, A. Specific activity of [11C]CO2 generated in a N2 gas target: effect of irradiation dose, irradiation history, oxygen content and beam energy. Radiochim. Acta 2000, 88, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Vallejo, V.; Gaja, V.; Koziorowski, J.; Llop, J. Specific activity of 11C-labelled radiotracers: A big challenge for PET chemists. In Positron Emission Tomography - Current Clinical and Research Aspects, Hsieh, C.-H., Ed.; Intechopen.com: 2012; pp. 183-210. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-R.; Suzuki, K. Sources of carbon which decrease the specific activity of [11C]CH3I synthesized by the single pass I2 method. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2005, 62, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, V.; Zenz, T.; Philippe, C.; Vraka, C.; Berrotéran-Infante, N.; Pfaff, S.; Nics, L.; Ozenil, M.; Langer, O.; Willeit, M.; et al. Molar activity – The keystone in 11C-radiochemistry: An explorative study using the gas phase method. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2018, 67, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.; Ulin, J.; Dahlstrom, K.; Jensen, M. Synthesis of [11C]iodomethane by iodination of [11C]methane. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, J.M.; Krohn, K.A.; Clark, J.C. Production of [11C]CH3I by single pass reaction of [11C]CH4 with I2. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1997, 24, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.R.; Huser, J.; Jivan, S.; McDonald, R.; Ruth, T.J. Methane Production in small volume high pressure gas targets. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Targetry & Target Chemistry, Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 75-79. https://wttc.triumf.ca/97-pdf.html.
- Buckley, K.R.; Huser, J.; Jivan, S.; Ruth, T.J. Methane production in small volume, high pressure gas target: Futher studies. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Targetry & Target Chemistry, St. Louis, Missouri, USA, 1999; pp. 179-181. https://wttc.triumf.ca/99-pdf.html.
- Kniess, T.; Rode, K.; Wuest, F. Practical experiences with the synthesis of [11C]CH3I through gas phase iodination reaction using a TRACERlabFXC synthesis module. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, O. [11C]Carbon monoxide in labeling chemistry and positron emission tomography tracer development: Scope and limitations. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, C.; Pike, V.W. [11C]Carbon monoxide: advances in production and application to PET radiotracer development over the past 15 years. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, Article ID 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, J.; Antoni, G.; Långström, B.; Itsenko, O. The development of 11C-carbonylation chemistry: A systematic view. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.C.; Buckingham, P.D. The preparation and storage of carbon-11 labelled gases for clinical use. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1971, 22, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qahtani, M.H.; Pike, V.W. Palladium(II)-mediated 11C-carbonylative coupling of diaryliodonium salts with organostannanes - a new, mild and rapid synthesis of aryl [11C]ketones. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 2000, 1033-1036. [CrossRef]
- Andersson, Y.; Långström, B. Synthesis of 11C-labelled ketones via carbonylative coupling reactions using [11C]carbon monoxide. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1995, 287-289. [CrossRef]
- Lidström, P.; Kihlberg, T.; Långström, B. [11C]Carbon monoxide in the palladium-mediated synthesis of 11C-labelled ketones. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1997, 2701-2706. [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.; Itsenko, O.; Rahman, O.; Ulin, J.; Sjöberg, C.-O.; Sandblom, P.; Larsson, L.-A.; Schou, M.; Halldin, C. An evaluation of a high-pressure 11CO carbonylation apparatus. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.; Ulin, J.; Schou, M.; Halldin, C. Reduction of [11C]CO2 to [11C]CO using solid supported zinc. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisler, S.K.; Nader, M.; Theobald, A.; Oberdorfer, F. Conversion of no-carrier-added [11C]carbon dioxide to [11C]carbon monoxide on molybdenum for the synthesis of 11C-labelled aromatic ketones. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Haskali, M.B.; Ruley, K.M.; Dreyfus, N.J.-F.; DuBois, S.L.; Paul, S.; Liow, J.-S.; Morse, C.L.; Kowalski, A.; Gladding, R.L.; et al. PET ligands [18F]LSN3316612 and [11C]LSN3316612 quantify O-linked-β-N-acetyl-glucosamine hydrolase in the brain. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, Article ID eaau2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Hong, J.; Itoh, T.; Fujita, M.; Inoue, O.; Innis, R.B.; Pike, V.W. [carbonyl-11C]Benzyl acetate: Automated radiosynthesis via Pd-mediated [11C]carbon monoxide chemistry and PET measurement of brain uptake in monkey. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudeau, M.; Zhang, M.; Tatoulian, M.; Lescot, C.; Ognier, S. Fast carbonylation reaction from CO2 using plasma gas/liquid microreactors for radiolabeling applications. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niisawa, K.; Ogawa, K.; Saito, J.; Taki, K.; Karasawa, T.; Nozaki, T. Production of no-carrier-added 11C-carbon disulfide and 11C-hydrogen cyanide by microwave discharge. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1984, 35, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Iio, M. On-line synthesis of [11C]cyanide from cyclotron-produced [11C]carbon dioxide. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 1092–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landais, P.; Finn, R. Online preparation of [11C]carbon dioxide from [11C]methane. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1989, 40, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Christman, D.R.; Ache, H.J.; Wolf, A.P. The preparation of cyanide-11C for use in the synthesis of organic radiopharmaceuticals II. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1971, 22, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christman, D.R.; Fin, R.D.; Karlstrom, K.I.; Wolf, A.P. Production of carrier-free H11CN for medical use and radiopharmaceutical syntheses. IX. J. Nucl. Med. 1973, 14, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwata, R.; Ido, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Iida, S. Optimization of [11C]HCN production and no-carrier-added [1-11C]amino acid synthesis. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Qu, W. [11C]HCN radiochemistry: Recent progress and future perspectives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4653–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaree, D.C.; Ropchan, J.R.; Nabulsi, N.; Huang, Y. A modification to improve the reliability of [11C]CN− production in the GE radiochemistry system. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Boothe, T.E.; Vora, M.M.; Hildner, J.C.; Emran, A.M.; Kothari, P.J. Syntheses with isotopically labelled carbon. Methyl iodide, formaldehyde and cyanide. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1984, 35, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouzel, C.; Sejourne, C.; Comar, D. Production of 11C-acetylene by methane pyrolysis. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1979, 30, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaalburg, W.; Reiffers, S.; Beerling, E.; Pratt, J.J.; Woldring, M.G.; Wynberg, H. The preparation of carbon-11 labelled 17α-ethynylestradiol. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1977, 13, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaalburg, W.; Feenstra, A.; Wiegman, T.; Beerling, H.D.; Reiffers, S.; Talma, A.; Woldring, M.G.; Wynberg, H. Carbon-11 labelled Moxestrol and 17α-methylestradiol as receptor binding radiopharmaceuticals. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1981, 18, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskali, M.B.; Pike, V.W. [11C]Fluoroform, a breakthrough for versatile labeling of PET radiotracer trifluoromethyl groups in high molar activity. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8156–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.J.; Pike, V.W.; Taddei, C. Rapid and efficient synthesis of [11C]trifluoromethylarenes from primary aromatic amines and [11C]CuCF3. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19557–19564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, S.; Telu, S.; Yang, B.Y.; Haskali, M.B.; Jakobsson, J.E.; Pike, V.W. Rapid syntheses of [11C]arylvinyltrifluoromethanes through treatment of (E)-arylvinyl(phenyl)iodonium tosylates with [11C]trifluoromethyl copper(I). Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4574–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Torres, K.M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Yang, B.Y.; Guehl, N.J.; Sung-Hyun, M.; Telu, S.; Normandin, M.D.; Pike, V.W.; Brugarolas, P. Syntheses of [11C]2- and [11C]3-trifluoromethyl-4-aminopyridine: potential PET radioligands for demyelinating diseases. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telu, S.; Jana, S.; Haskali, M.B.; Yeun Yang, B.; Jakobsson, J.E.; Zhao, Q.; Ramos-Torres, K.M.; Brugarolas, P.; Pike, V.W. Broad-scope syntheses of [11C/18F]trifluoromethylarenes from aryl(mesityl)iodonium salts. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, Article ID e202204004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouzel, C.; Amano, R.; Fournier, D. Synthesis of carbon-11 labelled diazomethane. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouzel, C.; Hinnen, F. Synthesis of carbon-11 labelled lower chloromethanes: Application in a methylenation reaction. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1994, 35, S92–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbach, C.; Machulla, H.J. Production of [11C]chloroform by direct chlorination of [11C]methane without catalyst support for the synthesis of [11C]diazomethane. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 65, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenant, C.; Crouzel, C. A new simple and attractive method of [11C]halogenomethanes production (Br11CH3, I11CH3). J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1991, 30, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, B.H.; Mulholland, G.K.; Vavrek, M.T. Convenient gas phase bromination of [11C]methane and production of [11C]methyl triflate. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1999, 26, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouzel, C.; Långström, B.; Pike, V.W.; Coenen, H.H. Recommendations for a practical production of [11C]methyl iodide. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, J.M.; Clark, J.C.; Larsen, P.; Krohn, K.A. Production of [11C]methyl iodide by reaction of 11CH4 with I2. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1995, 37, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.A.; Garcia, A.; Jin, L.; Houle, S. Radiotracer synthesis from [11C]iodomethane: A remarkably simple captive solvent method. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeda, D.; Dollé, F. [11C]Phosgene: A versatile reagent for radioactive carbonyl insertion into medicinal radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1680–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, G.A.; Hass-Lisewska, I.; Veenboer, J.T.; Lindner, L. Preparation of 11COCl2. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1978, 29, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diksic, M.; Jolly, D.; Farrokhzad, S. An on-line synthesis of “no-carrier-added” [11C]phosgene. Int. J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1982, 9, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeda, D.; Zanten, B.v.; Crouzel, C. The production of 11C-phosgene without added carrier. Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett. 1978, 33, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Crouzel, C.; Roeda, D.; Berridge, M.; Knipper, R.; Comar, D. 11C-labelled phosgene: an improved procedure and synthesis device. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1983, 34, 1558–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, J.E.; Lu, S.Y.; Telu, S.; Pike, V.W. [11C]Carbonyl difluoride-a new and highly efficient [11C]carbonyl group transfer agent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7256–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, J.E.; Telu, S.; Lu, S.Y.; Jana, S.; Pike, V.W. Broad scope and high-yield access to unsymmetrical acyclic [11C]ureas for biomedical imaging from [11C]carbonyl difluoride. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 10369–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, E.J.; Posarac, D.; Kwok, K.E.; Lim, C.J. Modeling, simulation and experimental study of methanol synthesis for 11C- radiopharmaceuticals. Chem. Prod. Process Model. 2008, 3, Article ID 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazano, C.; Maziere, M.; Berger, G.; Comar, D. Synthesis of methyl iodide-11C and formaldehyde-11C. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1977, 28, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christman, D.; Crawford, E.J.; Friedkin, M.; Wolf, A.P. Detection of DNA synthesis in intact organisms with positron-emitting [methyl-11C]thymidine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1972, 69, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Maziere, M.; Sastre, J.; Comar, D. Carrier-free 11C formaldehyde - An approach. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1980, 17, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, V.W.; Palmer, A.J.; Horlock, P.L.; Perun, T.J.; Freiberg, L.A.; Dunnigan, D.A.; Liss, R.H. Semi-automated preparation of a 11C-labelled antibiotic - [N-methyl-11C]erythromycin-A lactobionate. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1984, 35, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeda, D.; Dollé, F. Preparation of [11C]formaldehyde using a silver-containing ceramic catalyst. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2003, 46, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straatmann, M.G.; Welch, M.J. A general method for labeling proteins with 11C. J. Nucl. Med. 1975, 16, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Holschbach, M.; Schüller, M. A new and simple on-line method for the preparation of n.c.a. [11C]methyl iodide. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1993, 44, 779–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Pike, V.W.; Dowsett, K. Preparation of no-carrier-added [1-11C]ethylene and [1-11C]1,2-dibromoethane as new labelling agents. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, K.-i.; Kuge, Y.; Seki, K.-i.; Ohkura, K.; Motoki, N.; Nagatsu, K.; Tanaka, A.; Tsukamoto, E.; Tamaki, N. A simplified and improved synthesis of [11C]phosgene with iron and iron (III) oxide. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2002, 29, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramoullé, Y.; Roeda, D.; Dollé, F. A simplified [11C]phosgene synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Takada, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Nemoto, K.; Fukumura, T. Simple and effective method for producing [11C]phosgene using an environmental CCl4 gas detection tube. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, T.; Mori, W.; Ogawa, M.; Fujinaga, M.; Zhang, M.R. [11C]phosgene: Synthesis and application for development of PET radiotracers. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Någren, K.; Müller, L.; Halldin, C.; Swahn, C.-G.; Lehikoinen, P. Improved synthesis of some commonly used PET radioligands by the use of [11C]methyl triflate. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Någren, K.; Halldin, C.; Muller, L.; Swahn, C.G.; Lehikoinen, P. Comparison of [11C]methyl triflate and [11C]methyl-iodide in the synthesis of PET radioligands such as [11C]β-CIT and [11C]β-CFT. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, D.M. A simple synthesis of [11C]methyl triflate. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1992, 43, 1383–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, E.M.; Någren, K.; Mock, B.H.; Watkins, G.L. 30 years of [11C]methyl triflate. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 197, Article ID 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeps, K.-O.; Stone-Elander, S.; Halldin, C. On-line synthesis of [11C]nitroalkanes. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1989, 40, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Långström, B.; Antoni, G.; Gullberg, P.; Halldin, C.; Någren, K.; Rimland, A.; Svärd, H. The synthesis of 1-11C-labelled ethyl, propyl, butyl and isobutyl iodides and examples of alkylation reactions. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1986, 37, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeps, K.-O.; Halidin, C.; Stone-Elander, S.; Långström, B.; Greitz, T. Preparation of 11C-nitromethane and an example of its use as a radiolabeling precursor. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1988, 25, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, S.A.; Kato, K.; Långström, B. Purification of [11C]nitromethane for use in asymmetric nitroaldol reactions. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2003, 46, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeps, K.O.; Långström, B.; Stone-Elander, S.; Halldin, C. Synthesis of [1-11C]D-glucose and [1-11C]D-mannose from online produced [11C]nitromethane. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991, 42, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, M.; Shiue, C.Y.; Gonzalez, C.; Dembowski, B. The synthesis of [11C]methanethiol, a precursor for S-[11C]methylations. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1995, 37, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Ishiwata, K.; Ishii, S.-I.; Omura, H.; Senda, M. Enzymatic synthesis of carbon-11 labeled methionine and its derivatives with immobilized γ-cyano-α-aminobutyric acid synthase. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1999, 51, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, J.A.; Pike, V.W. Synthesis of no-carrier-added [11C]methanesulfonyl chloride as a new labeling agent for PET radiopharmaceutical development. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2003, 46, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Luthra, S.K.; Brock, C.S.; Stevens, M.F.G.; Price, P.M.; Brady, F. Antitumor imidazotetrazines. 40. Radiosyntheses of [4-11C-carbonyl]- and [3-N-11C-methyl]-8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3H)-one (temozolomide) for positron emission tomography (PET) studies. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5448–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Ogawa, M.; Okamura, T.; Gee, A.D.; Zhang, M.-R. Rapid ‘on-column’ preparation of hydrogen [11C]cyanide from [11C]methyl iodide via [11C]formaldehyde. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 3556–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.W.; Bender, D. [11C]Carbon disulfide: A versatile reagent for PET radiolabelling. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerberg, G.; Långström, B. On-line production of [11C]cyanogen bromide. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjurling, P.; Reineck, R.; Westerburg, G.; Gee, A.D.; Sutcliffe, J.; Långström, B. Synthia, a compact radiochemistry system for automated production of radiopharmaceuticals. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Targetry & Target Chemistry, TRIUMF, Vancouver, 1995; pp. 282-285. https://wttc.triumf.ca/95-pdf.html.
- Westerberg, G.; Långström, B. Synthesis of [11C]-and [13C]-cyanogen bromide. Useful electrophilic labelling precursors. Acta Chem. Scand. 1993, 47, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerberg, G.; Bamford, M.; Daniel, M.J.; Långström, B.; Sutherland, D.R. Synthesis of 5-acetylamino-4-[11C]guanidino-2,6-anhydro-3,4,5-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-enoic acid ([11C]GG167)—an influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1996, 38, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerberg, G.; Långström, B. Labelling of proteins with 11C in high specific radioactivity: [11C]albumin and [11C]transferrin. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1994, 45, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerberg, G.; Bergström, M.; Gustafson, S.; Lindqvist, U.; Sundin, A.; Långström, B. Labelling of polysaccharides using [11C]cyanogen bromide. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of 11C-hyaluronan uptake kinetics. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imahori, Y.; Fujii, R.; Ido, T.; Hirakawa, K.; Nakahashi, H. Positron labeled phorbol ester: Synthesis method for “non-carrier added” phorbol 13-[1-11C] butyrate using ketene reaction. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1989, 27, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R.; Imahori, Y.; Ido, T.; Yagyu, T.; Horii, H.; Wakita, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamamoto, Y.L.; Nakahashi, H. New synthesis system of (C-11)propyl ketene and its reactons with various alcohols. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1991, 29, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R.; Imahori, Y.; Ido, T.; Yagyu, T.; Horii, H.; Wakita, K.; Ueda, S.; Nakahashi, H. New Synthesis of [C-11]propyl ketene using HCl/He gas mixture and the reaction on various alcohols. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1991, 30, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
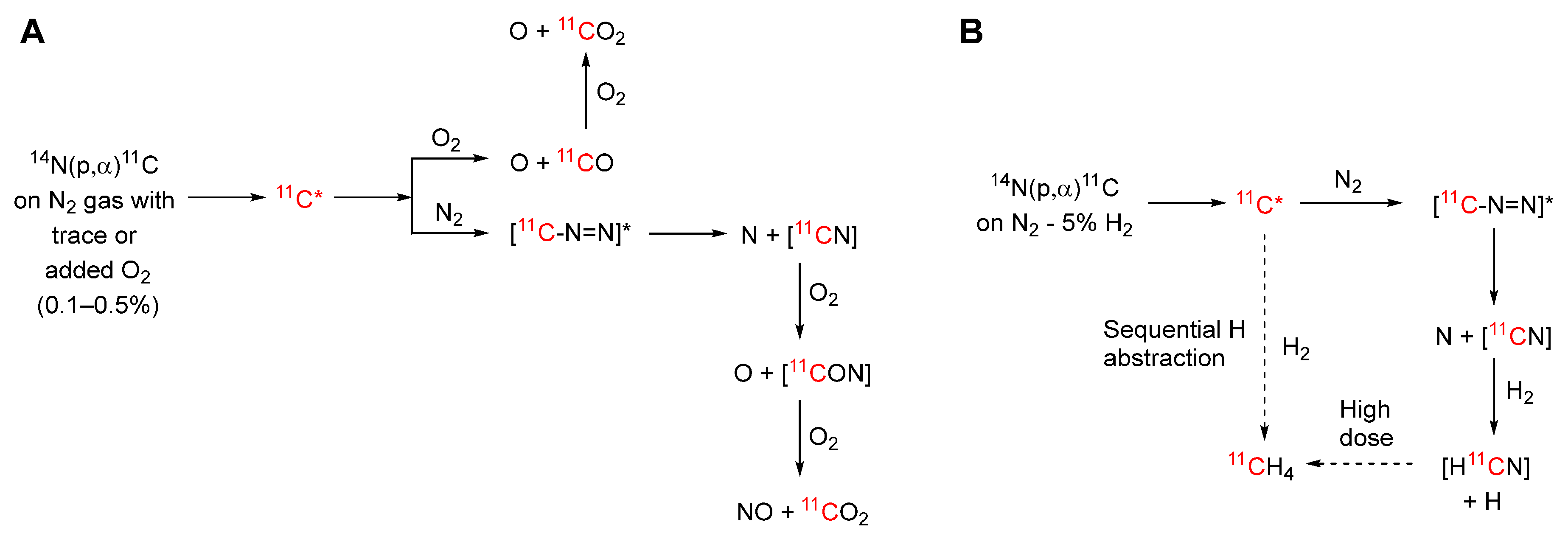


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




