Keywords polyethyleneimine; core-shell NiFe2O4@SiO2; magnetic separation; toxic metals; adsorption
1. Introduction
Toxic metals such as lead have been used by human mankind for thousands of years, but only with the industrial revolution and the rapid growth of the human population and industrial activities in the last 70 years, the penetration of toxic metals into the natural environment and water resources has enormously increased and represents a thread to human health [
1]. Many of the metals under concern are heavy metals such as Hg, Cd, and Pb. This is why the term “heavy metals” is frequently used for all toxic metals. However, toxic metals such as Be, Cr, and Ni should not be termed heavy metals as their density does not exceed 5 g/cm
2 and their chemistry is also dissimilar to heavy metals that have a high binding affinity to sulfur-based (bio)ligands in common [
1,
2].
The detection of toxic metals and their removal from water resources has been continuously an important scientific topic and various methods have been developed to remove toxic metals such as chemical precipitation (including coagulation and flocculation), adsorption, electrochemical reduction, removal through membrane processes, reverse osmosis, and ion exchange methods [
3]. Important goals are reducing the costs, simplifying the methods, avoid double contamination, and increase sensitivity [
4,
5,
6,
7]. Amongst these methods, adsorption (chemi- and physisorption) is the most interesting in terms of sensitivity and selectivity and functionalized nanoparticular materials seem to be favorable for their large surface to mass ratio [
4,
6,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
From the chemical viewpoint main challenges in the removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater lies in the efficiency and in the recyclability of the adsorbents [
3]. Polyethyleneimine (PEI) has been reported to be an efficient material showing fast uptake and fast release under different pH conditions [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. For recovery, most adsorbents were separated and then recycled through centrifugation or filtration but in recent years the use of magnetically separable adsorbent materials was introduced and seems very promising to achieve high recycling rates [
5,
17,
20,
21,
22,
23]. Frequently, the magnetic separation is based on hematite and magnetite embedded in core-shell nanoparticles [
17,
20,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29] and in recent years hematite and magnetite structures have been successfully replaced with ferrite structures such as nickel ferrite (NiFe
2O
4) [
30,
31], CoFe
2O
4 [
25,
32], or MnFe
2O
4 [
21,
33].
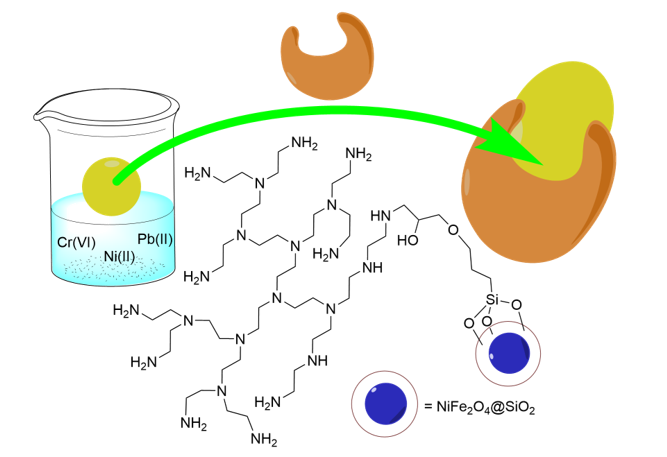
Herein we report a study on the use of polyethylene imine (PEI) grafted on core-shell NiFe2O4@SiO2 nanoparticles as adsorbent for the removal of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions from water. We studied the influence of parameters such as pH, temperature, metal ion concentration, and amount of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI adsorbent and also investigated the kinetics of the adsorption system.
In a recent very similar approach Fe
3O
4@SiO
2–PEI–NTDA nanoparticles (NP) in which Fe
3O
4@SiO
2 nanoparticles were functionalized with PEI and 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic-dianhydride (NTDA) were used to adsorb Pb
2+ ions in the presence of Cd
2+, Ni
2+, Cu
2+, and Zn
2+ [
17]. Further similar materials were Fe
3O
4@MIL-88A(Fe)‒APTMS NP based on the Fe-containing MOF MIL-88A(Fe) and (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilan (APTMS) applied for the removal of CrO
42‒, Cd
2+, and Pb
2+ [
34], CoFe
2O
4@MWCNT‒CTS NP based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and chitosan (CTS) for the adsorption of Pb
2+ [
32], MnFe
2O
4@GO‒TPA based on graphene oxide (GO) and tetraethylenepentamine (TPA) for the adsorption of Pb
2+ [
33], and very recently Fe
3O
4@SiO
2‒CTS–DTPA with diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (DTPA) binding at the NH functions of CTS for the removal of Pb
2+ [
35]. A similar comparative study for CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+ (along with Cd
2+ and Hg
2+) was previously led using amino-functionalized Fe
3O
4@GS nanomaterials based on non-further defined graphene (GS) [
36]. CrO
42– was efficiently removed using sodium lignosulfonate/PEI/sodium alginate beads very recently [
37]. Very recently polyaniline-grafted pine sawdust was used to efficiently adsorb Cu
2+, Co
2+, Cd
2+, Ni
2+, Pb
2+, Zn
2+ and Fe
2+ in a comparative study [
38]. In a very recent approach, 8-chloroacetyl–aminoquinoline (CAAQ) was attached through PEI as ligand to Fe
3O
4@SiO
2 nanoparticles for the capture of Fe
3+, Cu
2+, and Cr
3+ [
23].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) measurements were carried out on a Shimadzu 6100 using Cu-Kα irradiation on solid powder samples of freshly prepared and recovered materials of NiFe2O4@SiO2-PEI. PXRD of NiFe2O4 were recorded on an STOE-STADI MP diffractometer equipped with a Cu-Kα1 radiation (λ = 0.15406 Å) source and operating in transmission mode. Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) was measured using a Shimadzu AA-6880 spectrophotometer. TGA-DTA was recorded on a Shimadzu TGA-DTG-60H instrument. FT-IR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Alpha I spectrophotometer on KBr disks. FE-SEM and EDX analysis were carried out on a JEOL JSM-IT 100 instrument.
2.2. Reagents
All chemicals including NiCl2.6H2O, FeCl3.6H2O, FeCl2.6H2O, Si(OEt)4, trimethoxy(3-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)propyl)silane, and toluene were purchased from Merck and Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification.
2.3. Synthesis of the NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI adsorbent
NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2 was prepared according to our previously reported work [
30]. In brief, 10 g of PEI (Sigma-Aldrich, 5000 average molecular weight) were dissolved in 50 mL hot toluene and then cooled. This was mixed with 472 mg (2 mmol) trimethoxy(3-(oxiran-2-yl-methoxy)propyl)silane (M
W = 248.35 g/mol, from Sigma-Aldrich) and the mixture heated under reflux for 8 h. Then, 2.5 g of the NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2 nanoparticles were added at room temperature and the mixture was heated under reflux for 5 h. The resulting colorless solid was filtered, washed with toluene, and dried at 50 °C. For the analytics, see the results and discussion section.
2.4. Adsorption experiments
For the metal standard solutions 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mg/L of Na2Cr2O7.2H2O (for CrO42‒, MW = 297.99 g/mol), Ni(NO3)2.6H2O (for Ni2+, MW = 229.54 g/mol), and Pb(NO3)2.6H2O (for Pb2+, MW = 370.84 g/mol) were dissolved in 100 mL deionized water. This translates to 0.3356‒2.0135 mmol/L for CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+, 0.2178‒1.3070 mmol/L for Ni2+, and 0.1348‒0.8090 mmol/L for Pb2+. The pH was adjusted to 3 to 8 using diluted NaOH (1M) or HCl (1M) solutions. Adsorption procedure: A 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask was equipped with 50 mL of each metal ion solution (50‒300 mg/L), the adsorbent (0.01‒0.1 g) was added and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 45 min at pH values ranging from 3 to 8.
The adsorption capacity at equilibrium (qe) and the adsorption capacity at time t (qt) are defined as:
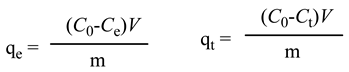
.
with
C0: initial concentration (mg/L),
Ce: equilibrium concentration(mg/L), m: amount of adsorbent (g),
V: volume of the solution (L) [
39].
2.5. Adsorbent recovery
After adsorption of the CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions at pH = 6.5; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ions; 298 K for 45 min, the magnetic adsorbent was separated from the reaction batch with the help of an external magnet and was recycled by washing with HCl solution (5%) followed by NaOH solution (5%) to remove the metals.
3. Results and discussion
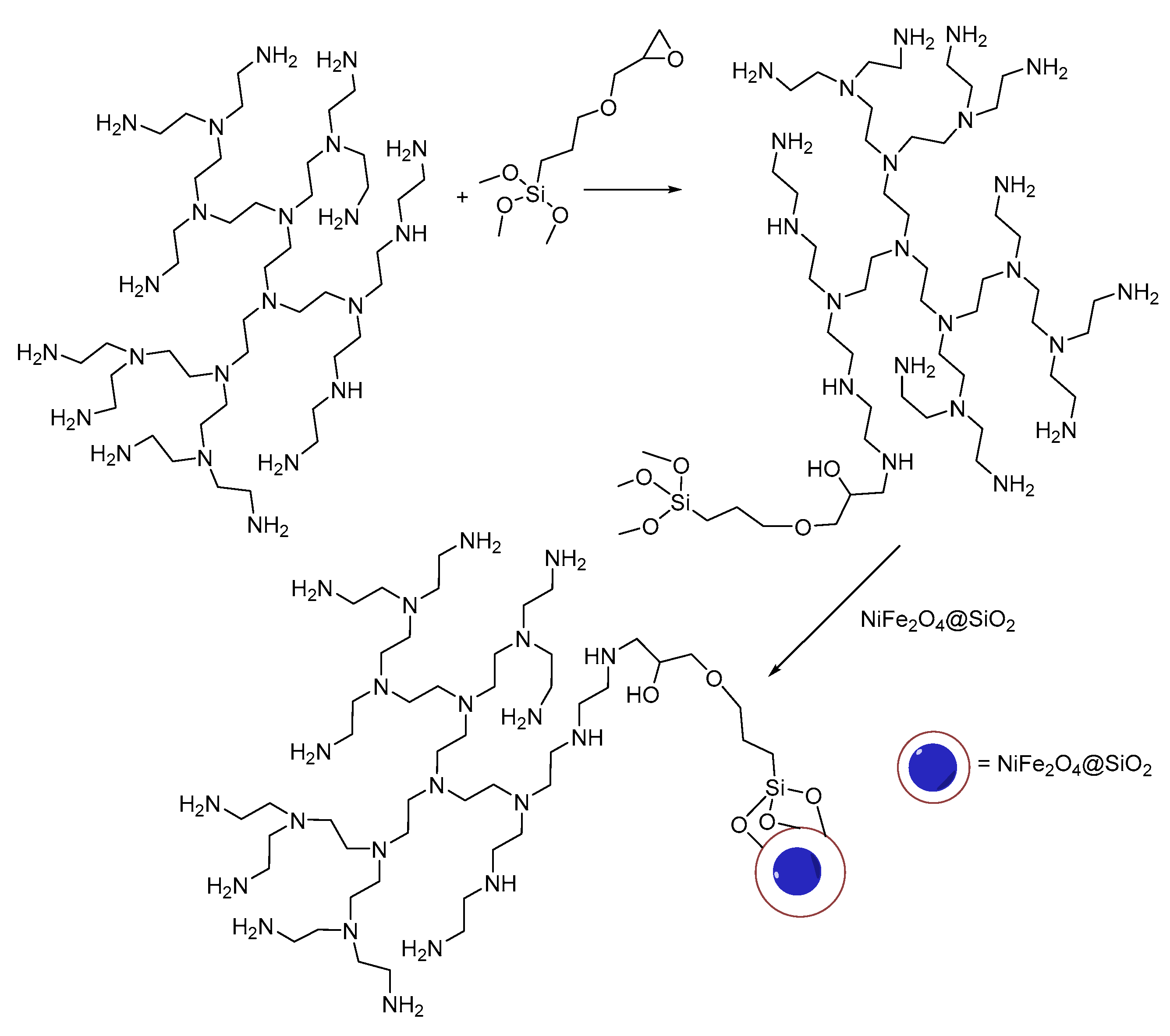
3.1. Synthesis and characterization of the adsorbent
The NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2–PEI adsorbent was prepared as shown in
Scheme 1. First, trimethoxy(3-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)propyl)silane was reacted with the PEI polymer followed by reaction with core-shell NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2 nanoparticles (details in the Materials and Methods Section).
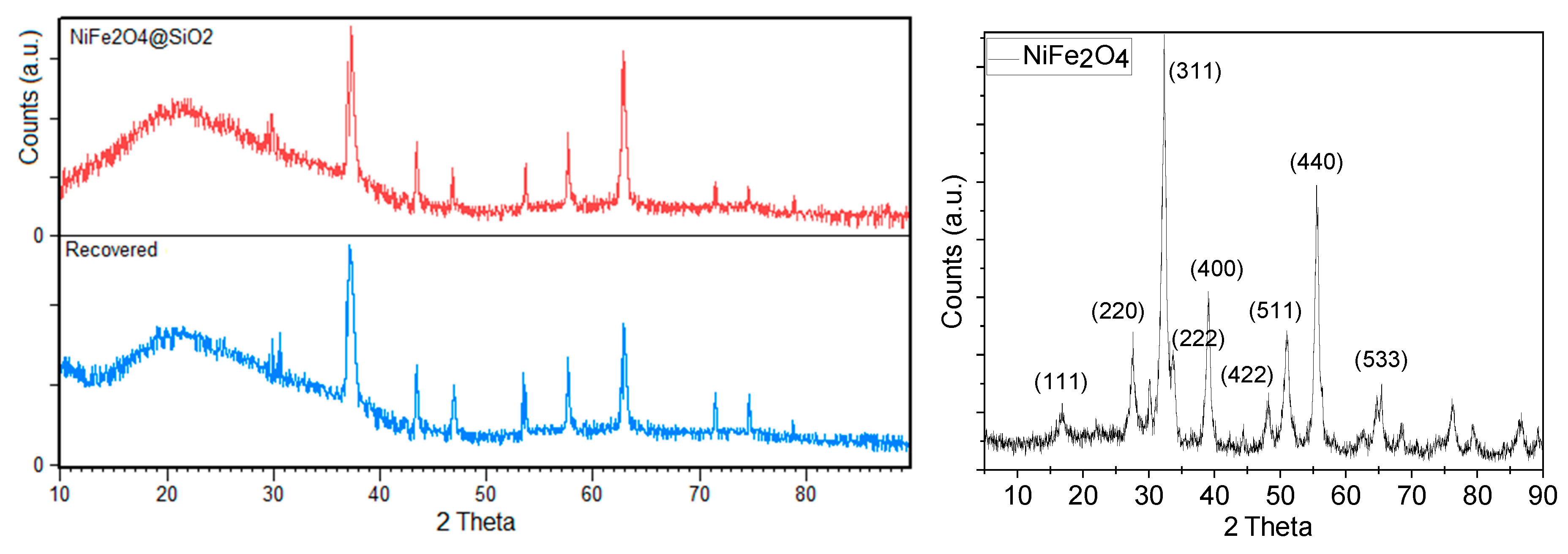
The powder XRD pattern of the NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2–PEI adsorbent showed signals at 2Ɵ = 37.3, 43.4, 46.8, 53.7, 57.7, 62.9, 71.4, and 74.6 ° characteristic for the cubic phase of magnetite and nickel ferrite (NiFe
2O
4, reference code: 00-003-0875) while reflections corresponding to silica were absent (
Figure 1).
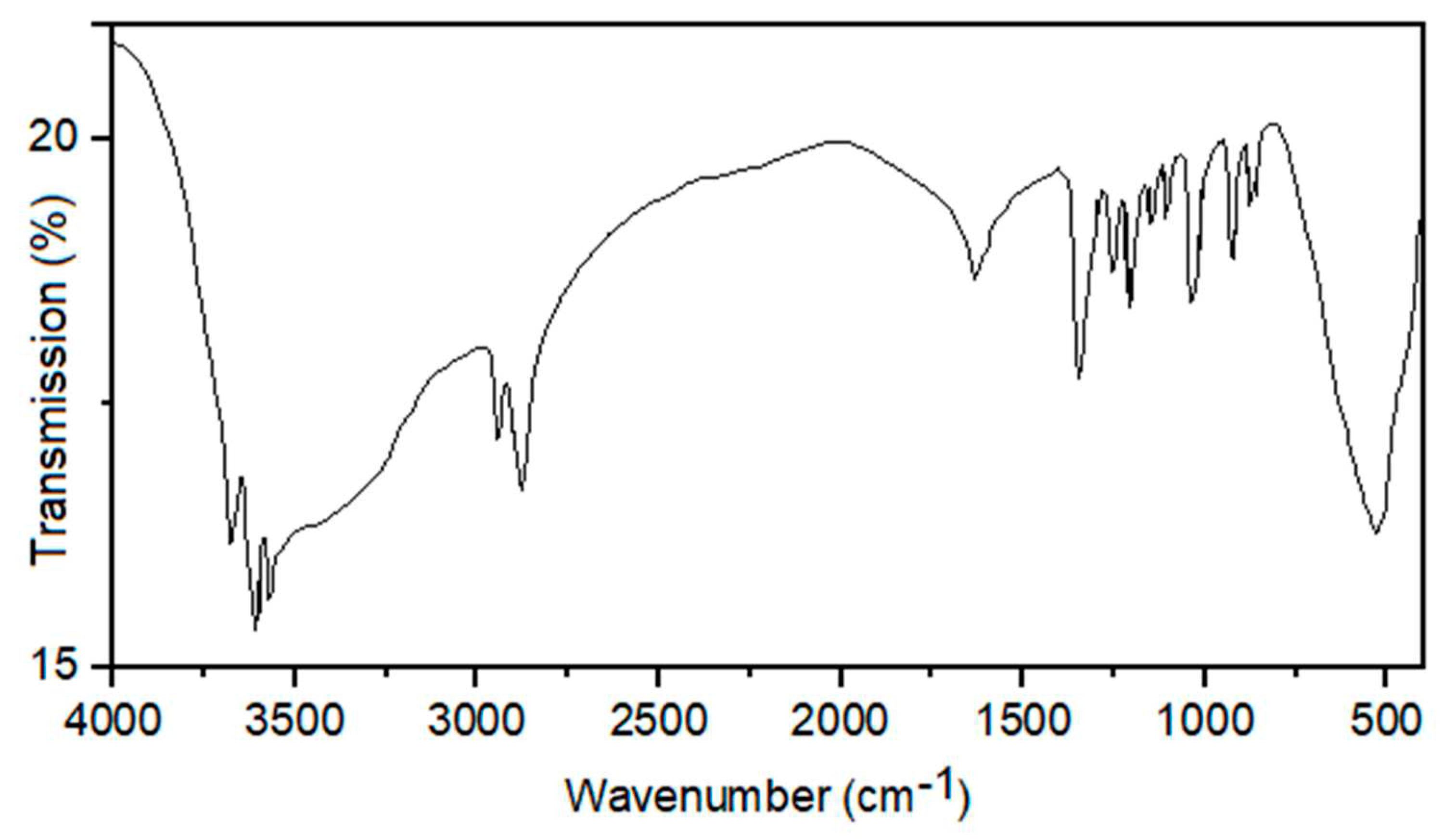
The FT-IR analysis of NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2–PEI (
Figure 2) showed bands at 3678, 3609, and 3573 cm
–1 assignable to N–H stretching vibrations, the broad peak between 3100 and 3700 cm
–1 is due to O–H stretching modes, while C(sp
3)–H stretches appear sharp at 2945 and 2879 cm
–1. The C–H bending modes are found at 1348 cm
–1. The bands located at 1634, 1210, 1153, 1110, 1038, 924, and 879, cm
–1 can be assigned to the Si–O–Si, Si–O, C–C, C–N, and C–O functionalities. Finally, the Fe–O lattice vibrations appear as a broad band centered at 530 cm
–1 [
23,
30,
37].
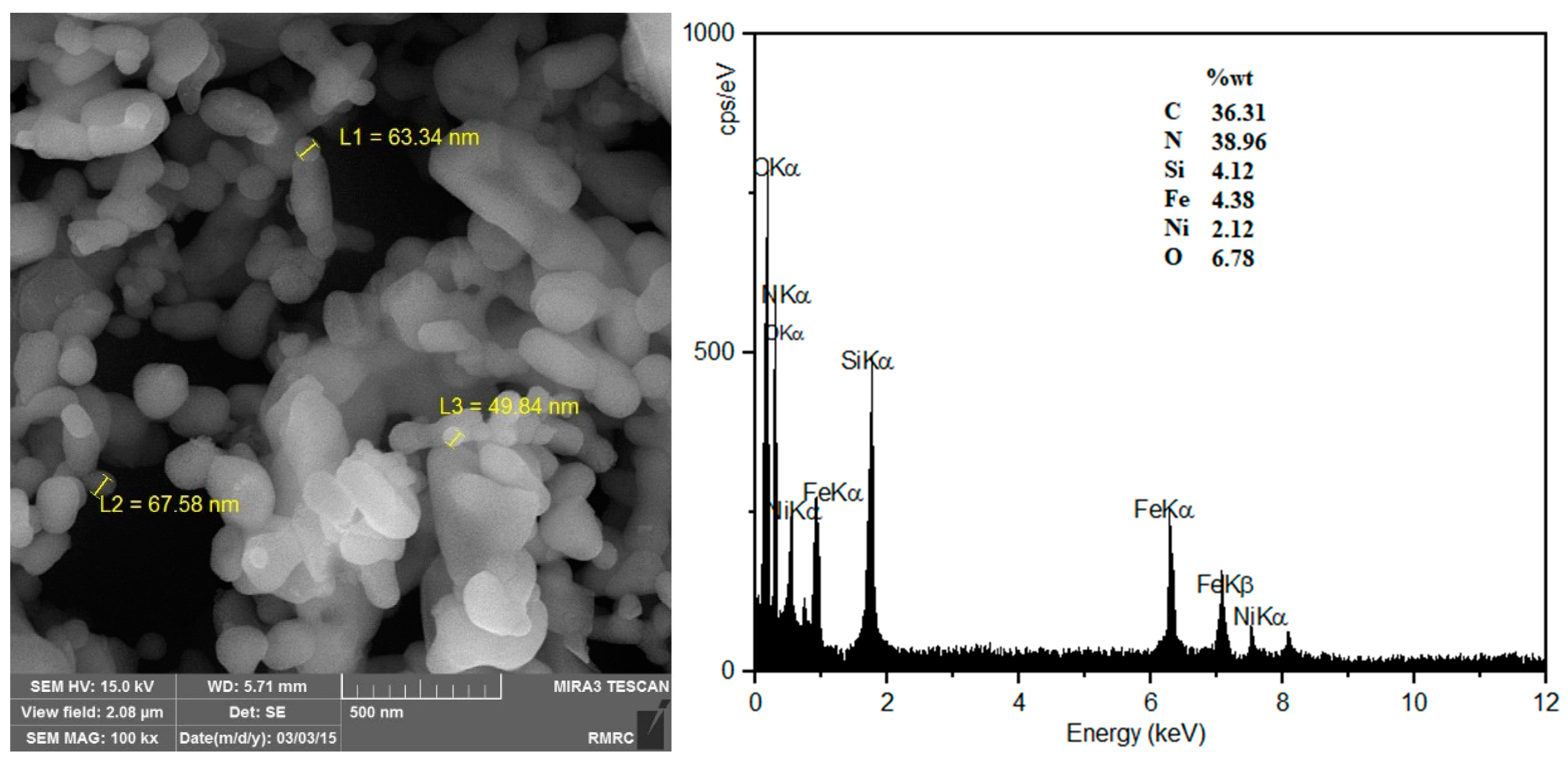
Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images of NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2–PEI show irregular shaped and partially agglomerated particles with diameters ranging from 50 to 100 nm (
Figure 3) similar to what we recently reported for NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2–PSA particles (PSA = propylsulfonic acid) that were prepared in a similar manner [
30]. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis showed C (36.31%), N (38.96%), Ni (2.12%), O (6.78%), Fe (4.38%), and Si (4.12%) (
Figure 3).
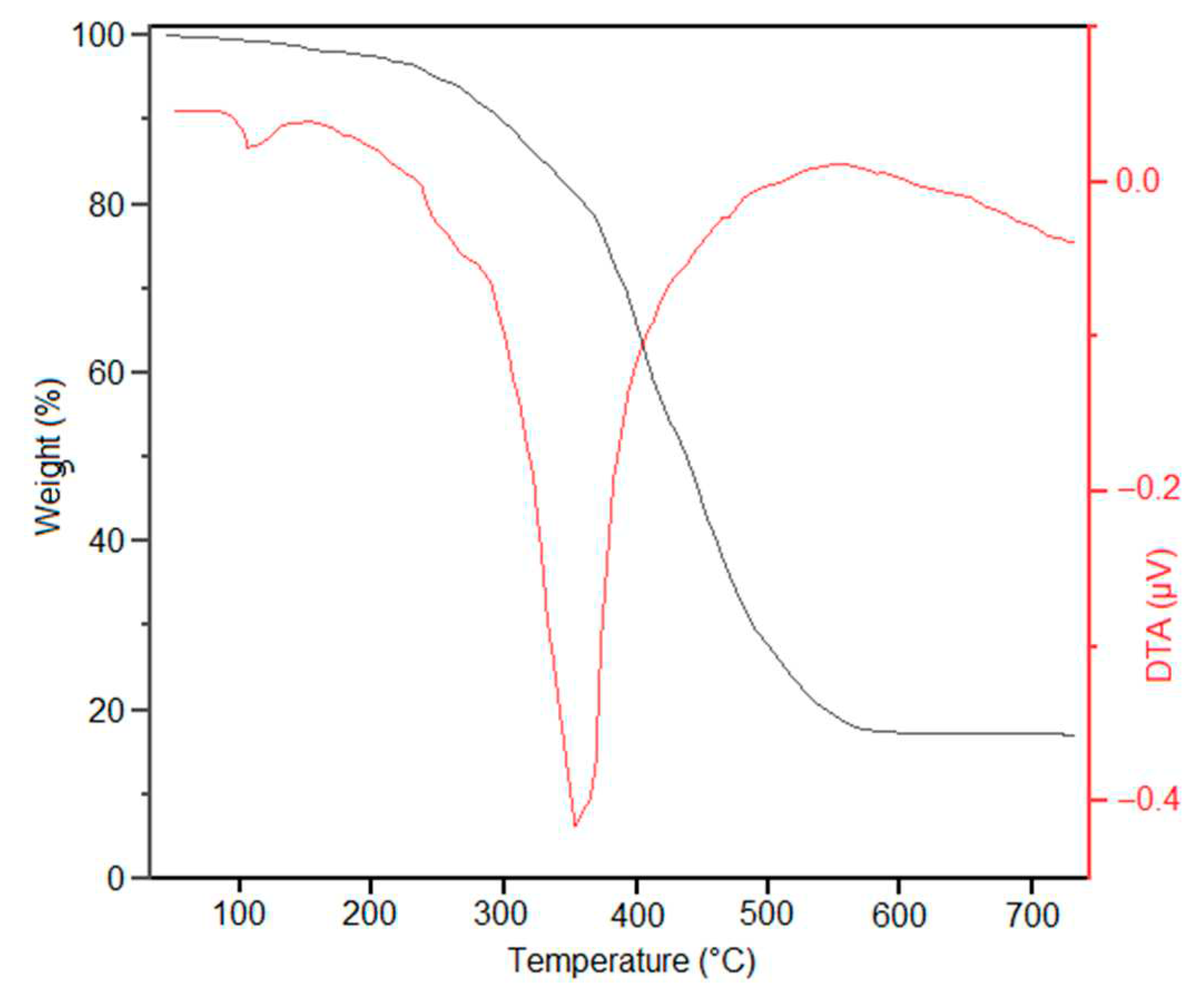
Thermogravimetric (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) showed a small weight loss of about 5% around 100 °C which is due to loss of adsorbed water. The major weight of about 77% of the original mass occurred in the range 200 to 500 °C (
Figure 4). The residual 18% represent the NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2 nanoparticles without the “organic” functionalization in excellent agreement with the EDX analysis showing a total of 75% for C and N.
3.2. Adsorption studies for CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions
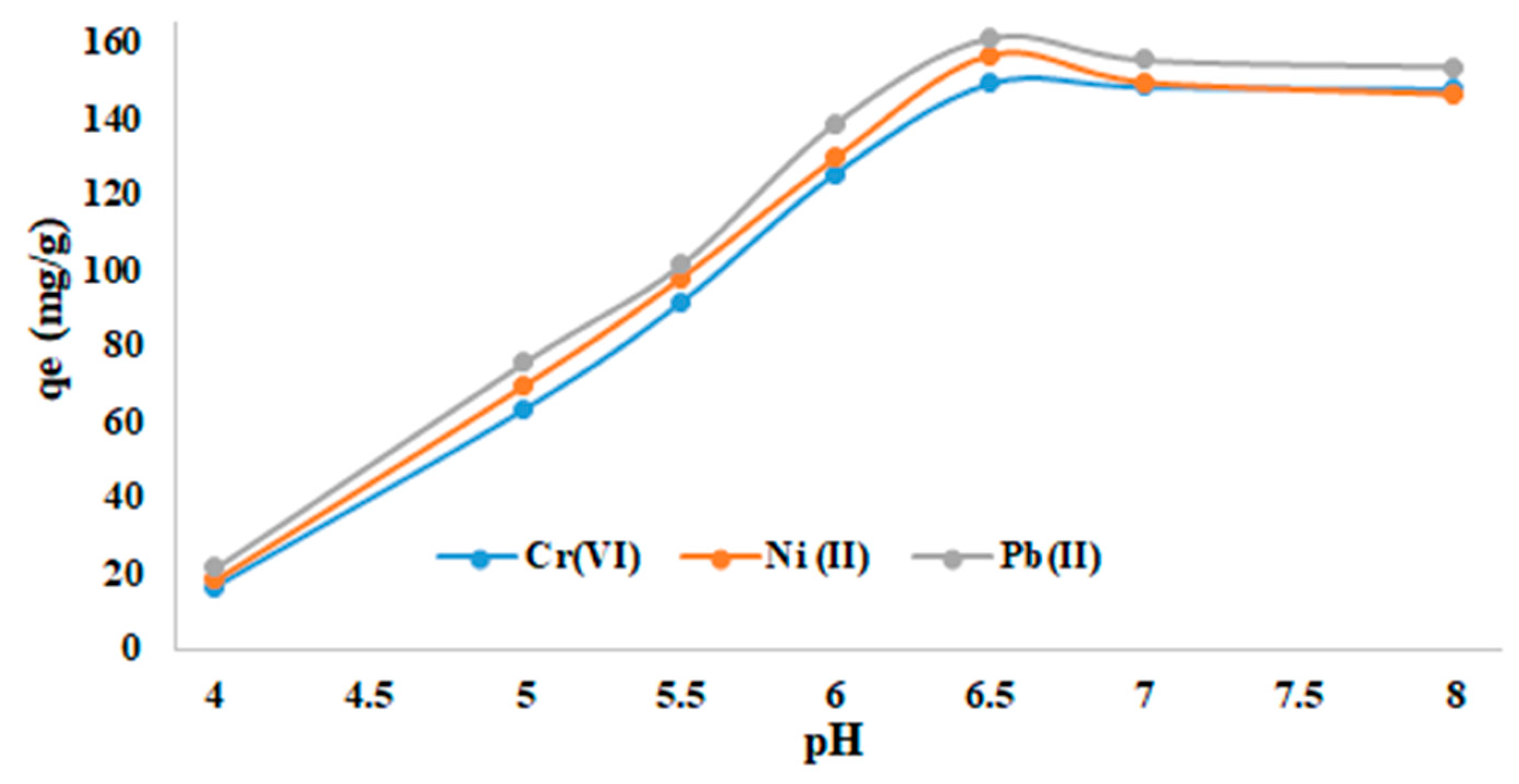
3.2.1. Effect of the pH
In order to evaluate the effect of pH on the adsorption of CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+, the pH war varied from 3 to 8 was while other parameters are fixed at 250 mg/L metal ion initial concentration, 0.075g adsorbent, 50 mL volume, and 298 K. The adsorption capacity showed a maximum at a pH of 6.5 and decreased with increasing pH (
Figure 5). In acidic media at pH ˂ 6 we assume a competition between protons (H
+) and the metal ions Ni
2+ and Pb
2+ in their coordination to the NH
2 groups of the adsorbent. The maximum is reached at pH = 6.5 with adsorption capacities of 149.25, 156.68, and 161.25 mg/g for CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+, respectively.
Very similar pH-dependent behavior as our materials with the maximum adsorption at pH = 6 was previously reported for the Pb
2+-adsorbing materials Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–NTDA [
17], PEI-bacterial cellulose [
19], and sodium alginate (ALG)/PEI composite hydrogels [
16], in line with PEI acting as coordinating agent in these materials. However, also for Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–CAAQ in which CAAQ acts as additional ligand [
23] the same behavior was found. The very recently reported adsorbent Fe
3O
4@SiO
2‒CTS–DTPA (DTPA = diethylenetriaminepentaacetate) [
35] shows a maximum Pb
2+ adsorption already in acidic solutions at pH = 3 and no loss of binding capacity between pH = 3 and pH = 6.
On the other hand, the very similar behavior of our adsorbent towards the cations Ni
2+ and Pb
2+ on one side and the anionic CrO
42‒ is peculiar as for other amine-containing materials such as the recently reported sodium lignosulfonate/PEI/sodium alginate beads [
37], the ethylenediamine-functionalized Fe
3O
4 (EDA@Fe
3O
4) particles [
40], amino-functionalized Fe
3O
4@GS nanomaterials [
36], polydopamine modified chitosan aerogels [
41], or the MOF APTMS@MIL-88A(Fe) (APTMS = (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilan) [
34], better CrO
42– adsorption was found at low pH (2 to 3) while cation adsorption is superior at higher pH. This is reasonable in view of the protonated amine functions at low pH allowing to strongly adsorb the CrO
42– anion while neutral amine function coordinate cations. The only explanation we have so far is that the CrO
42‒ has been largely reduced to Cr
3+ ions which then would absorb in a similar way as Ni
2+ and Pb
2+. This idea is supported by several reports that could show that Cr
3+ can be formed from CrO
42– through electron transfer from various materials [
15,
18,
26,
37,
41,
42,
43,
44]. Such CrO
42– to Cr
3+ reduction upon adsorption can be very efficient if a distinct electron-donating material is present as in the CTAB-intercalated MoS
2 nanosheets (CTAB = cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) that can be used for the simultaneous removal of Cr(IV) and Ni(II) [
45] or in the chitosan-modified multi-walled carbon nanotube composites (MWCNT-CTS) that adsorb CrO
42– exclusively as Cr
3+ [
46].
In future studies we will use X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to study the oxidations states of the adsorbed Cr as was done in the last two mentioned studies.
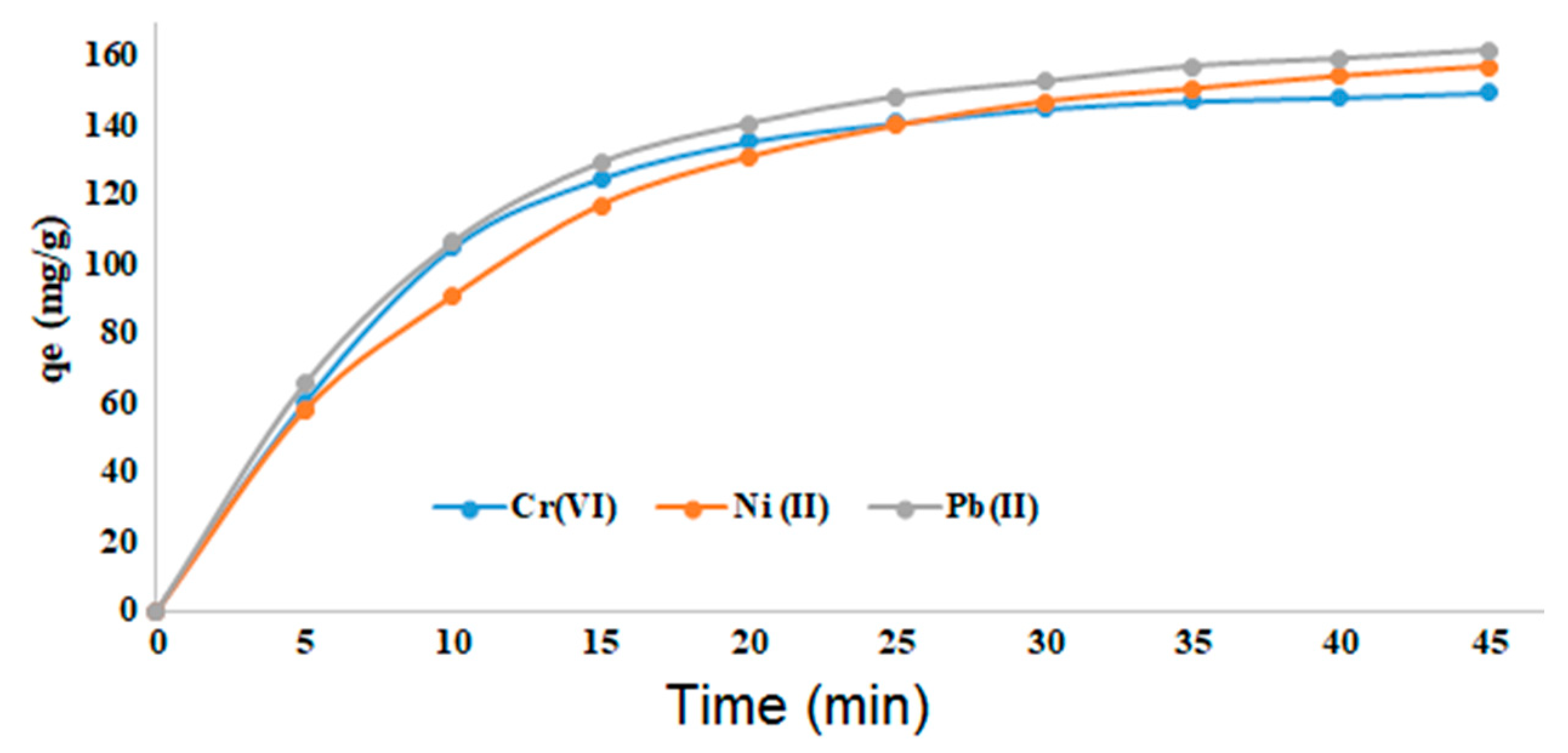
3.2.2. Effect of the contact time
Examining the effect of contact time in the adsorption process of the metals allowed us calculating the reaction rate and the time to reach equilibrium. For this purpose, the reaction parameters were kept constant with an initial concentration of metal salts of 250 mg/L, 0.075 g adsorbent, and pH = 6.5. The adsorption capacity increased rapidly within the first 5 min, at high rate within the first 20 min and then continues slowly. An almost equilibrium was reached within 45 min (
Figure 6).
For the previously reported similar materials Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–NTDA [
17] and Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–CAAQ [
23], the adsorption capacities reached plateau values only after more than 200 min [
17] or 90 min [
23], respectively which indicates that our system is markedly more active and lies in the same time-range as the previously reported PEI-bacterial cellulose [
19]. In contrast to this, very fast adsorption of Cu
2+, Co
2+, Cd
2+, Ni
2+, Pb
2+, Zn
2+ and Fe
3+ within 10 to 20 min was achieved with polyaniline grafted on pine saw dust [
38], underlining the suitability of polyamines and anilines in efficiently coordinating the metals.
3.3. Adsorption kinetic and mechanism
The mechanism of the adsorption of the metal ions were studied
via different kinetic models e.g. pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and Elovich models [
47]. The correlation coefficient (
R2) values for the different kinetic models were calculated by drawing log(q
e‒q
t)
vs. t (pseudo-first order),
t/q
t vs. t (pseudo-second order), and q
t vs ln
t (Elovich) diagrams (
Table 1). The agreement with pseudo-first order kinetics is slightly better than the pseudo-second order fit and much better than with the Elovich equation. This stands in contrast to the behavior of the reported adsorption of Pb
2+ by an activated carbon [
47] and we ascribe this to the more unspecific surface of the carbon in contrast to the well-defined coordination sites of PEI. This is supported by the very similar behavior of the Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–NTDA [
17] that showed also pseudo-first order kinetics for the Pb
2+ adsorption. The better agreement of experimental data with pseudo-second order kinetics reported for Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–CAAQ [
23] is in line with the additional CAAQ ligand showing superior binding than PEI.
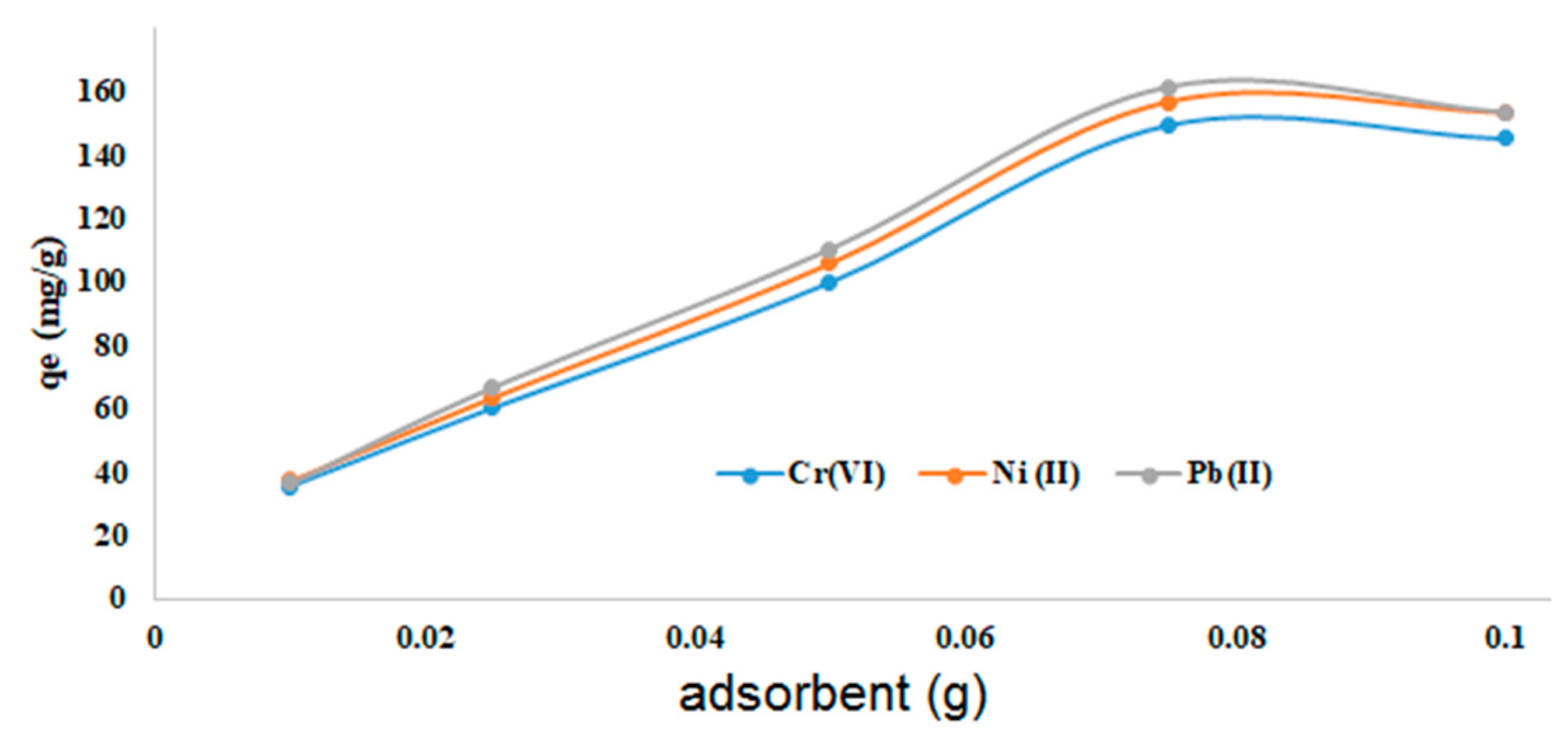
3.3.1. Effect of the amount of adsorbent
The effect of the amount of adsorbent was studied in the range from 0.01 g to 0.1 g while other parameters are held constant (conc. of adsorbates: 250 mg/L, pH = 6.5). With increasing amounts of adsorbent, the adsorption capacity increased up to about 0.08 g (
Figure 7). Further increase did not give higher adsorption. The slight decrease in adsorption capacity at high adsorbent loads might be due to aggregation and accumulation of particles and overall reduction of their surface.
A marked maximum adsorption maximum for Pb
2+ was found in the dosage-behavior for the recently reported adsorbent material Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI-NTDA [
17]. For this material also, aggregation was assumed to be responsible for this phenomenon. When comparing the two curves, our maximum is less pronounced, meaning that our system is more tolerant to larger amounts of adsorbent.
3.3.2. Effect of the metal ion concentration
In order to determine the maximum adsorption capacity of the adsorbent, the effect of different concentrations of metal ions was evaluated.
Figure 8 shows that the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent increases with the increase of the initial concentration of CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+ ions. The highest adsorption capacity was observed at a concentration of 250 mg/L. At higher concentrations, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent remains constant pointing to the saturation of the adsorbent sites.
3.4. Adsorption isotherms
The equilibrium isotherm studies could provide the information about the nature of the interaction between the adsorbed material and the adsorbent and can be used to determine the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent. In order to conduct a view of the way of CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+ ions adsorption, the mechanism was investigated by applying the linear forms of Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models [
48]. The calculated parameters for different isotherms are depicted in
Table 2. By looking at the parameters of isotherms we are able to get an insight into the adsorption mechanism. The Langmuir isotherm model is based on the hypothesis that a single-layer of adsorbent material on the surface structure of the adsorbent is saturated during adsorption, the adsorption sites are identical, the energy of the adsorption is not dependent on the surface coverage, and there is no interaction between the adsorbates (here, the adsorbed metal ions) [
47].
The correlation coefficient (
R2) was calculated for all isotherms and fitted to the experimental data. Values of 0.972 (CrO
42‒), 0.976 (Ni
2+), and 0.997 (Pb
2+)
R2 show that the Langmuir isotherm fitting agrees very well with the experimental results. Accordingly, the mechanism of the adsorption is monolayer adsorption on the surface of the adsorbent [
48,
49]. The same behavior was also found for similar adsorbent materials such as Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–CAAQ [
23], Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–NTDA [
17], and Fe
3O
4@SiO
2‒CTS/DTPA [
35], while for the CrO
42– adsorption on sodium lignosulfonate/PEI/sodium alginate beads [
37] the Langmuir and Freundlich models gave very similar
R2 values. The Freundlich isotherm applies to non-ideal adsorption on heterogeneous surfaces [
50,
51] and the Freundlich-type of behavior is in line with the very heterogeneous surface of the lignosulfonate/PEI/sodium alginate material [
37] in contrast to our adsorbent.
3.5. Adsorption thermodynamics
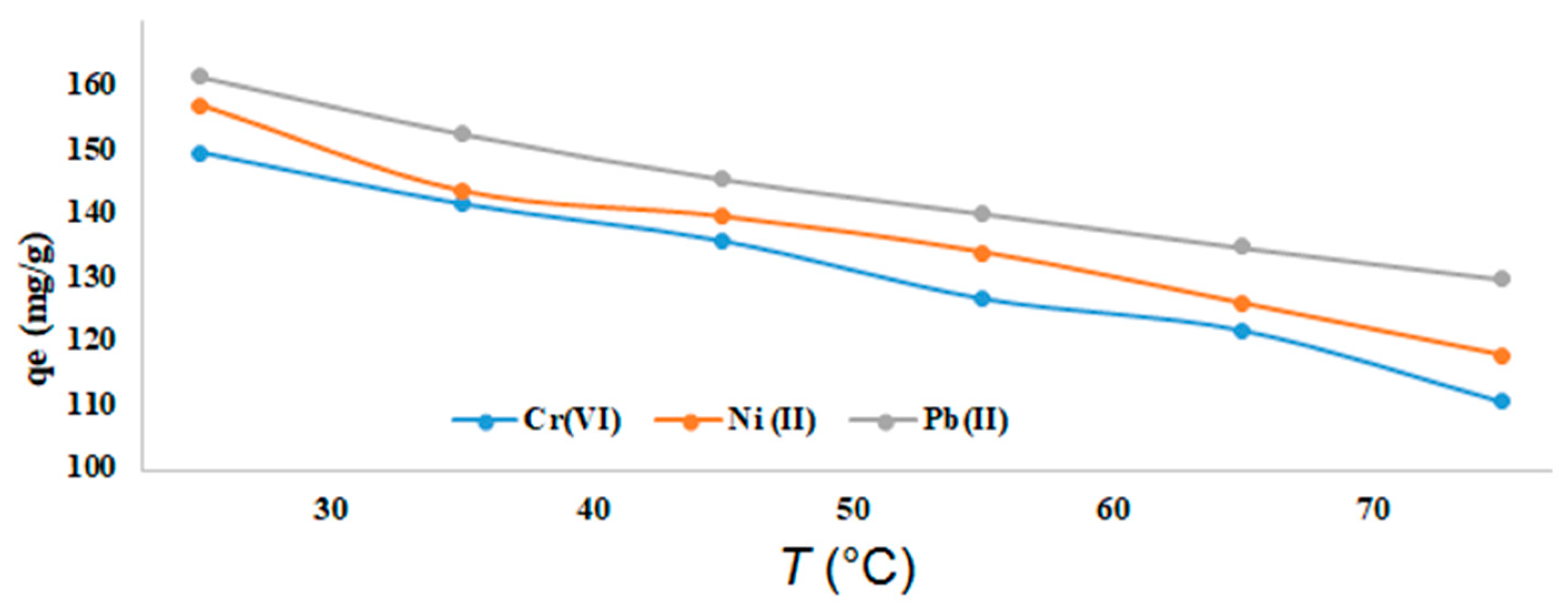
The effect of temperature on the adsorption capacity was investigated to determine the thermodynamic parameters and investigate the spontaneity of the adsorption process. The adsorption capacity decreased with increasing temperature from room temperature to 75°C (
Figure 9). This is in line with an exothermic nature of the adsorption process.
From this data, we calculated also the Gibbs free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS) of the system. The change in ΔG of the CrO
42‒, Ni
2+, and Pb
2+ ions at six different temperatures is obtained through the relationships between ΔG, ΔH, ΔS and ln Kc in the equations shown in
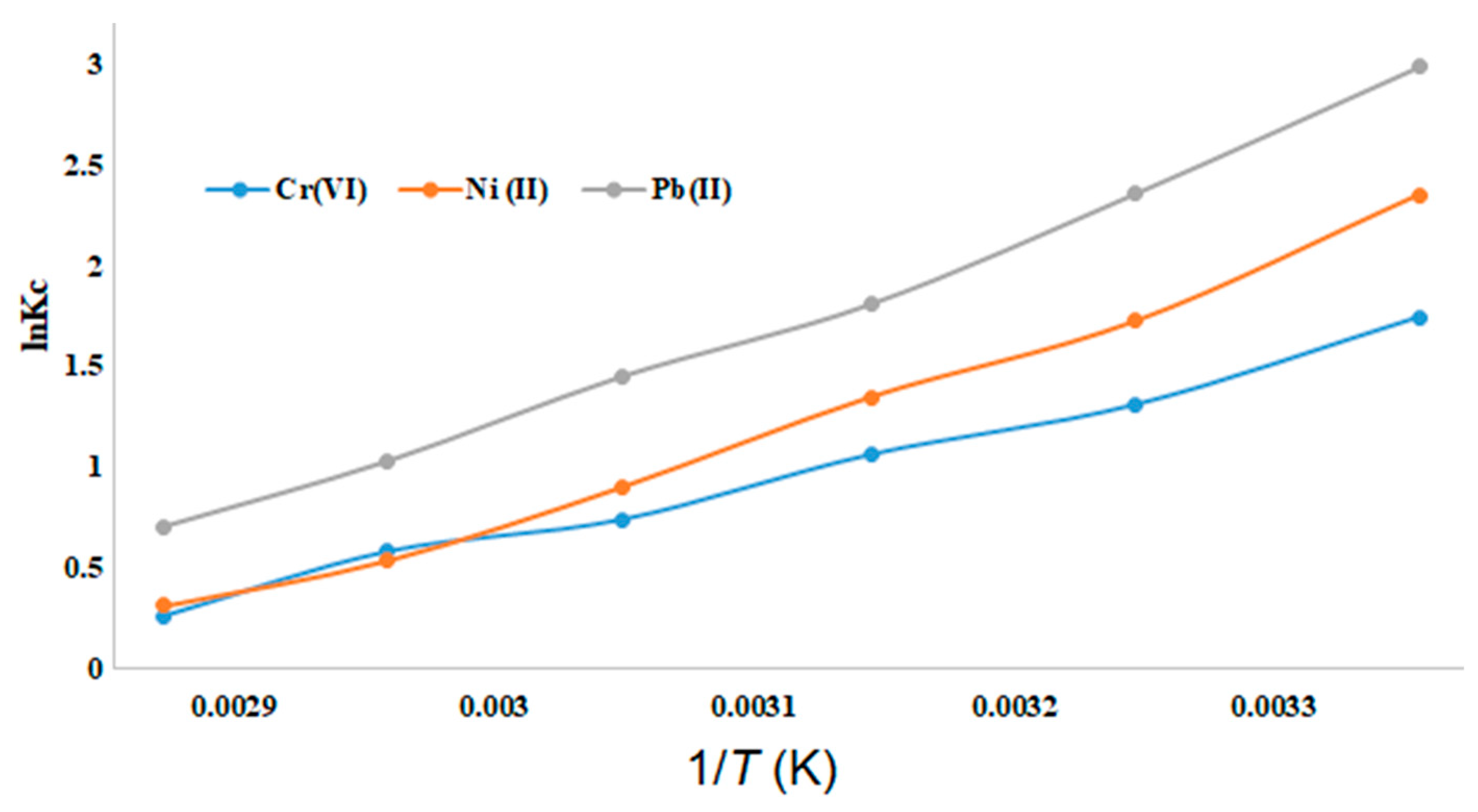
Table 3. ΔH and ΔS are obtained by plotting ln Kc against 1/
T (
Figure 10).
Thermodynamic parameters ΔG, ΔH and ΔS are shown in
Table 3. The negative value of ΔG is in line with spontaneous adsorption processes on the surface of the adsorbent. The negative values of ΔH and ΔS show the exothermic nature of the adsorption reaction, which is very probably binding to the amine functions of the PEI. The overall exothermic binding is in line with the rapid binding (compare
Figure 6) and is an important pre-requisite for the use of this material for efficient metal-recovery from solution.
As in the pH-dependent experiments, the anionic CrO
42‒ behaves remarkably similar to the Ni
2+ and Pb
2+ cations with negative ΔH
0, ΔS
0, and ΔG
0. This stands in contrast to the related sodium lignosulfonate/PEI/sodium alginate beads for which the CrO
42‒ adsorption showed positive ΔH
0 (7.5 kJ/mol) and ΔS
0 (70 J/K
.mol) values, but a negative ΔG
0 of –13.36 kJmol
–1 at 298 K [
37]. This difference supports our assumption that the CrO
42‒ ions in our test solutions are adsorbed as Cr
3+ ions on the adsorbent.
3.6. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) / energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis
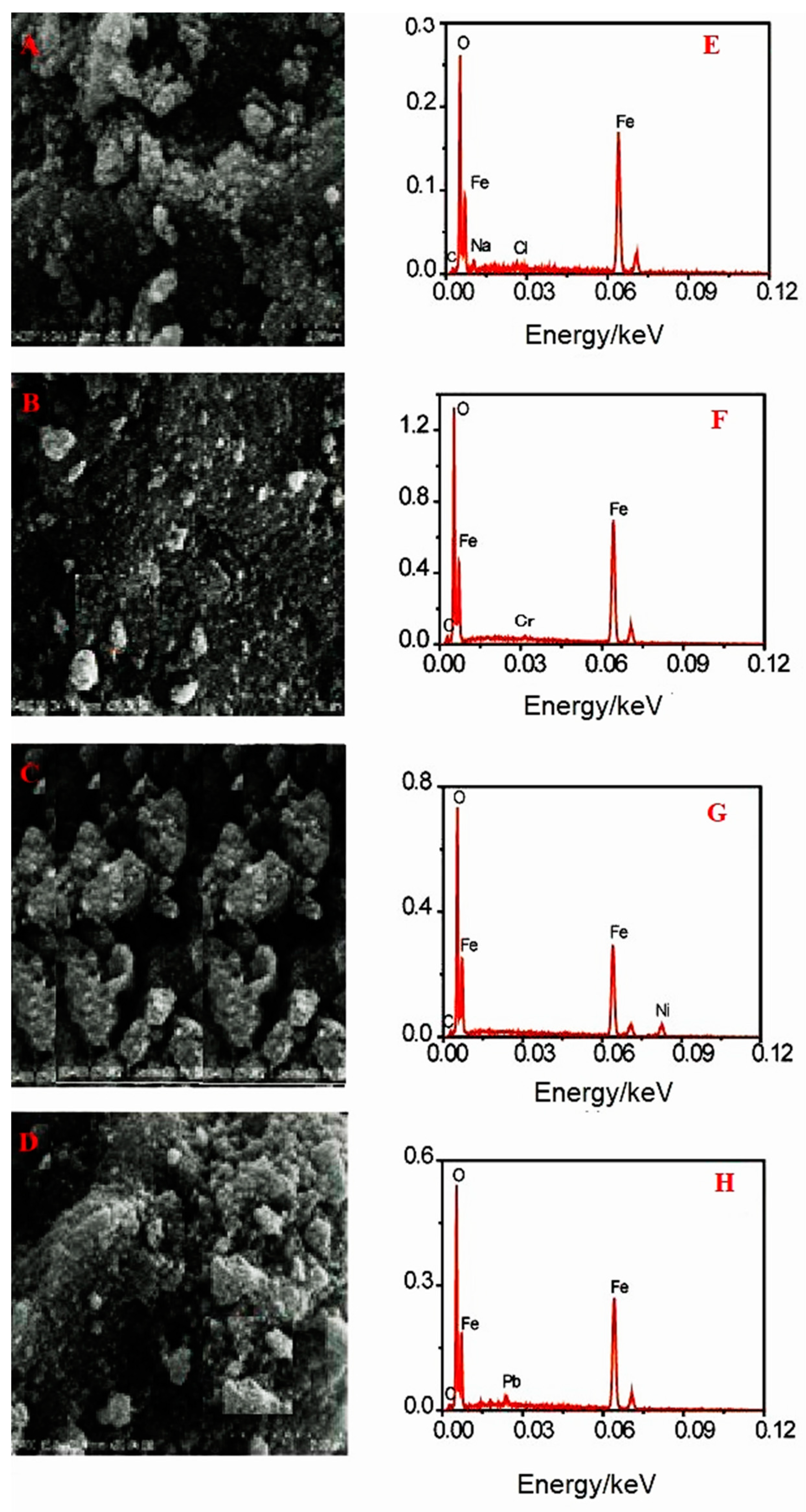
Figure 11A shows the SEM image of the as-prepared NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2-PEI adsorbent having a cauliflower-like morphology. The morphology does not change upon loading with Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Ni(II) (
Figure 11B to 11D). EDX spectra show the characteristic peaks of Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Ni(II) ions (
Figure 11F to 11G). For comparison we recorded the EDX of a re-cycled NiFe
2O
4@SiO
2#-PEI sample and we found traces of Na
+ and Cl
– (
Figure 11E) stemming from the washing procedure (first HCl, then NaOH, see Materials and Methods).
3.7. Adsorbent recovery
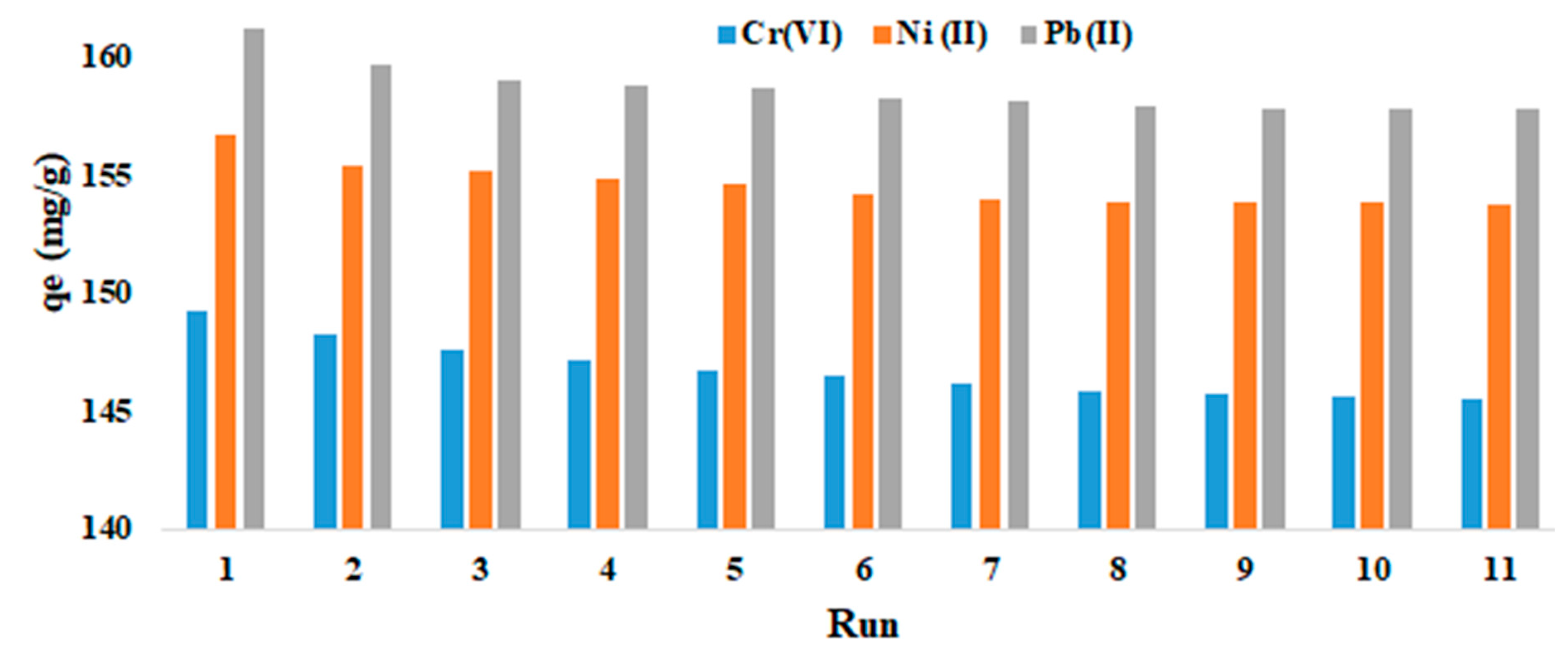
The recyclability was tested in 11 consecutive runs and the adsorbent showed good recovery (
Figure 12) for all three ions.
For the recently reported Fe
3O
4@SiO
2@PEI–CAAQ (CAAQ = 8-chloroacetyl–aminoquinoline) [
23], efficient recycling was only achieved when using Na
2EDTA
2+ solutions for the stripping of the metal cations, while desorption using HCl or HNO
3 steadily decreased the adsorption capacity. This underlines that the additional CAAQ ligand helps to stronger bind metal cations, but at the same time is detrimental to a rapid and efficient desorption.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a new adsorbent material NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI which is polyethylene imine (PEI) grafted on core-shell NiFe2O4@SiO2 nanoparticles was synthesized through a simple and easy procedure and characterized using PXRD, FE-SEM, EDX, FT-IR, and TGA-DTA analyses. The potential of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI in the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions were investigated under variation of pH, adsorbent amount, metal ion concentration, and temperature. The maximum adsorption was achieved at pH = 6.5 and 250 mg/L CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions concentration and 0.075 g adsorbent at room temperature. The adsorption mechanism was investigated using pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and Elovich models with the best match of the pseudo-first order model with the experimental results. The best fit to the adsorption isotherms was the Langmuir model and both findings are in line with a smooth homogeneous mono-layer adsorption. The adsorption of both the anionic CrO42‒, and the cations Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions increased with increasing time and decreased with increasing temperature and also the pH-dependency was very similar. Deconvolution of the T-dependent adsorption gave negative values for ΔG, ΔH and ΔS. For the metal cations Pb2+ and Ni2+ this is in line with binding of these cations to the amine-functions of the PEI. The very similar behavior of the anionic CrO42‒ is probably due to reduction of CrO42‒ to Cr3+ which shows comparable binding properties to Pb2+ and Ni2+. In future studies we will elaborate on this using XPS for the determination of the oxidation states of the Cr species bound to the adsorbent.
For the moment we can state that the new adsorbent material NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI is an interesting candidate for removal of toxic metals from wastewater, in view of its simple preparation, simple adsorbing kinetics, exothermic thermodynamics (chemical binding) and good recovery and recyclability. In the future we will further explore its potential by studying the adsorption of further metal cations such as Cu2+, Cr3+, and Gd3+ as well as the co-dependence of the adsorption of toxic metals with other cationic and anionic components in wastewater.
Author Contributions
The experimental work has been carried out by M.Kj., S.M.K., M.Z., and E.T.A. The original draft was written by M.Kj., A.K. and both authors have edited and revised the original draft. All authors agree with the submitted version of the manuscript.
Funding
E.T.A and A.K. acknowledge funding by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD; Eric Tobechukwu Anthony 91732061).
Availability of Data and Materials
Data will be made available on request.
Declarations Ethical Approval
Not applicable
Acknowledgments
Laboratory support by the Islamic Azad University, Buinzahra Branch is highly acknowledged.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
TOC text:
Polyethyleneimine (PEI) was covalently bound to NiFe2O4@SiO2 nanoparticles to form the new magnetically-separable material NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI for the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions.
References
- Kaim, W.; Schwederski, B.; Klein, A. Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life, Wiley Chichester 2nd. ed. 2013, ISBN: 978-1-118-65926-7.
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy Metals”—A Meaningless Term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Al-Qutaifia, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Zubaidi, S.L. Function of Nanomaterials in Removing Heavy Metals for Water and Wastewater Remediation: A Review. Environments 2022, 9, 123. [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Andra, S.; Kommineni, N.; Balu, S.K.; Bulusu, R.; Boseila, A.A.; Akamo, D.O., Ahmad, Z.; Khan, F.S.; Rahman, Md.H.; Berrada, M.; Cavalu, S. Recent Advances in Adsorptive Nanocomposite Membranes for Heavy Metals Ion Removal from Contaminated Water: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2022, 15, 5392. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.-X. Modified-biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy-metal ions adsorption: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107393. [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Tai, D.Z.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A. A comprehensive review on the adsorption of heavy metals by zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) based nanocomposite in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136320. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, L.; Yu, H. Application of co-pyrolysis biochar for the adsorption and immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated environmental substrates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126655. [CrossRef]
- Farouz, M.; El-Dek, S.I.; ElFaham, M.M.; Eldemerdash, U. Ecofriendly sustainable synthetized nano-composite for removal of heavy metals from aquatic environment. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 1585–1600. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhang, B.-G.; Dai, Y.-R. A critical review on the electrospun nanofibrous membranes for the adsorption of heavy metals in water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123608. [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220‒229. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Gu, X.; Gu, C.; Luo, J.; Gao, B. MIL series of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as novel adsorbents for heavy metals in water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128271. [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.K.; Moustafa, A.F. Industrial solid waste for heavy metals adsorption features and challenges; a review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10235–10253. [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.E.; Pervez, M.N.; Jianming, W.; Stylios, G.K.; Hassan, M.M.; Song, H.; Naddeo, V.; Figoli, A. Ag nanoparticles immobilized sulfonated polyethersulfone/polyethersulfone electrospun nanofiber membrane for the removal of heavy metals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5814. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, G.; Liu, C.; Chu, S.; Mo, C.; Liu, X. Progress and challenges in molecularly imprinted polymers for adsorption of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Trends Environ Anal Chem. 2022, 36, e00178. [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, K. PEI grafted amino-functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets for ultrafast and high selectivity removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption combined with reduction: Behaviors and mechanisms. Chem. Engin. J. 2020, 399, 125762. [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Liang, M.; Sayed, S.M.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Novel alginate/polyethyleneimine hydrogel adsorbent for cascaded removal and utilization of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 829–841. [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhao, J.; Lei, L.; Kang, X.; Lu, R.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z. Novel magnetically separable anhydride-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@PEI-NTDA nanoparticles as effective adsorbents: synthesis, stability and recyclable adsorption performance for heavy metal ions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 9533‒9545. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Tu, W.; Dai, G.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, S. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by polyethylenimine- and phosphorus-codoped hierarchical porous carbons. J. Coll. Interfac. Sci. 2018, 523, 110–120. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F. Polyethyleneimine-Bacterial Cellulose Bioadsorbent for Effective Removal of Copper and Lead Ions from Aqueous Solution. Biores. Technol. 2017, 244, 844–849. [CrossRef]
- Tomonaga, H.; Tanigaki, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Matsuyama, T.; Ida, J. Adsorption properties of poly(NIPAM-co-AA) immobilized on silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles prepared with different acrylic acid content for various heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 171, 213‒224. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Han, J. Functionalized biochar-supported magnetic MnFe2O4 nanocomposite for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 365‒376. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293‒299. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z. Network–Polymer–Modified Superparamagnetic Magnetic Silica Nanoparticles for the Adsorption and Regeneration of Heavy Metal Ions. Molecules 2023, 28, 7385. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Adsorption of heavy metal ions in water by surface functionalized magnetic composites: a review. Environmental Science: Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 907‒925. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Alexander, L.K. Enhanced synergetic effect of Cr(VI) ion removal and anionic dye degradation with superparamagnetic cobalt ferrite meso–macroporous nanospheres. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 125–135. [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, V.; Daniel, S.C.G.K.; Ruckmani, K.; Sivakumar, M. Fabrication of chitosan–magnetite nanocomposite strip for chromium removal. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 277–285. [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, D.S.; Shirivastava, V.S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals by magnetic nanoadsorbent: an equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 927–935. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, H.; Fan, H.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J. One-Step Fabrication of Recyclable Konjac Glucomannan-Based Magnetic Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Cr(VI) Adsorption. Molecules 2023, 28, 7100. [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.A.; AlOthman, Z.A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Labis, J.P.; Khan, A.; Al-Marghany, A.; Elafifi, H.E. One-Step Carbon Coating and Polyacrylamide Functionalization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Enhancing Magnetic Adsorptive-Remediation of Heavy Metals. Molecules 2017, 22, 2074. [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, M.; Taherkhani, M.; Kalhor, M. Preparation of some chromeno[4,3-d]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidine derivatives by ultrasonic irradiation using NiFe2O4@SiO2 grafted di(3-propylsulfonic acid) nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 10718‒10724. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Ling, D.; Lou, H.; Gu, H. 3D hierarchical flower-like nickel ferrite/manganese dioxide toward lead(II) removal from aqueous water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 178‒188. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ji, L.; Ma, P.-C.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W.; Li, Y. Development of carbon nanotubes/CoFe2O4 magnetic hybrid material for removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and Pb(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 104–114. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Dai, K.; Sun, S.; Liu, G.; Yao, J. Novel ternary nanohybrids of tetraethylenepentamine and graphene oxide decorated with MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles for the adsorption of Pb(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 337‒345. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Seleim, S.M.; Mohamed, A.K. Amino-decorated magnetic metal-organic framework as a potential novel platform for selective removal of chromium(VI), cadmium(II) and lead(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120979. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.: He, Q.; Peng, S. Enhanced selective adsorption of lead(II) from complex wastewater by DTPA functionalized chitosan-coated magnetic silica nanoparticles based on anion-synergism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126856. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Du, B.; Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Yan, L.; Xu, W. Synthesis of amino functionalized magnetic graphenes composite material and its application to remove Cr(VI), Pb(II), Hg(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) from contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 211‒220. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lv, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Wågberg, T.; Hu, G. Facile synthesis of sodium lignosulfonate/polyethyleneimine/sodium alginate beads with ultra-high adsorption capacity for Cr(VI) removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129270. [CrossRef]
- Yanovska, E.; Savchenko, I.; Petrenko, O.; Davydov, V. Adsorption of some toxic metal ions on pine sawdust in situ immobilized by polyaniline. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 861–868. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.H. The removal of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Methylene Blue (MB) from aqueous solution using Luffa Actangula Carbon: Kinetics, thermodynamic and isotherm and response methodology. Groundwater Sust. Develop. 2018, 6, 141‒149. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Shen, H.-Y.; Pan, S.-D.; Hu, M.-Q. Synthesis, characterization and properties of ethylenediamine-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic polymers for removal of Cr(VI) in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 295–302. [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-M.; An, Q.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Zhai, S.-R.; Yang, D.-J. Efficient removal of Pb(II), Cr(VI) and organic dyes by polydopamine modified chitosan aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 306–314. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Han, S.; Hao, C.; Jiang, C.; Wang, H.; Fan, X. Effective removal of heavy metals from water using porous lignin-based adsorbents. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130504. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, F.; Wang, C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Liu, W. Mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by magnetic greigite/biochar composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134414. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Du, W.; Liang, A.; Ho, S.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) by magnetically modified Enteromorpha prolifera based biochar and the toxicity analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122658. [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Fu, F.; Tang, B. CTAB–intercalated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for enhanced simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122728. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lee, X.; Macazo, F.C.; Grattieri, M.; Cai, R.; Minteer, S.D. Fast and Efficient Removal of Chromium(VI) Anionic Species by a Reusable Chitosan-Modified Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite. Chem. Engin. J. 2018, 339, 259–267. [CrossRef]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A review of the kinetics adsorption models and their application to the adsorption of lead by an activated carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [CrossRef]
- Ghashang, M.; Khosravian, P.; Ghayoor, H. Effective removal of penicillin from aqueous solution using Zinc oxide/natural-Zeolite composite nano-powders prepared via ball milling technique. Rec. Pat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 11, 154‒164. [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. On adsorptions in solution. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–471. [CrossRef]
- Haghighatian, S.; Mazarei, E.; Doroodmand, M.M.; Klein, A., Memarpoor-Yazdi, M. A new whole-cell biocatalyst for sulfur dioxide filtering and degradation. Biores. Technol. 2020, 314, 123755. [CrossRef]
Scheme 1.
Preparation of the polyethylene imine (PEI) grafted on core-shell NiFe2O4@SiO2 nanoparticles (NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI) though trimethoxy(3-(oxiran-2-yl-methoxy)propyl)silane.
Scheme 1.
Preparation of the polyethylene imine (PEI) grafted on core-shell NiFe2O4@SiO2 nanoparticles (NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI) though trimethoxy(3-(oxiran-2-yl-methoxy)propyl)silane.
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI (left) and of pristine NiFe2O4 (right).
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI (left) and of pristine NiFe2O4 (right).
Figure 2.
FT-IR spectrum of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 2.
FT-IR spectrum of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 3.
FE-SEM photograph (left) and EDX analysis (right) of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 3.
FE-SEM photograph (left) and EDX analysis (right) of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 4.
TGA and DTA analysis of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 4.
TGA and DTA analysis of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI.
Figure 5.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of the pH (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L adsorbate, 298 K).
Figure 5.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of the pH (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L adsorbate, 298 K).
Figure 6.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions over time (pH = 6.5; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ions; 298 K).
Figure 6.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions over time (pH = 6.5; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ions; 298 K).
Figure 7.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of adsorbent amount (45 min; pH = 6.5; 250 mg/L adsorbates; 298 K).
Figure 7.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of adsorbent amount (45 min; pH = 6.5; 250 mg/L adsorbates; 298 K).
Figure 8.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of initial metal ion concentration (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; pH = 6.5; 298 K).
Figure 8.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions: effect of initial metal ion concentration (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; pH = 6.5; 298 K).
Figure 9.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions over T (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ion conc. concentration; pH = 6.5).
Figure 9.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions over T (45 min; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ion conc. concentration; pH = 6.5).
Figure 10.
Linear plot of ln Kc vs 1/T for the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions.
Figure 10.
Linear plot of ln Kc vs 1/T for the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions.
Figure 11.
SEM images of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI before (A) and after Cr(VI) (B), Ni(II) (C), and Pb(II) (D) adsorption. EDX spectra of recovered NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI before metal ion adsorption (E) and after Cr(VI) (F), Ni(II) (G), and Pb(II) (H) adsorption. (Metal concentrations 10 mg L–1). Scale bars in A to D: S3400 15.0 kV 5.2 mm x 20.0 k SE (2.00 μm).
Figure 11.
SEM images of NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI before (A) and after Cr(VI) (B), Ni(II) (C), and Pb(II) (D) adsorption. EDX spectra of recovered NiFe2O4@SiO2–PEI before metal ion adsorption (E) and after Cr(VI) (F), Ni(II) (G), and Pb(II) (H) adsorption. (Metal concentrations 10 mg L–1). Scale bars in A to D: S3400 15.0 kV 5.2 mm x 20.0 k SE (2.00 μm).
Figure 12.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions at pH = 6.5; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ions; 298 K for 45 min in 11 consecutive runs.
Figure 12.
Adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions at pH = 6.5; 0.075 g adsorbent; 250 mg/L metal ions; 298 K for 45 min in 11 consecutive runs.
Table 1.
Parameters and correlation coefficient (R2) of kinetic models.
Table 1.
Parameters and correlation coefficient (R2) of kinetic models.
| Linear equations a
|
Parameters |
| Pseudo-first order |
CrO42‒ |
Ni2+ |
Pb2+
|
| k |
R2 |
qe (mg/g) |
k |
R2
|
qe (mg/g)
|
k |
R2
|
qe (mg/g)
|
| 0.118 |
0.999 |
151.07 |
0.097 |
0.992 |
169.78 |
0.102 |
0.996 |
159.66 |
| Pseudo-second order |
0.0014 |
0.981 |
163.93 |
0.0008 |
0.968 |
175.43 |
0.0011 |
0.980 |
178.57 |
| Elovich equation |
α |
R2
|
β |
α |
R2
|
β |
α |
R2
|
β |
| 135.57 |
0.928 |
0.026 |
10.85 |
0.983 |
0.022 |
79.89 |
0.963 |
0.023 |
a Pseudo-first order: log(qe–qt) = logqe(k t /2.303) with k is the rate constant (min‒1), t is the contact time (min),
Pseudo-second order: t/qt = (1/kqe2)+(t/qe), Elovich equation: qt = (ln(αβ)/β)+(lnt/β)with β, α are the Elovich constants. |
Table 2.
Parameters and correlation coefficient (R2) of isotherm models.
Table 2.
Parameters and correlation coefficient (R2) of isotherm models.
| |
CrO42‒ |
Ni2+
|
Pb2+
|
| Model |
Parameters |
|
|
| Langmuir |
b |
R2
|
qmax (mg/g)
|
b |
R2
|
qmax (mg/g)
|
b |
R2
|
qmax (mg/g)
|
| 0.075 |
0.972 |
181.81 |
0.105 |
0.976 |
178.57 |
0.441 |
0.997 |
166.67 |
| Freundlich |
kf
|
R2
|
n |
kf
|
R2
|
n |
kf
|
R2
|
n |
| 0.015 |
0.910 |
0.646 |
0.016 |
0.893 |
0.675 |
0.0014 |
0.814 |
0.553 |
| Temkin |
B |
R2
|
A |
B |
R2
|
A |
B |
R2
|
A |
| 0.0247 |
0.931 |
367.1 |
0.0226 |
0.885 |
298.3 |
0.0272 |
0.838 |
1.584 |
Table 3.
Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions.a.
Table 3.
Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of CrO42‒, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions.a.
| ΔG° (kJ/mol) (T = 298 K) |
ΔS° (J/K.mol) |
ΔH° (kJ/mol) |
| CrO42‒ |
Ni2+ |
Pb2+ |
CrO42‒ |
Ni2+ |
Pb2+ |
CrO42‒
|
Ni2+
|
Pb2+
|
| ‒4.18 |
‒5.58 |
‒7.37 |
‒67.96 |
‒98.92 |
‒106.64 |
‒24.43 |
‒35.06 |
‒38.96 |
|
a Kc (L/mg) is the equilibrium constant, R = 8.314 J/mol·K, T is the absolute temperature (K), Gibbs free energy ∆G°(kJ/mol), Enthalpy ∆H°(kJ/mol), Entropy ∆S° (J/K·mol). ΔG0 = –RTlnKC with KC = qe/Ce and RTlnKC = TΔS0.ΔH0. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
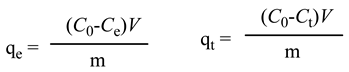 .
.