1. Introduction
AI and ML have emerged as the driving forces in the technological renaissance of the 21st century, dramatically reshaping different areas of technology, with cybersecurity seen as one of its user’s par excellence. The fundamental principles of artificial intelligence revolve around simulating cognitive functions related to human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem solving, and pattern recognition [
1].
The integration of AI and ML into cybersecurity marks a significant evolution in the field. In an era where digital threats are becoming more sophisticated and pervasive, traditional security measures are proving inadequate. AI and ML emerge as beacons of hope, offering innovative solutions to anticipate, detect, and respond to cyber threats more effectively. The rapid advancement of these technologies has enabled them to adapt and evolve in response to the dynamic nature of cyber threats, making them indispensable tools in the cybersecurity arsenal.
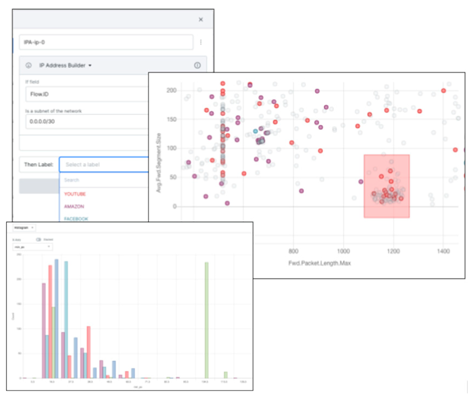
This integration in cybersecurity is demonstrated by various real-world applications and case studies, highlighting their efficacy in enhancing cyber defense mechanisms. A globally recognized Fortune 500 telecom company employed Snorkel Flow to classify encrypted network data flows into their associated application categories. They faced challenges like slow manual labeling of network traffic data and the need for adaptable solutions. Snorkel Flow enabled the telecom company to quickly produce a large training dataset for ML models, resulting in a system 26.2% more accurate than the baseline model and nearly as accurate as a fully-supervised model trained on all ground-truth examples. This approach allowed the company to develop adaptable solutions that outperformed static rules-based approaches, especially in dynamic data environments like SNIs [
2].
Snorkel Flow has no-code UI support for rapidly creating labeling functions with network data [
2]
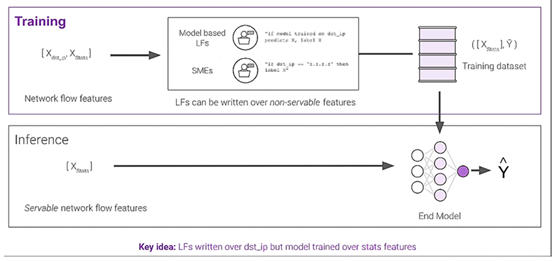
A second case study concerned a major AI center within the U.S. government that selected Snorkel Flow for developing AI/ML applications in cybersecurity. They used Snorkel Flow to programmatically label nearly 280,000 records for application type classification. The dataset consisted of network packets with over 2.7 million total records, described using various data features. The Snorkel Flow model was able to effectively use non-servable features like destination IP for labeling training data while relying on more reliable packet statistics for actual model training and prediction [
2].
Building and deploying labeling functions (LFs) with Snorkel Flow [
2].
These examples illustrate the transformative role AI and ML play in various aspects of cybersecurity, from detecting and responding to threats to predicting vulnerabilities and enhancing incident response. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the integration of these technologies in cybersecurity tools becomes increasingly vital for maintaining robust defense mechanisms.
However, the integration of AI and ML into cybersecurity is not without its challenges. A significant issue is the orchestration of diverse data sources and technologies to provide a comprehensive security posture. This complexity is compounded by the need for these systems to not only detect threats but also to predict and prevent potential future attacks. Despite the promise of AI and ML in enhancing cybersecurity measures, there is a gap in understanding how these technologies can be effectively integrated into existing cybersecurity frameworks, particularly in the realm of Open XDR technology.
Open XDR is an emerging approach in cybersecurity that aims to provide a more comprehensive and integrated solution for threat detection and response. Unlike traditional cybersecurity measures that often operate in isolated silos, Open XDR seeks to unify multiple security products into a cohesive system. This approach leverages a variety of data sources, including endpoints, networks, servers, and cloud workloads, to provide a holistic view of an organization’s security posture. Open XDR combines the capabilities of traditional XDR with open standards and integrations, allowing for greater flexibility and compatibility with a wide range of security tools and data sources.
The core advantage of Open XDR lies in its ability to process and correlate data from these disparate sources, providing a more accurate and comprehensive detection of threats. It extends beyond simple alert aggregation, employing advanced analytics, AI, and ML to analyze data for signs of sophisticated attacks that might otherwise go unnoticed. Furthermore, Open XDR supports proactive threat hunting and incident response, enabling organizations to swiftly mitigate and remediate detected threats. This integrated and intelligent approach to cybersecurity is particularly effective in today’s rapidly evolving digital threat landscape, offering enhanced capabilities for detecting and responding to both known and emerging threats.
This article aims to bridge this gap by providing a thorough analysis of the integration of AI and ML in cybersecurity, focusing on the application of Open XDR technology. It seeks to explore the synergies between various cybersecurity components, such as IDS, EDR, and SIEM, in the context of AI and ML. The paper intends to offer insights into the development of AI and ML, their roles in cybersecurity, and the challenges and opportunities they present in this field.
The structure of the work is thoughtfully organized to guide the reader through the complex landscape of AI and ML in cybersecurity. Following the introduction, a literature review delves into the evolving nature of the cybersecurity landscape and discusses the transformative role of Open XDR technology. It examines how XDR solutions integrate multiple security products for a cohesive system, highlighting the advantages of applying AI and ML to aggregated security data for enhanced threat detection and response.
Subsequently, the discussion section explores the multifaceted challenges and opportunities presented by the integration of AI and ML in cybersecurity. It addresses ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, and the need for continuous professional development in this rapidly advancing field. This section also emphasizes the importance of a skilled workforce capable of managing these advanced technologies and the necessity of aligning AI/ML integration with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, the article synthesizes the findings, underscoring the effectiveness of combining AI and ML with cybersecurity tools within an Open XDR framework. It emphasizes the enhanced capabilities in threat detection, response efficiency, and overall cybersecurity resilience achieved through this integration. The conclusion also highlights the future direction of AI and ML in cybersecurity, providing a comprehensive overview of their potential impact on the field.
In summation, it is discernible that the article is structured into five primary sections. The Introduction section sets the context for AI and ML in cybersecurity and the significance of Open XDR. The Literature Review provides an in-depth analysis of Open XDR and related cybersecurity technologies. The core of the paper is in
Section 3, where it delves into various aspects of AI/ML integration in cybersecurity, covering specific technologies and methods. The Discussion section explores the implications, challenges, and opportunities of this integration. Finally, the paper concludes with a summary of findings and potential future directions in
Section 5. This structured approach ensures a comprehensive exploration of the subject.
Through this structured approach, the article aims to provide a detailed and insightful perspective on the crucial role of AI and ML in enhancing cybersecurity measures, addressing the challenges of the digital threat landscape, and shaping the future of cybersecurity strategies.
2. Literature Review
In the transition from understanding the fundamental principles of AI and ML to their practical application in cybersecurity, the role of Open XDR becomes crucial. As the cybersecurity landscape continually evolves with more sophisticated threats, the integration of AI and ML emerges as a transformative solution. This integration, however, presents challenges in harmonizing these advanced technologies within complex cybersecurity frameworks.
Open XDR stands as a key innovation in this realm, signifying a shift from isolated security measures to a more cohesive and intelligent cybersecurity approach. The upcoming literature review will trace the evolution of Open XDR, examining its progression from initial concepts to its current integration of AI and ML. This exploration is essential for understanding how XDR is shaping the future trajectory of cybersecurity strategies.
Heraclitus, who lived from 535 to 475 B.C. in Ephesus, first uttered the phrase "Everything flows, never stays the same” [
2], Which means, everything is fluid, and nothing stays the same. As constant movement and change is the fundamental feature of reality, the cybersecurity landscape is in constant flux, adapting to ever-evolving threats. A pioneering step in this dynamic environment was the introduction of Open XDR technology. The innovation introduced by Open XDR seeks to redefine conventional cybersecurity frameworks by offering a synergistic, comprehensive, and proactive strategy to enhance cybersecurity [
3].
The development and improvement of XDR in cybersecurity over time can be traced through several key stages, reflecting the evolving challenges and technological advancements in the field. The Extended-Detection and Response is an evolution of, Endpoint -Detection, and Response. XDR unites visibility as well as control across all endpoints, network connectivity, as well as cloud workloads [
4].
At its inception, XDR was conceptualized as a solution to the limitations of traditional security tools such as firewalls, antivirus software, and IDS, which often operated in silos, leading to fragmented security postures. The initial objective of XDR was to integrate these disparate security tools to provide a more unified and effective approach to threat detection and response [
4].
The first generation of XDR focused on integrating various security components. These systems aimed to consolidate alerts and data from different sources, providing security teams with a more cohesive view of their security landscape. However, these early systems often relied heavily on manual processes and were limited in their ability to scale, adapt to new threats, or provide real-time responses [
4].
As cybersecurity threats became more sophisticated, the second generation of XDR systems began to incorporate AI and machine learning technologies. These advancements allowed for better anomaly detection, predictive analytics, and automated response capabilities. XDR systems could now learn from data, identify patterns indicative of cyber threats, and initiate responses more swiftly and accurately [
5].
Modern XDR solutions have embraced cloud integration and advanced analytics. They offer more extensive and scalable solutions, capable of processing vast amounts of data from cloud-based and on-premises sources. Today’s XDR systems leverage big data analytics and sophisticated AI algorithms to provide deeper insights, more accurate threat detection, and faster response times, significantly improving over previous generations in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and speed [
4,
5,
6]. Throughout its evolution, XDR has continuously adapted to the changing cyber threat landscape. Each generation of XDR has built upon the lessons learned from its predecessors, leading to improvements in integration, automation, scalability, and intelligence. The development of XDR reflects a broader trend in cybersecurity towards more holistic, adaptive, and proactive security solutions.
XDR is an integrated suite of security products that take a holistic approach to cybersecurity, providing centralized threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities across various layers of security. XDR solutions aim to unify multiple security products into a cohesive system that can process and correlate data from endpoints, networks, servers, cloud workloads, and email. Unlike traditional security measures, which typically operate in silos, XDR seeks to break down these barriers by combining the data from disparate sources into a single, streamlined analytical framework. This comprehensive visibility allows for more accurate threat detection and enhances the overall efficiency of the Security Operations Center (SOC) team in identifying and responding to incidents [
5].
The core advantage of XDR lies in its ability to apply advanced analytics, AΙ
, and ML to the aggregated security data, which helps to identify subtle, sophisticated threats that might otherwise go unnoticed. By leveraging these technologies, XDR platforms can detect patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity, offering a level of detection that is both deeper and broader than traditional methods. The integrated response aspect of XDR allows for quicker mitigation and remediation actions, reducing the time that attackers are in the system (dwell time) and minimizing potential damage. XDR represents an evolutionary step in threat detection and response, promising to simplify and strengthen cybersecurity operations with its expansive scope and intelligent, automated responses [
5].
In summation, the article compares Open XDR with other cybersecurity technologies like IDS, EDR, and SIEM. Open XDR is superior due to its comprehensive integration across various security platforms, enhancing threat detection and response. It effectively utilizes AI and ML for advanced data analysis, offering a holistic security view. However, Open XDR’s complexity in integrating diverse systems and managing extensive data is a challenge. In contrast, technologies like IDS and EDR focus on specific areas like network traffic and endpoint security, respectively, and may not provide as extensive coverage as Open XDR. SIEM systems offer real-time analysis but might lack the predictive capabilities that AI integration in Open XDR provides.
3. Enhancing Cybersecurity with AI and ML: The Evolution and Integration of Open XDR
The upcoming sections provide a deep dive into the integration of Open Extended Detection and Response with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, a pivotal advancement in cybersecurity. This exploration begins by examining how Open XDR leverages AI and ML to not only anticipate but also prevent cyber threats, effectively orchestrating a range of security tools and correlating data from diverse sources like Intrusion Detection Systems, Endpoint Detection and Response, Security Information and Event Management, and others. The focus then shifts to the unique capabilities of IDS in the cybersecurity infrastructure, highlighting the challenges it faces and the innovative solutions offered by AI and ML in enhancing its effectiveness.
Further, the text will delve into the transformative role of AI and ML in Endpoint Detection and Response solutions, emphasizing their contribution to a more resilient and adaptable cybersecurity ecosystem. The synergy between various cybersecurity components such as EDR, IDS, and Open XDR, enhanced through AI/ML integration, will be explored for its capacity to provide a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to threat detection and response.
Additionally, the role of Security Information and Event Management systems will be discussed, particularly in relation to how AI and ML technologies significantly improve their operational capabilities. The discussion will extend to the critical role of Active Directory in IT security and how AI/ML integration enhances its functionality.
The section also highlights the collaboration between AD and Open XDR, illustrating how their combined operation offers a nuanced approach to threat detection and response. Finally, the focus will be on the pivotal role of log data in modern cybersecurity, exploring how the integration of AI/ML with log forwarding and Open XDR culminates in a robust, predictive, and proactive cybersecurity framework. Through this comprehensive analysis, the text aims to illuminate the sophisticated interplay between various advanced technologies in cybersecurity, underscoring the crucial role of AI and ML in shaping a more secure digital future.
3.1. Integrating Open XDR with AI and Machine Learning Innovations
At the center of the innovation introduced by Open XDR is the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to anticipate and then prevent cyber threats before they are even implemented. The mechanism it uses, although complex, is extremely effective as it manages to orchestrate different types of security tools and correlate the data it collects from multifaceted sources [
5]. The data it collects may come from Intrusion Detection Systems, End point Detection & Response, Security Information and Event Management, Active Directory, Applications and Log Forwarders systems. Each of these elements brings a unique perspective and, when working together, offers a 360-degree view of an organization’s security landscape [
4].
However, innovation does not stop here. Open XDR further increases its capabilities by integrating geolocation data with comprehensive geographic threat intelligence. Geolocation serves as a compass, mapping the origin of threats and providing security officials with important information as specific countries have been bases for launching cyberattacks in the past. These geo-analytics, when combined with real-time threat intelligence, transform Open XDR into a great security tool. The above information enhances the system’s ability to distinguish patterns, correlate threats, and present personalized alerts, creating a sophisticated and flexible defense mechanism [
7,
8].
The elimination of these capabilities results in a system that goes beyond mere threat detection and can act as a deterrent. It not only detects malicious activities but responds by intercepting and cancelling them. This real-time action capability greatly increases organizations’ cyber security posture, putting them one step ahead of potential adversaries and ensuring a strong defensive perimeter [
9].
3.2. Endpoint Detection and Response
Endpoint Detection and Response solutions have consistently become prominent in the cybersecurity arena, reinforcing the issue of comprehensive endpoint predigital vulnerable nodes that often appear as prime targets for attackers in the digital space. These EDR platforms are designed with extreme precision and diligence with the goal of providing continuous, realistic surveillance time, as well as developing effective and immediate response mechanisms to any anomalous activity or threat that may be detected in endpoints. Whether desktop computers, mobile devices, or mobile phones, EDR systems are designed to provide a coherent and adaptable response to threats detected. Here, "coherent and adaptable response" refers to the system’s ability to correlate various types of information to deal most effectively with cyber threats [
10].
According to G. Karantzas and C. Patsakis [
11] the effectiveness of various EDR solutions against advanced threat vectors is not always efficient. Despite significant advancements in cybersecurity, it’s found that no EDR solution can effectively detect and prevent all attack vectors, particularly DLL sideloading. The study also highlights the limitations in EDR’s ability to detect kernel-level attacks. Additionally, the study underscores the importance of a comprehensive security strategy, incorporating human factors, diverse tools, and AI advancements, to enhance organizational defense against sophisticated cyber threats.
Undoubtedly the magnifying spectrum and the extremely complex nature of the data, which are processed by modern final detection and response systems, represent a remarkable challenge. This abundant flow of data, covering both logs and various behavioral metrics, as well as heuristic analysis techniques, requires the application of advanced algorithms and data processing technologies to extract and distinguish critical and comprehensive information from the most trivial noise. Therefore, the continued integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into EDR solutions is presented as a radical and sectorial change, which contributes to enhancing the effectiveness and accuracy of responses to multidimensional cyber threats [
4].
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, characterized by their undeniable and multidimensional capabilities in processing large amounts of data and recognizing complex patterns, introduce a number of important advantages in the field of End-to-End Detection and Response Systems. These algorithms, equipped with self-learning and masterful operation mechanisms, facilitate the optimization and automation of processes related to the detection of cyber threats [
1].
Leveraging a radically personalized set of data and historical incidents, AI/ML-integrated systems go beyond simply identifying already known and established threat patterns. Instead, they have the capacity to analyze and predict potential vulnerabilities, thereby strengthening the proactive security mechanisms of EDR platforms. Such integration is therefore a catalyst for achieving a more resilient and self-regulating cybersecurity ecosystem [
12,
13].
3.3. Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems have established their position as essential components in the cybersecurity infrastructure of modern organizations. Acting as watchdogs, IDS constantly monitor traffic within an organization’s network, checking it for anomalies or malicious activities. Their primary goal is to detect, alert and, in many advanced systems, prevent security breaches even before they can cause any harm [
16,
17].
However, despite their commendable function, IDSs are often plagued by a major obstacle: inundating the defending manager with various types of notifications. In networks with a large number of computers, thousands of alerts can be generated daily. This deluge of alerts, more often than not, leads to "alarm fatigue" – a phenomenon where critical alerts may be ignored or dismissed due to an organization’s security officer being unable to manage them. In this scenario, the very tool designed to strengthen defenses could inadvertently make them vulnerable [
18,
19].
The solution to this problem of network security came from the use of innovative technological methods, which brought great improvements in the effectiveness and accuracy of Intrusion Detection Systems. Using special supervised learning techniques, modern algorithms have the ability to analyze complex and large volumes of alerts accurately. This is possible as these algorithms use historical data to understand trends and patterns in network activities. Thus, they can effectively distinguish between activities that are normal and do not pose a threat, and activities that are suspicious or potentially dangerous. The result is a significant reduction in the number of false positives, i.e., when the system incorrectly detects normal activity as threatening [
20,
21].
On the other hand, using unsupervised learning techniques, algorithms no longer depend on historical data marked as "benign" or "malignant." This enables them to explore the "unknown," i.e., network traffic for possible anomalies or unusual patterns of behavior that have not been observed before.
The main benefit here is that these anomalies could be indications of new or emerging threats, so far unknown. In this way, the system not only protects against already known risks, but also allows the detective ability for possible future attacks, which may not yet have appeared in the training data. This ensures that organizations are prepared not only for the threats we already know, but also for new and unaware attacks [
22,
23].
K. M. Al-Gethami et al. [
14] highlights the importance of optimizing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) in the face of increasing cyber threats, particularly focusing on Machine Learning (ML)-based IDS. The empirical experiments conducted in the study reveal that several factors influence the classification accuracy of these systems. These include the methods of dataset utilization, outlier removal, the handling of mislabeled instances, and the application of ensemble learning techniques. These factors have varied impacts, with some negatively affecting classification accuracy, such as noise interference in the Random Forest (RF) algorithm. Identifying and understanding these factors is crucial for enhancing ML-based IDS effectiveness.
3.3.1. IDS and Open XDR
The combined use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning capabilities combined with the powerful potential of Open XDR, creates an unparalleled combination for security in the digital space. Open XDR, considering both supervised and unsupervised learning techniques, enables a more comprehensive, deep, and thorough analysis of cyberthreats. The important thing here is that Open XDR is not limited to just the threat detection process. Beyond this, the system has the ability to design and implement effective, timely and tailored responses to various threats, thereby ensuring a comprehensive security strategy that is simultaneously proactive, flexible, and retrospective. This means that organizations are not only protected from current threats but are also equipped for possible future attacks [
24,
25].
3.4. Synergy between EDR, IDS and Open XDR
In addition, the true value of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the context of Endpoint Detection and Response Systems becomes apparent when elements from additional security sources, such as Intrusion Detection Systems, are input into the analytical process. The collaborative interaction between IDS and EDR data, processed through AI/ML algorithms, results in rich correlations. These multidimensional correlations allow for more accurate identification of sophisticated, multidimensional offensive strategies that could be omitted if the data were examined independently [
15,
16].
In addition, AI/ML integration drastically enhances the responsiveness and flexibility of EDR solutions. In cyberspace where time is critical, AI-powered EDR systems are capable of determining with extraordinary speed the most effective response strategy to a recognized threat. This rapid response distinguishes the margin of risk exposure and thus reduces the likelihood of a material malicious effect. The ability to respond quickly and effectively is crucial in the era of modern cybersecurity, where threats are extremely dynamic, constantly evolving in both complexity and malicious intent [
15,
16,
17].
In addition to the above, the integration of Open XDR technology provides another dimension of effectiveness in the holistic framework of EDR systems. Open XDR, as an extensive detection and response platform, enables the aggregation, analysis, and correlation of data from a variety of insurance tools, beyond traditional IDS and EDR. This enhances the ability of AI/ML algorithms to deliver more in-depth and accurate analysis, potentially identifying more complex and discrete threats [
15,
16].
In this way, the integration of Open XDR extends the importance of collaborative interaction between different types of security data, increasing the breadth and depth of threat identification and thus improving the effectiveness of response to attacks. Therefore, the power of AI/ML and Open XDR technologies, when collaboratively integrated into a single EDR system, makes this system particularly capable of meeting the challenges of modern cybersecurity. This multidimensional and comprehensive approach is an essential step towards ensuring effective and proactive protection against constantly evolving and diversifying cyber threats [
9,
15,
16].
3.5. Security Information and Event Management
Security Information and Event Management systems have long been the focus of security in a variety of organizations, whether large or smaller. These systems are tasked with the important and complex task of collecting, processing, and analyzing extensive datasets coming from various sources, such as firewalls, network monitoring systems, application logs and others [
18].
Specifically, SIEMs adopt an integrated orientation towards forming a coherent and unified mosaic of an organization’s security posture. They make efforts to identify patterns, anomalies, and other signs that may indicate potential breaches or threats to information security. However, the role of SIEMs is multidimensional and technologically demanding, especially when it comes to processing large amounts of data and extracting reliable findings. This technological and analytical complexity requires the application of advanced methods and technologies, beyond traditional tools and techniques. It is here that Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning join the technological scene, offering the possibility for more accurate, dynamic, and fast analyses. This enables more effective monitoring, detection, and response to threats, as well as improving the organization’s overall security strategies [
19].
AI and ML, offering a suite of advanced analytical algorithms, contribute tremendously to enhancing the operational capabilities of SIEM systems with various distinct methodologies [
20]. Primarily, AI and ML algorithms allow for a more specialized and deep analytical investigation of security logs and alerts. This translates into extracting complex patterns and distinctive information elements that could easily escape the supervision of manual analytical processes or more initial algorithmic approaches. Second, the application of these algorithms is not limited solely to identifying known, predefined threats. The high adaptability and capacity of ML algorithms allows the identification of anomalies, i.e., activities that deviate from predefined or expected patterns, as well as the ability to identify potential, nascent threats that have not yet been catalogued in security databases [
18,
21].
In addition, through the use of AI and ML, Security Information and Event Management systems manage to leverage the strengthening of correlational analytics in a contactless way to date [
22]. In particular, processing data from a multitude of sources allows algorithms to reveal hidden correlations or sequential series of events that may indicate the preparation or execution of a coordinated attack, or even an insider threat [
23]. Such correlational analyses can reveal vulnerabilities or evidence of a security breach that, in the absence of advanced AI/ML algorithms, could easily go undetected within the overloaded volume of data [
24].
One of the most important advantages offered by AI/ML-enhanced SIEM systems is the ability for automated prioritization of alerts [
25]. In the context of a modern cyber insurance environment, where alarms are multiplying at an increasing rate, distinguishing between alerts that require immediate intervention and those that can wait becomes an extremely demanding process. AI/ML-enhanced systems manage to analyze historical data and evolving event patterns in order to rank alerts based on their urgency and severity, thus ensuring that the most critical issues are approached with due immediate priority [
25,
26,
27].
According to G. González-Granadillo et al. [
18] while most SIEM solutions offer user-friendly interfaces, their capabilities in handling large volumes of events are limited, highlighting the necessity for enhanced visualization and analysis tools for better decision-making. Another challenge noted is the limitations in data storage, often dependent on hardware availability and extra costs for additional products. Cloud-of-clouds storage emerges as a promising alternative for long-term data archival.
3.5.1. SIEM and Open XDR
When the advanced functionality of Security Information and Event Management systems, enhanced with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies, is integrated into an Open Extended Detection and Response framework, the results are anything short of transformative. This integration ensures a comprehensive view of security events affecting the entire organization, while at the same time providing increased flexibility and foresight in dealing with reported events [
28,
29].
This partnership enables the creation of a holistic 360-degree view of the security landscape, which not only helps provide a more unified and understandable picture of security risks and threats, but also makes organizations better equipped to both prevent and effectively address and eliminate various types of cyberthreats. Integrating AI/ML enhanced capabilities of SIEM systems into an Open XDR framework is therefore a critical step towards implementing a more robust, agile, and proactive cybersecurity ecosystem [
29,
30].
3.6. Directory Service - Active Directory (AD)
AD is emerging as a critical component in the IT architecture of the vast majority of modern organizations. This service offers graded and centralized authentication and access capabilities for user accounts and computing devices, resulting in increased transparency and efficiency in managing network resources [
31,
34]. Recognizing the prominence that AD occupies within directory services, it is vital to point out that it not only offers a comprehensive and unified panoramic view of the organization’s resources, but also gathers and records rich data on user activity and system interactions. Therefore, considering the critical role that AD plays in controlling access to and permissions to resources, ensuring the integrity and security of this service is a matter of paramount importance to the organization’s information security [
32,
33].
This extensive repository, characterized by complexity and comprehensiveness as it includes diverse aspects such as login activities, group interactions, and changes to user privileges and permissions, is emerging as a valuable repository for cybersecurity experts. However, the challenge of this vast dataset is to extract and distinguish truly actionable and semantically constructive information from an ocean of trivial or indeterminate entries and data trunks. It is at this point that the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are integrated with extremely promising prospects. The application of AI and ML algorithms and models contributes to automated analysis, extraction of key indicators and effective filtering of the repository in order to reveal specialized information that can enhance cybersecurity strategies and tactics [
34,
35,
36,
37].
Algorithms based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, when subjected to thorough training and optimization processes, become extremely effective in detecting anomalies and deviations from focused patterns of behavior. For example, an unforeseen change in a user’s login pattern, such as access to the system in the early hours of the morning or from previously unlogged in geographies, can be immediately detected by such algorithms. Similarly, informal mass modifications to user rights or notable escalations of their privileges – phenomena often used as indicators to detect insider threats or compromised accounts – are capable of detecting and responding to them accurately and promptly, as they have the ability to process data in real time [
38].
In addition, analyzing AD logs using algorithms based on AI and ML is capable of detecting even extremely thin, coordinated cyber-threats. This may be the case for scenarios in which cyberattackers diligently implement gradual changes over extended periods of time, in order to avoid detection by conventional security systems. The sensitivity of algorithms, combined with their ability to continuously learn and adapt, ensures that even these suggestive and multidimensional tactics do not go unnoticed, thus making this technology extremely valuable for advancing cybersecurity [
39,
40].
In summary, it is evident that Active Directory plays a critical role as a key tool for organizations in managing and enforcing security in their IT ecosystem. However, the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies makes it possible to extract an even more complex and penetrating level of analysis. Through continuous and evolutionary analysis of AD data, organizations are able to not only detect threats in real time, but also take proactive actions to neutralize or even prevent potential cyberattacks. In this way, integrating AI/ML into the Active Directory management system ensures a multifacetedly enhanced approach to cybersecurity, increasing the resilience of organizations’ IT infrastructure [
25,
41,
42].
3.7. Active Directory (AD) – Open XDR
The collaboration between AD and Open XDR is a critical achievement in cybersecurity, enhancing the ability to detect and respond to threats. AD, as a basic identity management system in many enterprises, provides information about the identity of users, their roles, and permissions. By leveraging data from AD, Open XDR is enhanced with different sources of information, including connectivity logs and user actions [
43].
Through the use of AI and ML, Open XDR analyzes Active Directory data to detect anomalies. For example, AI/ML algorithms can recognize unexpected changes in connectivity patterns or user activities, identifying potential threats. In addition, continuous training of ML models can identify patterns that were previously not identified as threatening [
44].
The collaborative operation of these two technology platforms represents a notable upgrade in the cyber threat approach, enhancing both risk reconnaissance and the effectiveness of proactive strategies. In this context, the integration of critical insurance data provided by "AD" is appropriately combined with the advanced analytical capability provided by "Open XDR" technology, in order to enable an integrated and multilevel response to cyber threats. In this context, the integration of critical insurance data, provided by one platform, is rationally combined with the advanced analytical and predictive ability provided by the other technology. This effective synergy is crucial to achieve a high level of safety. Cyber threats are managed with flexibility, precision and foresight, enabling organizations to maintain the integrity of their digital assets while achieving the desired continuous improvement of their security mechanisms [
45,
46,
47].
3.8. Applications – Applications and Open XDR
In the age of digital reality that we live in, software and applications, whether aimed at the business sector or the wider consumer audience, obviously record extensive volumes of data on a daily basis. The so-called logs in this regard are valuable stores of information because they provide detailed data on the functionality of applications, user interactions with software, response times of various systematic components, and many other relevant activities. This extensive accuracy in recording makes these records essential tools for continuous oversight and ensuring the integrity and security of an organization [
48,
49].
However, it should be noted that the challenging scale of volume and the increasing complexity of such data create significant difficulties in extracting and analyzing useful information. The delineated framework of traditional analytical tools, as well as the manual processing of data, are proving insufficient to meet this challenge. The extraction of data that can be exploited in practice becomes, therefore, a Herculean task, requiring complex methodologies and modern data processing techniques [
50].
The Open XDR technology platforms seek to create a holistic framework to ensure cybersecurity by systematically incorporating the importance of logs as central data sources for security analysis. The use of advanced technological approaches, such as AI and ML, allows these platforms to dramatically enhance their analytical capabilities [
40].
In particular, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms allows automated review and analysis of log files. Pattern recognition and anomaly detection are becoming more accurate, facilitating early identification and response to potential risks. AI, thanks to the advanced pattern recognition it offers, is capable of "sifting" the data coming from these files, pointing out any anomalies or deviations from the approved operating standards. Thus, the overall cybersecurity ecosystem is enriched with a multi-layered analysis and identification system, characterized by increased accuracy, speed and efficiency. Therefore, Open XDR platforms, through the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning, make it possible to adapt and develop more effective mechanisms to ensure cybersecurity. Machine learning algorithms, and in particular those adapted to specific application recording standards, offer significant potential for the specialized identification of deviations and unusual behaviors. This analysis is highly realistic and multidimensional, as it can detect phenomena such as unexpected fluctuations in the types of requests, abrupt changes in user interfaces or indication of possible exploitation of vulnerabilities in the application [
4,
5,
51,
52].
This specialized approach is emerging as an integral tool to address the complexities of modern cybersecurity, especially considering that malicious actors are using increasingly sophisticated and complex techniques to hack into systems or breach data. Traditional detection and precaution methods sometimes prove insufficient in the face of current complexity, making the use of machine learning algorithms not only desirable, but essential to achieve a realistically secure digital environment [
53].
The automated nature of Open XDR platforms, enhanced by AI and ML, guarantees the ability to analyze data in real time or approximate in real time [
54]. This increased data processing rate allows for rapid identification and recording of potential threats or security breaches detected through application logs. In particular, the rapid processing and analysis of data ensures that detection and response procedures to potential safety incidents are carried out in a prompt and effective manner, enabling preventive or remedial interventions in a minimum period of time. This is particularly critical in the context of cybersecurity, where time is one of the most critical factors in preventing or limiting the impact of a threat or breach [
55].
Essentially, the interaction between applications that generate invaluable log data and open XDR platforms, which use artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze that data, is fundamentally transforming the cybersecurity landscape. Organizations are not only able to monitor and understand the environment of their applications, but they are also more resilient against ever-evolving cyber threats [
56].
3.9. Log Forwarding and Open XDR
Log forwarding technology is gradually becoming an indispensable pillar in the cybersecurity architecture, especially in the context of the complex and distributed network infrastructures that characterize modern business activities. The aggregation of log data from a variety of sources — ranging from servers and physical devices to software applications and various other digital systems — not only contributes to increased flexibility and efficiency of security mechanisms, but also pays attention to critical parameters that could easily be overlooked due to the excessive number of logs generated at regular intervals [
57].
This is achieved through increased organization and aggregation of data, enabling more specialized and interactive analysis, which is crucial to address multidimensional and evolving cyber threats. Therefore, Log Forwarding technology represents a necessary strategy for the protection and utilization of digital resources in modern times. In the context of the modern era of digitalization, integrated management of EC logs appears to be a particularly crucial element in ensuring increased cybersecurity guarantees. Indicatively, the rapidly evolving technological environments of organizations, along with the extensive use of digital networks, bring about an ever-increasing variety and complexity of cyber threats [
32].
The aggregation of log data from different sources in a central system enables a holistic analysis of an organization’s digital activities. Such an integrated approach allows cybersecurity experts to conduct much more advanced security analyses, providing them with a panoramic and multidimensional view of the organization’s digital environment. This kind of overall viewpoint is crucial for uncovering and understanding more complex attack patterns, which may go undetected by one-dimensional techniques for analyzing individual logs. Therefore, centralized log management is an integral part of modern cybersecurity strategies and enhances the ability of organizations to address risky threats in the wider cyber [
58,
59].
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into the centralized log analytics approach is a complex, yet multifaceted, enhancement of existing capabilities. Through the application of machine learning algorithms, which are constantly updated and trained on large data sets, it is possible to detect much more detailed and accurate illegalities or anomalies [
59,
60,
61].
These algorithms manage to decode the internal logic and operational patterns of an organization, thus allowing them to identify with increased accuracy and sensitivity any deviations or suspicious activities that could signal cyberattacks or other threats to the security of network systems [
62].
In addition, the intelligence of AI/ML algorithms extends to their ability to perform complex cross-referencing of data from different sources. This helps to compose a more complete picture, as it allows for the united analysis of seemingly unconnected or independent events, which can reveal specific threats that could remain undetected through traditional methods of analysis. Therefore, the application of AI/ML technologies in log analysis is a decisive added value in modern cybersecurity [
63,
64].
AI fundamentally supports the evolution of advanced predictive models, offering a framework for effectively interpreting and correlating historical data with real-time information [
56]. Through training on datasets that include past security states, AI gains the ability to recognize patterns and potential vulnerabilities, enabling it to accurately predict impending cyberthreats. This proactive analytical capability is a vital element in building advanced security strategies in the digital space. By using these predictive models, organizations are equipped with the ability to perceive and prevent attacks or threats in a timely manner before they become harmful or adverse impacts occur. Therefore, the application of artificial intelligence in proactive cybersecurity becomes irreplaceable for the preparation and implementation of effective preventive mechanisms, thus ensuring the integrity and survival of digital infrastructures [
37,
65,
66,
67].
In conclusion, the system of central logging undoubtedly occupies a vital place in the architecture of modern cybersecurity. However, the full exploitation of its analytical potential takes place only when the contribution of advanced analytical and predictive technologies offered by AI/ML is considered [
68].
On the other hand, Open XDR is an enhanced security platform that offers deeper understanding and faster response to cyberthreats by applying sophisticated analysis algorithms. The synergy between log forwarding and Open XDR creates a set of complementary features that enhance the effectiveness of cybersecurity systems. While logs provide the initial data and information needed to detect suspicious activity, Open XDR adds a layer of analytical exploration and automated response [
4,
5].
The result is a powerful, automated system that can detect, assess and respond to cyber threats with greater accuracy and speed. This combination is a milestone in the development of robust, proactive cybersecurity mechanisms, enabling comprehensive and multidimensional analysis of security data. In this regard, AI and Machine Learning algorithms offer the possibility of multifaceted risk analysis and predictive assessment, allowing potential threats to be effectively addressed before they become active. The harmonization of these technologies recognizes the key to building a flexible and robust cybersecurity ecosystem capable of responding to the ever-changing challenges and threats of the digital world [
67,
69].
3.10. Real-world implementation of XDR
The real-world implementation of Open XDR in cybersecurity involves several key elements that enhance its effectiveness and usability. Open XDR is designed to integrate multiple security engines that correlate and evaluate normalized datasets stored in a lightweight data lake. This integration allows for the processing of telemetry from various sources like Threat Intelligence, User Behavioral Analytics, IDS, File Sandboxing, and Machine Learning-based anomaly detection. The combination of these elements enables Open XDR to accurately score potential incidents by considering all known information about the system, asset, or account [
71].
Challenges in implementing Open XDR can include lack of stakeholder awareness or buy-in, improper inventory and processing of systems and data sources, and insufficient collaboration among SOC, IT, and network management teams. To address these challenges, recommendations include creating an Information Security Policy, communicating the benefits of XDR to stakeholders, inventorying all potential data sources, choosing an XDR provider that can integrate with these data sources, identifying possible response actions, and ensuring the right staffing for implementation. A successful Open XDR platform integrates existing security tools and provides its own native capabilities, creating comprehensive security visibility and protection, and enabling faster response to security incidents [
71].
In terms of real-world effectiveness, Open XDR platforms have shown substantial benefits. They allow organizations to respond to security incidents in a matter of seconds or minutes, as opposed to days or weeks, which was often the case with traditional systems. This rapid response is possible due to the integration of various security data and the utilization of advanced AI and ML algorithms for real-time analysis. Open XDR’s multi-dimensional approach to data correlation and analysis significantly enhances the accuracy and speed of threat detection and response, providing a more resilient and proactive cybersecurity environment [
71].
In summary, the implementation of Open XDR in real-world scenarios has shown its ability to provide a more integrated, efficient, and effective approach to cybersecurity, addressing the complex and dynamic nature of modern cyber threats.
The real-world implementation of Open XDR in cybersecurity showcases its effectiveness in enhancing threat detection and response, as well as streamlining various security processes. Here are some examples and insights into how Open XDR is applied in practice:
Sophos’ Approach to Open XDR: Sophos, a cybersecurity company, has developed its version of Open XDR, emphasizing the importance of prevention alongside detection. Their Open XDR integrates with various cybersecurity solutions, offering comprehensive protection across endpoints and networks. This integration not only increases security but also optimizes the efficiency of security teams by reducing the ’gray zone’ of ambiguous threats and focusing on genuine risks. Sophos’ Open XDR is designed to fit seamlessly into existing workflows, making it a practical choice for diverse IT environments.[
72]
Gartner’s Market Guide for Extended Detection and Response: Gartner’s report highlights that Open XDR improves the productivity of Security Operations staff by streamlining a large stream of alerts into a condensed number of incidents for efficient manual investigation. Open XDR also reduces the need for extensive training and skills for operational tasks by providing a common management and workflow experience across security products [
73].
Stellar Cyber’s Open XDR Implementation: Stellar Cyber, an Open XDR vendor mentioned in Gartner’s report, offers a unique approach to Open XDR implementation. They combine the benefits of the "Build/Acquire Everything" model (providing a consistent user experience with integrated security solutions) and the "Integrate with Everything" model (allowing for flexibility in choosing security tools). Stellar Cyber’s platform includes built-in network detection and response (NDR), SIEM, threat intelligence platform (TIP), and AI-powered enhanced detection and response functions, which are then integrated with other security solutions like EDR, IDS, and user entity behavior analytics (UEBA) [
73].
These examples illustrate how Open XDR is being implemented in various settings, highlighting its versatility and effectiveness in modern cybersecurity landscapes. The integration of Open XDR with a range of security tools and its ability to adapt to different IT environments make it a valuable asset for organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
3.11. Consolidating Insights: A Comprehensive Summary Table for Section Enhancement
This table encapsulates the key aspects of each section, providing a concise overview of the methods, benefits, challenges, and references related to AI and ML in cybersecurity as discussed in the article.
| Section |
AI/ML Techniques and Innovations |
Benefits |
Challenges |
References |
| Open XDR Integration |
Advanced data orchestration and correlation from various sources; Geolocation data integration; Real-time threat intelligence |
Enhanced threat anticipation and prevention; Sophisticated defense mechanism |
Complexity in integrating diverse data sources and technologies |
[5,6,8,9,10] |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) |
Machine learning for anomaly detection and threat prediction; Self-learning algorithms |
Improved surveillance and response; Prediction of potential vulnerabilities |
Difficulty in detecting complex threats like DLL sideloading |
[1,5,10,11,13,14] |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) |
Supervised and unsupervised learning techniques for alert analysis; Historical data analysis for trend identification |
Reduced false positives; Ability to detect unknown threats |
Alarm fatigue due to high volume of alerts |
[15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23] |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
Advanced analytics for deep investigation; Automated prioritization of alerts |
Enhanced monitoring and detection; Improved decision-making capabilities |
Challenges in handling large volumes of events; Data storage limitations |
[18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,30,31] |
| Active Directory (AD) |
AI/ML for anomaly detection in user behavior; Real-time data processing |
Enhanced detection of coordinated cyber-threats; Real-time threat neutralization |
Complexity in extracting actionable information from vast datasets |
[32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
| AD and Open XDR Collaboration |
Combined analysis of AD data and Open XDR for nuanced threat detection |
Integrated approach to threat detection and response; Increased security |
N/A |
[44,45,46,47,48] |
| Applications and Open XDR |
AI/ML for log file analysis; Pattern recognition and anomaly detection |
Accurate identification of risks; Real-time data analysis for rapid response |
Challenges in processing large volumes of complex data |
[5,6,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Log Forwarding and Open XDR |
Centralized log data analysis; Cross-referencing data from different sources |
Comprehensive view of digital activities; Advanced security analysis |
Management of extensive log data; Need for advanced analytical technologies |
[5,6,33,38,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] |
4. Discussion
4.1. The Pivotal Role of Open XDR in Reinventing Cybersecurity Through AI and ML Integration
In the dynamic realm of digital security, the integration of AI/ML has become pivotal, particularly in the context of Open Extended Detection and Response. This transformative approach goes beyond traditional cybersecurity measures, offering a comprehensive, unified, and intelligent solution to tackle increasingly sophisticated digital threats [
3].
Open XDR represents a significant leap in cybersecurity, initially conceptualized to address the limitations of conventional tools like firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems. It has evolved into a synergistic platform that integrates disparate security components under one umbrella, enhanced by the advanced capabilities of AI and ML. This evolution marks a shift from isolated security measures to a more holistic, integrated approach, ensuring a more effective threat detection and response system [
4].
The integration of AI and ML significantly elevates the functionalities of various cybersecurity components. In EDR systems, for instance, AI and ML contribute to more accurate threat detection and predictive analytics. This enhancement allows EDR systems to move beyond mere detection, enabling a proactive approach to security threats. Similarly, in Intrusion Detection Systems, the application of AI and ML algorithms has revolutionized their capabilities. By efficiently analyzing vast data volumes and reducing false positives, AI/ML-integrated IDS ensures that cybersecurity teams can focus on genuine threats, thereby optimizing operational efficiency [
25].
The role of AI and ML in Security Information and Event Management systems is equally transformative. The enhanced SIEM systems can now conduct deeper and more complex analyses, identifying intricate patterns and emerging threats that might have been missed by traditional methods. This capability significantly bolsters an organization’s overall security strategy [
18,
24,
28].
The synergistic approach of Open XDR is where its true strength lies. By integrating and enhancing various cybersecurity tools, Open XDR facilitates a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to threat detection and response. This integration not only extends to identifying and reacting to threats but also encompasses predictive analytics and proactive threat management, underscoring the adaptive nature of modern cybersecurity measures [
5,
46].
Furthermore, the integration of Active Directory and log forwarding with Open XDR, augmented by AI and ML, epitomizes the power of integrated cybersecurity approaches. Analyzing data from AD and log files enables Open XDR to provide a nuanced and detailed understanding of the security landscape, leading to more efficient detection and response strategies [
45,
48,
49].
4.2. The Catalytic Role of Open XDR
Open XDR technology integrates diverse security data from endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, offering cybersecurity practitioners a unified view for threat management. This consolidation enhances the detection and response to cyber threats, enabling a more comprehensive security strategy. Additionally, AI/ML technologies are crucial in predicting emerging threats. By analyzing patterns and trends from massive data sets, AI/ML can proactively identify potential new cyber threats, allowing practitioners to develop preemptive defense strategies. These applications of AI/ML and Open XDR represent a significant shift towards more proactive and integrated cybersecurity approaches.
The integration of geolocation data and threat intelligence into the Open XDR platform manages to introduce an enhanced level of analytical intelligence into the wider range of cybersecurity technology solutions. Geolocation parameters provide important information about the geographical origin of potential threats, facilitating the discovery of systematic patterns or trends that are specific to specific regions [
8].
For example, if a detailed examination of the data reveals that a series of attacks originate in a specific geographic zone, then Open XDR’s detection and response algorithms can be tailored to account for this parameter. This allows for timelier and at the same time accurate interventions, making the security system more flexible and effective in combating specialized threats [
5,
46]. Therefore, responding to cyber-threats is not only about applying algorithms and technologies, but also about critically evaluating and integrating geographic data into a holistic security strategy that seeks to address the multidimensional features of cyberspace. Threat intelligence is a critical dimension in cybersecurity, providing a constantly updated catalogue of dynamic and evolving cyber threats. This wealth of data encompasses a wide range of factors, from the identification of threat actors and their methodological tactics to the analysis of vulnerabilities they may exploit [
4,
70].
The Open XDR platform, taking threat intelligence into account, creates a dynamic database that undergoes constant updates. The utilization of this updated data allows the anticipation and prevention of threats before they manage to breach defense systems, thus upgrading the level of security to a holistic and multidimensional perception of cyberspace [
70]. Therefore, Open XDR, in addition to being a simple detection and response tool, is transformed into an advanced proactive security system that integrates various levels of analysis and information, constituting a broader ecosystem for dealing with cyber threats. The true value of the Open XDR platform is revealed through its multidimensional ability to coordinate and correlate data from a variety of sources, such as Intrusion Detection (IDS), Network Endpoint Incident Response (EDR) and Security Information and Incident Management (SIEM) systems, while considering geographic information and threat intelligence data [
18,
24,
28,
43].
This holistic approach not only maximizes the potential for more accurate threat detection but is also a catalyst for improving and personalizing response strategies. To illustrate an exemplary scenario, if an activity initiated from a geographic area that is generally trusted unexpectedly coincides with a threat mode recorded in the system database, Open XDR can be proactive, either blocking or notifying those responsible for such activities. In this way, the platform proactively prevents the occurrence of potential attacks, enhancing the impact and effectiveness of security measures [
18,
28].
In addition, implementing a security approach that is sensitive to the geographical and threat context achieves a significant reduction in the occurrence of false positive signals. By understanding the complex parameters that characterize the geographic environment and the dynamically changing threat landscape, Open XDR is able to make more specialized and precise distinctions between those that pose real threats and those that are benign activities that would otherwise be easy to mistreat as aggressive actions [
5,
71]. This level of personalization and accuracy ensures that security teams can more efficiently direct their resources toward addressing real-world risks, thereby increasing the overall effectiveness of the organization’s security mechanisms. Ultimately, this specialized way of dealing with threats allows for a more focused and targeted use of available resources, ultimately enhancing the overall security posture of the organizational entity in question.
4.3. Integration Challenges of AI and ML in Cybersecurity Frameworks and the evolving nature of cyber threats
Addressing the complexities of integrating AI and ML into established cybersecurity frameworks, several key challenges emerge, particularly concerning interoperability and data privacy.
Interoperability is a significant hurdle in integrating AI and ML into cybersecurity frameworks. Existing cybersecurity infrastructures often comprise a variety of products and services developed by different vendors. This diversity can lead to interoperability problems, making it difficult for new AI and ML tools to communicate effectively with other platforms and systems. For instance, organizations might use an average of 47 different cybersecurity tools across their networks, sourced from around 10 different vendors. Coordinating the implementation of all these products and ensuring they work harmoniously is a considerable challenge. The complexity of integrating these various products can create a significant resource drain for cybersecurity teams, often requiring them to spend considerable time managing a complex web of products instead of responding to threats [
76].
Regarding data privacy, AI and ML integration in cybersecurity raises concerns about managing vast datasets, including sensitive or personal information. These concerns revolve around reidentification and deanonymization risks, where AI applications might be used to track individuals across different devices and environments. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data while utilizing it for AI/ML applications involves implementing robust data protection measures and complying with evolving data privacy laws and regulations. This challenge is further complicated by the continuous adaptation and learning requirements within AI/ML systems, necessitating dynamic data governance strategies that can keep pace with the rapidly changing cybersecurity landscape [
77].
The integration of AI and ML in cybersecurity is also essential to combat the rapidly evolving nature of cyber threats. These technologies empower security systems to adapt dynamically to changing attack methodologies, effectively mitigating risks and vulnerabilities. AI and ML’s capacity to analyze vast amounts of data with speed and precision enables the identification of anomalous patterns and potential threats in real-time, providing a critical edge in the ongoing battle against sophisticated cyber threats.
AI and ML applications in cybersecurity are diverse, including anomaly detection, predictive analysis, behavioral analytics, and threat intelligence. By leveraging these technologies, security teams are equipped with proactive measures, enabling preemptive responses to potential breaches and minimizing the impact of cyberattacks. The use of AI and ML in cybersecurity not only enhances the capabilities of cybersecurity professionals but also ensures more resilient systems to combat the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
However, while AI and ML offer significant advantages, it’s also important to consider their limitations, potential biases, and ethical concerns. A balanced, human-machine collaboration approach in cybersecurity defense is vital to ensure a responsible and effective deployment of AI-driven solutions. Organizations must continue investing in research, collaboration, and ongoing innovation to fully harness the potential of AI and ML in fortifying digital defenses [
78].
4.4. Brief mention of the approaches the paper proposes for the identified challenges and potential areas for future research
In this last section, we briefly touch upon the approaches our paper proposes for addressing the identified challenges and potential areas for future research. Our paper employs a thorough literature review methodology to understand how different cybersecurity components interact with AI and ML technologies. This approach helps us gain a comprehensive understanding of current technologies and their synergies.
We then place significant emphasis on Open XDR technology, discussing how it can integrate data from multiple sources for comprehensive security analysis, highlighting its critical role in enhancing cybersecurity measures.
Our article also delves into the roles of IDS, EDR, and SIEM systems. We explore how the integration of AI and ML can augment these components’ capabilities in threat detection and response.
Active Directory and the process of log forwarding are examined in the context of AI and ML integration, and we analyze how these elements contribute to a robust cybersecurity framework when combined with AI and ML technologies.
Addressing challenges related to ethical issues and data privacy concerns in the domain of AI and ML in cybersecurity is another focus of our paper. We emphasize the importance of aligning AI/ML integration with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
A significant portion of our research centers on the development of AI and ML for advanced data processing, pattern recognition, and predicting threats. We explore both supervised and unsupervised learning techniques in ML for their potential in bolstering cybersecurity measures.
We also discuss the necessity for ongoing professional development in the rapidly advancing field of AI and ML in cybersecurity, underscoring the importance of having a skilled workforce capable of managing these advanced technologies.
In conclusion, our paper affirms the effectiveness of merging AI and ML with cybersecurity tools within the Open XDR framework, emphasizing how this integration enhances threat detection, response efficiency, and overall cybersecurity resilience.
Looking ahead, potential areas for future research in AI and ML in cybersecurity, as suggested by our "Integrating AI/ML in Cybersecurity" article, include enhanced anomaly detection, research into AI-driven automated response systems, advancements in predictive threat intelligence, exploration of ethical considerations in AI and ML cybersecurity, and investigating how AI and ML can be integrated with emerging technologies like quantum computing and IoT for improved cybersecurity measures.
5. Conclusions
In the comprehensive analysis presented in "Integrating AI/ML in Cybersecurity: An Analysis of Open XDR Technology and its Application in Intrusion Detection and System Log Management," the pivotal role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) within the Open Extended Detection and Response (Open XDR) framework in advancing cybersecurity has been thoroughly explored. The integration of these advanced technologies has significantly revolutionized the efficiency and efficacy of cybersecurity measures.
The research delineates that AI and ML’s incorporation within Open XDR notably amplifies threat detection capabilities and predictive analytics. This integration facilitates a more nuanced, proactive, and sophisticated approach to addressing cybersecurity challenges, marking a significant leap from traditional cybersecurity methods.
In the realm of practical applications, Open XDR’s implementation across various organizational contexts has consistently demonstrated considerable improvements in detecting and responding to cybersecurity threats. Case studies and industry feedback accentuate the effectiveness of Open XDR in real-world scenarios, substantiating its robustness as a solution in the dynamic domain of cybersecurity.
Nevertheless, the integration of AI/ML with Open XDR is not without its challenges. The complexities inherent in these advanced technologies, coupled with concerns surrounding data privacy and the need for continual updates and professional development in this rapidly evolving field, pose considerable challenges. These factors necessitate a balanced and vigilant approach in the adoption and implementation of these technologies.
Looking toward the future, the intersection of AI/ML and cybersecurity presents a realm brimming with potential. Advancements in AI/ML technologies promise to further refine and revolutionize cybersecurity strategies, offering more sophisticated and adaptive solutions to counteract the increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Further research is advocated in the development of advanced AI algorithms, exploration of new data sources for threat detection, and assessment of the long-term efficacy of Open XDR systems. Such research endeavors are crucial for deepening understanding and fostering continuous improvement in cybersecurity technologies.
In conclusion, a collective call to action is extended to the cybersecurity community. It is imperative to engage in collaborative research and embrace the adoption of Open XDR across various sectors. The integration of AI/ML in cybersecurity, particularly through frameworks like Open XDR, represents not merely a technological evolution but a necessary stride toward securing the digital infrastructure of our future. This call for continuous innovation and vigilance in the face of evolving cyber threats underscores the importance of staying at the forefront of cybersecurity advancements.
In summation, the integration of AI/ML technologies into critical cybersecurity tools such as IDS, Open XDR systems, SIEM Systems, AD, applications, and Log Forwarding, highlights the increase in their effectiveness when orchestrated in the context of Open XDR framework. The integration of these technology platforms brings about a multidimensional and enhanced defense structure against an agile and dynamically changing cyber threat environment. Through the specialized correlation of different data streams and the application of adaptive, learning capabilities of AI and ML, these systems become empowered not only to detect, but also to secure and categorize alerts, turning them into practical insurance events. This multi-layered, personalized process provides an increased capability to accurately detect threats and respond to them promptly, accurately ultimately enabling an enhanced security strategy that is capable of dealing with sophisticated cyber threats. The result is a resilient cybersecurity environment that ensures organizations can effectively address risks and protect their digital assets [
1,
38,
72,
73]
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P. and K.D.; methodology, D.P.; software, D.P.; validation, D.P. and K.D.; formal analysis, D.P.; investigation, D.P.; resources, D.P.; data curation, D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.P.; writing—review and editing, D.P. and K.D.; visualization, D.P. and K.D.; supervision, D.P. and K.D.; project administration, D.P. and K.D..; funding acquisition, D.P. and K.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- S. Kumar, U. Gupta, A. K. Singh, and A. K. Singh, “Artificial Intelligence: Revolutionizing cyber security in the Digital Era,” Journal of Computers, Mechanical and Management, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 31–42, 2023. [CrossRef]
- 2. N. Acton, “AI in cybersecurity an introduction and case studies,” Snorkel AI. Accessed: Dec. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://snorkel.ai/ai-in-cybersecurity/.
- P. Wheelwright, Heraclitus. Colchis Books, 1968.
- P. Firstbrook and C. Lawson, “Innovation insight for extended detection and response,” Gartner ID G00718616, 2021.
- D. A. S. GEORGE, A. H. George, T. Baskar, and D. Pandey, “XDR: The Evolution of Endpoint Security Solutions-Superior Extensibility and Analytics to Satisfy the Organizational Needs of the Future,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology (IJARSCT), vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 493–501, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. S. George, S. Sagayarajan, T. Baskar, and A. H. George, “Extending Detection and Response: How MXDR Evolves Cybersecurity,” Partners Universal International Innovation Journal, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 268–285, 2023. [CrossRef]
- 7. I.-C. Olteanu, “Evaluating the response effectiveness of XDR technology in a scaled down environment”.
- N. Taneski, A. Petrovski, and D. Bogatinov, “Geography in geospatial intelligence-C4IRS and cyber security,” Security and crisis management–theory and practice, pp. 65–73, 2019.
- A. Butkovic, F. Orucevic, and A. Tanovic, “Using whois based geolocation and google maps api for support cybercrime investigations,” presented at the WSEAS International Conference on Circuits, Systems, Communications, Computers and Applications (CSCCA’13), 2013, pp. 194–201.
- P. R. Brandao and J. Nunes, “Extended Detection and Response”.
- 11. H. Kaur and R. Tiwari, “Endpoint detection and response using machine learning,” presented at the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing, 2021, p. 012013.
- G. Karantzas and C. Patsakis, “An Empirical Assessment of Endpoint Detection and Response Systems against Advanced Persistent Threats Attack Vectors,” Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy, vol. 1, no. 3, Art. no. 3, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Raff et al., “An investigation of byte n-gram features for malware classification,” Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, vol. 14, pp. 1–20, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Šrndić and P. Laskov, “Practical evasion of a learning-based classifier: A case study,” presented at the 2014 IEEE symposium on security and privacy, IEEE, 2014, pp. 197–211.
- K. M. Al-Gethami, M. T. Al-Akhras, and M. Alawairdhi, “Empirical evaluation of noise influence on supervised machine learning algorithms using intrusion detection datasets,” Security and Communication Networks, vol. 2021, pp. 1–28, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Panagiotakopoulos, “Assessing open and closed EDRs,” 2023. [CrossRef]
- Γ. Κωστόπουλος, “Aξιολόγηση Open Source Λύσεων στο χώρο της τεχνολογίας EDR,” 2023.
- F. Skopik, G. Settanni, and R. Fiedler, “A problem shared is a problem halved: A survey on the dimensions of collective cyber defense through security information sharing,” Computers & Security, vol. 60, pp. 154–176, 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. González-Granadillo, S. González-Zarzosa, and R. Diaz, “Security information and event management (SIEM): analysis, trends, and usage in critical infrastructures,” Sensors, vol. 21, no. 14, p. 4759, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Bhatt, P. K. Manadhata, and L. Zomlot, “The operational role of security information and event management systems,” IEEE security & Privacy, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 35–41, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. Žgela and I. Penga, “Security Information and Event Management–Capabilities, Challenges and Event Analysis in the Complex IT System,” in Central European Conference on Information and Intelligent Systems, Faculty of Organization and Informatics Varazdin, 2019, pp. 259–266. Accessed: Nov. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://search.proquest.com/openview/4d4bac43b7c2bce82f3d54cc1b380f25/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1986354.
- J. Pavlik, A. Komarek, and V. Sobeslav, “Security information and event management in the cloud computing infrastructure,” in 2014 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI), IEEE, 2014, pp. 209–214. Accessed: Nov. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7028677/.
- J. Frigård, “Security Information and Event Management Systems Monitoring Automation Systems,” Master’s Thesis, 2019. Accessed: Nov. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://trepo.tuni.fi/handle/10024/117593.
- G. Suarez-Tangil, E. Palomar, A. Ribagorda, and Y. Zhang, “Towards an intelligent security event information management system,” Advances in Security Information Management: Perceptions and Outcomes, 2014, Accessed: Nov. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://nms.kcl.ac.uk/guillermo.suarez-tangil/papers/2013nova-AIS-SIEM.pdf.
- P. Radoglou-Grammatikis et al., “Spear siem: A security information and event management system for the smart grid,” Computer Networks, vol. 193, p. 108008, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Badhwar, “The Case for AI Artificial intelligence (AI)/ML Machine learning (ML) in Cybersecurity,” in The CISO’s Next Frontier: AI, Post-Quantum Cryptography and Advanced Security Paradigms, Springer, 2021, pp. 45–73.
- E. Blasch et al., “Machine learning/artificial intelligence for sensor data fusion–opportunities and challenges,” IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 80–93, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Kinyua and L. Awuah, “AI/ML in Security Orchestration, Automation and Response: Future Research Directions.,” Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, vol. 28, no. 2, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Sheeraz et al., “Effective Security Monitoring Using Efficient SIEM Architecture,” Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci, vol. 13, pp. 1–18, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Younus and M. Alanezi, “A Survey on Network Security Monitoring: Tools and Functionalities,” Mustansiriyah Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 55–86, 2023.
- S. Dhamodaran, C. Dandothikar, C. S. P. Reddy, and J. T. Janapati, “An Extensive Review of Literature on IDS and IPS”.
- 32. J. Chilberto et al., “Identity Security with Azure Active Directory,” Cloud Debugging and Profiling in Microsoft Azure: Application Performance Management in the Cloud, pp. 215–234, 2020.
- D. Zhao et al., “Botnet detection based on traffic behavior analysis and flow intervals,” computers & security, vol. 39, pp. 2–16, 2013. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Iyer, A. M. Kabbur, and H. G. Wali, “Implementation of Active Directory for efficient management of networks,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 172, pp. 112–114, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Kotlaba, S. Buchovecká, and R. Lórencz, “Active Directory Kerberoasting Attack: Detection using Machine Learning Techniques.,” presented at the ICISSP, 2021, pp. 376–383.
- V. Uppströmer and H. Råberg, “Detecting lateral movement in microsoft active directory log files: A supervised machine learning approach,” 2019.
- O. Lukas and S. Garcia, “Deep generative models to extend active directory graphs with honeypot users,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06180, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Dhir, H. Hoeltgebaum, N. Adams, M. Briers, A. Burke, and P. Jones, “Prospective artificial intelligence approaches for active cyber defence,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.09981, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M. Hobbs, J. Abawajy, and M. Alazab, “Using feature selection for intrusion detection system,” in 2012 International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Gold Coast, Australia: IEEE, Oct. 2012, pp. 296–301. [CrossRef]
- G. Creech, “Developing a high-accuracy cross platform Host-Based Intrusion Detection System capable of reliably detecting zero-day attacks,” UNSW Sydney, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Dua and X. Du, Data mining and machine learning in cybersecurity. CRC press, 2016.
- E. S. Hosney, I. T. A. Halim, and A. H. Yousef, “An artificial intelligence approach for deploying zero trust architecture (zta),” presented at the 2022 5th International Conference on Computing and Informatics (ICCI), IEEE, 2022, pp. 343–350.
- J. Nichols, K. Spakes, C. Watson, and R. Bridges, “Assembling a cyber range to evaluate artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) security tools,” presented at the ICCWS 2021 16th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security, Academic Conferences Limited, 2021, p. 240.
- S. Muthuraj, M. Sethumadhavan, P. Amritha, and R. Santhya, “Detection and prevention of attacks on active directory using SIEM,” presented at the Information and Communication Technology for Intelligent Systems: Proceedings of ICTIS 2020, Volume 2, Springer, 2021, pp. 533–541.
- R. Younisse, M. Alkasassbeh, M. Almseidin, and H. Abdi, “AN EARLY DETECTION MODEL FOR KERBEROASTING ATTACKS AND DATASET LABELING,” Jordanian Journal of Computers and Information Technology, vol. 9, no. 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. Shin, Security enhancement in defense information system by active directory. University of Delaware, 2019.
- M. Copeland and M. Copeland, “Getting Started with Azure Sentinel and XDR Capabilities,” Cloud Defense Strategies with Azure Sentinel: Hands-on Threat Hunting in Cloud Logs and Services, pp. 77–103, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Firstbrook et al., “Top trends in cybersecurity 2022,” Gartner Inc, 2022.
- 49. J. Zhu et al., “Tools and benchmarks for automated log parsing,” presented at the 2019 IEEE/ACM 41st International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Practice (ICSE-SEIP), IEEE, 2019, pp. 121–130.
- X. Zhang et al., “Robust log-based anomaly detection on unstable log data,” presented at the Proceedings of the 2019 27th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, 2019, pp. 807–817.
- A. Shiravi, H. Shiravi, M. Tavallaee, and A. A. Ghorbani, “Toward developing a systematic approach to generate benchmark datasets for intrusion detection,” computers & security, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 357–374, 2012. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Rudd, A. Rozsa, M. Gunther, and T. E. Boult, “A Survey of Stealth Malware Attacks, Mitigation Measures, and Steps Toward Autonomous Open World Solutions,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 1145–1172, 2017. [CrossRef]
- 53. M. Labonne, “Anomaly-based network intrusion detection using machine learning,” Institut polytechnique de Paris, 2020.
- C. Kolias, G. Kambourakis, A. Stavrou, and S. Gritzalis, “Intrusion detection in 802.11 networks: Empirical evaluation of threats and a public dataset,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 184–208, 2015. [CrossRef]
- V. Chandola, A. Banerjee, and V. Kumar, “Anomaly detection: A survey,” ACM computing surveys (CSUR), vol. 41, no. 3, pp. 1–58, 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Amanullah et al., “Deep learning and big data technologies for IoT security,” Computer Communications, vol. 151, pp. 495–517, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Tavallaee, E. Bagheri, W. Lu, and A. A. Ghorbani, “A detailed analysis of the KDD CUP 99 data set,” presented at the 2009 IEEE symposium on computational intelligence for security and defense applications, Ieee, 2009, pp. 1–6.
- S. J. Stolfo, W. Fan, W. Lee, A. Prodromidis, and P. K. Chan, “Cost-based modeling for fraud and intrusion detection: Results from the JAM project,” presented at the Proceedings DARPA Information Survivability Conference and Exposition. DISCEX’00, IEEE, 2000, pp. 130–144.
- R. Meyers, “Data highway and the digital transformation: arguments for secure, centralised log management,” Network Security, vol. 2020, no. 10, pp. 17–19, 2020. [CrossRef]
- 60. T. Diotalevi et al., “Collection and harmonization of system logs and prototypal Analytics services with the Elastic (ELK) suite at the INFN-CNAF computing centre,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02612, 2021.
- S. Han, H. Mao, and W. J. Dally, “Deep Compression: Compressing Deep Neural Networks with Pruning, Trained Quantization and Huffman Coding.” arXiv, Feb. 15, 2016. Accessed: Oct. 29, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1510.00149.
- S. Udipi, “The event data management problem: getting the most from network detection and response,” Network Security, vol. 2021, no. 1, pp. 12–14, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Cappelletti and S. Maglione, “Developing log analysis for a worldwide distributed system,” 2021.
- T.-F. Yen and M. K. Reiter, “Are your hosts trading or plotting? telling p2p file-sharing and bots apart,” presented at the 2010 IEEE 30th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, IEEE, 2010, pp. 241–252.
- J. Bogatinovski and O. Kao, “Auto-Logging: AI-centred Logging Instrumentation,” presented at the 2023 IEEE/ACM 45th International Conference on Software Engineering: New Ideas and Emerging Results (ICSE-NIER), IEEE, 2023, pp. 95–100.
- J. JONES, A. IONIŢĂ, and I.-C. MIHAI, “AI and IoT Mapping and the Transition to an Interconnected Cyber Defence and Intelligence Capabilities,” presented at the International Conference on Cybersecurity and Cybercrime, 2022, pp. 5–22. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Bonfanti, “Artificial intelligence and the offence-defence balance in cyber security,” Cyber Security: Socio-Technological Uncertainty and Political Fragmentation. London: Routledge, pp. 64–79, 2022.
- R. Das and R. Sandhane, “Artificial intelligence in cyber security,” presented at the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing, 2021, p. 042072. [CrossRef]
- H.-J. Liao, C.-H. R. Lin, Y.-C. Lin, and K.-Y. Tung, “Intrusion detection system: A comprehensive review,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 16–24, 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. C. P. O. Trilho, “Intelligent Systems for Cyber Defence-An Architecture Framework for Cyber Defence using Artificial Intelligence,” 2022.
- “Keys to a Successful XDR Implementation, Automated threat hunting.” Accessed: Dec. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://stellarcyber.ai/keys-to-a-successful-xdr-implementation/.
- R. Humphries, “How four real-world truths about cybersecurity shaped our approach to XDR,” Sophos News. Accessed: Dec. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2021/12/07/how-four-real-world-truths-about-cybersecurity-shaped-our-approach-to-xdr/.
- J. Broth, “Unlocking Game-Changing Cybersecurity With Open XDR,” AiThority. Accessed: Dec. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://aithority.com/technology/unlocking-game-changing-cybersecurity-with-open-xdr/.
- M. A. Islam, “Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in security operations center,” Issues in Information Systems, vol. 24, no. 4, 2023.
- M. T. Khan, A. Akhunzada, and S. Zeadally, “Proactive defense for fog-to-things critical infrastructure,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 44–49, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Lewis and W. Crumpler, “Cybersecurity and the Problem of Interoperability,” Jan. 2020, Accessed: Dec. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.csis.org/analysis/cybersecurity-and-problem-interoperability.
- “Challenges of AI and Data Privacy—And How to Solve Them,” ISACA. Accessed: Dec. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/newsletters/atisaca/2021/volume-32/challenges-of-ai-and-data-privacy-and-how-to-solve-them.
- L. Kasowaki and K. Emir, “AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Leveraging Technology to Combat Threats,” Art. no. 11610, Dec. 2023, Accessed: Dec. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://easychair.org/publications/preprint/PjF7.
- S. Axelsson, “Intrusion detection systems: A survey and taxonomy,” 2000.
- E. M. Hutchins, M. J. Cloppert, and R. M. Amin, “Intelligence-driven computer network defense informed by analysis of adversary campaigns and intrusion kill chains,” Leading Issues in Information Warfare & Security Research, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 80, 2011.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).