Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Borrelia Strains
2.2. Protein Analysis
2.3. Collection of Sera
2.4. Ethical Statements
2.5. Serum Susceptibility
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protein Analysis
3.2. Serum Susceptibility
3.3. Protein Profiles of Analyzed Strains and Susceptibility to Human Complement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanek, G.; Wormser, G.P.; Gray, J.; Strle, F. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 2012;379:461–73.
- Stanek G, Strle F. Lyme borreliosis–from tick bite to diagnosis and treatment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 233–258.
- Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Reynolds, E.S. Borrelia bavariensis: vector switch, niche invasion, and geographical spread of a tick–borne bacterial parasite. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7:1–20.
- Kraiczy, P. Hide and Seek: How Lyme Disease spirochetes overcome complement attack. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 385.
- Schwab, J.; Hammerschmidt, C.; Richter, D.; Skerka, C.; Matuschka, F.R.; Wallich, R.; Zipfel, P.F.; Kraiczy, P. Borrelia valaisiana resist complement–mediated killing independently of the recruitment of immune regulators and inactivation of complement components. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e53659.
- Bhide, M.R. ; Travnicek, M.; Levkutova, M.; Curlik, J.; Revajova, V.; Levkut, M. Sensitivity of Borrelia genospecies to serum complement from different animals and human: a host–pathogen relationship. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 43,165–172.
- van Dam, A,P.; Oei, A.; Jaspars, R.; Fijen, C.; Wilske, B.; Spanjaard, L.; Dankert, J. Complement–mediated serum sensitivity among spirochetes that cause Lyme disease. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1228–1236.
- Estrada-Peña, A,; Cutler, S.; Potkonjak, A.; Vassier-Tussaut, M.; Van Bortel, W.; Zeller, H.; Fernández-Ruiz, N.; Mihalca, A.D. An updated meta–analysis of the distribution and prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. in ticks in Europe. Int. J. Health. Geogr. 2018, 17, 41.
- Ćakić, S.; Veinović, G.; Cerar, T.; Mihaljica, D.; Sukara, R.; Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Tomanović, T. Diversity of Lyme borreliosis spirochetes isolated from ticks in Serbia. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2019, 33, 512–520.
- Milutinović, M.; Masuzawa, T.; Tomanović, S.; Radulović, Z.; Fukui, T.; Okamoto, Y. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Francisella tularensis and their co–infections in hostseeking Ixodes ricinus ticks collected in Serbia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 45, 171–183.
- Potkonjak, A.; Kleinerman, G.; Gutiérrez, R.; Savić, S.; Vračar, V.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Jurišić, A.; Rojas, A.; Petrović, A.; Ivanović, I.; Harrus, S.; Baneth, G. Occurrence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Ixodes ricinus ticks with first identification of Borrelia miyamotoi in Vojvodina, Serbia. Vector. Borne. Zoonotic. Dis. 2016, 16, 631-635.
- Strnad, M.; Hönig, V.; Růžek, D.; Grubhoffer, L.; Rego, R.O.M. Europe-wide meta-analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato prevalence in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00609-17.
- Institute for Public Health of Serbia. Available from: https://www.batut.org.rs/download/izvestaji/Godisnji%20izvestaj%20zarazne%20bolesti%202017.pdf.
- Lohr, B.; Fingerle, V.; Norris, D.E.; Hunfeld, K.P. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis: Current state of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 219–245.
- Petrulionienė, A.; Radzišauskienė, D.; Ambrozaitis, A.; Čaplinskas, S.; Paulauskas, A.; Venalis, A. Epidemiology of Lyme disease in a highly endemic European zone. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020, 56, 115.
- Mladenović, J. Epidemiological aspects of Lyme disease on the theritory of Belgrade city. Doctoral dissertation, Faculty of Medicine, University of Nis, Serbia. 2014; 64 [in Serbian].
- Sukara, R.; Chochlakis, D.; Ćirović, D.; Penezić, A.; Mihaljica, D.; Ćakić, S.; Valčić, M.; Tselentis, Y.; Psaroulaki, A.; Tomanović, S . Golden jackals (Canis aureus) as hosts for ticks and tick-borne pathogens in Serbia. Ticks. Tick. Borne. Dis. 2018, 9, 1090-1097.
- Sukara, R.; Juwaid, S.; Ćirović, D.; Penezić, A.; Mihaljica, D.; Veinović, G.; Radojičić, S.; Hodžić, A.; Duscher, G.G.; Tomanović, S. Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. (FU98) and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Serbia. Acta Veterinaria-Beograd. 2019, 69, 312-324.
- Ruzić-Sabljić, E.; Zore, A.; Strle, F. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis after MluI restriction of genomic DNA. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 441–448.
- Barral, M.; García-Pérez, A.L.; Juste, R.A.; Hurtado, A.; Escudero, R.; Sellek, R.E.; Anda, P. Distribution of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks from the Basque Country, Spain. J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 177–184.
- Escudero, R.; Barral, M.; Pérez, A.; Vitutia, M.M.; García-Pérez, A.L.; Jiménez, S.; Sellek R.E.; Anda, P. Molecular and pathogenic characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates from Spain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4026–4033.
- Glinšek, U.; Udovič, T.; Cerar, T.; Strle, F.; Ružić–Sabljić, E. Protein profile determination of Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii isolated from skin and cerebrospinal fluid. World. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1287–1296.
- Ruzić-Sabljić, E.; Maraspin, V.; Lotric-Furlan, S.; Jurca, T.; Logar, M.; Pikelj-Pecnik, A.; Strle, F. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato strains isolated from human material in Slovenia. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2002, 114, 544–550.
- Zeidner, N.S.; Núncio, M.S.; Schneider, B,S.; Gern, L.; Piesman, J.; Otilia Brandão, O.; Filipe, A.R. A portuguese isolate of Borrelia lusitaniae induces disease in C3H/HeN mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 1055–1060.
- Collares-Pereira, M.; Couceiro, S.; Franca, I.; Kurtenbach, K.; Schäfer, S.M.; Vitorino, L.; Gonçalves, L.; Baptista, S.; Vieira, M.L.; Cunha, C First isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a human patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1316–138.
- Wagemakers, A.; Oei, A.; Fikrig, M.M.; Miellet, W.R.; Hovius, J.W. The relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi is cultivable in a modified Kelly–Pettenkofer medium, and is resistant to human complement. Parasit. Vectors. 2014, 7, 418.
- Koetsveld, J.; Draga, R.O.P.; Wagemakers, A.; Manger, A.; Oei, A.; Visser, C.E.; Hovius, J.W. In vitro susceptibility of the relapsing-fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi to antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2017, 61, e00535-17.
- Diza, E.; Papa, A.; Vezyri, E.; Tsounis, S.; Milonas, I.; Antoniadis, A. Borrelia valaisiana in cerebrospinal fluid. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1692–1693.
- Rijpkema, S.G.T.; Tazelaar, D.J.; Molkenboer, M,J,C,H.; Noordhoek, G,T.; Plantinga, G.; Schouls, L.M.; Schellekens, J.F.P. Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii and group VS116 by PCR in skin biopsies of patients with erythema migrans and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1997, 3, 109–116.
- Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Strle, F.; Cimperman, J.; Maraspin, V.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Pleterski-Rigler, D. Characterisation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato strains isolated from patients with skin manifestations of Lyme borreliosis residing in Slovenia. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 47–53.
- Fingerle, V.; Laux, H.; Munderloh, U.G.; Schulte–Spechtel, U.; Wilske, B. Differential expression of outer surface proteins A and C by individual Borrelia burgdorferi in different genospecies. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 189, 59–66.
- Neelakanta, G.; Li, X.; Pal, U.; Liu, X.; Beck, D.S.; DePonte, K.; Fish, D.; Kantor, F.S.; Fikrig, E. Outer surface protein B is critical for Borrelia burgdorferi adherence and survival within Ixodes ticks. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e33.
- Yang, X.F.; Pal, U.; Alani, S.M.; Fikrig, E.; Norgard, M.V. Essential role for OspA/B in the life cycle of the Lyme disease spirochete. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 641–648.
 B. afzelii in HIS;
B. afzelii in HIS;  B. afzelii in NHS;
B. afzelii in NHS;  B. garinii in HIS;
B. garinii in HIS;  B. garinii in NHS;
B. garinii in NHS;  B. bavariensis in HIS;
B. bavariensis in HIS; B. bavariensis in NHS;
B. bavariensis in NHS; 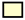 B. valaisiana in HIS;
B. valaisiana in HIS; 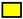 B. valaisiana in NHS;
B. valaisiana in NHS; 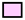 B. lusitaniae in HIS;
B. lusitaniae in HIS; 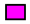 B. lusitaniae in NHS.
B. lusitaniae in NHS.
 B. afzelii in HIS;
B. afzelii in HIS;  B. afzelii in NHS;
B. afzelii in NHS;  B. garinii in HIS;
B. garinii in HIS;  B. garinii in NHS;
B. garinii in NHS;  B. bavariensis in HIS;
B. bavariensis in HIS; B. bavariensis in NHS;
B. bavariensis in NHS;  B. valaisiana in HIS;
B. valaisiana in HIS;  B. valaisiana in NHS;
B. valaisiana in NHS;  B. lusitaniae in HIS;
B. lusitaniae in HIS;  B. lusitaniae in NHS.
B. lusitaniae in NHS.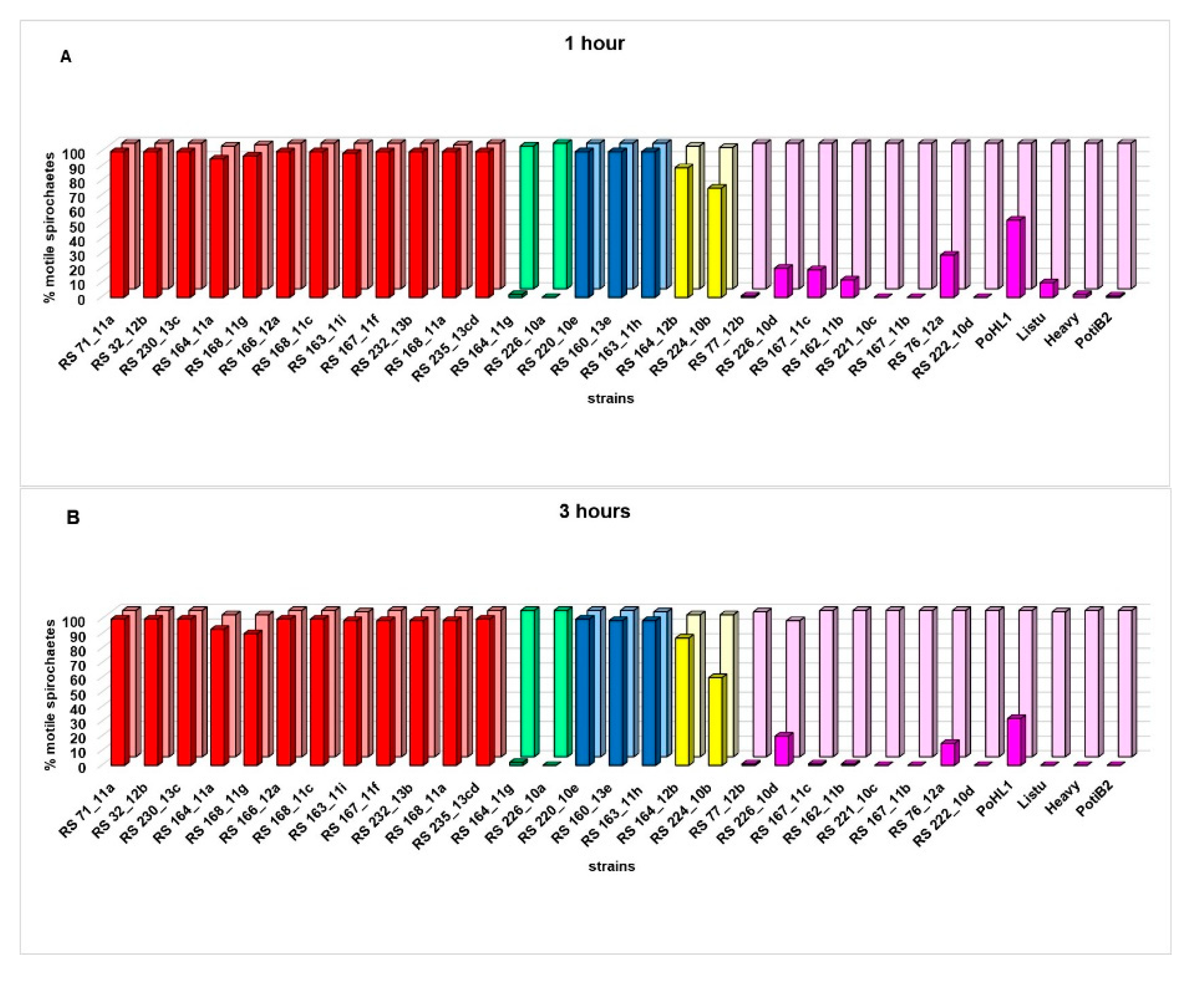
| Strain | Region (host) | NHS (1h) Median (range)a % |
HIS (1h) Median (range) % |
p- Value |
NHS (3h) Median (range) % |
HIS (3h) Median (range) % |
p- Value |
Susceptibility to NHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borrelia valaisana | ||||||||
| RS 164_12b | Serbia (tick) | 89 (85-91) | 98 (98-98) | >0.05 | 87 (77-89) | 97 (96-97) | >0.05 | Rb |
| RS 224_10b | Serbia (tick) | 75 (53-81) | 97 (96-99) | <0.05 | 60 (52-76) | 97 (95-97) | <0.05 | Sc |
| median (range) | 83 (53-91) | 98 (96-99) | 76.5 (52-89) | 97 (95-97) | ||||
| Borrelia afzelii | ||||||||
| RS 71_11a | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 32_12b | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 230_13c | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 164_11a | Serbia (tick) | 95 (94-98) | 98 (98-98) | >0.05 | 93 (90-93) | 97 (97-97) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 168_11g | Serbia (tick) | 97 (97-98) | 99 (98-99) | >0.05 | 90 (88-94) | 97 (94-97) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 166_12a | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 168_11c | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 163_11i | Serbia (tick) | 99 (98-100) | 100 (99-100) | >0.05 | 99 (97-100) | 99 (98-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 167_11f | Serbia (tick) | 100 (99-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 99 (98-100) | 100 (99-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 232_13b | Serbia (tick) | 100 (99-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 99 (98-100) | 100 (99-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 168_11a | Serbia (tick) | 100 (98-100) | 99 (100-100) | >0.05 | 99 (98-100) | 100 (99-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 235_13cd | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| median (range) | 100 (94-100) | 100 (98-100) | 100 (90-100) | 100 (94-100) | ||||
| Borrelia garinii | ||||||||
| RS 164_11g | Serbia (tick) | 2 (0-3) | 98 (97-99) | <0.05 | 2 (0-2) | 98 (97-99) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 226_10a | Serbia (tick) | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| median (range) | 0 (0-3) | 99.5 (97-100) | 0 (0-2) | 99.5 (97-100) | ||||
| Borrelia bavariensis | ||||||||
| RS 220_10e | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 160_13e | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 99 (96-100) | 99 (99-99) | >0.05 | R |
| RS 163_11h | Serbia (tick) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | 99 (99-100) | 100 (100-100) | >0.05 | R |
| median (range) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (100-100) | 100 (96-100) | 100 (99-100) | ||||
| Borrelia lusitaniae | ||||||||
| RS 77_12b | Serbia (tick) | 1 (0-2) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 1 (0-1) | 99 (99-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 226_10d | Serbia (tick) | 20 (4-50) | 100 (92-100) | <0.05 | 20 (3-45) | 93 (91-94) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 167_11c | Serbia (tick) | 19 (15-20) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 1 (0-1) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 162_11b | Serbia (tick) | 12 (3-14) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 1 (1-2) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 221_10c | Serbia (tick) | 0 (0-7) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 167_11b | Serbia (tick) | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-0) | 100 (98-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 76_12a | Serbia (tick) | 29 (26-35) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 15 (5-20) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| RS 222_10d | Serbia (tick) | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-0) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| PoHL1 | Portugal (human) | 53 (47-70) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 32 (27-50) | 100 (80-100) | <0.05 | S |
| Listu | Spain (tick) | 10 (5-18) | 100 (99-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-3) | 99 (98-100) | <0.05 | S |
| Heavy | Spain (tick) | 2 (0-5) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-1) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| PotiB2 | Portugal (tick) | 1 (1-3) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | 0 (0-1) | 100 (100-100) | <0.05 | S |
| median (range) | 4.5 (0-70) | 100 (92-100) | 1 (0-50) | 100 (91-100) |
| Species | OspA | OspB | OspC |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. afzelii | 12 (100%) | 12 (100%) | 10 (83%) |
| B. garinii | 2 (100%) | 2 (100%) | |
| B. bavariensis | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) |
| B. valaisiana | 2 (100%) | 1 (50%) | |
| B. lusitaniae | 11 (92) | 2 (17%) | 4 (33%) |
| All | 30 (97%) | 17 (55%) | 20 (65%) |
| Present protein (Protein profile group) |
B. afzelii No. 12 |
B. garinii No. 2 |
B. bavariensis No. 3 |
B. valaisiana No. 2 |
B. lusitaniae No. 12 |
All No. 31 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OspA, OspB, and OspC (I) |
10 (83%) RS 71_11a RS 32_12b RS 164_11a RS 168_11g RS 168_11c B RS 167_11f RS 232_13b RS 168_11a RS 235_13cd |
3 (100%) RS 220_10e RS 160_13e RS 163_11h |
1 (8%) PoHL1 |
14 (45%) | ||
|
Osp A and OspB (II) |
2 (17%) RS 230_13c RS 166_12a |
2 (7%) |
||||
| OspA and OspC (III) |
2 (100%) RS 164_11g RS 226_10a |
1 (50%) RS 164_12b |
3 (25%) RS 77_12b RS 226_10d RS 76_12a |
6 (19%) | ||
|
OspA (IV) |
1 (50%) RS 224_10b |
7 (59%) RS 167_11c RS 162_11b RS 221_10c RS 167_11b RS 222_10d Listu Heavy |
8 (26%) |
|||
| OspB (V) |
1 (8%) PotiB2 |
1 (3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





