Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
05 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Sources of Information
2.4. Search Strategy
2.5. Article Selection Process
2.6. Data Extraction Process
2.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Methods of Synthesis
3. Results
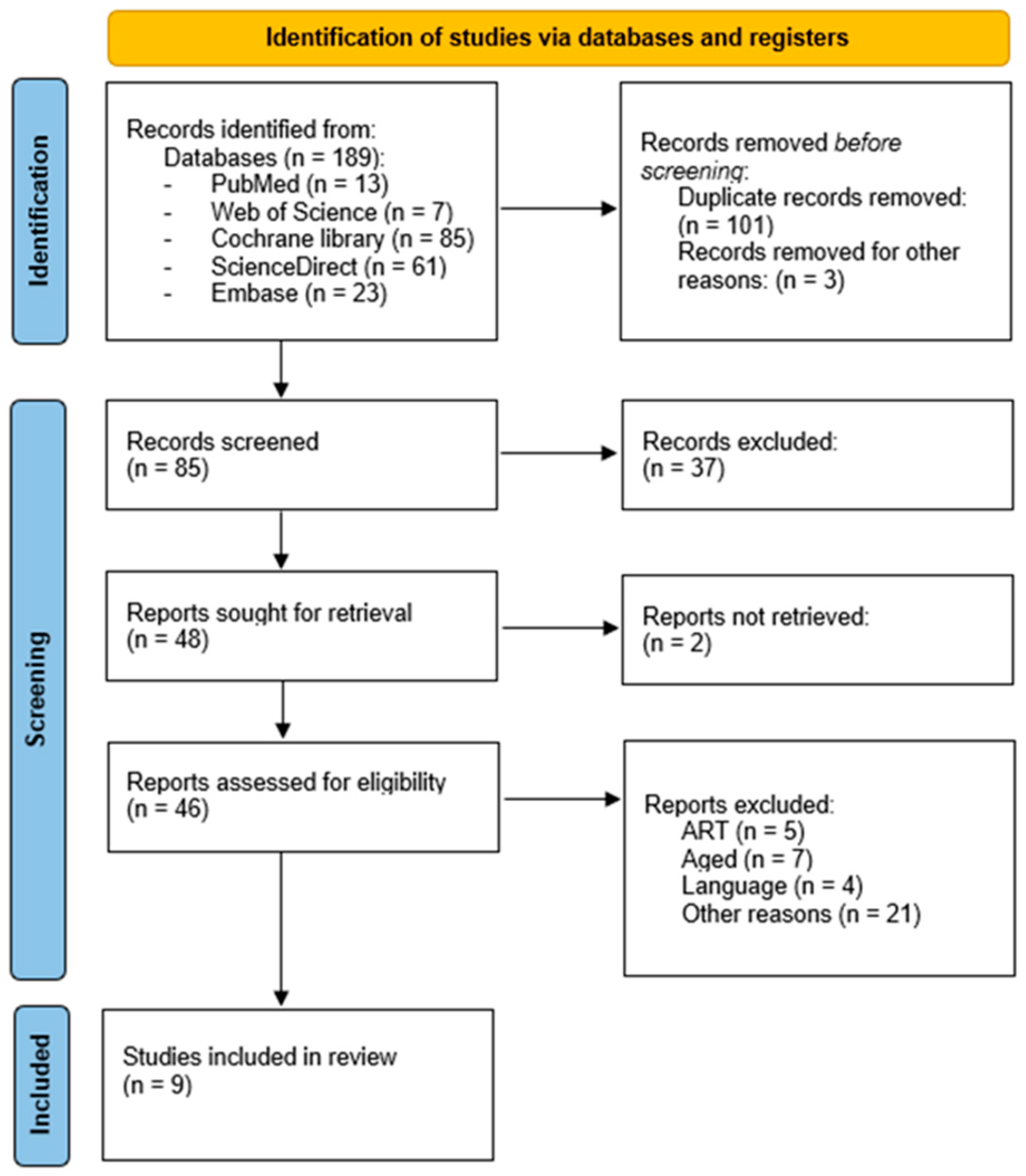
3.1. Selection of Studies
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies
3.3. Publication Bias
3.4. Relationship between Adherence to the MD and ART Outcomes
3.5. Quality of the evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Health topics: Infertility. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infertility (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Sociedad Española de Fertilidad. Libro Blanco Sociosanitario de la SEF: La Infertilidad en España: Situación Actual y Perspectivas. Imago Concept & Image Development, S.L. 2021. Available online: https://www.sefertilidad.net/docs/biblioteca/libros/libroBlanco.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Indicadores de Fecundidad: Edad Media a la Maternidad Por Orden Del Nacimiento Según Nacionalidad (Española/Extranjera) De La Madre. 2021. Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxiT3/Tabla.htm?t=1579 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Eurostat Statistics Explained. Fertility Statistics. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Fertility_statistics (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Batiza-Resendiz, V.A.; Aguilar-Melgar, A.; Luna-Rojas, R.M.; Pérez-Peña, E.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, A.; Ruvalcaba-Castrellón, L.A.; et al. Preservación de la fertilidad: opinión de un grupo de expertos. Ginecol. obstet. Méx 2020, 88, 767–805. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Salud de la Nación. Guía sobre fertilidad para equipos de atención primaria de la salud. 2015. Available online: https://iah.salud.gob.ar/doc/Documento107.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- De Geyter, C. Assisted reproductive technology: Impact on society and need for surveillance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019, 33, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.; Paul, R.; Chambers, G. Assisted reproductive technology in Australia and New Zealand. Sydney: National Perinatal Epidemiology and Statistics Unit, the University of New South Wales. 2020. Available online: https://npesu.unsw.edu.au/sites/default/files/npesu/data_collection/Assisted%20Reproductive%20Technology%20in%20Australia%20and%20New%20Zealand%202020.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Adamson, G.D.; Zegers-Hochschild, F.; Dyer, S.; Chambers, G.; Mouzon, J.; Ishihara, O.; et al. International Committee Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies. Preliminary World Report, 2018. Available online: https://www.icmartivf.org/wp-content/uploads/ICMART-ESHRE-WR2018-Preliminary-Report.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Villani, M.T.; Morini, D.; Spaggiari, G.; Furini, C.; Melli, B.; Nicoli, A.; et al. The (decision) tree of fertility: an innovative decision-making algorithm in assisted reproduction technique. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022, 39, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayiannis, D.; Kontogianni, M.D.; Mendorou, C.; Mastrominas, M.; Yiannakouris, N. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and IVF success rate among non-obese women attempting fertility. Hum Reprod. 2018, 33, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosato, V.; Temple, N.J.; La Vecchia, C.; Castellan, G.; Tavani, A.; Guercio, V. Mediterranean diet and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Nutr. 2019, 58, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansrivijit, P.; Oli, S.; Khanal, R.; Ghahramani, N.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Mediterranean diet and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2020, 25, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Parsaik, A.K.; Mielke, M.M.; Erwin, P.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Association of mediterranean diet with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 39, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Babio, N.; Carrell, D.T.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is positively associated with sperm motility: A cross-sectional analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Yao, J.; et al. Higher dietary inflammation potential and certain dietary patterns are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome risk in China: A case-control study. Nutr Res. 2022, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmidt, M.K.; Granda, D.; Madej, D.; Sicinska, E.; Kaluza, J. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Women and Reproductive Health across the Lifespan: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic, M.; De Vries, J.H.; Lindemans, J.; Macklon, N.S.; Van der Spek, P.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; et al. The preconception Mediterranean dietary pattern in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment increases the chance of pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2010, 94, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.A.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; et al. Declaración PRISMA 2020: una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; et al. The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ. 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide. Blackwell Publishing. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R.S. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’ Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses 2013. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Noli, S.A.; Ferrari, S.; Ricci, E.; Reschini, M.; Cipriani, S.; Dallagiovanna, C.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and the risk of unexpected poor response to ovarian stimulation in IVF cycles. Reprod Biomed Online. 2023, 47, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic, M.; De Vries, J.H.; Lindemans, J.; Macklon, N.S.; Van der Spek, P.J.; Steegers, E.A.; et al. The preconception Mediterranean dietary pattern in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment increases the chance of pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2010, 94, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayiannis, D.; Kontogianni, M.D.; Mendorou, C.; Mastrominas, M.; Yiannakouris, N. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and IVF success rate among non-obese women attempting fertility. Hum Reprod. 2018, 33, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskins, A.J.; Nassan, F.L.; Chiu, Y.H.; Arvizu, M.; Williams, P.L.; Keller, M.G.; et al. EARTH Study Team. Dietary patterns and outcomes of assisted reproduction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019, 220, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Bravi, F.; Noli, S.; Somigliana, E.; Cipriani, S.; Castiglioni, M.; et al. Mediterranean diet and outcomes of assisted reproduction: an Italian cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019, 221, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.M.; Lin, Y.; Lin, D.; Zou, C.; Zou, X.; Fu, L.; et al. Mediterranean diet improves embryo yield in IVF: a prospective cohort study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2019, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Mitsunami, M.; Arvizu, M.; Ford, J.B.; Souter, I.; et al. EARTH Study Team. Paternal adherence to healthy dietary patterns in relation to sperm parameters and outcomes of assisted reproductive technologies. Fertil Steril. 2022, 117, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Mitsunami, M.; Wang, S.; Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Ribas-Maynou, J.; Yeste, M.; et al. EARTH Study Team. Women’s Adherence to Healthy Dietary Patterns and Outcomes of Infertility Treatment. JAMA Netw Open. 2023, 6, e2329982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermack, A.J.; Lowen, P.; Wellstead, S.J.; Fisk, H.L.; Montag, M.; Cheong, Y.; et al. Effect of a 6-week “Mediterranean” dietary intervention on in vitro human embryo development: the Preconception Dietary Supplements in Assisted Reproduction double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 2020, 113, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Boutron, I.; et al. A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials In Cochrane Methods. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Aguayo-Albasini, J.L.; Flores-Pastor, B.; Soria-Aledo, V. Sistema GRADE: clasificación de la calidad de la evidencia y graduación de la fuerza de la recomendación. Cir Esp. 2014, 92, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, E.; López-del Burgo, C.; Ruiz-Zambrana, A.; Donazar, M.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; Martínez-González, M.A.; et al. Dietary patterns and difficulty conceiving: a nested case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2011, 96, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, E.; Bravi, F.; Noli, S.; Ferrari, S.; De Cosmi, V.; La Vecchia, I.; et al. Mediterranean diet and the risk of poor semen quality: cross-sectional analysis of men referring to an Italian Fertility Clinic. Andrology 2019, 7, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Babio, N.; Carrell, D.T.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is positively associated with sperm motility: A cross-sectional analysis. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Arnone, A.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Salzano, C.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Dietary Patterns and Body Composition in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Nutrients. 2019, 11, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pugliese, G.; De Alteriis, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Metabolically Healthy Obesity (MHO) vs. Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Phenotypes in PCOS: Association with Endocrine-Metabolic Profile, Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, and Body Composition. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricceri, F.; Giraudo, M.T.; Fasanelli, F.; Milanese, D.; Sciannameo, V.; Fiorini, L.; et al. Diet and endometrial cancer: a focus on the role of fruit and vegetable intake, Mediterranean diet and dietary inflammatory index in the endometrial cancer risk. BMC Cancer. 2017, 17, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Argento, F.R.; Becatti, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Coccia, M.E.; Fatini, C. Mediterranean Diet and Oxidative Stress: A Relationship with Pain Perception in Endometriosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesi, S.; Villani, A.; Mantzioris, E.; Takele, W.W.; Cowan, S.; Moran, L.J.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Diets in Fertility: An Evidence Review. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moludi, J.; Kamari, N.; Darbandi, M.; Mostafaei, S.; Moradi, S.; Pasdar, Y.; et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and infertility of women; Results from RaNCD Cohort Study. Nutr J. 2023, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łakoma, K.; Kukharuk, O.; Śliż, D. The Influence of Metabolic Factors and Diet on Fertility. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Search Strategy |
|---|
| #1 (“mediterranean diet” [Title/Abstract] OR “diet, mediterranean” [MeSH Terms]) |
| #2 (“reproductive techniques assisted” [Title/Abstract] OR “reproductive techniques, assisted [MeSH Terms] OR “IVF” [Title/Abstract] OR “fertilization in vitro” [Title/Abstract] OR “fertilization in vitro” [MeSH Terms] OR “insemination artificial” [Title/Abstract] OR “insemination, artificial” [MeSH Terms]) |
| #3 “Outcomes” [Title/Abstract] |
| #4 1 AND 2 AND 3 |
| Authors, Year | Country |
Age Range |
Sample Size (n) |
Objective |
Strengths and Limitations |
Study Type |
| Vujkovic M et al., 2010 [25] | Netherlands | 23-45 years |
161 women |
Investigate associations between preconception dietary patterns and outcomes of IVF/ICSI. | Limitations: Self-reported FFQ, limited external validity. Strengths: Prospective design, analysis of correlation between dietary patterns and biomarkers. |
Cohort |
| Karayiannis D et al., 2018 [26] | Greece | 22-41 years |
244 women |
Explore potential associations between MD and clinical outcomes of IVF among non-obese women from infertile couples. | Limitations: Self-administered dietary questionnaire, possible presence of confounding variables, limited causal inference. Strengths: Non-obese patients, comprehensive follow-up of the sample, assessment of intermediate and final outcomes. |
Cohort |
| Gaskins AJ et al., 2019 [27] | USA | 18-46 years |
357 women |
Evaluate the relationship between pre-treatment adherence to various dietary patterns (including MD) and outcomes of ART. | Limitations: Self-administered FFQ, possible presence of confounding variables, limited external validity. Strengths: Prospective design, comprehensive sample assessment, comparison of various dietary patterns. |
Cohort |
| Ricci E et al., 2019 [28] | Italy | 27-45 years | 474 women |
Study the relationship between MD and outcomes of ART in subfertile couples. | Limitations: Self-administered FFQ, non-validated measurements of some variables, low study power. Strengths: Prospective design, relatively large sample size. |
Cohort |
| Sun HM et al., 2019 [29] | China | 18-40 years | 590 women |
Explore the correlation between the pattern of MD in infertile women and their clinical outcomes in IVF cycles. | Limitations: Low external validity, non-validated FFQ. Strengths: Large sample size, non-obese patients. |
Cohort |
| Kermack AJ et al., 2020 [32] | United Kingdom | 18-41 years | 111 women |
Study the impact of increased dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and olive oil for 6 weeks prior to IVF or ICSI on morphokinetic markers of early embryonic development. | Limitations: Short dietary intervention (6 weeks); limited external validity. Strengths: Study design, double-blind randomization, comprehensive sample follow-up. |
Clinical trial |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2022 [30] | USA | 18-45 years | 245 men |
Investigate whether men’s adherence to dietary patterns promoted for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases is associated with semen parameters and outcomes of ART in their partners. | Limitations: Observational design, potential residual confounding factors. Strengths: Prospective design, comprehensive sample follow-up, consideration of intermediate and final outcomes, statistical adjustment for relevant confounding factors. |
Cohort |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2023 [31] | USA | 18-45 years |
612 women | Investigate whether women’s adherence to dietary patterns (including MD) is associated with infertility treatment outcomes. | Limitations: Single-center study, potential residual confounding factors, limited external validity. Strengths: Prospective design, analysis of multiple dietary patterns, high standardization level of covariables, exposures, and study outcomes. |
Cohort |
| Noli SA et al., 2023 [24] | Italy | 18-39 years | 296 women | Evaluate whether preconceptional adherence to MD can influence the risk of poor ovarian response in patients without criteria/risk factors for it. | Limitations: Cross-sectional design, self-administered dietary questionnaire, limited external validity. Strengths: Relatively large sample size, comprehensive statistical analysis. |
Cross-sectional |
| Reference | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noli SA et al., 2023 [24] | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | dk | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | dk | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| Reference | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vujkovic M et al., 2010 [25] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | - |
| Karayiannis D et al., 2018 [26] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * |
| Gaskins AJ et al., 2019 [27] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * |
| Ricci E et al., 2019 [28] | * | - | * | * | * | * | * | - |
| Sun HM et al., 2019 [29] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2022 [30] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | - |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2023 [31] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | - |
| Authors, Year | Determination of Adherence to the MD / Intervention |
Variables Analyzed to Determine ART Outcomes |
Results | Conclusions | Quality of Evidence (GRADE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vujkovic M et al., 2010 [25] | A 195-item FFQ with 22 food groups was used and adjusted for total energy intake. This was followed by a principal component analysis applied to the food groups to construct dietary patterns. Two patterns emerged: “health-conscious, minimally processed” and “MD” | 1) Fertilization rate 2) Embryo quality 3) Biochemical pregnancy |
The dietary pattern of the MD correlated positively with red blood cell folate (β=0.13) and vitamin B6 in blood (β=0.09) and follicular fluid (β=0.18). High adherence by the couple to the MD increased the likelihood of pregnancy (OR: 1.4). | A MD before conception by couples undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment contributes to the success of achieving pregnancy. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Karayiannis D et al., 2018 [26] | A questionnaire was used to assess adherence to the MD (PMD) previously developed by Panagiotakos et al., in 2007. | 1) Ovarian stimulation results 2) Fertilization rate 3) Embryo quality 4) Clinical pregnancy 5) Live birth |
Women in the lowest third of adherence to the MD had at least a 65% lower relative risk (95% CI) of achieving clinical pregnancy (p=0.01) and live births (p=0.01). No significant association of MedDietScore with intermediate study outcomes (ovarian stimulation results, fertilization rate, and measures of embryo quality) was observed. | Higher adherence to the MD is associated with a greater likelihood of clinical pregnancy and live births after IVF/ICSI treatment in non-obese women <35 years of age. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Gaskins AJ et al., 2019 [27] | Validated 131-item FFQ Subsequently, the Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS) was calculated to assess adherence to the MD. | 1) Fertilization rate 2) Number of mature oocytes 3) Implantation rate 4) Clinical pregnancy 5) Live birth |
Women in the second to fourth quartiles of adherence to the MD had a significantly higher likelihood of live birth compared to women in the first quartile. However, there was no additional benefit of adherence to the MD beyond the second quartile. Higher adherence to the “fertility-promoting” diet was linearly associated with ART outcomes. | No association was found between adherence to the MD and ART outcomes. However, higher adherence to the “fertility-promoting” (rich in folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, pesticide-residue-low agricultural products, whole grains, dairy, soy foods, and seafood) diet was associated with a higher likelihood of live birth after ART. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Ricci E et al., 2019 [28] | Information was collected using a valid and reproducible FFQ. The FFQ included the average weekly consumption of 78 individual foods or food groups. Adherence to the MD was assessed using the MDS developed by Trichopoulou et al., (2003). | 1) Number of retrieved high-quality oocytes 2) Embryo quality 3) Clinical pregnancy 4) Live birth |
No significant association was found with the components of the MDS. | No clear association was observed between adherence to the MD and successful IVF. | Very low ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Sun HM et al., 2019 [29] | A 69-item FFQ was used, and then adherence to the Mediterranean Diet was evaluated using the Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS) developed by Trichopoulou et al., (2003). | 1) Available embryos 2) Implantation rate 3) Number of fertilized oocytes 4) Clinical pregnancy |
The group with higher adherence to the MD showed a greater number of available embryos (p=0.028). Clinical pregnancy rate and implantation rate were similar between the two groups. In additional correlation tests and multivariate linear regression analysis, the number of fertilized oocytes and embryo production correlated positively with participants’ adherence to the MD. | Infertile women with higher adherence to the MD pattern were likely to obtain more available embryos in the IVF cycle. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Kermack AJ et al., 2020 [32] | The study group received olive oil for cooking, a spread made from olive oil, and a daily complementary beverage enriched with EPA (800 mg), DHA (1200 mg), and vitamin D (10 μg). | Embryo quality (validated morphokinetic parameters of embryonic development associated with a higher probability of blastocyst development, implantation, and clinical pregnancy). | The 4th cell cycle was accelerated in the study group, and a significantly shorter synchrony of the 3rd cell cycle was observed, along with an increase in KIDScore (known implantation data scores) on day 3, indicating better embryo quality in the study group. | This study suggests that a short period of dietary supplementation alters the embryo’s division rate (improved embryo quality). Further research is needed to assess whether the impact on embryonic development translates into better clinical outcomes. | High ⊕⊕⊕⊕ |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2022 [30] | Male pre-treatment dietary intake was assessed using a validated 131-item FFQ, from which three scores were calculated: (1) MDS, (2) AMD, (3) PMD. | 1) Fertilization rate 2) Implantation rate 3) Clinical pregnancy 4) Live birth |
There was a reverse association between men’s adherence to the PMD and the fertilization rate. However, there were no significant associations between men’s adherence to any of the analyzed dietary patterns and the odds of implantation, clinical pregnancy, or live birth in adjusted multivariable models. | Men’s adherence to various a priori defined dietary scores with documented cardiovascular benefits is not related to significant outcomes of ART. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Salas-Huetos A et al., 2023 [31] | Women’s pre-treatment diet was assessed using a validated FFQ from which three indices were calculated: (1) MDS, (2) AMD, (3) PMD. | 1) Clinical pregnancy 2) Total pregnancy loss 3) Clinical pregnancy loss 4) Live birth |
There was no association between women’s adherence to dietary patterns and the likelihood of clinical pregnancy or live birth after IVF or AI. | The findings of this study suggest that there is no association between adherence to the MD and ART outcomes. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Noli SA et al., 2023 [24] | A MD index (MDS) developed by Trichopoulou et al., (2003) was used and later modified for Italian dietary habits. | Poor ovarian response (retrieval of three or fewer suitable oocytes) in patients without criteria/risk factors for it | The risk of poor ovarian response was significantly lower for women in the second tertile of MDS compared to the first tertile (OR: 0.29) and for women in the second and third tertiles, grouped together, compared to the first tertile (OR: 0.34). | Low adherence to the MD could be a risk factor for poor ovarian response in patients without criteria/risk factors for it. | Low ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





