Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
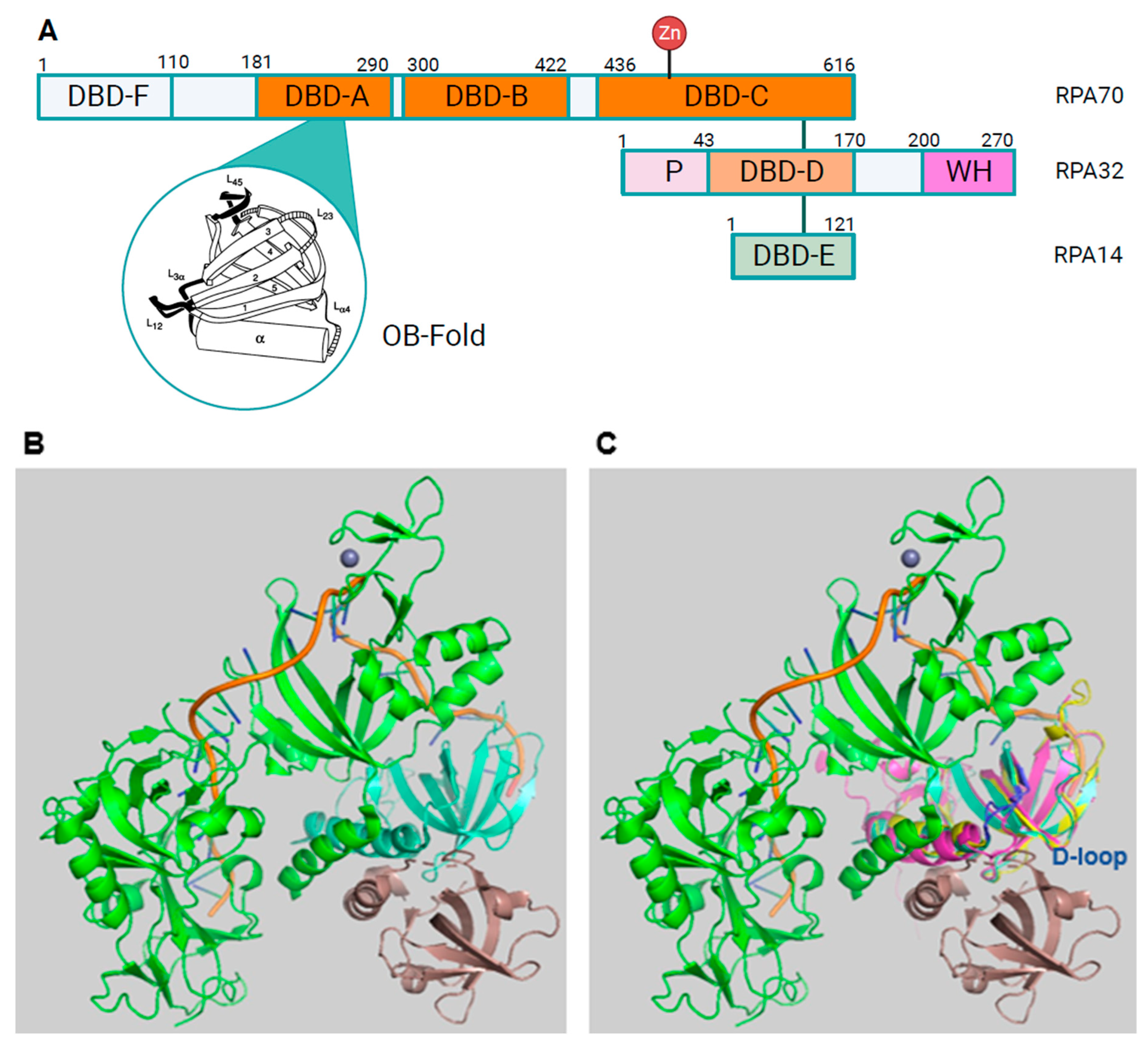
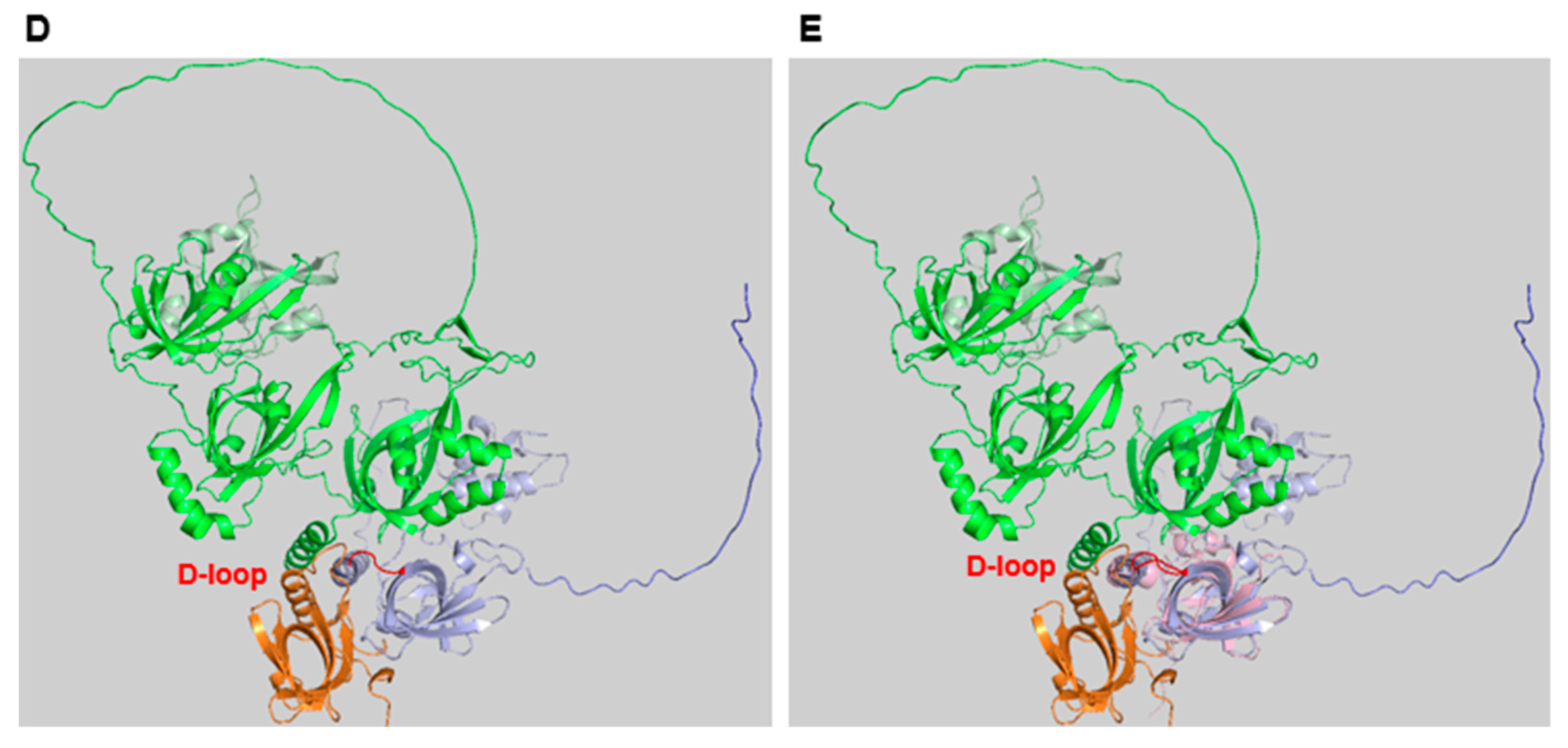
RPA Structure, ssDNA and protein binding
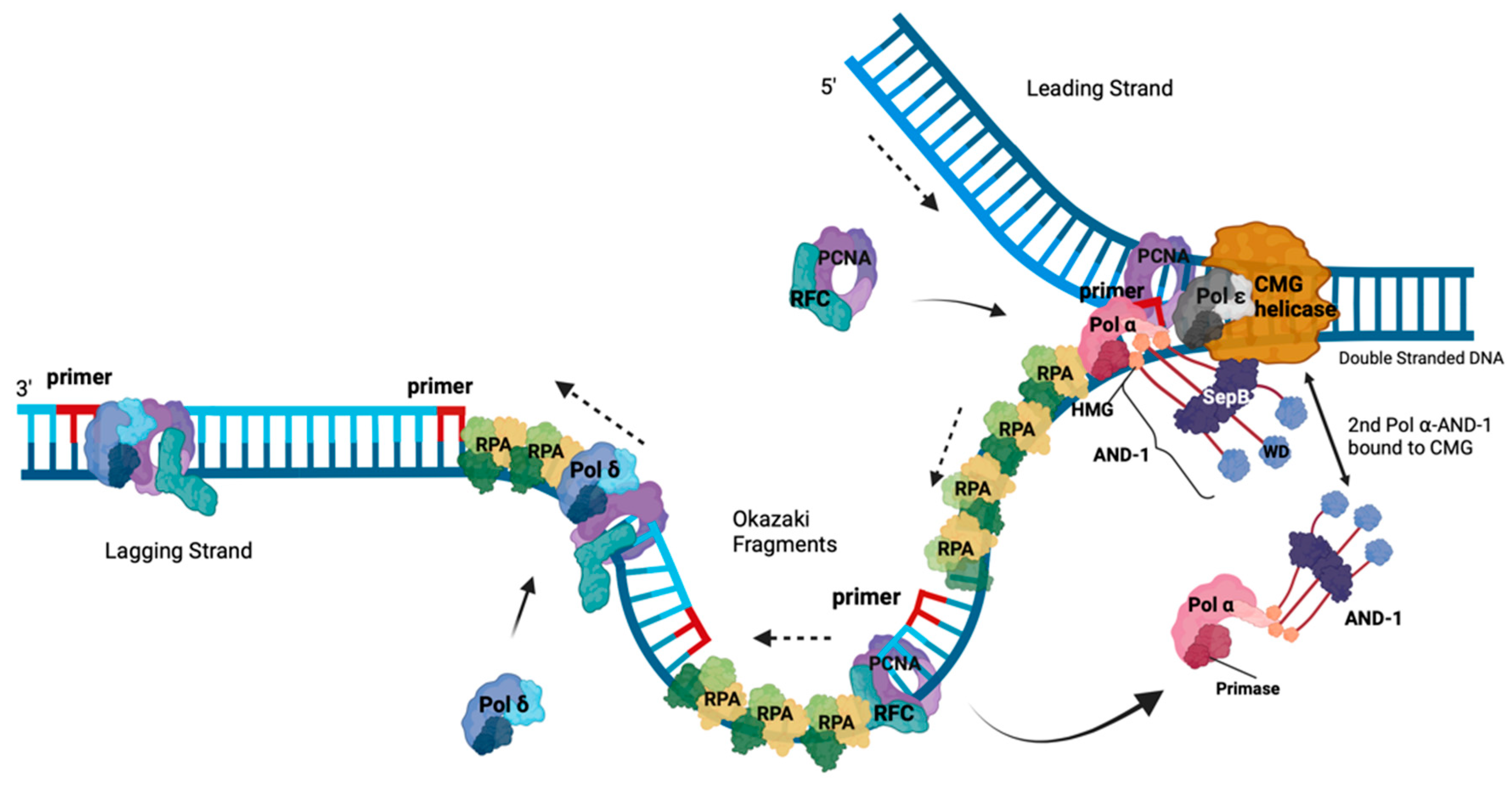
Roles Of RPA in DNA Replication
Understanding the INitiation of Okazaki fragment Synthesis at the Molecular Level
RPA and DNA rePAIR Processes
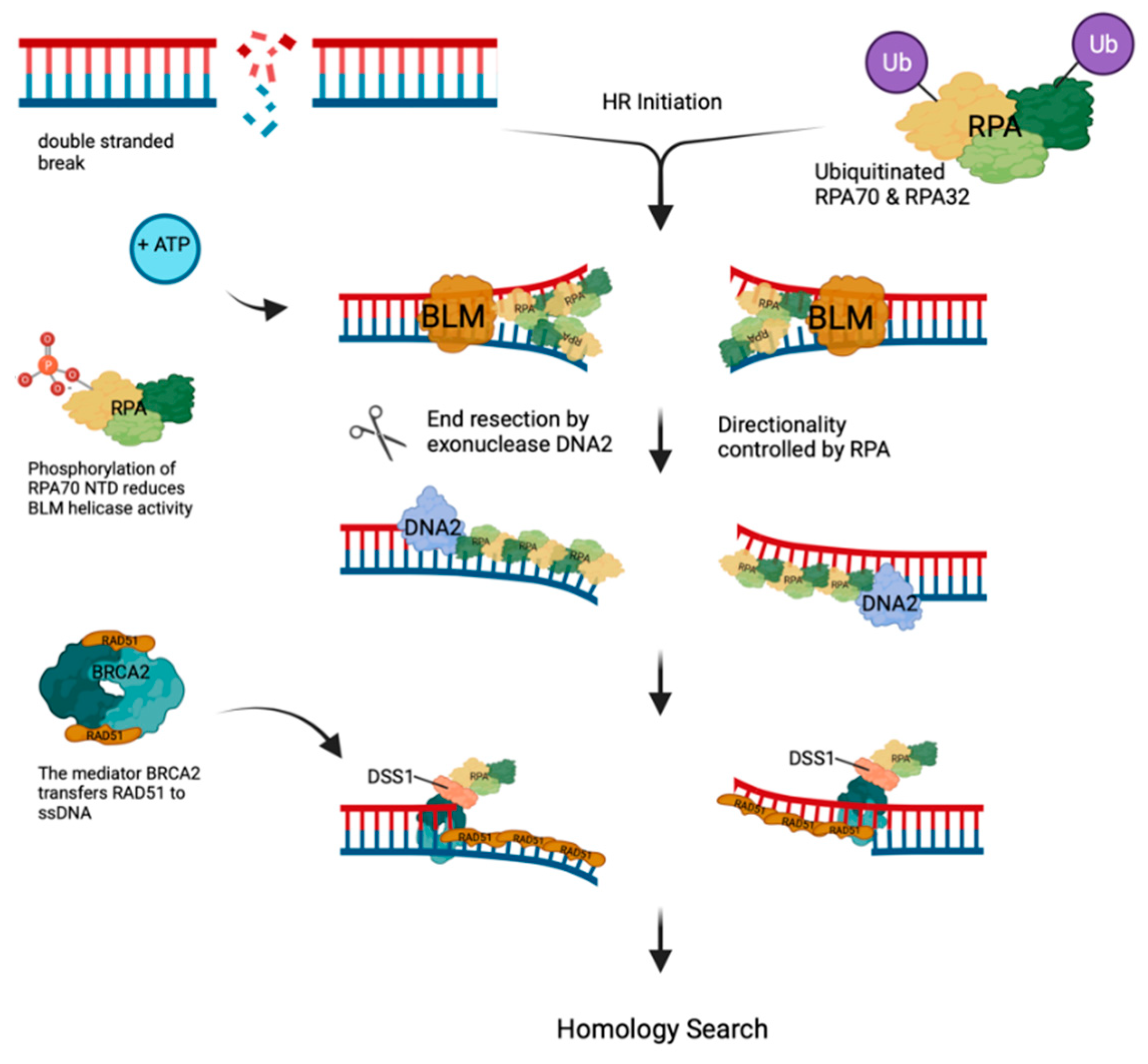
- Double-Strand Break (DSB) Repair, DSBs of cellular DNA are the most deleterious and toxic lesions [85]. Eukaryotic cells have two main pathways to repair DSBs, homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). HR utilizes a homologous DNA template to allow for accurate repair of DSBs whereas NHEJ only re-joins the broken ends, opening the possibility of the induction of insertions or deletions [51,85].
RPA in DNA damage Signalling
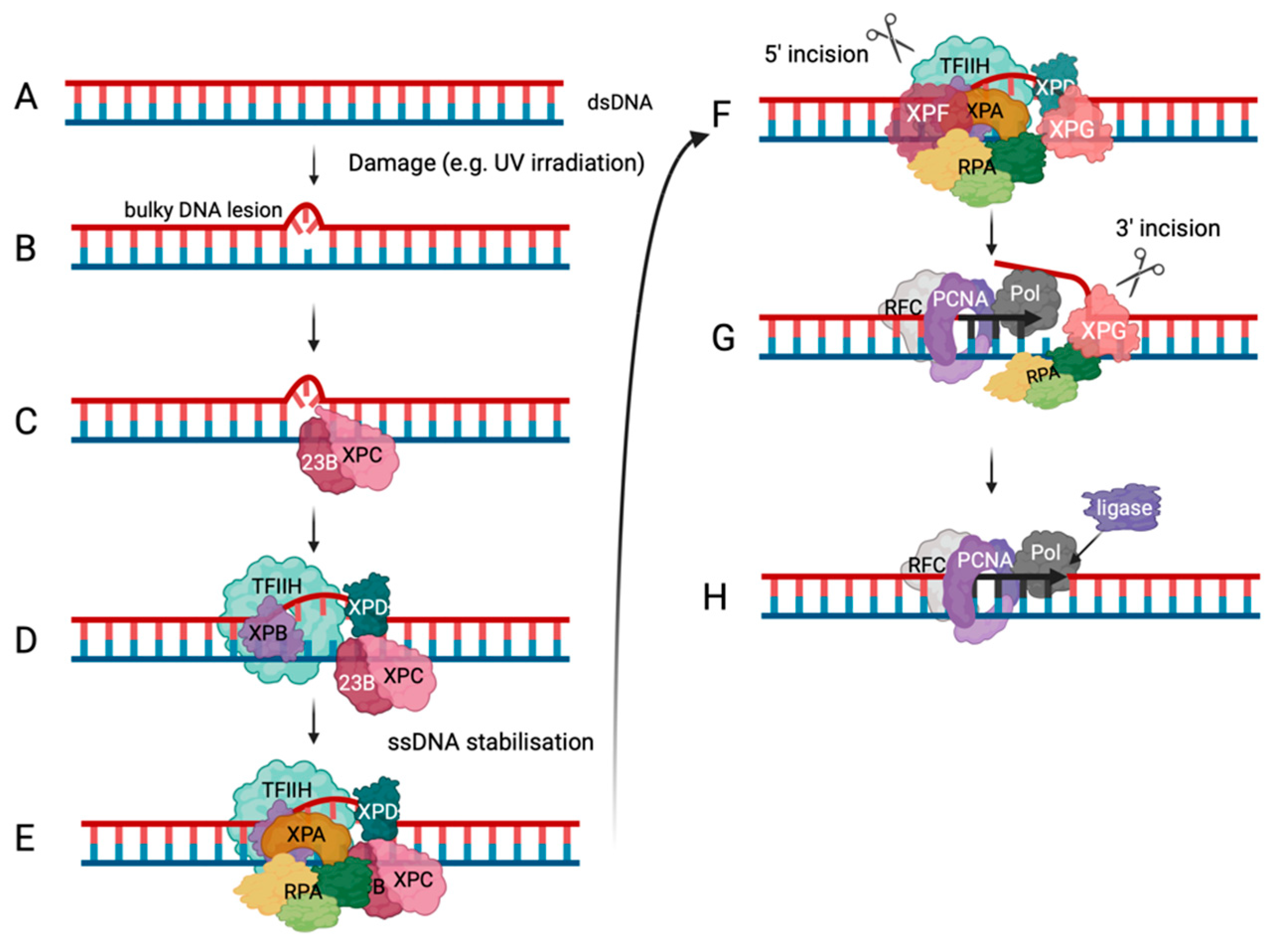
RPA in DNA Repair Pathways
RPA and DNA Recombination
RPA in Health Prospects
Conclusion s
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
| 9-1-1 complex | Rad 9-Hus 1-Rad 1 complex (fission yeast and human) equivalent to the Rad 17-Mec3-Ddc1 complex in budding yeast | ||
| aa | aminoacid | ||
| AND-1/CTF4/ | acidic and nucleoplasmic DNA- binding protein/Chromosome Trans- | ||
| WDHD1 | mission Fidelity 4/WD repeat and HMG-box DNA-binding protein 1 | ||
| A-T | Ataxia telangiectasia | ||
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated | ||
| ATR | ATM-Rad 3-related protein | ||
| ATRIP | ATR interacting protein | ||
| BER | base excision repair | ||
| BLM | Bloom’s helicase | ||
| CDC | cell division cycle | ||
| CDK | cyclin-dependent kinase | ||
| CMG | CDC45-MCM2-6-GINS | ||
| CST | CTC1-STN1-TEN1 | ||
| DBD | DNA-binding domain | ||
| DNA-PK | DNA-dependent protein kinase | ||
| DDR | DNA damage response | ||
| DSB | double-strand break | ||
| dsDNA | double-stranded DNA | ||
| G4 | G-quadruplexes | ||
| HR | homologous recombination | ||
| mt | mitochondrial | ||
| MCM | minichromosome maintenance | ||
| MMEJ | microhomology-mediated end joining | ||
| hPolprim1 | human primase-polymerase 1 | ||
| MMR | mismatch repair | ||
| NER | nucleotide excision repair | ||
| Nt | nucleotide | ||
| NTD | N-terminal domain | ||
| OB-fold | oligosaccharide/oligonucleotide-binding fold | ||
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen | ||
| PIKK | phosphotnositol-3 kinase-like protein kinase | ||
| Pol α | DNA polymerase α–primase | ||
| Pol δ | DNA polymerase δ | ||
| Pol ε | DNA polymerase ε | ||
| POT1 | protector of telomeres 1 | ||
| RAD | radiation-induced mutation | ||
| RFC | replication factor C | ||
| RFWD3 | RING finger and WD repeat | ||
| RPA | replication protein A | ||
| ROS | reactive oxygen species | ||
| SSB | single-stranded DNA-binding protein | ||
| ssDNA | single-stranded DNA | ||
| S. cerivisiae | Saccheromyces cerevisiae | ||
| SV40 | simian virus 40 | ||
| TFIIH | transcription factor II H | ||
| TopBP1 | topoisomerase II-binding protein 1 | ||
References
- Wold, M.S. Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marechal, A.; Zou, L. RPA-coated single-stranded DNA as a platform for post-translational modifications in the DNA damage response. Cell Res 2015, 25, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, M.K.; Lee, S.H.; Hurwitz, J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989, 86, 9757–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairman, M.P.; Stillman, B. Cellular factors required for multiple stages of SV40 replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, M.S.; Kelly, T.J. Purification and characterization of replication protein A, a cellular protein required for in vitro replication of simian virus 40 DNA. Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Snyder, R.O.; Wold, M.S. Binding properties of replication protein A from human and yeast cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olson, C.L.; Barbour, A.T.; Wuttke, D.S. Filling in the blanks: how the C-strand catches up to the G-strand at replicating telomeres using CST. Nature structural & molecular biology 2022, 29, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onwubiko, N.O.; Borst, A.; Diaz, S.A.; Passkowski, K.; Scheffel, F.; Tessmer, I.; Nasheuer, H.P. SV40 T antigen interactions with ssDNA and replication protein A: a regulatory role of T antigen monomers in lagging strand DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 3657–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szambowska, A.; Tessmer, I.; Prus, P.; Schlott, B.; Pospiech, H.; Grosse, F. Cdc45-induced loading of human RPA onto single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, W.; Zang, N.; Zhou, C. Structural characterization of human RPA70N association with DNA damage response proteins. eLife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, S.; Guo, Q.; Bao, K.; Yu, G.; Wang, X.; Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. A PARylation-phosphorylation cascade promotes TOPBP1 loading and RPA-RAD51 exchange in homologous recombination. Mol Cell 2022, 82, 2571–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkareva, E.; Korolev, S.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Bochkarev, A. Structure of the RPA trimerization core and its role in the multistep DNA-binding mechanism of RPA. The EMBO journal 2002, 21, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure and conformational change of a replication protein A heterotrimer bound to ssDNA. Genes Dev 2012, 26, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, E.; Klimovich, V.; Nager, A.R. A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 4126–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, T.R.; Petruseva, I.; Lavrik, O.; Saintome, C. Evidence for direct contact between the RPA3 subunit of the human replication protein A and single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, S.; Rehmet, K.; Concannon, C.; Nasheuer, H.P. Eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding proteins: central factors in genome stability. Subcell Biochem 2010, 50, 143–163. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, H.; Concannon, C.; Kremmer, E.; Carty, M.P.; Nasheuer, H.P. Ionizing radiation-dependent and independent phosphorylation of the 32-kDa subunit of replication protein A during mitosis. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 6028–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murzin, A.G. OB(oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding)-fold: common structural and functional solution for non-homologous sequences. The EMBO journal 1993, 12, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: making protein folding accessible to all. Nat Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestryakov, P.E.; Weisshart, K.; Schlott, B.; Khodyreva, S.N.; Kremmer, E.; Grosse, F.; Lavrik, O.I.; Nasheuer, H.P. Human replication protein A: The C-terminal RPA70 and the central RPA32 domains are involved in the interactions with the 3'-end of a primer-template DNA. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 17515–17524. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Wold, M.S. Replication protein A: single-stranded DNA's first responder: dynamic DNA-interactions allow replication protein A to direct single-strand DNA intermediates into different pathways for synthesis or repair. Bioessays 2014, 36, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, S.; Lai, L.; Niu, H.; Qi, Z. ssDNA accessibility of Rad51 is regulated by orchestrating multiple RPA dynamics. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueva, R.; Iliakis, G. Replication protein A: a multifunctional protein with roles in DNA replication, repair and beyond. NAR Cancer 2020, 2, zcaa022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, P.; Boche, I.; Hartmann, H.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Grosse, F.; Fanning, E.; Weisshart, K. Different activities of the largest subunit of replication protein A cooperate during SV40 DNA replication. FEBS Lett 2007, 581, 3973–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornreiter, I.; Erdile, L.F.; Gilbert, I.U.; von Winkler, D.; Kelly, T.J.; Fanning, E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. The EMBO journal 1992, 11, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, K.A.; Lao, Y.; He, Z.; Ingles, C.J.; Wold, M.S. Role of protein-protein interactions in the function of replication protein A (RPA): RPA modulates the activity of DNA polymerase α by multiple mechanisms. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 8443–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, X. Streamline proteomic approach for characterizing protein-protein interaction network in a RAD52 protein complex. J Proteome Res 2009, 8, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisshart, K.; Pestryakov, P.; Smith, R.W.; Hartmann, H.; Kremmer, E.; Lavrik, O.; Nasheuer, H.P. Coordinated regulation of replication protein A activities by its subunits p14 and p32. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 35368–35376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaithiyalingam, S.; Warren, E.M.; Eichman, B.F.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into eukaryotic DNA priming from the structure and functional interactions of the 4Fe-4S cluster domain of human DNA primase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 13684–13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, R.; Rainey, M.D.; Santocanale, C.; Nasheuer, H.P. Cell cycle-dependent formation of Cdc45-Claspin complexes in human cells are compromized by UV-mediated DNA damage. FEBS J 2013, 280, 4888–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Lou, J.; Xia, Y.; Su, B.; Liu, T.; Cui, J.; Sun, Y.; Lou, H.; Huang, J. hPrimpol1/CCDC111 is a human DNA primase-polymerase required for the maintenance of genome integrity. EMBO reports 2013, 14, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.G.; Mason, A.C.; Carreira, A.; Reardon, J.T.; Haring, S.J.; Borgstahl, G.E.; Kowalczykowski, S.C.; Sancar, A.; Wold, M.S. An alternative form of replication protein A expressed in normal human tissues supports DNA repair. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 4788–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.C.; Roy, R.; Simmons, D.T.; Wold, M.S. Functions of alternative replication protein A in initiation and elongation. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5919–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall-Duncan, T.; Luo, J.; Jurkovic, C.M.; Fischer, L.A.; Fujita, K.; Deshmukh, A.L.; Harding, R.J.; Tran, S.; Mehkary, M.; Li, V.; et al. Antagonistic roles of canonical and Alternative-RPA in disease-associated tandem CAG repeat instability. Cell 2023, 186, 4898–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleichert, F.; Botchan, M.R.; Berger, J.M. Mechanisms for initiating cellular DNA replication. Science 2017, 355, eaah6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasheuer, H.P.; Smith, R.; Bauerschmidt, C.; Grosse, F.; Weisshart, K. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication: regulation and mechanisms. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 2002, 72, 41–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vipat, S.; Gupta, D.; Jonchhe, S.; Anderspuk, H.; Rothenberg, E.; Moiseeva, T.N. The non-catalytic role of DNA polymerase epsilon in replication initiation in human cells. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Aria, V.; Baris, Y.; Yeeles, J.T.P. How Pol α-primase is targeted to replisomes to prime eukaryotic DNA replication. Mol Cell 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Baris, Y.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Yeeles, J.T.P. Structure of a human replisome shows the organisation and interactions of a DNA replication machine. The EMBO journal 2021, 40, e108819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrin, C.; Alvarez, V.; Ainsworth, J.; Fujisawa, R.; Alabert, C.; Labib, K.P. DONSON is required for CMG helicase assembly in the mammalian cell cycle. EMBO Rep 2023, 24, e57677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Sadano, K.; Miyata, N.; Ito, H.; Tanaka, H. Novel role of DONSON in CMG helicase assembly during vertebrate DNA replication initiation. The EMBO journal 2023, 42, e114131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, G.; Skagia, A.; Passaretti, P.; Fernandez-Cuesta, C.; Reynolds-Winczura, A.; Koscielniak, K.; Gambus, A. DONSON facilitates Cdc45 and GINS chromatin association and is essential for DNA replication initiation. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 9748–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.; Tamayo-Orrego, L.; Schmid, E.; Tarnauskaite, Z.; Kochenova, O.V.; Gruar, R.; Muramatsu, S.; Lynch, L.; Schlie, A.V.; Carroll, P.L.; et al. In silico protein interaction screening uncovers DONSON's role in replication initiation. Science 2023, 381, eadi3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Sonneville, R.; Jenkyn-Bedford, M.; Ji, L.; Alabert, C.; Hong, Y.; Yeeles, J.T.P.; Labib, K.P.M. DNSN-1 recruits GINS for CMG helicase assembly during DNA replication initiation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2023, 381, eadi4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrik, O.I.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Weisshart, K.; Favre, A. Alternative conformations of human replication protein A are detected by crosslinks with primers carrying a photoreactive group at the 3'-end. FEBS Lett. 1998, 441, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzhakov, A.; Kelman, Z.; Hurwitz, J.; O'Donnell, M. Multiple competition reactions for RPA order the assembly of the DNA polymerase delta holoenzyme. The EMBO journal 1999, 18, 6189–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prindle, M.J.; Loeb, L.A. DNA polymerase delta in DNA replication and genome maintenance. Environ Mol Mutagen 2012, 53, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovskiy, A.G.; Lisova, A.E.; Morstadt, L.M.; Babayeva, N.D.; Tahirov, T.H. Insight into RNA-DNA primer length counting by human primosome. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, 6264–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovskiy, A.G.; Babayeva, N.D.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Suwa, Y.; Pavlov, Y.I.; Tahirov, T.H. Mechanism of Concerted RNA-DNA Primer Synthesis by the Human Primosome. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 10006–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbe, L.K.; Kuchta, R.D. The p58 subunit of human DNA primase is important for primer initiation, elongation, and counting. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 4891–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Rechkoblit, O. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2018, 53, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, L.J.; Teague, R.; Doherty, A.J. Repriming DNA synthesis: an intrinsic restart pathway that maintains efficient genome replication. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 4831–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrady, K.; Li, A.W.H.; Doherty, A.J. Mechanism of primer synthesis by Primase-Polymerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 82, 102652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Stewart, J.A.; Kasbek, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wright, W.E.; Price, C.M. Human CST has independent functions during telomere duplex replication and C-strand fill-in. Cell Rep 2012, 2, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Baris, Y.; Taylor, M.R.; Yeeles, J.T.P. Structure of a human replisome shows the organisation and interactions of a DNA replication machine. The EMBO journal 2023, 42, e115685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maga, G.; Frouin, I.; Spadari, S.; Hübscher, U. Replication protein A as a "fidelity clamp" for DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 18235–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, S.A.; Williams, J.S.; Kunkel, T.A. DNA Polymerases Divide the Labor of Genome Replication. Trends Cell Biol 2016, 26, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkyn-Bedford, M.; Jones, M.L.; Baris, Y.; Labib, K.P.M.; Cannone, G.; Yeeles, J.T.P.; Deegan, T.D. A conserved mechanism for regulating replisome disassembly in eukaryotes. Nature 2021, 600, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgers, P.M.J.; Kunkel, T.A. Eukaryotic DNA Replication Fork. Annu Rev Biochem 2017, 86, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, N.; El-Hajj, Z.W.; Zheng, H.; Beattie, T.R.; Yu, A.; Reyes-Lamothe, R. Processive Activity of Replicative DNA Polymerases in the Replisome of Live Eukaryotic Cells. Mol Cell 2020, 80, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S.; Spenkelink, L.M.; Schauer, G.D.; Yurieva, O.; Mueller, S.H.; Natarajan, V.; Kaur, G.; Maher, C.; Kay, C.; O'Donnell, M.E.; et al. Tunability of DNA Polymerase Stability during Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Mol Cell 2020, 77, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ma, L.; Tsai, Y.F.; Abeywardana, T.; Shen, B.; Zheng, L. Okazaki fragment maturation: DNA flap dynamics for cell proliferation and survival. Trends Cell Biol 2023, 33, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, R.E.; Schauer, G.D.; Yao, N.Y.; Langston, L.D.; Yurieva, O.; Zhang, D.; Finkelstein, J.; O'Donnell, M.E. Reconstitution of a eukaryotic replisome reveals suppression mechanisms that define leading/lagging strand operation. eLife 2015, 4, e04988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Lin, X.; Chavez, B.L.; Agrawal, S.; Lusk, B.L.; Lim, C.J. Structures of the human CST-Polα–primase complex bound to telomere templates. Nature 2022, 608, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Song, H.; Chan, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Su<monospace>š</monospace>ac, L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Feigon, J. Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase-bound CST with polymerase α-primase. Nature 2022, 608, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.W.; Zinder, J.C.; Svetlov, V.; Bush, M.W.; Nudler, E.; Walz, T.; de Lange, T. Cryo-EM structure of the human CST–Polα/primase complex in a recruitment state. Nature structural & molecular biology 2022, 29, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thömmes, P.; Fett, R.; Schray, B.; Burkhart, R.; Barnes, M.; Kennedy, C.; Brown, N.C.; Knippers, R. Properties of the nuclear P1 protein, a mammalian homologue of the yeast Mcm3 replication protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maine, G.T.; Sinha, P.; Tye, B.K. Mutants of S. cerevisiae defective in the maintenance of minichromosomes. Genetics 1984, 106, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye, B.K. The MCM2-3-5 proteins: are they replication licensing factors? Trends Cell Biol 1994, 4, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Kamimura, Y.; Okawa, M.; Muramatsu, S.; Sugino, A.; Araki, H. GINS, a novel multiprotein complex required for chromosomal DNA replication in budding yeast. Genes Dev 2003, 17, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, M.L.; Simon, A.C.; Mainwaring, J.; Wirthensohn, D.; Holzer, S.; Pellegrini, L. The human CTF4-orthologue AND-1 interacts with DNA polymerase α/primase via its unique C-terminal HMG box. Open biology 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasheuer, H.P.; Onwubiko, N.O. Lagging Strand Initiation Processes in DNA Replication of Eukaryotes-Strings of Highly Coordinated Reactions Governed by Multiprotein Complexes. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganduri, S.; Lue, N.F. STN1-POLA2 interaction provides a basis for primase-pol α stimulation by human STN1. Nucleic Acids Research 2017, 45, 9455–9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, A.I.; Klimovich, V.; Jiang, X.; Ott, R.D.; Mizoue, L.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into hRPA32 C-terminal domain--mediated assembly of the simian virus 40 replisome. Nature structural & molecular biology 2005, 12, 332–339. [Google Scholar]
- Melendy, T.; Stillman, B. An interaction between replication protein A and SV40 T antigen appears essential for primosome assembly during SV40 DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 3389–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onwubiko, N.O.; Scheffel, F.; Tessmer, I.; Nasheuer, H.P. SV40 T antigen helicase domain regions responsible for oligomerisation regulate Okazaki fragment synthesis initiation. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W.; Steffen, C.; Grosse, F.; Nasheuer, H.P. Species specificity of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro requires multiple functions of human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 20541–20548. [Google Scholar]
- Weisshart, K.; Förster, H.; Kremmer, E.; Schlott, B.; Grosse, F.; Nasheuer, H.P. Protein-protein interactions of the primase subunits p58 and p48 with simian virus 40 T antigen are required for efficient primer synthesis in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 17328–17337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Weiner, B.E.; Zhang, H.; Fuller, B.E.; Gao, Y.; Wile, B.M.; Zhao, K.; Arnett, D.R.; Chazin, W.J.; Fanning, E. Structure of a DNA polymerase alpha-primase domain that docks on the SV40 helicase and activates the viral primosome. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 17112–17122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaithiyalingam, S.; Arnett, D.R.; Aggarwal, A.; Eichman, B.F.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into eukaryotic primer synthesis from structures of the p48 subunit of human DNA primase. Journal of molecular biology 2014, 426, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, A.T.; Wuttke, D.S. RPA-like single-stranded DNA-binding protein complexes including CST serve as specialized processivity factors for polymerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 81, 102611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteel, D.E.; Zhuang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Perrino, F.W.; Boss, G.R.; Goulian, M.; Pilz, R.B. A DNA Polymerase-{alpha}{middle dot}Primase Cofactor with Homology to Replication Protein A-32 Regulates DNA Replication in Mammalian Cells. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 5807–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, N.F.; Chan, J.; Wright, W.E.; Hurwitz, J. The CDC13-STN1-TEN1 complex stimulates Pol alpha activity by promoting RNA priming and primase-to-polymerase switch. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, E.; Walter, J.C. Predictomics webpage. Availabe online: (accessed on 28.11.).
- Chapman, J.R.; Taylor, M.R.; Boulton, S.J. Playing the end game: DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Mol Cell 2012, 47, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Guo, G.; Huang, J.; Hou, X.; Ham, H.; Kim, W.; Zhao, F.; Tu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. DOCK7 protects against replication stress by promoting RPA stability on chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 3322–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illuzzi, G.; Fouquerel, E.; Ame, J.C.; Noll, A.; Rehmet, K.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Dantzer, F.; Schreiber, V. PARG is dispensable for recovery from transient replicative stress but required to prevent detrimental accumulation of poly(ADP-ribose) upon prolonged replicative stress. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42, 7776–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, H.L.; Myers, J.S.; Cortez, D. ATRIP binding to replication protein A-single-stranded DNA promotes ATR-ATRIP localization but is dispensable for Chk1 phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 2005, 16, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgstahl, G.E.; Brader, K.; Mosel, A.; Liu, S.; Kremmer, E.; Goettsch, K.A.; Kolar, C.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Oakley, G.G. Interplay of DNA damage and cell cycle signaling at the level of human replication protein A. DNA repair 2014, 21, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, S.K.; Wold, M.S. Regulatory Functions of the N-terminal Domain of the 70-kDa Subunit of Replication Protein A (RPA). J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 21559–21570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuss, J.E.; Patrick, S.M.; Oakley, G.G.; Alter, G.M.; Robison, J.G.; Dixon, K.; Turchi, J.J. DNA damage induced hyperphosphorylation of replication protein A. 1. Identification of novel sites of phosphorylation in response to DNA damage. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8428–8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Wen, K.K.; García-Rubio, M.L.; Wold, M.S.; Aguilera, A.; Niedzwiedz, W.; Vyas, Y.M. WASp modulates RPA function on single-stranded DNA in response to replication stress and DNA damage. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedberg, E.C.; Aguilera, A.; Gellert, M.; Hanawalt, P.C.; Hays, J.B.; Lehmann, A.R.; Lindahl, T.; Lowndes, N.; Sarasin, A.; Wood, R.D. DNA repair: from molecular mechanism to human disease. DNA repair 2006, 5, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schärer, O.D. Nucleotide excision repair in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013, 5, a012609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, T.A.; Erie, D.A. DNA mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem 2005, 74, 681–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.; Gu, L.; Wong, I.; Li, G.M. Regulation of replication protein a functions in DNA mismatch repair by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 21607–21616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, S.R.; Lowndes, N.F. Immediate-Early, Early, and Late Responses to DNA Double Stranded Breaks. Front Genet 2022, 13, 793884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimonkar, A.V.; Genschel, J.; Kinoshita, E.; Polaczek, P.; Campbell, J.L.; Wyman, C.; Modrich, P.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. BLM-DNA2-RPA-MRN and EXO1-BLM-RPA-MRN constitute two DNA end resection machineries for human DNA break repair. Genes Dev 2011, 25, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Rösner, H.; Zhao, W.; Selemenakis, P.; He, Z.; Kawale, A.S.; Katz, J.N.; Rogers, C.M.; Neal, F.E.; Badamchi Shabestari, A.; et al. DNA binding and RAD51 engagement by the BRCA2 C-terminus orchestrate DNA repair and replication fork preservation. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.P.; Heyer, W.D.; Liu, J. Guardians of the Genome: BRCA2 and Its Partners. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foertsch, F.; Kache, T.; Drube, S.; Biskup, C.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Melle, C. Determination of the number of RAD51 molecules in different human cell lines. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3581–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.C.; Dombrowski, C.C.; Plank, J.L.; Jensen, R.B.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. BRCA2 chaperones RAD51 to single molecules of RPA-coated ssDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2221971120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špírek, M.; Mlcoušková, J.; Belán, O.; Gyimesi, M.; Harami, G.M.; Molnár, E.; Novacek, J.; Kovács, M.; Krejci, L. Human RAD51 rapidly forms intrinsically dynamic nucleoprotein filaments modulated by nucleotide binding state. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, 3967–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Vaithiyalingam, S.; San Filippo, J.; Maranon, D.G.; Jimenez-Sainz, J.; Fontenay, G.V.; Kwon, Y.; Leung, S.G.; Lu, L.; Jensen, R.B.; et al. Promotion of BRCA2-Dependent Homologous Recombination by DSS1 via RPA Targeting and DNA Mimicry. Mol Cell 2015, 59, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, N.; Caldwell, C.C.; Corless, E.I.; Tillison, E.A.; Tibbs, J.; Jocic, N.; Tabei, S.M.A.; Wold, M.S.; Spies, M.; Antony, E. Dynamics and selective remodeling of the DNA-binding domains of RPA. Nature structural & molecular biology 2019, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnianni, R.A.; Zhou, Z.X.; Lujan, S.A.; Al-Zain, A.; Garcia, V.; Glancy, E.; Burkholder, A.B.; Kunkel, T.A.; Symington, L.S. DNA Polymerase Delta Synthesizes Both Strands during Break-Induced Replication. Mol Cell 2019, 76, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, H. Repeat expansion diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 2018, 147, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderVere-Carozza, P.S.; Gavande, N.S.; Jalal, S.I.; Pollok, K.E.; Ekinci, E.; Heyza, J.; Patrick, S.M.; Masters, A.; Turchi, J.J.; Pawelczak, K.S. In Vivo Targeting Replication Protein A for Cancer Therapy. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 826655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.J.; Cech, T.R. Shaping human telomeres: from shelterin and CST complexes to telomeric chromatin organization. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2021, 22, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaug, A.J.; Goodrich, K.J.; Song, J.J.; Sullivan, A.E.; Cech, T.R. Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST. Nature 2022, 608, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasugi, T.; Gu, P.; Liang, F.; Staco, I.; Chang, S. Pot1b -/- tumors activate G-quadruplex-induced DNA damage to promote telomere hyper-elongation. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 9227–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




